Occupation of Poland (1939–1945): Difference between revisions
add info and sources |
→Forced labor and concentration camps: expanding on the camps and Holocaust |
||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
</blockquote> |
</blockquote> |
||
===Forced labor |
===Forced labor=== |
||
{{ |
{{Further|Forced labor in Germany during World War II}} |
||
Almost immediately after the invasion, Germans begun forcibly conscripting laborers. Jews were drafted to repair war damage as early as October, with women and children 12 or older required to work; shifts could take half a day and with little compensation.<ref name=ushmmfl>http://www.ushmm.org/outreach/en/article.php?ModuleId=10007732</ref> The laborers, Jews, Poles, and others, were employed in SS-owned enterprises (such as the [[German Armament Works]], Deutsche Ausrustungswerke, DAW), but also in many private German firms – such as [[Messerschmitt]], [[Junkers (Aircraft)|Junkers]], [[Siemens]], and [[IG Farben]].<ref name=ushmmfl/><ref name="Ferencz2002"/> |
Almost immediately after the invasion, Germans begun forcibly conscripting laborers. Jews were drafted to repair war damage as early as October, with women and children 12 or older required to work; shifts could take half a day and with little compensation.<ref name=ushmmfl>http://www.ushmm.org/outreach/en/article.php?ModuleId=10007732</ref> The laborers, Jews, Poles, and others, were employed in SS-owned enterprises (such as the [[German Armament Works]], Deutsche Ausrustungswerke, DAW), but also in many private German firms – such as [[Messerschmitt]], [[Junkers (Aircraft)|Junkers]], [[Siemens]], and [[IG Farben]].<ref name=ushmmfl/><ref name="Ferencz2002"/> |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
Labor shortages in the German war economy became critical especially after German defeat in the battle of [[Stalingrad]] in 1942–1943. This led to the increased use of prisoners as forced laborers in German industries.<ref name="Merten2013">{{cite book|author=Ulrich Merten|title=Forgotten Voices: The Expulsion of the Germans from Eastern Europe after World War II|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=EXxUAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA85|date=15 August 2013|publisher=Transaction Publishers|isbn=978-1-4128-5258-6|pages=85–86}}</ref> Following the German invasion and occupation of Polish territory, at least 1.5 million Polish citizens, including teenagers, became laborers in Germany, few by choice.<ref name="ushmm"/> A total of 2.3 millions of Polish citizens, including 300,000 POWs, were deported to Germany as forced laborers.<ref name="Piotrowski1998">{{cite book|author=Tadeusz Piotrowski|title=Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=hC0-dk7vpM8C&pg=PA22|year=1998|publisher=McFarland|isbn=978-0-7864-0371-4|page=22}}</ref> They tended to have to work longer hours for lower wages than their German counterparts.<ref name="ushmm"/> |
Labor shortages in the German war economy became critical especially after German defeat in the battle of [[Stalingrad]] in 1942–1943. This led to the increased use of prisoners as forced laborers in German industries.<ref name="Merten2013">{{cite book|author=Ulrich Merten|title=Forgotten Voices: The Expulsion of the Germans from Eastern Europe after World War II|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=EXxUAQAAQBAJ&pg=PA85|date=15 August 2013|publisher=Transaction Publishers|isbn=978-1-4128-5258-6|pages=85–86}}</ref> Following the German invasion and occupation of Polish territory, at least 1.5 million Polish citizens, including teenagers, became laborers in Germany, few by choice.<ref name="ushmm"/> A total of 2.3 millions of Polish citizens, including 300,000 POWs, were deported to Germany as forced laborers.<ref name="Piotrowski1998">{{cite book|author=Tadeusz Piotrowski|title=Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=hC0-dk7vpM8C&pg=PA22|year=1998|publisher=McFarland|isbn=978-0-7864-0371-4|page=22}}</ref> They tended to have to work longer hours for lower wages than their German counterparts.<ref name="ushmm"/> |
||
===Concentration and extermination camps=== |
|||
| ⚫ | A network of [[concentration camps]] were established on German-controlled territories, many of them in occupied Poland, including one of the largest and most infamous, [[Auschwitz]] (Oświęcim).<ref name="RubensteinRoth2003"/> Those camps were officially designed as labor camps, and many displayed the motto ''[[Arbeit macht frei]]'' ("Work brings freedom").<ref name="Ferencz2002">{{cite book|author=Benjamin B. Ferencz|title=Less Than Slaves: Jewish Forced Labor and the Quest for Compensation|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=2T5CPGvAGB4C&pg=PA25|year=2002|publisher=Indiana University Press|isbn=0-253-21530-7|pages=24-25}}</ref><ref name="RubensteinRoth2003"/> Only high ranking officials knew the that one of the purposes of some of the camps, known as [[extermination camps]], was mass murder of the undesirable minorities, primarily the Jews;<ref name="NobleStrauss2007">{{cite book|author1=Thomas F. X. Noble|author2=Barry Strauss|author3=Duane Osheim|coauthors=Kristen Neuschel, Elinor Accampo|title=Western Civilization: Beyond Boundaries, Volume II: Since 1560|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=mb8HAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA880|date=12 January 2007|publisher=Cengage Learning|isbn=1-111-80948-8|page=880}}</ref><ref name="RubensteinRoth2003">{{cite book|author1=Richard L. Rubenstein|author2=John K. Roth|title=Approaches to Auschwitz: The Holocaust and Its Legacy|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=IfoBx6skMCkC&pg=PA195|year=2003|publisher=Westminster John Knox Press|isbn=978-0-664-22353-3|pages=195–196}}</ref><ref name="Fox2013">{{cite book|author=Elaine Saphier Fox|title=Out of Chaos: Hidden Children Remember the Holocaust|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=-zfPJvAmUSYC&pg=PA275|date=31 August 2013|publisher=Northwestern University Press|isbn=978-0-8101-6661-5|page=275}}</ref> officially the prisoners were used in enterprises such as production of [[synthetic rubber]], as was the case of a plant owned by IG Farben, whose laborers came from Auschwitz III camp, or [[Monowice|Monowitz]].<ref name=ushmmfl/> Laborers from concentration camps were literally worked to death. in what was known as [[extermination through labor]].<ref name=ushmmfl/><ref name=ushmmnzs>http://www.ushmm.org/outreach/en/article.php?ModuleId=10007720</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | A network of [[concentration camps]] were established on German-controlled territories, many of them in occupied Poland, including one of the largest and most infamous, [[Auschwitz]] (Oświęcim).<ref name="RubensteinRoth2003"/> Those camps were officially designed as labor camps, and many displayed the motto ''[[Arbeit macht frei]]'' ("Work brings freedom").<ref name="Ferencz2002">{{cite book|author=Benjamin B. Ferencz|title=Less Than Slaves: Jewish Forced Labor and the Quest for Compensation|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=2T5CPGvAGB4C&pg=PA25|year=2002|publisher=Indiana University Press|isbn=0-253-21530-7|pages=24-25}}</ref><ref name="RubensteinRoth2003"/> Only high ranking officials knew the that one of the purposes of some of the camps, known as [[extermination camps]] (or death camps), was mass murder of the undesirable minorities, primarily the Jews;<ref name="NobleStrauss2007">{{cite book|author1=Thomas F. X. Noble|author2=Barry Strauss|author3=Duane Osheim|coauthors=Kristen Neuschel, Elinor Accampo|title=Western Civilization: Beyond Boundaries, Volume II: Since 1560|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=mb8HAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA880|date=12 January 2007|publisher=Cengage Learning|isbn=1-111-80948-8|page=880}}</ref><ref name="RubensteinRoth2003">{{cite book|author1=Richard L. Rubenstein|author2=John K. Roth|title=Approaches to Auschwitz: The Holocaust and Its Legacy|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=IfoBx6skMCkC&pg=PA195|year=2003|publisher=Westminster John Knox Press|isbn=978-0-664-22353-3|pages=195–196}}</ref><ref name="Fox2013">{{cite book|author=Elaine Saphier Fox|title=Out of Chaos: Hidden Children Remember the Holocaust|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=-zfPJvAmUSYC&pg=PA275|date=31 August 2013|publisher=Northwestern University Press|isbn=978-0-8101-6661-5|page=275}}</ref> officially the prisoners were used in enterprises such as production of [[synthetic rubber]], as was the case of a plant owned by IG Farben, whose laborers came from Auschwitz III camp, or [[Monowice|Monowitz]].<ref name=ushmmfl/> Laborers from concentration camps were literally worked to death. in what was known as [[extermination through labor]].<ref name=ushmmfl/><ref name=ushmmnzs>http://www.ushmm.org/outreach/en/article.php?ModuleId=10007720</ref> |
||
Auschwitz received the first contingent of 728 Poles on 14 June 1940, transferred from an overcrowded prison at [[Tarnów]]. Within a year the Polish inmate population was in thousands, and begun to be exterminated, including in the first gassing experiment in September 1941.<ref name="ushmm"/> According to Polish historian [[Franciszek Piper]], approximately 140,000–150,000 Poles went through Auschwitz, with about half of them perishing there due to executions, medical experiments, or due to starvation and disease.<ref name="ushmm"/> About 100,000 Poles were imprisoned in [[Majdanek]] camp, with similar fatality rate. About 30,000 Poles died at [[Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp|Mauthausen]], 20,000 at [[Sachsenhausen concentration camp|Sachsenhausen]] and [[Gross-Rosen]] each, 17,000 at [[Neuengamme concentration camp|Neuengamme]] and [[Ravensbrueck]] each, 10,000 at [[Dachau concentration camp|Dachau]], and tens of thousands perished in other camps and prisons.<ref name="ushmm"/> |
Auschwitz received the first contingent of 728 Poles on 14 June 1940, transferred from an overcrowded prison at [[Tarnów]]. Within a year the Polish inmate population was in thousands, and begun to be exterminated, including in the first gassing experiment in September 1941.<ref name="ushmm"/> According to Polish historian [[Franciszek Piper]], approximately 140,000–150,000 Poles went through Auschwitz, with about half of them perishing there due to executions, medical experiments, or due to starvation and disease.<ref name="ushmm"/> About 100,000 Poles were imprisoned in [[Majdanek]] camp, with similar fatality rate. About 30,000 Poles died at [[Mauthausen-Gusen concentration camp|Mauthausen]], 20,000 at [[Sachsenhausen concentration camp|Sachsenhausen]] and [[Gross-Rosen]] each, 17,000 at [[Neuengamme concentration camp|Neuengamme]] and [[Ravensbrueck]] each, 10,000 at [[Dachau concentration camp|Dachau]], and tens of thousands perished in other camps and prisons.<ref name="ushmm"/> |
||
===The Holocaust=== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Further|Holocaust in Poland}} |
|||
Following the [[invasion of Poland]] in 1939 most of the approximately 3.5 million [[Polish Jews]] were rounded up and [[Jewish ghettos in German-occupied Poland|put into newly established ghettos]] by Nazi Germany. The ghetto system was unsustainable, as by the end of 1941 the Jews had no savings left to pay the ''SS'' for food deliveries and no chance to earn their own keep.<ref name="Vogelsang">{{Citation |last=Vogelsang |first=Peter |last2=Larsen |first2=Brian B.M. |title=The Ghettos of Poland |url=http://www.holocaust-education.dk/holocaust/ghettoer.asp |publisher=Holocaust and Genocide Studies</ref> At the 20 January 1942 [[Wannsee Conference]], held near Berlin, new plans were outlined for the total genocide of the Jews, known as the "Final Solution of the [[Jewish Question]]".<ref name="Vogelsang">{{Citation |last=Vogelsang |first=Peter |last2=Larsen |first2=Brian B.M. |title=Wannsee Conference |url=http://www.holocaust-education.dk/holocaust/wannsee.aspp |publisher=Holocaust and Genocide Studies}}</ref> The extermination program was codenamed [[Operation Reinhard]].<ref name="CFCA">{{cite web |url=http://antisemitism.org.il/eng/Holocaust |title=Holocaust |publisher=The Coordination Forum for Countering Antisemitism |year=2013 |accessdate=27 December 2013 |author=CFCA |quote=From diary of Reich Propaganda Minister [[Joseph Goebbels]], dated 12 December 1941.}}</ref> |
|||
Three secret [[extermination camp]]s set up specifically for Operation Reinhard; [[Treblinka ]], [[Belzec extermination camp|Belzec]] and [[Sobibor extermination camp|Sobibor]].<ref name="YV-Reinhard-pdf">{{cite web |url=http://www.yadvashem.org/odot_pdf/microsoft%20word%20-%205724.pdf |title=Aktion Reinhard |publisher=Shoah Resource Center, The International School for Holocaust Studies |year=2013 |accessdate=31 October 2013 |author=Yad Vashem |format=PDF file, direct download 33.1 KB }}</ref> In addition to the Reinhard camps, mass killing facilities such as [[gas chamber]]s using [[Zyklon B]] were added to the [[Majdanek concentration camp]] in March 1942<ref name="YV-Reinhard-pdf" /> and at Auschwitz and [[Chełmno extermination camp|Chełmno]].<ref name="Fox2013"/> |
|||
<center><gallery> |
<center><gallery> |
||
Revision as of 05:32, 21 May 2014



The occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union during the Second World War (1939–1945) began with invasion of Poland in September 1939, and formally concluded with the defeat of Nazism by the Four Powers in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of foreign occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR). In summer-autumn of 1941 the lands annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Nazi Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army was able to repel the invaders and drive the Nazi forces out of the USSR and across Poland from the rest of Eastern and Central Europe.
