Cham Albanians: Difference between revisions
Sarandioti (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{About|the dialectological group of Northwestern Greece|an overview of different communities of Albanian origin in Greece|Albanian communities in Greece|other uses of the word Cham|Cham (disambiguation)}} |
{{About|the dialectological group of Northwestern Greece|an overview of different communities of Albanian origin in Greece|Albanian communities in Greece|other uses of the word Cham|Cham (disambiguation)}} |
||
{{neutrality}} |
|||
{{Infobox ethnic group |
{{Infobox ethnic group |
||
|group=Cham Albanians |
|group=Cham Albanians |
||
| Line 577: | Line 578: | ||
===Modern history=== |
===Modern history=== |
||
{{neutrality}} |
|||
====First years of Greek rule (1913–1923)==== |
====First years of Greek rule (1913–1923)==== |
||
[[File:454px-The Balkan boundaries after 1.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Territorial changes after the [[Second Balkan War]].]] |
[[File:454px-The Balkan boundaries after 1.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Territorial changes after the [[Second Balkan War]].]] |
||
| Line 677: | Line 679: | ||
====Population exchange and appropriation of property (1923–1926)==== |
====Population exchange and appropriation of property (1923–1926)==== |
||
{{neutrality}} |
|||
[[File:Chams on Filiates 1915.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Chams in Filiates in 1915, by Fred Boissonas]] |
[[File:Chams on Filiates 1915.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Chams in Filiates in 1915, by Fred Boissonas]] |
||
The real problems between the Greek state and the Cham citizens came only after the [[Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)|Greco-Turkish War]] of 1919–1922.<ref name = Victor/> At the conclusion of the war, Greece and Turkey signed the [[Treaty of Lausanne]], which included a [[population exchange between Greece and Turkey|population exchange between the two countries]]. The treaty used religion as the indicator of national affiliation, thus including all Muslims, even Albanians, in the population exchange. Under this treaty Muslims of Greece would have been exchanged with Christians of Turkey, with an exception of Muslims of Thrace and Christians of Instanbul.<ref>{{citation |
The real problems between the Greek state and the Cham citizens came only after the [[Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)|Greco-Turkish War]] of 1919–1922.<ref name = Victor/> At the conclusion of the war, Greece and Turkey signed the [[Treaty of Lausanne]], which included a [[population exchange between Greece and Turkey|population exchange between the two countries]]. The treaty used religion as the indicator of national affiliation, thus including all Muslims, even Albanians, in the population exchange. Under this treaty Muslims of Greece would have been exchanged with Christians of Turkey, with an exception of Muslims of Thrace and Christians of Instanbul.<ref>{{citation |
||
| Line 799: | Line 802: | ||
====Pangalos regime (1926)==== |
====Pangalos regime (1926)==== |
||
{{neutrality}} |
|||
[[File:Pangalos.jpg|thumb|right|130px|[[Theodoros Pangalos]]]] |
[[File:Pangalos.jpg|thumb|right|130px|[[Theodoros Pangalos]]]] |
||
An unexpected turn in Chams' fate occurred when an Arvanite general, known for his pro-Albanian feelings, became prime minister of Greece. On June 24, 1925, a group of officers, fearing that the political instability was putting the country at risk, overthrew the government in a coup and their leader, [[Theodoros Pangalos (general)|Theodoros Pangalos]] became the head of the dictatorial government. His main priorities in foreign relations were to establish good relations with Albania and to protect the rights of both the minorities, either Chams in Greece, or Greeks in Albania. For this reason he officially decided that Albanians of Chameria would not be deported to Turkey after 1926, putting an end to the population exchange. Also, he decided that refugees would not settle in Chameria, but rather in [[Western Thrace]], as was originally decided.<ref name = Psomiades>{{citation |
An unexpected turn in Chams' fate occurred when an Arvanite general, known for his pro-Albanian feelings, became prime minister of Greece. On June 24, 1925, a group of officers, fearing that the political instability was putting the country at risk, overthrew the government in a coup and their leader, [[Theodoros Pangalos (general)|Theodoros Pangalos]] became the head of the dictatorial government. His main priorities in foreign relations were to establish good relations with Albania and to protect the rights of both the minorities, either Chams in Greece, or Greeks in Albania. For this reason he officially decided that Albanians of Chameria would not be deported to Turkey after 1926, putting an end to the population exchange. Also, he decided that refugees would not settle in Chameria, but rather in [[Western Thrace]], as was originally decided.<ref name = Psomiades>{{citation |
||
Revision as of 17:38, 16 June 2009
The neutrality of this article is disputed. |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Albania | 250,000[1] |
| Greece | 40,000[1] |
| Turkey | 80,000–100,000[2] |
| United States of America | 50,000–70,000[1][2] |
| Languages | |
| Albanian also Greek, Turkish and English, depending on residing state | |
| Religion | |
| Islam, Orthodox Christianity | |
Cham Albanians, or Chams (Template:Lang-sq, Template:Lang-el Tsámidhes), are a sub-group of Albanians who originally resided in the coastal region of Epirus in northwestern Greece, an area known among Albanians as Chameria. The Chams have their own peculiar cultural identity, which is a mixture of Albanian and Greek influences as well as many specifically Cham elements. In return, the Chams have influenced the popular cultures of both Albania and Greece: one of the Cham dances, the Tsamiko, is considered a national dance in both countries, and Chams played an important role in starting the renaissance of the Albanian culture in the 19th century. The Chams speak their own dialect of the Albanian language, which is considered one of the two most conservative dialects, the other being Arvanitika.
The first presence of Albanian tribes in Epirus (the ancestors of both Chams and Arvanites) is dated before the 12th century, as a result of migratory process during the Slavic migration to the Balkans. Several Albanian principalities existed in Epirus during the Middle Ages, before the region came under Ottoman control. During the last centuries of Ottoman rule, the majority of the Chams converted to Islam, while a minority retained their original Orthodox faith. In the 19th century, the Chams played an important role in the struggles for independence of both Albania and Greece. Following the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913, the majority of Chameria came under Greek rule. For the next few decades, the Chams were marginalized and discriminated against by the Greek state, who viewed them with distrust. Their properties were confiscated, several thousand were expelled to Turkey, and their cultural identity was suppressed. Throughout the period, the Chams, supported by Albania, campaigned for recognition of minority rights, especially the right to be educated in Albanian. Although some Greek governments reined in the discriminatory practices and guaranteed these rights, they were never implemented as other governments revoked them.
Following the Italian occupation of Albania in 1939, the Chams became a prominent propaganda tool for the Italians. As a result, on the eve of the Greco-Italian War, the adult male Cham population was deported by the Greek authorities to internment camps. After the occupation of Greece, some Cham Albanians collaborated with Italian and German forces, while approximately the same number participated in the Albanian and Greek resistance movements; the majority however remained uninvolved in the war. Nevertheless, in 1944, the entire Muslim Cham population was expelled from Greece, by a republican resistance group, as a result of the participation of Chams in the communist resistance group of Greece, and the collaboration of some members of the minority. This expulsion intended to create a pure ethnic border and to facilitate the anti-communist movement in the aftermath of the war. Most of the Chams crossed the border into Albania, while others formed émigré communities in Turkey and the United States. Today, their descendants continue to live in these countries, although their religious affiliation has changed considerably in the past decades. At the same time, the Orthodox minority that remained in Greece has suffered from decades of suppression of their heritage and language. Since the fall of Communism in Albania, Chams have campaigned for the right of return to their homeland and restoration of their properties which were confiscated. After the war Greece accused the whole population for collaborating with occupation armies, using this as the argument not to recognize the existence of the Cham issue.
Name
| Part of a series on |
| Albanians |
|---|
 |
|
|
Etymology and definition
The name "Cham", together with that of the region, "Chameria", is of uncertain origin. It may derive from the local Greek hydronym Thyamis (Θύαμις in Greek, Çam in Albanian) or from the ancient Thraco-Illyrian tribe of Sameis.[3] In its original ethnographic and dialectological sense, the term Cham comprises the entire Albanian-speaking population of the Thesprotia and Preveza prefectures of Greek Epirus, including both the Muslim and Christian populations.[4]
Chams account for the greatest part of the erstwhile substantial Albanian minority in the wider area of the periphery of Epirus; outside "Chameria" proper, there are only two Albanian-speaking villages further north-east (near Konitsa in Ioannina prefecture), whose inhabitants belong to a different Albanian subgroup, that of the Labs.[5] Historical Albanian population groups of the region such as the 18th and 19th-century Souliotes also spoke the Cham Albanian dialect.[6][7] Today, in the Greek context the use of the term has become largely concentrated on the earlier Muslim minority.[5]
Ethnic appellations
Cham Albanians are known primarily by the Albanian form of the name Chams (Çam or Çamë) and the Greek name Tsamides (Τσάμηδες). It can be found in English sources also as a hybrid form of both names, Tsams.[8] Prior to 1944, Chams were often called by Greek sources Albanophones (Greek: Αλβανόφωνοι),[9][10] or simply Albanians of Epirus.[9]
In Greece, Muslim Chams were referred to by a number of names by different authors. They were called Albanochams (Αλβανοτσάμηδες, Alvanotsamides),[10] and by the misnames Turkalbanians (Τουρκαλβανοί, Tourkalvanoi)[3] or Turkochams (Τουρκοτσάμηδες, Tourkotsamides),[11] which are regarded as derogatory by Cham Albanians.[12]
At the same time, Orthodox Chams are often referred by Greeks as Arvanites (Αρβανίτες),[5][10] which primarily refers to the Albanophone Greeks of southern Greece but is commonly used as for all Albanian-speaking Greek citizens. The local Greek population also calls them Graeco-Chams (Ελληνοτσάμηδες, Elinotsamides),[10] while Muslim Albanians sometimes designate them as Kaur, which means "infidel" and refers to their religion and not to their ethnicity.[10] This term was used by Muslim Albanians for the non-Muslims during the Ottoman Empire.[10] Orthodox Chams use the appellation "Albanians" (Shqiptar in Albanian) for themselves.[13] Chams in Turkey are known by the name Arnauts (Arnavutlar), which applies to all ethnic Albanians in Turkey.[14]
Distribution
Cham communities now mostly exist in Albania, the United States and Turkey, as a result of their expulsion from their homeland, Chameria in Greece after World War II. A minority still lives in this region.[2]
Chameria

Chameria is the name applied by the Albanians to the region originally inhabited by the Chams, which extends from the Ionian coast to the Ioannina mountains in the east, and in the south almost as far as the Preveza gulf. This area corresponds to a few villages in the southern part of the Saranda district in Albania (the municipalities of Konispol, Xarrë and Markat)[15] and to the prefectures of Thesprotia and Preveza in Greece.[15] This area is part of the larger region of Epirus.
Much of the region is mountainous. Valley farmlands are located the central, southern and the western part of Thesprotia, while the terrain of the Preveza Prefecture is mostly hilly. There are two rivers in the region: the Thyamis and Acheron.
The main settlements in which Chams originally resided were: Paramythia,[16] Filiates,[16] Igoumenitsa,[2] Parapotamos,[17] Sybota,[18] Sagiada,[19]Perdika,[18] Parga[20] and Margariti.[10] Preveza and Ioannina also had significant Cham Albanian communities.[21] The Orthodox Chams originally resided in Fanari,[4] Louros[4] and Thesprotiko.[4][5]
Albania
After the expulsion of the Muslim Chams from Greece, they were spread throughout Albania. The majority of Muslim Chams settled on the outskirts of Vlorë, Durrës and Tirana. Several hundred Chams moved into properties along the Himara coast and in existing villages along the coast such as Borshi, or established entirely new villages, such as Vrina, near the Greek border.[2]
Diaspora
Some Chams live in Turkey and the United States. Their number is unknown, but according to some sources, they number 150,000.[2] The first wave of this diaspora left for Turkey during the Greco-Turkish population exchange of 1923. They have populated the areas of Erenköy and Kartal in Istanbul,[22] as well as a number of towns in the area of Bursa, especially Mudanya.[21] After the Second World War, others settled in Izmir, Gemlik and Aydin.[23] After 1944, another part migrated to the United States of America,[2] where they were mainly concentrated in Chicago, as well as Boston and New York.[24]
History
Medieval history
Early presence (up to 14th century)
The chronology of the first presence of Albanians in the region is unknown, due to the scarcity of historical documentation, but it must date before the 12th century.[25] The first undisputed mention of Albanians as an ethnic group in Byzantine sources dates from the second half of the 11th century, where they are named as the inhabitants of Arbanon in central Albania,[26] but it is thought that by that time they lived in Epirus too.[25]
This southward migratory process of Albanian tribes, which began during the late 10th and 11th centuries, would continue: Epirus at the time had a mixed population, with Slavs and Greeks living and cultivating the fertile lowlands, while the mountains were inhabited by Albanian and Vlach pastoralists.[27] The number of Albanians increased over the next centuries under the rule of the Despotate of Epirus,[28] but the first major documented migration occurs in the 14th century,[29] when Albanian tribesmen supported the successful Serbian campaign against the Byzantine possessions in Thessaly and Epirus.[28] This migration wave formed the basis of the Albanian populations in Greece: in Epirus, the evolution of a distinct dialect would eventually differentiate the Chams from their northern cousins,[30] while those Albanians who settled in southern Greece would become the ancestors of the Arvanites.[28]
Medieval states (1358–1434)

