Boxing
| File:MiguelCottoLeftPunchMargarito.jpg A rendered boxing bout featuring Antonio Margarito (left) versus Miguel Cotto. | |
| Also known as | Pugilism, English boxing, Western Boxing |
|---|---|
| Focus | Striking |
| Country of origin | Greece (Ancient Boxing) United Kingdom (Modern Boxing) |
| Creator | Unknown |
| Parenthood | Unknown |
| Olympic sport | Since 688 B.C. |
Boxing is a martial art where two participants, generally of similar weight, fight each other with their fists. Boxing is supervised by a referee and is typically engaged in during a series of one to three-minute intervals called rounds. There are three ways to win. Victory is achieved if the opponent is knocked out and unable to get up before the referee counts to ten seconds (a Knockout, or KO) or if the opponent is deemed too injured to continue (a Technical Knockout, or TKO). If there is no stoppage of the fight before an agreed number of rounds, a winner is determined either by the referee's decision or by judges' scorecards.
Although fighting with fists comes naturally to people, evidence of fist-fighting contests first appear on ancient Sumerian, Egyptian and Minoan reliefs. The ancient Greeks provide us our first historical records of boxing as a formal sport; they codified a set of rules and staged tournaments with professionals. The birth hour of boxing as a sport may be its acceptance as an Olympic game as early as 688 BC. Modern boxing evolved in Europe.
In some countries with their own fighting sports, the sport is referred to as "English Boxing" (e.g. in France to contrast with French boxing, or in Burma with Burmese boxing and in Thailand with Thai boxing). There are numerous different styles of boxing practiced around the world. Boxing does not allow kicks like the styles above.
Early history

Fist fighting depicted in Sumerian relief carvings from the 3rd millennium BC, while an ancient Egyptian relief from the 2nd millennium BC depicts both fist-fighters and spectators.[1] Both depictions show bare-fisted contests.[1] In 1927 Dr. E. A. Speiser, an archaeologist, discovered a Mesopotamian stone tablet in Baghdad, Iraq depicting two men getting ready for a prize fight. The tablet is believed to be 7,000 years old.[2] The earliest evidence for fist fighting with any kind of gloves can be found on Minoan Crete (c. 1500–900 BC), and on Sardinia, if we consider the boxing statues of Prama mountains (c. 2000–1000 BC).[1]
Ancient Greek boxing



Homer's Iliad (ca. 675 BC) contains the first detailed account of a boxing fight (Book XXIII).[3] According to the Iliad, Mycenaean warriors included boxing among their competitions honoring the fallen (ca. 1200 BC), though it is possible that the Homeric epics reflect later culture. Another legend holds that the heroic ruler Theseus, said to have lived around the 9th century BC, invented a form of boxing in which two men sat face to face and beat each other with their fists until one of them was killed. In time, the boxers began to fight while standing and wearing gloves (with spikes) and wrappings on their arms below the elbows, although otherwise they were competed naked.
Boxing was first accepted as an Olympic sport in 688 BC, being called Pygme or Pygmachia. Participants trained on punching bags (called a korykos). Fighters wore leather straps (called himantes) over their hands, wrists, and sometimes breast, to protect them from injury. The straps left their fingers free. Legend had it that the Spartans were the first to box as a way to prepare for sword and shield fighting.
Ancient Roman boxing
In ancient Rome, there were two forms of boxing both coming from Etruscan boxing. The athletic form of boxing remained popular throughout the Roman world. The other form of boxing was gladiatorial. Fighters were usually criminals and slaves who hoped to become champions and gain their freedom; however, free men, women, and even aristocrats also fought. Gladiators wore lead "cestae" over their knuckles and heavy leather straps on their forearms to protect against blows. The deeply scarred and cauliflower eared figure of the Boxer of Quirinal show what a brutal sport it could be (matches often ending in the death or maiming of an opponent).
Eventually, fist fighting became so popular that even emperors started fighting, and the practice was promoted by Caesar Neronis. A fight between the agile Dares and the towering Entellus is described at length in the Roman national epic Aeneid (1st century BC).[4]
In 393 A.D., the Olympics were banned by the Christian emperor Theodosius, and in 400 A.D., boxing was banned altogether by Theodoric the Great as boxing being an insult to God because it disfigures the face, the image of God. However, this edict had little effect outside the major cities of the Eastern Empire.[5] By this time, western Europe was no longer part of the Roman Empire. Boxing remained popular in Europe throughout the Middle Ages and beyond. Wrestling, fencing and racing (both chariot and foot) were never banned by the late Romans, as they did not cause disfigurement.
Modern boxing
Broughton's rules (1743)

Records of Classical boxing activity disappeared after the fall of the Roman Empire. However, there are detailed records of various fist-fighting sports that were maintained in different cities and provinces of Italy between the 12th and 17th centuries. There was also a sport in ancient Rus called Fistfight. The sport would later resurface in England during the early 18th century in the form of bare-knuckle boxing sometimes referred to as prizefighting. The first documented account of a bare-knuckle fight in England appeared in 1681 in the London Protestant Mercury, and the first English bare-knuckle champion was James Figg in 1719.[6] This is also the time when the word "boxing" first came to be used.
Early fighting had no written rules. There were no weight divisions or round limits, and no referee. In general, it was very chaotic. The first boxing rules, called the Broughton's rules, were introduced by heavyweight champion Jack Broughton in 1743 to protect fighters in the ring where deaths sometimes occurred.[7] Under these rules, if a man went down and could not continue after a count of 30 seconds, the fight was over. Hitting a downed fighter and grasping below the waist were prohibited. Broughton also invented and encouraged the use of "mufflers", a form of padded gloves, which were used in training and exhibitions. The first paper on boxing was published in the late 18th century by successful Birmingham boxer 'William Futrell' who remained undefeated until his one hour and seventeen minute fight at Smitham Bottom, Croydon, on July 9, 1788 against a much younger "Gentleman" John Jackson which was attended by the Prince of Wales.
