Turpan
Turpan
吐鲁番市 · تۇرپان شەھىرى | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Location of Turpan City (red) in Turpan Prefecture (yellow) and Xinjiang | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Region | Xinjiang |
| Prefecture | Turpan Prefecture |
| Township-level divisions | 3 subdistricts 2 towns 7 townships |
| Municipal seat | Laocheng Subdistrict (老城街道) |
| Population (2003) | |
| • Total | 254,900 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 838000 |
| Area code | 0995 |
Turpan (Template:Ug; simplified Chinese: 吐鲁番; traditional Chinese: 吐魯番; pinyin: Tǔlǔfān), also known as Turfan or Tulufan, is an oasis county-level city in Turpan Prefecture, in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Its population was 254,900 at the end of 2003.
History
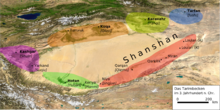
Turpan has long been the centre of a fertile oasis (with water provided by karez) and an important trade centre. It was historically located along the Silk Road's northern route, at which time it was adjacent to the kingdoms of Korla and Karashahr to the southwest and the town of Qarakhoja (Gaochang) to the southeast.
The peoples of the Kingdoms of Nearer and Further Jushi 車師 (the Turpan Oasis and the region to the north of the mountains near modern Jimasa), were closely related. It was originally one kingdom called Gushi 故師 (Wade–Giles: Ku-shih) which the Chinese conquered in 107 BC.[1] It was subdivided into two kingdoms by the Chinese in 60 BC. During the Han era the city changed hands several times between the Xiongnu and the Han, interspersed with short periods of independence.[2]
After the fall of the Han Dynasty, the region was virtually independent but tributary to various dynasties. Until the 5th century AD, the capital of this kingdom was Jiaohe (modern Yarghul – 16 km west of Turpan).[3]
From 487 to 541 AD, Turpan was an independent Kingdom ruled by a Turkic tribe known to the Chinese as the Tiele. The Rouran Khaganate defeated the Tiele and subjugated Turpan, but soon afterwards the Rouran were destroyed by the Göktürks.

Tang conquest
The Tang Dynasty reconquered the Tarim Basin by the 7th century AD. During the 7th, 8th, and early 9th centuries the Tibetan Empire, the Tang Chinese, and Turks fought to conquer the Tarim Basin. Sogdians and Chinese engaged in extensive commercial activities with each other under Tang rule. The Sogdians were mostly Mazdaist at this time. Turpan, renamed Xizhou by the Tang after their armies conquered it in 640AD,[4] had a history of commerce and trade along the Silk Road already centuries old; it had many inns catering to merchants and other travelers, while brothels are recorded as having been numerously available in Kucha and Khotan.[5] As a result of the Tang conquest, policies forcing minority group relocation and encouraging Han settlement lead to Turpan's name in Sogdian language becoming known as “Chinatown” or "Town of the Chinese".[4][6]
In Astana, a contract written in Sogdian detailing the sale of a Sogdian girl to a Chinese man was discovered dated to 639 AD. Individual slaves were common among silk route houses; early documents recorded an increase in the selling of slaves in Turpan.[7] Twenty-one 7th-century marriage contracts were found that showed, where one Sogdian spouse was present, for 18 of them their partner was a Sogdian. The only Sogdian men who married Chinese women were highly eminent officials.[8] Several commercial interactions were recorded, for example a camel was sold priced at 14 silk bolts in 673,[9][10] and a Chang'an native bought a girl age 11 for 40 silk bolts in 731 from a Sogdian merchant.[11] Five men swore that the girl was never free before enslavement, since the Tang Code forbade commoners to be sold as slaves.[4]
The Tang Dynasty became weakened considerably after the An Lushan Rebellion and the Tibetans took the opportunity to expand into Gansu and the Western Regions. The Tibetans took control of Turfan in 792.
Uyghur rule
In 803, the Uyghurs of the Uyghur Khaganate seized Turfan from the Tibetans. The Uyghur Khaganate however was destroyed by the Kirghiz and its capital Ordu-Baliq in Mongolia sacked in 840. The defeat resulted in the mass movement of the Uyghurs out of Mongolia and their dispersal into Gansu and Central Asia, and many joined other Uyghurs already present in Turfan.
