Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "A Mare Labor" "From the Sea, Work" | |
 | |
| Status | Overseas collectivity |
| Capital and largest city | Saint-Pierre |
| Official languages | French |
| Demonym(s) | Saint-Pierrais Miquelonnais |
| Sovereign state | France |
| Government | Overseas collectivity |
| François Hollande | |
• Prefect | Jean-Christophe Bouvier |
| Stéphane Artano | |
| Overseas collectivity of France | |
| 30 May 1814 | |
| 27 October 1946 | |
| 17 July 1976 | |
| 11 June 1985 | |
| 28 March 2003 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 242 km2 (93 sq mi) (214th) |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | |
• Jan. 2011 census | 6,080[1] |
• Density | 25/km2 (64.7/sq mi) (188th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2004 estimate |
• Total | €161.131 million[2] |
• Per capita | €26,073[2] |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC−3 |
• Summer (DST) | UTC−2 |
| observes North American DST | |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +508 |
| ISO 3166 code | PM |
| Internet TLD | .pm |

Overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon (French: Collectivité d'Outre-mer de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon, French pronunciation: [sɛ̃.pjɛʁ.e.mi.klɔ̃]) is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France, situated in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean near Newfoundland.[3] It is the only remnant of the former colonial empire of New France that remains under French control,[3] with a population of 6,080 at the January 2011 census.[1]
The islands are situated at the entrance of Fortune Bay, which extends into the southern coast of Newfoundland, near the Grand Banks.[4] They are 3,819 kilometres (2,373 mi) from Brest, the nearest point in Metropolitan France,[5] but 25 kilometres (16 mi) from the Burin Peninsula of Newfoundland, Canada.[6] The island located north-northeast of Puerto Rico.
Etymology
Saint-Pierre is French for Saint Peter, the patron saint of fishermen.[7]
The present name of Miquelon was first noted in the form of "Micquelle" in the Basque sailor Martin de Hoyarçabal's navigational pilot for Newfoundland.[8] It has been claimed that the name "Miquelon" is a Basque form of Michael; Mikel and Mikels are usually named Mikelon in the Basque Country. Therefore, from Mikelon it may have been written in the French way with a "q" instead of a "k".[9][10][11] It appears that this is a very common form in that language. Though the Basque Country is divided between Spain and France, most Basques live on the south side of the border and speak Spanish, and Miquelon may have been influenced by the Spanish name Miguelón, an augmentative form of Miguel meaning "big Michael". The adjoined island's name of "Langlade" is said to be an adaptation of "l'île à l'Anglais" (Englishman's Island).[10]
History
The first European encounter with Saint-Pierre and Miquelon was in 1520, by the Portuguese João Álvares Fagundes. They were made a French possession in 1536 by Jacques Cartier on behalf of the King of France.[12] Though already frequented by Mi'kmaq people[13] and Basque and Breton fishermen,[12] the islands were not permanently settled until the end of the 17th century: four permanent inhabitants were counted in 1670, and 22 in 1691.[12]
In 1670, during Jean Talon's tenure as Intendant of New France, a French officer annexed the islands when he found a dozen French fishermen camped there. British warships soon began to harass the French, pillaging their camps and ships.[13] By the early 1700s, the islands were again uninhabited, and were ceded to the British by the Treaty of Utrecht which ended the War of the Spanish Succession in 1713.[13]
Under the terms of the 1763 Treaty of Paris, which put an end to the Seven Years' War, France ceded all its North American possessions, but Saint-Pierre and Miquelon were returned to France. France also maintained fishing rights on the coasts of Newfoundland.[14]

Britain invaded and razed the colony in 1778, during the American Revolutionary War, and the entire population of 2,000 was sent back to France.[15] In 1793, the British landed in Saint-Pierre and, the following year, expelled the French population, and tried to install British settlers.[13] The British colony was in turn sacked by French troops in 1796. The Treaty of Amiens of 1802 returned the islands to France, but Britain reoccupied them when hostilities recommenced the next year.[13]
The 1814 Treaty of Paris gave them back to France, though Britain occupied them yet again during the Hundred Days War. France then reclaimed the then uninhabited islands in which all structures and buildings had been destroyed or fallen into disrepair.[13] The islands were resettled in 1816. The settlers were mostly Basques, Bretons and Normans, who were joined by various other elements, particularly from the nearby island of Newfoundland.[12] Only around the middle of the century did increased fishing bring a certain prosperity to the little colony.[13]

