Opposition to the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021)
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Opposition to the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) stems from numerous factors, including the view that the United States invasion of Afghanistan was illegal under international law and constituted an unjustified aggression, the view that the continued military presence constitutes a foreign military occupation, the view that the war does little to prevent terrorism but increases its likelihood, and views on the involvement of geo-political and corporate interests. Also giving rise to opposition to the war are civilian casualties, the cost to taxpayers, and the length of the war to date.
Disputed legality of the US invasion
[edit]
Opponents of the war[who?] have claimed that the attack on Afghanistan was illegal under international law, constituted unjustified aggression and would lead to the deaths of many civilians through the bombing campaign and by preventing humanitarian aid workers from bringing food into the country. By one estimate, around 5,000 Afghan civilians had been killed within just the first three months of the U.S. invasion.[1][2]
More broadly, the invasion of Afghanistan appeared to opponents to be a stepping stone to the 2003 Iraq War, increasing the geo-political reach of the United States:
The UN Charter is a treaty ratified by the United States and thus part of US law. Under the charter, a country can use armed force against another country only in self-defense or when the Security Council approves. Neither of those conditions was met before the United States invaded Afghanistan. The Taliban did not attack us on 9/11. Nineteen men – 15 from Saudi Arabia – did, and there was no imminent threat that Afghanistan would attack the US or another UN member country. The council did not authorize the United States or any other country to use military force against Afghanistan. The US war in Afghanistan is illegal.
— Marjorie Cohn, professor at Thomas Jefferson School of Law, president of the National Lawyers Guild[3]
Involvement in an Afghan civil war
[edit]Opposition also stems from the view that the US-led military forces are taking sides in an ongoing civil war in Afghanistan between its ethnic groups, backing minority Tajiks and Uzbeks against the Pashtun majority of Afghanistan.[4][5]
Several weeks into a massive US-led military offensive against the Taliban in four southern Afghan provinces in 2006, Afghan President Hamid Karzai spoke against the killing of so many Afghan citizens:[6]
It is not acceptable for us that in all this fighting, Afghans are dying. In the last three to four weeks, 500 to 600 Afghans were killed. [Even] if they are Taliban, they are sons of this land.
— Afghan President Hamid Karzai on June 22, 2006[7]
According to journalist Ahmed Rashid, the noted author of several books on Afghanistan, the Taliban are in the fabric of that country, and defeating the Taliban would involve killing "large numbers of Pashtuns", an ethnic group with a long history in southeastern Afghanistan.[8]
Afghan civilian opposition to the invasion
[edit]One of the best-known women's organization in Afghanistan, the Revolutionary Association of the Women of Afghanistan (RAWA), condemned the US invasion of Afghanistan, stating that "America ... has launched a vast aggression on our country".
They accused the US and its allies of "paying the least attention to the fate of democracy in Afghanistan" by first having supported for years a "Jehadis-fostering, Osama-fostering and Taliban-fostering" policy before the 2001 US invasion, only to now be "sharpening the dagger of the Northern Alliance" warlords and drug lords that were key allies of the U.S. in its invasion.[7][9]
Our people have been caught in the claws of the monster of a vast war and destruction. ... The continuation of US attacks and the increase in the number of innocent civilian victims not only gives an excuse to the Taliban, but also will cause the empowering of the fundamentalist forces in the region and even in the world.
— RAWA, Afghan women fighting for human rights and for social justice in Afghanistan, October 11, 2001[7]
Afghan civilian casualties
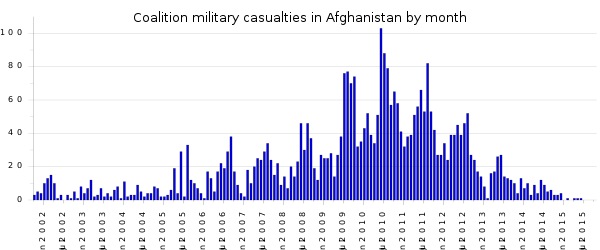
[edit]Coalition military casualties
[edit]The continued and mounting death tolls of foreign military forces in the decade-long war are another factor involved in the opposition to the war in Afghanistan, with hundreds currently dying per year. By October 2011, the 10th anniversary of the U.S. invasion, over 2,750 foreign soldiers had been killed in the war in Afghanistan.[10][11][12]
International public opinion
[edit]International public opinion was largely opposed to the war in Afghanistan. Polls around the world – including a 47-nation global survey in 2007, a 24-nation survey in 2008, both a 25-nation survey and a 13-nation survey in 2009, and a 22-nation survey in 2010 – have repeatedly shown considerable opposition to the presence of US and NATO military troops in Afghanistan.[14][15][16][17]
While support for the war in Afghanistan has been strongest in the United States and Israel,[18][19] recent polls have shown growing American opposition to the U.S. war, including majority opposition:
- September 2009 – United States: Growing American opposition to the war in Afghanistan reached an all-time high, while support for the U.S. war fell to an all-time low in September. A record majority 58% of Americans now oppose the war in Afghanistan, while only 39% support the U.S. war. The CNN – Opinion Research poll was conducted September 11–13, 2009.[20]
- September 2009 – United States: "Americans are broadly skeptical of President Obama's contention that the war in Afghanistan is necessary for the war against terrorism to be a success, and few see an increase in troops as the right thing to do." The plurality 42% of Americans want a reduction of the number of U.S. troops in Afghanistan. Only 26% of Americans think more troops should be sent to Afghanistan. 51% of Americans think the war is not worth fighting, while 46% think it is. Fewer than half of Americans think winning the war in Afghanistan is necessary to win the "war on terrorism", with about as many saying it is not. The Washington Post – ABC News poll was conducted September 10–12, 2009.[21][22]
If Americans pulled back and started paying attention to this war, it would become even less popular.
— A senior advisor to US General Stanley McChrystal, from the June 2010 article that resulted in his dismissal as commander of all foreign military forces in Afghanistan.[23][24]
International protests against the war
[edit]The ongoing decade-long War in Afghanistan has repeatedly been the subject of large protests around the world, with the first large-scale demonstrations beginning in the days leading up to the war's official launch on October 7, 2001 as US "Operation Enduring Freedom".
Foreign military occupation
[edit]If the populations of Afghanistan and the NATO countries were able to vote on this military occupation it could not continue indefinitely, and peace would finally be within reach.
In January 2009, an independent analysis by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace in Washington, D.C. claimed that "the majority of Afghans are now deeply opposed to the foreign troops on their soil" and that the presence of a foreign force in Afghanistan is the single most important factor behind the Afghan insurgency.[5][26][27] However, according to a May 2009 BBC poll, 69% of Afghans surveyed thought it was at least mostly good that the U.S. military came into remove the Taliban[28] and in a June 2009 Gallup survey found that about half of Afghan respondents felt that additional U.S. forces would help stabilize the security situation.[29]
On October 8, 2009, in a New York Times interview initiated by the White House, a senior White House official described the Afghan Taliban as an indigenous Afghan group that want to win back territory within their own country. The White House comment had come a day after the Taliban reasserted that their aim is "the obtainment of independence".[30]
Foreign military raids of Afghan homes
[edit]A key and long-standing point of opposition to the war in Afghanistan has been the constant raids of Afghan homes by foreign military forces that have persisted despite long-repeated pleas and protests by the Afghan government.[31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38]
In a visit to Washington in May 2005, Afghan President Hamid Karzai asked U.S. President George W. Bush to let the Afghan government have authority over house search operations regularly conducted by the U.S.-led foreign military forces in his country. Bush rejected the Afghan president's request.[33]
In September 2005, Karzai again tried asking the US-led military forces for changes, saying: "Going into the Afghan homes – searching Afghan homes without the authorization of the Afghan government – is something that should stop now. No coalition forces should go into Afghan homes without the authorization of the Afghan government."[33]
By the spring of 2006, mounting anger over the foreign military raids of Afghan homes, and accusations of foreign troops molesting women during the forced searches, helped prompt Afghan religious leaders to begin calling for armed resistance.[34]
In a December 2008 speech, Afghan President Hamid Karzai said that in the previous month he had again asked that the U.S. military in his country cooperate with his government, sending the U.S. government a list of demands about troop conduct in his country: "Part of that list was that they shouldn't, on their own, enter the houses of our people and bombard our villages and detain our people." He gave no indication of having received any response back from the U.S.[35]
In November 2010, he yet again repeated his protest during a Washington Post interview: "The raids are a problem always. They were a problem then, they are a problem now. They have to go away. The Afghan people don't like these raids, if there is any raid it has to be done by the Afghan government within the Afghan laws. This is a continuing disagreement between us."[36]
Destruction of Afghan homes and crops
[edit]In 2010, US-led offensives inflicted more than $100 million in damage to Afghan homes and fruit crops in southern Kandahar province, according to an Afghan government report in January 2011. The government delegation led by President Hamid Karzai's advisor said that the foreign military forces had inflicted unreasonable damage and caused the displacement of many people.[38][39]
Two months earlier, in November 2010, the Afghan Rights Monitor (ARM), a human rights group, also reported widespread damage of Afghan homes in the same three districts, Arghandab, Zhari, and Panjwai, where tens of thousands of foreign forces had been carrying out military offensives over the past year.[38][39]
Rejection of the terrorism argument
[edit]A Washington Post – ABC News poll in September 2009 reported that "Americans are broadly skeptical of President Obama's contention that the war in Afghanistan is necessary for the war against terrorism to be a success." Fewer than half of Americans think winning the war in Afghanistan is necessary to win the "war on terrorism", with about as many saying that it is not.[21]
A decade into the war, the Pew Research Center reported in September 2011 that the majority 75% of Americans do not think the war in Afghanistan has lessened the risk of terrorism in their country, and only a minority 25% thought it had. Far more Americans, the plurality 37%, think the U.S. war in Afghanistan has in fact increased the likelihood of terrorist attacks in the U.S.[40][41]
A poll at the end of August 2009 found that three-quarters of Britons do not think fighting in Afghanistan makes British people, or British streets, any safer from terrorism, as Gordon Brown and senior ministers repeatedly told them to justify the war.[42]
About a week and a half later, British member of parliament Eric Joyce, a former army major, resigned as aide to Defence Secretary Bob Ainsworth, saying "I do not think the public will accept for much longer that our losses can be justified by simply referring to the risk of greater terrorism on our streets."
