Higher education









Higher education, post-secondary education, or third level education is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after secondary education. Often delivered at universities, academies, colleges, seminaries, and institutes of technology, higher education is also available through certain college-level institutions, including vocational schools, trade schools, and other career colleges that award academic degrees or professional certifications. Tertiary education at non-degree level is sometimes referred to as further education or continuing education as distinct from higher education.
The right of access to higher education is mentioned in a number of international human rights instruments. The UN International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 declares, in Article 13, that "higher education shall be made equally accessible to all, on the basis of capacity, by every appropriate means, and in particular by the progressive introduction of free education". In Europe, Article 2 of the First Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights, adopted in 1950, obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education.
In the days when few pupils progressed beyond primary education, the term "higher education" was often used to refer to secondary education, which can create some confusion.[6]
Overview
Higher education is an educational level that follows a completion of a school providing a secondary education, such as a high school, secondary school, or gymnasium. Tertiary education, often called 'post-secondary education' in North America, is normally taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, as well as vocational education and training. Colleges, universities, and institutes of technology are the main institutions that provide tertiary education (sometimes known collectively as tertiary institutions) although there are also vocational schools, community colleges, independent colleges (e.g. institutes of technology), and universities in the United States, the institutes of technical and further education in Australia, CEGEP in Quebec, and the IEKs in Greece. They are sometimes known collectively as tertiary institutions or post-secondary education (PSE) institutions. Successful completion of a tertiary education program of study generally results in the awarding of certificates, diplomas, or academic degrees.
Higher education includes teaching, research, exacting applied work (e.g. in medical schools and dental schools), and social services activities of universities.[7] Within the realm of teaching, it includes both the undergraduate level, and beyond that, graduate-level (or postgraduate level). The latter level of education is often referred to as graduate school, especially in North America.
Since World War II, developed and many developing countries have increased the participation of the age group who mostly studies higher education from the elite rate, of up to 15 per cent, to the mass rate of 16 to 50 per cent.[8][9][10] In many developed countries, participation in higher education has continued to increase towards universal or, what Trow later called, open access, where over half of the relevant age group participate in higher education.[11] Higher education is important to national economies, both as an industry, in its own right, and as a source of trained and educated personnel for the rest of the economy. College educated workers have commanded a measurable wage premium and are much less likely to become unemployed than less educated workers.[12][13] However, the admission of so many students of only average ability to higher education inevitably requires a decline in academic standards, facilitated by grade inflation.[14][15] Also, the supply of graduates in many fields of study is exceeding the demand for their skills, which aggravates graduate unemployment and underemployment.[16]
Higher education in some countries, including the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Ireland, specifically refers to post-secondary institutions that offer Associate's degrees, Bachelor's degrees, Master's degrees, Education Specialist (Ed.S.) degrees or Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) degrees, or their equivalents, and also higher professional degrees in areas such as dentistry, law, medicine, optometry, pharmacology and veterinary medicine.[citation needed]
Such institutions may also offer non-degree certificates, which indicate completion of a set of courses comprising a body of knowledge on a particular topic, but the granting of such certificates is not the primary purpose of the institutions. Tertiary education is not a term used in reference to post-secondary institutions in the United States or Canada.[citation needed]
Entrance standards: Reading, mathematics, and writing
Demonstrated ability in reading, mathematics, and writing, as typically measured in the United States by the SAT or similar tests such as the ACT, have often replaced colleges' individual entrance exams, and is often required for admission to higher education.[17] There is some question as to whether advanced mathematical skills or talent are in fact necessary for fields such as history, English, philosophy, or art.[18]
Types
General
The general higher education and training that takes place in a university, college, or Institute of Technology usually includes significant theoretical and abstract elements, as well as applied aspects (although limited offerings of internships or SURF programs attempt to provide practical applications). In contrast, the vocational higher education and training that takes place at vocational universities and schools usually concentrates on practical applications, with very little theory.
In addition, professional-level education is always included within Higher Education, and usually in graduate schools, since many postgraduate academic disciplines are both vocationally, professionally, and theoretically/research oriented, such as in the law, medicine, pharmacy, dentistry, and veterinary medicine. A basic requirement for entry into these graduate-level programs is almost always a bachelor's degree, although alternative means of obtaining entry into such programmes may be available at some universities. Requirements for admission to such high-level graduate programs is extremely competitive, and admitted students are expected to perform well.
