Jaisalmer State
| Jaisalmer State | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kingdom 1156–1818 Princely State 1818–1947 | |||||||||
| 1156–1947 | |||||||||
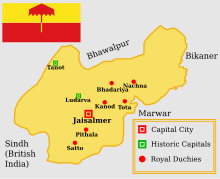 Map of Jaisalmer State with important Rawlot duchies. | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• 1931 | 41,600 km2 (16,100 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1931 | 76,255 | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1156 | ||||||||
| 1947 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Rajasthan, India | ||||||||
| Coat of arms based on The Princely Armory. Publ. by The Office of the Superintendent of Government Printing. Calcutta. 1877 | |||||||||


Jaisalmer State is the popular name of the kingdom established in the area of present-day Rajasthan by Rawal Jaisal when he moved the capital of reminiscent[clarification needed] of the Bhati dynasty from Ludarva to Jaisalmer (1156) because the old capital Ludarva was vulnerable. Bhati rajputs continued to rule Jaisalmer independently until 1818, when it signed a treaty with the British Empire effectively making it a British Protectorate, a Princely State entitled to a 15-gun salute.[1]
History
The state of Jaisalmer had its foundations in what remains of the Empire ruled by the Bhati dynasty. Early Bhati rulers ruled over large empire stretching from Ghazni[2] in modern day Afghanistan to Sialkot, Lahore and Rawalpindi in modern day Pakistan[3] to Bhatinda and Hanumangarh in Modern day India.[4] The empire crumbled over time because of continuous invasions from the central Asia. Bhati dominions continued to be shifted towards the South as they ruled Multan, then finally got pushed into Cholistan and Jaisalmer where Rawal Devaraja built Dera Rawal / Derawar.[5] Jaisalmer was the new capital founded in 1156 by Maharawal Jaisal Singh and the state took its name from the capital. On 11 December 1818 Jaisalmer became a British protectorate.[6][5]
Traditionally, in the Middle Ages, the main source of income for the kingdom was levies on caravans, but the economy was heavily affected when Bombay emerged as a major port and sea trade replaced the traditional land routes. Maharawals Ranjit Singh and Bairi Sal Singh attempted to turn around the economic decline but the dramatic reduction in trade impoverished the kingdom. A severe drought and the resulting famine from 1895 to 1900, during the reign of Maharawal Salivahan Singh, only made matters worse by causing widespread loss of the livestock that the increasingly agriculturally based kingdom relied upon.
Maharawal Jawahir Singh’s (1914–49) attempts at modernization also failed to turn the kingdom’s economy around and it remained isolated and backward compared with other areas of Rajasthan.
Rulers
Rawals
- 1153 – 1168: Rawal Jaisal Singh
- 1168 – 1200: Shalivahan Singh II
- 1200 – 1200: Baijal Singh
- 1200 – 1219: Kailan Singh
- 1219 – 1241: Chachak Deo Singh
- 1241 – 1271: Karan Singh I
- 1271 – 1275: Lakhan Sen
- 1275 – 1276: Punpal Singh
- 1276 – 1294: Jaitsi Singh I
- 1294 – 1295: Mulraj Singh I
- 1295 – 1306: Durjan Sal (Duda)
- 1306 – 1335: Gharsi Singh
- 1335 – 1402: Kehar Singh II
- 1402 – 1436: Lachhman Singh
- 1436 – 1448: Bersi Singh
- 1448 – 1457: Chachak Deo Singh II
- 1457 – 1497: Devidas Singh
- 1497 – 1530: Jaitsi Singh II
- 1530 – 1530: Karan Singh II of Jaisalmer
- 1530 – 1551: Lunkaran Singh
- 1551 – 1562: Maldev Singh
- 1562 – 1578: Harraj Singh
- 1578 – 1624: Bhim Singh of Jaisalmer
- 1624 – 1634: Kalyan Singh of Jaisalmer
- 1634 – 1648: Manohar Das Singh
- 1648 – 1651: Ram-Chandra Singh
- 1651 – 1661: Sabal Singh
Maharawals
- 1661 – 1702: Amar Singh of Jaisalmer (b. 16.. – d. 1702)
- 1702 – 1708: Jaswant Singh of Jaisalmer (d. af.1722)
- 1708 – 1722: Budh Singh (d. 1722)
- 1722 – 1762: Akhi Singh
- 1762 – 1820: Mulraj II (b. ... – d. 1820)
- 1820 – 1846: Guj Singh (b. ... – d. 1846)
- 1846 – Jun 1864: Ranjit Singh
- 1864 – 1891: Bairi Sal (b. ... – d. 1891)
- 12 Apr 1891 – 11 Apr 1914: Shalivahan Singh III (b. 1887 – d. 19...)
- 9 Jul 1914 – 15 Aug 1947: Jawahir Singh (b. 1882 – d. 1949)
Dewans (prime ministers)
- c.1885 – 1891: Mohata Nathmal
- c.1890 – 1903: Mehta Jagjiwan
- 189. – 1900: Thakur Kushal Singh (acting)
- 1900: Rawatmal Purohit Khetrapaliya (acting)
- c.1909: Lakshmi Das Sapat
- 1911 – Jun 1912: Mohammed Niyaz Ali Kazi Hapiri (b. 1866 – d. 19..)
- Jun 1912 – 21 Mar 1930: Murarji Rooji (Moraji Rao) Sapat
- c.1892 – 1902: HH Shri Panna Lal Ji Soni Nathani
- c.1930 – 1932: HH Shri Umedmal Ji II Soni Nathani (acting)
- 19.. – 19..: M.L. Khosala
- 19.. – 19..: Pandit Jamana Lal
- 19.. – 19..: Munshi Nand Kishore
- 19.. – 19..: Lala Rakhpat Raj
- 19.. – 19..: P.K. Shurugula
- 19.. – 19..: Brij Mohan Nath Zutshi
- 19.. – 19..: Anand Swaroop
- 19.. – 19..: Onkar Singh
- c.1940 – c.1942: Lakhpat Rai Sikund
See also
References
- ^ Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 24, p. 386.
- ^ "Rajasthan or the Central and Western Rajpoot States, Volume 2, page 197-198". Higginbotham And Co. Madras. 14 August 2018.
- ^ "Imperial Gazetter of India, Volume 21, page 272 - Imperial Gazetteer of India - Digital South Asia Library". Dsal.uchicago.edu. 18 February 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- ^ "Bhatinda Government: District at A glance- Origin". Bhatinda Government. 14 August 2018.
- ^ a b "Provinical Gazetteers Of India: Rajputana". Government of India. 14 August 2018.
- ^ Princely States of India
External links
 Media related to Jaisalmer State at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Jaisalmer State at Wikimedia Commons- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 129.