Both occupying powers were equally hostile to the existence of sovereign Poland, her culture and the Polish people, aiming at their destruction.[1] Before Operation Barbarossa, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated their Poland-related policies, most visibly in the four Gestapo-NKVD Conferences, where the occupants discussed plans for dealing with the Polish resistance movement and future destruction of Poland.[2]
About 6 million Polish citizens—nearly 21.4% of Poland's population—died between 1939 and 1945 as a result of the occupation,[3][4][5] half of whom were Polish Jews. Over 90% of the death toll came through non-military losses, as most of the civilians were targeted by various deliberate actions by Germans and the Soviets.[3] Overall, during German occupation of pre-war Polish territory, 1939–1945, the Germans murdered 5,470,000–5,670,000 Poles, including nearly 3,000,000 Jews.[4][5]
Administration
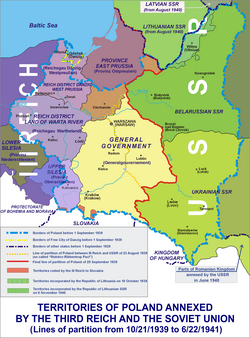
After Germany and the Soviet Union had partitioned Poland in 1939, most of the ethnically Polish territory ended up under the control of Germany while the areas annexed by the Soviet Union contained ethnically diverse peoples, with the territory split into bilingual provinces, some of which had a significant non-Polish majority (Ukrainians in the south and Belarusians in the north).[6] Many of them welcomed the Soviets, alienated in the interwar Poland. Nonetheless Poles comprised the largest single ethnic group in all territories annexed by the Soviet Union.[7]
Areas occupied by Germany
Under the terms of two decrees by Hitler, with Stalin's agreement (8 and 12 October 1939), large areas of western Poland were annexed by Germany. The size of these annexed territories was approximately 94,000 square kilometres with a population of about 10 million, the great majority of whom were Polish. Nearly 1 million Poles were expelled further east from this Nazi-controlled area. Soon, 600,000 Germans from Eastern Europe and 400,000 from the Third Reich were settled there.[8] The Nazis kept in place 1.7 million Poles deemed Germanizable, including between one and two hundred thousand children who had been taken from their parents.[9] Duiker and Spielvogel note that by 1942, the number of new German arrivals in pre-war Poland had already reached two million.[10]
The remaining block of territory was placed under a German administration called the General Government (in German: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), with its capital at Kraków. A German lawyer and prominent Nazi, Hans Frank, was appointed Governor-General of this occupied area on 12 October 1939.[11][12] Most of the administration outside strictly local level was replaced by German officials.[12][13] Non-German population on the occupied lands were subject to Germanization, economic exploitation, and slow but progressing extermination.[12][13][14]
A small strip of land that was part of Czechoslovakia before 1938 was also returned by Germany to its ally, Slovakia.[15]
Soviet administration zone
By the end of the Polish Defensive War against the two invaders, the Soviet Union had taken over 52.1% of the territory of Poland (~200,000 km²), with over 13,700,000 people. The ethnic composition of these areas were as follows: 38% Poles (~5.1 million people), 37% Ukrainians, 14.5% Belarusians, 8.4% Jews, 0.9% Russians and 0.6% Germans. There were also 336,000 refugees who fled from areas occupied by Germany, most of them Jews (198,000).[7] All territory invaded by the Red Army was annexed to the Soviet Union (after a rigged election),[16][17] with the exception of Wilno area, which was transferred to sovereign Lithuania.[18]
Treatment of Polish citizens under Nazi German occupation
Generalplan Ost, Lebensraum and expulsion of Poles
From the beginning, the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany was intended as fulfillment of the future plan of the German Reich described by Adolf Hitler in his book Mein Kampf as Lebensraum ("living space") for the Germanic peoples in Eastern Europe.[11] The occupation goal was to turn former Poland into ethnically German "living space", by deporting or exterminating non-German populace, or relegating it to the position of slave labour.[19][20][21]
The fate of Poles, as well as many other Slavs, was outlined in genocidal Generalplan Ost (General Plan for the East)[22] and a related Generalsiedlungsplan (General Plan for Settlement).[23] Over 30 years, approximately 12.5 millions of Germans were to be resettled into the Slavic areas, including Poland; with some versions planning for a movement of at least 100 millions Germans over a century.[23] The Slavic inhabitants of those lands were to be subject to liquidation by mass murder and expulsions[24][25][26].
further east, into less hospitable parts of Euroasia beyond the Ural Mountains, such as Siberia in Russia.[23] At the plans fulfillment, there would be no Slavs or Jews remaining in Eastern Europe.[23] Generalplan Ost, essentially a grand plan for ethnic cleansing, was divided into two parts, the Kleine Planung ("Small Plan"), which covered actions which were to be taken during the war, and the Grosse Planung ("Big Plan"), which covered actions to be undertaken after the war was won.[27][28][29] The plan envisaged differing percentages of the various conquered nations undergoing Germanisation, expulsion into the depths of Russia, and other gruesome fates, including purposeful starvation and murder, the net effect of which would be to ensure that the conquered territories would take on an irrevocably German character.[29][30]
By 1952, only about 3–4 million Poles were supposed to be left residing in the former Poland, and then only to serve as slaves for German settlers. German authorities planned to either ban or raise and hinder Polish marriages, promote abortions, murder those not fit for Germanization and for Polish nation to destroyed; all of occupied Poland by 1952 was to be cleared of Poles and become German as the Rhineland and settled by 4-5 million Germans.[31][32][33][34][35][36][37]
As early as October 1939, many Poles were expelled from the annexed lands to make room for German settlers.[11][38] Only those Poles selected for Germanization[clarification needed] were permitted to remain,[39] and if they resisted it, they were to be sent to concentration camps, because "German blood must not be utilized in the interest of a foreign nation".[40] By the end of 1940,at least 325,000 Poles from annexed lands were forcibly resettled in the General Government, forced to abandon most of their property.[11] There were numerous fatalities among the very young and elderly, who perished en route or in makeshift transit camps such as those in the towns of Potulice, Smukal, and Toruń.[11] The expulsions continued in 1941, with another 45,000 Poles forced to move eastwards, but following German invasion of the Soviet Union, the expulsions slowed down, as more and more trains were diverted for military logistics, rather than being made available for population transfers.[11] Nonetheless, in late 1942 and in 1943, large scale expulsions also took place in the General Government, affecting at least 110,000 Poles in the Zamość–Lublin region.[11] Tens of thousands of the expelled, with no place to go, were simply imprisoned in the Auschwitz (Oświęcim) and Majdanek concentration camps.[11]
Whereas Nazi plans called for the Poland's 3.3 million Jews were to be simply killed in the near future, the non-Jewish majority was to be controlled through the mass murder of its political, religious, and intellectual elites, which was meant to make the formation of any organized top-down resistance more difficult. Further, the populace of occupied territories was to be relegated to the role of an unskilled labor-force for German-controlled industry and agriculture.[11][41] This was in spite of racial theory that regarded most Polish leaders as actually being of German blood,[42] and partly because of it, on the grounds that German blood must not be used in the service of a foreign nation.[41]
German People's List
The German People's List (Deutsche Volksliste) classified Polish citizens into four groups.[43]
- Group 1 included so-called ethnic Germans who had taken an active part in the struggle for the Germanization of Poland;
- Group 2 included those ethnic Germans who had not taken such an active part, but had "preserved" their German characteristics;
- Group 3 included individuals of alleged German stock who had become "Polonized", but whom it was believed, could be won back to Germany. This group also included persons of non-German descent married to Germans or members of non-Polish groups who were considered desirable for their political attitude and racial characteristics;
- Group 4 consisted of persons of German stock who had become politically merged with the Poles.
