Thiopurine
Appearance
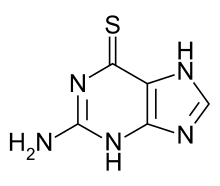


The thiopurine drugs are purine antimetabolites widely used in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, autoimmune disorders (e.g., Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis), and organ transplant recipients.
Metabolism is catalyzed by S-methyltransferase.[1]
Litigation over patents covering diagnostic kits to monitor the dosing of these drugs led to a US Supreme Court case, Mayo Collaborative Services v. Prometheus Laboratories, Inc. that dramatically changed the nature of patent law in the United States.[2][3]
See also
- 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
- 6-Thioguanine (6-TG)
- Azathioprine (AZA)
References
- ^ Sahasranaman S, Howard D, Roy S (August 2008). "Clinical pharmacology and pharmacogenetics of thiopurines". Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64 (8): 753–67. doi:10.1007/s00228-008-0478-6. PMID 18506437.
- ^ Supreme Court Decision. Mayo Collaborative Services v. Prometheus Laboratories, Inc., No. 10-1150, Slip Op. at 16. Decision
- ^ Gene Quinn, Killing Industry: The Supreme Court Blows Mayo v. Prometheus IP Watchdog (March 20, 2012).
External links