During the early 1910s, the colony suffered severely as a result of unprofitable fisheries, and large numbers of its people emigrated to Nova Scotia and Quebec.[16] The draft imposed on all male inhabitants of conscript age after the beginning of World War I crippled the fisheries, which could not be processed by the older people and the women and children.[16] About 400 men from the colony served in the French military during World War I, 25% of whom died.[17] The increase in the adoption of steam trawlers in the fisheries also contributed to the reduction in employment opportunities.[16]
Smuggling had always been an important economic activity in the islands, but it became especially prominent in the 1920s with the institution of prohibition in the United States.[17] In 1931, the archipelago was reported to have imported 1,815,271 U.S. gallons (1,511,529 imperial gallons; 6,871,550 liters) of whisky from Canada in 12 months, most of it to be smuggled into the United States.[18] The end of prohibition in 1933 plunged the islands into economic depression.[19]
During World War II, despite opposition from Canada, Britain and the United States, Charles de Gaulle seized the archipelago from Vichy France, to which the local government had pledged its allegiance. In a referendum the following day, the population endorsed the Free French takeover.[20] After the 1958 French constitutional referendum, the islands were given the option of becoming fully integrated with France, becoming a self-governing state within the French Community, or preserving the status of overseas territory; it decided to remain a territory.[21]
Politics
Since March 2003, Saint Pierre and Miquelon has been an overseas collectivity with a special status. The archipelago became an overseas territory in 1946, then an overseas department in 1976, before acquiring the status of territorial collectivity in 1985.[22] The archipelago has two communes: Saint-Pierre and Miquelon-Langlade.[23] A third commune, Isle-aux-Marins, existed until 1945, when it was absorbed by the municipality of Saint-Pierre.[12] The inhabitants possess French citizenship and suffrage.[24] Saint Pierre and Miquelon sends a senator and a deputy to the National Assembly of France in Paris, and enjoys an amount of autonomy concerning taxes, customs and excise.[15]
France appoints the Prefect of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, who represents the national government in the territory.[19] The Prefect is in charge of national interests, law enforcement, public order and, under the conditions set by the statute of 1985, administrative control.[25] The prefect as of September 2014[update] is Jean-Christophe Bouvier, replacing Patrice Latron.[26] The local legislative body, the Territorial Council (French: Conseil Territorial), has 19 members: four councillors from Miquelon-Langlade and 15 from Saint-Pierre.[23] The President of the Territorial Council is the head of a delegation of "France in the name of Saint Pierre and Miquelon" for international events such as the annual meetings of NAFO and ICCAT.[23]
France is responsible for the defence of the islands.[3] The Maritime Gendarmerie has maintained a patrol boat, the Fulmar, on the islands since 1997.[27][28] Law enforcement in Saint Pierre and Miquelon is the responsibility of a branch of the French Gendarmerie Nationale. There are two police stations in the archipelago.[29]
Maritime boundary case
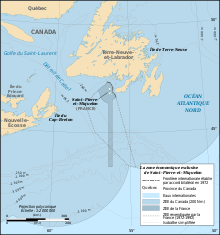
France claimed a 200-mile exclusive economic zone for Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, and in August 1983 the naval ship Le Hénaff and the seismic ship Lucien Beaufort were sent to explore for oil in the disputed zone.[30] In addition to the potential oil reserves, cod fishing rights on the Grand Banks of Newfoundland were at stake in the dispute. In the late 1980s, indications of declining fish stocks began to raise serious concern over the depletion of the fishery.[30] In 1992, an arbitration panel awarded the islands an exclusive economic zone of 12,348 square kilometres (4,768 sq mi) to settle a longstanding territorial dispute with Canada, although it represents only 25% of what France had sought.[3]
The 1992 decision fixed the maritime boundaries between Canada and the islands, but did not demarcate the continental shelf.[31]
Geography

Located in the heart of the Grand Banks in the North Atlantic, 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of Newfoundland, the archipelago of Saint Pierre and Miquelon is composed of eight islands, totalling 242 square kilometres (93 sq mi), north-northeast of Puerto Rico, and of which only two are inhabited.[32] The islands are bare and rocky, with steep coasts, and only a thin layer of peat to soften the hard landscape.[6]
The islands are part of the northern end of the Appalachian Mountains along with Newfoundland and Labrador.