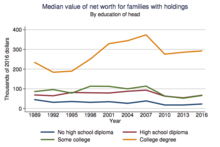

In the United States, there are large differences in wages and employment associated with different degrees. Medical doctors and lawyers are generally the highest paid workers, and have among the lowest unemployment rates. Among undergraduate fields of study, science, technology, engineering, math, and business generally offer the highest wages and best chances of employment, while education, communication, and liberal arts degrees generally offer lower wages and a lower likelihood of employment.[12][19][20][21]
Liberal arts
Academic areas that are included within the Liberal arts include Environmental Science, Great Books, History, Languages including English, Linguistics, Literature, Mathematics, Music, Philosophy, Political Science, Psychology, Religious studies, Science, Sociology and Theater.
Engineering
Teaching engineering is teaching the application of scientific, economic, social, and practical knowledge in order to design, build, maintain, and improve structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes. It may encompass using insights to conceive, model and scale an appropriate solution to a problem or objective. The discipline of engineering is extremely broad, and encompasses a range of more specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of technology and types of application. Engineering disciplines include: aerospace, biological, civil, chemical, computer, electrical, industrial, and mechanical.
Performing arts
The performing arts differ from the plastic arts or visual arts, insofar as the former uses the artist's own body, face and presence as a medium; the latter uses materials such as clay, metal or paint, which can be molded or transformed to create a work of art.
Performing arts institutions include Circus schools, Dance schools, Drama schools and Music schools
Plastic or visual arts
The plastic arts or visual arts are a class of art forms, that involve the use of materials, that can be moulded or modulated in some way, often in three dimensions. Examples are painting, sculpture, and drawing, etc.
Higher educational institutions in these arts include Film schools and Art schools.
Vocational
Higher vocational education and training takes place at the non-university tertiary level. Such education combines teaching of both practical skills and theoretical expertise. Higher education differs from other forms of post-secondary education such as that offered by institutions of vocational education, which are more colloquially known as trade schools. Higher vocational education might be contrasted with education in a usually broader scientific field, which might concentrate on theory and abstract conceptual knowledge.
Professional higher education
This describes a distinct form of Higher Education that offers a particularly intense integration with the world of work in all its aspects (including teaching, learning, research and governance) and at all levels of the overarching Qualifications Framework of the European Higher Education Area. Its function is to diversify learning opportunities, enhance employability, offer qualifications and stimulate innovation, for the benefit of learners and society.
The intensity of integration with the world of work (which includes enterprise, civil society and the public sector) is manifested by a strong focus on application of learning. This approach involves combining phases of work and study, a concern for employability, cooperation with employers, the use of practice-relevant knowledge and use-inspired research.[22]
Examples of providers of Professional Higher Education may include, Graduate Colleges of Architecture, Business, Journalism, Law, Library Science, Optometry, Pharmacy, Public Policy, Human Medicine, Professional Engineering, Podiatric Medicine, Scientific Dentistry, K-12 Education, and Veterinary Medicine.
Statistics
A report titled 'Education at a Glance 2014' published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development on 9 September 2014, revealed that by 2014, 84 percent of young people were completing upper secondary education over their lifetimes, in high-income countries. Tertiary-educated individuals were earning twice as much as median workers. In contrast to historical trends in education, young women were more likely to complete upper secondary education than young men. Additionally, access to education was expanding and growth in the number of people receiving university education was rising sharply. By 2014, close to 40 percent of people aged 25–34 (and around 25 percent of those aged 55–64), were being educated at university.[23]
Recognition of studies
The Lisbon Recognition Convention stipulates that degrees and periods of study must be recognised in all Signatory Parties of the Convention.