These rules did allow the fighters an advantage not enjoyed by today's boxers: They permitted the fighter to drop to one knee to begin a 30-second count at any time. Thus a fighter realizing he was in trouble had an opportunity to recover. However, this was considered "unmanly"[8] and was frequently disallowed by additional rules negotiated by the Seconds of the Boxers[9]. Intentionally going down in modern boxing will cause the recovering fighter to lose points in the scoring system. Furthermore, as the contestants did not have heavy leather gloves and wristwraps to protect their hands, a certain amount of restraint was required when striking the head.
London Prize Ring rules (1838)
In 1838, the London Prize Ring rules were codified. Later revised in 1853, they stipulated the following:[10]
- Fights occurred in a 24 feet (7.3 m)-square ring surrounded by ropes.
- If a fighter was knocked down, he had to rise within 30 seconds under his own power to be allowed to continue.
- Biting, headbutting and hitting below the belt were declared fouls.
Through the late nineteenth century, boxing or prizefighting was primarily a sport of dubious legitimacy. Outlawed in England and much of the United States, prizefights were often held at gambling venues and broken up by police. Brawling and wrestling tactics continued, and riots at prizefights were common occurrences. Still, throughout this period, there arose some notable bare knuckle champions who developed fairly sophisticated fighting tactics.
Marquess of Queensberry rules (1867)
In 1867, the Marquess of Queensberry rules were drafted by John Chambers for amateur championships held at Lillie Bridge in London for Lightweights, Middleweights and Heavyweights. The rules were published under the patronage of the Marquess of Queensberry, whose name has always been associated with them.
There were twelve rules in all, and they specified that fights should be "a fair stand-up boxing match" in a 24-foot-square ring. Rounds were three minutes long with one minute rest intervals between rounds. Each fighter was given a ten-second count if he was knocked down and wrestling was banned.
The introduction of gloves of "fair-size" also changed the nature of the bouts. An average pair of boxing gloves resembles a bloated pair of mittens and are laced up around the wrists.[12] The gloves can be used to block an opponent's blows. As a result of their introduction, bouts became longer and more strategic with greater importance attached to defensive maneuvers such as slipping, bobbing, countering and angling. Because less defensive emphasis was placed on the use of the forearms and more on the gloves, the classical forearms outwards, torso leaning back stance of the bare knuckle boxer was modified to more modern stance in which the torso is tilted forward and the hands are held closer to the face.
The English case of R v. Coney in 1882 found that a bare-knuckle fight was an assault occasioning actual bodily harm, despite the consent of the participants. This marked the end of widespread public bare-knuckle contests in England.
The first world heavyweight champion under the Queensberry Rules was "Gentleman Jim" Corbett, who defeated John L. Sullivan in 1892 at the Pelican Athletic Club in New Orleans.[13]
Throughout the early twentieth century, boxers struggled to achieve legitimacy, aided by the influence of promoters like Tex Rickard and the popularity of great champions from John L. Sullivan to Jack Dempsey. Shortly after this era, boxing commissions and other sanctioning bodies were established to regulate the sport and establish universally recognized champions.
Rules
The Marquess of Queensberry rules have been the general rules governing modern boxing since their publication in 1867.
A boxing match typically consists of a predetermined number of three-minute rounds, a total of up to 12 rounds (formerly 15). A minute is typically spent between each round with the fighters in their assigned corners receiving advice and attention from their coach and staff. The fight is controlled by a referee who works within the ring to judge and control the conduct of the fighters, rule on their ability to fight safely, count knocked-down fighters, and rule on fouls. Up to three judges are typically present at ringside to score the bout and assign points to the boxers, based on punches that connect, defense, knockdowns, and other, more subjective, measures. Each fighter has an assigned corner of the ring, where his or her coach, as well as one or more "seconds" may administer to the fighter at the beginning of the fight and between rounds. Each boxer enters into the ring from their assigned corners at the beginning of each round and must cease fighting and return to their corner at the signaled end of each round.
A bout in which the predetermined number of rounds passes is decided by the judges, and is said to "go the distance". The fighter with the higher score at the end of the fight is ruled the winner. With three judges, unanimous and split decisions are possible, as are draws. A boxer may win the bout before a decision is reached through a knockout; such bouts are said to have ended "inside the distance". If a fighter is knocked down during the fight, determined by whether the boxer touches the canvas floor of the ring with any part of their body other than the feet as a result of the opponent's punch and not a slip, as determined by the referee, the referee begins counting until the fighter returns to his or her feet and can continue. Should the referee count to ten, then the knocked-down boxer is ruled "knocked out" (whether unconscious or not) and the other boxer is ruled the winner by knockout (KO). A "technical knockout" (TKO) is possible as well, and is ruled by the referee, fight doctor, or a fighter's corner if a fighter is unable to safely continue to fight, based upon injuries or being judged unable to effectively defend themselves. Many jurisdictions and sanctioning agencies also have a "three-knockdown rule", in which three knockdowns in a given round result in a TKO. A TKO is considered a knockout in a fighter's record. A "standing eight" count rule may also be in effect, in which the referee counts no higher than eight to a boxer who regains his or her footing after a knockdown, allowing the referee time to assess if the boxer is able to continue.
In general, boxers are prohibited from hitting below the belt, holding, tripping, pushing, biting, spitting or wrestling. The boxer's shorts are raised so the opponent is not allowed to hit to the groin area. They also are prohibited from kicking, head-butting, or hitting with any part of the arm other than the knuckles of a closed fist (including hitting with the elbow, shoulder or forearm, as well as with open gloves, the wrist, the inside, back or side of the hand). They are prohibited as well from hitting the back, back of the neck or head (called a "rabbit-punch") or the kidneys. They are prohibited from holding the ropes for support when punching, holding an opponent while punching, or ducking below the belt of their opponent (dropping below the waist of your opponent, no matter the distance between). If a "clinch" – a defensive move in which a boxer wraps his or her opponents arms and holds on to create a pause – is broken by the referee, each fighter must take a full step back before punching again (alternatively, the referee may direct the fighters to "punch out" of the clinch). When a boxer is knocked down, the other boxer must immediately cease fighting and move to the nearest neutral corner of the ring until the referee has either ruled a knockout or called for the fight to continue.