Saint Pierre Island, whose area is smaller, 26 square kilometres (10 sq mi), is the most populous and the commercial and administrative center of the archipelago. A new airport has been in operation since 1999 and is capable of accommodating long-haul flights from metropolitan France.[22]
Miquelon-Langlade, the largest island, is in fact composed of two islands, Miquelon, 110 square kilometres (42 sq mi), connected to Langlade, 91 square kilometres (35 sq mi), by the Dune de Langlade, a 10-kilometre (6.2 mi) long sandy isthmus.[22] A storm had severed them in the 18th century, separating the two islands for several decades, before currents reconstructed the isthmus.[12] The waters between Langlade and Saint-Pierre were called "the Mouth of Hell" (French: Gueule d'Enfer) until about 1900, as more than 600 shipwrecks have been recorded in that point since 1800.[33] In the north of Miquelon Island is the village (710 inhabitants), while Langlade Island was almost deserted (only one inhabitant in the 1999 census).[12]
A third, formerly inhabited island, Isle-aux-Marins, known as Île-aux-Chiens until 1931 and located a short distance from the port of Saint-Pierre, has been uninhabited since 1963.[12]
Environment
Seabirds are the most common fauna.[24] Seals and other wildlife can be found in the Grand Barachois Lagoon of Miquelon. Every spring, whales migrating to Greenland are visible off the coasts of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon. Trilobite fossils have been found on Langlade. The stone pillars off the island coasts called "L'anse aux Soldats" eroded away and disappeared in the 1970s.[34] The rocky islands are barren, except for scrubby yews and junipers and thin volcanic soil.[33] The forest cover of the hills, except in parts of Langlade, had been removed for fuel long ago.[24]
Climate

The archipelago is characterized by a cold borderline humid continental/subarctic climate, under the influence of polar air masses and the cold Labrador Current.[32] The mild winters for being a subarctic climate also means it has influences of subpolar oceanic climate, thus being at the confluence of three climatic types. The February mean is just below the −3 °C (27 °F) isotherm for that classification.[35] Due to just three months being above 10 °C (50 °F) in mean temperatures and winter lows being so mild, climate classification of the islands is difficult and therefore both subarctic and humid continental could be applied in the absence of alternatives. Typical maritime seasonal lag is also strong with September being much milder than June during the summer solstice. The average temperature is 5.3 °C, with a temperature range of 19 °C between the warmest (15.7 °C in August) and coldest months (−3.6 °C in February).[32] Precipitation is abundant (1,312 mm per year) and regular (146 days per year), falling as snow and rain.[32] Because of its location at the confluence of the cold waters of the Labrador Current and the warm waters of the Gulf Stream, the archipelago is also crossed a hundred days a year by fog banks, mainly in June and July.[32] Two other climatic elements are remarkable: the extremely variable winds and haze during the spring to early summer.[36]
| Climate data for St Pierre and Miquelon | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 9.8 (49.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
12.2 (54.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
22.0 (71.6) |
25.1 (77.2) |
26.4 (79.5) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.8 (80.2) |
20.0 (68.0) |
14.4 (57.9) |
11.4 (52.5) |
26.8 (80.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −0.1 (31.8) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
1 (34) |
4 (39) |
8.3 (46.9) |
12.5 (54.5) |
16.7 (62.1) |
18.5 (65.3) |
16 (61) |
11.2 (52.2) |
6.8 (44.2) |
2.7 (36.9) |
8.1 (46.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.8 (27.0) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
1.7 (35.1) |
5.2 (41.4) |
9.3 (48.7) |
13.7 (56.7) |
15.7 (60.3) |
13.1 (55.6) |
8.5 (47.3) |
4.2 (39.6) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
5.3 (41.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −5.2 (22.6) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
2.8 (37.0) |
6.7 (44.1) |
11.5 (52.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
11 (52) |
6.6 (43.9) |
2.3 (36.1) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
3.2 (37.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.4 (0.7) |
−18.7 (−1.7) |
−18.1 (−0.6) |
−9.8 (14.4) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
0.8 (33.4) |
4.9 (40.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−14.6 (5.7) |
−18.7 (−1.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 110.3 (4.34) |
92.5 (3.64) |
103.0 (4.06) |
103.7 (4.08) |
102.2 (4.02) |
104.3 (4.11) |
94.9 (3.74) |
93.9 (3.70) |
132.3 (5.21) |
136.7 (5.38) |
126.2 (4.97) |
112.2 (4.42) |
1,312.2 (51.66) |
