Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Difference between revisions
rv repeated claim of profit-motivated drug company conspiracy |
HeyElliott (talk | contribs) Redundant, added info to refs, ce |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Neurodevelopmental disorder}} |
|||
'''Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)''' is one of the most commonly diagnosed [[mental disorder]]s among children, although it also occurs in adults. |
|||
{{Redirect|Attention Deficit|the album|Attention Deficit (album){{!}}''Attention Deficit'' (album)}} |
|||
{{pp|small=yes}} |
|||
{{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc|display-authors=6}} |
|||
{{Redirect-multi|3|ADD|ADHD|Hyperactive}} |
|||
{{Good article}} |
|||
{{Use British English|date=September 2022}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=January 2024}} |
|||
<!-- Citation template: this page uses the Vancouver citation convention with the parameter "vauthors=" preventing the display of a dot just after the initials of an author name. --> |
|||
{{Infobox medical condition |
|||
| name = Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
|||
| image = Primary Laos2.jpg |
|||
| caption = People with ADHD struggle more than others to sustain their attention on some tasks (such as schoolwork), but may maintain an [[Hyperfocus|unusually intense level of attention]] for tasks they find immediately rewarding or interesting. |
|||
| alt = An image of children |
|||
| field = {{hlist | [[Psychiatry]] | [[pediatrics]]}} |
|||
| symptoms = {{hlist | [[Inattention]] | [[carelessness]] | hyperactivity | [[executive dysfunction]] | disinhibition | emotional dysregulation | [[impulsivity]] | impaired working memory}} |
|||
| complications = |
|||
| onset = Typically at least some ADHD symptoms and impairments onset during the developmental period. Exceptions include if they were compensated for (e.g., by a high IQ or structured environment) or if the individual clearly suffered a neurologically compromising event. |
|||
| duration = |
|||
| causes = [[Genetic disorder|Genetic]] (inherited, [[de novo mutation|de novo]]) and to a lesser extent, [[environmental factors|environmental]] factors (exposure to biohazards during pregnancy, [[traumatic brain injury]]) |
|||
| risks = |
|||
| diagnosis = Based on symptoms after other possible causes have been ruled out |
|||
| differential = {{hlist | Individual without ADHD | symptomatic but unimpaired | [[bipolar disorder]] | [[cognitive disengagement syndrome]] | [[conduct disorder]] | [[major depressive disorder]] | [[autism spectrum disorder]] | [[oppositional defiant disorder]] | [[learning disorder]] | [[intellectual disability]] | [[anxiety disorder]]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.heysigmund.com/anxiety-and-adhd/ |title=Anxiety or ADHD? Why They Sometimes Look the Same and How to Tell the Difference | vauthors = Young K |website=Hey Sigmund |date=9 February 2017 |access-date=27 January 2023 |archive-date=26 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230126230720/https://www.heysigmund.com/anxiety-and-adhd/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | [[borderline personality disorder]] | [[fetal alcohol spectrum disorder]]}} |
|||
| prevention = |
|||
| treatment = {{hlist | [[Psychotherapy]] | lifestyle changes | medication}} |
|||
| medication = {{hlist | [[CNS stimulants]] ([[methylphenidate]], [[amphetamine]]) | non-stimulants ([[atomoxetine]], [[viloxazine]]) | alpha-2a agonists ([[guanfacine|guanfacine XR]], [[clonidine|clonidine XR]])}} |
|||
| prognosis = |
|||
| frequency = 0.8–1.5% (2019, using DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10)<ref name=GBD2019/> |
|||
| deaths = |
|||
}} |
|||
<!--Signs and symptoms --> |
|||
'''Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder''' ('''ADHD''') is a [[neurodevelopmental disorder]] characterised by [[executive dysfunction]] occasioning symptoms of [[inattention]], hyperactivity, [[impulsivity]] and [[emotional dysregulation]] that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise [[Developmental psychology|age-inappropriate]].{{refn|<ref name=DSM5>{{cite book |title=Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |publisher=American Psychiatric Publishing |url = https://archive.org/details/diagnosticstatis0005unse/page/58/mode/2up?q=attention+deficit |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-89042-555-8 |edition=5th |location=Arlington |pages=59–65}}</ref><ref name=DSM5TR>{{cite book |title=Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR) |title-link=DSM-5-TR |publisher=American Psychiatric Publishing |date=February 2022 |isbn=978-0-89042-575-6 |oclc=1288423302 |location=Washington, D.C. }}</ref><ref name="ICD-11" /><ref name="Foreman_2006" /><ref name="Faraone_2021">{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Zheng Y, Biederman J, Bellgrove MA, Newcorn JH, Gignac M, Al Saud NM, Manor I, Rohde LA, Yang L, Cortese S, Almagor D, Stein MA, Albatti TH, Aljoudi HF, Alqahtani MM, Asherson P, Atwoli L, Bölte S, Buitelaar JK, Crunelle CL, Daley D, Dalsgaard S, Döpfner M, Espinet S, Fitzgerald M, Franke B, Gerlach M, Haavik J, Hartman CA, Hartung CM, Hinshaw SP, Hoekstra PJ, Hollis C, Kollins SH, Sandra Kooij JJ, Kuntsi J, Larsson H, Li T, Liu J, Merzon E, Mattingly G, Mattos P, McCarthy S, Mikami AY, Molina BS, Nigg JT, Purper-Ouakil D, Omigbodun OO, Polanczyk GV, Pollak Y, Poulton AS, Rajkumar RP, Reding A, Reif A, Rubia K, Rucklidge J, Romanos M, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Schellekens A, Scheres A, Schoeman R, Schweitzer JB, Shah H, Solanto MV, Sonuga-Barke E, Soutullo C, Steinhausen HC, Swanson JM, Thapar A, Tripp G, van de Glind G, van den Brink W, Van der Oord S, Venter A, Vitiello B, Walitza S, Wang Y | title = The World Federation of ADHD International Consensus Statement: 208 Evidence-based conclusions about the disorder | journal = Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | volume = 128 | pages = 789–818 | date = September 2021 | pmid = 33549739 | pmc = 8328933 | doi = 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.01.022 | publisher = Elsevier BV | doi-access = free }}</ref>}}<!-- quote=to a degree that is inconsistent with developmental level --> |
|||
ADHD symptoms arise from [[executive dysfunction]],{{refn|<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pievsky MA, McGrath RE | title = The Neurocognitive Profile of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Review of Meta-Analyses | journal = Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology | volume = 33 | issue = 2 | pages = 143–157 | date = March 2018 | pmid = 29106438 | doi = 10.1093/arclin/acx055 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Schoechlin C, Engel RR | title = Neuropsychological performance in adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: meta-analysis of empirical data | journal = Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology | volume = 20 | issue = 6 | pages = 727–744 | date = August 2005 | pmid = 15953706 | doi = 10.1016/j.acn.2005.04.005 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hart H, Radua J, Nakao T, Mataix-Cols D, Rubia K | title = Meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of inhibition and attention in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: exploring task-specific, stimulant medication, and age effects | journal = JAMA Psychiatry | volume = 70 | issue = 2 | pages = 185–198 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23247506 | doi = 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.277 }}</ref><ref name="Joao P 2019">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hoogman M, Muetzel R, Guimaraes JP, Shumskaya E, Mennes M, Zwiers MP, Jahanshad N, Sudre G, Wolfers T, Earl EA, Soliva Vila JC, Vives-Gilabert Y, Khadka S, Novotny SE, Hartman CA, Heslenfeld DJ, Schweren LJ, Ambrosino S, Oranje B, de Zeeuw P, Chaim-Avancini TM, Rosa PG, Zanetti MV, Malpas CB, Kohls G, von Polier GG, Seitz J, Biederman J, Doyle AE, Dale AM, van Erp TG, Epstein JN, Jernigan TL, Baur-Streubel R, Ziegler GC, Zierhut KC, Schrantee A, Høvik MF, Lundervold AJ, Kelly C, McCarthy H, Skokauskas N, O'Gorman Tuura RL, Calvo A, Lera-Miguel S, Nicolau R, Chantiluke KC, Christakou A, Vance A, Cercignani M, Gabel MC, Asherson P, Baumeister S, Brandeis D, Hohmann S, Bramati IE, Tovar-Moll F, Fallgatter AJ, Kardatzki B, Schwarz L, Anikin A, Baranov A, Gogberashvili T, Kapilushniy D, Solovieva A, El Marroun H, White T, Karkashadze G, Namazova-Baranova L, Ethofer T, Mattos P, Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Plessen KJ, Kuntsi J, Mehta MA, Paloyelis Y, Harrison NA, Bellgrove MA, Silk TJ, Cubillo AI, Rubia K, Lazaro L, Brem S, Walitza S, Frodl T, Zentis M, Castellanos FX, Yoncheva YN, Haavik J, Reneman L, Conzelmann A, Lesch KP, Pauli P, Reif A, Tamm L, Konrad K, Oberwelland Weiss E, Busatto GF, Louza MR, Durston S, Hoekstra PJ, Oosterlaan J, Stevens MC, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Vilarroya O, Fair DA, Nigg JT, Thompson PM, Buitelaar JK, Faraone SV, Shaw P, Tiemeier H, Bralten J, Franke B | title = Brain Imaging of the Cortex in ADHD: A Coordinated Analysis of Large-Scale Clinical and Population-Based Samples | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 176 | issue = 7 | pages = 531–542 | date = July 2019 | pmid = 31014101 | pmc = 6879185 | doi = 10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18091033 }}</ref><ref name="Brown_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Brown TE | title = ADD/ADHD and Impaired Executive Function in Clinical Practice | journal = Current Psychiatry Reports | volume = 10 | issue = 5 | pages = 407–411 | date = October 2008 | pmid = 18803914 | doi = 10.1007/s11920-008-0065-7 | s2cid = 146463279 }}</ref><ref name="Malenka pathways" /><ref name="Executive functions">{{cite journal | vauthors = Diamond A | title = Executive functions | journal = Annual Review of Psychology | volume = 64 | pages = 135–168 | year = 2013 | pmid = 23020641 | pmc = 4084861 | doi = 10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750 | quote = {{abbr|EFs|executive functions}} and prefrontal cortex are the first to suffer, and suffer disproportionately, if something is not right in your life. They suffer first, and most, if you are stressed (Arnsten 1998, Liston et al. 2009, Oaten & Cheng 2005), sad (Hirt et al. 2008, von Hecker & Meiser 2005), lonely (Baumeister et al. 2002, Cacioppo & Patrick 2008, Campbell et al. 2006, Tun et al. 2012), sleep deprived (Barnes et al. 2012, Huang et al. 2007), or not physically fit (Best 2010, Chaddock et al. 2011, Hillman et al. 2008). Any of these can cause you to appear to have a disorder of EFs, such as ADHD, when you do not. }}</ref><ref name="Antshel_2014">{{cite book | vauthors = Antshel KM, Hier BO, Barkley RA | chapter = Executive Functioning Theory and ADHD |date=2014 | title = Handbook of Executive Functioning |pages=107–120 | veditors = Goldstein S, Naglieri JA |place=New York, NY |publisher=Springer |doi=10.1007/978-1-4614-8106-5_7 |isbn=978-1-4614-8106-5 }}</ref>}} and [[emotional dysregulation]] is often considered a core symptom.{{refn|<ref name="Retz_2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Retz W, Stieglitz RD, Corbisiero S, Retz-Junginger P, Rösler M | title = Emotional dysregulation in adult ADHD: What is the empirical evidence? | journal = Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics | volume = 12 | issue = 10 | pages = 1241–1251 | date = October 2012 | pmid = 23082740 | doi = 10.1586/ern.12.109 | s2cid = 207221320 }}</ref><ref name="auto2">{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Rostain AL, Blader J, Busch B, Childress AC, Connor DF, Newcorn JH | title = Practitioner Review: Emotional dysregulation in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder - implications for clinical recognition and intervention | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 60 | issue = 2 | pages = 133–150 | date = February 2019 | pmid = 29624671 | doi = 10.1111/jcpp.12899 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Shaw P, Stringaris A, Nigg J, Leibenluft E | title = Emotion dysregulation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 171 | issue = 3 | pages = 276–293 | date = March 2014 | pmid = 24480998 | pmc = 4282137 | doi = 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13070966 }}</ref>}} Difficulties with self-regulation such as time management, inhibition and sustained attention may result in poor academic performance, unemployment and numerous health risks,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Fleming M, Fitton CA, Steiner MF, McLay JS, Clark D, King A, Mackay DF, Pell JP | title = Educational and Health Outcomes of Children Treated for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder | journal = JAMA Pediatrics | volume = 171 | issue = 7 | pages = e170691 | date = July 2017 | pmid = 28459927 | pmc = 6583483 | doi = 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.0691 }}</ref> collectively predisposing to a diminished quality of life<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lee YC, Yang HJ, Chen VC, Lee WT, Teng MJ, Lin CH, Gossop M | title = Meta-analysis of quality of life in children and adolescents with ADHD: By both parent proxy-report and child self-report using PedsQL™ | journal = Research in Developmental Disabilities | volume = 51-52 | pages = 160–172 | date = 2016-04-01 | pmid = 26829402 | doi = 10.1016/j.ridd.2015.11.009 }}</ref> and a direct average reduction in life expectancy of 13 years.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Barkley RA, Fischer M | title = Hyperactive Child Syndrome and Estimated Life Expectancy at Young Adult Follow-Up: The Role of ADHD Persistence and Other Potential Predictors | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 23 | issue = 9 | pages = 907–923 | date = July 2019 | pmid = 30526189 | doi = 10.1177/1087054718816164 | s2cid = 54472439 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cattoi B, Alpern I, Katz JS, Keepnews D, Solanto MV | title = The Adverse Health Outcomes, Economic Burden, and Public Health Implications of Unmanaged Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A Call to Action Resulting from CHADD Summit, Washington, DC, October 17, 2019 | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 26 | issue = 6 | pages = 807–808 | date = April 2022 | pmid = 34585995 | doi = 10.1177/10870547211036754 | s2cid = 238218526 }}</ref> ADHD is associated with other neurodevelopmental and [[mental disorder]]s as well as some non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment, especially in modern society.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-02-12 |title='A horrible, perfect storm': Frustrations rise as shortage of Adderall, other ADHD medication continues |url=https://www.chicagotribune.com/2024/02/12/adhd-medication-shortage/ |access-date=2024-02-16 |website=Chicago Tribune }}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Adhdbrain.gif|200px|framed|The image on the left illustrates areas of activity in the [[brain]] of a person without ADHD. The image on the right illustrates the areas of activity of the brain of someone with ADHD.]] |
|||
Although people with ADHD struggle to persist on tasks with temporally delayed consequences, they may be able to maintain an unusually prolonged level of attention for tasks they do find intrinsically interesting or immediately rewarding;<ref name = "Barkley_2011">{{Cite journal | vauthors = Barkley RA, Murphy KR |date=2011-06-01 |title=The Nature of Executive Function (EF) Deficits in Daily Life Activities in Adults with ADHD and Their Relationship to Performance on EF Tests |journal=Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment |volume=33 |issue=2 |pages=137–158 |doi=10.1007/s10862-011-9217-x |issn=1573-3505}}</ref><ref name="Antshel_2014" /> this is known as [[hyperfocus]] (more colloquially)<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Groen Y, Priegnitz U, Fuermaier AB, Tucha L, Tucha O, Aschenbrenner S, Weisbrod M, Garcia Pimenta M | title = Testing the relation between ADHD and hyperfocus experiences | journal = Research in Developmental Disabilities | volume = 107 | pages = 103789 | date = December 2020 | pmid = 33126147 | doi = 10.1016/j.ridd.2020.103789 }}</ref> or perseverative responding.<ref>{{Cite web |title=APA PsycNet |url=https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2021-82653-001 |access-date=2024-03-03 |website=psycnet.apa.org }}</ref> This is a mental state in which a person is completely absorbed in a task to the point of apparently ignoring or "tuning out" everything else, often with difficulty disengaging<ref name = "Barkley_2011" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ashinoff BK, Abu-Akel A | title = Hyperfocus: the forgotten frontier of attention | journal = Psychological Research | volume = 85 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–19 | date = February 2021 | pmid = 31541305 | pmc = 7851038 | doi = 10.1007/s00426-019-01245-8 }}</ref> and can be related to risks such as for internet addiction<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ishii S, Takagi S, Kobayashi N, Jitoku D, Sugihara G, Takahashi H | title = Hyperfocus symptom and internet addiction in individuals with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder trait | journal = Frontiers in Psychiatry | volume = 14 | pages = 1127777 | date = 2023-03-16 | pmid = 37009127 | pmc = 10061009 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1127777 | doi-access = free }}</ref> and types of offending behaviour.<ref>{{Cite journal | vauthors = Worthington R, Wheeler S |date= January 2023 |title=Hyperfocus and offending behaviour: a systematic review |journal=The Journal of Forensic Practice |volume=25 |issue=3 |pages=185–200 |doi=10.1108/JFP-01-2022-0005 |issn=2050-8794 |s2cid=258330884|url= https://clok.uclan.ac.uk/46646/1/Manuscript%20with%20author%20details%2012.01.21.pdf }}</ref> |
|||
The official definitions of ADHD according to the US [[Surgeon General]] and ICD-9-CM ([[International Classification of Disease]] Revised Edition 2005) is a neurological deficit classified as "[[metabolic]] [[encephalopathy]]" affecting the release and [[homeostasis]] of [[neurological]] chemicals and the functioning of the [[limbic system]]. |
|||
ADHD represents the extreme lower end of the continuous dimensional trait (bell curve) of executive functioning and self-regulation, which is supported by twin, brain imaging and molecular genetic studies.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Larsson H, Anckarsater H, Råstam M, Chang Z, Lichtenstein P | title = Childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder as an extreme of a continuous trait: a quantitative genetic study of 8,500 twin pairs | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 53 | issue = 1 | pages = 73–80 | date = January 2012 | pmid = 21923806 | doi = 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02467.x }}</ref><ref name="Joao P 2019"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lee SH, Ripke S, Neale BM, Faraone SV, Purcell SM, Perlis RH, Mowry BJ, Thapar A, Goddard ME, Witte JS, Absher D, Agartz I, Akil H, Amin F, Andreassen OA, Anjorin A, Anney R, Anttila V, Arking DE, Asherson P, Azevedo MH, Backlund L, Badner JA, Bailey AJ, Banaschewski T, Barchas JD, Barnes MR, Barrett TB, Bass N, Battaglia A, Bauer M, Bayés M, Bellivier F, Bergen SE, Berrettini W, Betancur C, Bettecken T, Biederman J, Binder EB, Black DW, Blackwood DH, Bloss CS, Boehnke M, Boomsma DI, Breen G, Breuer R, Bruggeman R, Cormican P, Buccola NG, Buitelaar JK, Bunney WE, Buxbaum JD, Byerley WF, Byrne EM, Caesar S, Cahn W, Cantor RM, Casas M, Chakravarti A, Chambert K, Choudhury K, Cichon S, Cloninger CR, Collier DA, Cook EH, Coon H, Cormand B, Corvin A, Coryell WH, Craig DW, Craig IW, Crosbie J, Cuccaro ML, Curtis D, Czamara D, Datta S, Dawson G, Day R, De Geus EJ, Degenhardt F, Djurovic S, Donohoe GJ, Doyle AE, Duan J, Dudbridge F, Duketis E, Ebstein RP, Edenberg HJ, Elia J, Ennis S, Etain B, Fanous A, Farmer AE, Ferrier IN, Flickinger M, Fombonne E, Foroud T, Frank J, Franke B, Fraser C, Freedman R, Freimer NB, Freitag CM, Friedl M, Frisén L, Gallagher L, Gejman PV, Georgieva L, Gershon ES, Geschwind DH, Giegling I, Gill M, Gordon SD, Gordon-Smith K, Green EK, Greenwood TA, Grice DE, Gross M, Grozeva D, Guan W, Gurling H, De Haan L, Haines JL, Hakonarson H, Hallmayer J, Hamilton SP, Hamshere ML, Hansen TF, Hartmann AM, Hautzinger M, Heath AC, Henders AK, Herms S, Hickie IB, Hipolito M, Hoefels S, Holmans PA, Holsboer F, Hoogendijk WJ, Hottenga JJ, Hultman CM, Hus V, Ingason A, Ising M, Jamain S, Jones EG, Jones I, Jones L, Tzeng JY, Kähler AK, Kahn RS, Kandaswamy R, Keller MC, Kennedy JL, Kenny E, Kent L, Kim Y, Kirov GK, Klauck SM, Klei L, Knowles JA, Kohli MA, Koller DL, Konte B, Korszun A, Krabbendam L, Krasucki R, Kuntsi J, Kwan P, Landén M, Långström N, Lathrop M, Lawrence J, Lawson WB, Leboyer M, Ledbetter DH, Lee PH, Lencz T, Lesch KP, Levinson DF, Lewis CM, Li J, Lichtenstein P, Lieberman JA, Lin DY, Linszen DH, Liu C, Lohoff FW, Loo SK, Lord C, Lowe JK, Lucae S, MacIntyre DJ, Madden PA, Maestrini E, Magnusson PK, Mahon PB, Maier W, Malhotra AK, Mane SM, Martin CL, Martin NG, Mattheisen M, Matthews K, Mattingsdal M, McCarroll SA, McGhee KA, McGough JJ, McGrath PJ, McGuffin P, McInnis MG, McIntosh A, McKinney R, McLean AW, McMahon FJ, McMahon WM, McQuillin A, Medeiros H, Medland SE, Meier S, Melle I, Meng F, Meyer J, Middeldorp CM, Middleton L, Milanova V, Miranda A, Monaco AP, Montgomery GW, Moran JL, Moreno-De-Luca D, Morken G, Morris DW, Morrow EM, Moskvina V, Muglia P, Mühleisen TW, Muir WJ, Müller-Myhsok B, Murtha M, Myers RM, Myin-Germeys I, Neale MC, Nelson SF, Nievergelt CM, Nikolov I, Nimgaonkar V, Nolen WA, Nöthen MM, Nurnberger JI, Nwulia EA, Nyholt DR, O'Dushlaine C, Oades RD, Olincy A, Oliveira G, Olsen L, Ophoff RA, Osby U, Owen MJ, Palotie A, Parr JR, Paterson AD, Pato CN, Pato MT, Penninx BW, Pergadia ML, Pericak-Vance MA, Pickard BS, Pimm J, Piven J, Posthuma D, Potash JB, Poustka F, Propping P, Puri V, Quested DJ, Quinn EM, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Rasmussen HB, Raychaudhuri S, Rehnström K, Reif A, Ribasés M, Rice JP, Rietschel M, Roeder K, Roeyers H, Rossin L, Rothenberger A, Rouleau G, Ruderfer D, Rujescu D, Sanders AR, Sanders SJ, Santangelo SL, Sergeant JA, Schachar R, Schalling M, Schatzberg AF, Scheftner WA, Schellenberg GD, Scherer SW, Schork NJ, Schulze TG, Schumacher J, Schwarz M, Scolnick E, Scott LJ, Shi J, Shilling PD, Shyn SI, Silverman JM, Slager SL, Smalley SL, Smit JH, Smith EN, Sonuga-Barke EJ, St Clair D, State M, Steffens M, Steinhausen HC, Strauss JS, Strohmaier J, Stroup TS, Sutcliffe JS, Szatmari P, Szelinger S, Thirumalai S, Thompson RC, Todorov AA, Tozzi F, Treutlein J, Uhr M, van den Oord EJ, Van Grootheest G, Van Os J, Vicente AM, Vieland VJ, Vincent JB, Visscher PM, Walsh CA, Wassink TH, Watson SJ, Weissman MM, Werge T, Wienker TF, Wijsman EM, Willemsen G, Williams N, Willsey AJ, Witt SH, Xu W, Young AH, Yu TW, Zammit S, Zandi PP, Zhang P, Zitman FG, Zöllner S, Devlin B, Kelsoe JR, Sklar P, Daly MJ, O'Donovan MC, Craddock N, Sullivan PF, Smoller JW, Kendler KS, Wray NR | title = Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs | journal = Nature Genetics | volume = 45 | issue = 9 | pages = 984–994 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 23933821 | pmc = 3800159 | doi = 10.1038/ng.2711 }}</ref><ref name="Antshel_2014"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cecil CA, Nigg JT | title = Epigenetics and ADHD: Reflections on Current Knowledge, Research Priorities and Translational Potential | journal = Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy | volume = 26 | issue = 6 | pages = 581–606 | date = November 2022 | pmid = 35933504 | pmc = 7613776 | doi = 10.1007/s40291-022-00609-y }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Nigg JT, Sibley MH, Thapar A, Karalunas SL | title = Development of ADHD: Etiology, Heterogeneity, and Early Life Course | journal = Annual Review of Developmental Psychology | volume = 2 | issue = 1 | pages = 559–583 | date = December 2020 | pmid = 34368774 | pmc = 8336725 | doi = 10.1146/annurev-devpsych-060320-093413 }}</ref><ref name="auto3">{{Cite web |title=APA PsycNet |url=https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2010-24692-030 |access-date=2024-03-28 |website=psycnet.apa.org }}</ref><!-- For citation Nigg and Cecil, 2022 see Figure 1. --><!--Causes, diagnosis and epidemiology --> |