Violations of these rules may be ruled "fouls" by the referee, who may issue warnings, deduct points, or disqualify an offending boxer, causing an automatic loss, depending on the seriousness and intentionality of the foul. An intentional foul that causes injury that prevents a fight from continuing usually causes the boxer who committed it to be disqualified. A fighter who suffers an accidental low-blow may be given up to five minutes to recover, after which they may be ruled knocked out if they are unable to continue. Accidental fouls that cause injury ending a bout may lead to a "no decision" result, or else cause the fight to go to a decision if enough rounds (typically four or more, or at least three in a four-round fight) have passed.
Professional vs. amateur boxing
Throughout the 17th through 19th centuries, boxing bouts were motivated by money, as the fighters competed for prizes, promoters controlled the gate, and spectators bet on the result. The modern Olympic movement revived interest in amateur sports, and amateur boxing became an Olympic sport in 1908. In their current form, Olympic and other amateur bouts are typically limited to three or four rounds, scoring is computed by points based on the number of clean blows landed, regardless of impact, and fighters wear protective headgear, reducing the number of injuries, knockdowns, and knockouts. Currently scoring blows in amateur boxing are subjectively counted by ringside judges, but the Australian Institute for Sport has demonstrated a prototype of an Automated Boxing Scoring System, which introduces scoring objectivity, improves safety, and arguably makes the sport more interesting to spectators. Professional boxing remains by far the most popular form of the sport globally, though amateur boxing is dominant in Cuba and some former Soviet republics. For most fighters, an amateur career, especially at the Olympics, serves to develop skills and gain experience in preparation for a professional career.
Amateur boxing


Amateur boxing may be found at the collegiate level, at the Olympic Games and Commonwealth Games, and in many other venues sanctioned by amateur boxing associations. Amateur boxing has a point scoring system that measures the number of clean blows landed rather than physical damage. Bouts consist of three rounds of three minutes in the Olympic and Commonwealth Games, and three rounds of two minutes in a national ABA (Amateur Boxing Association) bout, each with a one-minute interval between rounds.
Competitors wear protective headgear and gloves with a white strip across the knuckle. A punch is considered a scoring punch only when the boxers connect with the white portion of the gloves. Each punch that lands cleanly on the head or torso is awarded a point. A referee monitors the fight to ensure that competitors use only legal blows. A belt worn over the torso represents the lower limit of punches – any boxer repeatedly landing low blows (below the belt) is disqualified. Referees also ensure that the boxers don't use holding tactics to prevent the opponent from swinging. If this occurs, the referee separates the opponents and orders them to continue boxing. Repeated holding can result in a boxer being penalized or ultimately disqualified. Referees will stop the bout if a boxer is seriously injured, if one boxer is significantly dominating the other or if the score is severely imbalanced.[14] Amateur bouts which end this way may be noted as "RSC" (referee stopped contest) with notations for an outclassed opponent (RSCO), outscored opponent (RSCOS), injury (RSCI) or head injury (RSCH).
Professional boxing
Professional bouts are usually much longer than amateur bouts, typically ranging from ten to twelve rounds, though four round fights are common for less experienced fighters or club fighters. There are also some two-[15] and three-round professional bouts[16], especially in Australia. Through the early twentieth century, it was common for fights to have unlimited rounds, ending only when one fighter quit, benefiting high-energy fighters like Jack Dempsey. Fifteen rounds remained the internationally recognized limit for championship fights for most of the twentieth century until the early 1980s, when the death of boxer Duk Koo Kim reduced the limit to twelve.
Headgear is not permitted in professional bouts, and boxers are generally allowed to take much more punishment before a fight is halted. At any time, however, the referee may stop the contest if he believes that one participant cannot defend himself due to injury. In that case, the other participant is awarded a technical knockout win. A technical knockout would also be awarded if a fighter lands a punch that opens a cut on the opponent, and the opponent is later deemed not fit to continue by a doctor because of the cut. For this reason, fighters often employ cutmen, whose job is to treat cuts between rounds so that the boxer is able to continue despite the cut. If a boxer simply quits fighting, or if his corner stops the fight, then the winning boxer is also awarded a technical knockout victory. In contrast with amateur boxing, professional male boxers have to be bare chested.[17]
Clothing
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2009) |
All boxers, regardless of their weight class, have certain kinds of clothing that are essential for bouts. Professional boxers wear different clothes from amateur ones but there is a basic idea or sense in them.
Present
Amateur Boxing
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2009) |
Amateur boxers have to wear headgear to avoid damage to the face and head. They have to wear a sleeveless T-Shirt along with a simple pair of shorts. These shorts can be very simple in terms of their appearance...
Professional Boxing
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2009) |
Professional boxers have to be bare-chested and have no head gear. However, they still retain the shorts. However, these shorts are more decorated and styled to fit with the boxer's particulars. The shorts would usually show the boxer's name or his nickname. They can be also coloured in a way to refer to the boxer's country origin. On the areas where the shorts are on the waist or hips, the shorts will have a sort of rough or 'scaly' appearance. On this area, there would normally be a big illustration of the brand of the shorts.
Past
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2009) |
All boxers who fought before the modern era usually wore a kind of garment that bears a striking resemblance to an ordinary underwear. But some amateurs still wear a simple T-Shirt on them.
Boxing style terminology
In boxing, no two fighters' styles are identical. A boxer's style evolves as he or she applies what they learn in practice, and performs in such a way as to suit him or herself. Nonetheless, many terms are used which broadly describe a boxer's style[citation needed]. Note that a boxer is not necessarily limited to being described by one of these terms. A fighter may be accomplished at both in-fighting and out-fighting, a good example of this being Bernard Hopkins.
Boxer/Out-fighter

A classic "boxer" or stylist (also known as an "out-fighter") seeks to maintain distance between himself and his opponent, fighting with faster, longer range punches, most notably the jab, and gradually wearing his opponent down. Due to this reliance on weaker punches, out-fighters tend to win by point decisions rather than by knockout, though some out-fighters have notable knockout records. They are often regarded as the best boxing strategists due to their ability to control the pace of the fight and lead their opponent, methodically wearing him down and exhibiting more skill and finesse than a brawler[citation needed]. Out-fighters need reach, hand speed, reflexes, and footwork.