In the summer of 1358, Nikephoros II Orsini, the last despot of Epirus of the Orsini dynasty, was defeated in battle against Albanian chieftains near the river Acheloos in Acarnania. Following the approval of the Serbian Tsar, these chieftains established two new states in Arta and Angelokastron (Aetolia).
At its peak in 1367–1403, the Despotate of Arta reached from the Acheron River and the southern border of the Vagnetia region (the medieval name of Thesprotia or Chameria) in the north to the Gulf of Corinth in the south, adjoining with the Principality of Gjon Zenebishti (in Argyrokastro, modern Gjirokastër) and the Despotate of Epirus (centered around in Ioannina).[29] After the death of Gjin Bua Shpata in 1399, the Despotate of Arta declined. Aside from the conflicts with the rulers of Ioannina, Gjin’s successor, Muriq Shpata, had to deal with the encroachment of the Venetians and of Count Carlo I Tocco of Cephalonia. Meanwhile despot Esau de' Buondelmonti of Ioannina called in support of his war against the Albanian nobles, the Ottoman forces leading to increasing incursions of the Ottomans in the region. After the death of Essau in 1411, the throne was offered to his nephew Carlo II Tocco. Not long after killing Muriq Shpata in battle in 1415, Carlo advanced on Arta. In 1416 he defeated Muriq's brother and successor Jakup Shpata, annexed the Despotate of Arta and united most of Epirus under a single ruler again.[28]
The second Albanian principality was the Principality of Gjirokastër, which incorporated parts of northern Vagenetia and the nearby regions, ruled by Gjon Zenebishti. In 1380, Gjon Zenebishi was appointed sebastokrator (prefect) of Vagenetia and was also made governor of the towns of Pyrgos and Sagiada, under the sovereignty of the Despot of Epirus. In 1414 Zenebishi was defeated by the Turks and fled to the Venetian-held island of Corfu, where he died in 1418.[28]
Ottoman rule (1434–1913)
The region of Epirus was conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the early 15th century. In 1443, the northernmost part of Epirus was briefly conquered by Gjergj Kastrioti Skanderbeg as part of his revolt against the Ottoman Empire, but on his death it fell to Venice. By the late 15th century however, the Ottomans had definitively expelled the Venetians from almost the whole area.[28][31] After the Ottoman conquest of the region, a number of Albanians were converted to Islam, while others maintained their Orthodox faith. Cham Albanians played an important role in both the Greek War of Independence and in the National Renaissance of Albania.[2]
From the establishment of the Ottoman rule until 1864, the region of Chameria was included in the Eyalet of Rumelia. It was divided between the sanjaks of Delvina and Ioannina, which were second order administrative divisions.[31] After 1864, this territory was organized under the Vilayet of Yanaya (Ioannina), which was further divided into the sanjaks of Ioannina, Preveza and Gjirokastra.[32] Between 1787 and 1822, Ali Pasha controlled the region, which was incorporated into his Pashalik of Yanina, a de facto independent state under only nominal Ottoman authority.[33]
Albanian language and identity
As Ottoman society was founded on the religion-based millet system and not on ethnic groups, schools in Chameria, as elsewhere where Albanians lived, were only in Turkish and Greek. Christian Albanians could learn in Greek schools, while Muslim Albanians in Turkish schools, but in every case, Albanian language schools were prohibited.[34] The situation would change only during the National Renaissance of Albania, when a number of local Albanians would establish private, unrecognized Albanian-language schools. In 1870, the despot of Paramythia, Grygorios, translated the New Testament into Albanian, as his followers could not understand well the Greek language.[35] While, in 1879, the first Albanian school of the region was created in Sagiada by father Stathi Melani. At that time, the region was under the short-lived rule of the League of Prizren.[31]
Islamization (16th–19th century)
Under Ottoman rule, Islamization was widespread amongst Albanians. In central and southern Albania, by the end of the seventeenth century the urban centers had largely adopted Islam. The growth of an Albanian Muslim elite of Ottoman officials, like pashas and beys, such as the Köprülü family, who played an increasingly important role in Ottoman political and economic life, further strengthened this trend.[31] In northern Chameria the vast majority became Muslims, while south of Acheron and down to Preveza, Albanians remained Orthodox.[1] Muslim Chams were mostly followers of the Bektashi order,[22] especially after the 18th century,[36] when the Bektashis made considerable gains in influence in the rugged areas of southern Albania and northern Greece.[36]
The process of Islamization of the Chams started in the 16th century, but it reached major proportions only in the 18th and 19th centuries. According to the population census (defter) of 1538, the population of the region was almost entirely Orthodox, with only a minority, estimated less than 5 per cent, having converted to Islam. The main instigator for the beginning of mass conversions in the region were the draconian measures adopted by the Ottomans after the two failed revolts of Dionysius the Philosopher, who had led an army made of Orthodox Albanians and Greeks, as well as a number of Muslim local farmers, against the Ottomans.[37] In their wake, the Ottoman pashas tripled the taxes owed by the non-Muslim population, as they regarded the Orthodox element a continuous threat of future revolts. Another reason for conversion was the absence of liturgical ceremonies in Chameria, especially in the northern part of the region.[37] According to the French historian Fernand Braudel, in the wider region of what today is Southern Albania and Northwestern Greece, "it lacked the church discipline; in the churches was not performed any religious ceremony, what meant that Christianity did not have deep roots there".[38] This combination resulted in the first wave of conversions in the beginning of the 18th century, by a number of poor farmers. At this time Muslims became the majority in a few villages like Kotsika, near Sagiada. During the entire 18th century, Muslims were still a minority among the Albanian population of the region, and became the majority only in the second half of 19th century. Estimates based on the defter of 1875 show that Muslim Chams had surpassed Orthodox Chams in numbers.[37]
In a number of cases however, only one person, usually the oldest male member of the family, converted into Islam, in order not to pay taxes, while all other members remained Christians. As a result, historians argue that the population of Chameria was either Christian or Crypto-Christian as late as the first half of the 19th century. During the second half though the majority of Chams became fully islamized and Crypto-Christianity ceased to exist.[37]
Pashalik of Janina (1787–1822)

In 1787, Ali Pasha, a Muslim Albanian brigand, was awarded the pashaluk of Trikala in reward for his support of the Sultan Abdülhamid I's war against Austria. Shortly afterwards, he seized control of Ioannina and Chameria. As a practically independent ruler, for the next 33 years, Ali expanded his influence through Albania and most of Ottoman Greece.
The first defeat Ali Pasha suffered was at the hand of the inhabitants of the villages of Souli. These were a group of Orthodox Chams, the Souliotes, who had managed to gain a sort of independence, through a military confederacy, without paying the taxes to the pasha.[33] In 1792 Ali declared war against them, the reason being their persistent refusal to acknowledge his authority, rather than the uncollected taxes.[39] In this war they managed to prevail over Ali's troops several times and to retain their independence until 1803, when they were forced by Ali Pasha to leave from Souli.[39] However, when Ali Pasha's rowing power came under attack from the Sultan's army, he forged an alliance with the Souliotes under Markos Botsaris, mostly because of their common ethnicity.[33] In January 1822 however, Ottoman agents assassinated Ali Pasha and sent his head to the Sultan.[31]
Greek Independence (1821–1829)

Orthodox Chams and especially the Souliotes were one of the main contributors to the war that achieved the Greek independence from the Ottoman Empire, liberating a number of regions, under the command of Markos Botsaris and Kitsos Tzavelas.[16][40][41][42]
The two most distinguished Souliotes of the independence struggle were Kitsos Tzavelas and Markos Botsaris. Tzavelas was born in Souli in 1800. He distinguished himself during the siege of Messolonghi and was responsible for liberating part of Central Greece. After independence, Tzavelas became a supporter of Ioannis Kapodistrias and eventually a leader in the Russian Party in the period of King Otto. Accused of planning a revolt against the King in 1834, Tzavelas was imprisoned by the Regency Council headed by Josef Ludwig von Armansperg, along with other politicians of the Russian Party.[42]
Tzavelas' compatriot and rival, Markos Botsaris, joined the Greek patriotic society known as the Filiki Eteria in 1814, and in 1820, with other Souliotes, made common cause with the Greeks against the Ottoman Empire. On the outbreak of the Greek revolt, he distinguished himself as a partisan leader in the fighting in western Central Greece, and was conspicuous in the defense of Missolonghi during the first siege of the town (1822-1823). On the night of 21 August 1823, at Karpenisi, he led the celebrated attack of 350 Souliotes on 4000 Muslim Albanians who formed the vanguard of the army with which Mustai Pasha was advancing to reinforce the besiegers. Botsaris managed to take Mustai Pasha prisoner during the raid, but he was shot in the head while leaving the encampment.[42][43]
National Renaissance of Albania (1870s–1912)
Chams also played an important role in the National Renaissance of Albania (Rilindja Kombetare). Several Chams were heads of cultural clubs and patriotic organizations, which aimed at the establishment of an independent Albanian state.[1] Amongst them, the most distinguished personalities during the last years before independence were Abedin Dino, Osman Taka and Thoma Çami.[31]
Abedin Dino was one of the founders of the League of Prizren (1878) and one of the main contributors in the Albanian independence.[31] He was appointed as the chief representative of the League of Prizren for Chameria, and established a local League branch in Ioannina. When the League was disbanded in 1881, he continued fighting against Ottoman forces in Albania. He was killed by the Ottoman army while on his way to participate in the formation of the League of Peja.[31]
Another leader of the Prizren League active at the same time was Osman Taka. When the League of Prizren was formed he was named as the head of the local branch in Preveza. When the Ottoman forces managed to seize the Preveza League in 1886, Osman Taka too was arrested, accused of treason, and sentenced to death. He was executed in Konispol in 1897.[31]
Thoma Çami was one of the main contributors to the revival of Albanian culture during this period. He was a founder and the first chairman of the organization "Bashkimi", the best-known cultural club of the National Renaissance. He also wrote the first scholarly history book for Albanian schools, but died before the declaration of independence.[31]
Chams had their own delegates in the 1912 Vlora congress, where the Albanian Independence was proclaimed. Four representatives from Chameria and two representatives of Ioannina took part in the congress, and the six of them were in favor of Independence. They were Jakup Veseli from Margariti, Kristo Meksi and Aristidh Ruci from Ioannina, Rexhep Demi from Filiates, Veli Gërra from Igoumenitsa, and Azis Tahir Ajdonati from Paramythia.[44]
Modern history
The neutrality of this article is disputed. |
First years of Greek rule (1913–1923)
Following the defeat of Ottoman forces in the region and the Balkan Wars of 1912-1913, an international boundary commission gave the northern part of the region of Epirus to the Principality of Albania, and the southern part to the Kingdom of Greece, leaving Greek and Albanian minority areas on either side of the border. Most of the Cham-populated border area to the far northwest, except for a few Cham villages assigned to Albania, came under the Greek half.[45]
After the annexation of Southern Epirus by Greece, Chams had the right to choose between Greek and Turkish nationality, under the 4th provision of the Athens peace treaty.[46][47] The Chams chose the Greek nationality instead of the Turkish. This convention gave special rights to religious minorities, but not to ethnic minorities, under the third provision.[48]
The Albanian language was prohibited from public life and only Greek was taught in schools.[10] Orthodox Cham Albanians were not counted as a different ethnic group than the Greeks, while the Muslim Chams were counted in the census only as a religious minority.[11] Muslim Chams were discriminated by Greek authorities, and they did not have the right to vote, despite being Greek citizens.[21]
In this period, Muslim Cham beys lost the political power they enjoyed during the reign of the Ottoman Empire, but they retained their economic influence.[20] The Muslim portion of the population was under a sui generis rule of the Greek authorities and the local muftis, who were recognized in these areas.[49] In the region of Epirus there were the muftis of Ioannina, Paramythia, Filiates, Margariti, Igoumenitsa, Parga, Preveza, Sagiada and Thesprotiko.[50]
Population exchange and appropriation of property (1923–1926)
The neutrality of this article is disputed. |