In 2004, Jack Cloonan, a 25-year veteran of the FBI who served between 1996 and 2002 on the joint CIA-FBI task force that tracked bin Laden, said the number of people in Al Qaeda was "minuscule". A membership list found near Kabul in 2001 during the US invasion of Afghanistan, and obtained by the task force, showed there had been a grand total of 198 members in the organization.[43]
With the US invasion of Afghanistan in 2001, al Qaeda elements moved to Pakistan and other countries.[43][44][45]
The al Qaeda presence [in Afghanistan] is very diminished. The maximum estimate is less than 100 operating in the country, no bases, no ability to launch attacks on either us or our allies.
On October 8, 2009, in a New York Times interview initiated by the White House, a senior White House official acknowledged that there are fewer than 100 al-Qaida fighters left in Afghanistan and that the Afghan Taliban, an indigenous Afghan group seeking to win back territory within their own country, do not themselves pose a direct security threat to the United States. He said: "When the two are aligned, it's mainly on the tactical front."[30]
The comments were made a day after the Taliban asserted that it did not pose a direct threat to the United States. The Taliban stated that their aim was "obtainment of independence and establishment of an Islamic system" in their country, and not to attack the West. "We did not have any agenda to harm other countries, including Europe, nor do we have such agenda today."[30]
On June 27, 2010, CIA Director Leon Panetta revealed that there were possibly fewer than 50 members of Al Qaeda, and at most 100, in Afghanistan.[45]
... The estimate on the number of Al Qaeda [in Afghanistan] is actually relatively small. At most, we're looking at 50 to 100, maybe less. ... There's no question that the main location of Al Qaeda is in the tribal areas of Pakistan.
In January 2009, an independent analysis by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace in Washington, D.C. dismissed the argument that a withdrawal of the foreign military presence would allow al-Qaeda to operate in Afghanistan, pointing out that, first, the US-led military forces do not control the periphery of the Afghan territory anyway, and, second, that targeted operations with the agreement of the Kabul government could be used instead.[26]
Others have also made the point that al-Qaeda operates in many other countries and simply does not need Afghanistan. The New York Times reported in November 2008 that a 2004 classified order identified at least 15 to 20 other countries outside of Afghanistan and Iraq where al-Qaeda militants were believed to be operating or to have sanctuary. The countries listed in the secret order signed by US Defense Secretary Donald H. Rumsfeld with the approval of US President George W. Bush included Syria, Pakistan, Yemen, Saudi Arabia and several other Persian Gulf states. Since 2004, the United States has repeatedly used the broad, secret authority granted by that order to conduct targeted operations against al-Qaeda and other militants in many countries outside of Afghanistan, including Somalia, Ethiopia, Syria, Pakistan, Yemen, Kenya, the Philippines, and elsewhere.[47][48][49][50][51]
If U.S. forces are there to prevent reestablishment of al-Qaeda bases – evidently there are none now – must there be nation-building invasions of Somalia, Yemen and other sovereignty vacuums?
— Conservative pundit George Will, September 1, 2009[52]
In an influential September 2009 article entitled "Time to Get Out of Afghanistan", conservative commentator George Will similarly argued that "forces should be substantially reduced", and "America should do only what can be done from offshore, using intelligence, drones, cruise missiles, airstrikes and small, potent Special Forces units" in targeted operations.[52]
U.S. Vice President Joe Biden and a number of other senior administration officials also favor moving toward a more scaled-back strategy that focuses on targeted, surgical operations against senior insurgent figures using drones and small special operations teams.[53][54][55][56]
Others have further made the point that al-Qaeda does not need a safe haven at all, and that terrorists can and have learned their craft in a Hamburg apartment, a home in Colorado, a flight school in Florida, or myriad other places around the world.[5][57][58]
As noted military historian Gwynne Dyer pointed out, "The 9/11 attacks were not planned in Afghanistan. They were planned by al Qaeda operatives in Germany and Florida, and it is very unlikely that the Taleban government of Afghanistan had advance warning of them."[58]
In his September 10, 2009 letter of resignation as the State Department's Senior Civilian Representative in Zabul Province, Afghanistan, in protest against the American war in Afghanistan, Matthew Hoh, a former U.S. Marine captain, stated:
I find specious the reasons we ask for bloodshed and sacrifice from our young men and women in Afghanistan. If honest, our stated strategy of securing Afghanistan to prevent al-Qaeda resurgence or regrouping would require us to additionally invade and occupy western Pakistan, Somalia, Sudan, Yemen, etc. ... The September 11th attacks, as well as the Madrid and London bombings, were primarily planned and organized in Western Europe; a point that highlights the threat is not one tied to traditional geographic or political boundaries.
— former U.S. Marine captain and State Department official Matthew Hoh, September 10, 2009[59]
In a September 16, 2009 Washington Post article, Paul R. Pillar, deputy chief of the counterterrorist center at the CIA from 1997 to 1999 and director of graduate studies at Georgetown University's Security Studies Program, questioned the assumption that al-Qaeda or other terrorist groups need a haven at all, pointing out that "terrorists' organizations have become more network-like, not beholden to any one headquarters."[5][60]
In a September 30, 2009 open letter to President Obama, foreign policy veteran William R. Polk stated: "Since terrorist attacks can be mounted from many places, the only effective long-term defense against them is to deal with their causes."[61]
The Al Qaeda network today also comprises semi-autonomous or self radicalized actors, who often have only peripheral or ephemeral ties to either the core cadre in Pakistan or affiliated groups elsewhere. According to U.S. officials Al Qaeda cells and associates are located in over 70 countries.
— Congressional Research Service report, February 5, 2010[44]
When asked by Bob Woodward why al-Qaeda, which is comparatively safe in its current sanctuaries in Pakistan, would even want to return to Afghanistan, the National Security Adviser of the United States, General James L. Jones, replied, "That's a good question. ... This is certainly one of the questions that we will be discussing. This is one of the questions, for example, that one could come back at with General McChrystal."[62]
Creating and training insurgents
[edit]According to the Carnegie report, the insurgency against the foreign military forces would abate with the removal of foreign troops from Afghanistan, and "the momentum of the Taliban would slow or stop altogether, because without a foreign occupier the Jihadist and nationalist feelings of the population would be much more difficult to mobilize."[26]
The Pew Research Center reported in February 2009: "As has been the case since 2006, more Americans believe decreasing – rather than increasing – the U.S. military presence abroad is the more effective way to reduce the threat of terrorist attacks on the United States. Half of Americans (50%) now believe that decreasing the U.S. military presence overseas would be the more effective policy, while just 31% say an increased presence would be more effective."[63]
The bulk of the insurgency fights not for the white banner of the Taliban, but rather against the presence of foreign soldiers and taxes imposed by an unrepresentative government in Kabul.
— former U.S. Marine captain and State Department official Matthew Hoh, September 10, 2009[59]
In his September 10, 2009 letter resigning over the American war in Afghanistan, which he had come to believe simply fueled the insurgency, Matthew Hoh, the State Department's Senior Civilian Representative in Zabul Province, wrote: "The Pashtun insurgency, which is composed of multiple, seemingly infinite, local groups, is fed by what is perceived by the Pashtun people as a continued and sustained assault, going back centuries, on Pashtun land, culture, traditions and religion by internal and external enemies. The U.S. and NATO presence and operations in Pashtun valleys and villages, as well as Afghan army and police units that are led and composed of non-Pashtun soldiers and police, provide an occupation force against which the insurgency is justified."[59][64][65]
As with the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, he advised that the U.S. reduce its combat forces in Afghanistan, if not remove them entirely.[65][66]
In a statement made to New York Times columnist Nicholas Kristof, a group of former intelligence officials and other experts decided to go public with their concerns and warned:[67]
Our policy makers do not understand that the very presence of our forces in the Pashtun areas is the problem. ... The more troops we put in, the greater the opposition. We do not mitigate the opposition by increasing troop levels, but rather we increase the opposition and prove to the Pashtuns that the Taliban are correct. ... The basic ignorance by our leadership is going to cause the deaths of many fine American troops with no positive outcome.
— statement by a group of former U.S. intelligence officials and other experts, September 2009[67]
The group included Howard Hart, a former CIA station chief in Pakistan who helped organize the anti-Soviet insurgency in the 1980s; David Miller, a former ambassador and National Security Council official; William J. Olson, a counterinsurgency scholar at the National Defense University; and another CIA veteran who spent 12 years in the region, was station chief in Kabul at the time the Soviets invaded Afghanistan in 1979, and later headed the CIA's Counterterrorism Center.[67]
In the 2009 documentary "Rethink Afghanistan", several other former U.S. intelligence officials and experts on Afghanistan also contend that the war in Afghanistan does nothing to protect the safety of American people, but, on the contrary, only threatens the safety and security of Americans, both in the U.S. and abroad:[68]
Both wars have made the Middle East and the world much more dangerous for Americans and for any American presence overseas. It's creating much greater hostility towards the U.S. and creating a whole lot more people that would be happy to kill Americans or join in some kind of terrorist operation.
— Graham Fuller, former CIA station chief in Kabul, in "Rethink Afghanistan"[68][better source needed]
In his September 30, 2009 open letter to President Obama, foreign policy veteran William R. Polk argued that trying to defeat the Taliban militarily is not in America's interest, saying: "The harder we try, the more likely terrorism will be to increase and spread."[61]
According to the August 2010 report by the Afghanistan Study Group: "The current U.S. military effort is helping fuel the very insurgency we are attempting to defeat."[69]
Geo-political and corporate interests
[edit]The current war in Afghanistan is not about democracy, women's rights, education or nation building. Al-Qaida, the other excuse, barely exists. Its handful of members long ago decamped to Pakistan. The war really is about oil pipeline routes and western domination of the energy-rich Caspian Basin.
