NetPositive: Difference between revisions
m WP:CHECKWIKI error fix for #03. Missing Reflist. Do general fixes if a problem exists. - using AWB (11450) |
Cyberbot II (talk | contribs) Rescuing 1 sources. #IABot |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
*[http://www.arstechnica.com/reviews/4q99/bebrow/bebrow-1.html Browsin' on BeOS article] |
*[http://www.arstechnica.com/reviews/4q99/bebrow/bebrow-1.html Browsin' on BeOS article] |
||
*[http://www.libpng.org/pub/png/pngs-img-netpos.html NetPositive 2.2 PNG screenshots] |
*[http://www.libpng.org/pub/png/pngs-img-netpos.html NetPositive 2.2 PNG screenshots] |
||
*[http://themis.sourceforge.net Themis home page] |
*[http://web.archive.org/web/20070516172726/http://themis.sourceforge.net:80/ Themis home page] |
||
*[http://8325.org/haiku List of NetPositive haiku error messages] |
*[http://8325.org/haiku List of NetPositive haiku error messages] |
||
{{Web browsers|desktop}} |
{{Web browsers|desktop}} |
||
Revision as of 10:31, 28 February 2016
| File:NetPositiveIcon.png | |
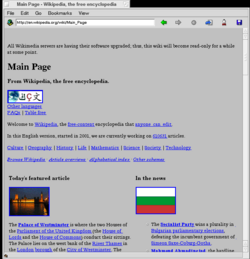 NetPositive 2.2 under BeOS R5 showing Wikipedia (no CSS support) | |
| Developer(s) | Be Inc. |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 2.2.2
/ November 1, 2001 |
| Operating system | BeOS |
| Type | Web browser |
| License | Proprietary |
NetPositive (often called Net+) is the default browser that comes with the Be Operating System (BeOS). It has partial support for JavaScript, but no Java or CSS support.[1] NetPositive was originally developed as a stop-gap measure [2] and was the only web browser available for BeOS, but that is no longer the case. The last official version of NetPositive before the Be, Inc. bankruptcy was 2.2/2.2.1 for US customers, but there also exists a 3.0d3 beta version, and a leaked 2.2.2 which changed from the RSA Encryption Engine to OpenSSL, possibly indicating that Be were cleaning the source of commercial code with an intent to open source, like the OpenTracker project.
Built binaries of NetPositive, including all encryption libraries, and other tools not provided by the OS itself, such as the HTTP and FTP engines, weigh in from 1.4 to 1.7 MB in size, uncompressed, depending on the strength of encryption provided.
NetPositive can be embedded into another application, or into the desktop of the OS itself, using the replicants system provided by the OS. When Active Desktop was launched on Windows, Microsoft promoted it as having been a major achievement. Be later claimed to have cloned the functionality using NetPositive (where Internet Explorer is used in Windows) in "nine lines of code".
A number of projects exist to clone NetPositive for BeOS, due to BeOS users' familiarity with its interface. The most advanced of these is Themis, which aims to capture the feel of NetPositive in a browser with modern features. There is also Net++, which aims to use the Gecko layout engine in the shell of the failed NetOptimist browser. For Haiku there is a successor for NetPositive, based on WebKit, called WebPositive.
It is still included in ZETA as the default browser for opening saved files and links from other applications, due to unfinished implementation of the native OS bindings in Mozilla Firefox for BeOS. However, Firefox is promoted as being the primary browser on the platform.
Error messages in Haiku
The browser was notable among BeOS users due to its haiku error messages, which led to the name of Haiku, an open-source BeOS clone. A late 1990s email joke which claimed that Microsoft was moving to Haiku error messages in Japanese versions of Windows was almost entirely made up of NetPositive error messages. For instance, a user might see the following error message if they try to access a website that is unavailable:
- Cables have been cut
- Southwest of Northeast somewhere
- We are not amused.
If the user tried unsuccessfully to authenticate against a website, they might see:
- Server's poor response
- Not quick enough for browser.
- Timed out, plum blossom.
References
- ^ "BeOS". The Stoa Consortium. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- ^ "Browsin' on BeOS". Arstechnica.com. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
