Tabby's Star
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 20h 06m 15.457s |
| Declination | +44° 27′ 24.61″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +11.705±0.017 |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Main sequence[1] |
| Spectral type | F3V |
| B−V color index | 0.557 |
| V−R color index | 0.349 |
| R−I color index | 0.305 |
| J−H color index | 0.212 |
| J−K color index | 0.264 |
| Astrometry | |
| Distance | 1480 ly (454 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 3.08[1][2] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.43[citation needed] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.58[citation needed] R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 4.7[citation needed] L☉ |
| Luminosity (visual, LV) | 5[citation needed] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.0±0.2[citation needed] cgs |
| Temperature | 6750±120[citation needed] K |
| Metallicity | 0.0±0.1[citation needed] |
| Rotation | 0.8797±0.0001 days[1] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 84±4[citation needed] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| KIC | data |
KIC 8462852[1] (also Tabby's Star or WTF Star) is an F-type main-sequence star located in the constellation Cygnus approximately 454 parsecs (1,480 ly) from Earth. Unusual light fluctuations of the star were discovered by citizen scientists as part of the Planet Hunters project, and in September 2015 astronomers and citizen scientists associated with the project posted a preprint of a paper on arXiv describing the data and possible interpretations.[1] The discovery was made from data collected by the Kepler space telescope,[1][3] which observes changes in the brightness of distant stars to detect exoplanets.[4]
Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the star's large irregular changes in brightness as measured by its unusual light curve, but none have fully explained all aspects of the curve. The leading hypothesis, based on a lack of observed infrared light, posits a swarm of cold, dusty comet fragments in a highly eccentric orbit.[5][6][7] Another hypothesis is that of a large number of small masses in "tight formation" orbiting the star.[3] It has been speculated that the changes in brightness could be signs of activity associated with intelligent extraterrestrial life constructing a Dyson swarm.[3][8][9][10] The SETI Institute's initial radio reconnaissance of KIC 8462852, however, found no evidence of technology-related radio signals from the star.[11][12][13][14][15]
KIC 8462852 is not the only star that has such large irregular dimmings. However, all other such stars are young stellar objects called YSO dippers that have different dimming patterns. An example of such an object is EPIC 204278916.[16][17]
Etymology
The names "Tabby's Star" and "Boyajian's Star" refer to the initial study's lead author, Tabetha S. Boyajian;[18][19] KIC 8462852 is also known as the "WTF Star", after the study's subtitle "Where's The Flux?"[20][21][22][23] (a joking reference to the colloquial expression of disbelief "WTF").[24]
Apparent location

KIC 8462852 in Cygnus[25] is located roughly halfway between the major visually apparent (visible to the naked eye) bright stars Deneb (α Cyg, α Cygni, Alpha Cygni) and Delta Cygni (δ Cyg, δ Cygni) as part of the Northern Cross.[26] KIC 8462852 is situated south of Omicron¹ Cygni (ο¹ Cygni, 31 Cygni), and northeast of the star cluster NGC 6866.[26] While only a few arcminutes away from the cluster, it is unrelated and closer to the Sun than it is to the star cluster.
With an apparent magnitude of 11.7, the star cannot be seen by the naked eye, but is visible with a 5-inch (130 mm) telescope[27] in a dark sky with little light pollution.