— Eric Margolis, defence analyst and journalist, August 2009[4]
Opposition to the war in Afghanistan often has at its core the view that the U.S. invasion, decade-long presence, and military build-up in Afghanistan are being conducted for geo-political purposes and U.S. corporate energy interests.[4][38][70]
Pipeline path 'clearing and holding' forces
[edit]In a June 2008 article in the Toronto Sun entitled "These wars are about oil, not democracy", defense analyst and journalist Eric Margolis remarked on the U.S. military bases happening to be adjacent to the planned pipeline route, and wrote: "Work will begin on the TAPI once Taliban forces are cleared from the pipeline route by U.S., Canadian and NATO forces. As American analyst Kevin Phillips writes, the U.S. military and its allies have become an 'energy protection force.'"[71][better source needed]
War in Afghanistan as a demonstration of U.S. military power
[edit]In a November 2, 2001 article entitled "US Bombs Are Boosting the Taliban", anti-Taliban Afghan leader Abdul Haq again presented the case he had repeatedly been making against U.S. military action in his country, but seemed resigned that the U.S. was not going to listen:[72]
The US is trying to show its muscle, score a victory and scare everyone in the world. They don't care about the suffering of the Afghans or how many people we will lose. And we don't like that. Because Afghans are now being made to suffer for these Arab fanatics, but we all know who brought these Arabs to Afghanistan in the 1980s, armed them and gave them a base. It was the Americans and the CIA. And the Americans who did this all got medals and good careers, while all these years Afghans suffered from these Arabs and their allies. Now, when America is attacked, instead of punishing the Americans who did this, it punishes the Afghans.
Thriving opium production since the invasion
[edit]
Opium production in Afghanistan has thrived since the U.S. invasion and overthrow of the Taliban government in 2001. According to United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) data, there was more opium poppy cultivation in each of the past five growing seasons (2004–2008), than in any one year during the Taliban five-year rule (1996–2001).[73][74]
UNODC reported in its November 2008 report that the majority 58% of opium poppy-growing farmers in Afghanistan began to cultivate opium after the 2001 U.S. invasion.[74]
In July 2000, the Taliban leader, Mullah Omar, argued that opium was against Islam and banned its cultivation. The Taliban edict, with the threat of jail for elders and mullahs who allowed its cultivation, resulted in a 90% reduction in opium cultivation between 2000 and 2001.[73][75]
Even compared to 2000 – the year before the Taliban opium ban of 2000–2001 saw effect – the overall opium-related income in the Afghan economy had risen nearly fourfold by 2008, reflecting higher export volumes as well as higher prices.[74]
Financial cost of the war to taxpayers and Western economies
[edit]By 2008, the U.S. military was spending nearly $100 million a day in Afghanistan.[76][77]
By one estimate in September 2009, the United States, which had approximately two-thirds of the foreign troops in Afghanistan, had already spent some $250 billion in Afghanistan since 2001.[78]
By October or November 2009, estimates by the Congressional Research Service placed the cost that could be accounted for at $300 billion spent or committed.[79]
The Congressional Research Service estimates that we have now spent or committed $300 billion, and that is only the money for which we can account. Some will say it is twice that, for this war, like the war in Iraq, was funded off-budget with no transparency. ... $300 billion. That is about $101 million per day for 2,950 days. Or, to put out another average, that is $3,947 per family of four that every American family has paid to date. ... To continue this war at its current level and to escalate it beyond its current scope is a trillion dollar question. Are those who would so cavalierly make this commitment willing to demand another $3,947.36 from every American family of four to pay for it? ... Thousands have protested federal spending to rebuild America's schools, roads, bridges and critical infrastructure, but are they willing to do the same when their taxes are being spent to rebuild Kabul?
— U.S. Congress Rep. Eric Massa, November 4, 2009[79]
In September 2009, the Christian Science Monitor reported that in the upcoming budget year, the U.S. war in Afghanistan would, for the first time, cost American taxpayers more than the U.S. war in Iraq. By the end of September 2010, the total military budget costs for both wars will have exceeded $1 trillion.[80]
By October 2009, news reports indicated U.S. costs of fighting the war in Afghanistan at $165 million every 24 hours.[81]
Officially, the United States' military costs for the war in Afghanistan were budgeted at $65 billion for fiscal 2010, a figure amounting to $178 million a day.[80]
However the true cost will probably be closer to $85 billion, or more, according to Gordon Adams, a defense expert at American University's School of International Service in Washington. That figure would amount to about $233 million a day.
Factoring in veteran health and other benefits, replenishment of military hardware, a higher price for oil, and the interest on debt incurred by the wars, Linda Bilmes, a Harvard University economist, and Joseph Stiglitz, a Columbia University Nobel Prize economist, estimated a "moderate-realistic" bill for the two wars of $5 trillion to U.S. taxpayers.[80]
In September 2009, foreign policy veteran William R. Polk suggested that the real cost of the war in Afghanistan to the U.S. economy would end up being over $3 trillion.[61]
In September 2009, the U.S. Congressional Budget Office estimated that a speedier withdrawal of U.S. troops from Afghanistan and Iraq, with a sharp reduction in troops over three years, could save taxpayers $1.1 trillion from the budget in the next decade.[82]
We've been there eight years already, and how many more years are we supposed to be there? How many more Americans are supposed to die? How many more tens and tens of billions of dollars are we supposed to be spending at a time when we have a record-breaking deficit?
In December 2009, U.S. President Barack Obama announced a surge of yet another thirty thousand U.S. troops into Afghanistan, increasing the buildup of the U.S. military in Afghanistan by another 40-45% and adding further red ink to the United States' $1.4 trillion deficit spending and national debt of over $12 trillion. The administration estimated the cost for this surge at $30 billion (presumably for an initial 18-month period). However, the chairman of the appropriations subcommittee with authority over the Pentagon's budget, U.S. Congress Rep. John Murtha, estimated that the surge would cost at least $40 billion – $10 billion more than the administration's estimate. The congressman also called for a surtax to finance the war, saying the U.S. risks the sort of inflation seen in the Vietnam War era.[85][86]
By February 2010, with thousands more U.S. troops still to arrive, the monthly cost of the war in Afghanistan to U.S. taxpayers had exceeded that of the U.S. war in Iraq – consuming $6.7 billion per month, compared with $5.5 billion in Iraq, and amounting to about $223 million per day.[27][87]
Military operations in Afghanistan have cost American taxpayers more than $200,000,000,000 in deficit spending since 2001.
By May 2010, the estimate for fiscal year 2010 that was being reported had risen to $105 billion, amounting to $288 million per day. Meanwhile, the cost of the war to U.S. taxpayers in fiscal year 2011 was being projected at $117 billion, a figure amounting to around $320 million per day. Todd Harrison of the Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments stated: "The cost just cascades. That's always been an issue in Afghanistan."[87]
By December 2010, estimates had the cost of the war running at as high as $13 billion a month, or over $433 million per day, and a USA Today / Gallup poll reported that over two-thirds of Americans, the 68% majority, worry that the costs of the war in Afghanistan make it more difficult to address the problems facing them at home.[38][91]
In February 2011, U.S. Defense Secretary Robert M. Gates bluntly warned that it would be unwise to ever again engage in such a "costly – and controversial – large-scale American military intervention" as in Afghanistan or Iraq.[92][93]
In my opinion, any future defense secretary who advises the president to again send a big American land army into Asia or into the Middle East or Africa should 'have his head examined,' as General MacArthur so delicately put it.
— U.S. Defense Secretary Robert M. Gates, February 25, 2011[92]
In February 2011, Indiana Senator Richard Lugar, the top Republican on the Foreign Relations Committee, ticked through the rising financial costs of the U.S. war in Afghanistan:[94]
- 100,000 U.S. military troops in Afghanistan,
- another 31,000 U.S. military troops deployed in the surrounding region to support the operations in Afghanistan,
- more than $100 billion in Obama's 2012 budget request for Afghanistan,
- an additional $13 billion to train Afghan forces,
- another $5 billion in civilian assistance.
He stated: "With al-Qaeda largely displaced from the country but franchised in other locations, Afghanistan does not carry a strategic value that justifies 100,000 U.S. troops and a $100 billion per year cost, especially given current fiscal restraints."[94]
The Senate Foreign Relations Chairman, Senator John Kerry, warned: "Make no mistake, it is unsustainable to continue spending $10 billion a month on a massive military operation with no end in sight."[94]
In March 2011, U.S. Congress Representative Bruce Braley, a member of the House Committee on Veterans Affairs, introduced the True Cost of War Act to require a full accounting on the long-term human and financials costs to the American people of the U.S. wars in Afghanistan and Iraq through 2020, including "interest on money borrowed, including interest for money already borrowed and anticipated interest payments on future borrowing."[95]
Rep. Braley stated: "The American people – especially at a time when Republicans have been pushing all these budget cuts – are entitled to know what the true costs are."[95]
According to the Congressional Research Service, through fiscal year 2010, Congress has appropriated $1,087,000,000,000 for the Department of Defense, for the State Department, and for medical costs paid by the Department of Veterans Affairs. This amount includes $751,000,000,000 related to operations in Iraq and $336,000,000,000 related to operations in Afghanistan.