The Uyghurs established a Kingdom in the Turpan region with its capital in Gaochang or Kara-Khoja. The kingdom was known as the Uyghuria Idikut state or Kara-Khoja Kingdom that lasted from 856 to 1389 AD. The Uyghurs were Manichaean but later converted to Buddhism and funded the construction the cave temples in the Bezeklik Caves. The Uyghurs formed an alliance with the rulers of Dunhuang. The Uyghur state later became a vassal state of the Kara-Khitans, and then as a vassal of the Mongol Empire. This Kingdom was led by the Idikuts, or Saint Spiritual Rulers. The last Idikut left Turpan area in 1284 for Kumul, then Gansu to seek protection of Yuan Dynasty, but local Uyghur Buddhist rulers still held power until Invasion of Moghul Hizir Khoja in 1389. The conversion of the local Buddhist population to Islam was completed nevertheless only in the second half of the 15th century.[12]
15th and 16th centuries
As late as 1420, the Timurid envoy Ghiyāth al-dīn Naqqāsh, who passed through Turpan on the way from Herat to Beijing, reported that many of the city's residents were "infidels". He visited a "very large and beautiful" temple with a statue of Shakyamuni; in one of the versions of his account it was also claimed that many Turpanians "worshipped the cross".[13]

The Moghul ruler of Turpan Yunus Khan, also known as Ḥājjī `Ali, (ruled 1462–1478) unified Moghulistan (roughly corresponding to today's Eastern Xinjiang) under his authority in 1472. Around that time, a conflict with the Ming China started over the issues of tribute trade: Turpanians benefited from sending "tribute missions" to China, which allowed them to receive valuable gifts from the Ming emperors and to do plenty of trading on the side; the Chinese, however, felt that receiving and entertaining these missions was just too expensive. (Muslim envoys to the early Ming China were impressed by the lavish reception offered to them along their route through China, from Suzhou to Beijing, such as described by Ghiyāth al-dīn Naqqāsh in 1420–1421.[14])

Yunus Khan was irritated by the restrictions on the frequency and size of Turpanian missions (no more than one mission in 5 years, with no more than 10 members) imposed by the Ming government in 1465, and by the Ming's refusal to bestow sufficiently luxurious gifts on his envoys (1469). Accordingly, in 1473 he went to war against China, and succeeded in capturing Hami in 1473 from the Oirat Mongol Henshen and holding it for a while, until Ali was repulsed by the Ming Dynasty into Turfan. He reoccupied Hami after Ming left. Henshen's Mongols recaptured Hami twice in 1482 and 1483, but the son of Ali, Ahmad Alaq, reconquered it in 1493 and captured the Hami leader and the resident of China in Hami (Hami was a vassal state to Ming). In response, the Ming Dynasty imposed an economic blockade on Turfan and kicked out all the Uyghurs from Gansu. It became so harsh for Turfan that Ahmed left. Ahmed's son Mansur succeeded him and took over Hami in 1517.[15][16] These conflicts were called the Ming Turpan Border Wars.
Several times, after occupying Hami, Mansur tried to attack China in 1524 with 20,000 men, but was beaten by Chinese forces. The Turpan kingdom under Mansur, in alliance with Oirat Mongols, tried to raid Suzhou in Gansu in 1528, but were severely defeated by Ming Chinese forces and suffered heavy casualties.[17] The Chinese refused to lift the economic blockade and restrictions that had led to the battles, and continued restricting Turpan's tribute and trade with China. Turfan also annexed Hami.[18]
19th century

Francis Younghusband visited Turpan in 1887 on his overland journey from Beijing to India. He said it consisted of two walled towns, a Chinese one with a population of no more than 5,000 and, about a mile (1.6 km) to the west, a Turk town of "probably" 12,000 to 15,000 inhabitants. The town (presumably the "Turk town") had four gateways, one for each of the cardinal directions, of solid brickwork and massive wooden doors plated with iron and covered by a semicircular bastion. The well-kept walls were of mud and about 35 ft (10.7 m) tall and 20 to 30 feet (6 to 9 m) thick, with loopholes at the top. There was a level space about 15 yards (14 m) wide outside the main walls surrounded by a musketry wall about 8 ft (2.4 m) high, with a ditch around it some 12 ft (3.7 m) deep and 20 ft (6 m) wide). There were drumtowers over the gateways, small square towers at the corners and two small square bastions between the corners and the gateways, "two to each front." Wheat, cotton, poppies, melons and grapes were grown in the surrounding fields.[19]
Turpan grapes impressed other travelers to the region as well. The 19th-century Russian explorer Grigory Grumm-Grzhimaylo, thought the local raisins may be "the best in the world", and noted the buildings of a "perfectly peculiar design" used for drying them.[20]
Geography and climate
| Turpan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Turpan is located about 150 km (93 mi) southeast of Ürümqi, Xinjiang's capital, in a mountain basin, on the northern side of the Turpan Depression, at an elevation of 30 m (98 ft) above sea level. Outside of Turpan is a small volcanic cone, the Turfan volcano, that is said to have erupted in 1120 as described in the Song Dynasty.[22]
Turpan has a harsh, drastic, cold desert climate (Köppen BWk), with very hot and long summers, and very cold but short winters, and brief spring and autumn in between. Annual precipitation is very low, amounting to only 15.7 millimetres (0.62 in). The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from −7.6 °C (18.3 °F) in January to 32.2 °C (90.0 °F) in July; the annual mean is 14.4 °C (57.9 °F).[21] With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 48% in December to 75% in September, sunshine is abundant and the city receives 2,912 hours of bright sunshine annually.