History of observations
KIC 8462852 was observed as early as the year 1890.[28][29][30] The star was cataloged in the Tycho, 2MASS, UCAC4 and WISE astronomical catalogs[31] (published in 1997, 2003, 2009 and 2012, respectively).[32][33][34][35]
The main source of information about the luminosity fluctuations of KIC 8462852 is the Kepler space observatory. During its primary and extended mission from 2009 to 2013 it continuously monitored the light curves of over 100,000 stars in a patch of sky in the constellations Cygnus and Lyra.[36]
Luminosity
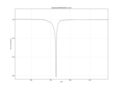
Observations of the luminosity of the star by the Kepler space telescope show small, frequent, non-periodic dips in brightness, along with two large recorded dips in brightness appearing[clarification needed] to occur roughly 750 days apart. The amplitude of the changes in the star's brightness, and the aperiodicity of the changes, mean that this star is of particular interest for astronomers.[10] The star's changes in brightness are consistent with many small masses orbiting the star in "tight formation".[3]
The first major dip, on 5 March 2011, obscured the star's brightness by up to 15%, and the other (on 28 February 2013) by up to 22%. In comparison, a planet the size of Jupiter would only obscure a star of this size by 1%, indicating that whatever is blocking light during the star's major dips is not a planet, but rather something covering up to half the width of the star.[10] Due to the failure of two of Kepler's reaction wheels, the star's predicted 750-day dip around February 2015 was not recorded;[1][9] further observations are planned for May 2017.[9] The irregular light dips do not show a pattern.[37]
In addition to the day-long dimmings, a study of a century's worth of photographic plates suggests that the star has gradually faded from 1890 to 1989 by about 20%, which would be unprecedented for any F-type main sequence star.[28][29] However, teasing accurate magnitudes from long-term photographic archives is a complex procedure, requiring adjustment for equipment changes, and is strongly dependent on the choice of comparison stars. A contrasting[clarification needed] study, examining the same photographic plates, concluded that the possible century-long dimming was likely a data artifact, and not a real astrophysical event.[30]
A third study, using light measurements by the Kepler observatory over a four-year period, determined that KIC 8462852 dimmed at about 0.34% per year before dimming more rapidly by about 2.5% in 200 days. It then returned to its previous slow fade rate. The same technique was used to study 193 stars in its vicinity and 355 stars similar in size and composition to KIC 8462852. None of these stars exhibited such dimming.[38]
Kepler light curves
-
All of the light curve data recorded of KIC 8462852 from 5 March 2011 to 17 April 2013.
-
5 March 2011 (Day 792 of Kepler observations)
-
28 February 2013 (Day 1519 of Kepler observations)
-
17 April 2013 (Day 1568 of Kepler observations)
Hypotheses
Based on KIC 8462852's spectrum and stellar type, its changes in brightness could not be attributed to intrinsic variability;[1] while a few hypotheses have been proposed involving material orbiting the star and blocking its light, none of these fully fit the observed data.
Some of the proposed explanations involve instrument or data artifacts, interstellar dust, a series of giant planets with very large ring structures,[39][40] a recently captured asteroid field,[1] the system undergoing Late Heavy Bombardment,[5][41] and an artificial megastructure orbiting the star.[42]
Younger star with coalescing material around it

Astronomer Jason Wright (who was consulted by Boyajian)[23][43] and others who have studied KIC 8462852 have suggested in a follow-up paper that if the star is younger than its position and speed would suggest, then it may still have coalescing material around it.[20]
A 0.8–4.2 micron spectroscopic study of the system using the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility (NASA IRTF) found no evidence for coalescing material within a few astronomical units of the mature central star.[5][41]
Planetary debris field

High-resolution spectroscopy and imaging observations have also been made, as well as spectral energy distribution analyses using the Nordic Optical Telescope in Spain.[1][39] A massive collision scenario would create warm dust that glows in infrared wavelengths, but there is no observed excess infrared energy, ruling out massive planetary collision debris.[10] Other researchers think the planetary debris field explanation is unlikely, given the very low probability that Kepler would ever witness such an event due to the rarity of collisions of such size.[1]
As with the possibility of coalescing material around the star, spectroscopic studies using the NASA IRTF found no evidence for hot close-in dust or circumstellar matter from an evaporating or exploding planet within a few astronomical units of the central star.[5][41] Similarly, a study of past infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer found no evidence for an excess of infrared emission from the star, which would have been an indicator of warm dust grains that could have come from catastrophic collisions of meteors or planets in the system. This absence of emission supports the hypothesis that a swarm of cold comets on an unusually eccentric orbit could be responsible for the star's unique light curve, but more studies are needed.[5][44]