— Congressional True Cost of War Act, March 8, 2011[95]
According to estimates near the beginning of 2011, the U.S. war in Afghanistan would cost U.S. taxpayers an $116 billion for that year – nearly twice the amounts being deeply slashed from domestic programs, including key U.S. infrastructure needs such as water, air traffic, and rail projects – while the minimum projected cost of the U.S. war for the next two years, $200 billion, exceeds the domestic budget deficit of all 50 states put together.[96][97]
By May 2011, the Washington Post reported that in the face of increasing deficit spending and more cuts to domestic programs in the U.S. the immense cost of the war in Afghanistan would likely be the primary factor in the discussions to reduce troops: Spending by the U.S. military alone on its operations in Afghanistan was heading to $113 billion for the fiscal year, with the military seeking another $107 billion for the next fiscal year. According to a senior administration official: "Where we're at right now is simply not sustainable."[98]
With the costs to maintain the Afghan army and police forces, estimated at $6 billion to $8 billion a year, far exceeding the means of the Afghan government whose annual budget totals only about $1.5 billion, he stated: "We're building an army that they'll never be able to pay for, which means we're going to have to pay for it for years and years to come."[98]
Military and civilian officials agree that the cost of the Afghan war is staggering, and another senior administration official involved with Afghanistan policy stated that the cost of the war was now "the new 800-pound gorilla" and policy discussion was shifting from "Is the strategy working?" to "Can we afford this?"[98]
In the United Kingdom, a comprehensive analysis by The Independent in July 2009, revealed that the cost of the war to British taxpayers had already exceeded £12 billion ($US 20 billion) – enough to pay for "23 new hospitals, 60,000 new teachers or 77,000 new nurses". A Ministry of Defence source indicated that the department feared the Afghan campaign was adding at least £250 million a year ($US 405 million) to their spending on veteran welfare services. In addition to these military costs, British taxpayer money is also being spent on Afghanistan by the Department of International Development (DfID), which will have spent close to £1 billion ($US 1.6 billion) between 2001 and 2012, and the Foreign Office (FCO) that had already spent £230 million ($US 375 million) since 2006 alone.[99]
Damage to the economy
[edit]In September 2011, a decade into the U.S.-led war, Linda Bilmes, a Harvard University economist, and Joseph Stiglitz, a Columbia University Nobel Prize economist, wrote that the enormous costs of the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq had profoundly damaged the U.S. economy:[100]
To date, the United States has spent more than $2.5 trillion on the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, the Pentagon spending spree that accompanied it and a battery of new homeland security measures instituted after Sept. 11. ... How have we paid for this? Entirely through borrowing. ... Spending on the wars and on added security at home has accounted for more than one-quarter of the total increase in U.S. government debt since 2001.
They wrote that the costs of the wars would continue to burden U.S. taxpayers and the U.S. economy for decades after whenever the U.S. military leaves those countries. The future debts from the war – including interest payments on all the borrowed money, replacing worn and destroyed military equipment, and decades of paying for the medical and disability benefits of hundreds of thousands of veterans – "are not listed anywhere in the federal government's budget" and would "continue to compromise America's investments in its future for decades."[100]
On September 19, 2011, U.S. President Barack Obama's proposed plan to reduce U.S. deficit spending stated that $1.1 trillion would be saved by withdrawing all U.S. combat troops from Afghanistan over the next three years (by 2014) and ending the war in Iraq. The $1.1 trillion in deficit spending on wars amounted to almost one-third of the proposed $3.6 trillion deficit-reduction package.[101]
Length of the war
[edit]We are mortgaging our Nation's economy on a war, which, even with increased commitment, will remain a draw for years to come. Success and victory, whatever they may be, will be realized not in years, after billions more spent, but in decades and generations.
— former U.S. Marine captain and State Department official Matthew Hoh, September 10, 2009[59]
The war in Afghanistan, launched October 7, 2001 as U.S. "Operation Enduring Freedom", has now stretched over a decade, entering an eleventh year on October 7, 2011 and marking for the U.S. the longest period of sustained warfare in its history – greater than the time the United States was involved in World War I, World War II and the Korean War combined.[96][102][103]
The war in Afghanistan surpassed the length of official United States participation in the Vietnam War, 8 years and 5 months, in the spring of 2010 to become the longest-running U.S. war ever.[38][102][104][105][106][107][108]
According to a study by the RAND Corporation, an American think tank working for the U.S. military, counter-insurgency campaigns won by governments have averaged 14 years.[109]
In a July 2009 interview, when asked when German troops would withdraw from Afghanistan, former German Defence Minister Peter Struck replied: "I'm afraid it could take another 10 years."[110]
In March 2011, U.S. Congressman Bruce Braley reported that American military commanders in Afghanistan very clearly expect – under the best-case scenario – a "significant U.S. presence" to continue in that country for approximately another decade. His report of the expectations of a continued U.S. military presence through 2020 came after a fact-finding trip to Afghanistan where he met with U.S. General David Petraeus, U.S. Ambassador and former general Karl Eikenberry, as well as other military officials.[95]
In December 2009, a week after U.S. President Barack Obama announced a surge of another thirty thousand U.S. military troops into Afghanistan, Afghan President Hamid Karzai, speaking at a news conference with U.S. Secretary of Defense Robert Gates, stated that the Afghan government being supported would not be able to secure the country on its own "for another 15 to 20 years", suggesting a U.S.-led military presence until at least 2024, if not 2030.[111][112][113]
At the end of December 2009, following a visit to Afghanistan as part of an eight-member congressional delegation, U.S. Congressman Brian Higgins warned that U.S. military assessments describe a "generational commitment" requiring at least two decades and that might not work, and he stated that President Obama needed to be more forthright with the American people about the length of time involved and the prospects.[114]
The military assessments say this is a generational commitment. I will tell you this whole 18 months of drawing down troops is not going to happen. The military assessments are very clear: In order to stabilize Afghanistan, you essentially have to rebuild it. You can't accomplish that in 18 months, five years, or in a decade, and you'll be lucky to accomplish that in 20 years. Gen. McChrystal told me he will know in 18 months if this will work.
— U.S. Congressman Brian Higgins, December 2009[114]
A January 2009 U.S. Defense Department report assessing progress in Afghanistan concluded that building a fully competent and independent Afghan government would be a lengthy process that would last, "at a minimum, decades."[115]
The head of the British Army and former ISAF commander, General Sir David Richards, stated on August 8, 2009 that he believed Britain could still be militarily involved in Afghanistan in "30 to 40 years" time, raising the possibility of a military presence in Afghanistan until the year 2050.[116]
Asked how long U.S. combat forces would be needed in Afghanistan, U.S. Defense Secretary Robert Gates replied it was "unpredictable" and "perhaps a few years". However, over the longer term, Gates said that even if security were achieved, progress in building Afghanistan's economy and government institutions would remain "a decades-long enterprise", and that the United States was "committed to that side of the equation for an indefinite period of time."[117]
American defense analyst John Pike of GlobalSecurity.org envisions a near-endless scenario in Afghanistan: "It's not going to end. And it may get worse before it gets better ... it's going to last for decades."[118]
More and more people feel that it is a never ending story, that this war has been dragging on now for longer than the second world war, that we see too little results and we really don't know why we are there.
— Patrick Keller, foreign and security policy analyst, September 2009[119]
Comparison to the length of the Soviet–Afghan War
[edit]After 7 years and 7 months of war in Afghanistan, Mikhail Gorbachev announced on July 20, 1987 the withdrawal of Soviet troops from Afghanistan, saying that the Soviet Union wanted to henceforth see an independent, sovereign Afghanistan with a non-aligned government. The complete withdrawal of Soviet troops took place over roughly one year and a half, ending on February 15, 1989, with the Soviet–Afghan War having lasted approximately 9 years and 2 months in its entirety.[120][121]
In December 2010, the U.S. war in Afghanistan, which officially began October 7, 2001, exceeded the length of the entire Soviet campaign in Afghanistan.[64][91][121]
Comparisons to the Soviet–Afghan War
[edit]There is barely an important piece of land in Afghanistan that has not been occupied by one of our soldiers at some time or another. Nevertheless, much of the territory stays in the hands of the terrorists. We control the provincial centres, but we cannot maintain political control over the territory that we seize.
— Marshal Sergei Akhromeyev, commander of Soviet armed forces, November 13, 1986[121]
In November 1986, with 109,000 troops in Afghanistan and the war soon heading into an 8th year, the military counter-insurgency was not working. Marshal Sergei Akhromeyev, commander of Soviet armed forces, was summoned to report on the situation to the USSR's politburo in the Kremlin. His strong assessment was that the army needed more resources, and he warned that without more men and equipment "this war will continue for a very long time". By the peak of the Soviet deployment in 1987, Moscow had 140,000 troops in Afghanistan.[121][122]
In September 2009, with 108,000 to 110,000 foreign troops in Afghanistan under U.S. command and the war soon heading into a 9th year, the military counter-insurgency was not working. A 66-page report by U.S. general Stanley McChrystal to the White House administration on the situation in Afghanistan, leaked in advance of an anticipated troop request, gave his strong assessment that more troops and resources were needed. McChrystal warned: "Resources will not win this war, but under-resourcing could lose it. Failure to provide adequate resources also risks a longer conflict, greater casualties, higher overall costs and ultimately, a critical loss of political support. Any of these risks, in turn, are likely to result in mission failure." After officially receiving McChrystal's request for more troops, U.S. president Barack Obama would announce that some 30,000 more U.S. troops would be sent to Afghanistan over the course of the following year.[52][123][124][125][126][127][128][129][130][23][131]
It is sometimes frightening to see how similar NATO military operations are to Soviet ones in the 1980s.
— Carnegie Endowment for International Peace policy brief, January 2009[26]
McChrystal, the U.S. general, at the same time called for a new strategy of pulling troops from sparsely populated rural areas to concentrate on defending higher population urban areas.[132][133] Tom Coghlan of The Times observed: "Students of Afghan history may note that this strategic conclusion was one previously reached by the Soviets, who also switched to a strategy of ceding remote areas and only defending population centres and the country's main arteries in 1986."[134]
On July 20, 1987, the withdrawal of Soviet troops from Afghanistan was announced, and within a little over a year and a half the Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan was completed.[122]
Comparisons to the Vietnam War
[edit]The decade-long war in Afghanistan has also been increasingly compared to the Vietnam War, and increasingly characterized as a quagmire.[51][135][136]
In the spring of 2010, the war in Afghanistan surpassed the length of official United States participation in the Vietnam War, 8 years and 5 months, as the longest-running U.S. war ever.[96][104][105][106]
What I found being in Afghanistan was all too familiar of problems not only in Iraq, but in Vietnam years ago. We are fighting a war a half a century later that we lost for similar reasons a half a century earlier.