|||
The official definition of ADHD found in the [[American Psychiatric Association]]'s [[Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders]]-IV (Text Revision) (DSM-IV-TR), defines three subtypes of ADHD: |
|||
The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in the majority of cases.<ref name=nimh/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Franke B, Michelini G, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Bilbow A, Buitelaar JK, Cormand B, Faraone SV, Ginsberg Y, Haavik J, Kuntsi J, Larsson H, Lesch KP, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Réthelyi JM, Ribases M, Reif A | title = Live fast, die young? A review on the developmental trajectories of ADHD across the lifespan | journal = European Neuropsychopharmacology | volume = 28 | issue = 10 | pages = 1059–1088 | date = October 2018 | pmid = 30195575 | pmc = 6379245 | doi = 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.08.001 }}</ref> For most people with ADHD, many genetic and environmental risk factors accumulate to cause the disorder.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Biederman J, Buitelaar JK, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Rohde LA, Sonuga-Barke EJ, Tannock R, Franke B | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Nature Reviews. Disease Primers | volume = 1 | pages = 15020 | date = August 2015 | pmid = 27189265 | doi = 10.1038/nrdp.2015.20 | s2cid = 7171541 | url = https://repository.ubn.ru.nl//bitstream/handle/2066/291735/291735.pdf }}</ref> The environmental risks for ADHD most often exert their influence in the prenatal period.<ref name = "Faraone_2021" /> However, in rare cases a single event might cause ADHD such as traumatic brain injury,<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Sinopoli |first1=Katia J. |last2=Schachar |first2=Russell |last3=Dennis |first3=Maureen |date=August 2011 |title=Traumatic brain injury and secondary attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: The effect of reward on inhibitory control |journal=Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology |language=en |volume=33 |issue=7 |pages=805–819 |doi=10.1080/13803395.2011.562864 |issn=1380-3395 |pmc=3184364 |pmid=21598155}}</ref><ref name="auto1">{{Cite web|url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354024684|title=The Connection between Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Therapeutic Approaches|accessdate=29 March 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Eme R | title = ADHD: an integration with pediatric traumatic brain injury | journal = Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics | volume = 12 | issue = 4 | pages = 475–483 | date = April 2012 | pmid = 22449218 | doi = 10.1586/ern.12.15 | s2cid = 35718630 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0890856709630756 | doi=10.1097/00004583-199806000-00015 | title=Premorbid Prevalence of ADHD and Development of Secondary ADHD After Closed Head Injury | date=1998 | journal=Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume=37 | issue=6 | pages=647–654 | vauthors = Gerring JP, Brady KD, Chen A, Vasa R, Grados M, Bandeen-Roche KJ, Bryan RN, Denckla MB | doi-access=free }}</ref> exposure to biohazards during pregnancy,<ref name = "Faraone_2021" /> a major genetic mutation<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Larsson H | title = Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = Molecular Psychiatry | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 562–575 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 29892054 | pmc = 6477889 | doi = 10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0 }}</ref> or extreme environmental deprivation early in life.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kennedy M, Kreppner J, Knights N, Kumsta R, Maughan B, Golm D, Rutter M, Schlotz W, Sonuga-Barke EJ | title = Early severe institutional deprivation is associated with a persistent variant of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: clinical presentation, developmental continuities and life circumstances in the English and Romanian Adoptees study | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 57 | issue = 10 | pages = 1113–1125 | date = October 2016 | pmid = 27264475 | pmc = 5042050 | doi = 10.1111/jcpp.12576 | doi-access = free }}</ref> There is no biologically distinct adult onset ADHD except for when ADHD occurs after traumatic brain injury.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Biederman J | title = Can Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Onset Occur in Adulthood? | journal = JAMA Psychiatry | volume = 73 | issue = 7 | pages = 655–656 | date = July 2016 | pmid = 27191055 | doi = 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0400 }}</ref><ref name="auto1"/><ref name="Faraone_2021"/> |
|||
* Predominantly Inattentive, |
|||
* Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive, and |
|||
* Combined Type. |
|||
{{TOC limit}} |
|||
Although most diagnoses of ADHD are made for children, the DSM definitions of ADHD do not confine the disorder solely to childhood and in fact many adults are also diagnosed. Current theory holds that approximately 30% of children diagnosed retain the disorder as adults. Although the disorder may not have been diagnosed in an individual during childhood, it is also currently thought that all adults with [[Adult attention-deficit disorder]] (AADD) had it in childhood. [[Hyperactivity]] and other symptoms may be less noticeable in adults with ADD/ADHD who have learned better [[coping skill]]s and other forms of [[adaptive behavior]] than they had as children. Particularly in adults, studies have shown a high correlation between ADHD and creativity. Many painters and performing artists seem to show significant evidence of ADHD, particularly those drawn to improvisational humor and stand up comedy (see [[Robin Williams]], the [[poster child]] for adult ADHD). |
|||
==Signs and symptoms== |
|||
==Terminology== |
|||
Inattention, hyperactivity (restlessness in adults), disruptive behaviour, and impulsivity are common in ADHD.<ref name=cdc2016facts/><ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder |url=https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd |access-date=2 January 2024 |website=National Institute of Mental Health |date=September 2023 }}</ref><ref name=":1">{{Cite web |title=Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Adults: What You Need to Know |url=https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/adhd-what-you-need-to-know |access-date=2 January 2024 |website=National Institute of Mental Health }}</ref> Academic difficulties are frequent, as are problems with relationships.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /><ref name="ICSI2012">{{cite web |date=Mar 2012 |publisher=National Guideline Clearinghous |title=Diagnosis and management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in primary care for school-age children and adolescents |url=http://guidelines.gov/content.aspx?f=rss&id=36812 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130301124247/http://guidelines.gov/content.aspx?f=rss&id=36812 |archive-date=1 March 2013 |access-date=10 October 2012 |page=79 |vauthors=Dobie C |display-authors=et al. }}</ref> The signs and symptoms can be difficult to define, as it is hard to draw a line at where normal levels of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity end and significant levels requiring interventions begin.<ref name ="Ramsay_2007">{{cite book |vauthors=Ramsay JR |title=Cognitive behavioral therapy for adult ADHD |publisher=Routledge |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-415-95501-0 |pages=4, 25–26}}</ref> |
|||
There is not yet a naming consensus. Below are listed several terms that have been used, past and present. One challenge in [[taxonomy]] is that some patterns of behavior are labeled by experts symptoms or sub-types of ADHD, while other experts label those same patterns as their own disorders, independent of ADHD. For the purposes of this article, the "Terminology" section will be used only to name ADHD and its near equivalents, while the names for its manifestations and subtypes will be listed in 'Symptoms', below. |
|||
According to the [[DSM-5|fifth edition of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'']] (DSM-5) and its text revision ([[DSM-5-TR]]), symptoms must be present for six months or more to a degree that is much greater than others of the [[age appropriate|same age]].<ref name=DSM5/><ref name=DSM5TR/> This requires at least six symptoms of either inattention or hyperactivity/impulsivity for those under 17 and at least five symptoms for those 17 years or older.<ref name=DSM5/><ref name=DSM5TR/> The symptoms must be present in at least two settings (e.g., social, school, work, or home), and must directly interfere with or reduce quality of functioning.<ref name=DSM5/> Additionally, several symptoms must have been present before age twelve.<ref name=DSM5TR/> According to the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and its text revision (DSM-5-TR), the required age of onset of symptoms is currently 12 years.<ref name=DSM5/><ref name=DSM5TR/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Epstein JN, Loren RE | title = Changes in the Definition of ADHD in DSM-5: Subtle but Important | journal = Neuropsychiatry | volume = 3 | issue = 5 | pages = 455–458 | date = October 2013 | pmid = 24644516 | pmc = 3955126 | doi = 10.2217/npy.13.59 }}</ref> |
|||
* '''Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder''' (ADHD): In 1987, ADD was in effect renamed to ADHD in the [[DSM-III-R]]. In it, ADHD was broken down into three subtypes (see 'symptoms' for more details): |
|||
** ''predominantly inattentive ADHD'' |
|||
** ''predominantly hyperactive-impulsive ADHD'' |
|||
** ''combined type ADHD'' |
|||
=== {{anchor|ADHD-PH}} Presentations === |
|||
* '''Attention deficit disorder''' (ADD): This term was first introduced in [[DSM-III]], the 1980 edition. Is considered by some to be obsolete, and by others to be a synonym for the predominantly inattentive type of ADHD. |
|||
<!-- This Anchor tag serves to provide a permanent target for incoming section links. Please do not remove it, nor modify it, except to add another appropriate anchor. If you modify the section title, please anchor the old title. It is always best to anchor an old section header that has been changed so that links to it will not be broken. See [[Template:Anchor]] for details. This template is {{subst:Anchor comment}} --> |
|||
ADHD is divided into three primary presentations:<ref name=DSM5TR/><ref name="Ramsay_2007" /> |
|||
* [[Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder predominantly inattentive|predominantly inattentive]] (ADHD-PI or ADHD-I) |
|||
* predominantly hyperactive-impulsive (ADHD-PH or ADHD-HI) |
|||
* combined presentation (ADHD-C). |
|||
The table "Symptoms" lists the symptoms for ADHD-I and ADHD-HI from two major classification systems. Symptoms which can be better explained by another psychiatric or medical condition which an individual has are not considered to be a symptom of ADHD for that person. In [[DSM-5]], subtypes were discarded and reclassified as presentations of the disorder that change over time. |
|||
* '''Attention-deficit syndrome''' (ADS): Equivalent to ADHD, but used to avoid the connotations of "disorder". |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
|+Symptoms |
|||
!Presentations |
|||
!width=45%|{{abbr|DSM-5|Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, 5th Edition}} and {{abbr|DSM-5-TR|Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, 5th Edition, Text Revision}} symptoms<ref name=DSM5/><ref name=DSM5TR/> |
|||
!width=45%|{{abbr|ICD-11|International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision}} symptoms<ref name="ICD-11" /> |
|||
|- |
|||
|Inattention |
|||
|<!-- DSM-5 -->Six or more of the following symptoms in children, and five or more in adults, excluding situations where these symptoms are better explained by another psychiatric or medical condition: |
|||
* Frequently overlooks details or makes careless mistakes |
|||
* Often has difficulty maintaining focus on one task or play activity |
|||
* Often appears not to be listening when spoken to, including when there is no obvious distraction |
|||
* Frequently does not finish following instructions, failing to complete tasks |
|||
* Often struggles to organise tasks and activities, to meet deadlines, and to keep belongings in order |
|||
* Is frequently reluctant to engage in tasks which require sustained attention |
|||
* Frequently loses items required for tasks and activities |
|||
* Is frequently easily distracted by extraneous stimuli, including thoughts in adults and older teenagers |
|||
* Often forgets daily activities, or is forgetful while completing them. |
|||
|<!-- ICD-11 -->Multiple symptoms of inattention that directly negatively impact occupational, academic or social functioning. Symptoms may not be present when engaged in highly stimulating tasks with frequent rewards. Symptoms are generally from the following clusters: |
|||
* Struggles to maintain focus on tasks that aren't highly stimulating/rewarding or that require continuous effort; details are often missed, and careless mistakes are frequent in school and work tasks; tasks are often abandoned before they are completed. |
|||
* Easily distracted (including by own thoughts); may not listen when spoken to; frequently appears to be lost in thought |
|||
* Often loses things; is forgetful and disorganised in daily activities. |
|||
The individual may also meet the criteria for hyperactivity-impulsivity, but the inattentive symptoms are predominant. |
|||
* '''Hyperkinetic syndrome''' (HKS): Equivalent to ADHD, but largely obsolete in the United States, still used in some places world wide. |
|||
|- |
|||
|Hyperactivity-Impulsivity |
|||
|<!-- DSM-5 -->Six or more of the following symptoms in children, and five or more in adults, excluding situations where these symptoms are better explained by another psychiatric or medical condition: |
|||
* Is often fidgeting or squirming in seat |
|||
* Frequently has trouble sitting still during dinner, class, in meetings, etc. |
|||
* Frequently runs around or climbs in inappropriate situations. In adults and teenagers, this may be present only as restlessness. |
|||
* Often cannot quietly engage in leisure activities or play |
|||
* Frequently seems to be "on the go" or appears uncomfortable when not in motion |
|||
* Often talks excessively |
|||
* Often answers a question before it is finished, or finishes people's sentences |
|||
* Often struggles to wait their turn, including waiting in lines |
|||
* Frequently interrupts or intrudes, including into others' conversations or activities, or by using people's things without asking. |
|||
|<!-- ICD-11 -->Multiple symptoms of hyperactivity/impulsivity that directly negatively impact occupational, academic or social functioning. Typically, these tend to be most apparent in environments with structure or which require self-control. Symptoms are generally from the following clusters: |
|||
* Excessive motor activity; struggles to sit still, often leaving their seat; prefers to run about; in younger children, will fidget when attempting to sit still; in adolescents and adults, a sense of physical restlessness or discomfort with being quiet and still. |
|||
* Talks too much; struggles to quietly engage in activities. |
|||
* Blurts out answers or comments; struggles to wait their turn in conversation, games, or activities; will interrupt or intrude on conversations or games. |
|||
* A lack of forethought or consideration of consequences when making decisions or taking action, instead tending to act immediately (e.g., physically dangerous behaviours including reckless driving; impulsive decisions). |
|||
The individual may also meet the criteria for inattention, but the hyperactive-impulsive symptoms are predominant. |
|||
* '''Minimal cerebral dysfunction''' (MCD): Equivalent to ADHD, but largely obsolete in the United States, though still commonly used internationally. |
|||
|- |
|||
* '''Minimal brain dysfunction''' or '''Minimal brain damage''' (MBD): Similar to ADHD, now obsolete. |
|||
|Combined |
|||
|<!-- DSM-5 -->Meet the criteria for both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive ADHD. |
|||
|<!-- ICD-11 -->Criteria are met for both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive ADHD, with neither clearly predominating. |
|||
|} |
|||
Girls and women with ADHD tend to display fewer hyperactivity and impulsivity symptoms but more symptoms of inattention and distractibility.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gershon J | title = A meta-analytic review of gender differences in ADHD | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 5 | issue = 3 | pages = 143–154 | date = January 2002 | pmid = 11911007 | doi = 10.1177/108705470200500302 | s2cid = 8076914 }}</ref> |
|||
== Cause == |
|||
Symptoms are expressed differently and more subtly as the individual ages.<ref name="Kooij_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kooij SJ, Bejerot S, Blackwell A, Caci H, Casas-Brugué M, Carpentier PJ, Edvinsson D, Fayyad J, Foeken K, Fitzgerald M, Gaillac V, Ginsberg Y, Henry C, Krause J, Lensing MB, Manor I, Niederhofer H, Nunes-Filipe C, Ohlmeier MD, Oswald P, Pallanti S, Pehlivanidis A, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Rastam M, Ryffel-Rawak D, Stes S, Asherson P | title = European consensus statement on diagnosis and treatment of adult ADHD: The European Network Adult ADHD | journal = BMC Psychiatry | volume = 10 | issue = 67 | pages = 67 | date = September 2010 | pmid = 20815868 | pmc = 2942810 | doi = 10.1186/1471-244X-10-67 | doi-access = free }}</ref>{{rp|6|quote=Whereas the core symptoms of hyperactivity, impulsivity and inattention, are well characterised in children, these symptoms may have different and more subtle expressions in adult life.}} Hyperactivity tends to become less overt with age and turns into inner restlessness, difficulty relaxing or remaining still, talkativeness or constant mental activity in teens and adults with ADHD.<ref name="Kooij_2010"/>{{rp|pp=6–7 |quote=For instance, where children with ADHD may run and climb excessively, or have difficulty in playing or engaging quietly in leisure activities, adults with ADHD are more likely to experience inner restlessness, inability to relax, or over talkativeness. Hyperactivity may also be expressed as excessive fidgeting, the inability to sit still for long in situations when sitting is expected (at the table, in the movie, in church or at symposia), or being on the go all the time. ... For example, physical overactivity in children could be replaced in adulthood by constant mental activity, feelings of restlessness and difficulty engaging in sedentary activities.}} Impulsivity in adulthood may appear as thoughtless behaviour, impatience, irresponsible spending and sensation-seeking behaviours,<ref name="Kooij_2010"/>{{rp|6|quote=Impulsivity may be expressed as impatience, acting without thinking, spending impulsively, starting new jobs and relationships on impulse, and sensation seeking behaviours.}} while inattention may appear as becoming easily bored, difficulty with organization, remaining on task and making decisions, and sensitivity to stress.<ref name="Kooij_2010"/>{{rp|6|quote=Inattention often presents as distractibility, disorganization, being late, being bored, need for variation, difficulty making decisions, lack of overview, and sensitivity to stress.}} |
|||
The exact cause(s) of ADHD are not conclusively known. Scientific evidence suggests most strongly that, in many cases, the disorder is genetically transmitted and is caused by an imbalance or deficiency in certain chemicals that regulate the efficiency with which the brain controls behavior. |
|||