Extremes have ranged from −28.9 °C (−20 °F) to 48.1 °C (119 °F), although a reading of 49.6 °C (121 °F) in July 1975 is regarded as dubious.[23]
However, the very heat and dryness of the summer, when combined with the area's ancient system of irrigation, allows the countryside around Turpan to produce great quantities of high-quality fruit.
| Climate data for Turpan, elevation 39 m (128 ft), (1991–2020 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
40.5 (104.9) |
43.6 (110.5) |
47.6 (117.7) |
49.1 (120.4) |
47.8 (118.0) |
43.4 (110.1) |
34.3 (93.7) |
23.0 (73.4) |
9.6 (49.3) |
49.1 (120.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −2.3 (27.9) |
7.0 (44.6) |
17.9 (64.2) |
27.8 (82.0) |
33.9 (93.0) |
38.8 (101.8) |
40.5 (104.9) |
39.0 (102.2) |
32.6 (90.7) |
22.5 (72.5) |
10.3 (50.5) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
22.3 (72.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −6.7 (19.9) |
1.3 (34.3) |
11.6 (52.9) |
20.7 (69.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
31.6 (88.9) |
33.1 (91.6) |
31.2 (88.2) |
24.6 (76.3) |
14.5 (58.1) |
4.4 (39.9) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
15.7 (60.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −10.3 (13.5) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
5.9 (42.6) |
14.2 (57.6) |
19.8 (67.6) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.5 (79.7) |
24.6 (76.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
9.1 (48.4) |
0.3 (32.5) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
10.2 (50.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −28.9 (−20.0) |
−24.5 (−12.1) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
4.7 (40.5) |
11.5 (52.7) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.6 (52.9) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−17.8 (0.0) |
−26.1 (−15.0) |
−28.9 (−20.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0.9 (0.04) |
0.5 (0.02) |
0.7 (0.03) |
0.9 (0.04) |
1.0 (0.04) |
2.6 (0.10) |
2.0 (0.08) |
2.0 (0.08) |
1.4 (0.06) |
1.2 (0.05) |
0.6 (0.02) |
0.9 (0.04) |
14.7 (0.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 12.9 |
| Average snowy days | 2.5 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 2.6 | 6.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 56 | 40 | 25 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 30 | 31 | 35 | 45 | 50 | 56 | 37 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 121.8 | 172.0 | 234.2 | 263.7 | 308.4 | 301.6 | 303.3 | 299.6 | 273.5 | 238.6 | 163.7 | 108.2 | 2,788.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 41 | 57 | 62 | 65 | 67 | 66 | 66 | 71 | 74 | 71 | 57 | 39 | 61 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[24][25][26] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: [27] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Turpan (Dongkan Station), elevation −49 m (−161 ft), (1991–2020 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −1.9 (28.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
18.6 (65.5) |
28.5 (83.3) |
34.5 (94.1) |
39.3 (102.7) |
40.8 (105.4) |
39.3 (102.7) |
33.2 (91.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
10.9 (51.6) |
0.0 (32.0) |
22.8 (73.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −8.0 (17.6) |
0.5 (32.9) |
11.1 (52.0) |
20.7 (69.3) |
26.8 (80.2) |
31.9 (89.4) |
33.3 (91.9) |
31.4 (88.5) |
24.8 (76.6) |
14.8 (58.6) |
3.8 (38.8) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
15.5 (59.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −12.8 (9.0) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