The real problems between the Greek state and the Cham citizens came only after the Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922.[51] At the conclusion of the war, Greece and Turkey signed the Treaty of Lausanne, which included a population exchange between the two countries. The treaty used religion as the indicator of national affiliation, thus including all Muslims, even Albanians, in the population exchange. Under this treaty Muslims of Greece would have been exchanged with Christians of Turkey, with an exception of Muslims of Thrace and Christians of Instanbul.[52]
The Greek government saw this as the perfect opportunity to get rid of Muslim Albanians, as Orthodox Chams could be easily assimilated.[53] Greek officials had two options. The first was to exchange Muslim Chams with Greeks from Turkey, under the population exchange, and the second one was to exchange them with a community of the Greek minority in Albania. They approached the Albanian government in 1923, but Albanian officials refused to consider the second scheme.[22]
Only after the pressure of the Italian and Albanian diplomacy, did Greece, in 1925, two years after the exchange had officially began, accept that Muslim Chams were not subject to the exchange. The Greek minister in London, Kaklamanos, promised that "the compulsory exchange shall not be applicable to the Moslem [sic] subjects of Albanian origin".[11][21] But Muslim Chams had to prove their ethnic origin in order to remain in Greece.[54] Under the Greek decision, which was presented by Eleftherios Venizelos to the local administration in Epirus, only those who were born in Albania or whose fathers were born in Albania could stay in Greece, thus excluding the genuine Chams of the Chameria region.[11]
Although they were not officially part of the exchange, Greek authorities forcibly sent a number of Cham Albanians to Turkey. Reports compiled by League of Nations representatives charged that local Greek authorities were intentionally making life unbearable for the Cham Muslims in order to force them out of Greece.[22] The exact number is unknown, since no official statistical data have been presented and because during 1923-1925, the number of exchanged Chams was not counted.[21] According to the contemproary Greek political historian Athanasios Pallis, only 1,700 were exempted and the League of Nations estimated that 2,993 Muslim Chams were forced to leave to Turkey, even after their compulsory exchange was prohibited, by declaring themselves as Turks rather than Albanians.[51][55][56][57] Prior to 1925, historian Miranda Vickers estimates that another 5,000 Chams had been forced to leave their homeland.[1] In Turkey, Cham Albanians were accommodated in Istanbul and Bursa. The majority of them were from Ioannina and outlying areas and Preveza.[21] About 16,000 Greek refugees from Asia Minor were settled in Epirus,[53] mainly in the same areas.[58]
The population exchange between Greece and Turkey did not effect only those Albanians who were sent to Turkey. The major problem after 1923 was the expropriation of the lands of the Muslim community in order to settle Greek refugees from Asia Minor. Four different laws were passed between 1923 and 1937 that expropriated the properties of Muslim Chams, while leaving those of the Orthodox Chams and the local Greeks intact.[11] Official Greek policy was that properties belonging to either Muslim citizens in Greece, who were exempt from the exchange of populations, or to foreign citizens, be preferentially expropriated.[59]
The first relevant law was passed on 15 February 1923, expropriating the lands and second homes of Muslim Chams, in order to give it to Greek refugees and to landless Greek farmers. Compensation was set at below 1914 market price, and not 1923 values. On the other hand, the compensation for the homes would be given by 1923 value. Nevertheless, some Chams were never compensated.[11]
As a result of this policy, a number of petitions were addressed to the Ministry of Agriculture or to the officials of the Refugee Settlement Commission from Muslims of Albanian origin in Paramythia, Dragoumi, Filiates, and other parts of the region, but no answer was given.[59] This law was reported even to the League of Nations, but its commission was satisfied by the Greek responses to the issues.[11]
Pangalos regime (1926)
The neutrality of this article is disputed. |

An unexpected turn in Chams' fate occurred when an Arvanite general, known for his pro-Albanian feelings, became prime minister of Greece. On June 24, 1925, a group of officers, fearing that the political instability was putting the country at risk, overthrew the government in a coup and their leader, Theodoros Pangalos became the head of the dictatorial government. His main priorities in foreign relations were to establish good relations with Albania and to protect the rights of both the minorities, either Chams in Greece, or Greeks in Albania. For this reason he officially decided that Albanians of Chameria would not be deported to Turkey after 1926, putting an end to the population exchange. Also, he decided that refugees would not settle in Chameria, but rather in Western Thrace, as was originally decided.[60]
Pangalos was an Albanian-speaker, and declared himself proud of his half-Albanian identity.[61] His priority in establishing good relations with Albania was soon materialized by four agreements between the two governments, among others addressing the confiscation of Cham properties before 1926, when Greek refugees from Asia Minor were settled in the region. This agreement stated that Chams would be compensated at least as much as foreign citizens or ethnic Greeks.[50] In a public statement he also recognized that Chams were an ethnic minority and promised that Albanian schools would be opened in the region.[60][62] But, after a few months he was overthrown, and his pro-Cham policies were immediately abolished.[60]
Discrimination and normalization (1927–1936)
In August 1926, Theodoros Pangalos was deposed by a counter-coup, and Pavlos Kountouriotis was restored as President of Greece. Before being ousted, General Pangalos had acknowledged the Chams as an ethnic minority within Greece, an action that had made Albanian diplomacy more persistent on pursuing the Cham claims.[37] Pangalos overthrow also meant a backtracking of Greece's official stance on the issue: discrimination against the Chams continued,[10] and in 1927, the Greek government abolished four of the nine Vakoufs, the muftis of Parga, Preveza, Sagiada and Thesprotiko.[50]
"A person of non-Greek ethnic origin, who has left Greece with no intention to return, may be declared as having lost the Greek citizenship. This also applies to an allogenis, born and domiciled abroad. His/her children living abroad may be declared as having lost their Greek citizenship if both their parents and their surviving parent have lost it as well. Decision on these matters is reached by the Interior Minister, with the concurring opinion of the Citizenship Council."
— Presidential decree on citizenship of 1927 [63]
Furthermore, beginning in 1927 with the publication of the relevant Presidential Decree, the Greek government implemented a policy depriving Muslim Chams and other minorities of their Greek citizenship, if they would leave Greece. Since then, and until as recently as 1998, the Greek government made a clear distinction between Greeks and non-Greeks in the citizenship laws. According to the 1927 decree, Greek citizens of non-ethnic Greek origin ("allogenis") could loose their citizenship if they left the country.[64] Such a practice is seen by scholars as a legal exclusion of Chams and other minorities from Greek society, since it made a distinction based on national affiliation, which was effectively set as a criterion above citizenship in Greek legal order.[64]
In 1929, the League of Nations asked Greece to open Albanian-language schools, since they had been officially recognized as an Albanian minority. The official position however of the then Greek prime minister, Eleftherios Venizelos, was that since the region had never had Albanian schools, even under the Ottoman Empire, this issue could not be compared with the rights demanded by the Greek minority in Albania.[62]
Nevertheless, following pressure from the League of Nations and as a result of the agreements signed during Pangalos' regime, Greece officially announced the establishment of four bilingual primary schools in Filiates, Igoumenitsa, Paramythia and Sagiada.[65] All these schools would be Greek, but Albanian would also be taught in the three first classes. An Albanian delegation led by the Albanian ambassador, Mid'hat Bey Frashëri, asked the Greek government for 15 schools, with full teaching in Albanian, in the main towns and villages of Chameria, a request that was immediately rejected by Greek officials.[66] After negotiations, the Albanian government accepted the Greek proposal and an agreement was signed in 1935 that would allow the Greeks of Albania to open new private schools in Himara and Korca, in exchange for the four bilingual schools in Chameria. But once again, the change of the Greek government with the coup d'état of Ioannis Metaxas made this agreement void.[65]
At this time, the Greek government tried to resolve another core issue pertaining to the Cham Albanians, the property dispute. In 1928, the Venizelos government had withdrawn from the Greco-Albanian agreement signed by Pangalos that would compensate Chams equally with other Greek citizens. Muslim Chams tried to regain their properties under the Law of 1926, which gave them the opportunity to dispute the confiscation of their properties before the courts. Following these actions, Greece passed two laws, in 1930 and 1931, which gave bigger compensations to the Muslim community, but not as much as to other Greek citizens.[62] The first law doubled the promised compensation, and forced the state authorities to give 3/4 of the promised compensation, even if they appealed the decisions in the courts. The second law returned some of the lands, that were not settled by Greeks, to Cham Albanians. Both laws were implemented in a limited scale only, because of the change of the Greek government and the establishment of the dictatorial Metaxas Regime.[11]
During this period, a number of villages were renamed in the region. More than 100 village names were changed in Thesprotia, Preveza and Ioannina.[32][67] Many other names had already been changed in 1913 when the region came under Greek sovereignty. Villages like Shëndiela in Preveza were translated into Greek Agia Kyriaki (Saint Kyriake), while other toponyms such as Ajdonati or Margëlliç had been immediately renamed with new Greek names (Paramythia and Margariti).[32] The majority of villages and towns of the region got new names, mainly Greek ones, in 1928 and 1929. Another period of Hellenization of toponyms occurred in the 1950s, when the remaining Albanian or Turkish names were finally renamed into Greek, with very few exceptions.[32] Today, only a small number of Albanian toponyms, like Semeriza (from Albanian Shemërizë, meaning Saint Mary), survive from Ottoman times.[4]
In September 1930, the proposal for exchange of the Cham minority with the Greek minority of Albania was renewed, this time initiated by Albania. King Zog of Albania attempted to reach an agreement with the Greek government on the resolution of all differences between the two countries. The Albanian government believed that a voluntary population exchange of the two minorities would resolve a number of internal problems for both sides and improve Greek-Albanian relations. However, this proposal was rejected by the Greek side, who feared that Albania would forcibly evict its Greek minority from the country, making the exchange non-voluntary.[68][69]
Crackdown under the Metaxas regime (1936–1940)
The harshest period of discrimination of Cham Albanians occurred during the dictatorial regime of Ioannis Metaxas, Prime Minister of Greece from 1936 to 1941.[20] The nationalistic character of his regime was imposed on all minorities in Greece. As Slavic-speakers, Vlachs and Roma, Albanian-speaking minorities were prohibited from using their own language outside home.[70] Those who used Albanian words in school or in the army, were punished physically or humiliated.[70][71] Such attitudes have led many parents to discourage their children from learning their mother tongue so as to avoid similar discrimination and suffering.[71] The Greek language was imposed in the schools and elders who had no knowledge of the language were forced to attend night-schools, in order to learn to read, write and even speak the Greek language.[70]
On the core issue of properties, the government led by Metaxas, not only did not compensate the local population for prior confiscations, but adopted a new law, which reduced the properties of Muslim Chams. The final law that nationalized the entire property of Chams and other Albanian nationals in Greece was passed in 1937. This law confiscated all properties of Albanians in Greece, except the primary homes and the small farms inside the villages, while the compensations provided for were delayed, something which was seen as a provocation, by Chams.[11]
At the same time, a negative influence about the position of Cham Albanians came from their motherland. Following the Italian invasion of Albania, the Albanian Kingdom had become a protectorate of the Kingdom of Italy. The Italians, especially governor Francesco Jacomoni, used the Cham issue as a means to rally Albanian support. Although in the event, Albanian enthusiasm for the "liberation of Chameria" was muted, Jacomoni sent repeated over-optimistic reports to Rome on Albanian support. As the possibility of an Italian attack on Greece drew nearer, he began arming Albanian irregular bands to use against Greece.[72]
On the eve of the Greco-Italian War, Greek authorities disarmed 1800 Cham conscripts and put them to work on local roads. On the following month they seized all Albanian males not called up and deported them to concentration camps or to island exile.[20][73] Until the invasion of Greece by the German army, the Muslim Cham population of the region of Chameria was composed of women, child and the elderly. The Muslim Chams would be restored to their land only after fascist Italy got control of the region.
Second World War and expulsion
Occupied Greece (1940–1944)
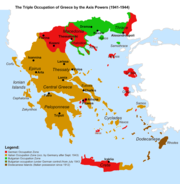
On June 1940 Daut Hoxha a Cham Albanian was found headless in the village of Vrina in Southern Albania. According to British historian Miranda Vickers, Hoxha was a military leader of the Cham struggle during the inter-war years, leading to him branded as a bandit by the Greek government.[2] Hoxha`s death was used as the final excuse from fascist Italy in order to attack Greece. Italian controlled newspapers and the authorities officially described him as “an Albanian from Chameria animated by great patriotic spirit” murdered from Greek spies inside Albania, declaring the imminent liberation of Chameria.[50] Due to the situation created in the border and the internment of the adult male population in concentration camps,[20] many Chams (estimated 2-3 thousand by Greek authors)[50] had secretly crossed the borders in order to compose armed groups. The Greco-Italian War started with the Italian military forces launching an invasion of Greece from Albanian territory. The invasion force included several hundred native Albanian and Chams in blackshirt battalions attached to the Italian army, united later under “Chameria Army Corps” under General C. Rossi.[50] Their performance however was distinctly lackluster, as most Albanians, poorly motivated, either deserted or defected. Indeed, the Italian commanders, including Mussolini, would later use the Albanians as scapegoats for the Italian failure.[72] The initial Greco-Italian conflict continued into 1941, when the forces of Nazi Germany invaded Greece. The country was occupied by German, Italian and Bulgarian armies, who divided the country in three distinct occupation zones.
Being under such preasure from the Greek state,[20] several hundred Muslim Chams, under the leadership of the influential Dino family, collaborated with the Nazis, as part of the Balli Kombetar organization and the local administration of Këshilla.[57] These armed bands took part alongside the German army in burning villages and killing Albanians and Greeks of the region.[10] But the local beys, the muftis and the majority of the population did not support such actions.[20][10]
On the other hand, several hundred Muslim Chams became part of the Greek People's Liberation Army (ELAS),[10] as well as National Anti-Fascist Liberation Army of Albania.[31] In the ELAS, Chams formed the IV Ali Demi battalion, named after a Cham Albanian who was killed in Vlora fighting against the Germans. At the time of its creation in 1944, it comprised 460 Muslim Albanians and 340 Orthodox Albanians and Greeks.[10] One year earlier, the National Anti-Fascist Liberation Army of Albania had likewise formed the Chameria battalion, in which about five hundred Chams were conscripted.[31]
Expulsion (1944–1945)
During the summer of 1944, when the German withdrawal was imminent, the right-wing head of the National Republican Greek League (EDES), Napoleon Zervas, asked the Cham Albanians to fight against EAM-ELAS. After their negative response, EDES forced many Chams to leave their homes.[20] According to the Greek historian Kosmas Antonopoulos, Zervas, was himself of Cham origin, being a descendant of the Souliotes, a community that had become assimilated into the Greek nation more than a century earlier.[74] Beyond the expulsion, as a result of the atrocities that occurred more then 2,000 of them were killed and others died during their exodus to Albania.[10]
Two attacks took place in July and August, with the participation of EDES 10th Division and local Greek peasants whose villages had been burned down by Cham collaborators. Many of the Cham villages were burned and the remaining inhabitants (some 18,000 to 35,000) fled across the border into Albania.[2][20][10][51] In the context of the emerging Greek Civil War, this operation was also meant to enlarge the coastal area north of Parga under EDES, and hence British, control. British historian Mark Mazower describes it as ethnic cleansing, which was accompanied by much destruction and plundering.[20] British officers described it as "a most disgraceful affair" involving "an orgy of revenge" with the local guerrillas '"looting and wantonly destroying everything". The British Foreign Office reported that "The bishop of Paramythia joined in the searching of houses for booty and came out of one house to find his already heavily laden mule had been meanwhile stripped by some andartes".[20]
In contrast with EDES, the left-wing ELAS was opposed to the idea of collective punishment against the Chams, as several hundred Muslim Chams had enlisted in its ranks. Furthermore, ELAS enjoyed good relations with the communist-led resistance in Albania.[20] When ELAS briefly gained control of the Thesprotia region in late 1944, about four to five thousand Albanians were able to return to their homes. After the Varkiza Agreement however, EDES forces again expelled them. During this process, led by a former officer of Zervas', Col. Zotos, a loose paramilitary grouping of former guerrillas and locals went on a rampage, in an attempt to force all Albanians of the region to leave. In the worst massacre, in the town of Filiates on 13 March, some sixty to seventy Chams were killed. Overall, some 300 Muslim Chams were murdered, while Orthodox Chams were allowed to stay in Greece.[20] The property of all Muslim Chams (whether they had collaborated with the Nazis or not) was confiscated in order to permit Greeks to settle in the area. After the war, only 117 Muslim Chams were left in Greece.[1]
Postwar situation (1945–1990)
Muslim Chams that fled in Albania, were given the status of refugees by the communist-led Albanian government and were organized under the aegis of the Anti-Fascist Committee of Cham Immigrants (CAFC). In 1946, they formed a congress, where they adopted a memorandum accusing Greece for their persecution, and asked the international community to react in order to return to their homeland and to receive reparations. The CAFC claimed that 28,000 Chams were evicted, 2,771 killed and 5,800 houses were looted and burned.[1][75]
The new post-war Communist government of Albania took the Cham issue to the Paris Peace Conference, demanding the repatriation of the Chams and the return of their property. The following month a delegation of the CAFC was sent to Athens to lodge a protest with the government of George Papandreou. These demands were never answered. The United Nations Assembly in New York did however acknowledge the humanitarian crisis facing the refugees, and gave US$ 1.2 million via the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration (UNRRA), specifically for refugees from northern Greece.[1]
Meanwhile, in 1945-1946, a Greek Special Court on Collaborators sentenced to death 2,109 Chams in absentia, while their immovable property was confiscated by the Greek state.[11] No criminal of Cham origin was ever brought to trial[1]
For those Chams of the Orthodox faith who remained in Greece after 1945, their Albanian identity was suppressed as a deeply repressive policy of assimilation ensued and, as before World War II, the Albanian language was not allowed to be spoken in public, nor taught in the schools. While, the demographic structure of northwest Greece was altered by the introduction of settlers, especially Vlachs, from other parts of Greece.[1]
In 1953, the Albanian government gave all Chams the Albanian citizenship and they were forced to integrate into Albanian society. Despite this many Chams still regard themselves as refugees deprived of their Greek citizenship and claim the right to return to their property in Greece.[2]
Current situation
Cham identity and politics in post-communist Albania
Following the fall of the Communist regime, the Chameria Political Association was formed in Tirana in 1991. Since its creation, its goal is the collection and recording of personal testimonies and accounts from Chams who left Greece in 1944-45 and are now living in Albania – personal archives, documents and other data - in a bid to preserve the historical memories that the older generation carry with them.[2]