— Anthony Cordesman, Center for Strategic and International Studies, 2009[135]
In September 2009, an article by the New York Times' Frank Rich noted a new aspect in the strong parallels between the wars, the eerie similarity between the political maneuvers in 2009 and a half-century before, when John F. Kennedy was weighing whether to send combat troops to Vietnam. "Military leaders lobbied for their new mission by planting leaks in the press." The Secretaries of Defense (Robert McNamara) and State, as well as the Joint Chief of Staff and the president's special military adviser all supported sending combat troops, while Kennedy himself had reservations.[137]
The Vietnam analogy remains haunting. On Mr. Obama's nightstand is Gordon Goldstein's acclaimed biography of McGeorge Bundy, "Lessons in Disaster", which describes the flawed decision-making of President Lyndon B. Johnson in the Vietnam quagmire.
— Albert R. Hunt, New York Times, October 4, 2009[138]
Growing U.S. opposition to the war in Afghanistan
[edit]In March 2009, a bipartisan group of 14 members of the United States House of Representatives – Walter Jones, Ron Paul, Dennis Kucinich, Neil Abercrombie, Roscoe Bartlett, Steve Kagen, Ed Whitfield, Lynn Woolsey, Bob Filner, Jim McGovern, Howard Coble, John Conyers, Marcy Kaptur, John Duncan, and Michael Michaud – signed a letter to President Obama urging him to reconsider his decision to send 17,000 more U.S. troops, and to "resist pressure to escalate further".[139][140]
Their letter Archived February 7, 2015, at the Wayback Machine to Obama argued that the military escalation could be counterproductive to creating stability in Afghanistan and could harm U.S. security, noting that a recent Carnegie Endowment study had concluded that "The only meaningful way to halt the insurgency's momentum is to start withdrawing troops. The presence of foreign troops is the most important element driving the resurgence of the Taliban."[139]
In September and October 2009, with U.S. military leaders requesting yet more troops – and polls showing the majority of American people opposed to the U.S. war in Afghanistan and to sending any more troops, more members of the United States House of Representatives and other leaders began to speak for and manifest their constituents' opposition.[20][21][56][141]
On September 10, 2009, Speaker of the United States House of Representatives Nancy Pelosi stated: "I don't think there is a great deal of support for sending more troops to Afghanistan in the country or in the Congress.".[142]
Senator Carl Levin, chairman of the Senate Armed Services Committee, stated: "There's a significant number of people in the country, and I don't know the exact percentages, that have questions about deepening our military involvement in Afghanistan."[142]
Senator Russell D. Feingold, a senior member of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee urged discussion of a timeline for ending American involvement in Afghanistan.[142]
Senator Dianne Feinstein, chairwoman of the Senate Intelligence Committee stated: "I do not believe we can build a democratic state in Afghanistan. I believe it will remain a tribal entity", adding that she wanted the U.S. military mission to "be time-limited".[143]
Senator Richard Durbin, assistant majority leader in the Senate, said: "Sending additional troops would not be the right thing to do."[143]
In September 2009, Senator John F. Kerry, chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee and a veteran and protester of the Vietnam War, warned of repeating the mistakes of Vietnam and said that the United States needed to have an exit strategy.[144][145][146][147]
Former Secretary of State Colin L. Powell, a retired four-star Army general, expressed skepticism that more troops would guarantee success.[144]
On October 4, 2009, Representative Barbara Lee with 21 other members of the United States House of Representatives introduced a bill, H.R. 3699, to prohibit any funding to increase the U.S. military buildup in Afghanistan beyond its current level.[148]
History tells us that there will not be a military-first solution to the situation in Afghanistan. Open-ended military intervention in Afghanistan is not in our national security interest and will only continue to give resonance to insurgent recruiters painting pictures of foreign occupation to a new generation.
— Representative Barbara Lee, October 4, 2009[148]
On October 8, 2009, key Democrats on Capitol Hill warned that a decision by President Obama to send more U.S. troops to Afghanistan could trigger a revolt within his own party, possibly including an attempt to cut off funds for the controversial military buildup.[141]
Representative David R. Obey, chairman of the U.S. House Appropriations Committee stated: "I believe we need to more narrowly focus our efforts and have a much more achievable and targeted policy in that region. Otherwise we run the risk of repeating the mistakes we made in Vietnam and the Russians made in Afghanistan."[141]
Representative John P. Murtha, also on the House Appropriations Committee and an influential voice on military affairs, stated: "The public is worn out by war. The troops, no matter what the military says, are exhausted."[141]
Senator Russell D. Feingold, a member of both the Senate Foreign Relations Committee and Senate Intelligence Committee, stated that if Obama decides to send more troops, the House of Representatives should contest it.
Senator Feingold, who favors a timetable for withdrawal and opposes McChrystal's troop surge, said in an interview that his constituents were weary of war and were in "almost unanimous agreement" that "we've stayed there a long time and we need to figure out appropriately what we can accomplish."[141]
On October 15, 2009, Senator Robert Byrd, in an emotional speech on the floor of the U.S. Senate, suggested that the eight-year-old U.S. war in Afghanistan had become lost in some broader scheme of nation-building. Referring to "mission creep" in Afghanistan, he said:[149]
I am compelled to ask: does it really, really take 100,000 U.S. troops to find Osama bin Laden? If al Qaida has moved to Pakistan, what will these troops in Afghanistan add to the effort to defeat al Qaida?
— Senator Robert Byrd, October 15, 2009 speech to the U.S. Senate[149]
On October 27, 2009, the Washington Post reported that a U.S. official in Afghanistan had resigned in protest over the U.S. war, in a move that sent ripples all the way to the White House. Matthew Hoh, a State Department Foreign Service officer serving as the Senior Civilian Representative in Zabul Province submitted his resignation on September 10, with a letter outlining the reasons for which he felt he had to resign over the war, writing, "I fail to see the value or the worth in continued U.S. casualties or expenditures or resources in support of the Afghan government in what is, truly, a 35-year old civil war."[59][65]
On November 4, 2009, U.S. Congress Rep. Eric Massa spoke before the U.S. House of Representatives to say enough is enough in Afghanistan. He stated: "Today is the 2,950th day of this war. It has cost us $300 billion, $3,947 per American family. Enough is enough. It is time to bring our troops home. ... the deployment of additional troops in Afghanistan and the continuation of this conflict is both not in the interest of our Nation, and, in fact, is on par with a potential error the size of our initial invasion in Iraq."[79]
In November 2009, the U.S. ambassador to Afghanistan, Lt.-Gen. Karl Eikenberry, the retired army general who commanded U.S. forces in Afghanistan in 2005–2007, warned President Obama against committing tens of thousands of extra troops to Afghanistan. His dramatic intervention into the debate on a troop surge reportedly infuriated U.S. General McChrystal, the commander of all foreign military forces in Afghanistan who had been requesting another 40,000 troops.[150]
In April 2010, Democratic Congressman Jim McGovern, Republican Congressman Walter Jones, and Democratic Senator Russ Feingold introduced legislation demanding an exit strategy and a timetable for withdrawal of the American military forces and military contractors in Afghanistan. While noting Obama's promise to begin bringing some troops back in July 2010, Rep. McGovern said: "It's not only important to know when the first soldier is to be redeployed or brought home, it's important to know when the last soldier is as well."[27][88]
The hundreds of billions of dollars we spend over there on war ... All that – mostly borrowed money – means that we're not investing at home. It means our roads and our bridges aren't being fixed. It means our schools aren't being fixed. It means we're not investing in healthcare, and a whole range of other things that we need to do to get our economy back on track.
— Rep. Jim McGovern, May 2010[88]
On July 1, 2010, 60% of Democratic representatives in the House voted in favor of the legislation to require a timetable and plan for the withdrawal of U.S. troops from Afghanistan. In all, 153 Democrats and 9 Republicans voted for the amendment. 93 Democrats and 7 Republicans also voted for an amendment from Rep. Barbara Lee that would have required the war funds to be spent only on withdrawing troops from Afghanistan. Nearly all Republicans opposed the amendments however, and neither passed.[151][152]
In January 2011, Republican figure Grover Norquist, founder of Americans for Tax Reform, called on conservatives to have a conversation on the possibility of withdrawing from Afghanistan. He called attention to a nationwide poll of conservatives that showed that the majority 71% of self-identified conservative voters, including over two-thirds (67%) of Tea Party supporters, are worried about the war's cost to taxpayers, and stated that, given the war's enormous price tag, it was time to consider leaving.[153][unreliable source?][154][non-primary source needed]
The same nationwide poll of conservatives, conducted in early January 2011, found that the majority two-thirds of conservative and Tea Party supporters call for a reduction of U.S. troop levels in Afghanistan (39% plurality) or a complete withdrawal from Afghanistan "as soon as possible" (27%). Only a minority 24% of conservative and Tea Party supporters think that the current levels of troops should be maintained.[153][154]
In February 2011, a bipartisan group of U.S. lawmakers again introduced legislation to end combat operations in Afghanistan and reduce spending of U.S. taxpayer dollars on the war. Led by Republican Congressmen Ron Paul of Texas, Walter Jones of North Carolina, and Democratic Congresswoman Barbara Lee of California, the amendment had 45 other co-sponsors. Republican congressmen opposed to the continued large-scale combat operations in Afghanistan convened a meeting for GOP members which had as principle speakers Americans for Tax Reform President Grover Norquist, Maj. Gen. John Batiste (ret.) and Lt. Col. Eric Egland (Reserve), a career intelligence officer with experience in Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Iraq. According to numerous polls, the majority of Americans now want a faster withdrawal from Afghanistan.[96][155]
The mounting costs of the war in Afghanistan, now totaling over $100 billion a year, have constrained efforts to invest in job creation and in strengthening our country and our economy.