Although not listed as an official symptom for this condition, [[emotional dysregulation]] or [[mood lability]] is generally understood to be a common symptom of ADHD.<ref name="Retz_2012"/><ref name="Kooij_2010"/>{{rp|6|quote=In addition, many adults with ADHD experience lifetime mood lability with frequent highs and lows, and short-fuse temper outburst.}} People with ADHD of all ages are more likely to have problems with [[social skills]], such as social interaction and forming and maintaining friendships.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Carpenter Rich E, Loo SK, Yang M, Dang J, Smalley SL | title = Social functioning difficulties in ADHD: association with PDD risk | journal = Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry | volume = 14 | issue = 3 | pages = 329–344 | date = July 2009 | pmid = 19515751 | pmc = 2827258 | doi = 10.1177/1359104508100890 }}</ref> This is true for all presentations. About half of children and adolescents with ADHD experience [[social rejection]] by their peers compared to 10–15% of non-ADHD children and adolescents. People with attention deficits are prone to having difficulty processing verbal and nonverbal language which can negatively affect social interaction. They may also drift off during conversations, miss social cues, and have trouble learning social skills.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Coleman WL | title = Social competence and friendship formation in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Adolescent Medicine | volume = 19 | issue = 2 | pages = 278–99, x | date = August 2008 | pmid = 18822833 }}</ref> |
|||
A 1990 study at the [[National Institute of Mental Health]] correlated ADHD with a series of [[metabolic]] abnormalities in the brain, providing further evidence that ADHD is a [[neurological]] disorder. While [[heredity]] is often indicated, problems in [[prenatal]] development, birth complications, or later neurological damage may contribute to ADHD. |
|||
Difficulties managing anger are more common in children with ADHD<ref>{{cite web |title=ADHD Anger Management Directory |publisher=Webmd.com |url=http://www.webmd.com/add-adhd/adhd-anger-management-directory |access-date=17 January 2014 |url-status=live |archive-date=5 November 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131105032151/http://www.webmd.com/add-adhd/adhd-anger-management-directory}}</ref> as are delays in [[communication disorder|speech, language]] and motor development.<ref name="ICD10"/><ref name="pmid22201208">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bellani M, Moretti A, Perlini C, Brambilla P | title = Language disturbances in ADHD | journal = Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences | volume = 20 | issue = 4 | pages = 311–315 | date = December 2011 | pmid = 22201208 | doi = 10.1017/S2045796011000527 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Poorer [[handwriting]] is more common in children with ADHD.<ref name="Racine_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Racine MB, Majnemer A, Shevell M, Snider L | title = Handwriting performance in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) | journal = Journal of Child Neurology | volume = 23 | issue = 4 | pages = 399–406 | date = April 2008 | pmid = 18401033 | doi = 10.1177/0883073807309244 | s2cid = 206546871 }}</ref> Poor handwriting in many situations can be a symptom of ADHD in itself due to decreased attentiveness. When this is a pervasive problem, it may also be attributable to [[dyslexic|dyslexia]]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Peterson RL, Pennington BF | title = Developmental dyslexia | journal = Lancet | volume = 379 | issue = 9830 | pages = 1997–2007 | date = May 2012 | pmid = 22513218 | pmc = 3465717 | doi = 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60198-6 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sexton CC, Gelhorn HL, Bell JA, Classi PM | title = The co-occurrence of reading disorder and ADHD: epidemiology, treatment, psychosocial impact, and economic burden | journal = Journal of Learning Disabilities | volume = 45 | issue = 6 | pages = 538–564 | date = November 2012 | pmid = 21757683 | doi = 10.1177/0022219411407772 | s2cid = 385238 }}</ref> or [[dysgraphia]]. There is significant overlap in the symptomatologies of ADHD, dyslexia, and dysgraphia,<ref name="Nicolson_2011">{{cite journal | vauthors = Nicolson RI, Fawcett AJ | title = Dyslexia, dysgraphia, procedural learning and the cerebellum | journal = Cortex; A Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior | volume = 47 | issue = 1 | pages = 117–127 | date = January 2011 | pmid = 19818437 | doi = 10.1016/j.cortex.2009.08.016 | s2cid = 32228208 }}</ref> and 3 in 10 people diagnosed with dyslexia experience co-occurring ADHD.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.webmd.com/add-adhd/adhd-dyslexia-tell-apart | title=Dyslexia and ADHD | access-date=19 May 2022 | archive-date=21 February 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230221112159/https://www.webmd.com/add-adhd/adhd-dyslexia-tell-apart | url-status=live }}</ref> Although it causes significant difficulty, many children with ADHD have an attention span equal to or greater than that of other children for tasks and subjects they find interesting.<ref name="Walitza_2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Walitza S, Drechsler R, Ball J | title = [The school child with ADHD] | language = de | journal = Therapeutische Umschau | volume = 69 | issue = 8 | pages = 467–473 | date = August 2012 | pmid = 22851461 | doi = 10.1024/0040-5930/a000316 | trans-title = The school child with ADHD }}</ref> |
|||
Causes under investigation include, but are not limited to: |
|||
===Comorbidities=== |
|||
*Brain differences: Brain scan technology has revealed differences in the size, symmetry, metabolism, and chemistry of the brain in those who have ADHD; however, it should be noted that there is yet no clear determination of the source of these differences. |
|||
====Psychiatric comorbidities==== |
|||
In children, ADHD occurs with other disorders about two-thirds of the time.<ref name="Walitza_2012" /> |
|||
Other neurodevelopmental conditions are common comorbidities. [[Autism spectrum disorder]] (ASD), co-occurring at a rate of 21% in those with ADHD, affects social skills, ability to communicate, behaviour, and interests.<ref name="Young_2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Young S, Hollingdale J, Absoud M, Bolton P, Branney P, Colley W, Craze E, Dave M, Deeley Q, Farrag E, Gudjonsson G, Hill P, Liang HL, Murphy C, Mackintosh P, Murin M, O'Regan F, Ougrin D, Rios P, Stover N, Taylor E, Woodhouse E | title = Guidance for identification and treatment of individuals with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder based upon expert consensus | journal = BMC Medicine | volume = 18 | issue = 1 | pages = 146 | date = May 2020 | pmid = 32448170 | pmc = 7247165 | doi = 10.1186/s12916-020-01585-y | publisher = Springer Science and Business Media LLC | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="NHS2018" /> Both ADHD and ASD can be diagnosed in the same person.<ref name=DSM5TR/>{{Page needed|date=April 2023}} [[Learning disabilities]] have been found to occur in about 20–30% of children with ADHD. Learning disabilities can include developmental speech and language disorders, and academic skills disorders.<ref name="BaileyHC">{{cite web |vauthors=Bailey E |title=ADHD and Learning Disabilities: How can you help your child cope with ADHD and subsequent Learning Difficulties? There is a way. |date=5 September 2007 |url=http://www.healthcentral.com/adhd/education-159625-5.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131203092339/http://www.healthcentral.com/adhd/education-159625-5.html |archive-date=3 December 2013 |url-status=live |access-date=15 November 2013 |publisher=Remedy Health Media, LLC. }}</ref> ADHD, however, is not considered a learning disability, but it very frequently causes academic difficulties.<ref name="BaileyHC" /> [[Intellectual disability|Intellectual disabilities]]<ref name=DSM5TR/>{{Page needed|date=April 2023}} and [[Tourette's syndrome]]<ref name="NHS2018" /> are also common. |
|||
*Genetic factors: It has been demonstrated that children who have at least one parent diagnosed with ADHD are more likely to be diagnosed as having ADHD themselves. Current research is examining which genes may be involved in ADHD. This investigative path also suggests an associated hypothesis that environmental factors, handed down from generation to generation, may trigger the symptoms associated with ADHD. There also exists a possiblity that a family with one diagnosed member may have a heightened awareness of the disorder, along with a willingness to seek formal diagnosis, which would make detection and diagnosis more likely, thus skewing the data on heritability. |
|||
ADHD is often comorbid with disruptive, impulse control, and conduct disorders. [[Oppositional defiant disorder]] (ODD) occurs in about 25% of children with an inattentive presentation and 50% of those with a combined presentation.<ref name=DSM5TR/>{{Page needed|date=April 2023}} It is characterised by angry or irritable mood, argumentative or defiant behaviour and vindictiveness which are age-inappropriate. [[Conduct disorder]] (CD) occurs in about 25% of adolescents with ADHD.<ref name=DSM5TR/>{{Page needed|date=April 2023}} It is characterised by aggression, destruction of property, deceitfulness, theft and violations of rules.<ref name="UTP2008">{{cite web |date=5 December 2007 |vauthors=Krull KR |title=Evaluation and diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children |url=https://www.uptodate.com/contents/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-in-children-and-adolescents-clinical-features-and-diagnosis |url-access=subscription |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090605040744/http://www.uptodate.com/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=behavior%2F8293#5 |archive-date=5 June 2009 |access-date=12 September 2008 |url-status=live |work=Uptodate |publisher=Wolters Kluwer Health}}</ref> Adolescents with ADHD who also have CD are more likely to develop [[antisocial personality disorder]] in adulthood.<ref name="pmid19428109">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hofvander B, Ossowski D, Lundström S, Anckarsäter H | title = Continuity of aggressive antisocial behavior from childhood to adulthood: The question of phenotype definition | journal = International Journal of Law and Psychiatry | volume = 32 | issue = 4 | pages = 224–234 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19428109 | doi = 10.1016/j.ijlp.2009.04.004 | url = https://lup.lub.lu.se/record/1412513 | access-date = 22 November 2021 | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220517212251/https://lup.lub.lu.se/search/publication/1412513 | archive-date = 17 May 2022 }}</ref> Brain imaging supports that CD and ADHD are separate conditions, wherein conduct disorder was shown to reduce the size of one's [[Temporal lobe|temporal]] lobe and [[limbic system]], and increase the size of one's [[orbitofrontal cortex]], whereas ADHD was shown to reduce connections in the [[cerebellum]] and [[prefrontal cortex]] more broadly. Conduct disorder involves more impairment in motivation control than ADHD.<ref name="pmid21094938">{{cite journal | vauthors = Rubia K | title = "Cool" inferior frontostriatal dysfunction in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder versus "hot" ventromedial orbitofrontal-limbic dysfunction in conduct disorder: a review | journal = Biological Psychiatry | volume = 69 | issue = 12 | pages = e69–e87 | date = June 2011 | pmid = 21094938 | doi = 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.023 | publisher = Elsevier BV/The Society of Biological Psychiatry | s2cid = 14987165 }}</ref> [[Intermittent explosive disorder]] is characterised by sudden and disproportionate outbursts of anger and co-occurs in individuals with ADHD more frequently than in the general population. |
|||
* Brain development in utero and during the first year of life, possibly related to drug use during pregnancy or environmental toxins. |
|||
Anxiety and mood disorders are frequent comorbidities. [[Anxiety disorder]]s have been found to occur more commonly in the ADHD population, as have [[mood disorder]]s (especially [[bipolar disorder]] and [[major depressive disorder]]). Boys diagnosed with the combined ADHD subtype are more likely to have a mood disorder.<ref name="Wilens_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wilens TE, Spencer TJ | title = Understanding attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder from childhood to adulthood | journal = Postgraduate Medicine | volume = 122 | issue = 5 | pages = 97–109 | date = September 2010 | pmid = 20861593 | pmc = 3724232 | doi = 10.3810/pgm.2010.09.2206 }}</ref> Adults and children with ADHD sometimes also have bipolar disorder, which requires careful assessment to accurately diagnose and treat both conditions.<ref name="pmid21717696">{{cite journal | vauthors = Baud P, Perroud N, Aubry JM | title = [Bipolar disorder and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: differential diagnosis or comorbidity] | language = fr | journal = Revue Médicale Suisse | volume = 7 | issue = 297 | pages = 1219–1222 | date = June 2011 | doi = 10.53738/REVMED.2011.7.297.1219 | pmid = 21717696 }}</ref><ref name="Wilens_2011">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wilens TE, Morrison NR | title = The intersection of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and substance abuse | journal = Current Opinion in Psychiatry | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 280–285 | date = July 2011 | pmid = 21483267 | pmc = 3435098 | doi = 10.1097/YCO.0b013e328345c956 }}</ref> |
|||
It has also been suggested that ADHD may result from a poor diet and other external factors rather than from any physiological source. Studies of changes in diets of children provide some anecdotal and scientific evidence for this, but current majority opinion seems to be that the available evidence is insufficient to either prove or disprove this. However, it has been noticed that a large portion of children with ADHD seem to be addicted to milk. It has been proposed by Norwegian and British scientists that this is due to the [[casomorphin]]s, [[peptide]]s formed by incomplete digestion of the [[whey]] protein. |
|||
[[Sleep disorders]] and ADHD commonly co-exist. They can also occur as a side effect of medications used to treat ADHD. In children with ADHD, [[insomnia]] is the most common sleep disorder with behavioural therapy being the preferred treatment.<ref name="pmid21600348">{{cite journal | vauthors = Corkum P, Davidson F, Macpherson M | title = A framework for the assessment and treatment of sleep problems in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Pediatric Clinics of North America | volume = 58 | issue = 3 | pages = 667–683 | date = June 2011 | pmid = 21600348 | doi = 10.1016/j.pcl.2011.03.004 }}</ref><ref name="pmid20451036">{{cite journal | vauthors = Tsai MH, Huang YS | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and sleep disorders in children | journal = The Medical Clinics of North America | volume = 94 | issue = 3 | pages = 615–632 | date = May 2010 | pmid = 20451036 | doi = 10.1016/j.mcna.2010.03.008 }}</ref> Problems with sleep initiation are common among individuals with ADHD but often they will be deep sleepers and have significant difficulty getting up in the morning.<ref name="Brown_2008" /> [[Melatonin]] is sometimes used in children who have sleep onset insomnia.<ref name="pmid20028959">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bendz LM, Scates AC | title = Melatonin treatment for insomnia in pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = The Annals of Pharmacotherapy | volume = 44 | issue = 1 | pages = 185–191 | date = January 2010 | pmid = 20028959 | doi = 10.1345/aph.1M365 | s2cid = 207263711 }}</ref> Specifically, the sleep disorder [[restless legs syndrome]] has been found to be more common in those with ADHD and is often due to [[iron deficiency anemia]].<ref name="pmid21365608">{{cite journal | vauthors = Merino-Andreu M | title = [Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and restless legs syndrome in children] | language = es | journal = Revista de Neurologia | volume = 52 | issue = Suppl 1 | pages = S85–S95 | date = March 2011 | pmid = 21365608 | doi = 10.33588/rn.52S01.2011037 | trans-title = Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and restless legs syndrome in children }}</ref><ref name="pmid20620105">{{cite journal | vauthors = Picchietti MA, Picchietti DL | title = Advances in pediatric restless legs syndrome: Iron, genetics, diagnosis and treatment | journal = Sleep Medicine | volume = 11 | issue = 7 | pages = 643–651 | date = August 2010 | pmid = 20620105 | doi = 10.1016/j.sleep.2009.11.014 }}</ref> However, restless legs can simply be a part of ADHD and requires careful assessment to differentiate between the two disorders.<ref name="pmid18656214">{{cite journal | vauthors = Karroum E, Konofal E, Arnulf I | title = [Restless-legs syndrome] | language = fr | journal = Revue Neurologique | volume = 164 | issue = 8–9 | pages = 701–721 | year = 2008 | pmid = 18656214 | doi = 10.1016/j.neurol.2008.06.006 }}</ref> [[Delayed sleep phase disorder]] is also a common comorbidity of those with ADHD.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Wajszilber D, Santiseban JA, Gruber R | title = Sleep disorders in patients with ADHD: impact and management challenges | journal = Nature and Science of Sleep | volume = 10 | pages = 453–480 | date = December 2018 | pmid = 30588139 | pmc = 6299464 | doi = 10.2147/NSS.S163074 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
Research is ongoing in many studies. |
|||
There are other psychiatric conditions which are often co-morbid with ADHD, such as [[substance use disorder]]s.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Long Y, Pan N, Ji S, Qin K, Chen Y, Zhang X, He M, Suo X, Yu Y, Wang S, Gong Q | title = Distinct brain structural abnormalities in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and substance use disorders: A comparative meta-analysis | journal = Translational Psychiatry | volume = 12 | issue = 1 | pages = 368 | date = September 2022 | pmid = 36068207 | pmc = 9448791 | doi = 10.1038/s41398-022-02130-6 }}</ref> Individuals with ADHD are at increased risk of [[substance abuse]].{{rp|9|quote=Comorbid substance use disorder (SUD) deserves special attention due to the high rates of ADHD within SUD populations. A bidirectional link between ADHD and SUD is reported with ADHD symptoms over represented in SUD populations and SUD in ADHD populations.}} This is most commonly seen with [[alcoholic beverage|alcohol]] or [[cannabis (drug)|cannabis]].<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|9|quote=Alcohol and cannabis are the most frequently abused substances in these populations followed by lower rates of cocaine and amphetamine abuse.}} The reason for this may be an altered reward pathway in the brains of ADHD individuals, self-treatment and increased psychosocial risk factors.{{rp|9|quote=The causes for such comorbidity are likely to be complex including altered reward processing in ADHD, increased exposure to psychosocial risk factors and self treatment. }} This makes the evaluation and treatment of ADHD more difficult, with serious substance misuse problems usually treated first due to their greater risks.<ref name="NICE2009-part2">{{cite book |author=National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health |title=Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management of ADHD in Children, Young People and Adults |date=2009 |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53652/ |publisher=British Psychological Society |isbn=978-1-85433-471-8 |series=NICE Clinical Guidelines |volume=72 |location=Leicester |pages=[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53663/#ch2.s8 18–26], [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53663/#ch2.s41 38] |chapter=Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |chapter-url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53663/ |url-status=live |archive-date=13 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160113133612/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53652/ |via=NCBI Bookshelf}}</ref> Other psychiatric conditions include [[reactive attachment disorder]],<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Storebø OJ, Rasmussen PD, Simonsen E | title = Association Between Insecure Attachment and ADHD: Environmental Mediating Factors | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 20 | issue = 2 | pages = 187–196 | date = February 2016 | pmid = 24062279 | doi = 10.1177/1087054713501079 | url = https://findresearcher.sdu.dk:8443/ws/files/134088245/Association_Between_Insecure_Attachment_and_ADHD.pdf | access-date = 22 November 2021 | url-status = live | s2cid = 23564305 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211209135025/https://findresearcher.sdu.dk:8443/ws/files/134088245/Association_Between_Insecure_Attachment_and_ADHD.pdf | archive-date = 9 December 2021 }}</ref> characterised by a severe inability to appropriately relate socially, and [[cognitive disengagement syndrome]], a distinct attention disorder occurring in 30–50% of ADHD cases as a comorbidity, regardless of the presentation; a subset of cases diagnosed with ADHD-PIP have been found to have CDS instead.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Becker SP, Willcutt EG, Leopold DR, Fredrick JW, Smith ZR, Jacobson LA, Burns GL, Mayes SD, Waschbusch DA, Froehlich TE, McBurnett K, Servera M, Barkley RA | title = Report of a Work Group on Sluggish Cognitive Tempo: Key Research Directions and a Consensus Change in Terminology to Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 62 | issue = 6 | pages = 629–645 | date = June 2023 | pmid = 36007816 | pmc = 9943858 | doi = 10.1016/j.jaac.2022.07.821 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Barkley RA | title = Sluggish cognitive tempo (concentration deficit disorder?): current status, future directions, and a plea to change the name | journal = Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology | volume = 42 | issue = 1 | pages = 117–125 | date = January 2014 | pmid = 24234590 | doi = 10.1007/s10802-013-9824-y | url = https://psychology.uiowa.edu/sites/psychology.uiowa.edu/files/groups/nikolas/files/Barkley,%202014.pdf | url-status = live | s2cid = 8287560 | author-link = Russell Barkley | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170809102631/https://psychology.uiowa.edu/sites/psychology.uiowa.edu/files/groups/nikolas/files/Barkley,%202014.pdf | archive-date = 9 August 2017 }}</ref> Individuals with ADHD are three times more likely to develop and be diagnosed with an [[eating disorder]] compared to those without ADHD; conversely, individuals with eating disorders are two times more likely to have ADHD than those without eating disorders.<ref name="Nazar_2016">{{cite journal | vauthors = Nazar BP, Bernardes C, Peachey G, Sergeant J, Mattos P, Treasure J | title = The risk of eating disorders comorbid with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = The International Journal of Eating Disorders | volume = 49 | issue = 12 | pages = 1045–1057 | date = December 2016 | pmid = 27859581 | doi = 10.1002/eat.22643 | url = https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/the-risk-of-eating-disorders-comorbid-with-attentiondeficithyperactivity-disorder(9a8e868e-de6e-4e19-9561-f8a576836848).html | access-date = 26 October 2022 | url-status = live | s2cid = 38002526 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20221208035350/https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/the-risk-of-eating-disorders-comorbid-with-attentiondeficithyperactivity-disorder(9a8e868e-de6e-4e19-9561-f8a576836848).html | archive-date = 8 December 2022 }}</ref> |