In 1994, Albania passed a law that declared the 27th of June, the anniversary of the Paramythia massacre of 1944, as the Day of Greek Chauvinist Genocide Against the Albanians of Chameria and built a memorial at the town of Konispol.[76] Albanians pay tribute to the victims every 27 June in Saranda and Konispol. This event is called the "Cham march" (Marshimi çam). In 2006, the biggest Cham March, with around 10,000 people participating, occurred at the Albanian-Greek border. The participants designated themselves as Greek (and Albanian) citizens and expressed the desire for "a peaceful return to their homeland and to the graves of their forefathers" [2]
In March 2004, the Institute of Cham Studies (ICS) was established with a board of 7 members. According to Miranda Vickers, the Institute’s primary aim is to attempt to “fill the huge gap in knowledge about the entire Cham issue”. In the same year, the Chams also created their own political party, the Party for Justice and Integration (PJI), in order to campaign in the forthcoming parliamentary elections.[2]
In 2005, a diplomatic incident occurred when the President of Greece, Karolos Papoulias canceled his planned meeting with Albanian counterpart, Alfred Moisiu, in Saranda, because 200 Chams were demonstrating about the Cham issue. The Greek Ministry of Foreign Affairs stated that the Albanian authorities did not take adequate measures in order to protect the Greek President "by deterring known extremist elements, who are trying to hinder the smooth development of Greek-Albanian relations". The Albanian president`s office stated that President Moisiu expressed "deep sorrow at this unexplainable decision, which was based upon misinformation, of the small, peaceful and well monitored demonstration".[2]
Recently, a few Chams have managed to find their way back to their families' old homes, and have tried to rebuild them. At the same time, several hundred ethnic Greek minority families from Albania have settled in towns such as Filiates.[2]
Chams in Greece
Orthodox Cham Albanians still live in the region in three prefectures.[2][5][10][13] According to a study by the Euromosaic project of the European Union, they live along the border with Albania in Thesprotia prefecture, the northern part of the Preveza prefecture in the region called Thesprotiko, and a few villages in Ioannina prefecture.[5]
Throughout the Cold War, their Albanian identity was suppressed by a deeply repressive policy of assimilation. As before World War II, the Albanian language was not allowed to be spoken in public, nor taught in the schools. As a result, Albanian is only spoken privately at home, and the assimilation of Orthodox Albanians gathered momentum and they have struggled ever since to maintain their identity.[1][2] Albanian however is still spoken in the region and some of the older inhabitants are Albanian monolinguals.[77] The language is spoken even by young people, because when the local working-age population migrate seeking a job in Athens, or abroad, the children are left with their grandparents, thus creating a continuity of speakers.[77]
On the other hand, the Greek authorities, out of mistrust towards the remaining Albanians, despite their Orthodox denomination, have furthered a demographic shift in the region, by introducing settlers, chiefly Vlachs.[1] Today, the majority of these Orthodox Chams are called Arvanites (a Greek-identifying group of Albanian origin, living in southern Greece) by others, but self-identify as Shqiptar, which means Albanians. In contrast with Arvanites, they have retained, not only a distinct ethnic identity, but also the Albanian national identity.[13]
Chams in Turkey
Muslim Chams in Turkey form the second largest community of Chams, after Albania.[2] This community was established after the two World Wars. After the First World War, Chams were forced to leave for Turkey during the population exchange,[22][51][57] and another migration wave followed after the Second World War, when a minority of the Chams expelled from Greece chose Turkey over Albania because of their anti-communist sentiments.[23]
The exact number of Muslim Chams in Turkey is unknown, but various estimates conclude that they number between 80,000 to 100,000,[23] from a total population of 500,000 to 1.3 million Albanians that live in Turkey.[78] The Chameria Human Rights Association declares that most of them have been linguistically assimilated, although they maintain Albanian consciousness and regional Cham traditions.[24] A considerable number of Chams in Turkey have changed their surnames to Cam or Cami, which in Turkish means pine, in order to preserve their origin.[23] They are organized within the "Albanian-Turkish Brotherhood Association" (Template:Lang-sq, Template:Lang-tr), which fights for the rights of Albanians.[23]
Chams in the United States
Chams in the United States are the forth most numerous population of Chams, after Albania, Turkey and Greece.[2] The majority of this community migrated to the United States shortly after their expulsion from Greece, because the Communist government in Albania discriminated and persecuted them.[2] They managed to retain their traditions and language,[2] and have created the Chameria Human Rights Association (see below), which aims to protect their rights.[79]
Cham Issue
Political positions
The "Cham issue" has been raised by Albania since the 1990s. It involves the repatriation of the Muslim Chams who were expelled at the end of World War II, and the granting of minority rights. The Chams also demand the restoration of their properties, and reject a financial compensation.[1] Greece on the other hand states that the expulsion of the Chams is a closed chapter in the relations between the two countries. However, Greece agreed to the creation of a bilateral commission, focused solely on the property issue as a technical problem. The commission was formally set up in 1999, but has not yet functioned.[1]
Chams complain that Albania has not raised the Cham issue as much as it should.[2] It was raised officially only during a visit to Athens of former Albanian Prime Minister Ilir Meta at the end of 1999, during his meeting with his Greek counterpart, Kostas Simitis, but it received a negative response.[1] The fact that Greece is a member of the European Union and NATO, which Albania wishes to join, is one of the main factors why the Albanian government is reticent about the issue.[2]
The Greek government on the other hand considers the Cham issue as a closed chapter. According to the Greek official position, the Chams would not be allowed to return to Greece "because they have collaborated with the Italian-German invaders during the Second World War, and as such they are war criminals and are punished according to Greek laws".[1] In an attempt to give a solution, in 1992 Prime Minister Konstantinos Mitsotakis proposed a trade-off in relation to their properties, only for the cases where their owners had certifiably not been convicted or participated in crimes against their fellow Greek citizens. Mitsotakis also proposed that the Albanian government likewise compensate ethnic Greeks who had lost properties due to alleged persecution during the communist regime in Albania.[57] This proposal however was rejected.
The Cham Issue has not been in the agenda of international organizations.[2] Since 1991, delegates of the Cham community have begun an attempt to internationalize the Cham Issue, but the only official support for this issue has come from Turkey.[1] Meanwhile, in 2006, Members of the Party of Justice and Integration met European MEPs, including the chairwoman of Southwest Europe Commitee on the European Parliament, Doris Pack and introduced their concerns about the Cham Issue. Although this group of MEPs drafted a resolution about this issue, it was never put into vote, for unknown reasons.[2]
Citizenship issue
Following their expulsion in 1944, initially only the 1,930 Chams who were sentenced to death as collaborators were deprived of their Greek citizenship. The remainder, who represented the vast majority, lost theirs under a special law of 1947.[11] Orthodox Chams remained in Greece and retained the Greek citizenship, but without any minority rights.[2] In 1953 the Albanian government forcefully granted the Albanian citizenship to the Chams, while in Turkey and the United States, the Chams have acquired the respective citizenships.[1]
The Chams demand the restoration of the Greek citizenship as a first step towards solving the Cham issue. The restoration of the citizenship, rather that the regaining of the confiscated properties, is reported to be considered as the primary issue.[2] They argue that the removal of their citizenship was a collective punishment, when even the Greek courts have charged only a minority of Chams for alleged crimes.[80] They have asked the Greek government to have a dual citizenship,[2] a policy followed by Greece in the case of the Greek minority in Albania.[80]
Property issue
After the World War II, Cham Albanian`s properties were put under escrow, by the Greek state. In 1953, the Greek parliament passed a law, that considered as "abandoned" the rural immovable properties, whose owner had left Greece without permission or passport.[11] After three years the properties were nationalized. While homes were nationalized in 1959, when a law passed by the Greek parliament considered them abandoned and allowed their conquest by other inhabitants of the region. These two laws nationalized Chams properties, and allowed others to settle in their homes, but the ownership was under the Greek state.[11] In the decades of `60-s and `70-s an ad hoc commission for the property alienation in Thesprotia gave by draw the rural properties to farmers with and without land, while homes and urban properties in Igoumenitsa, Paramithia, Margariti, Filiates, Perdika and Sybota were given to homeless people.[11]
Minority issue
Another problem in the Cham issue is the minority status. Chams not only demand their repatriation and minority rights, but they have asked minority rights even for Orthodox Chams residing in Greece.[1] This position is supported even by politicians in Albania. In January 2000, the current Prime Minister of Albania, Sali Berisha, then head of the opposition demanded more rights for the Cham minority in Greece, which includes cultural rights for Albanians living in Greece, such as the opening of an Albanian-language school in the town of Filiates.[1]
Incidents
The Cham issue has become a dispute in both countries, and several diplomatic incidents have occurred. While, there is a reported paramilitary formation in the northern Greek region of Epirus, called the Liberation Army of Chameria[2][81] As of 2001, the Greek police reported that the group consisted of approximately 30-40 Albanians. It has not the official support of the Albanian government.[2]
Organizations

