Highways in Australia: Difference between revisions
→Brisbane to Darwin: removed one too many "*" in list |
Isfckingevil (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 418: | Line 418: | ||
| tba |
| tba |
||
|- align="center" |
|- align="center" |
||
| colspan="4" |''''' |
| colspan="4" |'''''2700 kilometres''''' |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|} |
|} |
||
Revision as of 07:02, 1 November 2009
This is a list of highways in Australia, listed alphabetically along with its route number and location. Note that some highways service more than one state or territory.
Route numbering systems
Australia is a vast and sparsely populated country. Its earliest highways radiate in a spoke-like pattern from capital cities in each State. These highways link major country towns to the capital cities. Intercapital transport was initially mainly by sea and rail.
As the population increased, roads connecting the towns located on different highways were constructed. Victoria, for example, has the largest highway network, with every major town linked directly to every other major town in the state. Increased demand for freight and passenger transport led to construction of intercity highways, although much freight still goes by rail.
National Route Numbering System


In 1955, the Australian National Route Numbering System was introduced to simplify navigation across Australia. The National Route Numbers are marked by white shields which are present in directional signs, distance signs or trailblazers. The general rule is that odd-numbered highways travel in north-south directions and even-numbered highways in east-west directions, with only a few exceptions. National Route 1 was assigned to a network of highways and roads which together linked all capital cities and coastal towns circumnavigating the mainland.
In the 1970s the National Highway scheme was introduced. It is made up of highways that give the most direct point-to-point route between capitals. These highways are federally funded. They are recognised by their distinct green and gold shields.
The National Route system initially linked the centres of towns and cities and terminated at the junction of other national routes. The growth of bypasses around towns and cities changes the situation somewhat. National Routes often terminate at the metropolitan city limits rather than the individual city centres.
State Route Numbering System
Important urban and inter-regional routes not covered by the National Highway or National Route systems were marked under the State Route system. They are recognised by blue shield markers. They were practically adopted in all states by the end of the 1980s. In some states, some less important National Routes had been downgraded to State Routes.
In New South Wales, they are also adopted in metropolitan areas of Wollongong and Newcastle using three-digit numbers instead of two-digit found elsewhere. In regional Victoria and South Australia, the blue shield state route numbers were superseded in the late 1990s with the alphanumeric system, which is also used in Tasmania. See below.
Alphanumeric Route Numbering System


In the 1990s there was a major change to the route marking systems. Victoria and South Australia had completely overhauled their systems. They discarded the National and State Route Numbering Systems and introduced the alphanumeric marking scheme following the example set by Tasmania in the late 1970s.
The route numbers inherited from the original National Route Numbering System remains with a few exceptions, however they are now prefixed with letters denoting their grade. For example, Western Freeway is M8 until Ballarat and continues beyond as A8 Western Highway.They are not used in the Melbourne metropolitan area where the blue-shield metropolitan route system is retained.
New South Wales is slowly preparing to introduce the alphanumeric system with new road signs being fitted with such numbers and then being "coverplated" with the existing route number. It has not been announced when this system will officially be introduced.
There are no plans to introduce such a system in Western Australia.
"M" Routes
Primary highways. These are typically dual carriageway motorway standard highways. They connect capital cities to each other or to bigger rural cities and also applicable to major city freeways. Interchanges may either be graded or level. They carry high volumes of traffic and bypass settlements, towns and sometimes cities.
"A" Routes
Single carriageway interstate or interregional primary highways. Traffic volume less than "M" routes but with ample overtaking lanes, sealed shoulders and markings. They may pass through or bypass town centres.
"B" Routes
Secondary highways linking together major towns on different "A" routes including certain lesser important former national routes. In addition, they may include major bypassed sections of former "A" or "M" routes and significant tourist routes. They are reasonably good quality sealed roads with shoulders either sealed or not.
"C" Routes
Roads linking smaller settlements and towns to "A", "B" or "M" routes. May also be applied to short bypassed sections of former "A" routes. Fully sealed surface but of moderate to poor quality and may or may not have shoulders.
"D" Routes
These are unsealed roads linking very small remote towns. The term is used in this sense only in South Australia so far and is generally applied to unsealed roads and tracks or unsealed extensions of "B" or "C" routes. Roads/tracks are of various quality for an unsealed road. Use of 4 wheel drive vehicles are recommended for some "D" Routes. Another meaning, in New South Wales, "D" routes refer to detour routes. An example of this is the D5 which provides motorists with an alternate route when the M5 tunnel is closed.