|||
== Controversy == |
|||
====Trauma==== |
|||
While ADD/ADHD is a known psychiatric condition, there are various theories about the cause and some controversy over the number of persons diagnosed and the cost of medications. Some [[denial (psychology)|denial]] in families may also relate to the negative perception of the condition as a hereditary brain disorder. |
|||
ADHD, [[Psychological trauma|trauma]], and [[Adverse childhood experiences|Adverse Childhood Experiences]] are also comorbid,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Schneider M, VanOrmer J, Zlomke K | title = Adverse Childhood Experiences and Family Resilience Among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder | journal = Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics | volume = 40 | issue = 8 | pages = 573–580 | date = 2019 | pmid = 31335581 | doi = 10.1097/DBP.0000000000000703 | s2cid = 198193637 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Moon DS, Bong SJ, Kim BN, Kang NR | title = Association between Maternal Adverse Childhood Experiences and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in the Offspring: The Mediating Role of Antepartum Health Risks | journal = Soa--Ch'ongsonyon Chongsin Uihak = Journal of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 32 | issue = 1 | pages = 28–34 | date = January 2021 | pmid = 33424239 | pmc = 7788667 | doi = 10.5765/jkacap.200041 }}</ref> which could in part be potentially explained by the similarity in presentation between different diagnoses. The symptoms of ADHD and [[Post-traumatic stress disorder|PTSD]] can have significant behavioural overlap—in particular, motor restlessness, difficulty concentrating, distractibility, irritability/anger, emotional constriction or dysregulation, poor impulse control, and forgetfulness are common in both.<ref name="Ford_2009">{{Cite journal |vauthors=Ford JD, Connor DF |date=1 June 2009 |title=ADHD and post-traumatic stress disorder |journal=Current Attention Disorders Reports |volume=1 |issue=2 |pages=60–66 |doi=10.1007/s12618-009-0009-0 |issn=1943-457X |s2cid=145508751}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Harrington KM, Miller MW, Wolf EJ, Reardon AF, Ryabchenko KA, Ofrat S | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder comorbidity in a sample of veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder | journal = Comprehensive Psychiatry | volume = 53 | issue = 6 | pages = 679–690 | date = August 2012 | pmid = 22305866 | pmc = 6519447 | doi = 10.1016/j.comppsych.2011.12.001 }}</ref> This could result in trauma-related disorders or ADHD being mis-identified as the other.<ref name="Szymanski_2011">{{Cite journal |vauthors=Szymanski K, Sapanski L, Conway F |date=1 January 2011 |title=Trauma and ADHD – Association or Diagnostic Confusion? A Clinical Perspective |journal=Journal of Infant, Child, and Adolescent Psychotherapy |location=Philadelphia PA |publisher=Taylor & Francis Group |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=51–59 |doi=10.1080/15289168.2011.575704 |issn=1528-9168 |eissn=1940-9214 |s2cid=144348893}}</ref> Additionally, traumatic events in childhood are a risk factor for ADHD<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zhang N, Gao M, Yu J, Zhang Q, Wang W, Zhou C, Liu L, Sun T, Liao X, Wang J | title = Understanding the association between adverse childhood experiences and subsequent attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies | journal = Brain and Behavior | volume = 12 | issue = 10 | pages = e32748 | date = October 2022 | pmid = 36068993 | pmc = 9575611 | doi = 10.1002/brb3.2748 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Nguyen MN, Watanabe-Galloway S, Hill JL, Siahpush M, Tibbits MK, Wichman C | title = Ecological model of school engagement and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in school-aged children | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 28 | issue = 6 | pages = 795–805 | date = June 2019 | pmid = 30390147 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-018-1248-3 | s2cid = 53263217 }}</ref> - it can lead to structural brain changes and the development of ADHD behaviours.<ref name="Szymanski_2011"/> Finally, the behavioural consequences of ADHD symptoms cause a higher chance of the individual experiencing trauma (and therefore ADHD leads to a concrete diagnosis of a trauma-related disorder).<ref>{{Cite journal | vauthors = Miodus S, Allwood MA, Amoh N |date=5 January 2021 |title=Childhood ADHD Symptoms in Relation to Trauma Exposure and PTSD Symptoms Among College Students: Attending to and Accommodating Trauma |journal=Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders |volume=29 |issue=3 |pages=187–196 |doi=10.1177/1063426620982624 |s2cid=234159064 |issn=1063-4266 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Is It ADHD or Trauma? |url=https://childmind.org/article/is-it-adhd-or-trauma/ |access-date=2024-04-18 |website=Child Mind Institute }}</ref> |
|||
====Non-psychiatric==== |
|||
=== Skepticism towards ADHD as a diagnosis === |
|||
{{see also|Accident-proneness#Hypophobia}} |
|||
Critics have complained that the ADHD diagnostic criteria are sufficiently general or vague to allow virtually any child with persistent unwanted behaviors to be classified as having ADHD of one type or another. |
|||
Some non-psychiatric conditions are also comorbidities of ADHD. This includes [[epilepsy]],<ref name="NHS2018">{{cite web |title=ADHD Symptoms |url=https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd/symptoms/#related-conditions-in-children-and-teenagers |website=nhs.uk |access-date=15 May 2018 |date=20 October 2017 |archive-date=1 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210201015023/https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd/symptoms/#related-conditions-in-children-and-teenagers |url-status=live }}</ref> a neurological condition characterised by recurrent seizures.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Williams AE, Giust JM, Kronenberger WG, Dunn DW | title = Epilepsy and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: links, risks, and challenges | journal = Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment | volume = 12 | pages = 287–296 | date = 2016 | pmid = 26929624 | pmc = 4755462 | doi = 10.2147/NDT.S81549 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Silva RR, Munoz DM, Alpert M | title = Carbamazepine use in children and adolescents with features of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 35 | issue = 3 | pages = 352–358 | date = March 1996 | pmid = 8714324 | doi = 10.1097/00004583-199603000-00017 | doi-access = free }}</ref> There are well established associations between ADHD and obesity, [[asthma]] and sleep disorders,<ref name="pmid27664125">{{cite journal | vauthors = Instanes JT, Klungsøyr K, Halmøy A, Fasmer OB, Haavik J | title = Adult ADHD and Comorbid Somatic Disease: A Systematic Literature Review | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 22 | issue = 3 | pages = 203–228 | date = February 2018 | pmid = 27664125 | pmc = 5987989 | doi = 10.1177/1087054716669589 | type = Systematic Review }}</ref> and an association with celiac disease.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gaur S | title = The Association between ADHD and Celiac Disease in Children | journal = Children | volume = 9 | issue = 6 | page = 781 | date = May 2022 | pmid = 35740718 | pmc = 9221618 | doi = 10.3390/children9060781 | publisher = MDPI | doi-access = free }}</ref> Children with ADHD have a higher risk for [[migraine]] headaches,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hsu TW, Chen MH, Chu CS, Tsai SJ, Bai YM, Su TP, Chen TJ, Liang CS | title = Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and risk of migraine: A nationwide longitudinal study | journal = Headache | volume = 62 | issue = 5 | pages = 634–641 | date = May 2022 | pmid = 35524451 | doi = 10.1111/head.14306 | s2cid = 248553863 }}</ref> but have no increased risk of tension-type headaches. In addition, children with ADHD may also experience headaches as a result of medication.<ref name="Salem_2017">{{cite journal | vauthors = Salem H, Vivas D, Cao F, Kazimi IF, Teixeira AL, Zeni CP | title = ADHD is associated with migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 27 | issue = 3 | pages = 267–277 | date = March 2018 | pmid = 28905127 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-017-1045-4 | publisher = Springer Science and Business Media LLC | s2cid = 3949012 }}</ref><ref name="Pan_2021">{{cite journal | vauthors = Pan PY, Jonsson U, Şahpazoğlu Çakmak SS, Häge A, Hohmann S, Nobel Norrman H, Buitelaar JK, Banaschewski T, Cortese S, Coghill D, Bölte S | title = Headache in ADHD as comorbidity and a side effect of medications: a systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = Psychological Medicine | volume = 52 | issue = 1 | pages = 14–25 | date = January 2022 | pmid = 34635194 | pmc = 8711104 | doi = 10.1017/s0033291721004141 | publisher = Cambridge University Press | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
A growing number of critics have wondered why the number of children diagnosed with ADHD in the U.S. and UK has grown so dramatically over a short period of time. |
|||
A 2021 review reported that several neurometabolic disorders caused by [[inborn errors of metabolism]] converge on common neurochemical mechanisms that interfere with biological mechanisms also considered central in ADHD pathophysiology and treatment. This highlights the importance of close collaboration between health services to avoid clinical overshadowing.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cannon Homaei S, Barone H, Kleppe R, Betari N, Reif A, Haavik J | title = ADHD symptoms in neurometabolic diseases: Underlying mechanisms and clinical implications | journal = Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | volume = 132 | pages = 838–856 | date = January 2022 | pmid = 34774900 | doi = 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.11.012 | s2cid = 243983688 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
It has often been suggested that the causes of the apparent ADHD epidemic lie in cultural patterns that variously encourage or sanction the use of drugs as a simple and expeditious cure for complex problems that may stem primarily from social and environmental triggers rather than any innate disorder. Some critics assert that many children are diagnosed with ADHD and put on drugs as a substitute for parental attention, whereas many parents of ADHD children assert that the associated demand for attention goes beyond what can be humanly provided, causing massive disruption to other individuals and relationships, as well as to environments with dysfunctionally structured relationships such as are manifest in many classrooms. This criticism also includes the use of prescription drugs as a substitute for parental duties such as communication and supervision. |
|||
In June 2021, ''[[Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews]]'' published a [[systematic review]] of 82 studies that all confirmed or implied elevated accident-proneness in ADHD patients and whose data suggested that the type of accidents or injuries and overall risk changes in ADHD patients over the lifespan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Brunkhorst-Kanaan N, Libutzki B, Reif A, Larsson H, McNeill RV, Kittel-Schneider S | title = ADHD and accidents over the life span - A systematic review | journal = Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | volume = 125 | pages = 582–591 | date = June 2021 | pmid = 33582234 | doi = 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.002 | publisher = Elsevier | s2cid = 231885131 | doi-access = free }}</ref> In January 2014, ''[[Accident Analysis & Prevention]]'' published a [[meta-analysis]] of 16 studies examining the relative risk of [[traffic collision]]s for drivers with ADHD, finding an overall relative risk estimate of 1.36 without controlling for exposure, a relative risk estimate of 1.29 when controlling for [[publication bias]], a relative risk estimate of 1.23 when controlling for exposure, and a relative risk estimate of 1.86 for ADHD drivers with [[oppositional defiant disorder]] and/or [[conduct disorder]] [[Comorbidity|comorbidities]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Vaa T | title = ADHD and relative risk of accidents in road traffic: a meta-analysis | journal = Accident; Analysis and Prevention | volume = 62 | pages = 415–425 | date = January 2014 | pmid = 24238842 | doi = 10.1016/j.aap.2013.10.003 | publisher = Elsevier | hdl-access = free | hdl = 11250/2603537 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2018-06-01 |title=Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) |url=https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd/ |access-date=2024-02-16 |website=nhs.uk }}</ref> |
|||
Another source of skepticism towards making the diagnosis of "ADHD or not ADHD" may arise from the rising diagnosis of subclinical forms of ADHD. So called 'Shadow-syndromes' or 'sub-syndromes' stand for weaker forms of ADHD and are described in various degrees by John J. Ratey and Catherine Johnson on their book ''Shadow Syndromes: The Mild Forms of Major Mental Disorders That Sabotage Us''. |
|||
===Problematic digital media use=== |
|||
=== Hunter-versus-farmer theory=== |
|||
{{See also|Screen time|Internet addiction disorder|Problematic smartphone use|Problematic social media use|Video game addiction}} |
|||
{{Excerpt|Digital media use and mental health|ADHD}} |
|||
===Suicide risk=== |
|||
A broad theory, not necessarily in conflict with the current medical research findings, is the [[hunter vs. farmer theory]], first presented by [[Thom Hartmann]], which holds that in some ways, some ADD attributes in some humans may be a form of [[adaptive behavior]] developed over a long period to match the environment. In easier terms, the change was refinement of skills to suit changing needs. Under the theory, as civilized society evolved, the attributes of a hunter gave way to those of a farmer for most people as the survival skills needed changed. |
|||
Systematic reviews conducted in 2017 and 2020 found strong evidence that ADHD is associated with increased [[suicide]] risk across all age groups, as well as growing evidence that an ADHD diagnosis in childhood or adolescence represents a significant future suicidal risk factor.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Balazs J, Kereszteny A | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and suicide: A systematic review | journal = World Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 7 | issue = 1 | pages = 44–59 | date = March 2017 | pmid = 28401048 | pmc = 5371172 | doi = 10.5498/wjp.v7.i1.44 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="Garas_2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Garas P, Balazs J | title = Long-Term Suicide Risk of Children and Adolescents With Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder-A Systematic Review | journal = Frontiers in Psychiatry | volume = 11 | pages = 557909 | date = 21 December 2020 | pmid = 33408650 | pmc = 7779592 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.557909 | id = 557909 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Potential causes include ADHD's association with functional impairment, negative social, educational and occupational outcomes, and financial distress.<ref name="Septier_2019">{{cite journal | vauthors = Septier M, Stordeur C, Zhang J, Delorme R, Cortese S | title = Association between suicidal spectrum behaviors and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | volume = 103 | pages = 109–118 | date = August 2019 | pmid = 31129238 | doi = 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.05.022 | url = https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/431399/1/Septier_et_al_ADHD_SUICIDE_R2_CLEANED.docx | access-date = 7 December 2021 | url-status = live | s2cid = 162184004 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211104140233/https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/431399/1/Septier_et_al_ADHD_SUICIDE_R2_CLEANED.docx | archive-date = 4 November 2021 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Beauchaine TP, Ben-David I, Bos M | title = ADHD, financial distress, and suicide in adulthood: A population study | journal = Science Advances | volume = 6 | issue = 40 | pages = eaba1551 | date = September 2020 | pmid = 32998893 | pmc = 7527218 | doi = 10.1126/sciadv.aba1551 | id = eaba1551 | bibcode = 2020SciA....6.1551B }}</ref> A 2019 meta-analysis indicated a significant association between ADHD and suicidal spectrum behaviours (suicidal attempts, ideations, plans, and completed suicides); across the studies examined, the prevalence of suicide attempts in individuals with ADHD was 18.9%, compared to 9.3% in individuals without ADHD, and the findings were substantially replicated among studies which adjusted for other variables. However, the relationship between ADHD and suicidal spectrum behaviours remains unclear due to mixed findings across individual studies and the complicating impact of comorbid psychiatric disorders.<ref name="Septier_2019" /> There is no clear data on whether there is a direct relationship between ADHD and suicidality, or whether ADHD increases suicide risk through comorbidities.<ref name="Garas_2020" /> |
|||
===IQ test performance=== |
|||
Hartmann takes an approach from biological [[evolution]] to argue that ADHD is not a disorder, but an expression of [[biodiversity]]. In his book ''ADD - Attention Deficit Disorder'' (1997), Hartmann developed the idea that people having ADHD symptoms may have simply inherited a collection of genes that were selected for the time when hunting was particularly important. From an evolutionary point of view, it is quite acceptable that humans—like other animals—differ in their biology and pass on their traits from generation to generation. This idea is the basis of another of his works, ''The Edison Gene: ADHD and the Gift of the Hunter Child'' (2003). |
|||
Certain studies have found that people with ADHD tend to have lower scores on [[intelligence quotient]] (IQ) tests.<ref name="Frazier_2004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Frazier TW, Demaree HA, Youngstrom EA | title = Meta-analysis of intellectual and neuropsychological test performance in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Neuropsychology | volume = 18 | issue = 3 | pages = 543–555 | date = July 2004 | pmid = 15291732 | doi = 10.1037/0894-4105.18.3.543 | s2cid = 17628705 }}</ref> The significance of this is controversial due to the differences between people with ADHD and the difficulty determining the influence of symptoms, such as distractibility, on lower scores rather than intellectual capacity. In studies of ADHD, higher IQs may be over-represented because many studies exclude individuals who have lower IQs despite those with ADHD scoring on average nine points lower on standardised intelligence measures.<ref name="Mackenzie_2016">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mackenzie GB, Wonders E | title = Rethinking Intelligence Quotient Exclusion Criteria Practices in the Study of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder | journal = Frontiers in Psychology | volume = 7 | pages = 794 | date = 2016 | pmid = 27303350 | pmc = 4886698 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00794 | doi-access = free }}</ref> However, other studies contradict this, saying that in individuals with high intelligence, there is an increased risk of a missed ADHD diagnosis, possibly because of compensatory strategies in said individuals.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Rommelse N, van der Kruijs M, Damhuis J, Hoek I, Smeets S, Antshel KM, Hoogeveen L, Faraone SV | title = An evidenced-based perspective on the validity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the context of high intelligence | journal = Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | volume = 71 | pages = 21–47 | date = December 2016 | pmid = 27590827 | doi = 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.032 | hdl-access = free | s2cid = 6698847 | hdl = 2066/163023 }}</ref> |
|||