Chams have created a number of organizations, such as political parties, non-governmental associations and the Chameria Institute.
Chameria Association in Albania
The National Political Association "Çamëria" (in Albanian: Shoqëria Politike Atdhetare "Çamëria"), a pressure group advocating the return of the Chams to Greece, receipt of compensation and greater freedom for the Orthodox Chams in Greece, was founded on January 10, 1991. [2] This associations holds a number of activities every year, with the help of the Party for Justice and Integration, as well as other organizations. Annually on June 27th, the Cham March is organized in Konispol. This march is held to remember the expulsion of the Chams.[82]
Chameria Association in the US
Chameria Human Rights Association (Shoqëria për të drejtat e Njeriut, Çamëria) is a Non Governmental Organization, based in Washington, DC, USA, which protects and lobbies for the rights of Chams.
It describes as its mission: the Right of Return of Chams "to their homes in Greece and live there in peace and prosperity with their Greek brothers"; the Property Rights; Other Legal Rights "ensuring to the Cham people all other legal and minority rights deriving from the Greek Constitution and Laws, the Treaties and laws of the European Union, and other rights originating from international treaties and conventions to which Greece is a party"; and the conservation and propagation of the rich history, culture, language, and other cultural aspects of the Cham people.[79]
Democratic Foundation of Chameria

Another organization of Cham Albanians is based in The Hague, Netherlands. The Democratic Foundation of Chameria (Fondacioni Demokratik Çamëria) was founded in 2006 and aims to resolve the Cham issue, internationalizing the question in peaceful ways. Every year it organizes protests outside the International Court of Justice, where it intends to bring the Cham issue, if the governments of both countries will not find a solution.[83]
The organization aims to resolve the Cham issue in three directions: "lawfully and peacefully drawing attention to the legal position, the living and working conditions of the inhabitants and former inhabitants of Chameria; entering into negotiations with all types of organisations, both governmental and non-governmental; safeguarding the legal interest of inhabitants and former inhabitants of Chameria by means of legal proceedings, when necessary."[83]
Party for Justice and Integration
In 2004, in Albania was formed the Party for Justice and Integration (Partia për Drejtësi dhe Integrim), which would represent the Chams in politics. The party declares in its statute that it belongs to the center right, which is the political homeland for the vast majority of Chams marginalized by the Communist regime. Since the demise of the one-party state, the Chams have consistently put their faith in the center right parties to pursue their rights with Greece. However, the Chams are fully aware that Tirana’s politicians, whether Democrats or Socialists, only really focus on the Cham question during election time.[2]
The party won the plurality of seats in the municipality of Saranda, Delvina, Konispol, Markat, Xarrë and was one of the main parties in big municipalities like Vlora, Fier, etc, on the last municipal elections in 2007.[84]
Chameria Institute
In March 2004, the Institute of Cham Studies (Instituti i Studimeve Çame), also known as Chameria Institute or Institute of Studies on the Cham issue was established with a board of 7 members. The Institute’s primary aim is to attempt to “fill the huge gap in knowledge about the entire Cham issue”. One of the first actions taken by the board of the ICS was to hold the first ever Cham Conference in Tirana in May 2004. [2]
Its declares as its mission, "to make researches [sic] in the history and culture fields of the cham community as an inherent and important part of the Albanian nation." Also it seeks "to evolve and stimulate public scientific debate and to accomplish studies", "to organize scientific activities and publishes their outputs." Institute of Cham Studies seeks "to create a wide contacts network with analog research centers in Albania and abroad (Balkan, Europe and Northern America) and participating in mutual activities."[85]
Cultural Association "Bilal Xhaferri"
In 1993, a group of journalists and writers of Cham origin, founded in Tirana the Cultural Association "Bilal Xhaferri" (Shoqata Kulturore "Bilal Xhaferri"), nicknamed also as "the Cultural Community of Chameria" (Komuniteti Kulturor i Çamërisë). The association is an non-profit organization which aims to keep and promote the values of Cham Albanian culture and tradition. The association has established a publishing house, which publishes books especially about Chams and Chameria. It is named after the well-known dissident writer, Bilal Xhaferri and since its creation has published in Albania, Kosovo and the Republic of Macedonia, his hand-written memoirs and stories which were incomplete due to Xhaferri`s premature death.[86][87]
Demographics
Today, Cham Albanians are thought to number 440,000.[1][2] The majority of them live in Albania, while other communities live in Greece, Turkey and the USA. Their religion is Islam and Orthodoxy.
Historical demographics
The population of the region of Chameria were mainly Albanian and Greek, with smaller minorities. There is a dispute regarding the size of the Albanian population of the region. In Greek censuses, only Muslims of the region were counted as Albanians. According to 1913 Greek census, in Chameria region were living 25,000 Muslims[53] who had as mother tongue Albanian, in a total population of about 60,000, while in 1923 there were 20,319 Muslim Chams. In Greek census of 1928, there were 17,008 Muslims who had as mother tongue the Albanian language. [11]
The only census that counted Orthodox population of the region of Albanian ethnicity, was made by fascist Italy in 1941, but Greek authors claim that the way it was accomplished was exaggerated. This census found that in the region lived 54,000 Albanians, of whom 26,000 Orthodox and 28,000 Muslim and 20,000 Greeks.[11] After the war, according to Greek censuses where ethno-linguistic groups were counted, Muslim Chams were 113 in 1947 and 127 in 1951.
class="wikitable "
Current demographics
The exact number of Albanians still residing in the Chameria region is uncertain, since the Greek government does not include ethnic and linguistic categories in any official census. In 2002, in Chameria, the Orthodox Albanian population was estimated at 40,000, the majority of them being descendants of the Orthodox Chams who were allowed to remain in Greece, but also including a sizeable minority of recent, post-1991 immigrants.[1] In 1985, the Albanian population of Epirus, including Chameria and two villages in Konitsa was estimated 30,000.[88] While the total population of Thesprotia, Preveza and Ioannina prefectures is 275,086.[89]
Albanian is still spoken by a minority of inhabitants in Igoumenitsa.[90] According to Ethnologue, Albanian language is spoken by about 10,000 Albanians in Epirus and the village of Lechovo, in Florina.[91]
Estimations conclude that Muslim Chams today number at 400,000, the majority of whom live in Albania,[2] where they numbered ca. 250,000 in 2007,[2] while in Turkey they are 80,000 to 100,000,[23] and the rest live in the United States.[2] The only exact number of Chams in Albania comes from 1991, when Chameria Association held a census, in which were registered about 205,000 Chams.[1]
| Chams in Albania by town (1991)[1] | |
|---|---|
| Place | Number |
| Shkodër | 1,150 |
| Krujë and Laç | 720 |
| Tirana | 29,700 |
| Lezhë | 35 |
| Durrës | 35,000 |
| Kavajë | 10,500 |
| Vlorë | 42,300 |
| Fier | 39,800 |
| Sarandë | 12,100 |
| Delvinë | 2,900 |
Religion
Nowadays, 90% of Chams are of Muslim descent, while the rest, living in Greece, are of Orthodox Christian descent.[1][2] Chams living in Albania are overwhelmingly Muslim, but it is difficult to estimate their current religious affiliation: the former Communist regime had proclaimed the country "the only atheistic state in the world", and even after its fall, the majority of the population self-declared agnostic, or irreligious. Current estimates conclude that this applies to a majority of Albanians, with 65-70 percent of the population not adhering to any religion.[92][93][94] Conversely, in Greece and Turkey almost all of Chams adhere to their country's respective prevailing religion.[50][23]
Dialect

Cham Albanians speak the Cham dialect (Çamërisht), which is a subbranch of the Tosk Albanian dialect.[95] The Cham dialect is the second southernmost dialect of the Albanian language, the other being the Arvanitic dialect of southern Greece, which is also a form of Tosk Albanian. As such, Arvanitika and Cham dialect retain a number of common features.[5]
Albanian linguists say that this dialect is of great interest for the dialectological study and the ethno-linguistic analysis of the Albanian language. Like Arvanitika and the Arbëresh varieties of Italy, the dialect retains some old features of the Albanian, such as the old consonant clusters /kl/, /gl/, which in standard Albanian are q and gj, and /l/ instead of /j/.[96]
| Cham Albanian | Standard Albanian | Tosk Albanian | Arvanitika | English |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kljumësht | Qumësht | Qumësht | Kljumsht | Milk |
| Gluhë | Gjuhë | Gjuhë | Gljuhë | Language |
| Gola | Goja | Goja | Gljoja | Mouth |
Linguists say that these features give the Cham dialect a conservative character, which is due to the close proximity and its continuous contacts with the Greek language. They argue that this conservative character, which is reflected in a number of peculiar features of the dialect, is endangered, as are the Albanian toponyms of the region, which are no longer in use, and which have provided valuable material for research into the historical evolution of Albanian.[96]
Literature and Media
Literature

The first Albanian-language book written in the region of Chameria was the Greek-Albanian dictionary by Markos Botsaris, a Suliot of Epirus. This dictionary was the biggest Albanian dictionary of its time, which 1,484 Albanian lexemes.[7] According to albanologist Robert Elsie, it is not of any particular literary significance, but is important for our knowledge of the now extinct Suliot-Albanian dialect,[97] a subbranch of the Cham dialect.[7] The dictionary is preserved at the Bibliothèque Nationale in Paris.[97]
During the 19th century, Chams started creating bejtes, which were a new kind of poems, mainly in Southern Albania. The most well-known bejtexhi was Muhamet Kyçyku (Çami), born in Konispol. He is the only poet in Albania that has written in the Cham dialect and was apparently also the first Albanian author to have written longer poetry. The work for which he is best remembered is a romantic tale in verse form known as Erveheja (Ervehe), originally entitled Ravda ("Garden"), written about 1820. Kyçyku is the first poet of the Albanian National Renaissance.[98]
In the modern period, the best-known Albanian writer is Bilal Xhaferri, who is considered as the most influential dissident under the Communist regime. He was born in Ninat, but was forced to migrate in the United States at an early age because of his anticommunism. He lived and died in Chicago, at 51 years of age, but he contributed to Albanian literature with more than 12 books of novels and poems. Canadian albanologist Robert Elsie considers him "the best Cham Albanian writer and poet."[98]
Media