Metropolitan Route Numbering System
In the 1990s in Sydney and Brisbane, urban route numbering system were streamlined in the new Metroad scheme. They are recognised by distinctive hexagonal shields and superseded the state route, freeway and National Route schemes along their path. Metroads radiate in a spoke pattern from city centres to highways outside metropolitan limits. In addition, Metroads also cover major city ring roads. Metroads are made of urban highways, main roads and urban freeways.
Non-Metroads retain the earlier state route system.
Australian highways
Below is the listing of National highways (and their destination routes), followed by highways sorted by states and territories and their corresponding routes. This list has over 100 entries. To view these highways alphabetically click here.
National highways
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Highway | Canberra to Yarra | 73 | |
| Hume Highway | Yarra to Sydney | 187 | |
| 260 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barton Highway | Canberra to Yass | 52 | |
| Hume Highway | Yass to Albury | 294 | |
| Hume Freeway | Wodonga to Melbourne (Thomastown) | 290 | |
| Western Ring Road | Melbourne | 15 | |
| 651 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hume Highway | Sydney to Albury | 539 | |
| Hume Freeway | Wodonga to Melbourne (Thomastown) | 290 | |
| Western Ring Road | Melbourne | 15 | |
| 844 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hume Highway | Sydney to Tarcutta | 392 | |
| Sturt Highway | Tarcutta to Buronga | 597 | |
| Mildura to Gawler | 370 | ||
| Main North Road | Gawler to Adelaide | 44 | |
| 1403 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sydney-Newcastle Freeway | Sydney to Newcastle | 127 | |
| New England Highway | Newcastle to Wallangarra | 581 | |
| Wallangarra to Warwick | 95 | ||
| Cunningham Highway | Warwick to Ipswich | 127 | |
| Ipswich Motorway | Ipswich to Brisbane | 14 | |
| 944 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Ring Road | Melbourne | 15 | |
| Hume Freeway | Melbourne (Thomastown) to Seymour | 89 | |
| Goulburn Valley Freeway | Seymour to Shepparton (except Nagambie) | 45 | |
| Goulburn Valley Highway | Shepparton to Tocumwal (including Nagambie) | 110 | |
| Newell Highway | Tocumwal to Goondiwindi | 1062 | |
| Leichhardt Highway | Goondiwindi to North Goondiwindi | 21 | |
| Gore Highway | North Goondiwindi to Toowoomba | 202 | |
| Warrego Highway | Toowoomba to Ipswich | 97 | |
| Ipswich Motorway | Ipswich to Brisbane | 14 | |
| 1655 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Ring Road | Melbourne | 15 | |
| Western Freeway | Melbourne (Deer Park) to Ballarat | 115 | |
| Western Highway | Ballarat to VIC/SA Border | 314 | |
| Dukes Highway | VIC/SA Border to Tailem Bend | 189 | |
| Princes Highway | Tailem Bend to Murray Bridge | 25 | |
| South Eastern Freeway | Murray Bridge to Crafers | 66 | |
| Adelaide-Crafers Highway | Crafers to Adelaide | 10 | |
| 719 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main North Road | Adelaide to Gepps Cross | tba | |
| Grand Junction Road | Gepps Cross to Regency Park | tba | |
| South Road | Regency Park to Wingfield | tba | |
| Salisbury Highway | Wingfield to Mawson Lakes | tba | |
| Port Wakefield Road | Mawson Lakes to Snowtown | tba | |
| Princes Highway | Snowtown to Port Augusta | tba | |
| Stuart Highway | Port Augusta to SA/NT Border | tba | |
| Stuart Highway | SA/NT Border to Daly Waters | tba | |
| Stuart Highway | Daly Waters to Darwin | tba | |
| 3,035 kilometres | |||
| Route # | Road name | Destinations | Distance (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Great Eastern Highway | Perth to Redcliffe | tba | |
| Great Eastern Highway Bypass | Redcliffe to Hazelmere | tba | |
| Roe Highway | Hazelmere to Midvale | tba | |
| Great Eastern Highway | Midvale to Coolgardie | tba | |
| Coolgardie-Esperance Highway | Coolgardie to Norseman | tba | |
| Eyre Highway | Norseman to Eucla | tba | |
| Eyre Highway | Eucla to Port Augusta | tba | |
| Princes Highway | Port Augusta to Snowtown | tba | |
| Port Wakefield Road | Snowtown to Gepps Cross | tba | |
| Main North Road | Gepps Cross to Adelaide | tba | |
| 2700 kilometres | |||
- Roe Highway Midvale (Perth) to Middle Swan (Perth)
- Great Northern Highway Middle Swan (Perth) to Port Hedland
- Great Northern Highway Port Hedland to Wyndham
- Victoria Highway Wyndham to Katherine
- Stuart Highway Katherine to Darwin
- Ipswich Motorway Brisbane to Ipswich
- Warrego Highway Ipswich to Morven
- Landsborough Highway Morven to Cloncurry
- Barkly Highway Cloncurry to Camooweal
- Barkly Highway Camooweal to Tennant Creek
- Stuart Highway Tennant Creek to Daly Waters
- Stuart Highway Daly Waters to Darwin
- Bruce Highway Brisbane to Cooroy
- Bruce Highway Cooroy to Cairns
- Brooker Highway Hobart to Granton
- Midland Highway Granton to Launceston
- Bass Highway Launceston to Burnie
State Highways
- File:Qld M1.PNG
- Gateway Motorway, Queensland
- Pacific Motorway, Queensland
- Monash Freeway, Victoria
- West Gate Freeway, Victoria
- Princes Freeway, Victoria
- CityLink, Victoria
Southern Expressway, South Australia
- Eastern Freeway, Victoria
- EastLink, Victoria
 Princes Highway, South Australia; Victoria
Princes Highway, South Australia; Victoria Princes Highway, South Australia
Princes Highway, South Australia
- Brand Highway, Western Australia
- Canning Highway, Western Australia
- Carpentaria Highway, Northern Territory
- Captain Cook Highway, Queensland
- Coolgardie-Esperance Highway, Western Australia
- Great Eastern Highway, Western Australia
- Great Northern Highway, Western Australia
- Gulf Developmental Road, Queensland
- Kennedy Highway, Queensland
- Kwinana Freeway, Western Australia
- Leach Highway, Western Australia
- North West Coastal Highway, Western Australia
- Old Coast Road, Western Australia
- Pacific Highway, New South Wales; Queensland
- Princes Highway, New South Wales
- Savannah Way, Northern Territory; Queensland
- South Coast Highway, Western Australia
- South Western Highway, Western Australia
 Bass Highway, Tasmania
Bass Highway, Tasmania Gold Coast Highway, Queensland
Gold Coast Highway, Queensland Tasman Highway, Tasmania
Tasman Highway, Tasmania
- Burnett Highway, Queensland
- D'Aguilar Highway, Queensland
- New England Highway, Queensland