After registration in the List, individuals from Groups 1 and 2 automatically became German citizens. Those from Group 3 acquired German citizenship subject to revocation. Those from Group 4 received German citizenship through naturalization proceedings; resistance to Germanization constituted treason because "German blood must not be utilized in the interest of a foreign nation," and such people were sent to concentration camps.[43] Persons ineligible for the List were classified as stateless, and all Poles from the occupied territory, that is from the Government General of Poland, as distinct from the incorporated territory, were classified as non-protected.[43]
Encouraging ethnic strife
According to the 1931 Polish census, out of prewar population of 35 million, 66% spoke Polish language as their mother tongue, and most of the Polish native speakers were Roman Catholics. With regards to the remainder, 15% were Ukrainians, 8.5% Jews, 4.7% Belarusians, and 2.2% Germans.[11][44] Germans intended to exploit the fact that the Second Polish Republic was an ethnically diverse territory, and their policy aimed to "divide and conquer" the ethnically diverse population of the occupied Polish territory, to prevent any unified resistance from forming.[11] One of the attempts to divide the Polish nation was a creation of a new ethnicity called "Goralenvolk".[11] Some minorities, like Kashubians, were forcefully enrolled of into the Deutsche Volksliste, as a measure to compensate for the losses in the Wehrmacht (unlike Poles, Deutsche Volksliste members were eligible for military conscription).[11][45]
In a top-secret memorandum, "The Treatment of Racial Aliens in the East", dated 25 May 1940, Heinrich Himmler, head of the SS, wrote: "We need to divide the East's different ethnic groups up into as many parts and splinter groups as possible".[46] Historians, J. Grabowski and Z.R. Grabowski wrote in 2004:
The Germanisation of Polish territories occurred by deporting and exterminating the Jews and Poles, depriving Poles and Jews off their rights and supporting the local Germans and the ethnic Germans resettled from the East. The German minority living in this ethnically mixed region was required to adhere to strict codes of behaviour and was held accountable for all unauthorised contacts with their Polish and, even more so, their Jewish neighbours. The system of control and repression strove to isolate the various ethnic (‘racial’) groups, encouraging denunciations and thus instilling fear in the populace.[47]
Forced labor
Almost immediately after the invasion, Germans begun forcibly conscripting laborers. Jews were drafted to repair war damage as early as October, with women and children 12 or older required to work; shifts could take half a day and with little compensation.[48] The laborers, Jews, Poles, and others, were employed in SS-owned enterprises (such as the German Armament Works, Deutsche Ausrustungswerke, DAW), but also in many private German firms – such as Messerschmitt, Junkers, Siemens, and IG Farben.[48][49]
Forced laborers were subject to harsh discriminatory measures. Announced on the 8 March 1940 was the Polish decrees which were used as a legal basis for foreign laborers in Germany.[50] The decrees required Poles to wear identifying purple P's on their clothing, made them subject to a curfew, and banned them from using public transportation as well as many German "cultural life" centers and "places of amusement" (this included churches and restaurants).[11][50] Sexual relations between Germans and Poles was forbidden as Rassenschande (race defilement) under penalty of death.[11][50] To keep them segregated from the German population, they were often housed in segregated barracks behind barbed wire.[11]
Labor shortages in the German war economy became critical especially after German defeat in the battle of Stalingrad in 1942–1943. This led to the increased use of prisoners as forced laborers in German industries.[51] Following the German invasion and occupation of Polish territory, at least 1.5 million Polish citizens, including teenagers, became laborers in Germany, few by choice.[11] A total of 2.3 millions of Polish citizens, including 300,000 POWs, were deported to Germany as forced laborers.[52] They tended to have to work longer hours for lower wages than their German counterparts.[11]
Concentration and extermination camps
A network of concentration camps were established on German-controlled territories, many of them in occupied Poland, including one of the largest and most infamous, Auschwitz (Oświęcim).[53] Those camps were officially designed as labor camps, and many displayed the motto Arbeit macht frei ("Work brings freedom").[49][53] Only high ranking officials knew the that one of the purposes of some of the camps, known as extermination camps (or death camps), was mass murder of the undesirable minorities, primarily the Jews;[54][53][55] officially the prisoners were used in enterprises such as production of synthetic rubber, as was the case of a plant owned by IG Farben, whose laborers came from Auschwitz III camp, or Monowitz.[48] Laborers from concentration camps were literally worked to death. in what was known as extermination through labor.[48][56]
Auschwitz received the first contingent of 728 Poles on 14 June 1940, transferred from an overcrowded prison at Tarnów. Within a year the Polish inmate population was in thousands, and begun to be exterminated, including in the first gassing experiment in September 1941.[11] According to Polish historian Franciszek Piper, approximately 140,000–150,000 Poles went through Auschwitz, with about half of them perishing there due to executions, medical experiments, or due to starvation and disease.[11] About 100,000 Poles were imprisoned in Majdanek camp, with similar fatality rate. About 30,000 Poles died at Mauthausen, 20,000 at Sachsenhausen and Gross-Rosen each, 17,000 at Neuengamme and Ravensbrueck each, 10,000 at Dachau, and tens of thousands perished in other camps and prisons.[11]
The Holocaust
Following the invasion of Poland in 1939 most of the approximately 3.5 million Polish Jews were rounded up and put into newly established ghettos by Nazi Germany. The ghetto system was unsustainable, as by the end of 1941 the Jews had no savings left to pay the SS for food deliveries and no chance to earn their own keep.[57] At the 20 January 1942 Wannsee Conference, held near Berlin, new plans were outlined for the total genocide of the Jews, known as the "Final Solution of the Jewish Question".[57] The extermination program was codenamed Operation Reinhard.[58] Three secret extermination camps set up specifically for Operation Reinhard; Treblinka , Belzec and Sobibor.[59] In addition to the Reinhard camps, mass killing facilities such as gas chambers using Zyklon B were added to the Majdanek concentration camp in March 1942[59] and at Auschwitz and Chełmno.[55]
-
Young Polish girl wearing Letter "P" patch.
-
Polish-forced-workers' badge
-
Poster in German and Polish listing the Polish decrees obligations
-
Identity card for a Polish forced worker in Germany
-
German notice of death penalty for Poles refusing to work during the harvest
Cultural genocide
Nazi Germany engaged in a concentrated effort to destroy Polish culture. To that end, numerous cultural and educational institutions were closed or destroyed, from schools and universities, through monuments and libraries, to laboratories and museums. Many employees of said institutions were arrested and executed as part wider persecutions of Polish intellectual elite. Schooling of Polish children was curtailed to a few years of elementary education, as outlined by Himmler's May 1940 memorandum: "The sole goal of this schooling is to teach them simple arithmetic, nothing above the number 500; writing one's name; and the doctrine that it is divine law to obey the Germans. . . . I do not think that reading is desirable".[11]
Extermination of elites
Proscription lists (Sonderfahndungsbuch Polen), prepared before thee war started, identified more than 61,000 Polish elite and intelligentsia leaders deemed as unfriendly towards Germany.[60] Already in the 1939 German invasion, dedicated units of SS and police (the Einsatzgruppen), advancing behind the frontline units, aided by some regular German army units and "self-defense" forces composed of members of German minority in Poland, the Volksdeutsche, were tasked with arresting or outright killing of those resisting the Germans.[11] This was known as Operation Tannenberg".[61] This included not only those resisting actively, but also those simply capable of doing so by the virtue of their social status.[11] As a result, tens of thousands of people found "guilty" of being educated (members of the intelligentsia, from clergymen to government officials, doctors, teachers and journalists) or wealthy (landowners, business owners, and so on) were either executed on spot, sometimes in mass executions, or imprisoned, some destined for the concentration camps.[11] Some of the mass executions were reprisal actions for actions of the Polish resistance, with German officials adhering to the collective guilt principle and holding entire communities responsible for the actions of unidentified perpetrators.[11]
One of the most infamous German operations was the Außerordentliche Befriedungsaktion (AB-Aktion in short, German for Special Pacification), a German campaign during World War II aimed at Polish leaders and the intelligentsia, including many university professors, teachers and priests.[62][63] In the spring and summer of 1940, more than 30,000 Poles were arrested by the German authorities of German-occupied Poland.[11][62] Several thousands were executed outside Warsaw, in the Kampinos forest near Palmiry, and inside the city at the Pawiak prison.[11][63] Most of the remainder were sent to various German concentration camps.[62]
Suppression of the Roman Catholic Church and other religions

According to historian Ian Kershaw, in his scheme for the Germanization of Eastern Europe, Hitler made clear that there would be "no place in this utopia for the Christian Churches".[64] Catholicism had a presence in Poland stretching back almost 1000 years. By 1939, around 65% of Poles professed to be Catholic.[65] The Nazi plan for Poland entailed the destruction of the Polish nation, which necessarily required attacking the Polish Church, particularly in those areas annexed to Germany.[66] Thousands of priests died in prisons and concentration camps; thousands of churches and monasteries were confiscated, closed or destroyed; and priceless works of religious art and sacred objects were lost forever. Church leaders were targeted as part of an overall effort to destroy Polish culture.
Historically, the Catholic Church had been a leading force in Polish resistance against foreign domination, thus the Nazis targeted clergy, monks and nuns in their terror campaigns to eliminate Polish culture. Nazi ideology was hostile to Christianity and Hitler held the teachings of the Catholic Church in contempt. Ethnic "Poles" - the mainly Catholic ethnic majority of Poland - were viewed as "sub-humans". Following their 1939 invasion of West Poland, the Nazis instigated a policy of murdering or suppressing the ethnic Polish elites: including religious leaders.[11] During the 1939 invasion, special death squads of SS and police arrested or executed those considered capable of resisting the occupation: including clergymen.[11] Of the brief period of military control from 1 September 1939 – 25 October 1939, Davies wrote: "according to one source, 714 mass executions were carried out, and 6,376 people, mainly Catholics, were shot. Other put the death toll in one town alone at 20,000. It was a taste of things to come."[67]
In the aftermath of invasion, the Primate of Poland, Cardinal August Hlond, submitted an official account of the persecutions of the Polish Church to the Vatican.[68] In his final observations for Pope Pius XII, Hlond wrote: "Hitlerism aims at the systematic and total destruction of the Catholic Church in the rich and fertile territories of Poland which have been incorporated into the Reich...".[68] The Vatican used its press and radio to tell the world in January 1940 of terrorization of the Polish people. On 16 and 17 November 1940, Vatican Radio said that religious life for Catholics in Poland continued to be brutally restricted and that at least 400 clergy had been deported to Germany in the preceding four months:[69]
The Catholic Associations in the General Government also have been dissolved, the Catholic educational institutions have been closed down, and Catholic professors and teachers have been reduced to a state of extreme need or have been sent to concentration camps. The Catholic press has been rendered impotent. In the part incorporated into the Reich, and especially in Posnania, the representatives of the Catholic priests and orders have been shut up in concentration camps. In other dioceses the priests have been put in prison. Entire areas of the country have been deprived of all spiritual ministrations and the church seminaries have been dispersed.