The Chams' culture and politics are represented by three local media in Albania and the United States. Due to the harsh Communist regime in Albania, Chams did not manage to publish any media in the 1945–1990 period.[86] On the other hand, Cham emigrants in the United States established a newspaper and a magazine, both edited by Bilal Xhaferri, and headquartered in Chicago. The first Cham Albanian newspaper was published in 1966, named "Chameria - motherland". (Çamëria - Vatra amtare), and is still being published in Chicago,[24] while the magazine "Eagle's wind" (Krahu i Shqiponjës) started publishing in 1974.[86]
The newspaper "Chameria - motherland" is mainly political, and tries to internationalize the Cham issue. In 1991 it became the official newspaper of the National Political Association "Çamëria", and since 2004 it is also the official newspaper of Party for Justice and Integration. The newspaper is published in Albania by a joint editorial board of the organization and the party, while in the United States it is published by Chameria Human Rights Association.[82]
On the other hand, the magazine "Eagle's wind" is primarily a cultural magazine and is no longer published in the US since 1982. The Cultural Organization "Bilal Xhaferri" republished the magazine in Tirana, and since 1994 it is self-described as a monthly "cultural Cham magazine".[86][87]
Traditions
Music
Cham Albanians have their own features, which differ from other groups of Albanian music. Cham Albanian folk music is divided in three main categories: the iso-polyphonic music, the polyphonic music and the folk ballads of the region. The characteristics of the last two types are common among the Greeks and Vlachs of the wider region.[99]
According to German scholar Doris Stockman, Cham music "may give an impact to further explain the inner Albanian relationships, among the vocal practices of the various folk groups in South Balkan, more than it had been done that far, as well as to offer new material to comparative studies concerning the complex of problems of the folk polyphony in Europe".[100]
Iso-polyphony is a form of traditional Albanian polyphonic music. This specific type of Albanian folk music is proclaimed by UNESCO as a "Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity". Chams sing a different type, called the cham iso-polyphony. Although they border with Lab Albanians, their iso-polyphony is influenced more by the Tosk type.[100][101][102][103]
Dances
Cham Albanian dances are well-known in Albania and Greece and are considered today as traditional dances in both countries. The best-known is Tsamiko, the Dance of Zalongo and the Dance of Osman Taka.
Traditionally, Tsamiko is danced only by men, but in modern times, both men and women take part. It is a national dance of Albania and one of the two national dances of Greece.[104] The dance follows a strict and slow tempo with emphasis put not on the steps, but in the "attitude, style and grace" of the dancer.[105]

The Dance of Zalongo refers to an event during the war between the Souliotes and Ali Pasha, when the villages of Souli were being evacuated by the defeated population. A group of 22 Souliot women and their children were trapped by Muslim troops in the mountains of Zalongo in Epirus, on 16 December 1803. In order to avoid capture and enslavement, they threw first their children and then themselves off a steep cliff, committing suicide. According to tradition they did this while dancing and singing, jumping down one after the other. This event created this popular dance song about the event, which is danced throughout the two countries today.[106]
The Dance of Osman Taka is linked with Osman Taka, a Cham Albanian leader who fought against Ottoman forces, and who managed to escape from death by amazing Ottoman forces with this dance. It is an old Cham dance, but under this name its known only since the 19th century.[105]
These dances are one of the main elements of Cham Albanian identity, although they are equally popular among other Albanians as well as Greeks.[107]
Folklore

The majority of the traditional Cham songs pay tribute to medieval lords and the wars against Ali Pasha. They often have common subjects with regional Greek folklore, like the the bridge of Arta, and the wife of Ali Pasha, Eufrosini.[98][108] In 1889, the Danish ethnographer Holgert Pedersen collected Cham folk tales and published them in Copenhagen nine years later, in the book "On Albanian folklore" (Zur albanesischen Volkskunde).[109] More than 30 Cham folk tales were collected, the majority of whom about bravery and honour.[110] Other folktales have been published in English in 1928, in the book "Tricks of Women & Other Albanian Tales".[111] The Chams of the southern Chameria region believe that they are descended from the legendary "jelims", giants from southern Albanian mythology, whose name derives from the Slavic transmission of the Greek word Έλλην (ellin) which means "Greek".[112] A peculiar characteristic of Albanian mythology is the "cult of the snake", which was particularly widespread amongst Chams. The snakes are thought as protector of the house and as a benefaction.[113]
Lifestyle
Dress
The folk outfits of the region are colorful. The most common men's outfit for Muslims and orthodox was the kilt known as fustanella, embroidered with silver thread, the doublet, short shirt with wide sleeves, the fez, the leather clogs with red topknots and white knee socks. Other parts of the outfit were the silver chest ornamental and the holster embroidered with silver thread used to carry a gun or a pistol.[114]
This kind of dress was common for all Albanians, but there was difference in the length in the south where men, including the Chams, wore shorter ones, up to the knee. The kilt of high society men was made of many folds (about 250 - 300) and later was substituted by slacks and the former one was only used on special occasions.[114]

The common outfit for the women became a kind of oriental silk or cotton baggy pants. They wear the cotton pants daily, whereas the silk ones only on special occasions. Other parts of this outfit were: the silk shirt weaved in their home looms and the vest embroidered with gold or silver thread, which sometimes was completed with a velvet waistcoat on it. [114]
During 1880–1890 the town women mostly wore long skirts or dresses. They were dark red or violet and embroidered with gold thread. Other parts of this outfit were the sleeveless waistcoats, silk shirts with wide sleeves embroidered with such a rare finesse. On special occasions they also put on a half-length coat matching the color of the dress. It was embroidered with various flowery motives.[114] Another beautiful part of the outfit is the silver belt, the silk head kerchief and a great number of jewelry such as earrings, rings, bracelets, necklaces etc.[114]
Architecture
The main architectural monuments in the region of Chameria that belonged to Chams were mosques, homes and Muslim cemeteries, as well as old Albanian towers, known in Albanian as Kullas, which have survived, only because they are in the middle of forests scrub land, in old military zones near the Albanian border. The majority of them have been disappeared.[115]
But, there are very few surviving mosques, which were transformed into museums, following the model of the Yugoslav communists, despite the existence of some Muslims in many localities. Muslim cemeteries are frequently desecrated by modern building works, particularly road building.[115]
At the same time, Cham domestic and administrative buildings, mosques and cultural monuments are slowly covered by vegetation. Pasture lands once used by Chams for their cattle is now converged into forests, because of the depopulation of the region. Thus the geographical and architectural legacy of Cham occupation in north western Greece is gradually vanishing.[2]
Cuisine
Cham Albanians cuisine is seen as a mixture of Albanian and Greek cuisine, and maintains the main characteristics of the Mediterranean and the Ottoman cuisine. Being in the seacoast, Chams have held as one of the main dishes, baked fish with olive oil and garlic. [114] Their cuisine use different kinds of cheese and Greek salad. Lamb is mostly baked, with yogurt, differently from other cuisines. This dish has become one of the most preferred in Albania.[114]