As employers

Universities may employ a number of people. Depending on the funding, a university typically hires one teacher per 3–25 students. According to the ideal of research-university, the university teaching staff is actively involved in the research of the institution. In addition, the university usually also has dedicated research staff and a considerable support staff. Typically to work in higher education as a member of the academic faculty, a candidate must first obtain a doctorate in an academic field, although some lower teaching positions require only a master's degree.[citation needed]
Most of the administrative staff works in different administrative sections, such as Student Affairs.[citation needed] In addition, there may be central support units, such as a university library which have a dedicated staff.[24]
The professional field involving the collection, analysis, and reporting of higher education data is called institutional research. Professionals in this field can be found at locations in addition to universities, e.g. state educational departments.[citation needed]
Post secondary institutions also employ graduate students in various assistantship roles. In the US, close to 50% of graduate students are employed as graduate assistants at some point. These apprenticeship-like positions provide opportunities for students to gain experience in, and exposure to, professional roles in exchange for funding of their academic programs.[25]
Recent Controversy
From the early 1950s to the present, more and more people in the United States have gone on to pursue degrees or certificates of higher education. However this has sparked some debate in recent years as some advocates say that a degree is not what it was once worth to employers. To clarify some advocates say that the financial costs that universities require from their students has gone up so dramatically that it is leaving many students in debt of loans of an average of $33,000.[26] Advocates advise parents to not send their children to college unless these children are committed to pursuing their future education. An increasing number of freshman every year drop out of their perspective programs or do not possess the maturity to have a balanced life away from home.[27]
However statistics from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicate that the college educated are employed at a rate nearly twice that of the national average when compared to high school graduates.[28] The type of degree one pursues will determine how safe and prosperous his/her career path is because in a study, published by the Pew Charitable Trusts, it shows that among Americans ages 21 to 24, the drop in employment and income was much steeper among people who lacked a college degree. "Among those whose highest degree was a high school diploma, only 55% had jobs even before the downturn, and that fell to 47% after it. For young people with an associates degree, the employment rate fell from 64 to 57. Bachelor's degree slipped from 69 to 65."[29] Professor Lisa Kahn of Yale stated that for people who graduated from college in the most recent recession, they were in a better position to gain better security than others.
Ultimately a survey, the Great Jobs and Great Lives Gallup-Purdue Index report, released in May, found the type of college that students attend and in some cases even majors they choose have very little to do with their overall success and well-being later in life. What matters more, the index found, is feeling supported and making emotional connections during school.[30]
See also
- Higher education by country
- List of higher education associations and alliances
- Governance in higher education
- Higher education accreditation
- Higher education bubble
- Higher education policy
- Higher Education Price Index
- UnCollege
- Hochschule
- League of European Research Universities
- Technical and Further Education (TAFE)
Notes
- ^ Oldest University
- ^ Verger, Jacques: "Patterns", in: Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de (ed.): A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 978-0-521-54113-8, pp. 35–76 (35)
- ^ Top Universities World University Rankings Retrieved 2010-1-6
- ^ Our History - Università di Bologna
- ^ Paul L. Gaston (2010). The Challenge of Bologna. p. 18. ISBN 1-57922-366-4.
{{cite book}}: External link in|title= - ^ For example, Higher Education: General and Technical, a 1933 National Union of Teachers pamphlet by Lord Eustace Percy, which is actually about secondary education and uses the two terms interchangeably.
- ^ Pucciarelli F., Kaplan Andreas M. (2016) Competition and Strategy in Higher Education: Managing Complexity and Uncertainty, Business Horizons, Volume 59
- ^ Trow, Martin (1973) Problems in the transition from elite to mass higher education. Carnegie Commission on Higher Education, Berkeley, http://www.eric.ed.gov/ERICWebPortal/search/detailmini.jsp?_nfpb=true&_&ERICExtSearch_SearchValue_0=ED091983&ERICExtSearch_SearchType_0=no&accno=ED091983, accessed 1 August 2013
- ^ Brennan, John (2004) The social role of the contemporary university: contradictions, boundaries and change, in Center for Higher Education Research and Information (ed.)
- ^ Ten years on: changing education in a changing world (Buckingham: The Open University Press), https://www.open.ac.uk/cheri/documents/ten-years-on.pdf, accessed 9 February 2014
- ^ Trow, Martin (2007) [2005] Reflections on the transition from elite to mass to universal access: forms and phases of higher education in modern societies since WWII, Springer International Handbooks of Education volume 18, 2007, 243-280
- ^ a b Michael Simkovic, Risk-Based Student Loans (2013)
- ^ OECD, Education at a Glance (2011)
- ^ Cote, James; Allahar, Anton (2007), Ivory Tower Blues: A University System in Crisis, University of Toronto Press, p. 256, ISBN 978-0802091826
- ^ Arum, Richard; Roska, Josipa (2011), Academically Adrift: Limited Learning on College Campuses, University of Chicago Press, p. 272, ISBN 978-0226028569
- ^ Barshay, Jill (4 August 2014). "Reflections on the underemployment of college graduates". Hechniger Report. Teachers College at Columbia University. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- ^ O'Shaughnessy, Lynn (26 July 2009). "The Other Side of 'Test Optional'". The New York Times. p. 6. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- ^ Andrew Hacker (July 28, 2012). "Is Algebra Necessary?". The New York Times. Retrieved July 29, 2012.