— Vatican Radio, November 1940

Nazi policy towards the Church was at its most severe in the territories it annexed to Greater Germany, where they set about systematically dismantling the Church - arresting its leaders, exiling its clergymen, closing its churches, monasteries and convents. Many clergymen were murdered.[11][70] In these areas the Polish Church was to be thoroughly eradicated, though German Catholics could remain or settle there.[66] In Pomerania the Nazi Gauleiter Albert Forster permitted German priests, and believed that Poles themselves could be Germanized, but under the exceptionally aggressive policies of Arthur Greiser, the Nazi Gauleiter of the Warta region, German Catholics and the Protestant Church suffered in his campaign to eradicate the Polish Church, prompting the head of the German Bishops Conference to ask the Pope for assistance.[71]
From 1940, the Nazis established dedicated Clergy Barracks at Dachau Concentration Camp.[72][73] Of a total of 2,720 clergy recorded as imprisoned at Dachau, some 2,579 (or 94.88%) were Catholic.[73] By far the greatest number of clerical prisoners came from Poland - in all some 1,748 Polish Catholic clerics, of whom some 868 died in the camp.[73] The Nazis introduced a racial hierarchy - keeping Poles in harsh conditions, while favouring German priests.[74] 697 Poles arrived in December 1941, and a further 500 of mainly elderly clergy were brought in October the following year. Inadequately clothed for the bitter cold, of this group only 82 survived. A large number of Polish priests were chosen for Nazi medical experiments. In November 1942, 20 were given phlegmons. 120 were used by Dr Schilling for malaria experiments between July 1942 and May 1944. Several Poles met their deaths with the "invalid trains" sent out from the camp, others were liquidated in the camp and given bogus death certificates. Some died of cruel punishment for misdemeanors - beaten to death or run to exhaustion.[75]
The presecutions of Polish clergy was particularly severe in the annexed territories. Already in 1939, 80% of the Catholic clergy of the Warthegau region had been deported to concentration camps.[76] In West Prussia, 460 were arrested of 690 Polish priests were arrested; the survivors simply fled; only 20 were still serving in 1940. Of the arrested, 214 were executed; the rest were deported to General Government.[76] Fatalities were numerous: everywhere in Wrocław, 49.2% of the clergy were dead; in Chełmno, 47.8%; in Łódź, 36.8%; in Poznań, 31.1%.[76] In the Warsaw diocese, 212 clergy were murdered; in Wilno, 92; in Lwów, 81; in Kraków, 30; in Kielce, 13.[76] Nuns shared a similar fate; about 400 nuns were imprisoned at Bojanowo concentration camp.[76] Many seminary students and nuns were conscripted as forced laborers.[76] In Poznań, all but two churches were closed or repurposed; in Łódź, only four remained open.[76]
Poland's higher clergy was not exempt from repression; some were forced to retire, whereas others were outrigjt arrested, imprisoned and even executed. Among those, Bishops Marian Leon Fulman, Władysław Goral, Michał Kozal, Antoni Julian Nowowiejski and Leon Wetmański were sent to concentration camps, with Goral, Nowowiejski, Kozal and Wetmański perishing in Sachsenhausen, Dachau, Soldau and Auschwitz, respectively.[76][77][78]
The smaller Evangelical churches of Poland also suffered. Entirety of the Protestant clergy of the Cieszyn region of Silesia were arrested and deported to concentration camps at Mauthausen, Buchenwald, Dachau and Oranienburg.[76] Protestant clergy leaders who perished in those purges included charity activist Karol Kulisz, theology professor Edmund Bursche, and Bishop of the Evangelical Church of the Augsburg Confession in Poland, Juliusz Bursche.[76]
The Polish Home Army was conscious of the link between morale and religious practice and the Catholic religion was integral to much Polish resistance, particularly during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944.[79] Despite persecution, Catholic priests preached national spirit and encouraged resistance across Poland, and the Resistance was full of clergy.[80]
Germanization


In the territories annexed to Nazi Germany, in particular with regards to the in westernmost incorporated territories—the so-called Wartheland— the Nazis' aimed for a complete "Germanization", i.e. full cultural, political, economic and social assimilation.[11] Polish language was prohibited to be taught even in elementary schools; landmarks from streets to cities were renamed en masse (Łódź became Litzmannstadt, and so on).[11] All manner of Polish enterprises, up to small shops, were taken over, with prior owners rarely compensated.[11] Signs posted in public places prohibited non-Germans from entering these places warning: "Entrance is forbidden to Poles, Jews, and dogs.", or Nur für Deutsche ("Only for Germans"), commonly found on many public utilities and places such as trams, parks, cafes, cinemas, theaters, and others.[11][81][82]


The Nazis kept an eye out for Polish children who possessed Nordic racial characteristics.[83] An estimated total of 50,000 children, majority taken from orphanages and foster homes in the annexed lands, but some separated from their parents, were taken into a special Germanization program.[11][43] Polish women deported to Germany as forced laborers and who bore children were a common victim of this policy, with their infants regularly taken.[11][84] If the child passed the battery of racial, physical and psychological tests, they were sent on to Germany for "Germanization".[85] At least 4,454 children were given new German names,[86] forbidden to use Polish language,[87] and reeducated Nazi institutions.[11] Few were ever reunited with their original families.[11] Those deemed as unsuitable for Germanization for being "not Aryan enough" were sent to orphanages or even to concentration camps like Auschwitz, where many perished, often killed by intercardiac injections of phenol.[11] For Polish forced laborers, in some cases if an examination of the parents suggested that the child might not be "racially valuable", the mother was compelled to have an abortion.[11][84] Infants who did not pass muster would be removed to a state orphanage (Ausländerkinder-Pflegestätte), where many died from the lack of food.[88]
Resistance




Despite the military defeat of the Polish Army in September 1939, the Polish government itself never surrendered, instead evacuating West, where it formed the Polish government in Exile.[11] The government in exile was represented in the occupied Poland by the Government Delegation for Poland, headed by the Government Delegate for Poland.[89] The main role of the civilian branch of the Underground State was to preserve the continuity of the Polish state as a whole, including its institutions. These institutions included the police, the courts, and schools.[90] By the final years of the war, the civilian structure of the Underground State included an underground parliament, administration, judiciary (courts and police), secondary and higher level education, and supported various cultural activities such as publishing of newspapers and books, underground theatres, lectures, exhibitions, concerts and safeguarded various works of art.[89][91] It also dealt with providing social services, including to the destitute Jewish population (through the Council to Aid Jews, or Żegota).[89] Through the Directorate of Civil Resistance (1941–1943) the civil arm was also involved in lesser acts of resistance, such as minor sabotage, although in 1943 this department was merged with the Directorate of Covert Resistance, forming the Directorate of Underground Resistance, subordinate to Polish Home Army (Armia Krajowa).[91]
In response to the occupation, Poles formed one of the largest underground movement in Europe.[11][92] Resistance to the Nazi German occupation began almost at once. The Home Army (in Polish Armia Krajowa or AK), loyal to the Polish government in exile in London and a military arm of the Polish Underground State, was formed from a number of smaller groups in 1942.[93] There was also the People's Army (Polish Armia Ludowa or AL), backed by the Soviet Union and controlled by the Polish Workers' Party (Polish Polska Partia Robotnicza or PPR), through signicantly less numerous than the Home Army.[11][94] In February 1942, when AK was formed, it numbered about 100,000 members.[95] In the beginning of 1943, it had reached a strength of about 200,000.[95] In the summer of 1944 when Operation Tempest begun AK reached its highest membership numbers.[95] Estimates of AK membership in the first half of 1944 and summer that year vary, through about 400,000 estimate is common.[95] When the imminent arrival of the Soviet army, the AK launched an uprising in Warsaw against the German army on 1 August 1944. The uprising, receiving little assistance from the nearby Soviet forces, eventually failed, significantly reducing the Home Army's power and position.[11] About 200,000 Poles, most of them civilians, lost their lives in the Uprising.[96]
The Polish Home Army was conscious of the link between morale and religious practice and the Catholic religion was integral to much Polish resistance, particularly during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944.[79] Adam Sapieha, Archbishop of Lvov, became the defacto head of the Polish church following the invasion. He openly criticised Nazi terror tactics.[97] One of the principal figures of the Polish Resistance, Sapieha opened a clandestine seminary in an act of cultural resistance. Among the seminarians was Karol Wojtyla, the future Pope John Paul II.[98] Wojtyla had been a member of the Rhapsodic Theatre, an underground resistance group which sought to sustain Polish culture through forbidden readings of poetry and drama performances.[99]
Impact on the Polish population
The Polish civilian population suffered under German occupation in several ways. Large numbers were expelled from land intended for German colonisation, and forced to resettle in the General-Government area. Hundreds of thousands of Poles were deported to Germany for forced labour in industry and agriculture, where many thousands died. Poles were also conscripted for labour in Poland, and were held in labour camps all over the country, again with a high death rate. There was a general shortage of food, fuel for heating and medical supplies, and there was a high death rate among the Polish population as a result. Finally, thousands of Poles were killed as reprisals for resistance attacks on German forces or for other reasons. In all, about 3 million (non-Jewish) Poles died as a result of the German occupation, more than 10% of the pre-war population. When this is added to the 3 million Polish Jews who were killed as a matter of policy by the Germans, Poland lost about 22% of its population, the highest proportion of any European country in World War II.[100][101]
Poland had a large Jewish population, and according to Davies, more Jews were both killed and rescued in Poland, than in any other nation: the rescue figure usually being put at between 100-150,000.[102] Thousands of Poles have been honoured as Righteous Among the Nations - constituting the largest national contingent.[103] When AK Home Army Intelligence discovered the true fate of transports leaving the Jewish Ghetto, the Council to Aid Jews (Zegota) was established in late 1942, in cooperation with church groups. The organisation saved thousands. Emphasis was placed on protecting children, as it was nearly impossible to intervene directly against the heavily guarded transports. The Germans implemented several different laws to separate Poles and Jews in the ghettos with Poles living on the "Aryan Side" and the Jews living on the "Jewish Side", despite the risk of death many Poles risked their lives by forging "Aryan Papers" for Jews to make them appear as non-Jewish Poles so they could live on the Aryan side and avoid Nazi persecution.[104] Another law implemented by the Germans was that Poles were forbid from from buying from Jewish shops in which if they did they were subject to execution.[105] Jewish children were also distributed among safe houses and church networks.[106] Jewish children were often placed in church orphanages and convents.[107]
Some three million non-Jewish Polish citizens perished during the course of the war, over two million of whom were ethnic Poles (the remainder being mostly Ukrainians and Belarusians). The vast majority of those killed were civilians, mostly killed by the actions of Nazi Germany.[108][109]
Rather than being sent to concentration camps, most non-Jewish Poles died through in mass executions, starvation, singled out murder cases, ill health and forced labour. Apart from Auschwitz, the main six "extermination camps" in Poland were used almost exclusively to kill Jews.[citation needed] Stutthof concentration camp was used for mass extermination of Poles. A number of civilian labour camps (Gemeinschaftslager) for Poles (Polenlager) were established inside Polish territory. Many Poles died in German camps. The first non-German prisoners at Auschwitz were Poles, who were the majority of inmates there until 1942, when the systematic killing of the Jews began. The first killing by poison gas at Auschwitz involved 300 Poles and 700 Soviet prisoners of war, among them ethnic Ukrainians, Russians and others. Many Poles and other Eastern Europeans were also sent to concentration camps in Germany: over 35,000 to Dachau, 33,000 to the camp for women at Ravensbrück, 30,000 to Mauthausen and 20,000 to Sachsenhausen, for example.
The population in the General Government's territory was initially about 12 million in an area of 94,000 square kilometres, but this increased as about 860,000 Poles and Jews were expelled from the German-annexed areas and "resettled" in the General Government. Offsetting this was the German campaign of extermination of the Polish intelligentsia and other elements thought likely to resist (e.g. Operation Tannenberg). From 1941, disease and hunger also began to reduce the population. Poles were deported in large numbers to work as forced labour in Germany: eventually about a million were deported, and many died in Germany.