As the majority of Mediterranean cuisines, Chams prefer vegetables and they use a lot of oil. Deserts used by Chams, are mostly influenced by the Ottoman cuisine, with Bakllava, Kadaif, being the most-preferred. Qumështor (Pie with milk) and byrek sheqeri (Pie with sugar) are widely used by Chams[114] and the majority of the inhabitants of Epirus.[116] The last two, are integral parts of the Albanian cuisine and the Greek one. The most used appetizers are Trahana and Tarator, while soups with seafood are part of their cuisine. Chams are well-known in Albania for the different ways of making bread and traditional Albanian pies, the byreks.[114]
Notable individuals
- Abedin Dino, founder of the League of Prizren, one of the main contributors in the Albanian independence.[31]
- Ali Demi, WW II hero of Albania born in Filiates, Greece in 1918, and died during a battle with Axis forces in Vlora, Albania in 1943. After him was created the first Cham battalion in ELAS army, the battalion "Ali Demi".[10]
- Aristidh Ruci, from Ioannina, representative of Janina in Vlora Congress, signatory of Albanian Declaration of Independence.[44]
- Azis Tahir Ajdonati, from Paramythia, representative of Chameria in Vlora Congress, signatory of Albanian Declaration of Independence.[44]
- Bilal Xhaferri, writer, born in Konispol, Albania.[117]
- Diamandis Zervas, Souliot leader, and main contributor against the Ali Pasha's conflicts.[118]
- Dimos Zervas, leader of the Zervas Souliot clan and main contributor against the Ali Pasha's conflicts.[119]
- Gjon Zenebishi, medieval Albanian lord, and prince of Gjirokastër, born in Vagenetia (i.e. Thesprotia/Chameria)[31]
- Hasan Tahsini, also known as Hoca Tahsin, Hodja Tahsin, Tahsin Efendi, Ahmet Nebil mathematician, philosopher and psychologist.[120]
- Gjin Bua Shpata, medieval Albanian lord, and despot of Arta, Angelokastron and Lepanto, born in Vagenetia (i.e. Thesprotia/Chameria)[31]
- Jakup Veseli, from Margariti, representative of Chameria in Vlora Congress, signatory of Albanian Declaration of Independence.[44]
- Kitsos Tzavelas, Orthodox Cham, Souliot leader, and main contributor in the Greek War of Independence. [16][41][42][43]
- Kristo Meksi, from Ioannina, representative of Janina in Vlora Congress, signatory of Albanian Declaration of Independence.[44]
- Markos Botsaris, Orthodox Cham, Souliot leader, and main contributor in the Greek War of Independence. The first one that has wrotten in the Cham Albanian dialect.[16][41][42][43]
- Mazar and Nuri Dino, collaborationists with Nazi Germany in Chameria, members of the Balli Kombëtar organization.[31]
- Muhamet Kyçyku (Çami), considered as the first poet of the National Renaissance, one of the best-known bejtexhinjs of Albania.[98]
- Osman Taka, one of the main contributors to the National Renaissance of Albania and a well-known dancer of his time.[31]
- Rexhep Demi, from Filiates, representative of Chameria in Vlora Congress, signatory of Albanian Declaration of Independence.[44]
- Thoma Çami, (1852-1909), from Paramythia, founder and chairman of organisation "Bashkimi", the best-known cultural club, of Rilindja Kombetare.[31]
- Veli Gërra, from Igoumenitsa, representative of Chameria in Vlora Congress, signatory of Albanian Declaration of Independence.[44]
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Vickers, Miranda, The Cham Issue - Albanian National & Property Claims in Greece, Defence Academy of the United Kingdom, p. 21 Cite error: The named reference "Vickers, Miranda 2002" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am Vickers, Miranda, The Cham Issue - Where to Now?, Defence Academy of the United Kingdom, p. 21 Cite error: The named reference "Vickers" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b Babiniotis, George (2002), Lexicon of the Modern Greek Language (in Greek) (2nd ed.), Athens: Lexicology Centre, p. 761, ISBN 960-86190-1-7
- ^ a b c d e Xhufi, Pëllumb (2006), "Çamët ortodoks", Studime Historike (in Albanian), 38 (2), Albanian Academy of Sciences
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g Euromosaic project (2006). ""L'arvanite/albanais en Grèce"" (html) (in French). Brussels: European Commission. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ Great Britain Naval Intelligence Division (1944), Greece, vol. 3, University Press, p. 32, retrieved 2009-03-16,
...who belongs to the Cham branch of south Albanian Tosks (see volume I, pp.363-5). In the mid-eighteenth century these people (the Souliotes) were a semi-autonomous community...
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|editorn-first=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|editorn-last=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Jochalas, Titos P. (1980), Το Ελληνο-αλβανικόν λεξικόν του Μάρκου Μπότσαρη : φιλολογική έκδοσις εκ του αυτογράφου [The Greek-Albanian dictionary of Markos Botsaris: filologhic edition of the original] (in Greek), Athens, Greece: Academy of Athens
- ^ Winnifrith, Tom (2002), Badlands, Borderlands: A History of Northern Epirus/Southern Albania, London, United Kingdom: Duckworth, p. 219, ISBN 0-7156-3201-9, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b Pallis, A. A. (1929), "The Greek census of 1928", The Geographical Journal, 73 (6), Blackwell Publishing: 543–548, doi:10.2307/1785338
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Kretsi, Georgia (2002), "The Secret Past of the Greek-Albanian Borderlands. Cham Muslim Albanians: Perspectives on a Conflict over Historical Accountability and Current Rights", Ethnologia Balkanica (6), Munich, Germany: Waxmann Verlag: 171-195, ISBN [[Special:BookSources/3-8258-0575-3 |3-8258-0575-3 [[Category:Articles with invalid ISBNs]]]], ISSN 1111-0411, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Check|issn=value (help); More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|editorfirst=ignored (|editor-first=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|editorlast=ignored (|editor-last=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Ktistakis, Giorgos (2006), Περιουσίες Αλβανών και Τσάμηδων στην Ελλάδα: Aρση του εμπολέμου και διεθνής προστασία των δικαιωμάτων του ανθρώπου' [Properties of Albanians and Chams in Greece: Nullification of the State of War and international protection of human rights] (.pdf), Minorities in Balkans (in Greek), Athens, Greece: Center of Studying of Minority Groups, p. 53, retrieved 2009-03-24
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Özkırımlı, Umut; Washington, Spyros A. (2008), Tormented by History: Nationalism in Greece and Turkey, New York: Columbia University Press, p. 50, ISBN 0-231-70052-0
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Banfi, Emanuele (6), "Minorités linguistiques en Grèce: Langues cachées, idéologie nationale, religion." (in French), Paris: Mercator Program Seminar, p. 27
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help); Unknown parameter|moth=ignored (help) - ^ The Free Dictionary. "Arnaut" (html). Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ a b Vickers, Miranda; Pettifer, James (1997), Albania: From Anarchy to a Balkan Identity, London: C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, p. 207, ISBN 1-85065-279-1
- ^ a b c d e Hammond, NGL (1981), Epirus: The Geography, the Ancient Remains, the History and Topography of Epirus and Adjacent Areas, Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press, p. 27, ISBN 0-405-14058-4
- ^ "Official site of Parapotamos Municipality" (in Greek). Parapotamos Municipality. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ a b Leake, William Martin (1967), Travels in Northern Greece, New York, United States of America: M. Hakkert, p. 27, ISBN 1-4021-6771-7
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ "Official site of Sagiada Municipality" (in Greek). Sagiada Municipality. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Mazower, Mark (2000), "Three Forms of Political Justice, 1944-1945", After The War Was Over: Reconstructing the Family, Nation and State in Greece, 1943-1960 (illustrated ed.), Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, p. 25-26, ISBN 0-691-05842-3, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f Yildirim, Onur (2006), Diplomacy and Displacement: Reconsidering the Turco-Greek Exchange of Populations, 1922-1934, Istanbul, Turkey: CRC Press, p. 121, ISBN 0-415-97982-X, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e Fabbe, Kristin (2007), Defining Minorities and Identities - Religious Categorization and State-Making Strategies in Greece and Turkey (PDF), Washington, United States of America: Presentation at: The Graduate Student Pre-Conference in Turkish and Turkic Studies University of Washington, p. 49
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|day=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g Berisha, Mal (2000), Diaspora Shqiptare në Turqi (in Albanian), New York: ACCL Publishing, p. 13
{{citation}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Bollati, Sali (June 2005). "Interview with the head of Chameria organization / Bollati: Chameria today" (in Albanian / English). New York, United States of America. Iliria Newspapaer.
{{cite news}}: More than one of|author=and|last=specified (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ a b Arnakis, George C. (1962), "History of Modern Hellinism: The beginnings and its changes.", Speculum (in Greek and English), 37, Mediaeval Academy of America: 94,
The descent of Albanian immigrants took place much later, but, in any event, prior to the twelfth century as far as northern Greece is concerned.
- ^ Fine, John Van Antwerp (1991). The Early Medieval Balkans. University of Michigan Press. p. 336. ISBN 0-472-08149-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Jovan, Cvijic (1918), "The Geographical Distribution of the Balkan Peoples", Geographical Review, 5 (5), American Geographical Society: 345-361,
But even in this region and in Epirus at the end of the tenth and the beginning of the eleventh century the valleys and plains were inhabited by the Greeks and Slavs, while the Albanians and the Arumani occupied only the mountains.
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994). The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-08260-5.
The rugged mountains of the region helped Michael to prepare the defense of his lands against the Crusader attack. He maintained good relations with the Albanian and Vlach chieftains in the area, and their men provided able troops for his army....large-scale migration of Albanians from the mountains of Albania occurred. This migration, particularly heavy in Epirus and Thessaly, carried them all over Greece, and many came to settle in Attica and the Peloponnesus as well.
- ^ a b Kazhdan, Alexander (Ed.) (1991). Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford University Press. pp. 52–53. ISBN 978-0-19-504652-6.
- ^ Duka, Ferit (2007). Society and Economy in Ottoman Çameria: Kazas of Ajdonat and Mazrak (Second Half of the 16th Century). Vol. 1. pp. 25–39.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Anamali, Skënder and Prifti, Kristaq. Historia e popullit shqiptar në katër vëllime. Botimet Toena, 2002, ISBN 99927-1-622-3.
- ^ a b c d Kokolakis, Michalis (2004), Η ΤΟΥΡΚΙΚΗ ΣΤΑΤΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΤΗΣ ΗΠΕΙΡΟΥ ΣΤΟ ΣΑΛΝΑΜΕ ΤΟΥ 1895 (PDF) (in Greek), Athens, Greece: Institute of Modern Greek Studies, pp. 261–312, retrieved 2009-03-18
- ^ a b c Fleming, Katherine Elizabeth (1999). The Muslim Bonaparte: Diplomacy and Orientalism in Ali Pasha's Greece. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-00194-4.
- ^ Somel, Selçuk Akşin (2001), The Modernization of Public Education in the Ottoman Empire, 1839-1908: Islamization, Autocracy, and Discipline, Istanbul, Turkey: BRILL, p. 414, ISBN 90-04-11903-5, retrieved 2009-03-18
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Mouselimis, Spyros (1976), Ιστορικοί περίπατοι ανά τη Θεσπρωτία (in Greek), Thessaloniki, Greece, p. 128
{{citation}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Jazexhi, Olsi (2007), The Bektashi Order of Dervishes (PDF), Algeris, Algeria, p. 11
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b c d e Isufi, Hajredin (2004), "Aspects of Islamization in Çamëri", Historical Studies (in Albanian), 3 (4), Tirana, Albania: Institute of History: 17–32
- ^ Isufi (2004) citing: (Braudel, Fernand (1977), Mediterranean and the Mediterranean World in the Age of Philip Second, vol. I (2 ed.), California, United States of America: Harper Collins, p. 1418, ISBN 978-0-06-090567-5
- ^ a b Clogg, Richard (1976), The Movement for Greek Independence, 1770-1821: A Collection of Documents, New York, United States of America: Barnes & Noble, p. 232, ISBN 0-06-491216-7, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Clogg, Richard (2002), Minorities in Greece: Aspects of a Plural Society, London, United Kingdom: C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, p. 203, ISBN 1-85065-706-8, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Pettifer, James; Nazarko, Mentor (2007), After Strengthening Religious Tolerance for a Secure Civil Society in Albania and the Southern Balkans, Amsterdam, Netherlands: IOS Press, p. 139, ISBN 1-58603-779-X, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e Clair, William St. (1972), That Greece Might Still be Free: The Philhellenes in the War of Independence, Cambridge, United Kingdom: Open Book Publishers, p. 412, ISBN 1-906924-00-7, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Gandon, John; Graham-Bell, Geoffrey (2000), De Jongh, Brian (ed.), The Companion Guide to Mainland Greece (3rd revised ed.), Woodbridge, Suffolk, United Kingdom: Companion Guides, p. 559, ISBN 1-900639-35-1, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g Vlora, Ekrem (2001), Kujtime [Memories] (in Albanian), Tirana, Albania: Shtëpia e librit & Komunikimit, ISBN 99927-661-6-6
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Clogg, Richard (2002), Concise History of Greece (Second ed.), Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, p. 67, ISBN 0-521-00479-9, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ "Peace Treaty Between Greece and the Ottoman Empire", Balkan Studies, 26, Los Angeles, California, United States: University of California: 26, 1985
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece (2006). "1913 Athens Peace Convention (Limited preview)" (doc) (in English and Greek). Athens, Greece: Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Greece. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ Dinstein, Yoram (1996), Israel Year Book on Human Rights, 1995, Jerusalem, Israel: Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, p. 456, ISBN 90-411-0026-1, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Potz, Richard; Wieshaider, Wolfgang (2004), Islam and the European Union, Brussels, Belgium: Peeters Publishers, p. 102-103, ISBN 90-429-1445-9, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g Manta, Eleftheria (2004), ΟΙ ΜΟΥΣΟΥΛΜΑΝΟΙ ΤΣΑΜΗΔΕΣ ΤΗΣ ΗΠΕΙΡΟΥ (1923-2000) [Cham Muslims of Epirus (1923-2000)] (in Greek), Thessaloniki, Greece: Ίδρυμα Μελετών Χερσονήσου του Αίμου, p. 225, ISBN 0-521-00479-9
- ^ a b c d Roudometof, Victor (2002), Collective Memory, National Identity, and Ethnic Conflict: Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian question, Westport, Connecticut, United States of America: Greenwood Publishing Group, p. 179, ISBN 0-275-97648-3, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Haddad, Emma (2008), The Refugee in International Society: Between Sovereigns, Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, p. 121, ISBN 0-521-86888-2
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Pentzopoulos, Dimitris (7), The Balkan Exchange of Minorities and Its Impact on Greece, London, United Kingdom: C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, p. 128, ISBN 1-85065-674-6, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help); More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Tsitselikis, Konstantinos (2002), "Exchange of population: A paradigm of legal perversion", in European Commission for Democracy through Law (ed.), The Protection of National Minorities by Their Kin-state, Strasbourg, France: Council of Europe, p. 141, ISBN 92-871-5082-6