4.5 (40.1) |
13.8 (56.8) |
19.7 (67.5) |
24.9 (76.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
24.7 (76.5) |
18.3 (64.9) |
8.6 (47.5) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
9.3 (48.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0.8 (0.03) |
0.4 (0.02) |
0.6 (0.02) |
1.0 (0.04) |
1.0 (0.04) |
2.5 (0.10) |
2.0 (0.08) |
1.9 (0.07) |
1.3 (0.05) |
0.9 (0.04) |
0.4 (0.02) |
0.6 (0.02) |
13.4 (0.53) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 12.8 |
| Average snowy days | 2.2 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 4.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 56 | 41 | 26 | 24 | 25 | 28 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 41 | 48 | 57 | 37 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 161.9 | 193.2 | 246.9 | 267.1 | 307.9 | 304.8 | 306.1 | 302.3 | 282.0 | 254.7 | 186.0 | 140.0 | 2,952.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 55 | 64 | 66 | 66 | 67 | 67 | 67 | 71 | 77 | 76 | 65 | 50 | 66 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[24][28] | |||||||||||||
Demography

According to the 2000 census, the city of Turpan had a population of 251,652 (population density 15.99 inh./km²). The breakdown by nationality was as follows:
| Ethnicity | Inhabitants | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Uyghur | 177,106 | 70.38% |
| Han | 55,238 | 21.95% |
| Hui | 18,482 | 7.34% |
| Tujia | 182 | 0.07% |
| Manchu | 132 | 0.05% |
| Tu | 98 | 0.04% |
| Mongol | 77 | 0.03% |
| Tibetan | 70 | 0.03% |
| Kazakh | 56 | 0.02% |
| Miao | 45 | 0.02% |
| Russian | 33 | 0.01% |
| Zhuang | 31 | 0.01% |
| Dongxiang | 30 | 0.01% |
| Iranian | 72 | 0.03% |
Transport
Turpan is served by China National Highway 312. It is the junction for the Lanzhou-Xinjiang and the Southern Xinjiang Railways.
See also

- Bezeklik Thousand Buddha Caves
- Silk Road transmission of Buddhism
- Gaochang
- Tarim mummies
- Jiaohe Ruins
- Flaming Mountains
- Dingling (with a special section about the Fufuluo)
- Turpan Museum
- Ayding Lake
- Chunche
- Grape Valley
- Turpan Karez Paradise
Footnotes
- ^ Hill (2009), p. 109.
- ^ Hill (2009), p. 442.
- ^ [1]
- ^ a b c HANSEN, Valerie. "The Impact of the Silk Road Trade on a Local Community: The Turfan Oasis, 500-800" (PDF). Yale University Press. Retrieved 14 July 2010.
- ^ Xin Tangshu 221a:6230. In addition, Susan Whitfield offers a fictionalized account of a Kuchean courtesan's experiences in the 9th century without providing any sources, although she has clearly drawn on the description of the prostitutes' quarter in Chang’an in Beilizhi; Whitfield, 1999, pp. 138-154.
- ^ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12288967
- ^ Wu Zhen 2000[citation needed] (p. 154 is a Chinese-language rendering based on Yoshida's Japanese translation of the Sogdian contract of 639).
- ^ Rong Xinjiang, 2001, pp. 132-135. Of the 21 epitaphs, 12 are from Quan Tangwen buyi (supplement to the complete writings of the Tang), five from Tangdai muzhi huibian (Collected epitaphs of the Tang), three were excavated at Guyuan, Ningxia, and one is from another site.
- ^ Yan is a common ending for Sogdian first names meaning ‘for the benefit of’ a certain deity. For other examples, see Cai Hongsheng, 1998, p. 40.
- ^ Ikeda contract 29.
- ^ Ikeda contract 31. Yoshida Yutaka and Arakawa Masaharu saw this document, which was clearly a copy of the original with space left for the places where the seals appeared.