Notable out-fighters include Gene Tunney[18], Billy Conn[19], Willie Pep[20], Meldrick Taylor and Muhammad Ali[21].
Boxer/Puncher
A boxer-puncher is a well-rounded boxer who is able to fight at close range with a combination of technique and power, often with the ability to knock opponents out with a combination and in some instances a single shot. Their movement and tactics are similar to that of an out-fighter (although they are generally not as mobile as an out-fighter), but instead of winning by decision, they tend to wear their opponents down using combinations and then move in to score the knockout. A boxer must be well rounded to be effective using this style.
Notable punchers include, Manny Pacquiao, Sam Langford[22], Henry Armstrong[23], Joe Louis[24], Sugar Ray Robinson[25], Tony Zale, Archie Moore, Carlos Monzon[26], Khaosai Galaxy, Oscar De La Hoya.
Brawler/Slugger
A brawler is a fighter who generally lacks finesse and footwork in the ring, but makes up for it through sheer punching power. Many brawlers tend to lack mobility, preferring a less mobile, more stable platform and have difficulty pursuing fighters who are fast on their feet. They may also have a tendency to ignore combination punching in favour of continuous beat-downs with one hand and by throwing slower, more powerful single punches (such as hooks and uppercuts). Their slowness and predictable punching pattern (single punches with obvious leads) often leaves them open to counter punches, so successful brawlers must be able to absorb substantial amounts of punishment. A brawler's most important assets are power and chin (the ability to absorb punishment while remaining able to continue boxing).
Notable brawlers include Stanley Ketchel[27], Max Baer[28], Rocky Graziano[29], Sonny Liston[30] and George Foreman.
Swarmers/In-fighter
In-fighters/swarmers (sometimes called "pressure fighters") attempt to stay close to an opponent, throwing intense flurries and combinations of hooks and uppercuts. A successful in-fighter often needs a good "chin" because swarming usually involves being hit with many jabs before they can maneuver inside where they are more effective. In-fighters operate best at close range because they are generally shorter and have less reach than their opponents and thus are more effective at a short distance where the longer arms of their opponents make punching awkward. However, several fighters tall for their division have been relatively adept at in-fighting as well as out-fighting. The essence of a swarmer is non-stop aggression. Many short in-fighters utilize their stature to their advantage, employing a bob-and-weave defense by bending at the waist to slip underneath or to the sides of incoming punches. Unlike blocking, causing an opponent to miss a punch disrupts his balance, permits forward movement past the opponent's extended arm and keeps the hands free to counter. Some in-fighters have been known for being notoriously hard to hit. The key to a swarmer is aggression, endurance, chin, and bobbing-and-weaving.
Notable swarmers include Mike Tyson, Harry Greb[31], Jack Dempsey[32], Rocky Marciano[33], Joe Frazier, Glyn Daniels and also Jake LaMotta
Counter puncher
Counter punchers are slippery in the pocket defensive style fighters. They use their well rounded defence to avoid or block shots. When their opponent throws a punch they use their defense to avoid blows and then they return one. They mostly fight at a close range; but some counter punchers remain at the distance of an out fighter. To be successful using this style he or she must have well rounded overall skills, a sharp boxing brain, and while blazing speed isn't always necessary, good speed at the least is required.
Notable counter punchers include Pernell Whitaker, James Toney, Marvin Hagler, Evander Holyfield, Juan Manuel Marquez, and Floyd Mayweather Jr
Style matchups
There is a generally accepted rule of thumb about the success each of these boxing styles has against the others. In general, an in-fighter has an advantage over an out-fighter, an out-fighter has an advantage over a puncher, and a puncher has an advantage over an in-fighter[citation needed]; these form a cycle with each style being stronger relative to one, and weaker relative to another, with none dominating, as in rock-paper-scissors. Naturally, many other factors, such as the skill level and training of the combatants, determine the outcome of a fight, but the widely held belief in this relationship among the styles is embodied in the cliché amongst boxing fans and writers that "styles make fights."
Punchers tend to overcome swarmers or in-fighters because, in trying to get close to the slugger, the in-fighter will invariably have to walk straight into the guns of the much harder-hitting puncher, so, unless the former has a very good chin and the latter's stamina is poor, the brawler's superior power will carry the day. A famous example of this type of match-up advantage would be George Foreman's knockout victory over Joe Frazier.

Although in-fighters struggle against heavy punchers, they typically enjoy more success against out-fighters or boxers. Out-fighters prefer a slower fight, with some distance between themselves and the opponent. The in-fighter tries to close that gap and unleash furious flurries. On the inside, the out-fighter loses a lot of his combat effectiveness, because he cannot throw the hard punches. The in-fighter is generally successful in this case, due to his intensity in advancing on his opponent and his good agility, which makes him difficult to evade. For example, the swarming Joe Frazier, though easily dominated by the slugger George Foreman, was able to create many more problems for the boxer Muhammad Ali in their three fights. Joe Louis, after retirement, admitted that he hated being crowded, and that swarmers like untied/undefeated champ Rocky Marciano would have caused him style problems even in his prime.
The boxer or out-fighter tends to be most successful against a brawler, whose slow speed (both hand and foot) and poor technique makes him an easy target to hit for the faster out-fighter. The out-fighter's main concern is to stay alert, as the brawler only needs to land one good punch to finish the fight. If the out-fighter can avoid those power punches, he can often wear the brawler down with fast jabs, tiring him out. If he is successful enough, he may even apply extra pressure in the later rounds in an attempt to achieve a knockout. Most classic boxers, such as Muhammad Ali, enjoyed their best successes against sluggers.
Equipment
Since boxing involves forceful, repetitive punching, precautions must be taken to prevent damage to bones in the hand. Most trainers do not allow boxers to train and spar without hand/wrist wraps and boxing gloves. Hand wraps are used to secure the bones in the hand, and the gloves are used to protect the hands from blunt injury, allowing boxers to throw punches with more force than if they did not utilize them. Gloves have been required in competition since the late nineteenth century, though modern boxing gloves are much heavier than those worn by early twentieth-century fighters. Prior to a bout, both boxers agree upon the weight of gloves to be used in the bout, with the understanding that lighter gloves allow heavy punchers to inflict more damage. The brand of gloves can also affect the impact of punches, so this too is usually stipulated before a bout. A mouth guard is important to protect the teeth and gums from injury, and to cushion the jaw, resulting in a decreased chance of knockout.