A cloud of disintegrating comets

One proposed explanation for the reduction in light is that it is due to a cloud of disintegrating comets orbiting the star elliptically.[1][5][7][45] This scenario would assume that KIC 8462852's planetary system has something similar to the Oort cloud and that gravity from a nearby star caused comets from said cloud to fall closer into system, thereby obstructing KIC 8462852's spectra. Evidence supporting this hypothesis includes an M-type red dwarf within 132 billion kilometers (885 AU) of KIC 8462852.[1] However, the notion that disturbed comets from such a cloud could exist in high enough numbers to obscure 22% of the star's observed luminosity has been doubted.[10]
Submillimetre wavelength observations searching for farther-out cold dust in an asteroid belt akin to the Sun's Kuiper Belt suggest that a distant "catastrophic" planetary disruption explanation is unlikely; the possibility of a disrupted asteroid belt scattering comets into the inner system is still to be determined.[46]
An artificial megastructure

Astronomer Jason Wright[23][43] and others who have studied KIC 8462852 hypothesized that the objects eclipsing the star could be parts of a megastructure made by an alien civilization, such as a Dyson swarm,[3][20][42][45][47][48] a hypothetical structure that an advanced civilization might build around a star to intercept some of its light for their energy needs.[49][50][51] Due to extensive media coverage on this matter, KIC 8462852 has been compared by Kepler's Steve Howell with KIC 4150611,[52] another star with an odd light curve (which proved, after years of research, to be a part of a five-star system).[53] Regarding the current light curve data of KIC 8462852, Wright has emphasized the importance of upcoming spectral studies.[54] According to Wright, the likelihood of extraterrestrial intelligence being the cause of the dimming is very low; however, the star remains an outstanding SETI target because natural explanations have yet to fully explain the dimming phenomenon.[20][42]
Follow-up studies
Many optical telescopes are monitoring KIC 8462852 in anticipation of another multi-day dimming event, with planned follow-up observations of a dimming event using large telescopes equipped with spectrographs to determine if the eclipsing mass is a solid object, or if composed of dust or gas.[55] Additional follow-up observations may involve the ground-based Green Bank Telescope, the Very Large Array Radio Telescope,[39][56] and future orbital telescopes dedicated to exoplanetology such as WFIRST, TESS, and PLATO.[42][51]
A fund-raising campaign was led by Tabetha Boyajian, the author of the initial study on KIC 8462852's anomalous light curve. The project proposes to use the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network to continue observation of the star in the future and observe it in additional wavelengths to reveal new details on the composition of the objects obfuscating the star. The campaign raised over US$100,000, enough for one year of observations.[57]
SETI results
In October 2015, the SETI Institute used the Allen Telescope Array to look for radio emissions from possible intelligent extraterrestrial life in the vicinity of the star.[58][59] After an initial two-week survey, the SETI Institute reported that it found no evidence of technology-related radio signals from the star system.[11][12][13][14] No narrowband radio signals were found at a level of 180–300 Jy in a 1 Hz channel, or medium-band signals above 10 Jy in a 100 kHz channel.[60] Another SETI-related study, one using archival VERITAS gamma-ray observatory observations from 2009 to 2015, found no evidence of pulsed optical beacons associated with KIC 8462852.[61]
Astronomer Jason Wright and his colleagues plan to conduct another search beginning in October 2016 using West Virginia's Green Bank Telescope.[62][63]
EPIC 204278916
A star called EPIC 204278916, as well as some other young stellar objects, was observed to have similar dips to those observed in KIC 8462852. However, they differ in many aspects. EPIC 204278916 shows much deeper dips than KIC 8462852, and the dips seem to be grouped over a short period of time, whereas the dips at KIC 8462852 are spread out over several years. Further, EPIC 204278916 is surrounded by a proto-stellar disc, while KIC 8462852 appears to be a normal F-type star displaying no evidence of a disc.[16]
See also
- PSR B1919+21, a pulsar mistaken for an alien radio signal (LGM-1)
- Stars named after people
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Boyajian, T. S.; LaCourse, D. M.; Rappaport, S. A.; Fabrycky, D.; Fischer, D. A.; et al. (April 2016). "Planet Hunters IX. KIC 8462852 – where's the flux?". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 457 (4): 3988–4004. arXiv:1509.03622. Bibcode:2016MNRAS.457.3988B. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw218.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Pecaut, Mark J.; Mamajek, Eric E. (September 2013). "Intrinsic Colors, Temperatures, and Bolometric Corrections of Pre-main-sequence Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 208 (1). 9. arXiv:1307.2657. Bibcode:2013ApJS..208....9P. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/208/1/9.