— Democratic National Committee resolution, February 2011[156]
In February 2011, the Democratic National Committee passed a resolution calling for an acceleration of the U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan. Citing the Gallup poll released that month that found that the strong majority 72% of Americans favor action to "speed up the withdrawal of troops from Afghanistan", the policy resolution called for "a swift withdrawal of US armed forces and military contractors in Afghanistan which must include a significant and sizable reduction no later than July 2011."[97][156]
Concerns that the war could derail Obama's presidency
[edit]Many[who?] that had hopes in President Obama's presidency but opposed the war in Afghanistan were concerned that the war could derail plans for his presidency the way the Vietnam War ruined the presidency of Lyndon B. Johnson.[61][138][157][158][159][160]
As long as we are there, the war will continue, with disastrous consequences for all the things you want to do and we Americans need you to do.
Speaking against the war in Afghanistan, Senator Russ Feingold said: "It doesn't make sense in the long run. It's going to be bad for the president politically, as well as being a very unwise policy in terms of our national security."[155]
Troop reductions and removals
[edit]- On November 5, 2007, South Korea's Defense Ministry announced that its 210-troop military deployment would be recalled despite the fact that Washington had asked Seoul to extend their deployment, which was scheduled to expire at the end of the year. South Korea's 150 military engineers and 60 military medics were to leave Afghanistan on December 14, 2007. The recall followed South Korea's promise to withdraw its troops from Afghanistan by the end of 2007 to secure the August 2007 release of 23 South Korean missionaries that had been kidnapped because of their country's involvement in the U.S.-led military efforts. The South Korean military deployment had been in Afghanistan approximately 5 years and 9 months starting in February 2002.[161][162]
- In November 2007, Swiss Defence Minister Samuel Schmid announced the planned withdrawal of the last of its military deployment to Afghanistan that had started in 2003.[163]
- On December 19, 2007, the Netherlands announced that it would begin to remove Dutch troops from Afghanistan in 2010, with Dutch troops leaving Afghanistan from July 2010. Foreign Minister Maxime Verhagen stated, "I am certain that Dutch troops will leave in 2010." He also made clear, "I indicated that in writing ... to the NATO secretary general, who has confirmed it."[164]
- In February 2008, Switzerland's last soldiers still in Afghanistan had returned home and its military deployment to Afghanistan since 2003 was officially concluded. The Swiss military contingent had been in Afghanistan approximately 4 years and 8 months starting in June 2003.[163]
- On September 10, 2008, Canadian Prime Minister Stephen Harper pledged that Canada will withdraw the bulk of its military forces in Afghanistan in 2011, saying that a decade of war is enough and, "You have to put an end date on these things." He acknowledged that neither the Canadian public nor the troops themselves had any appetite to stay longer in the war and said that only a small group of advisers might remain.[165]
- On September 6, 2009, The Independent reported that British Prime Minister Gordon Brown had put the United States on notice that he planned to cut the number of British troops in Afghanistan by at least half within "three to five years, maximum". The partial troop withdrawal would bring British troop numbers in Afghanistan from over 9,000 to fewer than 5,000. On September 4, 2009, Brown had confirmed in a keynote speech that he was considering a short-term increase in British troops in Afghanistan as a prelude to a British exit.[166]
- On September 14, 2009, Canadian Prime Minister Stephen Harper reaffirmed that Canada would withdraw its troops in 2011 even if President Barack Obama asked him for an extension. A spokesperson for Harper said "Canada's position is clear – The military component of the mission ends in 2011." Harper had first announced Canada's troop removal in 2008, stating that Canada had done its part after being in Afghanistan since after the 2001 U.S. invasion, and in Kandahar, one of Afghanistan's most dangerous provinces, since 2006.[167]
- On September 16, 2009, Japanese Prime Minister Yukio Hatoyama signalled through key cabinet choices that he would keep his election pledge to withdraw Japan's military support from the U.S.-led war in Afghanistan. Hatoyama appointed as his Defence Minister 71-year-old Toshimi Kitazawa, a strong opponent of the country's military support for the U.S. wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, and included in his cabinet Mizuho Fukushima, leader of his coalition partner, the Social Democratic Party (SDP), which is committed to upholding Japan's "peace" constitution and its explicit ban on the use of force in resolving international disputes. The appointments suggest that Japanese military ships providing fuel and water to U.S. and British naval vessels in the Indian Ocean will be called home when the current term of their deployment expires in February.[168]
- On September 17, 2009, Italian Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi said it would be best for foreign troops to leave Afghanistan soon. He also announced that he planned to bring home at least 500 of Italy's 2,800 troops deployed in Afghanistan "in the next few weeks". Italy had increased its troop level by 500 before Afghanistan's August 20 national election. A key coalition partner in Berlusconi's government, Reforms Minister Umberto Bossi said he hoped Italy's 2,800 troops could leave Afghanistan within 3 months by Christmas. Berlusconi's announcement followed the deaths of six Italian soldiers in a suicide bombing in Kabul the day before, which had brought to 20 the number of Italian troops that have been killed since Italy's troops arrived in Afghanistan in 2004.[169][170]
We are all convinced it's best for everybody to get out soon.
— Italian Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi, September 17, 2009[169]
- On September 22, 2009, British Prime Minister Gordon Brown insisted he was focused on cutting back on the number of British troops in Afghanistan as soon as Afghan security forces were able to carry out their own security duties. The Times had reported that Britain was considering deploying a further 1,000 troops to its contingent of 9,000 troops in Afghanistan in response to the report from the American commander of all foreign military forces in Afghanistan, U.S. General Stanley McChrystal. Brown had previously stated in a keynote speech that he was considering a short-term increase in British troops in Afghanistan as a prelude to a British exit. The British toll since the U.S.-led invasion in 2001 stood at 217 deaths.[166][171]
- On October 6, 2009, the Dutch parliament voted by a large majority to pull Dutch troops out of Afghanistan in August 2010 as scheduled and bring them home. The motion to respect the scheduled withdrawal date was drawn up by two of the three parties in the coalition government, and was voted for by a large majority of Dutch MPs, despite pressure by the United States again for a second extension of the Dutch military involvement in Afghanistan.[172][173]
- On October 14, 2009, Japanese Defence Minister Toshimi Kitazawa said that Japan will end its Indian Ocean naval refuelling mission that supports the U.S.-led military campaign in Afghanistan. Kitazawa said: "We will calmly withdraw (our ships) when the law expires next January". While in opposition, Prime Minister Yukio Hatoyama's party argued that Japan, officially pacifist since World War II, should not abet "American wars".[174][175]
- On January 6, 2010, Canadian Prime Minister Stephen Harper made clear that virtually all Canadian soldiers will be out of Afghanistan by the end of 2011, stating: "We will not be undertaking any activities that require any kind of military presence, other than the odd guard guarding an embassy." He emphasized again, "The bottom line is that the military mission will end in 2011."[176][177]
- In February 2010, the Deputy Prime Minister of the Netherlands, Wouter Bos, promised to bring Dutch troops home from Afghanistan by the end of the year, as scheduled. The Dutch public, as well as the Dutch Parliament, favor the withdrawal of their military from Afghanistan. The Netherlands is also facing a forecasted 2010 budget deficit of 6.1% of GDP.[178] Bos reiterated to Dutch voters the pledge he had already made to them in 2007, saying at a party meeting:
By the end of this year, the last soldier should have left Uruzghan. We're keeping our promise to the Dutch people.
— Deputy Prime Minister of the Netherlands Wouter Bos, February 2010[178]
- On February 21, 2010, the Dutch coalition government of Prime Minister Jan Peter Balkenende collapsed when Balkenende, under entreaties from the United States, tried to extend the Dutch military presence in Afghanistan yet again, despite the government having previously promised Dutch voters that troops would be brought home in August 2010. As in many parts of Europe, the war in Afghanistan has been increasingly unpopular with voters in the Netherlands. The fall of the Balkenende government over the issue made it all but guaranteed that Dutch troops will be gone from Afghanistan by the end of the year. A spokesman for the Dutch Ministry of Defense stated: "The military mission will stop the 1st of August. They have time until the end of the year to pick up their gear and their stuff and bring it back to the Netherlands."[172][173][179]
- On June 21, 2010, Poland's acting president and speaker of parliament, Bronislaw Komorowski, stated: "2011 should be the year for winding down Poland's engagement and 2012 should be the year we pull out." The front-runner in Poland's presidential race, he stated: "If I win these elections, I wish to start curbing our engagement and then to pull out (the troops) during my presidency." Grzegorz Napieralski, the third-place candidate being courted by both leading candidates in the tight race, reiterated his party's demand for an Afghan pullout "as soon as possible." Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk, whose ruling party is backing Komorowski's presidential bid, had also said in June that Poland would press the U.S. and NATO coalition to draw up plans to end the mission as soon as possible.[180]
- On June 24, 2010, Poland urged its NATO allies to draft plans to leave Afghanistan and announced that Polish troops would be brought home by 2012 regardless of what other countries decided. Following a National Security Countil meeting devoted to Afghanistan, Acting President Bronislaw Komorowski told a news conference that he had asked the government to work out a national strategy for pulling out of the war, with 2012 as the absolute deadline. A senior Polish security official said that NATO was heading towards a "strategic catastrophe" in Afghanistan. Stanislaw Koziej, head of Poland's National Security Bureau stated: "NATO is strategically exhausted by Afghanistan ... We must seek a way out of this situation."[181][better source needed]
2012 is the deadline when it comes to Poland's presence in Afghanistan.