Studies of adults suggest that negative differences in intelligence are not meaningful and may be explained by associated health problems.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bridgett DJ, Walker ME | title = Intellectual functioning in adults with ADHD: a meta-analytic examination of full scale IQ differences between adults with and without ADHD | journal = Psychological Assessment | volume = 18 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–14 | date = March 2006 | pmid = 16594807 | doi = 10.1037/1040-3590.18.1.1 }}</ref> |
|||
Hence the idea that thinking in terms of attentional 'differences' rather than attentional 'disorders' may be helpful, by helping focus energy towards the individual's strengths and uniqueness. |
|||
==Causes== |
|||
=== ADD/ADHD a hoax? === |
|||
ADHD arises from brain maldevelopment especially in the prefrontal executive networks that can arise either from genetic factors (different gene variants and mutations for building and regulating such networks) or from acquired disruptions to the development of these networks and regions; involved in [[executive functioning]] and self-regulation.<ref name="Faraone_2021"/><ref name="Antshel_2014" /> Their reduced size, functional connectivity, and activation contribute to the pathophysiology of ADHD, as well as imbalances in the noradrenergic and dopaminergic systems that mediate these brain regions.<ref name="Faraone_2021" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Biederman J | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a selective overview | journal = Biological Psychiatry | volume = 57 | issue = 11 | pages = 1215–1220 | date = June 2005 | pmid = 15949990 | doi = 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.10.020 | s2cid = 23671547 }}</ref> |
|||
Genetic factors play an important role; ADHD has a heritability rate of 70-80%. The remaining 20-30% of variance is mediated by de-novo mutations and non-shared environmental factors that provide for or produce brain injuries; there is no significant contribution of the rearing family and social environment.{{refn|<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Larsson H | title = Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = Molecular Psychiatry | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 562–575 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 29892054 | pmc = 6477889 | doi = 10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0 | s2cid = 47016805 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=APA PsycNet |url=https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2010-02209-001 |access-date=2024-01-12 |website=psycnet.apa.org }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Demontis D, Walters RK, Martin J, Mattheisen M, Als TD, Agerbo E, Baldursson G, Belliveau R, Bybjerg-Grauholm J, Bækvad-Hansen M, Cerrato F, Chambert K, Churchhouse C, Dumont A, Eriksson N, Gandal M, Goldstein JI, Grasby KL, Grove J, Gudmundsson OO, Hansen CS, Hauberg ME, Hollegaard MV, Howrigan DP, Huang H, Maller JB, Martin AR, Martin NG, Moran J, Pallesen J, Palmer DS, Pedersen CB, Pedersen MG, Poterba T, Poulsen JB, Ripke S, Robinson EB, Satterstrom FK, Stefansson H, Stevens C, Turley P, Walters GB, Won H, Wright MJ, Andreassen OA, Asherson P, Burton CL, Boomsma DI, Cormand B, Dalsgaard S, Franke B, Gelernter J, Geschwind D, Hakonarson H, Haavik J, Kranzler HR, Kuntsi J, Langley K, Lesch KP, Middeldorp C, Reif A, Rohde LA, Roussos P, Schachar R, Sklar P, Sonuga-Barke EJ, Sullivan PF, Thapar A, Tung JY, Waldman ID, Medland SE, Stefansson K, Nordentoft M, Hougaard DM, Werge T, Mors O, Mortensen PB, Daly MJ, Faraone SV, Børglum AD, Neale BM | title = Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Nature Genetics | volume = 51 | issue = 1 | pages = 63–75 | date = January 2019 | pmid = 30478444 | pmc = 6481311 | doi = 10.1038/s41588-018-0269-7 | hdl-access = free | hdl = 10023/20827 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2022 |title=Intergenerational transmission of ADHD behaviors: More evidence for heritability than life history theor |url=https://europepmc.org/article/ppr/ppr531866#impact |access-date=2024-01-12 |website=europepmc.org}}</ref><ref name="Grimm_2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Grimm O, Kranz TM, Reif A | title = Genetics of ADHD: What Should the Clinician Know? | journal = Current Psychiatry Reports | volume = 22 | issue = 4 | pages = 18 | date = February 2020 | pmid = 32108282 | pmc = 7046577 | doi = 10.1007/s11920-020-1141-x }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Larsson H, Chang Z, D'Onofrio BM, Lichtenstein P | title = The heritability of clinically diagnosed attention deficit hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan | journal = Psychological Medicine | volume = 44 | issue = 10 | pages = 2223–2229 | date = July 2014 | pmid = 24107258 | pmc = 4071160 | doi = 10.1017/S0033291713002493 | hdl-access = free | hdl = 10616/41709 }}</ref>}} Very rarely, ADHD can also be the result of abnormalities in the chromosomes.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cederlöf M, Ohlsson Gotby A, Larsson H, Serlachius E, Boman M, Långström N, Landén M, Lichtenstein P | title = Klinefelter syndrome and risk of psychosis, autism and ADHD | journal = Journal of Psychiatric Research | volume = 48 | issue = 1 | pages = 128–130 | date = January 2014 | pmid = 24139812 | doi = 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.10.001 }}</ref> |
|||
There are some claims that ADD/ADHD is simply a hoax. Many of these charges are that there has been a conspiracy between medical and counseling professionals and the pharmaceutical companies, or that the former has been misled by the latter, which have profited greatly from the sale of medication such as Ritalin and Adderall, and have advertised their products extensively. Since medications became available, there has been an increased number of persons diagnosed. This might be explained by increased awareness or easy solution for doctors. |
|||
=== Genetics === |
|||
However, the results achieved in clinical tests with such medication and anecdotal evidence of parents, teachers, and both child and adult sufferers has proved there is both a condition and successful treatment options for most people who meet the criteria for a diagnosis. |
|||
{{See also|Missing heritability problem}} |
|||
In November 1999, ''[[Biological Psychiatry (journal)|Biological Psychiatry]]'' published a [[literature review]] by psychiatrists [[Joseph Biederman]] and Thomas Spencer on the [[pathophysiology]] of ADHD that found the average [[heritability]] estimate of ADHD from [[Twin study|twin studies]] to be 0.8,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Biederman J, Spencer T | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as a noradrenergic disorder | journal = Biological Psychiatry | volume = 46 | issue = 9 | pages = 1234–1242 | date = November 1999 | pmid = 10560028 | doi = 10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00192-4 | publisher = [[Elsevier]] | s2cid = 45497168 | author-link1 = Joseph Biederman }}</ref> while a subsequent [[Family study|family]], twin, and [[Adoption study|adoption studies]] literature review published in ''[[Molecular Psychiatry]]'' in April 2019 by psychologists [[Stephen Faraone]] and Henrik Larsson that found an average heritability estimate of 0.74.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Larsson H | title = Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = Molecular Psychiatry | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 562–575 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 29892054 | pmc = 6477889 | doi = 10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0 | publisher = [[Nature Research]] | author-link1 = Stephen Faraone }}</ref> Additionally, [[Evolutionary psychiatry|evolutionary psychiatrist]] [[Randolph M. Nesse]] has argued that the 5:1 [[Sex differences in psychology|male-to-female sex ratio]] in the [[Mental disorders and gender|epidemiology of ADHD]] suggests that ADHD may be the [[Variability hypothesis|end of a continuum where males are overrepresented at the tails]], citing clinical psychologist [[Simon Baron-Cohen]]'s [[Empathising–systemising theory|suggestion]] for the [[Sex differences in autism|sex ratio in the epidemiology of autism]] as an analogue.<ref name="Baron-Cohen 2002">{{cite journal | vauthors = Baron-Cohen S | title = The extreme male brain theory of autism | journal = Trends in Cognitive Sciences | volume = 6 | issue = 6 | pages = 248–254 | date = June 2002 | pmid = 12039606 | doi = 10.1016/S1364-6613(02)01904-6 | url = https://www.cell.com/trends/cognitive-sciences/fulltext/S1364-6613(02)01904-6 | access-date = 9 July 2020 | publisher = [[Elsevier]] | url-status = live | s2cid = 8098723 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20130703172532/http://www.cell.com/trends/cognitive-sciences/fulltext/S1364-6613(02)01904-6 | archive-date = 3 July 2013 | author-link = Simon Baron-Cohen }}</ref><ref name="Nesse 2005 p. 918">{{cite book| vauthors = Nesse RM |author-link1=Randolph M. Nesse | veditors = Buss DM |editor-link=David Buss|title=The Handbook of Evolutionary Psychology |chapter=32. Evolutionary Psychology and Mental Health |page=918 |year=2005 |edition=1st |place=[[Hoboken, New Jersey|Hoboken, NJ]] |publisher=[[Wiley (publisher)|Wiley]] |isbn=978-0-471-26403-3}}</ref><ref name="Nesse 2016 p. 1019">{{cite book | vauthors = Nesse RM |author-link1=Randolph M. Nesse | veditors = Buss DM |editor-link1=David Buss |year=2016 |orig-date=2005 |title=The Handbook of Evolutionary Psychology, Volume 2: Integrations |edition=2nd |chapter=43. Evolutionary Psychology and Mental Health |page=1019 |place=[[Hoboken, New Jersey|Hoboken, NJ]] |publisher=[[Wiley (publisher)|Wiley]] |isbn=978-1-118-75580-8}}</ref> |
|||
A further problem is that ADD and ADHD are [[syndrome]]s, associations of symptoms. There is no well established cause for the condition. This means that it may actually be a blanket term covering a multitude of conditions with a variety of causes. |
|||
[[Evolution by natural selection|Natural selection]] has been acting against the genetic variants for ADHD over the course of at least 45,000 years, indicating that it was not an adaptative trait in ancient times.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Esteller-Cucala P, Maceda I, Børglum AD, Demontis D, Faraone SV, Cormand B, Lao O | title = Genomic analysis of the natural history of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using Neanderthal and ancient Homo sapiens samples | journal = Scientific Reports | volume = 10 | issue = 1 | pages = 8622 | date = May 2020 | pmid = 32451437 | pmc = 7248073 | doi = 10.1038/s41598-020-65322-4 | bibcode = 2020NatSR..10.8622E }}</ref> The disorder may remain at a stable rate by the balance of genetic mutations and removal rate (natural selection) across generations; over thousands of years, these genetic variants become more stable, decreasing disorder prevalence.<ref>{{Cite web |title=APA PsycNet |url=https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2008-18235-008 |access-date=2024-03-05 |website=psycnet.apa.org }}</ref> Throughout human evolution, the EFs involved in ADHD likely provide the capacity to bind contingencies across time thereby directing behaviour toward future over immediate events so as to maximise future social consequences for humans.<ref>{{Cite web |title=APA PsycNet |url=https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2004-00163-014 |access-date=2024-03-28 |website=psycnet.apa.org }}</ref> |
|||
Confusion may also arise from the fact ADD/ADHD symptoms vary with each individual, and some mimic those of other causes. A known fact is that, as the body (and brain) matures and grows, the symptoms and adaptability of the individual also change. Many children diagnosed with ADD/ADHD seem to outgrow it as they mature. Clearly, other individuals experience the symptoms their entire lives. |
|||
ADHD has a high [[heritability]] of 74%, meaning that 74% of the presence of ADHD in the population is due to genetic factors. There are multiple gene variants which each slightly increase the likelihood of a person having ADHD; it is [[polygenic disease|polygenic]] and arises through the combination of many gene variants which each have a small effect.<ref name="Faraone_2018">{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Larsson H | title = Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = Molecular Psychiatry | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 562–575 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 29892054 | pmc = 6477889 | doi = 10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0 | publisher = Springer Science and Business Media LLC }}</ref><ref name="Faraone_2021"/> The siblings of children with ADHD are three to four times more likely to develop the disorder than siblings of children without the disorder.<ref>{{cite book |vauthors=Nolen-Hoeksema S |title=Abnormal Psychology |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-07-803538-8 |page=267 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Education |edition=6th}}</ref> |
|||
== Symptoms == |
|||
The association of maternal smoking observed in large population studies disappears after adjusting for family history of ADHD, which indicates that the association between maternal smoking during pregnancy and ADHD is due to familial or genetic factors that increase the risk for the confluence of smoking and ADHD.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Skoglund C, Chen Q, D'Onofrio BM, Lichtenstein P, Larsson H | title = Familial confounding of the association between maternal smoking during pregnancy and ADHD in offspring | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 55 | issue = 1 | pages = 61–68 | date = January 2014 | pmid = 25359172 | pmc = 4217138 | doi = 10.1111/jcpp.12124 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Obel C, Zhu JL, Olsen J, Breining S, Li J, Grønborg TK, Gissler M, Rutter M | title = The risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children exposed to maternal smoking during pregnancy - a re-examination using a sibling design | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 57 | issue = 4 | pages = 532–537 | date = April 2016 | pmid = 26511313 | doi = 10.1111/jcpp.12478 | url = https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/b67579b4-68c2-4010-86c4-0392822d2662 }}</ref> |
|||
* In ''children'' the disorder is characterized by inattentiveness to external direction, impulsive behavior and restlessness. However, children with the inattentive type are actually often sluggish and hypo-active. |
|||
* In ''adults'' the problem is often an inability to structure their lives and plan simple daily tasks. Thus, inattentiveness and restlessness often become secondary problems. |
|||
ADHD presents with reduced size, functional connectivity and activation<ref name="Faraone_2021" /> as well as low noradrenergic and dopaminergic functioning<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Biederman J | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a selective overview | journal = Biological Psychiatry | volume = 57 | issue = 11 | pages = 1215–1220 | date = June 2005 | pmid = 15949990 | doi = 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.10.020 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hinshaw SP | title = Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Controversy, Developmental Mechanisms, and Multiple Levels of Analysis | journal = Annual Review of Clinical Psychology | volume = 14 | issue = 1 | pages = 291–316 | date = May 2018 | pmid = 29220204 | doi = 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050817-084917 }}</ref> in brain regions and networks crucial for executive functioning and self-regulation.<ref name="Faraone_2021" /><ref name="auto3"/><ref name="Antshel_2014" /> Typically, a number of genes are involved, many of which directly affect brain functioning and neurotransmission.<ref name="Faraone_2021" /> Those involved with dopamine include [[Dopamine transporter|DAT]], [[DRD4]], [[DRD5]], [[TAAR1]], [[MAOA]], [[Catechol O-methyltransferase|COMT]], and [[Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase|DBH.]]<ref name="Kebir_2011">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kebir O, Joober R | title = Neuropsychological endophenotypes in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review of genetic association studies | journal = European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience | volume = 261 | issue = 8 | pages = 583–594 | date = December 2011 | pmid = 21409419 | doi = 10.1007/s00406-011-0207-5 | s2cid = 21383749 }}</ref><ref name="Berry_2007"/><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sotnikova TD, Caron MG, Gainetdinov RR | title = Trace amine-associated receptors as emerging therapeutic targets | journal = Molecular Pharmacology | volume = 76 | issue = 2 | pages = 229–235 | date = August 2009 | pmid = 19389919 | pmc = 2713119 | doi = 10.1124/mol.109.055970 }}</ref> Other genes associated with ADHD include [[Serotonin transporter|SERT]], [[HTR1B]], [[SNAP25]], [[GRIN2A]], [[ADRA2A]], [[TPH2]], and [[Brain-derived neurotrophic factor|BDNF]].<ref name="Gizer_2009">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gizer IR, Ficks C, Waldman ID | title = Candidate gene studies of ADHD: a meta-analytic review | journal = Human Genetics | volume = 126 | issue = 1 | pages = 51–90 | date = July 2009 | pmid = 19506906 | doi = 10.1007/s00439-009-0694-x | s2cid = 166017 }}</ref> A common variant of a gene called [[latrophilin 3]] is estimated to be responsible for about 9% of cases and when this variant is present, people are particularly responsive to stimulant medication.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Arcos-Burgos M, Muenke M | title = Toward a better understanding of ADHD: LPHN3 gene variants and the susceptibility to develop ADHD | journal = Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders | volume = 2 | issue = 3 | pages = 139–147 | date = November 2010 | pmid = 21432600 | pmc = 3280610 | doi = 10.1007/s12402-010-0030-2 }}</ref> The [[DRD4–7R|7 repeat variant of dopamine receptor D4]] (DRD4–7R) causes increased inhibitory effects induced by [[dopamine]] and is associated with ADHD. The DRD4 receptor is a [[G protein-coupled receptor]] that inhibits [[adenylyl cyclase]]. The DRD4–7R mutation results in a wide range of behavioural [[phenotype]]s, including ADHD symptoms reflecting split attention.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Nikolaidis A, Gray JR | title = ADHD and the DRD4 exon III 7-repeat polymorphism: an international meta-analysis | journal = Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience | volume = 5 | issue = 2–3 | pages = 188–193 | date = June 2010 | pmid = 20019071 | pmc = 2894686 | doi = 10.1093/scan/nsp049 }}</ref> The DRD4 gene is both linked to novelty seeking and ADHD. The genes [[glucose-fructose oxidoreductase|GFOD1]] and [[T-cadherin|CDH13]] show strong genetic associations with ADHD. CHD13's association with ASD, [[schizophrenia]], bipolar disorder, and [[Depression (mood)|depression]] make it an interesting candidate causative gene.<ref name="Grimm_2020"/> Another candidate causative gene that has been identified is [[Latrophilin 3|ADGRL3]]. In [[zebrafish]], knockout of this gene causes a loss of dopaminergic function in the ventral [[diencephalon]] and the fish display a hyperactive/impulsive [[phenotype]].<ref name="Grimm_2020" /> |
|||
A diagnosis of ADHD is made based on a checklist of symptoms that can be found in [[DSM-IV-TR]]. A hyperlink to the [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]] (CDC) web page summarizing these criteria is given in the [[#External links|External links]] section below. |
|||
For [[genetic variation]] to be used as a tool for diagnosis, more validating studies need to be performed. However, smaller studies have shown that [[genetic polymorphism]]s in genes related to [[catecholaminergic]] neurotransmission or the [[SNARE (protein)|SNARE]] complex of the [[synapse]] can reliably predict a person's response to [[Stimulant|stimulant medication]].<ref name="Grimm_2020" /> Rare genetic variants show more relevant clinical significance as their penetrance (the chance of developing the disorder) tends to be much higher.<ref name="Zayats_2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Zayats T, Neale BM | title = Recent advances in understanding of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): how genetics are shaping our conceptualization of this disorder | journal = F1000Research | volume = 8 | page = 2060 | date = 12 February 2020 | pmid = 31824658 | pmc = 6896240 | doi = 10.12688/f1000research.18959.2 | doi-access = free }}</ref> However their usefulness as tools for diagnosis is limited as no single gene predicts ADHD. ASD shows genetic overlap with ADHD at both common and rare levels of genetic variation.<ref name="Zayats_2020" /> |
|||
The CDC emphasizes that a diagnosis of ADHD should only be made by trained health care providers. This is important as many of the criteria can be readily misinterpreted and the prescribed drugs can be very dangerous. |
|||
== |
=== Environment === |
||
ADHD is considered by some to be a problem all over the industrialized world, although in no other country are children diagnosed with this disorder as often as in the United States. |
|||