Treatment of Polish citizens under Soviet occupation



By the end of Polish Defensive War the Soviet Union took over 52.1% of territory of Poland (~200,000 km²), with over 13,700,000 people. The estimates vary; Elżbieta Trela-Mazur gives the following numbers in regards to ethnic composition of these areas: 38% Poles (ca. 5,1 million people), 37% Ukrainians, 14,5% Belarusians, 8,4% Jews, 0,9% Russians and 0,6% Germans. There were also 336,000 refugees from areas occupied by Germany, most of them Jews (198,000).[7] Areas occupied by USSR were annexed to Soviet territory, with the exception of area of Wilno, which was transferred to Lithuania, although soon attached to USSR, when Lithuania became a Soviet republic.
Initially the Soviet occupation gained support among some members the non-Polish population who had chafed under the nationalist policies of the Second Polish Republic. Much of the Ukrainian population initially welcomed the unification with the rest of Ukraine which Ukrainians had failed to achieve in 1919 when their attempt for self-determination was crushed by Poland and Soviet Union.[111]
There were large groups of pre-war Polish citizens, notably Jewish youth and, to a lesser extent, the Ukrainian peasants, who saw the Soviet power as an opportunity to start political or social activity outside of their traditional ethnic or cultural groups. Their enthusiasm however faded with time as it became clear that the Soviet repressions were aimed at all groups equally, regardless of their political stance.[112]
British historian Simon Sebag Montefiore states that Soviet terror in the occupied eastern Polish lands was as cruel and tragic as Nazi in the west. Soviet authorities brutally treated those who might oppose their rule, deporting by 10 November 1940, around 10% of total population of Kresy, with 30% of those deported dead by 1941.[113] They arrested and imprisoned about 500,000 Poles during 1939–1941, including former officials, officers, and natural "enemies of the people", like the clergy, but also noblemen and intellectuals. The Soviets also executed about 65,000 Poles. Soldiers of the Red Army and their officers behaved like conquerors, looting and stealing Polish treasures. When Stalin was told about it, he answered: "If there is no ill will, they [the soldiers] can be pardoned".[114]
In one notorious massacre, the NKVD-the Soviet secret police—systematically executed 21,768 Poles, among them 14,471 former Polish officers, including political leaders, government officials, and intellectuals. Some 4,254 of these were uncovered in mass graves in Katyn Forest by the Nazis in 1943, who then invited an international group of neutral representatives and doctors to study the corpses and confirm Soviet guilt, but the findings from the study were denounced by the Allies as "Nazi propaganda".
The Soviet Union had ceased to recognise the Polish state at the start of the invasion.[115][116] As a result, the two governments never officially declared war on each other. The Soviets therefore did not classify Polish military prisoners as prisoners of war but as rebels against the new legal government of Western Ukraine and Western Byelorussia.[n] The Soviets killed tens of thousands of Polish prisoners of war. Some, like General Józef Olszyna-Wilczyński, who was captured, interrogated and shot on 22 September, were executed during the campaign itself.[117][118] On 24 September, the Soviets killed 42 staff and patients of a Polish military hospital in the village of Grabowiec, near Zamość.[119] The Soviets also executed all the Polish officers they captured after the Battle of Szack, on 28 September.[120] Over 20,000 Polish military personnel and civilians perished in the Katyn massacre.[121][122]
The Poles and the Soviets re-established diplomatic relations in 1941, following the Sikorski-Mayski Agreement; but the Soviets broke them off again in 1943 after the Polish government demanded an independent examination of the recently discovered Katyn burial pits.[123] The Soviets then lobbied the Western Allies to recognize the pro-Soviet Polish puppet government of Wanda Wasilewska in Moscow.[124]
On 28 September 1939, the Soviet Union and Germany had changed the secret terms of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact. They moved Lithuania into the Soviet sphere of influence and shifted the border in Poland to the east, giving Germany more territory.[125] By this arrangement, often described as a fourth partition of Poland,[122] the Soviet Union secured almost all Polish territory east of the line of the rivers Pisa, Narew, Western Bug and San. This amounted to about 200,000 square kilometres of land, inhabited by 13.5 million Polish citizens.[6]
The Red Army had originally sowed confusion among the locals by claiming that they were arriving to save Poland from the Nazis.[126] Their advance surprised Polish communities and their leaders, who had not been advised how to respond to a Bolshevik invasion. Polish and Jewish citizens may at first have preferred a Soviet regime to a German one,[127] but the Soviets soon proved as hostile and destructive towards the Polish people and their culture as the Nazis.[128][129] They began confiscating, nationalising and redistributing all private and state-owned Polish property.[130] During the two years following the annexation, they arrested approximately 100,000 Polish citizens[131] and deported between 350,000 and 1,500,000, of whom between 150,000 and 1,000,000 died, mostly civilians.[b][4][5][132]
Land reform and collectivisation
The Soviet base of support was Rstrengthened by a land reform program initiated by the Soviets in which most of the owners of large lots of land were labeled "kulaks" and dispossessed of their land which was then divided among poorer peasants.
However, the Soviet authorities then started a campaign of forced collectivisation, which largely nullified the earlier gains from the land reform as the peasants generally did not want to join the Kolkhoz farms, nor to give away their crops for free to fulfill the state-imposed quotas.
Restructuring of Polish governmental and social institutions
While Germans enforced their policies based on racism, the Soviet administration justified their Stalinist policies by appealing to the Soviet ideology,[133] which in reality meant the thorough Sovietization of the area. Immediately after their conquest of eastern Poland, the Soviet authorities started a campaign of Sovietization[134][135] of the newly acquired areas. No later than several weeks after the last Polish units surrendered, on 22 October 1939, the Soviets organized staged elections to the Moscow-controlled Supreme Soviets (legislative body) of Western Byelorussia and Western Ukraine.[17] The result of the staged voting was to become a legitimization of Soviet annexation of eastern Poland.[136]
Subsequently, all institutions of the dismantled Polish state were closed down and reopened under the Soviet appointed supervisors. Lwow University and many other schools were reopened soon but they were restarted anew as Soviet institutions rather than continuing their old legacy. Lwow University was reorganized in accordance with the Statute Books for Soviet Higher Schools. The tuition, that along with the institution's Polonophile traditions, kept the university inaccessible to most of the rural Ukrainophone population, was abolished and several new chairs were opened, particularly the chairs of Russian language and literature. The chairs of Marxism-Leninism, Dialectical and Historical Materialism aimed at strengthening of the Soviet ideology were opened as well.[7] Polish literature and language studies ware dissolved by Soviet authorities. Forty-five new faculty members were assigned to it and transferred from other institutions of Soviet Ukraine, mainly the Kharkiv and Kiev universities. On 15 January 1940 the Lvov University was reopened and started to teach in accordance with Soviet curricula.[137]
Simultaneously, Soviet authorities attempted to remove the traces of Polish history of the area by eliminating much of what had any connection to the Polish state or even Polish culture in general.[7] On 21 December 1939, the Polish currency was withdrawn from circulation without any exchange to the newly introduced rouble, which meant that the entire population of the area lost all of their life savings overnight.[138]
All the media became controlled by Moscow. Soviet authorities implemented a political regime similar to a police state,[139][140][141][142] based on terror. All Polish parties and organizations were disbanded. Only the Communist Party was allowed to exist along with organizations subordinated to it.
All organized religions were persecuted. All enterprises were taken over by the state, while agriculture was made collective.[143]
Rule of Terror
An inherent part of the Sovietization was a rule of terror started by the NKVD and other Soviet agencies. The first victims of the new order were approximately 250,000 Polish prisoners of war captured by the USSR during and after the Polish Defensive War (see Polish prisoners of war in Soviet Union (after 1939)).[144] As the Soviet Union did not sign any international convention on rules of war, they were denied the status of prisoners of war and instead almost all of the captured officers and a large number of ordinary soldiers[145] were then murdered (see Katyn massacre) or sent to Gulag.[146] Thousands of others would fall victim to NKVD massacres of prisoners in mid-1941, after Germany invaded the Soviet Union.
Similar policies were applied to the civilian population as well. The Soviet authorities regarded service for the pre-war Polish state as a "crime against revolution"[147] and "counter-revolutionary activity",[148] and subsequently started arresting large numbers of Polish intelligentsia, politicians, civil servants and scientists, but also ordinary people suspected of posing a threat to the Soviet rule. Among the arrested members of the Polish intelligentsia were former prime ministers Leon Kozłowski and Aleksander Prystor, as well as Stanisław Grabski, Stanisław Głąbiński and the Baczewski family. Initially aimed primarily at possible political opponents, by January 1940 the NKVD aimed its campaign also at its potential allies, including the Polish communists and socialists. Among the arrested were Władysław Broniewski, Aleksander Wat, Tadeusz Peiper, Leopold Lewin, Anatol Stern, Teodor Parnicki, Marian Czuchnowski and many others.[149]
Deportation

In 1940 and the first half of 1941, the Soviets deported more than 1,200,000 Poles, most in four mass deportations. The first deportation took place 10 February 1940, with more than 220,000 sent to northern European Russia; the second on 13 April 1940, sending 320,000 primarily to Kazakhstan; a third wave in June–July 1940 totaled more than 240,000; the fourth occurred in June 1941, deporting 300,000. Upon resumption of Polish-Soviet diplomatic relations in 1941, it was determined based on Soviet information that more than 760,000 of the deportees had died – a large part of those dead being children, who had comprised about a third of deportees.[150]
Approximately 100,000 former Polish citizens were arrested during the two years of Soviet occupation.[131] The prisons soon got severely overcrowded.[112] with detainees suspected of anti-Soviet activities and the NKVD had to open dozens of ad-hoc prison sites in almost all towns of the region.[136] The wave of arrests led to forced resettlement of large categories of people (kulaks, Polish civil servants, forest workers, university professors or osadniks, for instance) to the Gulag labour camps and exile settlements in remote areas of the Soviet Union.[135] Altogether roughly a million people were sent to the east in four major waves of deportations.[151] According to Norman Davies,[152] almost half of them were dead by the time the Sikorski-Mayski Agreement had been signed in 1941.[153]
According to the Soviet law, all residents of the annexed area, dubbed by the Soviets as citizens of former Poland,[154] automatically acquired Soviet citizenship. However, actual conferral of citizenship still required the individual's consent and the residents were strongly pressured for such consent.[155] The refugees who opted out were threatened with repatriation to Nazi controlled territories of Poland.[3][156][157]
Exploitation of ethnic tensions
In addition, the Soviets exploited past ethnic tension between Poles and other ethnic groups, inciting and encouraging violence against Poles calling the minorities to "rectify the wrongs they had suffered during twenty years of Polish rule".[158] Pre-war Poland was portrayed as a capitalist state based on exploitation of the working people and ethnic minorities. Soviet propaganda claimed that unfair treatment of non-Poles by the Second Polish Republic was a justification of its dismemberment. Soviet officials openly incited mobs to perform killings and robberies[159] The death toll of the initial Soviet-inspired terror campaign remains unknown.