- ^ a b c d e Andersen, Ross (13 October 2015). "The Most Mysterious Star in Our Galaxy". The Atlantic. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ Grush, Loren (16 October 2015). "Why it's so hard for astronomers to discuss the possibility of alien life". The Verge. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f Clavin, Whitney; Johnson, Michele (24 November 2015). "Strange Star Likely Swarmed by Comets". NASA. Retrieved 24 November 2015.
- ^ Griffin, Andrew (25 November 2015). "Star that could have 'alien megastructure' around it is almost certainly covered by a swarm of comets, Nasa says". The Independent. Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ^ a b Bodman, Eva H. L.; Quillen, Alice (27 November 2015). "KIC 8462852: Transit of a Large Comet Family". arXiv:1511.08821 [astro-ph.EP].
- ^ Kaplan, Sarah (15 October 2015). "The strange star that has serious scientists talking about an alien megastructure". The Washington Post. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ a b c Aron, Jacob (18 September 2015). "Citizen scientists catch cloud of comets orbiting distant star". New Scientist. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ a b c d e Plait, Phil (14 October 2015). "Did Astronomers Find Evidence of an Alien Civilization? (Probably Not. But Still Cool.)". Slate. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ a b "Looking For Deliberate Radio Signals From KIC 8462852". 5 November 2015. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- ^ a b "Looking for Deliberate Radio Signals from KIC 8462852" (Press release). The SETI Institute. 5 November 2015. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ^ a b Harp, G. R.; Richards, Jon; Shostak, Seth; Tarter, J. C.; Vakoch, Douglas A.; et al. (5 November 2015). "Radio SETI Observations of the Anomalous Star KIC 8462852". arXiv:1511.01606 [astro-ph.EP].
- ^ a b Schuetz, Marlin; Vakoch, Douglas A.; Shostak, Seth; Richards, Jon (8 December 2015). "Optical SETI Observations of the Anomalous Star KIC 8462852". arXiv:1512.02388 [astro-ph.EP]. Submitted to The Astrophysical Journal Letters
- ^ Schuetz, Marlin; Vakoch1, Douglas A.; Shostak, Seth; Richards, Jon (24 June 2016). "Optical SETI Observations of the Anomalous Star KIC 8462852" (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 825 (1). Retrieved 30 November 2016.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Scaringi, S.; Manara, C. F.; Barenfeld, S. A.; Groot, P. J.; Isella, A.; et al. (December 2016). "The peculiar dipping events in the disk-bearing young-stellar object EPIC 204278916". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 463 (2): 2265–2272. arXiv:1608.07291. Bibcode:2016MNRAS.463.2265S. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2155.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Nowakowski, Tomasz (30 August 2016). "Irregular dimming of a young stellar object investigated by astronomers". Phys.org. Retrieved 5 September 2016.