— Acting President of Poland Bronislaw Komorowski, June 24, 2010[181]
- On August 1, 2010, the Netherlands officially ended its military involvement of 1,950 troops in Afghanistan. The withdrawal came with the collapse of the Dutch government of Prime Minister Jan Peter Balkenende earlier in the year when Balkenende, under entreaties from the United States, tried to extend the Dutch military presence in Afghanistan yet again despite opposition from the public. During the Netherlands' four-year involvement in the war, 24 Dutch troops were killed and 140 were wounded. The Dutch pullout is being followed by other withdrawals of foreign military forces from Afghanistan. Canada is withdrawing its entire military force of 2,800 troops next year in 2011, Poland in 2012, and the United Kingdom in 2014 or 2015.[172][173][182][183]
- On November 20, 2010, NATO members signed a deal to begin reducing troops in Afghanistan in 2011 and hand over security control to Afghan forces by 2014, if conditions were favourable. However, American officials described the date as "an aspirational timeline" and NATO officials said "This isn't a calendar-based process." The United Kingdom, however, made clear to its NATO allies that after 2014 they would not be involved in combat operations:[184][185]
- On November 20, 2010, British Prime Minister David Cameron pledged to withdraw all British combat troops from Afghanistan after the end of 2014, saying "This is a firm deadline which we will meet." Defence Secretary Liam Fox also underlined the Prime Minister's commitment that Britain's combat role in Afghanistan would be over by 2015.[185][186]
Let's be clear, this is a deadline and I believe the British public deserve a deadline.
We have been in Afghanistan for nine years and we have paid a high price.
— British Prime Minister David Cameron, November 20, 2010[185]
- On January 10, 2011, former French Prime Minister Dominique de Villepin called for an earlier withdrawal of France's troops from Afghanistan than 2014. Opposition politician Segolene Royale renewed a call for a "democratic debate" and for a fixed withdrawal date.[187]
- On June 23, 2011, U.S. President Barack Obama announced that the US combat role in Afghanistan would end completely by 2014, with the United States needing to regroup and concentrate on its problems at home. He announced that 10,000 U.S. troops would be withdrawn in 2011, another 23,000 by the middle of 2012, and then "at a steady pace" until 2014, completing a transition from combat to "support". He stated: "This is the beginning – but not the end – of our effort to wind down this war."[188]
Over the last decade, we have spent a trillion dollars on war, at a time of rising debt and hard economic times. ... Now, we must invest in America's greatest resource – our people. We must unleash innovation that creates new jobs and industry, while living within our means. We must rebuild our infrastructure and find new and clean sources of energy. ... America, it is time to focus on nation building here at home.
— U.S. President Barack Obama, June 23, 2011[188]
- On July 6, 2011, British Prime Minister David Cameron announced that 500 British troops would return home in 2012. France and Belgium also recently announced troop reductions.[189][190]
- On July 7, 2011, Canada officially ended its direct involvement in any combat operations in Afghanistan, withdrawing its nearly 3,000 troops. Prime Minister Stephen Harper had pledged in 2008 and 2009 to withdraw all Canadian military troops from Afghanistan, only to then announce in 2010 that 950 Canadian troops would stay until 2014 to train Afghan military and police forces. The Canadian government informed NATO that its trainers would not operate in dangerous parts of the country or in the field with Afghan troops: Some 350 will be support staff or will work in NATO headquarters offices in Kabul, with the rest serving mainly as mentors or advisors within heavily fortified training centres in Kabul and in two small groups at schools in the generally peaceful cities of Herat and Mazar-e Sharif.[189][190][191][192]
- On July 12, 2011, French President Nicolas Sarkozy announced that France would withdraw 1,000 troops by the end of 2012, and all its combat units by the end of 2014, speeding up its withdrawal along with other countries. He stated "You have to know how to end a war." The majority of people in France want their military withdrawn from Afghanistan.[193]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Vidal, John (November 19, 2001). "Another coalition stands up to be counted". The Guardian. Retrieved November 11, 2006.
- ^ "Protesters demand end to bombing". BBC. November 10, 2001. Retrieved November 11, 2006.
- ^ Anonymous. "Afghanistan: Where Empires Go to Die". Truthout. Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c Quittin' time in Afghanistan
- ^ a b c d Paul R. Pillar. "Terrorists' Real Haven Isn't on the Ground, It's Online". Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Keith Garvin (June 22, 2006). "Afghan Problem 'a Lot Deeper Than Bin Laden'". ABC News. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c RAWA (October 11, 2001). "Taliban should be overthrown by the uprising of Afghan nation". Retrieved November 11, 2006.
- ^ "Ahmed Rashid Offers An Update On The Taliban". WBUR. February 17, 2010. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "The US has Returned Fundamentalism to Afghanistan". Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ iCasualties.org Afghanistan coalition military fatalities
- ^ Stephen Fidler & John W. Miller (September 25, 2009). "U.S. Allies Await Afghan Review". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Declan Walsh (October 7, 2011). "US had 'frighteningly simplistic' view of Afghanistan, says McChrystal". The Guardian. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Operation Enduring Freedom icasualties.org". Archived from the original on April 6, 2010. Retrieved November 9, 2010.
- ^ "Global Unease With Major World Powers". Pew Research Center's Global Attitudes Project. June 27, 2007. Archived from the original on February 22, 2023. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Global Economic Gloom – China and India Notable Exceptions". Pew Research Center's Global Attitudes Project. June 12, 2008. Archived from the original on February 28, 2023. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "25-Nation Pew Global Attitudes Survey, 2009, p.39 (PDF p.43)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 11, 2009. Retrieved September 20, 2009.
- ^ "Obama More Popular Abroad Than At Home, Global Image of U.S. Continues to Benefit". Pew Research Center's Global Attitudes Project. June 17, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "47-Nation Pew Global Attitudes Survey p.24, p.116" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 12, 2010. Retrieved September 20, 2009.
- ^ "25-Nation Pew Global Attitudes Survey, 2009, p.22 (PDF p.26) Opposition to War in Afghanistan" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 11, 2009. Retrieved September 20, 2009.
- ^ a b "Poll: Support for Afghan war at all-time low". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "A Skeptical View of Afghanistan". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Behind the Numbers - Anti-War Stirrings Greet Call For More Troops". Archived from the original on October 11, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "General Stanley McChrystal: The Runaway General by Michael Hastings". Rolling Stone. Archived from the original on June 24, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Chris McGreal (June 22, 2010). "General alarm as Barack Obama summons Stanley McChrystal to the White House". the Guardian. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Afghans have no hope in this week's vote
- ^ a b c d Focus and Exit: An Alternative Strategy for the Afghan War
- ^ a b c "Katrina vanden Heuvel - A flawed strategy and a failed war in Afghanistan". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Afghan Poll 2009" (PDF). BBC News. Retrieved August 3, 2011.
- ^ "Gallup poll". Gallup.com. September 30, 2009. Retrieved August 3, 2011.
- ^ a b c US may shift Afghan war tactics: report
- ^ Many in Afghanistan oppose Obama's troop buildup plans
- ^ "Rethinking the Afghanistan Mission". Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c John Pike. "Afghanistan: Karzai Asks U.S.-Led Coalition To Change Strategy Against Terrorism". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Afghanistan: chaos central". February 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Afghan leader sends demands to U.S. on troop conduct - USATODAY.com". USA Today. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Karzai wants U.S. to reduce military operations in Afghanistan". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Afghans Want a Deal on Foreign Troops". The New York Times. August 26, 2008. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Please Mr. President! Some Truth About Afghanistan". The Huffington Post. December 20, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Nato offensive inflicts Afghans $100 mln damage in Kandahar
- ^ "United in Remembrance, Divided over Policies". Pew Research Center for the People and the Press. September 1, 2011. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Pew Research Center poll August 2011
- ^ "Poll shows most Britons oppose war in Afghanistan". Archived from the original on July 13, 2012. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "The Al Qaeda Clubhouse: Members lacking". Archived from the original on January 10, 2010. Retrieved June 28, 2010.