- Reid Highway, Western Australia
- Roe Highway, Western Australia
 Isis Highway, Queensland
Isis Highway, Queensland Esk Highway, Tasmania
Esk Highway, Tasmania Capricorn Highway, Queensland
Capricorn Highway, Queensland
- Lasseter Highway, Northern Territory
- Tonkin Highway, Western Australia

- Anzac Highway, South Australia
- Lake Highway, Tasmania
 Leichhardt Highway, Queensland
Leichhardt Highway, Queensland Stirling Highway, Western Australia
Stirling Highway, Western Australia
- Davey Street, Tasmania
- Huon Highway, Tasmania
- Macquarie Street, Tasmania
- Southern Outlet, Tasmania
 Flinders Highway, Queensland
Flinders Highway, Queensland Canning Highway, Western Australia
Canning Highway, Western Australia West Tamar Highway, Tasmania
West Tamar Highway, Tasmania
- Carnarvon Highway, Queensland
- Dawson Highway, Queensland
- Gregory Highway, Queensland
 Leach Highway, Western Australia
Leach Highway, Western Australia East Tamar Highway, Tasmania
East Tamar Highway, Tasmania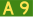 Port River Expressway, South Australia
Port River Expressway, South Australia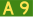 Arthur Highway, Tasmania
Arthur Highway, Tasmania
- Lyell Highway, Tasmania
- Murchison Highway, Tasmania
- Zeehan Highway, Tasmania