In addition to genetics, some environmental factors might play a role in causing ADHD.<ref name="Sonu_2013" /><ref name="cdc2016">{{cite web |author=CDC |title=Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) |publisher=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |url=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/research.html |date=16 March 2016 |access-date=17 April 2016 |url-status=live |archive-date=14 April 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160414160548/http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/research.html}}</ref> Alcohol intake during pregnancy can cause [[fetal alcohol spectrum disorder]]s which can include ADHD or symptoms like it.<ref name="Burger_2011">{{cite journal | vauthors = Burger PH, Goecke TW, Fasching PA, Moll G, Heinrich H, Beckmann MW, Kornhuber J | title = [How does maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy affect the development of attention deficit/hyperactivity syndrome in the child] | language = de | journal = Fortschritte der Neurologie-Psychiatrie | volume = 79 | issue = 9 | pages = 500–506 | date = September 2011 | pmid = 21739408 | doi = 10.1055/s-0031-1273360 | trans-title = How does maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy affect the development of attention deficit/hyperactivity syndrome in the child | type = Review | s2cid = 140766296 }}</ref> Children exposed to certain toxic substances, such as [[lead poisoning|lead]] or [[polychlorinated biphenyls]], may develop problems which resemble ADHD.<ref name="nimh" /><ref name="Eubig_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Eubig PA, Aguiar A, Schantz SL | title = Lead and PCBs as risk factors for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Environmental Health Perspectives | volume = 118 | issue = 12 | pages = 1654–1667 | date = December 2010 | pmid = 20829149 | pmc = 3002184 | doi = 10.1289/ehp.0901852 | type = Review. Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural. Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S. }}</ref> Exposure to the [[organophosphate]] insecticides [[chlorpyrifos]] and [[Alkyl phosphate|dialkyl phosphate]] is associated with an increased risk; however, the evidence is not conclusive.<ref name="de_Cock_2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = de Cock M, Maas YG, van de Bor M | title = Does perinatal exposure to endocrine disruptors induce autism spectrum and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders? Review | journal = Acta Paediatrica | volume = 101 | issue = 8 | pages = 811–818 | date = August 2012 | pmid = 22458970 | doi = 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2012.02693.x | type = Review. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't | s2cid = 41748237 }}</ref> Exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy can cause problems with central nervous system development and can increase the risk of ADHD.<ref name="nimh">{{cite web |title=Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (Easy-to-Read) |url=http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-easy-to-read/index.shtml |publisher=National Institute of Mental Health |year=2013 |access-date=17 April 2016 |url-status=live |archive-date=14 April 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160414031036/http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-easy-to-read/index.shtml}}</ref><ref name="Abbott_2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Abbott LC, Winzer-Serhan UH | title = Smoking during pregnancy: lessons learned from epidemiological studies and experimental studies using animal models | journal = Critical Reviews in Toxicology | volume = 42 | issue = 4 | pages = 279–303 | date = April 2012 | pmid = 22394313 | doi = 10.3109/10408444.2012.658506 | type = Review | s2cid = 38886526 }}</ref> [[Nicotine]] exposure during pregnancy may be an environmental risk.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Tiesler CM, Heinrich J | title = Prenatal nicotine exposure and child behavioural problems | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 23 | issue = 10 | pages = 913–929 | date = October 2014 | pmid = 25241028 | pmc = 4186967 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-014-0615-y }}</ref> |
|||
According to the [[2000]] edition of [[DSM-IV-TR]], ADHD affects three to seven [[percent]] of all children in the U.S. According to [[2002]] data from the [[CDC]]'s annual [[National Health Interview Survey]], released in [[2004]], nearly 4 million children younger than 18 in the United States had been diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The 2002 data indicated that twice as many boys were diagnosed with ADHD as girls (10% vs. 4%). Some experts theorize that ADHD is under-diagnosed in girls, since their symptoms tend to be less dramatic than those in boys and thus draw less attention from parents and teachers. |
|||
Extreme [[premature birth]], very [[low birth weight]], and extreme neglect, abuse, or social deprivation also increase the risk<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Botting N, Powls A, Cooke RW, Marlow N | title = Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders and other psychiatric outcomes in very low birthweight children at 12 years | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 38 | issue = 8 | pages = 931–941 | date = November 1997 | pmid = 9413793 | doi = 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01612.x | url = https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01612.x | access-date = 22 March 2022 | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220517212252/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01612.x | archive-date = 17 May 2022 }}</ref><ref name="nimh" /><ref name="Thapar-2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Thapar A, Cooper M, Jefferies R, Stergiakouli E | title = What causes attention deficit hyperactivity disorder? | journal = Archives of Disease in Childhood | volume = 97 | issue = 3 | pages = 260–265 | date = March 2012 | pmid = 21903599 | pmc = 3927422 | doi = 10.1136/archdischild-2011-300482 | type = Review. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't }}</ref> as do certain infections during pregnancy, at birth, and in early childhood. These infections include, among others, various viruses ([[measles]], [[Varicella zoster virus|varicella zoster]] [[encephalitis]], [[rubella]], [[enterovirus 71]]).<ref name="Millichap_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Millichap JG | title = Etiologic classification of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 121 | issue = 2 | pages = e358–e365 | date = February 2008 | pmid = 18245408 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2007-1332 | type = Review | s2cid = 24339363 }}</ref> At least 30% of children with a [[traumatic brain injury]] later develop ADHD<ref name="Eme-2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Eme R | title = ADHD: an integration with pediatric traumatic brain injury | journal = Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics | volume = 12 | issue = 4 | pages = 475–483 | date = April 2012 | pmid = 22449218 | doi = 10.1586/ern.12.15 | type = Review | s2cid = 35718630 }}</ref> and about 5% of cases are due to brain damage.<ref name="Erk_2009" /> |
|||
== Psychological testing for ADHD == |
|||
Some studies suggest that in a small number of children, artificial [[food dye]]s or [[preservatives]] may be associated with an increased prevalence of ADHD or ADHD-like symptoms,<ref name="nimh" /><ref name="pmid22232312">{{cite journal | vauthors = Millichap JG, Yee MM | title = The diet factor in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 129 | issue = 2 | pages = 330–337 | date = February 2012 | pmid = 22232312 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2011-2199 | url = http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/129/2/330.long | url-status = live | s2cid = 14925322 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150911071727/http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/129/2/330.long | archive-date = 11 September 2015 }}</ref> but the evidence is weak and may only apply to children with [[food sensitivities]].<ref name="Sonu_2013" /><ref name="pmid22232312" /><ref name="EncycFoodSafety">{{cite encyclopedia |vauthors=Tomaska LD, Brooke-Taylor S |title=Food Additives – General |pages=[{{google books|mX1XAQAAQBAJ |page=449|plainurl=yes}} 449]–54 |encyclopedia=Encyclopedia of Food Safety |volume=3 |veditors=Motarjemi Y, Moy GG, Todd EC |publisher=Elsevier/Academic Press |location=Amsterdam |edition=1st |date=2014 |isbn=978-0-12-378613-5 |oclc=865335120}}</ref> The [[European Union]] has put in place regulatory measures based on these concerns.<ref name="FDAdyecomm">{{cite web |date=March 2011 |url=https://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/FoodAdvisoryCommittee/UCM248549.pdf |title=Background Document for the Food Advisory Committee: Certified Color Additives in Food and Possible Association with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children |publisher=U.S. Food and Drug Administration |url-status=live |archive-date=6 November 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151106080629/https://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/FoodAdvisoryCommittee/UCM248549.pdf}}</ref> In a minority of children, [[food intolerance|intolerances]] or [[food allergy|allergies]] to certain foods may worsen ADHD symptoms.<ref name="Nigg_2014" /> |
|||
Psychological testing for ADHD symptoms generally consists of obtaining multiple types of assessments. These usually include a clinical interview reviewing the DSM-IV criteria for ADHD diagnosis. The interview also needs to rule out as much as possible other types of syndromes which can cause attention problems, such as [[depression]], [[anxiety]], [[allergies]] and [[ADD psychosis|psychosis]]. Rating scales can be administered which provide measurement of the person's own view of their symptoms, as well as the views of parents, teachers, and significant others. |
|||
Individuals with [[hypokalemic sensory overstimulation]] are sometimes diagnosed as having attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), raising the possibility that a subtype of ADHD has a cause that can be understood mechanistically and treated in a novel way. The sensory overload is treatable with oral [[potassium gluconate]]. |
|||
Finally, computerized tests of attention can be helpful in providing a further independent assessment. These different assessments may not be consistent, but do provide a view of the person's difficulties. Subjectivity of the analysis can be compounded by the fact that physicians generally need not order psychological testing in order to make the diagnosis of ADHD, but many doctors use this kind of assessment to avoid over-diagnosis and treatment. The process of obtaining referrals for such assessments is being promoted vigorously by the [[New Freedom Commission on Mental Health|President's New Freedom Commission on Mental Health]]. |
|||
{{Anchor|ADH and Sugar}}<!-- Do not delete this code as it is used to link to this location regarding sugar and ADHD from other articles.--> |
|||
===Other forms of testing=== |
|||
Research does not support popular beliefs that ADHD is caused by eating too much refined sugar, watching too much television, bad parenting, poverty or family chaos; however, they might worsen ADHD symptoms in certain people.<ref name="cdc2016facts">{{cite web |title=Facts About ADHD |publisher=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |url=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/facts.html |date=6 January 2016 |access-date=20 March 2016 |url-status=live |archive-date=22 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160322103310/http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/facts.html}}</ref> |
|||
The youngest children in a class have been found to be more likely to be diagnosed as having ADHD, possibly due to them being developmentally behind their older classmates.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Holland J, Sayal K | title = Relative age and ADHD symptoms, diagnosis and medication: a systematic review | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 28 | issue = 11 | pages = 1417–1429 | date = November 2019 | pmid = 30293121 | pmc = 6800871 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-018-1229-6 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Disorders of Childhood: Development and Psychopathology |vauthors=Parritz R |publisher=Cengage Learning |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-285-09606-3 |pages=[https://books.google.com/books?id=VAj2rPTN1j0C&pg=PA151 151]}}<!-- |access-date=17 January 2014--></ref> One study showed that the youngest children in fifth and eight grade was nearly twice as likely to use stimulant medication than their older peers.<ref>{{cite book |vauthors=Stockman JA |title=Year Book of Pediatrics 2014 E-Book |date=2016 |publisher=Elsevier Health Sciences |isbn=978-0-323-26527-0 |page=163 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5b65DAAAQBAJ&pg=PT163 |access-date=4 June 2020 |archive-date=26 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200726123927/https://books.google.com/books?id=5b65DAAAQBAJ&pg=PT163 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[Neurometrics]], [[Positron Emission Tomography|PET]] scans, or [[SPECT]] scans have been used for a more objective diagnosis. However, these are not usually suitable for very young children. |
|||
In some cases, an inappropriate diagnosis of ADHD may reflect a [[dysfunctional family]] or a poor [[educational system]], rather than any true presence of ADHD in the individual.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.euro.who.int/document/MNH/ebrief14.pdf |title=Mental health of children and adolescents |date=15 January 2005 |access-date=13 October 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091024102724/http://www.euro.who.int/document/MNH/ebrief14.pdf |archive-date=24 October 2009 |website=WHO Europe}}</ref>{{Better source needed|date=May 2022|reason=The current source is a briefing for a conference, with unclear provenance.}} In other cases, it may be explained by increasing academic expectations, with a diagnosis being a method for parents in some countries to get extra financial and educational support for their child.<ref name="Erk_2009" /> Behaviours typical of ADHD occur more commonly in children who have experienced violence and emotional abuse.<ref name="NICE 2009">{{cite book |title=Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management of ADHD in Children, Young People and Adults |author=National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health |series=NICE Clinical Guidelines |volume=72 |publisher=British Psychological Society |location=Leicester |isbn=978-1-85433-471-8 |date=2009 |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53652/ |via=NCBI Bookshelf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160113133612/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53652/ |archive-date=13 January 2016 }}</ref> |
|||
==Treatment == |
|||
== Pathophysiology == |
|||
There are many options available to treat people diagnosed with ADHD. |
|||
Current models of ADHD suggest that it is associated with functional impairments in some of the brain's [[neurotransmitter systems]], particularly those involving [[dopamine]] and [[norepinephrine]].<ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci">{{cite book |title=Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience |vauthors=Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE |publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-07-148127-4 |veditors=Sydor A, Brown RY |edition=2nd |location=New York |pages=266, 315, 318–323 |chapter=Chapters 10 and 13 |quote=Early results with structural MRI show thinning of the cerebral cortex in ADHD subjects compared with age-matched controls in prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex, areas involved in working memory and attention.}}</ref> The dopamine and norepinephrine pathways that originate in the [[ventral tegmental area]] and [[locus coeruleus]] project to diverse regions of the brain and govern a variety of cognitive processes.<ref name="VTA+LC projection systems">{{cite journal | vauthors = Chandler DJ, Waterhouse BD, Gao WJ | title = New perspectives on catecholaminergic regulation of executive circuits: evidence for independent modulation of prefrontal functions by midbrain dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons | journal = Frontiers in Neural Circuits | volume = 8 | pages = 53 | date = May 2014 | pmid = 24904299 | pmc = 4033238 | doi = 10.3389/fncir.2014.00053 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="Malenka pathways" /> The [[dopamine pathway]]s and [[LC-NA system|norepinephrine pathway]]s which project to the [[prefrontal cortex]] and [[striatum]] are directly responsible for modulating [[executive function]] (cognitive control of behaviour), motivation, reward perception, and motor function;<ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /><ref name="Malenka pathways" /> these pathways are known to play a central role in the [[wikt:pathophysiology|pathophysiology]] of ADHD.<ref name="VTA+LC projection systems" /><ref name="Malenka pathways" /><ref name="pmid22169776" /><ref name="pmid22983386" /> Larger models of ADHD with additional pathways have been proposed.<ref name="pmid22169776">{{cite journal | vauthors = Castellanos FX, Proal E | title = Large-scale brain systems in ADHD: beyond the prefrontal-striatal model | journal = Trends in Cognitive Sciences | volume = 16 | issue = 1 | pages = 17–26 | date = January 2012 | pmid = 22169776 | pmc = 3272832 | doi = 10.1016/j.tics.2011.11.007 | quote = Recent conceptualizations of ADHD have taken seriously the distributed nature of neuronal processing. Most of the candidate networks have focused on prefrontal-striatal-cerebellar circuits, although other posterior regions are also being proposed. }}</ref><ref name="pmid22983386">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cortese S, Kelly C, Chabernaud C, Proal E, Di Martino A, Milham MP, Castellanos FX | title = Toward systems neuroscience of ADHD: a meta-analysis of 55 fMRI studies | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 169 | issue = 10 | pages = 1038–1055 | date = October 2012 | pmid = 22983386 | pmc = 3879048 | doi = 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11101521 | lccn = 22024537 | oclc = 1480183 | eissn = 1535-7228 }}</ref> |
|||
These options include a variety of medications, behavior-changing therapies, and educational interventions. |
|||
=== |
=== Brain structure === |
||
[[File:Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder - Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder - Reduced brain volume on the left side from ADHD.jpg|thumb|upright=1.3|The left prefrontal cortex, shown here in blue, is often affected in ADHD]] |
|||
The first-line medication used to treat ADHD are mostly [[stimulants]], which work by stimulating the areas of the brain responsible for focus, attention, and impulse control. These include: |
|||
In children with ADHD, there is a general reduction of volume in certain brain structures, with a proportionally greater decrease in the volume in the left-sided [[prefrontal cortex]].<ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /><ref name="Krain2006">{{cite journal | vauthors = Krain AL, Castellanos FX | title = Brain development and ADHD | journal = Clinical Psychology Review | volume = 26 | issue = 4 | pages = 433–444 | date = August 2006 | pmid = 16480802 | doi = 10.1016/j.cpr.2006.01.005 }}</ref> The [[posterior parietal cortex]] also shows thinning in individuals with ADHD compared to controls. Other brain structures in the prefrontal-striatal-cerebellar and prefrontal-striatal-thalamic circuits have also been found to differ between people with and without ADHD.<ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /><ref name="pmid22169776" /><ref name="pmid22983386" /> |
|||
*[[Caffeine]] -- though not an official mainstream treatment, the ubiquitous use of caffeine means that it is probably one of the most frequently used, unofficial treatments for ADHD. Caffeine is found in coffee, tea and cola soft drinks. Many students and adults will self-medicate with caffeine. Signs that one is self-medicating would be the observation that one's focus improves with the stimulant, and that one cannot function as well without it. Users often report that drinking caffeine in the evening does not impair their sleep, and that in fact, it may help soothe and relax them, thus helping them sleep better. Drinking only 1-2 cups daily is probably not self-medication, but someone who needs over 5 cups daily throughout the day in order to stay awake and focus may possibly be self-medicating. |
|||
*[[Nicotine]] -- found in cigarettes, many students and adults will self-medicate by needing to smoke several times daily. |
|||
*[[Methylphenidate]] -- Available in: |
|||
**Regular formulation, sold as Ritalin, Metadate, Methylin. Duration: 4-6 hours per dose. Usually taken morning, lunchtime, and in some cases, afternoon. |
|||
**Long acting formulation, sold as Ritalin SR, Metadate ER. Duration: 8 hours per dose. Usually taken twice daily. |
|||
**All-day formulation, sold as Ritalin LA, Metadate CD, Concerta. Duration: 10-12 hours per dose. Usually taken once a day. |
|||
*Amphetamines -- |
|||
**[[Dextroamphetamine]] -- Available in: |
|||
***Regular formulation, sold as Dexedrine. Duration: 4-6 hours per dose. Usually taken 2-3 times daily. |
|||
***Long-acting formulation, sold as Dexedrine Spansules. Duration: 8-12 hours per dose. Taken once a day. |
|||
**[[Adderall]], a trade name for a mixture of dextroamphetamine and laevoamphetamine salts. -- Available in: |
|||
***Regular formulation, [[Adderall]]. Duration: 4-6 hours a dose. |
|||
***Long-acting formulation, [[Adderall XR]]. Duration: 12 hours. Taken once a day. |
|||
**[[Methamphetamine]] -- Available in: |
|||
***Regular formulation, sold as Desoxyn by Ovation Pharmacutical Company. Usually taken twice daily. |
|||
* [[Atomoxetine]]. A Selective [[Norepinephrine]] Reuptake Inhibitor ([[Selective_norepinephrine_reuptake_inhibitor|SNRI]]) introduced in 2002, it is the newest class of drug used to treat ADHD, and the first non-stimulant medication to be used as a first-line treatment for ADHD. Available in: |
|||
**Once daily formulation, sold by [[Eli Lilly and Company]] as [[Strattera]]. Duration: 24 hours per dose. Taken once a day. |
|||