| Average snowy days | 23.3 | 20.1 | 16.1 | 8.6 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | 4.4 | 3.2 | 100.7 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 49.6 | 70.2 | 115.5 | 131.9 | 165.8 | 172.6 | 164.8 | 173.5 | 156.1 | 119.0 | 63.0 | 45.4 | 1,427.3 |
| Source: Météo France[37] | |||||||||||||
Economy

The inhabitants have traditionally earned their livelihood by fishing and by servicing fishing fleets operating off the coast of Newfoundland.[3] The climate and the small amount of available land hardly favour activity such as farming and livestock (weather conditions are severe, which confines the growing season to a few weeks, and the soil contains significant peat and clay and is largely infertile).[38] Since 1992, the economy has been in steep decline, following the depletion of fish stocks, the limitation of fishing areas and the ban imposed on all cod fishing by the Canadian Government.[39]
The rise in unemployment has been curtailed by the state financial aid for the retraining of businesses and individuals. The construction of the new airport also helped sustain the activity in the construction industry and public works.[22] Fish farming, crab fishing and agriculture are being developed to diversify the local economy.[3] The future of Saint Pierre and Miquelon rests on tourism, fisheries and aquaculture. Explorations are underway to exploit deposits of oil and gas.[22] Tourism relies on the proximity to Canada, while commerce and crafts make up the bulk of the business sector.[38]
The labour market is characterized by high seasonality, due to climatic hazards. Traditionally, all outdoor activities (construction, agriculture, etc.) were suspended between December and April.[40] In 1999, the unemployment rate was 12.8%, and a third of the employed worked in the public sector. The employment situation was worsened by the complete cessation of deep sea fishing, the traditional occupation of the islanders, as the unemployment rate in 1990 was lower at 9.5%.[12] The unemployment for 2010 shows a decrease from 2009, from 7.7% to 7.1%.[40] Exports are very low (5.1% of GDP) while imports are significant (49.1% of GDP).[41] About 70% of the islands' supplies are imported from Canada or from France via Nova Scotia.[24]
The official currency is the euro.[42] The Canadian dollar is also widely accepted, but change is usually given in euros.[43] The "Institut d'émission des départements d'outre-mer" (IEDOM), the French public institution responsible for issuing currency in the overseas territories that use the euro on behalf of the Bank of France, has had an agency in Saint Pierre since 1978.[44] The islands have issued their own stamps from 1885 to the present, except for a period between 1 April 1978 and 3 February 1986 when French stamps were used.[45]
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1847 | 1,665 | — |
| 1860 | 2,916 | +75.1% |
| 1870 | 4,750 | +62.9% |
| 1897 | 6,352 | +33.7% |
| 1902 | 6,842 | +7.7% |
| 1907 | 4,760 | −30.4% |
| 1911 | 4,209 | −11.6% |
| 1921 | 3,918 | −6.9% |
| 1926 | 4,030 | +2.9% |
| 1931 | 4,321 | +7.2% |
| 1936 | 4,175 | −3.4% |
| 1945 | 4,354 | +4.3% |
| 1951 | 4,606 | +5.8% |
| 1957 | 4,879 | +5.9% |
| 1962 | 5,025 | +3.0% |
| 1967 | 5,235 | +4.2% |
| 1974 | 5,840 | +11.6% |
| 1982 | 6,041 | +3.4% |
| 1990 | 6,277 | +3.9% |
| 1999 | 6,316 | +0.6% |
| 2006 | 6,125 | −3.0% |
| 2011 | 6,080 | −0.7% |
| INSEE (1847–1962;[46] 1967–2011[47]) | ||
The total population of the islands at the January 2011 census was 6,080,[1] of which 5,456 lived in Saint-Pierre and 624 in Miquelon-Langlade.[48] At the 1999 census, 76% of the population was born on the archipelago, while 16.1% were born in metropolitan France, a sharp increase from the 10.2% in 1990. In the same census, less than 1% of the population reported being a foreign national.[12] The archipelago has a high emigration rate, especially among young adults, who often leave for their studies without returning afterwards.[12] Even at the time of the great prosperity of the cod fishery, the population growth had always been constrained by the geographic remoteness, harsh climate and infertile soils.[12]
Ethnography
While some ruins show a presence of indigenous American people on the archipelago, it is unlikely that there were year-round settlements beyond occasional fishing and hunting expeditions.[36] The current population is the result of inflows of settlers from the French ports, mostly Normans, Basques, Bretons and Saintongeais, and also from Acadia and Newfoundland.[36]
Languages
The inhabitants speak French; their customs and traditions are similar to the ones found in metropolitan France.[24] The French spoken on the archipelago is closer to Metropolitan French than to Canadian French but maintains a number of unique features.[49] Basque, formerly spoken in private settings by people of Basque ancestry, disappeared from the island by the late 1950s.[50]
Religion
The majority of the population is Roman Catholic,[24] and the islands are home to the Roman Catholic Vicariate Apostolic of Iles Saint-Pierre and Miquelon.
