Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christians
| Languages | |
|---|---|
| Vernacular: Lebanese Arabic | |
| Religion | |
| Christianity (Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch) |

Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christians (Arabic: المسيحية الأرثوذكسية الرومية في لبنان) refers to Lebanese people who are adherents of the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch in Lebanon, which is an autocephalous Greek Orthodox Church within the wider communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, and is the second largest Christian denomination in Lebanon after the Maronite Christians.
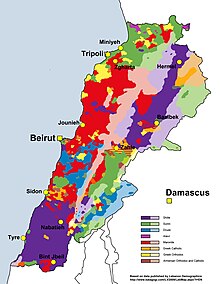
Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christians are believed to constitute about 8% of the total population of Lebanon.[1][2][3] Most of the Greek Orthodox Christians live either in the capital city of Beirut, the Metn hinterland, the Hasbayya and Rashayya districts in the southeast, and the North Governorate, in the Koura region (south of Tripoli) and Akkar.
Under the consensus of the unwritten agreement known as the National Pact among the different political leaders of Lebanon, the Deputy Speaker of Parliament and the Deputy Prime Minister in Lebanon are assumed to be Greek Orthodox Christians.[4]
History
The Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch adheres to the Eastern Orthodox Church, which is composed of several autocephalous jurisdictions united by common doctrine and by their use of the Byzantine rite. They are the second largest Christian denomination within Christianity in Lebanon. Historically, these churches grew out of the four Eastern Patriarchates (Jerusalem, Antioch, Alexandria, and Constantinople) of the original five major episcopal sees (the Pentarchy) of the Roman Empire which included Rome. The final split between Rome and the Eastern Churches, who came to oppose the views and claims of the Popes of Rome, took place in 1054. From that time, with the exception of a brief period of reunion in the fifteenth century, the Eastern Churches have continued to reject the claims of the Patriarchate of Rome (the Catholic Church) to universal supremacy and have rejected the concept of papal infallibility. Doctrinally, the main point at issue between the Eastern and Western Churches is that of the procession of the Holy Spirit and there are also divergences in ritual and discipline.
The Greek Orthodox include many free-holders, and the community is less dominated by large landowners than other Christian denominations. In present-day Lebanon, Eastern Orthodox Christians have become increasingly urbanized, and form a major part of the commercial and professional class of Beirut and other cities. Many are found in the Southeast (Nabatieh/Beqaa) and North, near Tripoli. They are highly educated and well-versed in finance. The Greek Orthodox church has become known in the past for its pan-Arab orientation, possibly because it exists in various parts of the Arab world. The Greek Orthodox church has often served as a bridge between Lebanese Christians and the Arab countries.
Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christians have a long and continuous association with Eastern Orthodox Churches in European countries like Greece, Cyprus, Russia, Ukraine, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Romania. The church exists in many parts of the Arab world and Greek Orthodox Christians have often been noted for pan-Arab or pan-Syrian leanings; historically, it has had less dealings with Western countries than the Maronite Church. The Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christians are believed to constitute about 8% of the total population of Lebanon,[2][3] including the Palestinian Greek Orthodox community, many of whom have been given Lebanese citizenship.
Greek Orthodox Christians support a variety of political parties and factions, including non-sectarian parties such as the Syrian Social Nationalist Party, the Lebanese Communist Party, and the Democratic Left Movement; and mostly Christian parties such as the Free Patriotic Movement, the Marada Movement, the Lebanese Forces, and the Kataeb.
Greek Orthodox Christian settlements
In Lebanon, the Greek Orthodox Christians are found in Beirut, the Southeast (Nabatieh/Beqaa) and North, near Tripoli, Koura, and also in Akkar, Batroun, Matn, Aley, Zahlé, Miniyeh-Danniyeh, Hasbaya, Baabda, Marjeyoun, Tripoli, Rashaya, Jbeil, and Zgharta.
Cities and towns with a majority Greek Orthodox population in Lebanon
Achrafieh, Amioun, Kousba, Anfeh, Deddeh, Kfaraakka, Aaba, Afsdik, Bdebba, Batroumine, Bishmizzine, Btourram, Bkeftine, Bsarma, Btaaboura, Charbila, Darchmezzine, Fih, Kaftoun, Kelhat, Kfarhata, Kfarhazir, Kfarsaroun, Ras Maska, Miniara, Cheikh Mohammad, Zawarib, Hamat, Douma, Dhour El Choueir, Bteghrine, Mansourieh, Broummana, Kafarakab, Bhamdoun, Souk El Gharb, Marjayoun, Deir Mimas, Rachaya Al Foukhar, Aita al-Foukhar, Jeddayel, Mounsif, Chikhane, Gharzouz, Bekhaaz, Berbara and others.
Cities and towns with an important Greek Orthodox minority
Ras Beirut, Tripoli, El Mina, Chekka, Bourj Hammoud, Zahleh, Halba, Batroun, Bikfaya, Baskinta, Antelias, Ras el Matn, Aley, Bechamoun, Machgara, Hasbaya, Kfeir, Niha Bekaa, Rit, and others.