The subcortical volumes of the [[accumbens]], [[amygdala]], [[Caudate nucleus|caudate]], [[hippocampus]], and [[putamen]] appears smaller in individuals with ADHD compared with controls.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hoogman M, Bralten J, Hibar DP, Mennes M, Zwiers MP, Schweren LS, van Hulzen KJ, Medland SE, Shumskaya E, Jahanshad N, Zeeuw P, Szekely E, Sudre G, Wolfers T, Onnink AM, Dammers JT, Mostert JC, Vives-Gilabert Y, Kohls G, Oberwelland E, Seitz J, Schulte-Rüther M, Ambrosino S, Doyle AE, Høvik MF, Dramsdahl M, Tamm L, van Erp TG, Dale A, Schork A, Conzelmann A, Zierhut K, Baur R, McCarthy H, Yoncheva YN, Cubillo A, Chantiluke K, Mehta MA, Paloyelis Y, Hohmann S, Baumeister S, Bramati I, Mattos P, Tovar-Moll F, Douglas P, Banaschewski T, Brandeis D, Kuntsi J, Asherson P, Rubia K, Kelly C, Martino AD, Milham MP, Castellanos FX, Frodl T, Zentis M, Lesch KP, Reif A, Pauli P, Jernigan TL, Haavik J, Plessen KJ, Lundervold AJ, Hugdahl K, Seidman LJ, Biederman J, Rommelse N, Heslenfeld DJ, Hartman CA, Hoekstra PJ, Oosterlaan J, Polier GV, Konrad K, Vilarroya O, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Soliva JC, Durston S, Buitelaar JK, Faraone SV, Shaw P, Thompson PM, Franke B | title = Subcortical brain volume differences in participants with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adults: a cross-sectional mega-analysis | journal = The Lancet. Psychiatry | volume = 4 | issue = 4 | pages = 310–319 | date = April 2017 | pmid = 28219628 | pmc = 5933934 | doi = 10.1016/S2215-0366(17)30049-4 }}</ref> Structural MRI studies have also revealed differences in white matter, with marked differences in inter-hemispheric asymmetry between ADHD and typically developing youths.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Douglas PK, Gutman B, Anderson A, Larios C, Lawrence KE, Narr K, Sengupta B, Cooray G, Douglas DB, Thompson PM, McGough JJ, Bookheimer SY | title = Hemispheric brain asymmetry differences in youths with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = NeuroImage. Clinical | volume = 18 | pages = 744–752 | date = February 2018 | pmid = 29876263 | pmc = 5988460 | doi = 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.02.020 }}</ref> |
|||
Second-line medications include: |
|||
*[[benzphetamine]] -- a less powerful stimulant. Research on the effectiveness of this drug is not yet complete. |
|||
* [[Provigil]]/[[Alertec]]/[[modafinil]] -- Research on this drug is not yet complete. |
|||
* [[Cylert]]/[[Pemoline]] --a stimulant used with great success until the late 1980s when it was discovered that this medication could cause liver damage. Although some physicians do continue to prescribe Cylert, it can no longer be considered a first-line medicine. In March 2005 the makers of Cylert announced that it would discontinue the medication's production. |
|||
[[Functional magnetic resonance imaging|Function MRI]] (fMRI) studies have revealed a number of differences between ADHD and control brains. Mirroring what is known from structural findings, fMRI studies have showed evidence for a higher connectivity between subcortical and cortical regions, such as between the caudate and prefrontal cortex. The degree of hyperconnectivity between these regions correlated with the severity of inattention or hyperactivity <ref name="Damiani_2021">{{cite journal | vauthors = Damiani S, Tarchi L, Scalabrini A, Marini S, Provenzani U, Rocchetti M, Oliva F, Politi P | title = Beneath the surface: hyper-connectivity between caudate and salience regions in ADHD fMRI at rest | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 30 | issue = 4 | pages = 619–631 | date = April 2021 | pmid = 32385695 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-020-01545-0 | hdl-access = free | s2cid = 218540328 | hdl = 2318/1755224 }}</ref> Hemispheric lateralization processes have also been postulated as being implicated in ADHD, but empiric results showed contrasting evidence on the topic.<ref name="Tarchi_2022">{{cite journal | vauthors = Tarchi L, Damiani S, Fantoni T, Pisano T, Castellini G, Politi P, Ricca V | title = Centrality and interhemispheric coordination are related to different clinical/behavioral factors in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state fMRI study | journal = Brain Imaging and Behavior | volume = 16 | issue = 6 | pages = 2526–2542 | date = December 2022 | pmid = 35859076 | pmc = 9712307 | doi = 10.1007/s11682-022-00708-8 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mohamed SM, Börger NA, Geuze RH, van der Meere JJ | title = Brain lateralization and self-reported symptoms of ADHD in a population sample of adults: a dimensional approach | journal = Frontiers in Psychology | volume = 6 | pages = 1418 | date = 2015 | pmid = 26441789 | pmc = 4585266 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01418 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
Because most of the medications used to treat ADHD are [[Schedule II]] under the U.S. [[Drug Enforcement Administration|DEA]] schedule system, and are considered powerful stimulants with a potential for [[prescription drug diversion|diversion]] and [[drug abuse|abuse]], there is controversy surrounding prescribing these drugs for children and adolescents. However, research studying ADHD sufferers who either receive treatment with stimulants or go untreated has indicated that those treated with stimulants are in fact much less likely to abuse any substance than ADHD sufferers who are not treated with stimulants.{{ref|1}} |
|||
=== Neurotransmitter pathways === |
|||
===Alternative treatments=== |
|||
Previously, it had been suggested that the elevated number of [[dopamine transporters]] in people with ADHD was part of the pathophysiology, but it appears the elevated numbers may be due to adaptation following exposure to stimulant medication.<ref name="pmid22294258">{{cite journal | vauthors = Fusar-Poli P, Rubia K, Rossi G, Sartori G, Balottin U | title = Striatal dopamine transporter alterations in ADHD: pathophysiology or adaptation to psychostimulants? A meta-analysis | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 169 | issue = 3 | pages = 264–272 | date = March 2012 | pmid = 22294258 | doi = 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11060940 | lccn = 22024537 | hdl = 11577/2482784 | doi-access = free | oclc = 1480183 | eissn = 1535-7228 }}</ref> Current models involve the [[mesocorticolimbic projection|mesocorticolimbic dopamine pathway]] and the [[locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system]].<ref name="VTA+LC projection systems" /><ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /><ref name="Malenka pathways" /> ADHD psychostimulants possess treatment efficacy because they increase neurotransmitter activity in these systems.<ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /><ref name="Malenka pathways">{{cite book |vauthors=Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE |veditors=Sydor A, Brown RY |title=Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience |year=2009 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical |location=New York |isbn=978-0-07-148127-4 |pages=148, 154–157 |edition=2nd |chapter=Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin | quote={{abbr|DA|dopamine}} has multiple actions in the prefrontal cortex. It promotes the 'cognitive control' of behavior: the selection and successful monitoring of behavior to facilitate attainment of chosen goals. Aspects of cognitive control in which DA plays a role include working memory, the ability to hold information 'on line' in order to guide actions, suppression of prepotent behaviors that compete with goal-directed actions, and control of attention and thus the ability to overcome distractions. Cognitive control is impaired in several disorders, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. ... Noradrenergic projections from the {{abbr|LC|locus coeruleus}} thus interact with dopaminergic projections from the {{abbr|VTA|ventral tegmental area}} to regulate cognitive control. ... it has not been shown that {{abbr|5HT|serotonin}} makes a therapeutic contribution to treatment of ADHD.}}</ref><ref name="cognition enhancers" /> There may additionally be abnormalities in [[Serotonin|serotonergic]], [[glutamate (neurotransmitter)|glutamatergic]], or [[cholinergic]] pathways.<ref name="cognition enhancers" /><ref name="Cortese-2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cortese S | title = The neurobiology and genetics of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): what every clinician should know | journal = European Journal of Paediatric Neurology | volume = 16 | issue = 5 | pages = 422–433 | date = September 2012 | pmid = 22306277 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejpn.2012.01.009 }}</ref><ref name="pmid22939004">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lesch KP, Merker S, Reif A, Novak M | title = Dances with black widow spiders: dysregulation of glutamate signalling enters centre stage in ADHD | journal = European Neuropsychopharmacology | volume = 23 | issue = 6 | pages = 479–491 | date = June 2013 | pmid = 22939004 | doi = 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.07.013 | s2cid = 14701654 }}</ref> |
|||
There are ''many'' alternative treatments for ADHD, and all of them are as heavily disputed as the mainstream. This section attempts to deal with the most prominent of the alternative treatments. |
|||
=== Executive function and motivation === |
|||
====Feingold diet==== |
|||
The symptoms of ADHD arise from a deficiency in certain [[executive function]]s (e.g., [[attentional control]], [[inhibitory control]], and [[working memory]]).<ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /> Executive functions are a set of [[Cognition|cognitive processes]] that are required to successfully select and monitor behaviours that facilitate the attainment of one's chosen goals.<ref name="Malenka pathways" /><ref name="Executive functions" /> The executive function impairments that occur in ADHD individuals result in problems with staying organised, time keeping, excessive [[procrastination]], maintaining concentration, paying attention, ignoring distractions, regulating emotions, and remembering details.<ref name="Brown_2008" /><ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /><ref name="Malenka pathways" /> People with ADHD appear to have unimpaired long-term memory, and deficits in long-term recall appear to be attributed to impairments in working memory.<ref name="pmid24232170">{{cite journal | vauthors = Skodzik T, Holling H, Pedersen A | title = Long-Term Memory Performance in Adult ADHD | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 21 | issue = 4 | pages = 267–283 | date = February 2017 | pmid = 24232170 | doi = 10.1177/1087054713510561 | s2cid = 27070077 }}</ref> Due to the rates of brain maturation and the increasing demands for executive control as a person gets older, ADHD impairments may not fully manifest themselves until adolescence or even early adulthood.<ref name="Brown_2008" /> Conversely, brain maturation trajectories, potentially exhibiting diverging longitudinal trends in ADHD, may support a later improvement in executive functions after reaching adulthood.<ref name="Tarchi_2022" /> |
|||
[[Ben F. Feingold|Dr Ben F. Feingold]], once a [[Professor of Allergy]] in [[San Francisco]], claimed that hyperactivity was increasing in proportion to the level of food additives and proposed a specific diet believing that it would help 50% of hyperactive children. |
|||
The [[Feingold diet]] excluded [[cola|cola drink]]s, [[chocolate]], [[preservative]]s and flavor [[food additive|additive]]s, as well as [[salicylate]]s that occur naturally in fruit such as [[tomato]]es, [[strawberry|strawberries]], [[pineapple]]s and [[Orange (fruit)|orange]]s. However pineapple juice was suggested as a "safe" drink. |
|||
ADHD has also been associated with motivational deficits in children. Children with ADHD often find it difficult to focus on long-term over short-term rewards, and exhibit impulsive behaviour for short-term rewards.<ref name="Motivation">{{cite journal | vauthors = Modesto-Lowe V, Chaplin M, Soovajian V, Meyer A | title = Are motivation deficits underestimated in patients with ADHD? A review of the literature | journal = Postgraduate Medicine | volume = 125 | issue = 4 | pages = 47–52 | date = July 2013 | pmid = 23933893 | doi = 10.3810/pgm.2013.07.2677 | quote = Behavioral studies show altered processing of reinforcement and incentives in children with ADHD. These children respond more impulsively to rewards and choose small, immediate rewards over larger, delayed incentives. Interestingly, a high intensity of reinforcement is effective in improving task performance in children with ADHD. Pharmacotherapy may also improve task persistence in these children. ... Previous studies suggest that a clinical approach using interventions to improve motivational processes in patients with ADHD may improve outcomes as children with ADHD transition into adolescence and adulthood. | s2cid = 24817804 }}</ref> |
|||
The effectiveness of the Feingold diet has been heavily disputed. Most studies have shown that only 5% of children diagnosed with ADHD benefited from the diet. Other studies have shown a figure of 60%. |
|||
=== Paradoxical reaction to neuroactive substances === |
|||
====Vitaman B<small><sub>6</sub></small>==== |
|||
Another sign of the structurally altered signal processing in the central nervous system in this group of people is the conspicuously common [[Paradoxical reaction]] ({{circa|10–20%}} of patients). These are unexpected reactions in the opposite direction as with a normal effect, or otherwise significant different reactions. These are reactions to neuroactive substances such as [[local anesthetic]] at the dentist, [[sedative]], [[caffeine]], [[antihistamine]], weak [[neuroleptics]] and central and peripheral [[painkillers]]. Since the causes of ''paradoxical reactions'' are at least partly genetic, it may be useful in critical situations, for example before operations, to ask whether such abnormalities may also exist in family members.<ref name="PMID21886668">B. Langguth, R. Bär, N. Wodarz, M. Wittmann, R. Laufkötter: ''Paradoxical reaction in ADHD.'' In: ''Deutsches Ärzteblatt international.'' Band 108, Nummer 31–32, August 2011, S. 541; author reply 541–541; author reply 542, (in German).[[doi:10.3238/arztebl.2011.0541a]], PMID 21886668, {{PMC|3163785}}.</ref><ref>Rainer Laufkötter, Berthold Langguth, Monika Johann, Peter Eichhammer, Göran Hajak: ''ADHS des Erwachsenenalters und Komorbiditäten.'' In: ''psychoneuro.'' 31, 2005, S. 563, (in German).[[doi:10.1055/s-2005-923370]].</ref> |
|||
In the [[1980s]] the [[vitamin]] B<small><sub>6</sub></small> promoted as a helpful remedy for children with learning difficulties including inattentiveness. After that, [[zinc]] was promoted for ADD and [[autism]]. [[Multivitamin]]s later became the claimed solution. Thus far, no reputable research has appeared to support any of these claims, except in cases of [[malnutrition]]. |
|||
==Diagnosis== |
|||
====Neurofeedback==== |
|||
ADHD is diagnosed by an assessment of a person's behavioural and mental development, including ruling out the effects of drugs, medications, and other medical or psychiatric problems as explanations for the symptoms.<ref name="NICE2009-part2" /> ADHD diagnosis often takes into account feedback from parents and teachers<ref name="Lake2011">{{cite book |vauthors=Dulcan MK, Lake MB |url={{google books|HvTa2nArhOsC|plainurl=yes}} |title=Concise Guide to Child and Adolescent Psychiatry |date=2011 |publisher=American Psychiatric Publishing |isbn=978-1-58562-416-4 |edition=4th illustrated |pages=[https://books.google.com/books?id=HvTa2nArhOsC&pg=PA34 34] |chapter=Axis I Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood or Adolescence: Attention-Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders |chapter-url={{google books|HvTa2nArhOsC |page=23|plainurl=yes}} |via=Google Books}}</ref> with most diagnoses begun after a teacher raises concerns.<ref name="Erk_2009">{{cite book |vauthors=Mayes R, Bagwell C, Erkulwater JL |title=Medicating Children: ADHD and Pediatric Mental Health |publisher=Harvard University Press |date=2009 |pages=4–24 |isbn=978-0-674-03163-0 |edition=illustrated }}</ref> While many tools exist to aide in the diagnosis of ADHD, their validity varies in different populations, and a reliable and valid diagnosis requires confirmation by a clinician while supplemented by standardized rating scales and input from multiple informants across various settings.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Peterson |first1=Bradley S. |last2=Trampush |first2=Joey |last3=Brown |first3=Morah |last4=Maglione |first4=Margaret |last5=Bolshakova |first5=Maria |last6=Rozelle |first6=Mary |last7=Miles |first7=Jeremy |last8=Pakdaman |first8=Sheila |last9=Yagyu |first9=Sachi |last10=Motala |first10=Aneesa |last11=Hempel |first11=Susanne |date=2024-04-01 |title=Tools for the Diagnosis of ADHD in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review |url=https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/153/4/e2024065854/196923/Tools-for-the-Diagnosis-of-ADHD-in-Children-and |journal=Pediatrics |volume=153 |issue=4 |doi=10.1542/peds.2024-065854 |pmid=38523599 |issn=0031-4005}}</ref> It may be viewed as the extreme end of one or more continuous [[human trait]]s found in all people.<ref name="NICE2009-Diagnosis" /> Imaging studies of the brain do not give consistent results between individuals; thus, they are only used for research purposes and not a diagnosis.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.merckmedicus.com/pp/us/hcp/diseasemodules/adhd/pathophysiology.jsp |title=MerckMedicus Modules: ADHD –Pathophysiology |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100501074844/http://www.merckmedicus.com/pp/us/hcp/diseasemodules/adhd/pathophysiology.jsp |archive-date=1 May 2010 |date=August 2002 }}</ref> |
|||
There has been a lot of interesting work done with [[neurofeedback]] and ADHD. Children are taught, using video game-like technology, how to control their brain waves. This has a very high success rate, but is not widely used, or covered by insurance. Many professionals consider the treatment promising, but state that there is not yet sufficient evidence that it works after the immediate treatment is complete. |
|||
In North America and Australia, DSM-5 criteria are used for diagnosis, while European countries usually use the ICD-10. The DSM-IV criteria for diagnosis of ADHD is {{nowrap|3–4 times}} more likely to diagnose ADHD than is the ICD-10 criteria.<ref name="Singh_2008" /> ADHD is alternately classified as [[neurodevelopmental disorder]]<ref name="Caroline2010">{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PaO3jsaGkeYC&pg=PA133 |title=Encyclopedia of Cross-Cultural School Psychology |publisher=Springer Science & Business Media |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-387-71798-2 |veditors=Caroline SC |page=133 |access-date=1 February 2016 |archive-date=22 December 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201222193428/https://books.google.com/books?id=PaO3jsaGkeYC&pg=PA133 |url-status=live }}</ref> or a [[disruptive behaviour disorder]] along with [[Oppositional defiant disorder|ODD]], [[Conduct disorder|CD]], and [[antisocial personality disorder]].<ref name="google-book-ref">{{Cite book |vauthors=Wiener JM, Dulcan MK |title=Textbook Of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry |publisher=American Psychiatric Publishing |edition=illustrated |year=2004 |isbn=978-1-58562-057-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EIgGKcp0SpkC |access-date=2 November 2014 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160506182138/https://books.google.com/books?id=EIgGKcp0SpkC |archive-date=6 May 2016}}</ref> A diagnosis does not imply a [[neurological disorder]].<ref name="NICE 2009" /> |
|||
==Possible causes== |
|||
ADHD is broadly defined and pervasive, and the symptoms attributed to ADHD likely have a variety of different causes. The initial triggers could include genetic vulnerabilities, viral or bacterial infections, brain injury, or nutritional deficits. There has been a surge in alternative approaches to ADHD, but these have been vigorously disputed. |
|||
Associated conditions that should be screened for include anxiety, depression, ODD, CD, and learning and language disorders. Other conditions that should be considered are other neurodevelopmental disorders, [[tic]]s, and [[sleep apnea]].<ref name="Wolraich-2011">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wolraich M, Brown L, Brown RT, DuPaul G, Earls M, Feldman HM, Ganiats TG, Kaplanek B, Meyer B, Perrin J, Pierce K, Reiff M, Stein MT, Visser S | title = ADHD: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 128 | issue = 5 | pages = 1007–1022 | date = November 2011 | pmid = 22003063 | pmc = 4500647 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2011-2654 }}</ref> |
|||
===Neuro-chemical imbalance=== |
|||
There is increasing evidence that variants in the gene for the [[dopamine transporter]] are related to the development of ADHD (Roman et al., 2004, Am J Pharmacogenomics 4:83-92). This evidenceis consonant with the theory of inefficacy of dopamine in people with ADD/ADHD, as according to other recent studies, people with ADHD usually have an abnormally high amount of dopamine transporter, which clears dopamine from between neurons before the full effect is gained from the dopamine. The stimulant medications used to treat the disorder are all capable of either inhibiting the action of dopamine transporter (as methylphenidate does) or promoting the release of dopamine itself (as the amphetamine-class medications do). Therefore, it is theorized that stimulant medication allows the brain to enhance the effect of dopamine more efficiently by blocking the dopamine transporters or increasing the release of dopamine. Currently this theory is the most widely accepted model of ADD/ADHD etiology in the scientific and medical community. |
|||