- Brockman Highway, Western Australia
- Bussell Highway, Western Australia
- Vasse Highway, Western Australia
 Tablelands Highway, Northern Territory
Tablelands Highway, Northern Territory Mallee Highway, South Australia; Victoria
Mallee Highway, South Australia; Victoria Plenty Highway, Northern Territory
Plenty Highway, Northern Territory Salisbury Highway, South Australia
Salisbury Highway, South Australia Mount Lindesay Highway, Queensland
Mount Lindesay Highway, Queensland Sandover Highway, Northern Territory
Sandover Highway, Northern Territory
- Brisbane Valley Highway, Queensland
- D'Aguilar Highway, Queensland
 Barossa Valley Highway, South Australia
Barossa Valley Highway, South Australia
- Roper Highway, Northern Territory
- South Western Highway, Western Australia
 Kakadu Highway, Northern Territory
Kakadu Highway, Northern Territory Monaro Highway, Victoria
Monaro Highway, Victoria Monaro Highway, New South Wales
Monaro Highway, New South Wales Mid-Western Highway, New South Wales
Mid-Western Highway, New South Wales Palmerston Highway, Queensland
Palmerston Highway, Queensland Albany Highway, Western Australia
Albany Highway, Western Australia
- Barrier Highway, South Australia
- Main North Road, South Australia

- Barrier Highway, New South Wales
- Great Western Highway, New South Wales
- Mitchell Highway, New South Wales
 Oxley Highway, New South Wales
Oxley Highway, New South Wales Arnhem Highway, Northern Territory
Arnhem Highway, Northern Territory Kamilaroi Highway, New South Wales
Kamilaroi Highway, New South Wales Gwydir Highway, New South Wales
Gwydir Highway, New South Wales Brookton Highway, Western Australia
Brookton Highway, Western Australia Olympic Highway, New South Wales
Olympic Highway, New South Wales Cunningham Highway, Queensland
Cunningham Highway, Queensland Bruxner Highway, New South Wales
Bruxner Highway, New South Wales Captain Cook Highway, Queensland
Captain Cook Highway, Queensland Carnarvon Highway, New South Wales; Queensland
Carnarvon Highway, New South Wales; Queensland Illawarra Highway, New South Wales
Illawarra Highway, New South Wales
- Balonne Highway, Queensland
- Bunya Highway, Queensland
- Moonie Highway, Queensland
- Wide Bay Highway, Queensland
 Kings Highway, New South Wales
Kings Highway, New South Wales Isis Highway, Queensland
Isis Highway, Queensland Castlereagh Highway, Queensland
Castlereagh Highway, Queensland Castlereagh Highway, New South Wales
Castlereagh Highway, New South Wales Riverina Highway, New South Wales
Riverina Highway, New South Wales Dawson Highway, Queensland
Dawson Highway, Queensland Kennedy Highway, Queensland
Kennedy Highway, Queensland Gregory Highway, Queensland
Gregory Highway, Queensland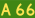 Riddoch Highway, South Australia
Riddoch Highway, South Australia Peak Downs Highway, Queensland
Peak Downs Highway, QueenslandMitchell Highway, Queensland
 Mitchell Highway, New South Wales
Mitchell Highway, New South Wales West Coast Highway, Western Australia
West Coast Highway, Western Australia Northern Highway, Victoria
Northern Highway, Victoria Cobb Highway, New South Wales
Cobb Highway, New South Wales Calder Highway, Victoria
Calder Highway, Victoria Silver City Highway, New South Wales
Silver City Highway, New South Wales Buchanan Highway, Northern Territory
Buchanan Highway, Northern Territory Mulligan Highway, Queensland
Mulligan Highway, Queensland
- Barwon Highway, Queensland
- Brisbane Valley Highway, Queensland
- D'Aguilar Highway, Queensland
- Esk-Hampton Road, Queensland
- Gore Highway, Queensland
- Leichhardt Highway, Queensland
- New England Highway, Queensland
 Tod Highway, South Australia
Tod Highway, South Australia
- Goldfields Highway, Western Australia
- Great Eastern Highway, Western Australia