Culture
Every year in the summer there is a Basque Festival, with demonstrations of harrijasotzaile (stone heaving), aizkolari (lumberjack skills), and pelota.[51] The local cuisine is mostly based on seafood such as lobster, snow crab, mussels and especially cod.[52]
Ice hockey is very popular in Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, with local teams often competing in Newfoundland-based leagues. Several players from the islands have played on French and Canadian teams and even participated on the French national ice hockey team in the Olympics.
Street names are not commonly used on the islands. Directions and locations are commonly given using nicknames and the names of nearby residents.[53]
The only time the guillotine was ever used in North America was in Saint-Pierre in the late 19th century. Joseph Néel was convicted of killing Mr. Coupard on Île aux Chiens on 30 December 1888, and executed by guillotine on 24 August 1889. The guillotine had to be shipped from Martinique and it did not arrive in working order. It was very difficult to get anyone to perform the execution; finally a recent immigrant was coaxed into doing the job. This event was the inspiration for the film The Widow of Saint-Pierre (La Veuve de Saint-Pierre) released in 2000. The guillotine is now in a museum in Saint-Pierre.
Transportation
For many years[when?], there has been no direct air link between the islands and mainland France.[22] A new airport opened in 1999 and was intended to overcome this problem, but the situation remained unchanged. Nevertheless, the new facility has a very modern "all weather conditions landing system".[citation needed] All flights from and to Saint-Pierre pass through Canada.[22] Air Saint-Pierre's ATR 42 aircraft flies seasonally from the Canadian airports of Sydney and Stephenville, and year-round from Halifax, Montreal and St John's.[54]
With regular service from April to November or December, a passenger-only ferry connects the Newfoundland town of Fortune with Saint-Pierre. The same ferry operates year-round between Saint-Pierre, Langlade and Miquelon.[55]
Communications
The factual accuracy of parts of this article (those related to television broadcasts) may be compromised due to out-of-date information. (November 2013) |

Saint-Pierre and Miquelon has four radio stations, all of them on the FM band (the last stations converted from the AM band in 2004). Three of the stations are on Saint-Pierre, two of which are owned by Outre-Mer 1ère, along with one 1ère station on Miquelon. At night, these stations broadcast France-Inter. The other station (Radio Atlantique) is an affiliate of Radio France Internationale. The nation is linked to North America and Europe by satellite communications for telephone and television service.
The department of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon is served by three television stations: Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon 1ère (call letters FQN) on Channel 8, with a repeater on Channel 31, and France Ô on Channel 6. While Saint-Pierre and Miquelon use the French SECAM-K1 standard for television broadcasts, the local telecommunications provider (SPM Telecom) carries many North American television stations and cable channels, converted from North America's NTSC standard. In addition, Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon 1ère is carried on Shaw Direct satellite and most digital cable services in Canada, converted to NTSC.
SPM Telecom is also the department's main Internet Service Provider, with its internet service being named "Cheznoo" (a play on Chez-Nous, French for "Our Place"). SPM Telecom also offers cellular phone and mobile phone service (for phones that adhere to the GSM standard). SPM Telecom uses the GSM 900 MHz band,[56] which is different from the GSM 850 MHz and 1900 MHz bands used in the rest of North America.
As of 2015[update], Saint Pierre and Miquelon was ranked third in the world for internet download speed, behind Singapore and Hong Kong.[57]
The islands are treated as a separate country-level entity among radio amateurs, identifiable with ITU prefix "FP". Visiting radio amateurs, mainly from the US, activate Saint-Pierre and Miquelon every year on amateur radio frequencies. The islands are well known among radio amateurs, who collect contacts with these stations for Islands on the Air and DX Century Club awards; the geographic location of Saint Pierre and Miquelon gives a very good takeoff for shortwave communication all over the world.[citation needed]
Education and healthcare
The archipelago has 4 primary schools, 1 middle school with an annex in Miquelon, 1 state high school and 1 vocational high school.