Restoration of Polish sovereignty
Over 600,000 Soviet soldiers died fighting Nazi troops in Poland.[160][dead link] While formal Polish sovereignty was almost immediately restored when the forces of Nazi Germany were expelled in 1945, in reality the country remained under firm Soviet control as it remained occupied by the Soviet Army Northern Group of Forces until 1956. To this day the events of those and the following years are one of the stumbling blocks in Polish-Russian foreign relations. Polish requests for the return of property looted during the war or any demand for an apology for Soviet-era crimes are either ignored or prompt a brusque restatement of history as seen by the Kremlin, along the lines of "we freed you from Nazism: be grateful."[161]
Casualties

Over 6 million Polish citizens – nearly 21.4% of the pre-war population of the Second Polish Republic — died between 1939 and 1945.[162] Over 90% of the death toll involved non-military losses, as most civilians were targets of various deliberate actions by the Germans and Soviets.[162]
Both occupiers wanted not only to gain Polish territory, but also to destroy Polish culture and the Polish nation as a whole.[1]
Tadeusz Piotrowski, Professor of Sociology at the University of New Hampshire has provided a reassessment of Poland's losses in World War II. Polish war dead include 5,150,000 victims of Nazi crimes against ethnic Poles and the Holocaust, the treatment of Polish citizens by occupiers included 350,000 deaths during the Soviet occupation in 1940–41 and about 100,000 Poles killed in 1943–44 in the Ukraine. Of the 100,000 Poles killed in the Ukraine, 80,000 perished during the massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army. Losses by ethnic group were 3,100,000 Jews; 2,000,000 ethnic Poles; 500,000 Ukrainians and Belarusians.[108]
The official Polish government report prepared in 1947 listed 6,028,000 war deaths out of a population of 27,007,000 ethnic Poles and Jews; this report excluded ethnic Ukrainian and Belarusian losses. However some historians in Poland now believe that Polish war losses were at least 2 million ethnic Poles and 3 million Jews as a result of the war.[163]
Another assessment, Poles as Victims of the Nazi Era, prepared by USHMM, lists 1.8 to 1.9 million ethnic Polish dead in addition to 3 million Polish Jews.[11]
POW deaths totaled 250,000; in Germany (120,000) and in the USSR (130,000).[164]
The genocide of Romani people (porajmos) was 35,000 persons.[165] Jewish Holocaust victims totaled 3,000,000[166]
See also
- Polish resistance movement in World War II
- Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany (1939-1944)
- Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany
- Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union
- Polish minority in Germany
- Polish minority in the Soviet Union
- World War II crimes in Poland
References
- ^ a b "The prisons, ghettos, internment, transit, labor and extermination camps, roundups, mass deportations, public executions, mobile killing units, death marches, deprivation, hunger, disease, and exposure all testify to the 'inhuman policies of both Hitler and Stalin' and 'were clearly aimed at the total extermination of Polish citizens, both Jews and Christians. Both regimes endorsed a systematic program of genocide.'" Judith Olsak-Glass, Review of Piotrowski's Poland's Holocaust in Sarmatian Review, January 1999.
- ^ "Terminal horror suffered by so many millions of innocent Jewish, Slavic, and other European peoples as a result of this meeting of evil minds is an indelible stain on the history and integrity of Western civilization, with all of its humanitarian pretensions" (Note: "this meeting" refers to the most famous third (Zakopane) conference).
Conquest, Robert (1991). "Stalin: Breaker of Nations". New York, N.Y.: Viking. ISBN 0-670-84089-0 - ^ a b c Template:En icon Tadeusz Piotrowski (1997). Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide... McFarland & Company. p. 295. ISBN 0-7864-0371-3.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) See also review - ^ a b c AFP/Expatica, Polish experts lower nation's WWII death toll, expatica.com, 30 August 2009
- ^ a b c Polska 1939–1945. Straty osobowe i ofiary represji pod dwiema okupacjami, ed. Tomasz Szarota and Wojciech Materski, Warszawa, IPN 2009, ISBN 978-83-7629-067-6 (Introduction reproduced here)
- ^ a b Jan Tomasz Gross, Revolution from Abroad, pp. 4, 5, Princeton, 2005, ISBN 0-691-09603-1. [verification needed] Quote: "The eastern half of Poland could be divided into three zones north to south. A clear Ukrainian majority resided in the south, except in some areas where the number of Poles more or less equaled their Ukrainian neighbors; in the central part, in Polesie and Wołyń, a small Polish minority (14 and 16% respectively) faced a mostly Orthodox peasantry (Ukrainian to the south, then "local" and finally, on the northern fringe increasingly Belarusian); and in the northern part, in Białystok, Wilno and Nowogródek voivodships, Poles were in majority, confronted by a numerically strong Belarusian minority. Jews constituted the principal minority in urban areas" Cite error: The named reference "Gross" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b c d e Template:Pl icon"Among the population of Eastern territories were circa 38% Poles, 37% Ukrainians, 14.5% Belarusians, 8.4% Jewish, 0.9% Russians and 0.6% Germans"
Elżbieta Trela-Mazur (1997). Włodzimierz Bonusiak, Stanisław Jan Ciesielski, Zygmunt Mańkowski, Mikołaj Iwanow (ed.). Sowietyzacja oświaty w Małopolsce Wschodniej pod radziecką okupacją 1939–1941 (Sovietization of education in eastern Lesser Poland during the Soviet occupation 1939–1941). Kielce: Wyższa Szkoła Pedagogiczna im. Jana Kochanowskiego. p. 294. ISBN 978-83-7133-100-8.{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) Cite error: The named reference "Trela-Mazur" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Piotr Eberhardt, Political Migrations in Poland, 1939–1948. Warsaw 2006, p.24
- ^ Pierre Aycoberry, The Social History of the Third Reich, 1933–1945, p 228, ISBN 1-56584-549-8
- ^ William J. Duiker, Jackson J. Spielvogel, World History, 1997. Page 794: By 1942, two million ethnic Germans had been settled in Poland.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at "Poles: Victims of the Nazi Era". United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Retrieved 24 May 2013.
- ^ a b c R. F. Leslie (1980). The History of Poland Since 1863. Cambridge University Press. p. 216. ISBN 978-0-521-27501-9.
- ^ a b Roy A. Prete; A. Hamish Ion (1984). Armies of Occupation. Wilfrid Laurier Univ. Press. pp. 135–138. ISBN 978-0-88920-156-9.
- ^ Jerzy Jan Lerski (1996). Historical Dictionary of Poland, 966-1945. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 158. ISBN 978-0-313-26007-0.
- ^ Mikuláš Teich; Dušan Kováč; Martin D. Brown (3 February 2011). Slovakia in History. Cambridge University Press. p. 195. ISBN 978-1-139-49494-6.
- ^ George Sanford (7 May 2007). Katyn and the Soviet Massacre of 1940: Truth, Justice and Memory. Routledge. p. 47. ISBN 978-1-134-30299-4.
- ^ a b Template:Pl icon Bartłomiej Kozłowski (2005). ""Wybory" do Zgromadzeń Ludowych Zachodniej Ukrainy i Zachodniej Białorusi". Polska.pl. NASK. Retrieved 13 March 2006. Cite error: The named reference "Elections" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Elazar Barkan; Elizabeth A. Cole; Kai Struve (2007). Shared History, Divided Memory: Jews and Others in Soviet-occupied Poland, 1939-1941. Leipziger Universitätsverlag. p. 155. ISBN 978-3-86583-240-5.
- ^ Jon Huer (26 October 2012). Call From the Cave: Our Cruel Nature and Quest for Power. Hamilton Books. p. 166. ISBN 978-0-7618-6016-7.
- ^ Stefan Wolff (2003). The German Question Since 1919: An Analysis with Key Documents. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 47–48. ISBN 978-0-275-97269-1.
- ^ Donald L. Niewyk; Francis R. Nicosia (13 August 2013). The Columbia Guide to the Holocaust. Columbia University Press. p. 276. ISBN 978-0-231-52878-8.
- ^ Ostkrieg: Hitler's War of Extermination in the East Stephen Fritz - 2011 - Since the ultimate destination of those displaced remained unclear, “natural wastage” on a vast scale must have been assumed, so genocide was implicit in Generalplan Ost from the beginning
- ^ a b c d Michael Geyer (2009). Beyond Totalitarianism: Stalinism and Nazism Compared. Cambridge University Press. pp. 152–153. ISBN 978-0-521-89796-9.
- ^ THE ORIGINS OF GENOCIDE - SCHALLER: Raphael Lemkin as a Historian of Mass Violence Dominik J. Schaller, Jürgen Zimmerer Routledge, 2013 expulsion and murder of millions of Slavs as encapsulated in Generalplan Ost page 101
- ^ Doing Medicine Together: Germany and Russia Between the Wars Susan Gross Solomon Its activities were overshadowed by the genocidal Operation Barbarossa, and by the forced resettlement and extermination policies of General Plan Ost, page 52
- ^ The Holocaust in the Soviet Union: Studies and Sources on the Destruction of the Jews in the Nazi-occupied Territories of the USSR, 1941-1945 Lucjan Dobroszycki, Jeffrey S. Gurock M.E. Sharpe, One of the components of the genocide program was the Wannsee plan envisaging the annihilation of the ... General Plan Ost, which provided for the liquidation of the Slav peoples page 36
- ^ Joseph Poprzeczny (19 February 2004). Odilo Globocnik, Hitler's Man in the East. McFarland. pp. 186–187. ISBN 978-0-7864-8146-0.
- ^ Joseph Poprzeczny (19 February 2004). Odilo Globocnik, Hitler's Man in the East. McFarland. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-7864-8146-0.
- ^ a b Prit Buttar (21 May 2013). Between Giants: The Battle for the Baltics in World War II. Osprey Publishing. pp. 59–60. ISBN 978-1-4728-0288-0.
- ^ Geoff Eley (29 May 2013). Nazism as Fascism: Violence, Ideology, and the Ground of Consent in Germany 1930-1945. Routledge. p. 189. ISBN 1-135-04481-3.
- ^ Germany and Eastern Europe: Cultural Identities and Cultural Differences" by Keith Bullivant, Geoffrey J. Giles, Walter Pape, Rodopi 1999, page 32
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20120413024247/http://www.atsweb.neu.edu/holocaust/Hitlers_Plans.htm HITLER'S PLANS FOR EASTERN EUROPE Selections from Janusz Gumkowkski and Kazimierz Leszczynski POLAND UNDER NAZI OCCUPATION ;;The provisions of the Plan were that 80-85 per cent of the Poles would have to be deported from the German settlement area - to regions in the East. This, according to German calculations, would involve about 20 million people. About 3-4 million - all of them peasants - suitable for Germanization as far as "racial values" were concerned - would be allowed to remain. They would be distributed among German majorities and Germanized within a single generation(...) The ultimate purpose of Nazi policy was to destroy the Polish nation on the whole of Polish soil whether that annexed by the Reich or that of the Government General. Eloquent proof of this is provided by the directives on the treatment of Poles in the Government General -- Restpolen, as they were described in the third section of the memorandum.