- ^ a b c Al Qaeda and Affiliates – Historical Perspective, Global Presence, and Implications for US Policy (Congressional Research Service, February 5, 2010)
- ^ a b c ABC News. "CIA: At most, 50-100 Al Qaeda in Afghanistan". ABC News Blogs. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Obama aide downplays extra troops in Afghanistan". The Washington Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Schmitt, Eric; Mazzetti, Mark (November 10, 2008). "Secret Order Lets U.S. Raid Al Qaeda". The New York Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ U.S. kicks hornet's nest in Yemen
- ^ Old threat rings true today
- ^ Seumas Milne (January 27, 2010). "Only pressure to withdraw can stop this blood price". the Guardian. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "The Afghan War Moves South". The Huffington Post. October 5, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "George F. Will - Time for the U.S. to Get Out of Afghanistan". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "NATO Officials Say They Will Back Afghan Effort to Turn Insurgents Against Taliban". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Yochi J. Dreazen (October 1, 2009). "Gates Doubts U.S.'s Afghan Strategy". WSJ. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "From McChrystal's Mouth to Obama's Ear". The New York Times. September 30, 2009. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b Advisers split complicates Obama's Afghan decision[dead link]
- ^ "Will Obama abandon Afghanistan?". September 23, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Dyer, Gwynne (September 15, 2009). "West should vote with its feet". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved November 1, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "A letter from Afghanistan that every American must read". War in Context. October 27, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ The Christian Science Monitor. "Afghanistan: Why Obama is rethinking 'war of necessity'". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c d "An Open Letter to President Obama". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "No Deadline Set for Decision on Troops". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Obama Faces Familiar Divisions Over Anti-Terror Policies". Pew Research Center for the People and the Press. February 18, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Matthew Hoh September 10, 2009 letter of resignation
- ^ a b c "U.S. official resigns over Afghan war". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ The Christian Science Monitor. "Matthew Hoh: new poster boy for critics of Afghanistan war". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "The Afghanistan Abyss". The New York Times. September 6, 2009. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b "Former CIA Operatives Agree: American Occupation of Afghanistan Threatens US Security". Common Dreams. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Dreyfuss, Bob (September 10, 2010). "The Afghanistan Study Group Challenges US Strategy, With Flawed but Useful Report". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
{{cite magazine}}: Cite magazine requires|magazine=(help) - ^ "What good friends left behind". the Guardian. September 20, 2003. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Afghanistan News June 22, 2008". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Comment: US bombs are boosting the Taliban". the Guardian. November 2, 2001. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. "Afghanistan Opium Survey 2007" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 28, 2008. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. "Afghanistan Opium Survey 2008" (PDF). Retrieved September 20, 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Afghanistan's cash crop wilts". msnbc.com. Archived from the original on August 5, 2011. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Men With Guns, in Kabul and Washington
- ^ Caught in a swirl of deceit
- ^ America has been here before
- ^ a b c "Congressional Record, Volume 155 Issue 163 (Wednesday, November 4, 2009)". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c The Christian Science Monitor. "ECONOMIC SCENE: Afghanistan will cost US more than Iraq". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Login". Retrieved February 6, 2015.[dead link]
- ^ "Faster troop withdrawal may save $1 trillion". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Some reasons why the war in Afghanistan is insanity
- ^ "John Nichols". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Afghanistan Surge to Cost $40 Billion, Democrat Says (Update2)". Bloomberg News. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Cost of Afghan war explodes with new strategy - USATODAY.com". USA Today. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Afghan war costs now outpace Iraq's - USATODAY.com". USA Today. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "Demand an Afghanistan Exit Strategy". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Bill Text - 111th Congress (2009-2010) - THOMAS (Library of Congress)". Archived from the original on August 10, 2009. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ "Bill Text - 111th Congress (2009-2010) - THOMAS (Library of Congress)". Archived from the original on July 14, 2012. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b "Obama's isolation grows on the Afghanistan war - USATODAY.com". USA Today. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Gates Warns Against More Wars Like Iraq and Afghanistan". The New York Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ ""Never Get Involved in a Land War in Asia": Gates' West Point Speech and a Tipping Point in Afghanistan". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "Poll: With bin Laden dead, is it time to end war?". USATODAY.COM. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c d "Commanders Expect A 'Significant' U.S. Presence In Afghanistan For 8 To 10 More Years: Dem Rep". The Huffington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c d "Bid to end Afghan war funding hits GOP roadblock". SFGate. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Afghanistan Withdrawal Resolution Passes Democratic National Committee Without Dissent". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "Cost of war in Afghanistan will be major factor in troop-reduction talks - The Washington Post". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Revealed: £12bn hidden costs of Afghan war - Home News - UK - The Independent". The Independent. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "America's too-costly war on terror". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Sheldon Alberts. "Republicans cry class warfare as Obama pushes higher taxes for wealthy". www.montrealgazette.com. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b "War and Sacrifice in the Post-9/11 Era". Pew Research Center's Social & Demographic Trends Project. October 5, 2011. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Let Us Not Become the Evil We Deplore". Common Dreams. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "SignOnSanDiego.com > News > Nation -- U.S. involved in Iraq war longer than it was in World War II". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Idaho Mountain Express: From critic of one 'shameful' war to booster of another - May 26, 2010". Archived from the original on February 29, 2012. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b HT. "Does the Finnish customer know best?". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "New U.S. commander in Afghanistan is a consummate politician". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Quagmire? Nine years on, Americans grow weary of war in Afghanistan
- ^ "Obama's Afghan war – a race against time". Reuters. Archived from the original on August 30, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Druckversion - Two Views on Afghanistan Mission: 'The War Is a Breeding Program for Terrorists' - SPIEGEL ONLINE - News - International". SPIEGEL ONLINE. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "A Game That's Not So Great". The New York Times. December 13, 2009. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ Afghanistan pro-con: It will become a quagmire[permanent dead link]
- ^ Afghan Says Army Will Need Help Until 2024
- ^ a b 20-year commitment needed in Afghanistan, Higgins says
- ^ "Civilian Goals Largely Unmet in Afghanistan". The New York Times. October 12, 2009. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ "Army chief: We'll be in Afghanistan until 2050". Express.co.uk. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Gates: No Troop Request In Afghanistan Review". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ John Pike. "Risk of death soars for Canada's troops". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "More troops and new strategy for Afghanistan will be hard to come by". DW.DE. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Official chronology of the withdrawal from Afghanistan
- ^ a b c d "Login". Times. Archived from the original on October 10, 2011. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Declan Walsh. "Afghan election: Pressure grows for Hamid Karzai to strike a deal". The Guardian. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Top US general calls for new strategy in Afghanistan". New Statesman. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Alex Spillius (September 21, 2009). "Afghan mission risks 'failure' without more troops, says US general". Telegraph. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "A D.C. whodunit: Who leaked and why?". Reuters. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Sources: McChrystal Wants Up to 40,000 More Troops in Afghanistan". Fox News. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Commander to send troop request for Afghanistan[dead link]
- ^ "Aides: Mullen Likely to Sign off on Afghanistan Troop Request". Fox news. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ Troop request on table as Obama weighs Afghan mission >
- ^ Analysis: Obama Borrows Soviet's Afghan Endgame>
- ^ "U.S. puppet cuts his strings". Archived from the original on May 28, 2010. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- ^ "White House Believes Karzai Will Be Re-elected". The New York Times. September 28, 2009. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ "Deadly Attack on Remote Posts Highlights Afghan Risks". New York Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Login". Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.[dead link]
- ^ a b Afghan War Draws Comparisons to Vietnam
- ^ Can America win in Afghanistan?
- ^ "Obama at the Precipice". The New York Times. September 27, 2009. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b "Letter From Washington - A Voice Worth Heeding on Afghanistan - NYTimes.com". The New York Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Can Congress Save Obama from Afghan Quagmire?". The Huffington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "FCNL: We're Sorry" (PDF). FCNL. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 7, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Obama could face party revolt on Afghanistan". Los Angeles Times. October 9, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c Anonymous. "Democrats in Congress Wary of Afghanistan Escalation". Archived from the original on September 23, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Obama struggles to gather support for Afghan surge". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Baker, Peter; Bumiller, Elisabeth (September 26, 2009). "Advisers to Obama Are Split on Afghan Troop Request - NYTimes.com". The New York Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Top US senator pleads for patience on Afghanistan
- ^ Kerry points to Vietnam lessons on Afghanistan
- ^ John Kerry (September 27, 2009). "John Kerry: Testing Afghanistan Assumptions - WSJ". WSJ. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Congresswoman Lee Introduces Legislation Prohibiting Funding for Military Escalation in Afghanistan". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c US Lawmakers Question Afghanistan Strategy
- ^ "Login". Archived from the original on January 10, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Anonymous. "Robert Naiman - On Afghanistan, Michael Steele Speaks for Me". Archived from the original on March 20, 2011. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "In war-funding vote, Democrats cast doubts on Obama's Afghan policy". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Tea Party eyes the cost of war in Afghanistan". IVN.us. Archived from the original on September 11, 2011. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Afghanistan Study Group – Survey Results of Conservatives". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "Bipartisan Group Of Lawmakers Introduce Afghanistan Withdrawal Legislation". The Huffington Post. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "The DNC Wants Out of Afghanistan". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Afghanistan - the proxy war". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Amy Goodman. "Afghanistan war threatens to make us 'the evil we deplore'". madison.com. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Reassessing Obama's 'war of necessity'". Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Eighth year of Afghan War should be the last". The Hofstra Chronicle. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "South Korean troops leaving Afghanistan". UPI. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Washington asks Seoul for money for Afghanistan". Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b "Switzerland ends military mission in Afghanistan". SWI Swissinfo.ch. Archived from the original on May 26, 2012. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Netherlands confirms 2010 Afghanistan pullout". ABC News. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Harper says 2011 'end date' for Afghanistan mission". September 10, 2008. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b "British troop numbers to be cut in Afghanistan". The Independent. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Canadian PM says he won't extend Afghan mission
- ^ "Login". Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Berlusconi: Best to exit Afghanistan soon[dead link]
- ^ "Berlusconi Says Italy to Withdraw 500 Afghanistan Troops Soon". Bloomberg News. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ UK's Brown seeks fewer UK troops in Afghanistan
- ^ a b c "Parliament votes against new Afghan mission". DutchNews.nl. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "Dutch Government Collapses Over Its Stance on Troops for Afghanistan". The New York Times. February 21, 2010. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ "Japan to end Afghan refuelling mission". Financial Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ Japan to end Afghan refuelling mission in January
- ^ Afghanistan will be 'strictly civilian mission' after 2011, PM says[permanent dead link]
- ^ Afghan Pullout Final: PM
- ^ a b John W. Miller in Brussels and Maarten Van Tartwijk in Amsterdam (February 19, 2010). "Dutch Parliament Debates Afghanistan". WSJ. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Dutch political crisis over war". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Afghan war moves centre-stage in Polish election". Archived from the original on July 13, 2011. Retrieved June 26, 2010.
- ^ a b Thomson Reuters Foundation. "Thomson Reuters Foundation". Retrieved February 6, 2015.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ "BBC News - Dutch troops end Afghanistan deployment". BBC News. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Dutch troops leave Afghanistan". ABC News. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Leading article: Our Afghan exit is now overdue". The Independent. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b c "Error". Archived from the original on November 23, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "WebCite query result". Archived from the original on November 21, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Afghanistan: des voix s'élèvent pour accélérer le retrait des forces françaises". leparisien.fr. February 6, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Obama announces US troops in Afghanistan will be home by 2014
- ^ a b "Canada ends combat mission in Afghanistan". NewsComAu. Retrieved May 25, 2016.
- ^ a b "Many in Kandahar fear looming disaster as Canada withdraws". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Afghanistan 'training mission' doesn't add up". November 15, 2010. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Canadian combat troops exit Afghanistan - Canadian trainers enter". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Business & Financial News, Breaking US & International News - Reuters.com". Reuters. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