The students who wish to further their studies after high school are granted access to scholarships to study overseas. Many students go to France, although some go to Canada (mainly in Quebec and New Brunswick), and the United States.[58]
Saint Pierre's institute for higher learning is the Institut Frecker, which is associated with Memorial University of Newfoundland.[citation needed] Since 2000, Frecker had been operated by the Government of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, with support of the federal government of Canada and the provincial government of Newfoundland and Labrador.[citation needed]
Saint-Pierre and Miquelon's health care system is entirely public and free.[58] In 1994, France and Canada signed an agreement allowing the residents of the archipelago to be treated in St. John's.[58] In 2015 St-Pierre and Miquelon indicated they would start looking for a new healthcare provider as recent rate hikes by Eastern Health in Newfoundland were too expensive (increasing to $3.3 million in 2014 from $2.5 million in 2010). Currently Halifax, Nova Scotia or Moncton, New Brunswick are possible locations.[59] Hôpital François Dunan provides basic care and emergency care for residents of both islands.[60]
See also
References
- ^ a b c INSEE, Government of France. "Populations légales 2011 pour les départements et les collectivités d'outre-mer" (in French). Retrieved 26 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Check|first=value (help) - ^ a b "Evaluation du PIB 2004 de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon – janvier 2007" (PDF). p. 24. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f "Saint Pierre and Miquelon". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- ^ Premio Real (22 February 2005). "Les iles Saint-Pierre et Miquelon – Notes de la conférence donnée à l'Institut Canadien, devant la Société Géographique de Québec, le 29 avril 1880, par Son Excellence le comte de Premio-Real, consul-général d'Espagne". Ia600302.us.archive.org. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "Flight distance from Brest, France to Saint Pierre and Miquelon". Travelmath.com. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b "St. Pierre et Miquelon". Newfoundland and Labrador Heritage. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "PATRON SAINT INDEX TOPIC: fishermen, anglers". Catholic Community Forum. Archived from the original on 20 February 2007.
- ^ Hoyarçabal, Martin de: Les voyages aventureux du Capitaine Martin de Hoyarsal, habitant du çubiburu (Bordeaux, France, 1579)
- ^ "The Basques of Saint Pierre and Miquelon". Buber's Basque Page. 30 April 2006. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b "Tourism Agencies in Saint Pierre et Miquelon". St-pierre-et-miquelon.com. Retrieved 27 September 2007.
- ^ Cormier, Marc Albert: Toponymie ancienne et origine des noms Saint-Pierre, Miquelon et Langlade. The Northern Mariner Vol. 7, Ottawa, 1997. pp 1:29–44
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Le recensement de la population à Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon" (PDF). INSEE. August 2000. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g France's Overseas Frontier: Départements Et Territoires D'outre-mer, p. 33, at Google Books By Robert Aldrich, John Connell
- ^ Atlantic Canada, p. 15, at Google Books By Benoit Prieur
- ^ a b The French Atlantic: travels in culture and history, p. 97, at Google Books By Bill Marshall
- ^ a b c Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "St Pierre". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ^ a b The Fog of War: Censorship of Canada's Media in World War II, p. 59, at Google Books By Mark Bourrie
- ^ "St. Pierre And Miquelon Imported 1,815,271 Gallons From Canada in Twelve Months". The New York Times. 25 October 1931. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b "St Pierre and Miquelon". BBC News. 2 November 2011. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ War, cooperation, and conflict: the European possessions in the Caribbean ..., p. 179, at Google Books By Fitzroy André Baptiste
- ^ "St Pierre Stays French". The Calgary Herald. 18 December 1958. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Le recensement de la population à Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon en 2006". Insee. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b c "Saint-Pierre et Miquelon, Statut spécifique". Sodepar. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f Saint-Pierre and Miquelon at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ "La préfecture". Portail internet des services de l'Etat. 7 December 2008. Archived from the original on 1 April 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Préfet de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon". Portail internet des services de l'Etat. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ^ Berly, Michel; Bastien, Jean-Marie. "Historique: Site non officiel de la gendarmerie nationale" (in French). Retrieved 7 August 2010.