- ^ Wojciech Roszkowski, Historia Polski 1914–1997, Warsaw 1998
- ^ Model Nazi: Arthur Greiser and the Occupation of Western Poland Autorzy Catherine Epstein page 216
- ^ Auschwitz and the Second World War in Poland: a lecture given at the Representations of Auschwitz international conference at the Jagiellonian University, July 1995 Norman Davies Universitas, Poland, once Judenrein or "free of Jews" , was to have been cleared of all Poles except for 3-4 million judged suitable
- ^ Polacy W Ruchu Oporu Narodów Europy Stanisław Okęcki - 1987 The plan provided for annihilating the Polish nation and germanization of the Polish territory. ... Early in 1940 Dr. Hans Ehrlich drew up the first version of ' Generalplan-Ost' (General Plan for the East), which was subsequently elaborated Only some 3-4 million peasants were to remain, but were to be relocated so as to be surrounded by a German majority
- ^ The Routledge History of the Holocaust pod redakcją Jonathan C. Friedman, page 132
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web p. 204 ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ Pierre Aycoberry, The Social History of the Third Reich, 1933–1945, p 228, ISBN 1-56584-549-8
- ^ "Chapter 13. Chapter XIII – GERMANIZATION AND SPOLIATION"
- ^ a b "Chapter XIII – GERMANIZATION AND SPOLIATION"
- ^ Richard C. Lukas, Did the Children Cry? Hitler's War against Jewish and Polish Children, 1939–1945. Hippocrene Books, New York, 2001.
- ^ a b c d Nazi Conspiracy & Aggression Volume I Chapter XIII Germanization & Spoliation
- ^ Powszechny Spis Ludnosci r. 1921
- ^ Diemut Majer, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, "Non-Germans" Under the Third Reich: The Nazi Judicial and Administrative System in Germany and Occupied Eastern Europe with Special Regard to Occupied Poland, 1939–1945 Von Diemut Majer, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, JHU Press, 2003, p.240, ISBN 0-8018-6493-3.
- ^ See: Helmut Heiber, "Denkschrift Himmler Uber die Behandlung der Fremdvolkischen im Osten", Vierteljahrshefte für Zeitgeschichte 1957, No. 2. (In) Michael Burleigh; Wolfgang Wippermann (1991). The racial state: Germany, 1933–1945. Cambridge University Press. pp. (337–). ISBN 978-0-521-39802-2. Retrieved 22 April 2011.
- ^ Jan Grabowski and Zbigniew R. Grabowski (2004). Germans in the Eyes of the Gestapo: The Ciechanów District, 1939–1945. Cambridge University Press: Contemporary European History, No 13. pp. 21–43.
- ^ a b c d http://www.ushmm.org/outreach/en/article.php?ModuleId=10007732
- ^ a b Benjamin B. Ferencz (2002). Less Than Slaves: Jewish Forced Labor and the Quest for Compensation. Indiana University Press. pp. 24–25. ISBN 0-253-21530-7.
- ^ a b c Ulrich Herbert, William Templer, Hitler's foreign workers: enforced foreign labor in Germany under the Third Reich, Cambridge University Press, 1997, ISBN 0-521-47000-5,Google Print, p.71-73
- ^ Ulrich Merten (15 August 2013). Forgotten Voices: The Expulsion of the Germans from Eastern Europe after World War II. Transaction Publishers. pp. 85–86. ISBN 978-1-4128-5258-6.
- ^ Tadeusz Piotrowski (1998). Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947. McFarland. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-7864-0371-4.
- ^ a b c Richard L. Rubenstein; John K. Roth (2003). Approaches to Auschwitz: The Holocaust and Its Legacy. Westminster John Knox Press. pp. 195–196. ISBN 978-0-664-22353-3.
- ^ Thomas F. X. Noble; Barry Strauss; Duane Osheim (12 January 2007). Western Civilization: Beyond Boundaries, Volume II: Since 1560. Cengage Learning. p. 880. ISBN 1-111-80948-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Elaine Saphier Fox (31 August 2013). Out of Chaos: Hidden Children Remember the Holocaust. Northwestern University Press. p. 275. ISBN 978-0-8101-6661-5.
- ^ http://www.ushmm.org/outreach/en/article.php?ModuleId=10007720
- ^ a b {{Citation |last=Vogelsang |first=Peter |last2=Larsen |first2=Brian B.M. |title=The Ghettos of Poland |url=http://www.holocaust-education.dk/holocaust/ghettoer.asp |publisher=Holocaust and Genocide Studies Cite error: The named reference "Vogelsang" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ CFCA (2013). "Holocaust". The Coordination Forum for Countering Antisemitism. Retrieved 27 December 2013.
From diary of Reich Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels, dated 12 December 1941.
- ^ a b Yad Vashem (2013). "Aktion Reinhard" (PDF file, direct download 33.1 KB). Shoah Resource Center, The International School for Holocaust Studies. Retrieved 31 October 2013.
- ^ Piotr Eberhardt, http://rcin.org.pl/Content/15652/WA51_13607_r2011-nr12_Monografie.pdf, POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES STANISŁAW LESZCZYCKI INSTITUTE OF GEOGRAPHY AND SPATIAL ORGANIZATION MONOGRAPHIES, 12. Page 46
- ^ Michał Rapta, Wojciech Tupta, Grzegorz Moskal (2009). Mroczne sekrety willi "Tereska": 1939-1945. Historia Rabki. p. 104. ISBN 978-83-60817-33-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Jan S. Prybyla (2010). When Angels Wept: The Rebirth and Dismemberment of Poland and Her People in the Early Decades of the Twentieth Century. Wheatmark, Inc. pp. 133–136. ISBN 978-1-60494-325-2.
- ^ a b Dr Robert Rozett; Dr Shmuel Spector (26 November 2013). Encyclopedia of the Holocaust. Routledge. p. 101. ISBN 978-1-135-96950-9.
- ^ Ian Kershaw; Hitler a Biography; 2008 Edn; WW Norton & Company; London p.661
- ^ Jozef Garlinski; Poland and the Second World War; Macmillan Press, 1985; p 60
- ^ a b Jozef Garlinski; Poland and the Second World War; Macmillan Press, 1985; p 60
- ^ Norman Davies; Rising '44: the Battle for Warsaw; Vikiing; 2003; pp.85-6
- ^ a b The Nazi War Against the Catholic Church; National Catholic Welfare Conference; Washington D.C.; 1942; pp. 34-51
- ^ The Nazi War Against the Catholic Church; National Catholic Welfare Conference; Washington D.C.; 1942; pp. 49–50
- ^ Libionka, Dariusz (2004). "The Catholic Church in Poland and the Holocaust, 1939-1945" (PDF). The Holocaust And The Christian World: Reflections On The Past Challenges For The Future. New Leaf Press. pp. 74–78. ISBN 978-0-89221-591-1.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ Jozef Garlinski; Poland and the Second World War; Macmillan Press, 1985; p.63.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica: Dachau, by Michael Berenbaum.
- ^ a b c Paul Berben; Dachau: The Official History 1933-1945; Norfolk Press; London; 1975; ISBN 0-85211-009-X; pp. 276-277
- ^ Paul Berben; Dachau: The Official History 1933-1945; Norfolk Press; London; 1975; ISBN 0-85211-009-X; p.148.
- ^ Paul Berben; Dachau: The Official History 1933-1945; Norfolk Press; London; 1975; ISBN 0-85211-009-X; p.148-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j https://www.catholicculture.org/culture/library/view.cfm?recnum=472
- ^ Pierre Blet (1999). Pius XII and the Second World War: According to the Archives of the Vatican. Paulist Press. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-8091-0503-8.
- ^ Avraham Harman Institute of Contemporary Jewry The Hebrew University Eli Lederhendler Stephen S. Wise Professor of American Jewish History and Institutions, Jerusalem (2 February 2006). Jews, Catholics, and the Burden of History. Oxford University Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-19-534571-1.
- ^ a b Norman Davies; Rising '44: the Battle for Warsaw; Vikiing; 2003; p.402
- ^ Jozef Garlinski; Poland and the Second World War; Macmillan Press, 1985; p. 74
- ^ Polish Western Affairs. Instytut Zachodni. 1989. p. 48.
- ^ Alma Mater (in Polish). Alma Mater, Issue 64. November 2004. p. 46.
- ^ Lebensraum, Aryanization, Germanization and Judenrein, Judenfrei: concepts in the holocaust or shoah
- ^ a b HITLER'S PLANS FOR EASTERN EUROPE
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web p 250 ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web p. 249 ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ Melissa Eddy (8 May 2007). "Stolen: The Story of a Polish Child 'Germanized' by the Nazis". StarNewsOnline (Wilmington, NC). Associated Press. Retrieved 16 September 2008.
If they met racial guidelines, they were taken; one girl got back home.
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web p. 400-1 ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ a b c Grzegorz Ostasz, The Polish Government-in-Exile's Home Delegature. Article on the pages of the London Branch of the Polish Home Army Ex-Servicemen Association. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ Stanisław Salmonowicz (1994). Polskie Państwo Podziemne: z dziejów walki cywilnej, 1939–45. Wydawnictwa Szkolne i Pedagogiczne. ISBN 978-83-02-05500-3. Retrieved 2 January 2012., p. 37-46.
- ^ a b Józef Garliński (April 1975). "The Polish Underground State 1939–1945". Journal of Contemporary History. 10 (2). Sage Publications, Ltd.: 219–259. doi:10.1177/002200947501000202. JSTOR 260146., p. 220-223
- ^ Zamoyski, Adam.The Polish Way. New York: Hippocrene Books, 1987
- ^ Marek Ney-Krwawicz, The Polish Underground State and The Home Army (1939–45). Translated from Polish by Antoni Bohdanowicz. Article on the pages of the London Branch of the Polish Home Army Ex-Servicemen Association. Retrieved 14 March 2008.
- ^ Template:Pl icon Armia Ludowa. Encyklopedia PWN. Retrieved 21 December 2006.
- ^ a b c d Template:Pl icon Armia Krajowa. Encyklopedia WIEM. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- ^ Borowiec, Andrew (2001). Destroy Warsaw! Hitler's punishment, Stalin's revenge. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger. ISBN 0-275-97005-1. p. 179.
- ^ http://www.yadvashem.org/download/about_holocaust/christian_world/libionka.pdf
- ^ http://www.independent.com.mt/articles/2005-04-03/leader/john-pauls-heritage-without-frontiers-73821/
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica Online: Blessed John Paul II; web Apr 2013
- ^ Adam Jones (27 September 2006). Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction. Routledge. p. 175. ISBN 978-1-134-25980-9.
- ^ Tadeusz Piotrowski (1998). Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947. McFarland. pp. 305–. ISBN 978-0-7864-0371-4.
- ^ Norman Davies; Rising '44: the Battle for Warsaw; Viking; 2003; p.200
- ^ Norman Davies; Rising '44: the Battle for Warsaw; Vikiing; 2003; p594
- ^ Donald L. Niewyk, Francis R. Nicosia (2000). The Columbia Guide to the Holocaust. Columbia University Press. p. 114–. ISBN 978-0-231-11200-0.
- ^ Iwo Pogonowski, Jews in Poland, Hippocrene, 1998. ISBN 0-7818-0604-6. Page 99.
- ^ Norman Davies; Rising '44: the Battle for Warsaw; Vikiing; 2003; p.200
- ^ http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/Holocaust/Zegota.html
- ^ a b Piotrowski, Tadeusz (2005). "Project InPosterum: Poland World War II Casualties". Retrieved 15 March 2007.
