Prostaglandin H2

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Prostaglandin+H2 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32O5 | |
| Molar mass | 352.465 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Prostaglandin H2 is a type of prostaglandin and a precursor for many other biologically significant molecules. It is synthesized from arachidonic acid in a reaction catalyzed by a cyclooxygenase enzyme.[1]
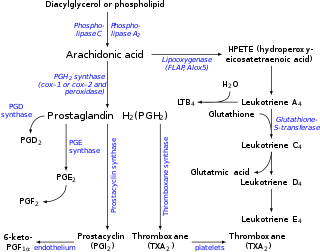
It is acted upon by:
- Prostacyclin synthase to create prostacyclin
- Thromboxane-A synthase to create thromboxane A2 and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) (see 12-Hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)
- Prostaglandin D2 synthase to create prostaglandin D2
- Prostaglandin E synthase to create prostaglandin E2
It rearranges non-enzymatically to:
- A mixture of 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (see 12-Hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)

References
- ^ "The Cyclooxygenase Reaction Mechanism". ACS Publications. Retrieved 18 April 2016.