Achrafieh was once ruled by seven prominent Greek Orthodox Christian families that formed Beirut's High Society for centuries: Trad, Geday, Fernaine, Araman, Bustros, Sursock, Fayyad, and Tueini.
Notable Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christians
- Lydia Canaan – singer-songwriter poet, humanitarian, activist, and pioneering first rock star of the Middle East
- Farid Makari – politician, former Lebanese Minister, Member of Parliament, Deputy Speaker of the Lebanese Parliament
- Charles Debbas – former President (1926–1934)
- Marcos Baghdatis – tennis player
- Charles Malik – former President of the United Nations General Assembly and Minister of Foreign Affairs
- Antoun Saadeh – philosopher and founder of the Syrian Social Nationalist Party
- Antoine Andraos – politician and a vice-president of the Movement of the Future
- Elias Murr – former Deputy Prime Minister
- Michel Murr – former Deputy Prime Minister
- Michel Sassine – former Lebanese Minister, Member of Parliament, Deputy Speaker of Parliament, and Deputy Prime Minister
- Mounir Abou Fadel – Member and Vice Speaker of the Lebanese Parliament
- George Antonius – author and diplomat, pioneering historian of Arab nationalism
- Moukheiber Al Ashkar – journalist
- George N. Atiyeh – librarian and scholar
- Souha Bechara – resistance fighter and member of the Lebanese Communist Party
- Yousef Beidas – banker
- Gabrielle Bou Rached – model and actress
- Elie Frizli – politician
- Fawaz Gerges – professor and author
- Farid Habib – member of the Lebanese Forces party
- Nicolas Hayek – entrepreneur, co-founder, CEO and Chairman of the Board of the Swatch Group
- Saint Joseph of Damascus – priest and educator who was canonized as a saint in 1993
- Samir Kassir – professor of history at Saint-Joseph University, journalist and a prominent leftist political activist
- Wehbe Katicha – politician and former general in the Lebanese Army
- Elias Khoury – novelist, playwright, critic, and a prominent public intellectual
- Giselle Khoury – talk show host on the Al Arabiya news channel
- Jacobo Majluta Azar – former President of the Dominican Republic
- Mikhail Mishaqa – first historian of modern Ottoman Syria
- Tarek Mitri – scholar and independent politician
- Samir Mouqbel – Deputy Prime Minister of Lebanon
- Ibrahim Najjar – lawyer and politician
- Octavia Nasr – journalist who covers Middle-Eastern affairs
- Mona Ofeich – politician
- Assi Rahbani – composer, musician, and producer
- Ziad Rahbani – producer, lyricist, composer, arranger, orchestra conductor, pianist, and singer
- Mansour Rahbani – composer, musician, poet, and producer
- Raphael of Brooklyn – first Orthodox bishop to be consecrated in North America
- Salim Saade – politician and member of the Syrian Social Nationalist Party
- Christina Sawaya – beauty queen
- Lady Cochrane Sursock – philanthropist, a prominent public figure, and an advocate of the arts in Lebanon
- Nassim Nicholas Taleb – essayist and scholar whose work focuses on problems of randomness, probability, and uncertainty
- Petro Trad – lawyer, politician, and former President of the French Mandate of Lebanon for a brief period (22 July 1943 – 21 September 1943)
- Gebran Tueni (journalist) – journalist and a figure of the Arab Renaissance
- Ghassan Tueni – veteran journalist, politician, and diplomat who headed An Nahar, one of the Arab World's leading newspapers
- Nayla Tueni – journalist and politician
- Karim Azkoul – diplomat and philosopher
- Jad Azkoul – musician
Gallery
-
Saint George Orthodox Cathedral in Downtown Beirut
-
The St. Georges Greek-Orthodox Cathedral on Nejme Square
See also
- Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Beirut
- Arab Orthodox
- Antiochian Greek Christians
- Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch
- Eastern Orthodox Church
- Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral, Beirut
- Religion in Lebanon
- Christianity in Lebanon
- Roman Catholicism in Lebanon
- Lebanese Maronite Christians
- Lebanese Melkite Christians
- Lebanese Protestant Christians
- Demographics of Lebanon
- Freedom of religion in Lebanon
- Eastern Orthodoxy in Syria
- Eastern Orthodoxy in Jordan
- Eastern Orthodoxy in Jordan
- Eastern Orthodoxy in Israel
- Eastern Orthodoxy in Saudi Arabia
- University of Balamand
- Lebanese Shi'a Muslims
- Lebanese Sunni Muslims
- Lebanese Druze
References
- ^ "Minority Rights Group International – working to secure the rights of minorities and indigenous peoples".
- ^ a b Lebanon – International Religious Freedom Report 2010 U.S. Department of State. Retrieved on 14 February 2010.
- ^ a b Lebanon – July–December, 2010 International Religious Freedom Report U.S. Department of State. Retrieved on 1 June 2012.
- ^ Harb, Imad (March 2006). "Lebanon's Confessionalism: Problems and Prospects". USIPeace Briefing. United States Institute of Peace. Archived from the original on 9 July 2008. Retrieved 20 January 2009.