Boxers practice their skills on two basic types of punching bags. A small, tear-drop-shaped "speed bag" is used to hone reflexes and repetitive punching skills, while a large cylindrical "heavy bag" filled with sand or a synthetic substitute is used to practice power punching and body blows. In addition to these distinctive pieces of equipment, boxers also utilize more general use training equipment to build strength, speed, and agility. Common training equipment includes free weights, rowing machines, jump rope, and medicine balls.
Technique
Stance
The modern boxing stance differs substantially from the typical boxing stances of the 19th and early 20th centuries. The modern stance has a more upright vertical-armed guard, as opposed to the more horizontal, knuckles-facing-forward guard adopted by early 20th century hook users such as Jack Johnson.
-
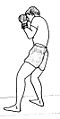
Upright stance
-
Semi-crouch
-
Full crouch
In a fully upright stance, the boxer stands with the legs shoulder-width apart and the rear foot a half-step behind the lead foot. Right-handed or orthodox boxers lead with the left foot and fist. Both feet are parallel, and the right heel is off the ground. The lead (left) fist is held vertically about six inches in front of the face at eye level. The rear (right) fist is held beside the chin and the elbow tucked against the ribcage to protect the body. The chin is tucked into the chest to avoid punches to the jaw which commonly cause knock-outs and is often kept slightly offcenter. Wrists are slightly bent to avoid damage when punching and the elbows are kept tucked in to protect the ribcage. Some boxers fight from a crouch, leaning forward and keeping their feet closer together. The stance described is considered the "textbook" stance and fighters are encouraged to change it around once its been mastered as a base. Case in point, many fast fighters have their hands down and have almost exaggerated footwork, while brawlers or bully fighters tend to slowly stalk their opponents.
Left-handed or southpaw fighters use a mirror image of the orthodox stance, which can create problems for orthodox fighters unaccustomed to receiving jabs, hooks, or crosses from the opposite side. The southpaw stance, conversely, is vulnerable to a straight right hand.
North American fighters tend to favor a more balanced stance, facing the opponent almost squarely, while many European fighters stand with their torso turned more to the side. The positioning of the hands may also vary, as some fighters prefer to have both hands raised in front of the face, risking exposure to body shots.
Modern boxers can sometimes be seen tapping their cheeks or foreheads with their fists in order to remind themselves to keep their hands up (which becomes difficult during long bouts). Boxers are taught to push off with their feet in order to move effectively. Forward motion involves lifting the lead leg and pushing with the rear leg. Rearward motion involves lifting the rear leg and pushing with the lead leg. During lateral motion the leg in the direction of the movement moves first while the opposite leg provides the force needed to move the body.
Punches
There are four basic punches in boxing: the jab, straight right/left hand, hook and uppercut. If a boxer is right-handed (orthodox), his left hand is the lead hand and his right hand is the rear hand. For a left-handed boxer or southpaw, the hand positions are reversed. For clarity, the following discussion will assume a right-handed boxer.
-
Cross - in counter-punch with a looping
-
Short straight-punch – in short range and close range
-
Cross-counter (counter punch)
-
Half uppercut - a combination of a wide Uppercut/straight punch
-
Half hook - a combination of a wide Hook/straight punch
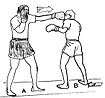
- Jab – A quick, straight punch thrown with the lead hand from the guard position. The jab is accompanied by a small, clockwise rotation of the torso and hips, while the fist rotates 90 degrees, becoming horizontal upon impact. As the punch reaches full extension, the lead shoulder can be brought up to guard the chin. The rear hand remains next to the face to guard the jaw. After making contact with the target, the lead hand is retracted quickly to resume a guard position in front of the face. The jab is recognised as the most important punch in a boxer's arsenal because it provides a fair amount of its own cover and it leaves the least amount of space for a counter punch from the opponent. It has the longest reach of any punch and does not require commitment or large weight transfers. Due to its relatively weak power, the jab is often used as a tool to gauge distances, probe an opponent's defenses, harass an opponent, and set up heavier, more powerful punches. A half-step may be added, moving the entire body into the punch, for additional power. Some notable boxers who have been able to develop relative power in their jabs and use it to punish or 'wear down' their opponents to some effect include Larry Holmes and Wladimir Klitschko.
- Cross – A powerful, straight punch thrown with the rear hand. From the guard position, the rear hand is thrown from the chin, crossing the body and traveling towards the target in a straight line. The rear shoulder is thrust forward and finishes just touching the outside of the chin. At the same time, the lead hand is retracted and tucked against the face to protect the inside of the chin. For additional power, the torso and hips are rotated counter-clockwise as the cross is thrown. Weight is also transferred from the rear foot to the lead foot, resulting in the rear heel turning outwards as it acts as a fulcrum for the transfer of weight. Body rotation and the sudden weight transfer is what gives the cross its power. Like the jab, a half-step forward may be added. After the cross is thrown, the hand is retracted quickly and the guard position resumed. It can be used to counter punch a jab, aiming for the opponent's head (or a counter to a cross aimed at the body) or to set up a hook. The cross can also follow a jab, creating the classic "one-two" combination. The cross is also called a "straight" or "right", especially if it does not cross the opponent's outstretched jab.
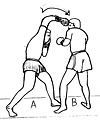
- Hook – A semi-circular punch thrown with the lead hand to the side of the opponent's head. From the guard position, the elbow is drawn back with a horizontal fist (knuckles pointing forward) and the elbow bent. The rear hand is tucked firmly against the jaw to protect the chin. The torso and hips are rotated clockwise, propelling the fist through a tight, clockwise arc across the front of the body and connecting with the target. At the same time, the lead foot pivots clockwise, turning the left heel outwards. Upon contact, the hook's circular path ends abruptly and the lead hand is pulled quickly back into the guard position. A hook may also target the lower body and this technique is sometimes called the "rip" to distinguish it from the conventional hook to the head. The hook may also be thrown with the rear hand.