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ James, Alice (2001), "Memories of Anatolia : generating Greek refugee identity", Balcanologica (in English and French), V (1–2), Paris, France: Federation of Journals in the Humanities and Social Sciences (Revues)
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Pallis, Athanasios A. (1925), "Exchange of Populations in the Balkans", The Anglo-Hellenic League, London, United Kingdom: The Anglo-Hellenic League
- ^ a b c d Mai, Nicola; Schwandner-Sievers, Stephanie (2005), Russell, King (ed.), The New Albanian Migration, Sussex, United Kingdom: Sussex Academic Press, p. 87, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ See also: Wikipedia contributors (31 March 2009), Greek refugees, Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ a b Kritikos, Georgios (2005), "The Agricultural Settlement of Refugees: A Source of Productive Work and Stability in Greece, 1923-1930" (pdf), Agricultural History, 79 (3), Little Rock, Arkansas, United States of America: Department of History , University of Arkansas at Little Rock: 321-346, doi:10.1525/ah.2005.79.3.321, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help) - ^ a b c Psomiades, Haris (1972), "The Diplomacy of Theodoros Pangalos 1925-1926", Balkan Studies (in English and Greek), 13 (1), Athens, Greece: Balkan Studies: 1–16
- ^ Kentrotis, Kyriakos D. (1984), "Die Frage des muslimanichen Tehamen", Diegriechich-albanichen Beziehungen (in German), pp. 288–295
- ^ a b c Hart, Laurie Kain (1999), "Culture, Civilization, and Demarcation at the Northwest Borders of Greece", American Ethnologist, 26 (1), New York, United States of America: Blackwell Publishing on behalf of the American Anthropological Association: 196–220, doi:10.1525/ae.1999.26.1.196
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|accessed=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Kostopoulos, Tasos (2003), "The dark side of the new Greek history: The deprivation of citizenship (1926-2003)", Synhrona themata (in Greek), 83, Athens, Greece: Synchrona themata: 53–57
- ^ a b Tsitselikis, Konstandinos (2004), Citizenship in Greece: Present challenges and future changes (PDF), Thessaloniki, Greece: University of Macedonia, p. 9, retrieved 2009-03-17
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help) - ^ a b Meta, Beqir (2005), "Kosova and Çamëria in the First Half of the XXth Century – A Comparative Look", Historical Studies (in Albanian), 3 (4), Tirana, Albania: Albanian Institute of History: 53-72
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help) - ^ Halili, Rigels (2007), "The issue of Epirus in political writings of Mid'hat bey Frashëri", Nationalities Affairs (31), Warsaw, Poland: Albanian Institute of History: 275–286
- ^ For a more detailed view on settlement renames see Institute of Neo-Hellenic Studies` collection
- ^ M. V., Sakellariou (1997), Epirus, 4000 years of Greek history and civilization, Athens, Greece: Ekdotike Athenon, p. 388, ISBN 960-213-371-6,
The Albanians believed that a voluntarily exchange of the Greeks of Northern Epirus for the Muslims of Chameria...Northern Epirus.
- ^ Hetaireia Makedonikōn Spoudōn. Hidryma Meletōn Cheresonēsou tou Haimou (1995), Balkan studies, vol. 36, Thessaloniki, Greece: Institute for Balkan Studies, Society for Macedonian Studies, p. 88
- ^ a b c Tsitsipis, Lukas D.; Elmendorf, William W. (1983), "Language Shift among the Albanian Speakers of Greece", Anthropological Linguistics, 25 (3), Indiana, United States of America: The Trustees of Indiana University: 288–308,
Metaxas' linguistic totalitarianism as part of his political platform is well remembered by senior Arvanitika informants. They mention that he introduced open discrimination against the Arvanitika language and punished its use at school or in the army.
- ^ a b Greek Helsinki Monitor (1995): "Report: The Arvanites". Online report
- ^ a b Fischer, Bernd Jürgen (1999). Albania at War, 1939-1945. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. pp. 75–76. ISBN 978-1-85065-531-2.
- ^ Petrov, Bisser (2005), "The Problem of Collaboration in Post-war Greece 1944-46", Balkan Studies, 25 (3), Los Angeles, California, United States: University of California: 15–36,
Chams recruited in the army, and replaced their active service by labour service. Some time later the authorities rounded up all men, who had not been mobilized and sent them to camps and islands.
- ^ Αντωνόπολος, Κοσμάς Εμμανουήλ (1964), Εθνική Αντίστασις 1941-1945 (in Greek), vol. 3, p. 1829, retrieved 2009-03-25,
Ο Ναπολέων Ζέρβας ήτο απόγονος των Σουλιωτών Ζερβαίων
- ^ Cham Anti-Fascist Commitee (1946). "Document of the Committee of Chams in exile, on Greek persecution of the Chams, submitted to the Human Rights Commission of the United Nations in 1946" (html) (in Albanian and English). Tirana, Albania: Cham Anti-Fascist Commitee. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ Albanian Parliament (1994). "Law Nr.7839, datë 30.6.1994, "For declaring 27th June in the national calendar as 'The Day of Genocide Against Albanians of Chameria from Greek Chauvinism' and the to built a memorial in Konispol"" (html) (in Albanian). Tirana, Albania: Center of Official Publication website. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ a b Foss, Arthur (1978), Epirus, Botston, United States of America: Faber, p. 224, ISBN 0-571-10488-6
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ages=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ "Türkiyedeki Kürtlerin Sayısı!" (in Turkish). Milliyet. 2008-06-06. Retrieved 2008-06-07.
- ^ a b Chameria Human Rights Association (2009). "Official site of the Chameria Human Rights Association" (html) (in Albanian and English). Tirana, Albania. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ a b Interview of Tahir Muhedini, president of Party for Justice and Integration, in "Standard" newspaper, February 2009
- ^ Laggaris, Panagiotis (2003), ""Η ΝΕΑ ΕΛΛΗΝΙΚΗ ΜΕΤΑΝΑΣΤΕΥΤΙΚΗ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΗ ΚΑΙ ΤΑ ΕΘΝΙΚΑ ΜΑΣ ΣΥΜΦΕΡΟΝΤΑ" (The New Greek Migration Policy and Our Ethnic Interest)" (html), Problimatismoi (in Greek) (14), Athens, Greece: Hellenic Institute of Strategic Studies, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|mont=ignored (help) - ^ a b Party For Justice and Integration (2009). "Official site of the Party for Justice and Integration" (html) (in Albanian and English). Tirana, Albania. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ a b Democratic Foundation of Chameria (2009). "Official website of the Democratic Foundation of Chameria" (html). The Hague, Nethernlands. Retrieved 2009-04-16.
- ^ Central Commision of Elections (2009). "Official site of the Central Commision of Elections" (html) (in Albanian and English). Tirana, Albania. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ Institute of Cham Studies (2009). "Official site of the Institute of Cham Studies" (html) (in Albanian and English). Tirana, Albania. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ a b c d Biberaj, Elez (1998), Albania in Transition: The Rocky Road to Democracy, Boulder, Colorado, United States of America: Westview Press, p. 288, ISBN 0-8133-3688-0, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b magazine "Krahu i Shqiponjës" (2009). "Official site of the magazine "Krahu i Shqiponjës"" (html) (in Albanian and English). Tirana, Albania: Cultural Association "Bilal Xhaferri". Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ Ciampi, Gabriele (1985), Le sedi dei Greci Arvaniti [The settlements of the Greek Arvanites] (in Italian), vol. 92, Roma, Italy: Rivista Geografica Italiana, p. 29
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ 2001 "Census data". Census (in Greek). Greek Statistic Agency. 2001. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ Vickers, Miranda; Petiffer, James (2007), The Albanian Question: Reshaping the Balkans, London, United Kingdom: I.B. Tauris, p. 238, ISBN 1-86064-974-2, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Gordon, Raymond G.; Gordon, Jr., Raymond G.; Grimes, Barbara F. (2005), Ethnologue: Languages of the World (15 ed.), Dallas, Texas, United States of America: Summer Institute of Linguistics (SIL) International, p. 789, ISBN 1-55671-159-X, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ L'Albanie en 2005 - [1]
- ^ Zuckerman, Phil. "Atheism: Contemporary Rates and Patterns," chapter in The Cambridge Companion to Atheism, ed. by Michael Martin, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK (2005) [2]
- ^ Goring, Rosemary (ed). Larousse Dictionary of Beliefs & Religions (Larousse: 1994); pg. 581-584. Table: "Population Distribution of Major Beliefs" [3]
- ^ Newmark, Leonard; Hubbard, Philip; Prifti, Peter R. (1982), Standard Albanian: A Reference Grammar for Students, Stanford, California, United States of America: Stanford University Press, p. 226, ISBN 0-8047-1129-1, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b Shkurtaj, Gjovalin (2005), "The dialectological and ethno-linguistic values of the language of Chameria", in Bashkim Kuçuku (ed.), The Cham Issue and the European Integration (in English and Albanian), Tirana, Albania: "Arbëria" Publishing House, p. 242-245, ISBN 99943-688-2-6
{{citation}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help) - ^ a b Elsie, Robert (1986), Dictionary of Albanian Literature, London, United Kingdom: Greenwood Press, p. 17, ISBN 0-313-25186-X, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d Elsie, Robert (2005), Centre for Albanian Studies (ed.), Albanian Literature: A short history, London, United Kingdom: I.B.Tauris, p. 41, ISBN 1-84511-031-5, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Plantenga, Bart (2004), Yodel-ay-ee-oooo: The Secret History of Yodeling Around the World., Abingdon, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom: Routledge, p. 86-87, ISBN 0-415-93990-9, retrieved 2009-03-15
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ a b Tole, Vasil S. (1999), Folklori Muzikor-Polifonia Shqiptare [Albanian Folk Polyphony] (in Albanian), Tirana, Albania: SHBLU, p. 198, ISBN 99927-0-176-5, retrieved 2009-03-31
- ^ Tole, Vasil S. (2001), Enciklopedia e muzikës popullore shqiptare [Encyclopedia of Albanian Folk Music] (in Albanian), vol. 3, Tirana, Albania: ILAR, p. 198, retrieved 2009-03-31,
On the general classification of our folk music, cham iso-polyphony is ranked with the tosk iso-polyphony, with two and three voices.
- ^ Dojaka, Abaz (1966), ""Dasma çame" ["Cham Dance"]", Studime Historike [History Studies] (in Albanian) (2), Tirana, Albania: Institute of History, Albanian Academy of Sciences
- ^ Kruta, Beniamin (1991), Polifonia dy zërëshe e Shqipërisë së Jugut [Two voice polyphony of Southern Albania] (in Albanian), Tirana, Albania: Institute of Popular Culture, Albanian Academy of Sciences
- ^ Schiel; Schiel, Margret (2004), Volkstänze aus Griechenland [Folk dances from Greece] (in German), Cologne, Germany: Romiosini, p. 172, ISBN 3-923728-14-X
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|firs1=ignored (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ a b Jaffé, Nigel Allenby (1990), Folk Dance of Europe, European Folk Dances, London, United Kingdom: Folk Dance Enterprises, p. 207-208, ISBN 0-946247-14-5, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Grove, George (1954), Dictionary of music and musicians, vol. 7 (5 ed.), New York: St. Martin's Press, retrieved 2009-03-16
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|editorn-first=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|editorn-last=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|editorn-link=ignored (help) - ^ Nitsiakos, Vassilis; Manos, Ioannis; Agelopoulos, Georgios; Angelidou, Aliki; Dalkavoukis, Vassilis (1990), Balkan Border Crossings, Berlin, Germany: LIT Verlag, Berlin-Hamburg-Münster, p. 371-377, ISBN 3-8258-0918-8, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ "Eufrozini (translated by Robert Elsie)". Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ Pedersen, Holgert (1898), Zur albanesischen Volkskunde (in Danish and Albanian), Copenhagen, Denmark: E. Möller
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Aliu, Kadri (1993), "Perla të folklorit kombëtar të pavlerësuara [Unvalued pearls of national folklore]", Çamëria - Vatra amtare (in Albanian) (224), Tirana, Albania: Shoqëria Politike Atdhetare "Çamëria"
- ^ Cooper, Paul Fenimore; Dozon, Auguste; Pedersen, Holger (1928), Tricks of Women, & Other Albanian Tales, New York, United States of America: W. Morrow & Company, p. 204, retrieved 2009-03-31
- ^ Elsie, Robert (2000), A Dictionary of Albanian Religion, Mythology, and Folk Culture, London, United Kingdom: C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 2001, p. 131, ISBN 0-8147-2214-8, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ Hyseni, Shyqyri (2006), "Kulte tradicionale shqiptare [Albanian traditional cults]", Studime Albanologjike [Albanological studies] (in Albanian) (36), Tirana, Albania: Institute of Albanology, Albanian Academy of Sciences: 349–361
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Jonuzi, Afërdita "Ethnographic phenomenon of the Chameria region", chapter on the book "The cham issue and the European Integration", ISBN 99943-688-2-6, p.245-247
- ^ a b Pettifer, James; Vickers, Miranda (2004), "The Challenge to Preserve the Cham Heritage", Shekulli (in Albanian), Tirana, Albania: Spektër group
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Deserts of Konitsa" (in Greek). Konitsa Municipality. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ Elsie, Robert; Hutchings, Raymond (2003), Historical Dictionary of Albania, Lanham, Maryland, United States of America: Scarecrow Press, p. 584, ISBN 0-8108-4872-4
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ de Malherbe, Raoul (2001) [1884], L\'Orient. 1718-1845: Histoire, politique, religion, moeurs, etc. [The East. 1718-1845: History, politics, religion, customs, etc.] (in French), vol. 2, Boston, United States of America: Adamant Media Corporation, p. 458, ISBN 0-543-95853-1, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help) - ^ de Beauchamp, Alphonse (1823), The Life of Ali Pacha, of Jannina: Late Vizier of Epirus, Surnamed Aslan, Or the Lion, London, United Kingdom: L. Relfe, p. 108-134, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help) - ^ Brock, Adrian C. (2006), Internationalizing the History of Psychology, New York, United States of America: New York University Press, p. 78-79, ISBN 0-8147-9944-2, retrieved 2009-03-31
{{citation}}: More than one of|pages=and|page=specified (help); Unknown parameter|ean=ignored (help)
Further reading
History
- Fabbe, Kristin (2007). "Defining Minorities and Identities - Religious Categorization and State-Making Strategies in Greece and Turkey" (PDF).
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994). The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-08260-5.
- Fleming, Katherine Elizabeth (1999). The Muslim Bonaparte: Diplomacy and Orientalism in Ali Pasha's Greece. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-00194-4.
- Mazower, Mark (2000). After The War Was Over: Reconstructing the Family, Nation and State in Greece, 1943-1960. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-05842-9.
- Roudometof, Victor (2002). Collective memory, national identity, and ethnic conflict: Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian question. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-275-97648-4.
- Yildirim, Onur (2006). Diplomacy and Displacement: Reconsidering the Turco-Greek Exchange of Populations, 1922-1934. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-415-97982-5.
Post-war politics and current situation
- "Document of the Committee of Cham Albanians in exile, on Greek persecution of the Chams, submitted to the Human Rights Commission of the United Nations in 1946". Texts and Documents of Albanian History. Elsie, Robert. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
- "L'arvanite/albanais en Grèce". L'étude Euromosaic (in French). 2006. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
- Vickers, Miranda (2002). "The Cham Issue - Albanian National & Property Claims in Greece". Retrieved 2009-03-18.
- Vickers, Miranda (2007). "The Cham Issue - Where to Now?" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-03-18.
News
- "Chams still pressing for return of Greek citizenship and property". Radio Free Europe. 19 September 2002.
- "Albania protest halts Greek visit". BBC. 1 November 2005.