- ^ Wenz, John (9 February 2016). "NASA's Next Great Telescope Will Settle This Alien Megastructure Mystery For Good". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ^ Wright, Jason T. (30 August 2016). "What Could Be Going on with Boyajian's Star? Part I". Pennsylvania State University. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ^ a b c d Wright, Jason (15 October 2015). "KIC 8462852: Where's the Flux?". AstroWright. Pennsylvania State University. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ Newsome, John (16 October 2015). "Space anomaly gets extraterrestrial intelligence experts' attention". CNN News. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ "Discovery of a strange star could mean alien life". Fox News. 15 October 2015. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ a b c King, Bob (16 October 2015). "What's Orbiting KIC 8462852 – Shattered Comet or Alien Megastructure?". Universe Today. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ Strom, Marcus (15 October 2015). "It's either aliens or a swarm of comets: scientists baffled by WTF 001, our galaxy's strangest star". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ "KIC10 Search Results". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 16 October 2015.
- ^ a b Sinnott, Roger W. (2010). Sky & Telescope's Pocket Sky Atlas (3rd ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Publishing. ISBN 978-1-931559-31-7.
- ^ Masi, Gianluca (16 October 2015). "KIC 8462852: A star and its secrets". The Virtual Telescope Project 2.0. Retrieved 22 October 2015.
- ^ a b Aron, Jacob (15 January 2016). "Comets can't explain weird 'alien megastructure' star after all". New Scientist. Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- ^ a b Schaefer, Bradley E. (13 January 2016). "KIC 8462852 Faded at an Average Rate of 0.165+-0.013 Magnitudes Per Century From 1890 To 1989". arXiv:1601.03256 [astro-ph.SR].
- ^ a b Hippke, Michael; Angerhausen, Daniel (8 February 2016). "KIC 8462852 did likely not fade during the last 100 years". arXiv:1601.07314v2 [astro-ph.EP].
- ^ "TYC 3162-665-1". SIMBAD. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ "Hipparcos". European Space Agency. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ "About 2MASS". California Institute of Technology. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ "USNO CCD Astrograph Catalog (UCAC)". United States Naval Observatory. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ Clavin, Whitney; Harrington, J. D. (14 March 2012). "NASA Releases New WISE Mission Catalog of Entire Infrared Sky". NASA. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ "Kepler: FAQ". NASA. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ Michael, George (January 2016). "The Great ET Paradox: Why We are Likely to Find Them Before They Find Us". Skeptic. 21 (1): 16–18.
- ^ Montet, Benjamin T.; Simon, Joshua D. (3 August 2016). "KIC 8462852 Faded Throughout the Kepler Mission". arXiv:1608.01316 [astro-ph].
- ^ a b c Rzetelny, Xaq (16 October 2015). "Something—we're not sure what—is radically dimming a star's light". Ars Technica. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ^ Siegel, Ethan (16 October 2015). "No, Astronomers Probably Haven't Found 'Alien Megastructures'". Forbes. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ^ a b c Lisse, Carey; Sitko, Michael; Marengo, Massimo (December 2015). "IRTF/SPeX Observations of the Unusual Kepler Light Curve System KIC8462852". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 815 (2). L27. arXiv:1512.00121. Bibcode:2015ApJ...815L..27L. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/815/2/L27.
- ^ a b c d Wright, Jason T.; Cartier, Kimberly M. S.; Zhao, Ming; Jontof-Hutter, Daniel; Ford, Eric B. (January 2016). "The Ĝ Search for Extraterrestrial Civilizations with Large Energy Supplies. IV. The Signatures and Information Content of Transiting Megastructures". The Astrophysical Journal. 816 (1). 17. arXiv:1510.04606. Bibcode:2016ApJ...816...17W. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/816/1/17.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Laker, Chris (16 October 2015). "'Alien megastructure' may explain light patterns from 'bizarre' star, say scientists". BT.com. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ^ Marengo, Massimo; Hulsebus, Alan; Willis, Sarah (November 2015). "KIC 8462852: The Infrared Flux". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 814 (1). L15. arXiv:1511.07908. Bibcode:2015ApJ...814L..15M. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/814/1/L15.