- ^ "Ocean Guardian II: September 13–14, 2005; Evaluation Report" (PDF). Canadian Coast Guard. Retrieved 7 August 2010.
- ^ "La Gendarmerie Nationale". Portail internet des services de l'Etat. 24 February 2011. Archived from the original on 12 April 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Canadian foreign policy: defining the national interest, p. 32, at Google Books By Steven Kendall Holloway
- ^ "St Pierre and Miquelon – Squaring off for a seabed scrap". The Economist. 7 May 2009. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d e "Rapport annuel 2010 IEDOM Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon" (PDF). p. 16. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b James Marsh. "Saint-Pierre and Miquelon". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "La Géologie des îles Saint-Pierre et Miquelon". Encyclopédie des îles Saint-Pierre & Miquelon (in French). Miquelon Conseil. Archived from the original on 11 January 2006.
- ^ "Saint Pierre Temperature Averages". Weatherbase. Retrieved 3 February 2015.
- ^ a b c "Présentation". L'Outre-Mer. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "Statistiques: Saint Pierre, Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon". Météo France. Retrieved 28 August 2013.
- ^ a b Economie – L'Outre-Mer Archived 2012-05-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Law, Bill (8 March 2006). "French islands bid for oil-rich sea". BBC News. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ a b "Rapport annuel 2010 IEDOM Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon" (PDF). p. 29. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "Evaluation du PIB 2004 de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon – janvier 2007" (PDF). p. 32. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "Council decision of 31 December 1998 concerning the monetary arrangements in the French territorial communities of Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon and Mayotte". 31 December 1998. Retrieved 30 May 2010.
- ^ The rough guide to Canada, p. 493, at Google Books By Tim Jepson, Phil Lee, Tania Smith, Emma Rose Rees, Christian Williams
- ^ "Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon". IEDOM. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "ST. PIERRE ET MIQUELON". Online Catalogue. Stanley Gibbons. Retrieved 1 December 2007.
- ^ "Population totale au recensement: Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon (serie historique 1847–1962)". Bdm.insee.fr. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "Population totale au recensement: Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon". Bdm.insee.fr. 31 December 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ INSEE, Government of France. "Populations légales 2011 pour les communes de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon" (in French). Retrieved 26 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Check|first=value (help) - ^ "Le français parlé aux îles Saint-Pierre et Miquelon". Le GrandColombier.com. 29 April 2010. Archived from the original on 5 April 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Marc Cormier. "The Basque colony of Saint-Pierre et Miquelon". Archived from the original on 2 June 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "'Zazpiak Bat' Basque Club" (in French). Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- ^ "Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon". 2011, Année des Outre-mer. 28 January 2011. Archived from the original on 20 November 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Emile SASCO. "Historique des Rues de Saint-Pierre". Encyclopédie des îles Saint-Pierre & Miquelon (in French). Miquelon Conseil. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011.
- ^ "Tourism in Saint-Pierre and Miquelon islands – How to get here". Comité Régional du Tourisme. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "Conseil Territorial de Saint-Pierre et Miquelon - Régie Transports Maritimes - Rotations du Cabestan" (in French). Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ "GSM Coverage Maps – Saint-Pierre and Miquelon". Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ "Download Speed by Countries". Retrieved 13 May 2015.
- ^ a b c "Overview". Saint-Pierre and Miquelon Community Profile. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ Walsh, Adam. "St-Pierre-Miquelon shopping around for a health provider, N.L. prices too steep". CBC News. Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- ^ "Portail internet des services de l'Etat: Le Centre Hospitalier François Dunan" (in French). Archived from the original on 19 May 2009. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
Further reading
- Thomas, Martin (1997). "Deferring to Vichy in the Western Hemisphere: The St. Pierre and Miquelon Affair of 1941". International History Review. 19 (4): 809–835. doi:10.1080/07075332.1997.9640805.
External links
- Template:Dmoz
- Local autonomous government of Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Government of Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon Template:Fr icon
- Tourism and Travel in Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
- Comité Régional du Tourisme (local government initiative)
- History of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
46°47′N 56°12′W / 46.783°N 56.200°W
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Appalachian Mountains
- Dependent territories in North America
- Special territories of the European Union
- Islands of the North Atlantic Ocean
- Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- French-speaking countries and territories
- Overseas departments and territories of France
- States and territories established in 1946
- Territorial disputes of Canada
- Former departments of France in France
- Territorial disputes of France