- ^ 关于明代前期土鲁番统治者世系的几个问题 - 中国边疆网 - 中国社会科学院
- ^ Bellér-Hann., Ildikó (1995), A History of Cathay: a translation and linguistic analysis of a fifteenth-century Turkic manuscript, Bloomington: Indiana University, Research Institute for Inner Asian Studies, p. 159, ISBN 0-933070-37-3. Christianity is mentioned in the Turkic translation of Ghiyāth al-dīn's account published by Bellér-Hann, but not in the earlier Persian versions of his story.
- ^ Bellér-Hann 1995, pp. 160–175
- ^ Trudy Ring, Robert M. Salkin, Sharon La Boda (1996). International Dictionary of Historic Places: Asia and Oceania. Taylor & Francis. p. 323. ISBN 1-884964-04-4. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Godrich & Fang 1976
- ^ Luther Carrington Goodrich, Chao-ying Fang (1976). Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368–1644. Columbia University Press. p. 1038. ISBN 0-231-03833-X. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- ^ Jonathan D. Spence, John E. Wills, Jr., Jerry B. Dennerline (1979). From Ming to Ch'ing: Conquest, Region, and Continuity in Seventeenth-Century China. Yale University Press. p. 177. ISBN 0-300-02672-2. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Younghusband, Francis E. (1896). The Heart of a Continent, pp. 139-140. John Murray, London. Facsimile reprint: (2005) Elbiron Classics. ISBN 1-4212-6551-6 (pbk); ISBN 1-4212-6550-8 (hardcover).
- ^ Grigory Grumm-Grzhimaylo (Г. Грум-Гржимайло), East Turkestan (Восточный Туркестан), in Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary. Template:Ru icon (The original quote: «Турфан же славится и своим изюмом, который можно считать лучшим в мире (высушивается в совершенно своеобразного типа сушильнях)», i.e. "Turfan is also famous for its raisins, which may be deemed the best in the world. They are dried in drying houses of a completely peculiar type".
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
CMAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Turfan". Global Volcanism Program. Retrieved 21 August 2011.
- ^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ a b 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 25 May 2010.
- ^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
References
- Goodrich, L. Carrington; Fang, Chaoying, eds. (1976), "Ḥājjī `Ali", Dictionary of Ming Biography, 1368–1644. Volume I (A-L), Columbia University Press, pp. 479–481, ISBN 0-231-03801-1
- Hill, John E. (2009) Through the Jade Gate to Rome: A Study of the Silk Routes during the Later Han Dynasty, 1st to 2nd Centuries CE. BookSurge, Charleston, South Carolina. ISBN 978-1-4392-2134-1.
- Hill, John E. 2004. The Peoples of the West from the Weilue 魏略 by Yu Huan 魚豢: A Third Century Chinese Account Composed between 239 and 265 CE. Draft annotated English translation. [2]
- Hulsewé, A. F. P. and Loewe, M. A. N. 1979. China in Central Asia: The Early Stage 125 BC – AD 23: an annotated translation of chapters 61 and 96 of the History of the Former Han Dynasty. E. J. Brill, Leiden.
- Puri, B. N. Buddhism in Central Asia, Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, Delhi, 1987. (2000 reprint).
- Stein, Aurel M. 1912. Ruins of Desert Cathay: Personal narrative of explorations in Central Asia and westernmost China, 2 vols. Reprint: Delhi. Low Price Publications. 1990.
- Stein, Aurel M. 1921. Serindia: Detailed report of explorations in Central Asia and westernmost China, 5 vols. London & Oxford. Clarendon Press. Reprint: Delhi. Motilal Banarsidass. 1980.[3]
- Stein Aurel M. 1928. Innermost Asia: Detailed report of explorations in Central Asia, Kan-su and Eastern Iran, 5 vols. Clarendon Press. Reprint: New Delhi. Cosmo Publications. 1981.
- Yu, Taishan. 2004. A History of the Relationships between the Western and Eastern Han, Wei, Jin, Northern and Southern Dynasties and the Western Regions. Sino-Platonic Papers No. 131 March, 2004. Dept. of East Asian Languages and Civilizations, University of Pennsylvania.
External links
- Along the ancient silk routes: Central Asian art from the West Berlin State Museums, an exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF), which contains material from Turpan
- Silk Road Seattle - University of Washington (The Silk Road Seattle website contains many useful resources including a number of full-text historical works, maps, photos, etc.)
- Karez (Qanats) of Turpan, China
- Images and travel impressions along the Silk Road - Turpan PPS in Spanish