- Uppercut – A vertical, rising punch thrown with the rear hand. From the guard position, the torso shifts slightly to the right, the rear hand drops below the level of the opponent's chest and the knees are bent slightly. From this position, the rear hand is thrust upwards in a rising arc towards the opponent's chin or torso. At the same time, the knees push upwards quickly and the torso and hips rotate anti-clockwise and the rear heel turns outward, mimicking the body movement of the cross. The strategic utility of the uppercut depends on its ability to "lift" the opponent's body, setting it off-balance for successive attacks. The right uppercut followed by a left hook is a deadly combination employing the uppercut to lift the opponent's chin into a vulnerable position, then the hook to knock the opponent out.
These different punch types can be thrown in rapid succession to form combinations or "combos". The most common is the jab and cross combination, nicknamed the "one-two combo". This is usually an effective combination, because the jab blocks the opponent's view of the cross, making it easier to land cleanly and forcefully.
A large, swinging circular punch starting from a cocked-back position with the arm at a longer extension than the hook and all of the fighter's weight behind it is sometimes referred to as a "roundhouse", "haymaker", or sucker-punch. Relying on body weight and centripetal force within a wide arc, the roundhouse can be a powerful blow, but it is often a wild and uncontrolled punch that leaves the fighter delivering it off balance and with an open guard. Wide, looping punches have the further disadvantage of taking more time to deliver, giving the opponent ample warning to react and counter. For this reason, the haymaker or roundhouse is not a conventional punch, and is regarded by trainers as a mark of poor technique or desperation. Sometimes it has been used, because of its immense potential power, to finish off an already staggering opponent who seems unable or unlikely to take advantage of the poor position it leaves the puncher in.
Another unconventional punch is the rarely used "bolo punch", in which the opponent swings an arm out several times in a wide arc, usually as a distraction, before delivering with either that or the other arm.
Defense
There are several basic maneuvers a boxer can use in order to evade or block punches, depicted and discussed below.
- Slip – Slipping rotates the body slightly so that an incoming punch passes harmlessly next to the head. As the opponent's punch arrives, the boxer sharply rotates the hips and shoulders. This turns the chin sideways and allows the punch to "slip" past. Muhammad Ali was famous for extremely fast and close slips, as was an early Mike Tyson.
- Sway or Fade – To anticipate a punch and move the upper body or head back so that it misses or has its force appreciably lessened. Also called "rolling with the punch" or " Riding The Punch".
- Duck or Break – To drop down with the back straight so that a punch aimed at the head glances or misses entirely.
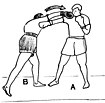
- Bob and Weave – Bobbing moves the head laterally and beneath an incoming punch. As the opponent's punch arrives, the boxer bends the legs quickly and simultaneously shifts the body either slightly right or left. Once the punch has been evaded, the boxer "weaves" back to an upright position, emerging on either the outside or inside of the opponent's still-extended arm. To move outside the opponent's extended arm is called "bobbing to the outside". To move inside the opponent's extended arm is called "bobbing to the inside". Joe Frazier, Jack Dempsey, Mike Tyson and Rocky Marciano were masters of bobbing and weaving.
- Parry/Block – Parrying or blocking uses the boxer's shoulder, hands or arms as defensive tools to protect against incoming attacks. A block generally receives a punch while a parry tends to deflect it. A "palm" or "cuff" is a block which intentionally takes the incoming punch on that portion of the defender's glove.
- The Cover-Up – Covering up is the last opportunity (other than rolling with a punch) to avoid an incoming strike to an unprotected face or body. Generally speaking, the hands are held high to protect the head and chin and the forearms are tucked against the torso to impede body shots. When protecting the body, the boxer rotates the hips and lets incoming punches "roll" off the guard. To protect the head, the boxer presses both fists against the front of the face with the forearms parallel and facing outwards. This type of guard is weak against attacks from below.
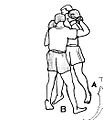
- The Clinch – Clinching is a rough form of grappling and occurs when the distance between both fighters has closed and straight punches cannot be employed. In this situation, the boxer attempts to hold or "tie up" the opponent's hands so he is unable to throw hooks or uppercuts. To perform a clinch, the boxer loops both hands around the outside of the opponent's shoulders, scooping back under the forearms to grasp the opponent's arms tightly against his own body. In this position, the opponent's arms are pinned and cannot be used to attack. Clinching is a temporary match state and is quickly dissipated by the referee.
Guards
There are several defensive positions (guards or styles) used in boxing. Within each style, there is considerable variation among fighters, as some fighters may have their guard higher for more head protection while others have their guard lower to provide better protection against body punches. Many fighters vary their defensive style throughout a bout in order to adapt to the situation of the moment, choosing the position best suited to protect them.
Boxers who use an upright stance protect their chin with the rear hand in either the low or mixed guard styles depicted below. Crouch fighters tend to use the "peek-a-boo" style, discussed below.
- Peek-a-boo – Sometimes known as the "earmuffs," the hands are placed next to each other in front of the face (fighters tend to vary the exact positioning) and elbows are brought in tight to the body (this position can be achieved by bringing the elbows as close together while not straining yourself to do so). This defensive style is what a boxer is taught to do when he begins to box, after he gains experience he can decide to change or vary the guard. This style is middle-of-the-road style in terms of counterpunching and damage reduction. A boxer can counter punch from this stance, but it is difficult. However, there have been boxers who can do this very well. This defense covers up a fighter well, but there are holes. Hooks do damage by going around the hands and by hitting just behind the elbows. Winky Wright uses this style very well from a damage reduction stand point. Another famous example is Mike Tyson, who in his early career used the Peek-a-Boo with great success.
- Cross-armed – The forearms are placed on top of each other horizontally in front of the face with the glove of one arm being on the top of the elbow of the other arm. This style is greatly varied when the back hand rises vertically. This style is the most effective for reducing head damage. The only head punch that a fighter is susceptible to is a jab to the top of the head. The body is open, but most fighters who use this style bend and lean to protect the body, but while upright and unaltered the body is there to be hit. This position is very difficult to counterpunch from, but virtually eliminates all head damage.