- ^ Łuczak, Czesław (1994). "Szanse i trudności bilansu demograficcznego Polski w latach 1939–1945". Dzieje Najnowsze (1994/2).
- ^ Template:Pl icon Marek Wierzbicki, Stosunki polsko-białoruskie pod okupacją sowiecką (1939–1941). „Białoruskie Zeszyty Historyczne" (НА СТАРОНКАХ КАМУНІКАТУ, Biełaruski histaryczny zbornik) 20 (2003), p. 186–188. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ Piotrowski, Tadeusz (1988). "Ukrainian Collaborators". Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918–1947. McFarland. pp. 177–259. ISBN 0-7864-0371-3.
How are we ... to explain the phenomenon of Ukrainians rejoicing and collaborating with the Soviets? Who were these Ukrainians? That they were Ukrainians is certain, but were they communists, Nationalists, unattached peasants? The Answer is "yes" – they were all three
- ^ a b Template:En icon Militargeschichtliches Forschungsamt (corporate author); Gottfried Schramm (1997). Bernd Wegner (ed.). From Peace to War: Germany, Soviet Russia and the World, 1939–1941. Berghahn Books. pp. 47–79. ISBN 1-57181-882-0.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help); Invalid|display-authors=3(help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help) - ^ [Simon Sebag Montefiore. Stalin. The Court of the Red Tsar, page 313. Vintage Books, New York 2003. Vintage ISBN 1-4000-7678-1]
- ^ [Simon Sebag Montefiore. Stalin. The Court of the Red Tsar, page 312. Vintage Books, New York 2003. Vintage ISBN 1-4000-7678-1]
- ^ Telegrams sent by Schulenburg, German ambassador to the Soviet Union, from Moscow to the German Foreign Office: No. 317 of 10 September 1939, No. 371 of 16 September 1939, No. 372 of 17 September 1939. The Avalon Project, Yale Law School. Retrieved 14 November 2006.
- ^ Template:Pl icon 1939 wrzesień 17, Moskwa Nota rządu sowieckiego nie przyjęta przez ambasadora Wacława Grzybowskiego (Note of the Soviet government to the Polish government on 17 September 1939, refused by Polish ambassador Wacław Grzybowski). Retrieved 15 November 2006.
- ^ Sanford, p. 23; Template:Pl icon Olszyna-Wilczyński Józef Konstanty, Encyklopedia PWN. Retrieved 14 November 2006.
- ^ Template:Pl icon Template:Wayback Polish Institute of National Remembrance. Internet Archive, 16.10.03. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ Template:Pl icon Rozstrzelany Szpital (Executed Hospital). Tygodnik Zamojski, 15 September 2004. Retrieved 28 November 2006.
- ^ Template:Pl icon Szack. Encyklopedia Interia. Retrieved 28 November 2006.
- ^ Fischer, Benjamin B., ""The Katyn Controversy: Stalin's Killing Field", Studies in Intelligence, Winter 1999–2000. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ a b Sanford, p. 20–24.
- ^ Soviet note unilaterally severing Soviet-Polish diplomatic relations, 25 April 1943. English translation of Polish document. Retrieved 19 December 2005; Sanford, p. 129.
- ^ Sanford, p. 127; Martin Dean Collaboration in the Holocaust. Retrieved 15 July 2007.
- ^ Template:Pl icon Template:Wayback (September Campaign 1939) from PWN Encyklopedia. Internet Archive, mid-2006. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ Davies, Europe: A History, pp. 1001–1003.
- ^ Gross, pp. 24, 32–33.
- ^ Stachura, p.132.
- ^ Piotrowski, pp. 1, 11–13, 32.
- ^ Piotrowski, p.11
- ^ a b Template:Pl icon Represje 1939–41 Aresztowani na Kresach Wschodnich (Repressions 1939–41. Arrested on the Eastern Borderlands.) Ośrodek Karta. Retrieved 15 November 2006. Cite error: The named reference "Karta" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Rieber, pp. 14, 32–37.
- ^ Template:Pl icon Wojciech Roszkowski (1998). Historia Polski 1914–1997. Warsaw: Wydawnictwa Naukowe PWN. p. 476. ISBN 83-01-12693-0.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Template:Pl icon various authors (1998). Adam Sudoł (ed.). Sowietyzacja Kresów Wschodnich II Rzeczypospolitej po 17 września 1939. Bydgoszcz: Wyższa Szkoła Pedagogiczna. p. 441. ISBN 83-7096-281-5.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ a b Template:En icon various authors (2001). "Stalinist Forced Relocation Policies". In Myron Weiner, Sharon Stanton Russell (ed.). Demography and National Security. Berghahn Books. pp. 308–315. ISBN 1-57181-339-X.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Template:En icon Jan Tomasz Gross (2003). Revolution from Abroad. Princeton: Princeton University Press. p. 396. ISBN 0-691-09603-1. [1]
- ^ "Ivan Franko National University of L'viv". Archived from the original on 10 February 2006. Retrieved 14 March 2006.
- ^ Template:Pl iconKarolina Lanckorońska (2001). "I – Lwów". Wspomnienia wojenne; 22 IX 1939 – 5 IV 1945. Kraków: ZNAK. p. 364. ISBN 83-240-0077-1.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Template:En icon Craig Thompson-Dutton (1950). "The Police State & The Police and the Judiciary". The Police State: What You Want to Know about the Soviet Union. Dutton. pp. 88–95.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Template:En icon Michael Parrish (1996). The Lesser Terror: Soviet State Security, 1939–1953. Praeger Publishers. pp. 99–101. ISBN 0-275-95113-8.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Template:En icon Peter Rutland (1992). "Introduction". The Politics of Economic Stagnation in the Soviet Union. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 9. ISBN 0-521-39241-1.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Template:En icon Victor A. Kravchenko (1988). I Chose Justice. Transaction Publishers. p. 310. ISBN 0-88738-756-X.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Template:Pl icon Encyklopedia PWN, "OKUPACJA SOWIECKA W POLSCE 1939–41", last accessed on 1 March 2006, online, Polish language
- ^ Encyklopedia PWN 'KAMPANIA WRZEŚNIOWA 1939', last retrieved on 10 December 2005, Polish language
- ^ Out of the original group of Polish prisoners of war sent in large number to the labour camps were some 25,000 ordinary soldiers separated from the rest of their colleagues and imprisoned in a work camp in Równe[[{{subst:DATE}}|{{subst:DATE}}]] [disambiguation needed], where they were forced to build a road. See: Template:En icon "Decision to commence investigation into Katyn Massacre". Institute of National Remembrance website. Institute of National Remembrance. 2004. Archived from the original on 19 July 2006. Retrieved 15 March 2006.
- ^ Template:En icon Marek Jan Chodakiewicz (2004). Between Nazis and Soviets: Occupation Politics in Poland, 1939–1947. Lexington Books. ISBN 0-7391-0484-5.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Template:En icon Gustaw Herling-Grudziński (1996). A World Apart: Imprisonment in a Soviet Labor Camp During World War II. Penguin Books. p. 284. ISBN 0-14-025184-7.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Template:Pl icon Władysław Anders (1995). Bez ostatniego rozdziału. Lublin: Test. p. 540. ISBN 83-7038-168-5.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Template:Pl icon Jerzy Gizella (10 November 2001). "Lwowskie okupacje". Przegląd polski.
- ^ Assembly of Captive European Nations, First Session
- ^ The actual number of deported in the period of 1939–1941 remains unknown and various estimates vary from 350,000 (Template:Pl icon Encyklopedia PWN 'OKUPACJA SOWIECKA W POLSCE 1939–41', last retrieved on 14 March 2006, Polish language) to over 2 millions (mostly World War II estimates by the underground). The earlier number is based on records made by the NKVD and does not include roughly 180,000 prisoners of war, also in Soviet captivity. Most modern historians estimate the number of all people deported from areas taken by Soviet Union during this period at between 800,000 and 1,500,000; for example R. J. Rummel gives the number of 1,200,000 million; Tony Kushner and Katharine Knox give 1,500,000 in their Refugees in an Age of Genocide, p.219; in his Lethal Politics: Soviet Genocide and Mass Murder Since 1917, p.132. See also: Marek Wierzbicki, Tadeusz M. Płużański (March 2001). "Wybiórcze traktowanie źródeł". Tygodnik Solidarność (2 March 2001). and Template:Pl icon Albin Głowacki (September 2003). "Formy, skala i konsekwencje sowieckich represji wobec Polaków w latach 1939–1941". In Piotr Chmielowiec (ed.). Okupacja sowiecka ziem polskich 1939–1941. Rzeszów-Warsaw: Instytut Pamięci Narodowej. ISBN 83-89078-78-3. Archived from the original on 3 October 2003.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Template:En icon Norman Davies (1982). God's Playground. A History of Poland, Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 449–455. ISBN 0-19-925340-4.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Bernd Wegner, From Peace to War: Germany, Soviet Russia, and the World, 1939–1941, Bernd Wegner, 1997, ISBN 1-57181-882-0. Google Print, p.78
- ^ Template:Pl icon Stanisław Ciesielski; Wojciech Materski; Andrzej Paczkowski (2002). "Represje 1939–1941". Indeks represjonowanych (2nd ed.). Warsaw: Ośrodek KARTA. ISBN 83-88288-31-8. Retrieved March 2006.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Jan Tomasz Gross (2003). Revolution from Abroad. Princeton: Princeton University Press. p. 396. ISBN 0-691-09603-1. [2]
- ^ Jan T. Gross, op.cit., p.188
- ^ Template:En icon Zvi Gitelman (2001). A Century of Ambivalence: The Jews of Russia and the Soviet Union, 1881 to the Present. Indiana University Press. p. 116. ISBN 0-253-21418-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Jan Tomasz Gross, Revolution from Abroad: The Soviet Conquest of Poland's Western Ukraine and Western Belorussia, Princeton University Press, 2002, ISBN 0-691-09603-1, p. 35
- ^ Gross, op.cit., page 36
- ^ WW II: The Chronicle of Stone
- ^ "Pretty pictures: Russia's president makes some surprising new friends". The Economist. 2 March 2006. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- ^ a b Jessica Jager, Review of Piotrowski's Poland's Holocaust, UC Santa Barbara
- ^ This revision of estimated war losses was the topic of articles in the Polish academic journal Dzieje Najnowsze # 2-1994 by Czesław Łuczak and Krystyna Kersten.
- ^ Vadim Erlikman. Poteri narodonaseleniia v XX veke : spravochnik. Moscow 2004. ISBN 5-93165-107-1
- ^ Donald Kendrick, The Destiny of Europe's Gypsies. Basic Books 1972 ISBN 0-465-01611-1
- ^ Martin Gilbert. Atlas of the Holocaust 1988 ISBN 0-688-12364-3
External links
- Articles with links needing disambiguation from May 2013
- Use dmy dates from May 2012
- History of Poland (1939–45)
- Jewish Polish history
- Military history of Poland
- Germany–Poland relations
- Poland–Soviet Union relations
- World War II occupied territories
- The Holocaust in Poland
- German military occupations
- Soviet military occupations
- Soviet occupation of Eastern Poland 1939–41
- 1939 in international relations