- ^ a b Fecht, Sarah (13 October 2015). "Have We Detected Megastructures Built By Aliens Around A Distant Star? Or Just A Cloud Of Comets? Scientists Want To Investigate Further". Popular Science. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ Thompson, M. A.; Scicluna, P.; Kemper, F.; Geach, J. E.; Dunham, M. M.; et al. (May 2016). "Constraints on the circumstellar dust around KIC 8462852". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters. 458 (1): L39–L43. arXiv:1512.03693. Bibcode:2016MNRAS.458L..39T. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slw008.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Good night, sleep tight: Advanced alien civilisations rare or absent in the local Universe" (Press release). ASTRON. 15 September 2015. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ Williams, Lee (15 October 2015). "Astronomers may have found giant alien 'megastructures' orbiting star near the Milky Way". The Independent. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ Jones, Morris (November–December 2015). "Reconsidering macro-artefacts in SETI searches". Acta Astronautica. 116: 161–165. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.07.011.
- ^ O'Neill, Ian (14 October 2015). "Has Kepler Discovered an Alien Megastructure?". Discovery.com. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- ^ a b Siemion, Andrew (29 September 2015). "Prepared Statement by Andrew Siemion – Hearing on Astrobiology". House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology. SpaceRef.com. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ Kramer, Miriam (18 October 2015). "Scientists have not actually found an alien megastructure orbiting a distant star". Mashable. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- ^ Gregg, Trevor A.; Prsa, A.; Welsh, W. F.; Orosz, J. A.; Fetherolf, T. (January 2013). A Syzygy of KIC 4150611. 221st Meeting of the American Astronomical Society. 6-10 January 2013. Long Beach, California. 142.12. Bibcode:2013AAS...22114212G.
- ^ Orwig, Jessica (15 October 2015). "We spoke with some of the astronomers who discovered the 'alien' megastructure to find out if it's fact or fiction". Business Insider.
- ^ Wall, Mike (28 October 2015). "'Alien Megastructure' Mystery May Soon Be Solved". Space.com. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ^ Mack, Eric (17 October 2015). "The story behind 'alien megastructures' scientists may have found (but probably didn't)". CNET. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ Fecht, Sarah (16 June 2016). "'Alien Megastructure' Star Kickstarter Just Met Its Goal". Popular Science. Retrieved 16 June 2016.
- ^ Wall, Mike (19 October 2015). "Search For Intelligent Aliens Near Bizarre Dimming Star Has Begun". Space.com. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ Orwig, Jessica (23 October 2015). "Scientists are days from finding out if that mysterious star could actually harbor aliens". Business Insider.
- ^ Harp, G. R.; Richards, Jon; Shostak, Seth; Tarter, J. C.; Vakoch, Douglas A.; Munson, Chris (July 2016). "Radio SETI Observations of the Anomalous Star KIC 8462852". The Astrophysical Journal. 825 (2). 155. arXiv:1511.01606. Bibcode:2016ApJ...825..155H. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/825/2/155.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Abeysekara, A. U.; Archambault, S.; Archer, A.; Benbow, W.; Bird, R.; et al. (February 2016). "A Search for Brief Optical Flashes Associated with the SETI Target KIC 8462852". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 818 (2). L33. arXiv:1602.00987. Bibcode:2016ApJ...818L..33A. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/818/2/L33.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Wall, Mike (22 August 2016). "Alien Megastructure? 'Tabby's Star' Continues to Baffle Scientists". Space.com. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
- ^ "Dish to listen for ET around strange star". BBC.com. 26 October 2016. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
External links
- Kepler light curve data at STScI.edu
- "The Most Mysterious Star in the Universe" on YouTube, a TED Talk by Tabetha Boyajian