- Philly Shell, Hitman or Crab – The lead arm is placed across the torso usually somewhere in between the belly button and chest and the lead hand rests on the opposite side of the fighter's torso. The back hand is placed on the side of the face. The lead shoulder is brought in tight against the side of the face. This style is used by fighters who like to counterpunch. To execute this guard a fighter must be very athletic and experienced. This style is so effective for counterpunching because it allows fighters to slip punches by rotating and dipping their upper body and causing blows to glance off the fighter. After the punch glances off, the fighter's back hand is in perfect position to hit his out-of-positioned opponent. The shoulder lean is used in this stance. To execute the shoulder lean a fighter rotates and ducks when his opponent's punch is coming towards him and then rotates back towards his opponent while his opponent is bringing his hand back. The fighter will throw a punch with his back hand as he is rotating towards his undefended opponent. The weakness to this style is that when a fighter is stationary and not rotating he is open to be hit, so a fighter must be athletic and well conditioned to effectively execute this style. To beat this style fighters like to jab their opponent's shoulder causing the shoulder and arm to be in pain and to demobilize that arm.
Boxers generally attempt to land high, fast combinations and then quickly shift position to avoid a possible response by their opponent. Strategically, the ring's centre is generally the desired position since a boxer is able to conserve movement by forcing the opponent to circle around them. When in the centre, the boxer is also less likely to be knocked backwards against the ropes surrounding the ring and cornered. Depending on the boxer's style, the centre is the desired location as cornering opponents is always a good strategy. Most fighters, though, will not move around the boxer in the center because doing so makes them vulnerable to shots thrown at good angles. Movement is the most important tool in the ring and allows the fighter to avoid punches that were not telegraphed. If a boxer is standing still, his opponent has a better chance of hitting him. A fighter anticipating a shot while stationary is less likely to be able to evade the shot than a fighter already in motion.
Less common strategies
- The "rope-a-dope" strategy : Used by Muhammad Ali in his 1974 "Rumble in the Jungle" bout against George Foreman, the rope-a-dope method involves laying back on the ropes, covering up defensively as much as possible and allowing the opponent to land punches. Weathering the blows, the boxer lures the opponent into expending energy whilst conserving his/her own. If successful, the attacking opponent will eventually tire, creating defensive flaws which the boxer can exploit. In modern boxing, the rope-a-dope is generally discouraged since most opponents are not fooled by it and few boxers possess the physical toughness to withstand a prolonged, unanswered assault.
- Bolo punch : Occasionally seen in Olympic boxing, the bolo is an arm punch which owes its power to the shortening of a circular arc rather than to transference of body weight; it tends to have more of an effect due to the surprise of the odd angle it lands at rather than the actual power of the punch. This is more of a gimmick than a technical maneuver; this punch is not taught, being on the same plane in boxing technicality as is the Ali shuffle. Nevertheless, a few professional boxers have used the bolo-punch to great effect, including former welterweight champions Sugar Ray Leonard, Ceferino Garcia and Kid Gavilan.
- Overhand right : The overhand right is a punch not found in every boxer's arsenal. Unlike the right cross, which has a trajectory parallel to the ground, the overhand right has a looping circular arc as it is thrown over-the-shoulder with the palm facing away from the boxer. It is especially popular with smaller stature boxers trying to reach taller opponents. Boxers who have used this punch consistently and effectively include former heavyweight champions Rocky Marciano and Tim Witherspoon. The overhand right has become a popular weapon in other tournaments that involve fist striking. Mighty Mo employed it to score a dramatic 2nd Round KO over 7 ft 2 in tall Hong-Man Choi in the K-1 Yokohama Grand Prix Tournament and the overhand right has become a signature move for former UFC light heavyweight champion Chuck Liddell.
- Check hook : A check hook is employed to prevent aggressive boxers from lunging in. There are two parts to the check hook. The first part consists of a regular hook. The second, trickier part involves the footwork. As the opponent lunges in, the boxer should throw the hook and pivot on his left foot and swing his right foot 180 degrees around. If executed correctly, the aggressive boxer will lunge in and sail harmlessly past his opponent like a bull missing a matador. This is rarely seen in professional boxing as it requires a great disparity in skill level to execute. Floyd Mayweather, Jr. demonstrated a picture-perfect example of this punch against Ricky Hatton in their 2007 encounter. Hatton was caught with the check hook as he was lunging in; Hatton continued forward as he was knocked off balance and proceeded to ram his head into the ring post as Mayweather stepped out of harm's way. When interviewed, Mayweather stated that he was taught the check hook in the Michigan amateurs. Technically speaking it has been said that there is no such thing as a check hook and that it is simply a hook applied to an opponent that has lurched forward and past his opponent who simply hooks him on the way past. Others have argued that the check hook exists but is an illegal punch due to it being a pivot punch which is illegal in the sport.
The corner
In boxing, each fighter is given a corner of the ring where he rests in between rounds and where his trainers stand. Typically, three men stand in the corner besides the boxer himself; these are the trainer, the assistant trainer and the cutman. The trainer and assistant typically give advice to the boxer on what he is doing wrong as well as encouraging him if he is losing. The cutman is a cutaneous doctor responsible for keeping the boxer's face and eyes free of cuts and blood. This is of particular importance because many fights are stopped because of cuts that threaten the boxer's eyes.
In addition, the corner is responsible for stopping the fight if they feel their fighter is in grave danger of permanent injury. The corner will occasionally literally throw in a white towel to signify a boxer's surrender. This can be seen in the fight between Diego Corrales and Floyd Mayweather. In that fight, Corrales' corner surrendered despite Corrales' steadfast refusal.
Boxing Hall of Fame
The sport of boxing has two internationally recognized boxing halls of fame; the International Boxing Hall of Fame (IBHOF) and the World Boxing Hall of Fame (WBHF), with the IBHOF being the more widely recognized boxing hall of fame.