- Buntine Highway, Northern Territory
- Delamere Road, Northern Territory
 D'Aguilar Highway, Queensland
D'Aguilar Highway, Queensland
- Flinders Highway, South Australia
- Lincoln Highway, South Australia
 Southern Ports Highway, South Australia
Southern Ports Highway, South Australia Muirs Highway, Western Australia
Muirs Highway, Western Australia Vasse Highway, Western Australia
Vasse Highway, Western Australia Great Southern Highway, Western Australia
Great Southern Highway, Western Australia Henty Highway, Victoria
Henty Highway, Victoria Midland Highway, Victoria
Midland Highway, Victoria
- South Gippsland Freeway, Victoria
- South Gippsland Highway, Victoria
- Bass Highway, Victoria
 Bass Highway, Victoria
Bass Highway, Victoria South Gippsland Highway, Victoria
South Gippsland Highway, Victoria Western Port Highway, Victoria
Western Port Highway, Victoria Western Port Highway, Victoria
Western Port Highway, Victoria
Major Arterial Roads
 Nepean Highway, Victoria
Nepean Highway, Victoria Great Western Highway, New South Wales
Great Western Highway, New South Wales Pacific Highway, New South Wales
Pacific Highway, New South Wales Adelaide-Mannum Road, South Australia
Adelaide-Mannum Road, South Australia Boyer Road, Tasmania
Boyer Road, Tasmania Marlborough Highway, Tasmania
Marlborough Highway, Tasmania Moorooduc Highway, Victoria
Moorooduc Highway, Victoria Mole Creek Road, Tasmania
Mole Creek Road, Tasmania
- South Road, South Australia
- Victor Harbor Road, South Australia
 Sheffield Road, Tasmania
Sheffield Road, Tasmania Castra Road, Tasmania
Castra Road, Tasmania Kindred Road, Tasmania
Kindred Road, Tasmania
- Gawler Road, Tasmania
- Preston Road, Tasmania
- Gunns Plains Road, Tasmania
- S Riana Road, Tasmania
- Pine Road, Tasmania
- W Pine Road, Tasmania
 Ridgley Highway, Tasmania
Ridgley Highway, Tasmania Forth Road, Tasmania
Forth Road, Tasmania South Road, South Australia
South Road, South Australia Lyell Highway, Tasmania
Lyell Highway, Tasmania
- Zeehan Highway, Tasmania
- Henty Road, Tasmania
- File:800px-Australian Alphanumeric State Route B31 svg.png
- Cambridge Road, Tasmania
- Richmond Road, Tasmania
- Colebrook Road, Tasmania
- Mud Walls Road, Tasmania

- Great Western Highway, New South Wales
- Liverpool Road, New South Wales
 East Derwent Highway, Tasmania
East Derwent Highway, Tasmania South Arm Highway, Tasmania
South Arm Highway, Tasmania Lake Leake Highway, Tasmania
Lake Leake Highway, Tasmania Whitehorse Road, Victoria
Whitehorse Road, Victoria Goodwood Road, Tasmania
Goodwood Road, Tasmania Domain Highway, Tasmania
Domain Highway, Tasmania Bell's Line of Road, New South Wales
Bell's Line of Road, New South Wales Great Western Highway, New South Wales
Great Western Highway, New South Wales
- Poatina Road, Tasmania
- Cressy Road, Tasmania
 Great Eastern Highway, Western Australia
Great Eastern Highway, Western Australia Meander Valley Highway, Tasmania
Meander Valley Highway, Tasmania Princes Highway, New South Wales
Princes Highway, New South Wales
- Main North Road, South Australia
- Wilmington-Ucolta Road, South Australia

- Princes Highway, New South Wales
- Wanneroo Road (Perth-Lancelin Highway), Western Australia
 Gordon River Road, Tasmania
Gordon River Road, Tasmania Glenora Road, Tasmania
Glenora Road, Tasmania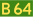 Huon Road, Tasmania
Huon Road, Tasmania- File:800px-Australian Alphanumeric State Route B68 svg.png
- Sandy Bay Road, Tasmania
- Channel Highway, Tasmania