- ^ Scott L. Thomas, Deferred Costs and Economic Returns to College Major, Quality, and Performance, 41 RES. HIGHER EDUC. 281 (2000)
- ^ Charlotte Christiansen et. al, The Risk Return Trade-off in Human Capital Investment, 14 LABOR ECON. 971, 984-85 (2007)
- ^ Dan A. Black et. al, The Economic Reward for Studying Economics, 41 ECON. INQUIRY 365 (2003)
- ^ "Harmonising Approaches to Professional Higher Education in Europe". Harmonising Approaches to Professional Higher Education in Europe. EURASHE. 2013. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- ^ Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (September 2014). "Higher levels of education paying off for young, says OECD". Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- ^ "Cornell University Library Staff Web". Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- ^ Haley, K., Hephner LaBanc, B., & Koutas, P. (2011). New school, new job, new life: Transitions of graduate assistants in student affairs. Journal of College Orientation and Transition, 18(2), 5 - 19.
- ^ Cohen, Richard (2014-10-06). "Richard Cohen: The actual value of a college education". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 2015-10-11.
- ^ "Some Career Pathways Require a Four-Year Degree, Many Don't - US News". US News & World Report. Retrieved 2015-10-11.
- ^ "U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics". www.bls.gov. Retrieved 2015-10-11.
- ^ Pérez-peña, Richard (2013-01-09). "Study Shows College Degree's Value During Economic Downturn". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2015-10-11.
- ^ "College Grads Question How Much a Degree Is Worth". US News & World Report. 2015-02-10. Retrieved 2015-10-11.
References
- Bakvis, Herman and David M. Cameron (2000), "Post-secondary education and the SUFA". IRPP.
- Commission Reports: A National Dialogue: The Secretary of Education's Commission on the Future of Higher Education, United States Department of Education, 2006. [1]
- Davies, Antony and Thomas W. Cline (2005). The ROI on the MBA, BizEd.
- Douglass, John A. and Todd Greenspan, eds. "The History of the California Master Plan for Higher Education."
- El-Khawas, E. (1996). Campus trends. Washington, DC.: American Council on Education.
- Ewell, P.T. (1999). Assessment of higher education and quality: Promise and politics. In S.J. Messick (Ed.), Assessment in higher education: Issues of access, quality, student development, and public policy. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
- Finn, C. E. (1988, Jul.-Aug.). Judgment time for higher education: In the court of public opinion. Change, 20(4), 34-39.
- Forest, James and Kinser, Kevin. (2002). Higher Education in the United States: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO.
- Green, Madeleine, F., ed. 1988. Leaders for a New Era: Strategies for Higher Education. New York: Macmillan.
- Miller, Patrick L. (1979). Choosing a College. Madison, Wis.: Inter-Varsity Christian Fellowship. p. 43. Briefly considers the criteria by which a student might select a college or university for study. ISBN 0-87784-172-1
- Roszak, Theodore, ed. (1968). The Dissenting Academy. New York: Pantheon Books. x, 304 p.
- Snyder, Benson R. (1970). The Hidden Curriculum. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Spellings, Margaret, "A Test of Leadership: Charting the Future of U.S. Higher Education", A Report of the Commission Appointed by Secretary of Education Margaret Spellings, September 2006. (highlights of report)
- Veblen, Thorstein (1918). The Higher Learning in America: A Memorandum on the Conduct of Universities by Businessmen. New York: Huebsch
External links
- Association for the Study of Higher Education
- American Educational Research Association
- Center for Higher Education Policy Studies
- World Bank Tertiary Education
- college.gov - U.S. Department of Education
- Accrediting Counsel for Independent Colleges and Schools
- "College, Inc.", PBS FRONTLINE documentary, May 4, 2010
- College Parents Matter ("Tools and scripts to improve communication with your college student")