The WBHF was founded by Everett L. Sanders in 1980. Since its inception the WBHOF has never had a permanent location or museum, which has allowed the more recent IBHOF to garner more publicity and prestige. Boxing's International Hall of Fame was inspired by a tribute an American town held for two local heroes in 1982. The town, Canastota, New York, (which is about 15 miles (24 km) east of Syracuse, via the New York State Thruway), honored former world welterweight/middleweight champion Carmen Basilio and his nephew, former world welterweight champion Billy Backus. The people of Canastota raised money for the tribute which inspired the idea of creating an official, annual hall of fame for notable boxers.
The International Boxing Hall of Fame opened in Canastota in 1989. The first inductees in 1990 included Jack Johnson, Benny Leonard, Jack Dempsey, Henry Armstrong, Sugar Ray Robinson, Archie Moore, and Muhammad Ali. Other world-class figures include Roberto "Manos de Piedra" Duran, Ismael Laguna, Eusebio Pedroza, Carlos Monzon, Azumah Nelson, Rocky Marciano, Pipino Cuevas, and Ken Buchanan. The Hall of Fame's induction ceremony is held every June as part of a four-day event.
The fans who come to Canastota for the Induction Weekend are treated to a number of events, including scheduled autograph sessions, boxing exhibitions, a parade featuring past and present inductees, and the induction ceremony itself.
Governing and sanctioning bodies

| Governing Body | Website |
|---|---|
| British Boxing Board of Control (BBBofC) | http://www.bbbofc.com/ |
| Nevada State Athletic Commission | http://boxing.nv.gov/ |
| American Association of Professional Ringside Physicians (AAPRP) | http://www.aaprp.org/ |
| Sanctioning Body | Website |
| World Boxing Association (W.B.A.) | http://www.wbaonline.com/ |
| World Boxing Council (W.B.C.) | http://www.wbcboxing.com/ |
| International Boxing Federation (I.B.F.) | http://www.ibf-usba-boxing.com/ |
| World Boxing Organization (W.B.O.) | http://www.wbo-int.com/ |
| International Boxing Organization (I.B.O.) | http://www.iboboxing.com/ |
See also
- Automated Boxing Scoring System
- Boxing at the Summer Olympics
- Concussion
- List of female boxers
- Women's boxing
- White Collar Boxing
- Helmet boxing
- List of current world boxing champions
- List of Triple Champions of Boxing
- Boxing training
References
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (November 2009) |
- ^ a b c Encyclopaedia Britannica entry for Boxing
- ^ Boxing Ancient History & Cartoon Fun from Brownielocks
- ^ Homer, Iliad, 23.655-696
- ^ Virgil, Aeneid, 5.421
- ^ BBC. The origins of Boxing, BBC History
- ^ James B. Roberts and Alexander G. Skutt (1999). James Figg, IBOHF
- ^ John Rennie (2006) East London Prize Ring Rules 1743
- ^ Anonymous ("A Celebrated Pugilist"), The Art and Practice of Boxing, 1825
- ^ Daniel Mendoza, The Modern Art of Boxing, 1790
- ^ Clay Moyle and Arly Allen (2006), 1838 Prize Rules
- ^ Leonard–Cushing fight Part of the Library of Congress/Inventing Entertainment educational website. Retrieved 12/14/06.
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica (2006). Queensbury Rules, Britannica
- ^ Tracy Callis (2006). James Corbett, Cyberboxingzone.com
- ^ Andrew Eisele (2005). Olympic Boxing Rules, About.com
- ^ BoxRec Boxing Records
- ^ BoxRec Boxing Records
- ^ Bert Randolph Sugar (2001). "Boxing," World Book Online Americas Edition [1]
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.162
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.254
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.384
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.190, 194
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.120
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.204
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.337
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.403
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.353
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.114,115
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.50
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.293
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, "Doug Grant",2008 p.330
- ^ James Roberts, Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.98, 99
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.75
- ^ James Roberts and Alexander Skutt, The Boxing Register, 1999, p.339, 340
General references
- Accidents Take Lives of Young Alumni (July/August 2005). Illinois Alumni, 18(1), 47.
- Beating the heck outta their instruments
- Death Under the Spotlight: The Manuel Velazquez Boxing Fatality Collection
- Fleischer, Nat, Sam Andre, Nigel Collins, Dan Rafael (2002). An Illustrated History of Boxing. Citadel Press. ISBN 0-8065-2201-1
- Fox, James A. (2001). Boxing. Stewart, Tabori and Chang. ISBN 1-58479-133-0
- Godfrey, John "Boxing" from Treatise Upon the Useful Science of Defense, 1747
- Gunn M, Ormerod D. The legality of boxing. Legal Studies. 1995;15:181.
- Halbert, Christy (2003). The Ultimate Boxer: Understanding the Sport and Skills of Boxing. Impact Seminars, Inc. ISBN 0-9630968-5-0
- Hatmaker, Mark (2004). Boxing Mastery: Advanced Technique, Tactics, and Strategies from the Sweet Science. Tracks Publishing. ISBN 1-884654-21-5
- McIlvanney, Hugh (2001). The Hardest Game: McIlvanney on Boxing. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-658-02154-0
- Myler, Patrick (1997). A Century of Boxing Greats: Inside the Ring with the Hundred Best Boxers. Robson Books (UK) / Parkwest Publications (US). ISBN 1-86105-258-8.
- Price, Edmund The Science of Self Defense: A Treatise on Sparring and Wrestling, 1867
- Robert Anasi (2003). The Gloves: A Boxing Chronicle. North Point Press. ISBN 0-86547-652-7
- Schulberg, Budd (2007). Ringside: A Treasury of Boxing Reportage. Ivan R. Dee. ISBN 1-56663-749-X
- Silverman, Jeff (2004). The Greatest Boxing Stories Ever Told: Thirty-Six Incredible Tales from the Ring. The Lyons Press. ISBN 1-59228-479-5
- Scully, John Learn to Box with the Iceman
- U.S. Amateur Boxing Inc. (1994). Coaching Olympic Style Boxing. Cooper Pub Group. 1-884-12525-5
- A Pictoral History Of Boxing, Sam Andre and Nat Fleischer, Hamlyn, 1988, ISBN 0-600-50288-0