- Appin Road, New South Wales
- Putty Road, New South Wales
 Frankford Road, Tasmania
Frankford Road, Tasmania Biralee Road, Tasmania
Biralee Road, Tasmania Batman Highway, Tasmania
Batman Highway, Tasmania Waterfall Way, New South Wales
Waterfall Way, New South Wales Wilmington-Ucolta Road, South Australia
Wilmington-Ucolta Road, South Australia Lachlan Valley Way, New South Wales
Lachlan Valley Way, New South Wales Main North Road, South Australia
Main North Road, South Australia
- Central Coast Highway, New South Wales
- Pacific Highway, New South Wales
 Golden Highway, New South Wales
Golden Highway, New South Wales Goldfields Way, New South Wales
Goldfields Way, New South Wales Castlereagh Highway, New South Wales
Castlereagh Highway, New South Wales Kidman Way, New South Wales
Kidman Way, New South Wales Picton Road, New South Wales
Picton Road, New South Wales Camden Valley Way, New South Wales
Camden Valley Way, New South Wales Escort Way, New South Wales
Escort Way, New South Wales Summerland Way, New South Wales
Summerland Way, New South Wales Burley Griffin Way, New South Wales
Burley Griffin Way, New South Wales Fossickers Way, New South Wales
Fossickers Way, New South Wales Surf Coast Highway, Victoria
Surf Coast Highway, Victoria
- Bellarine Highway, Victoria
- Hollow Tree Road, Tasmania
- Nepean Highway, Victoria
 Pacific Highway, New South Wales
Pacific Highway, New South Wales Hopkins Highway, Victoria
Hopkins Highway, Victoria Geraldton-Mount Magnet Road, Western Australia
Geraldton-Mount Magnet Road, Western Australia Hamilton Highway, Victoria
Hamilton Highway, Victoria Glenelg Highway, Victoria
Glenelg Highway, Victoria Pyrenees Highway, Victoria
Pyrenees Highway, Victoria Henty Highway, Victoria
Henty Highway, Victoria Sunraysia Highway, Victoria
Sunraysia Highway, Victoria
 Wimmera Highway, Victoria
Wimmera Highway, Victoria Loddon Valley Highway, Victoria
Loddon Valley Highway, Victoria McIvor Highway, Victoria
McIvor Highway, Victoria
- Goulburn Valley Highway, Victoria
- Maroondah Highway, Victoria
- Melba Highway, Victoria
- Midland Highway, Victoria
 Maroondah Highway, Victoria
Maroondah Highway, Victoria
- Goulburn Valley Highway, Victoria
- Maroondah Highway, Victoria
 Maroondah Highway, Victoria
Maroondah Highway, Victoria Warburton Highway, Victoria
Warburton Highway, Victoria
- Bass Highway, Victoria
- Strzelecki Highway, Victoria
- Gillies Highway, Queensland
- Perth-Bunbury Highway (proposed), Western Australia
Minor Arterial Roads
 Burwood Highway, Victoria
Burwood Highway, Victoria Mountain Highway, Victoria
Mountain Highway, VictoriaBorung Highway, Victoria
Borung Highway, Victoria
 Burwood Highway, Victoria
Burwood Highway, Victoria Hyland Highway, Victoria
Hyland Highway, Victoria Kiewa Valley Highway, Victoria
Kiewa Valley Highway, Victoria Omeo Highway, Victoria
Omeo Highway, Victoria Melton Highway, Victoria
Melton Highway, Victoria
- Alpine Way, New South Wales
- Barry Way, New South Wales
- Bathurst-Ilford Road, New South Wales
- Bucketts Way, New South Wales
- Bylong Valley Way, New South Wales
- Derby Highway, Western Australia
- Dampier Highway, Western Australia
- Goldfields Highway, Western Australia
- Goulburn-Oberon Road, New South Wales
- Henry Lawson Way, New South Wales
- Irrigation Way, New South Wales
- Lachlan Valley Way, New South Wales
- O'Connell Road, New South Wales
- Thunderbolts Way, New South Wales
- Wombeyan Caves Road, New South Wales
Outback Tracks
 Duncan Road, Western Australia
Duncan Road, Western Australia Buntine Highway, Western Australia
Buntine Highway, Western Australia
- Anne Beadell Highway, South Australia; Western Australia
- Birdsville Track, Queensland; South Australia
- Canning Stock Route, Western Australia
- Cape Leveque Road, Western Australia
- Connie Sue Highway, Western Australia
- Duncan Road, Northern Territory
- Gary Highway, Western Australia
- Gibb River Road, Western Australia
- Great Central Road, Western Australia
- Gunbarrel Highway, Northern Territory; South Australia; Western Australia
- Kalumburu Road, Western Australia
- Oodnadatta Track, South Australia
- Strzelecki Track, South Australia
- Tanami Road, Western Australia
- Tanami Track, Northern Territory
Tourist Roads
 Great Ocean Road, Victoria
Great Ocean Road, Victoria Murray Valley Highway, Victoria
Murray Valley Highway, Victoria Phillip Island Road, Victoria
Phillip Island Road, Victoria Great Alpine Road, Victoria
Great Alpine Road, Victoria
State listing
For state listings see:
- List of highways in New South Wales
- List of highways in Victoria
- List of highways in Queensland
- List of highways in South Australia
- List of highways in Western Australia
- List of highways in Tasmania
- List of highways in Northern Territory