Self-rating scales, such as the [[ADHD rating scale]] and the [[Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale]], are used in the screening and evaluation of ADHD.<ref name="Smith(2007) in Mash & Barkley EBA">{{Cite book |title=Assessment of Childhood Disorders |vauthors=Smith BJ, Barkley RA, Shapiro CJ |publisher=Guilford Press |year=2007 |isbn=978-1-59385-493-5 |veditors=Mash EJ, Barkley RA |edition=4th |location=New York, NY |pages=53–131 |chapter=Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder }}</ref> [[Electroencephalography]] is not accurate enough to make an ADHD diagnosis.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Al Rahbi HA, Al-Sabri RM, Chitme HR | title = Interventions by pharmacists in out-patient pharmaceutical care | journal = Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal | volume = 22 | issue = 2 | pages = 101–106 | date = April 2014 | pmid = 24648820 | pmc = 3950532 | doi = 10.1016/j.jsps.2013.04.001 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Adamou M, Fullen T, Jones SL | title = EEG for Diagnosis of Adult ADHD: A Systematic Review With Narrative Analysis | journal = Frontiers in Psychiatry | volume = 11 | pages = 871 | date = 25 August 2020 | pmid = 33192633 | pmc = 7477352 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00871 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lenartowicz A, Loo SK | title = Use of EEG to diagnose ADHD | journal = Current Psychiatry Reports | volume = 16 | issue = 11 | pages = 498 | date = November 2014 | pmid = 25234074 | pmc = 4633088 | doi = 10.1007/s11920-014-0498-0 }}</ref> |
|||
New studies consider the possibility that [[norepinephrine]] also plays a role. (see ''Krause, Dresel, Krause in Psycho 26/2000 p.199ff''). |
|||
===Classification=== |
|||
===Smoking during pregnancy=== |
|||
====Diagnostic and Statistical Manual==== |
|||
The finding of another possible cause stemmed from the observation that children of women who smoked during pregnancy are more likely to be diagnosed with ADHD (Kotimaa et al., [[2003]], J Am Acad Child Adol Psychiatry 42, 826-833). Given that [[nicotine]] is known to cause [[hypoxia]] (too little oxygen) in the uterus, and that hypoxia causes brain damage, smoking during pregnancy could be an important contributing factor leading to ADHD. It may even help explain in part the increase in ADHD diagnoses, as the number of women smokers has increased. However, there are not nearly enough women smoking during pregnancy to account for all the ADHD diagnoses. It is also possibile that cause and effect could be confounded in this study, since many mothers who smoke during pregnancy may be ADHD suffers themselves; therefore the cause may simply be the shared genetic material of mother and child, rather than the mother's smoking. |
|||
As with many other psychiatric disorders, a formal diagnosis should be made by a qualified professional based on a set number of criteria. In the United States, these criteria are defined by the [[American Psychiatric Association]] in the [[Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders|DSM]]. Based on the DSM-5 criteria published in 2013 and the DSM-5-TR criteria published in 2022, there are three presentations of ADHD: |
|||
# ADHD, predominantly inattentive presentation, presents with symptoms including being easily distracted, forgetful, daydreaming, disorganization, poor sustained attention, and difficulty completing tasks. |
|||
===Deficiencies in nutrition=== |
|||
# ADHD, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation, presents with excessive fidgeting and restlessness, hyperactivity, and difficulty waiting and remaining seated. |
|||
It has been established conclusively that a small percentage of children are sensitive to dyes and other food additives, sugar, caffeine, etc. (Jacobson and Schardt, 1999, Diet, ADHD & Behavior, Center for Science in the Public Interest, Washington, DC). |
|||
# ADHD, combined presentation, is a combination of the first two presentations. |
|||
This subdivision is based on presence of at least six (in children) or five (in older teenagers and adults)<ref>{{cite web |title=Adult ADHD: Diagnosis |url=https://www.camh.ca/en/professionals/treating-conditions-and-disorders/adult-adhd/adult-adhd---diagnosis |access-date=17 April 2022 |website=CAMH |archive-date=21 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210621130901/https://www.camh.ca/en/professionals/treating-conditions-and-disorders/adult-adhd/adult-adhd---diagnosis |url-status=live }}</ref> out of nine long-term (lasting at least six months) symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity–impulsivity, or both.<ref name=DSM5/><ref name=DSM5TR/> To be considered, several symptoms must have appeared by the age of six to twelve and occur in more than one environment (e.g. at home and at school or work). The symptoms must be inappropriate for a child of that age<ref name="pmid21991721">{{cite journal | vauthors = Berger I | title = Diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: much ado about something | journal = The Israel Medical Association Journal | volume = 13 | issue = 9 | pages = 571–574 | date = September 2011 | pmid = 21991721 | url = http://www.ima.org.il/FilesUpload/IMAJ/0/40/20032.pdf | access-date = 23 May 2013 | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200728130553/https://www.ima.org.il/filesupload/imaj/0/40/20032.pdf | archive-date = 28 July 2020 }}</ref> and there must be clear evidence that they are causing social, school or work related problems.<ref name="pmid23755024">{{cite journal | vauthors = Steinau S | title = Diagnostic Criteria in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder - Changes in DSM 5 | journal = Frontiers in Psychiatry | volume = 4 | pages = 49 | year = 2013 | pmid = 23755024 | pmc = 3667245 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00049 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
Nutritional data has been well summarized in a review article (Burgess et al., 2000, Am J Clin Nutr 71:327-330). Children with ADHD have lower levels of key fatty acids. In fact, one study found that the lower the levels, the worse the symptoms. The possibility that fatty acid deficiency is a trigger for ADHD is especially plausible as nutrition scientists have recently demonstrated that the American diet is extremely deficient in omega-3 fatty acids. At the same time, ADHD diagnoses are rapidly increasing. More support for this idea comes from findings that breast-fed children have much lower levels of ADHD, and that until quite recently, infant formula contained NO omega-3 fatty acids. These findings are only [[correlation]]al, and do not prove a conclusive connection. |
|||
The DSM-5 and the DSM-5-TR also provide two diagnoses for individuals who have symptoms of ADHD but do not entirely meet the requirements. ''Other Specified ADHD'' allows the clinician to describe why the individual does not meet the criteria, whereas ''Unspecified ADHD'' is used where the clinician chooses not to describe the reason.<ref name=DSM5/><ref name=DSM5TR/> |
|||
However, creating a deficiency of omega-3 fatty acids in pregnant rats produces pups that are hyperactive and that have altered brain levels of dopamine in the same brain regions as seen in humans and other rat models of hyperactivity. |
|||
====International Classification of Diseases==== |
|||
===Sleep apnea=== |
|||
In the eleventh revision of the [[International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems]] ([[ICD-11]]) by the [[World Health Organization]], the disorder is classified as Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (with the code 6A05). The defined subtypes are similar to those of the DSM-5: ''predominantly inattentive presentation'' (6A05.0); ''predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation''(6A05.1); ''combined presentation'' (6A05.2). However, the ICD-11 includes two residual categories for individuals who do not entirely match any of the defined subtypes: ''other specified presentation'' (6A05.Y) where the clinician includes detail on the individual's presentation; and ''presentation unspecified'' (6A05.Z) where the clinician does not provide detail.<ref name="ICD-11">{{cite encyclopedia |title=6A05 Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |date=February 2022<!-- The most recent update as of the access date --> |orig-date=2019<!-- This is when it was adopted by the World Health Assembly --> |url=https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/821852937 |encyclopedia=International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision |access-date=8 May 2022 |archive-date=1 August 2018 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20180801205234/https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en%23/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/294762853#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/821852937 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
There is also new evidence that brief pauses in breathing ([[apnea]]) during infancy may be a cause of ADHD. Dr. Glenda Keating of [[Emory University]] presented data at the [[Society for Neuroscience]] annual meeting in October 2004, showing that repetitive drops in blood oxygen levels in newborn rats similar to that caused by apnea in some human infants is followed by a long-lasting reduction in dopamine levels, associated with ADHD. Apnea occurs in up to 85% of prematurely born human infants. ([http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2004/10/041025124027.htm ScienceDaily]) |
|||
In the tenth revision ([[ICD-10]]), the symptoms of ''hyperkinetic disorder'' were analogous to ADHD in the ICD-11. When a [[conduct disorder]] <!-- a type of disorder, its not CD --> (as defined by ICD-10)<ref name="ICD10">{{cite book |title=International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision |year=2010 |publisher=World Health Organisation |chapter=F90 Hyperkinetic disorders |chapter-url=http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/F90 |access-date=2 November 2014 |url-status=live |archive-date=2 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141102133725/http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2010/en#/F90}}</ref> is present, the condition was referred to as ''hyperkinetic conduct disorder''. Otherwise, the disorder was classified as ''disturbance of activity and attention'', ''other hyperkinetic disorders'' or ''hyperkinetic disorders, unspecified''. The latter was sometimes referred to as ''hyperkinetic syndrome''.<ref name="ICD10" /> |
|||
===Head injuries=== |
|||
It has been known for some decades that [[head injury|head injuries]] can cause a person to experience and display ADHD-like symptoms. |
|||
====Social construct theory==== |
|||
== Twentieth century history == |
|||
The [[social construct theory of ADHD]] suggests that, because the boundaries between normal and abnormal behaviour are socially constructed (i.e. jointly created and validated by all members of society, and in particular by [[physician]]s, parents, teachers, and others), it then follows that subjective valuations and judgements determine which diagnostic criteria are used and thus, the number of people affected.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Parens E, Johnston J | title = Facts, values, and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): an update on the controversies | journal = Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health | volume = 3 | issue = 1 | pages = 1 | date = January 2009 | pmid = 19152690 | pmc = 2637252 | doi = 10.1186/1753-2000-3-1 | doi-access = free }}</ref> [[Thomas Szasz]], a supporter of this theory, has argued that ADHD was "invented and then given a name".<ref>{{Cite book |vauthors=Szasz T |chapter=Psychiatric Medicine: Disorder |chapter-url={{google books|29HP1q6JrgYC |page=77|plainurl=yes}} |title=Pharmacracy: medicine and politics in America |url={{google books|29HP1q6JrgYC|plainurl=yes}} |via=Google Books |publisher=Praeger |location=Westport, CT |year=2001 |pages=[{{google books|29HP1q6JrgYC |page=101|plainurl=yes}} 101] |isbn=978-0-275-97196-0 |quote=Mental diseases are ''invented'' and then given a name, for example attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).}}</ref> |
|||
===Adults=== |
|||
* [[1902]] - the English [[pediatrician]] [[George Still]] described a condition analogous to ADHD. He regarded it as innate and not caused by the environment. |
|||
{{Main|Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder}} |
|||
* The [[Spanish Flu|1918–1919 influenza pandemic]] left many survivors with [[encephalitis]], affecting their neurological functions. Some of these exhibited immediate behavioral problems which correspond to ADD. This caused many to believe that the condition was the result of injury rather than genetics. |
|||
* [[1937]] - Dr. Bradley in Providence RI reported that a group of children with behavioral problems improved after being treated with stimulant medication. http://faculty.ashrosary.org/faculty/counseling/ADHDNotes.htm |
|||
* [[1957]] - the stimulant [[Methylphenidate]] ([[Ritalin]]) became available. |
|||
* [[1960]] - Stella Chess described "Hyperactive Child Syndrome" introducing the concept of hyperactivity ''not'' being caused by brain damage. (http://campus.houghton.edu/orgs/psychology/student/adhd/sld004.htm) |
|||
*By [[1966]], following observations that the condition existed without any objectively observed pathological disorder or injury, researchers changed the terminology from ''Minimal Brain Damage'' to ''Minimal Brain Dysfunction''. (Source: ''Oxford English Dictionary Online'') |
|||
*1970s - Canadian [[Virginia Douglas]] released various publications to promote the idea that attention deficit was of more significance than the hyperactivity, influencing the [[American Psychiatric Association]]. http://faculty.ashrosary.org/faculty/counseling/ADHDNotes.htm |
|||
*~[[1971]] - the [[Church of Scientology]] set up the [[Citizen's Commission on Human Rights]] (CCHR), which lobbied using the media against psychiatric medication in general, and [[Ritalin]] in particular. |
|||
* [[1973]] - [[Ben F. Feingold|Dr Ben F. Feingold]], once a [[Professor of Allergy]] in [[San Francisco]], claimed that hyperactivity was increasing in proportion to the level of food additives. |
|||
* [[1980]] - the name ''Attention Deficit Disorder'' (ADD) was first introduced in DSM-III, the 1980 edition. |
|||
* [[1987]] - the DSM-IIIR was released changing the diagnosis to "Undifferentiated Attention Deficit Disorder." http://www.socialresearchmethods.net/Gallery/Scott/page2.html |
|||
* [[1994]] - [[DSM-IV]] described three groupings within ADHD, which can be simplified as: mainly inattentive; mainly hyperactive-impulsive; and both in combination. |
|||
* [[1998]] - the NIH developed and issued a ''Consensus Statement'' attesting to the existence of ADHD. A link is provided in the [[#External Links|External Links]] section below. |
|||
Adults with ADHD are diagnosed under the same criteria, including that their signs must have been present by the age of six to twelve. The individual is the best source for information in diagnosis, however others may provide useful information about the individual's symptoms currently and in childhood; a family history of ADHD also adds weight to a diagnosis.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|7,9}} While the core symptoms of ADHD are similar in children and adults, they often present differently in adults than in children: for example, excessive physical activity seen in children may present as feelings of restlessness and constant mental activity in adults.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|6}} |
|||
==Evidence for ADHD as an organic phenomenon== |
|||
Worldwide, it is estimated that 2.58% of adults have persistent ADHD (where the individual currently meets the criteria and there is evidence of childhood onset), and 6.76% of adults have symptomatic ADHD (meaning that they currently meet the criteria for ADHD, regardless of childhood onset).<ref name="Song_2021">{{cite journal | vauthors = Song P, Zha M, Yang Q, Zhang Y, Li X, Rudan I | title = The prevalence of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A global systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = Journal of Global Health | volume = 11 | pages = 04009 | date = February 2021 | pmid = 33692893 | pmc = 7916320 | doi = 10.7189/jogh.11.04009 | publisher = International Global Health Society | oclc = 751737736 | eissn = 2047-2986 }}</ref> In 2020, this was 139.84 million and 366.33 million affected adults respectively.<ref name="Song_2021"/> Around 15% of children with ADHD continue to meet full DSM-IV-TR criteria at 25 years of age, and 50% still experience some symptoms.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|2|quote=In the meta-analysis of these data from Faraone and colleagues it was concluded that about 15% retain the full diagnosis by age 25 years, with a further 50% in partial remission, indicating that around two-thirds of children with ADHD continue to have impairing levels of ADHD symptoms as adults.}} {{As of|2010}}, most adults remain untreated.<ref name="pmid21494335">{{cite journal | vauthors = Culpepper L, Mattingly G | title = Challenges in identifying and managing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults in the primary care setting: a review of the literature | journal = Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry | volume = 12 | issue = 6 | pages = PCC.10r00951 | year = 2010 | pmid = 21494335 | pmc = 3067998 | doi = 10.4088/PCC.10r00951pur }}</ref> Many adults with ADHD without diagnosis and treatment have a disorganised life, and some use [[Substance abuse|non-prescribed drugs]] or [[Alcoholism|alcohol]] as a coping mechanism.<ref name="Art.218">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gentile JP, Atiq R, Gillig PM | title = Adult ADHD: Diagnosis, Differential Diagnosis, and Medication Management | journal = Psychiatry | volume = 3 | issue = 8 | pages = 25–30 | date = August 2006 | pmid = 20963192 | pmc = 2957278 | quote = likelihood that the adult with ADHD has developed coping mechanisms to compensate for his or her impairment }}</ref> Other problems may include relationship and job difficulties, and an increased risk of criminal activities.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mohr-Jensen C, Steinhausen HC | title = A meta-analysis and systematic review of the risks associated with childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder on long-term outcome of arrests, convictions, and incarcerations | journal = Clinical Psychology Review | volume = 48 | pages = 32–42 | date = August 2016 | pmid = 27390061 | doi = 10.1016/j.cpr.2016.05.002 }}</ref><ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|6|quote=Typically, adults with ADHD will not settle after the age of 30 but continue to change and/or lose jobs and relationships, either through boredom or being fired. They are usually underachievers with an estimated annual twenty two days of excess lost role performance. As a consequence relationships and jobs are often short lived. Relationships that last are often impaired due to the inability to listen with concentration to the spouse, not finishing or procrastinating tasks, often being on a 'short fuse' and interrupting conversations. ... Criminality in adulthood is predicted by ADHD and comorbid conduct disorder in childhood, especially with substance abuse and anti-social personality disorder in adulthood. ... ADHD patients are significantly more arrested, convicted, and incarcerated compared to normal controls, and ADHD is increasingly diagnosed in adults in forensic psychiatry.}} Associated mental health problems include depression, anxiety disorders, and learning disabilities.<ref name="Art.218" /> |
|||
Brain imaging research using [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) has shown that differences exist between the brains of children with and without ADHD, though these differences have not been shown in any way to be pathological in nature. Additionally [[Positron emission tomography|PET]] studies have shown there might be a link between a person's ability to pay continued attention to external directives and the use of [[glucose]] - the body's major fuel - in the brain. In adults diagnosed with ADHD, the brain areas that control attention use less glucose and appear to be less active, suggesting that a lower level of activity in some parts of the brain may cause inattention (''Zametkin et al.''). However, there is no evidence that this low level of glucose in fact causes the low level of attention to external direction; it could in fact be no more than an indicator for low attention, or in the alternative, superior self-direction. |
|||
Some ADHD symptoms in adults differ from those seen in children. While children with ADHD may climb and run about excessively, adults may experience an inability to relax, or may talk excessively in social situations.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|6}} Adults with ADHD may start relationships impulsively, display sensation-seeking behaviour, and be short-tempered.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|6}} Addictive behaviour such as substance abuse and [[gambling]] are common.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|6}} This led to those who presented differently as they aged having outgrown the DSM-IV criteria.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|5–6}} The DSM-5 criteria does specifically deal with adults unlike that of DSM-IV, which does not fully take into account the differences in impairments seen in adulthood compared to childhood.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|5}} |
|||
Also worth noting are the results of some studies using [[Single photon emission computed tomography|SPECT]] (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography). One study (''Lou et al. in Arch. Neurol. 46(1989) 48-52'') found people labeled as ADHD have reduced blood circulation in the [[striatum]]. But even more significant may be the discovery that people with ADHD seem to have a significantly higher concentration of [[dopamine]] transporters in the [[striatum]] (''Dougherty et al. in Lancet 354 (1999) 2132-2133; Dresel et al. in Eur.J.Nucl.Med. 25 (1998) 31-39''). Researchers have also shown that individuals labeled as either bipolar or ADHD often have variant dopamine receptor alleles. Researchers have reported, for example, that DRD4 7 repeat alleles appear more frequently in certain aboriginal cultures with low population densities such as the Amazon, whereas DRD4 2 repeat alleles are especially common in higher population density regions, including the Orient. |
|||
For diagnosis in an adult, having symptoms since childhood is required. Nevertheless, a proportion of adults who meet the criteria for ADHD in adulthood would not have been diagnosed with ADHD as children. Most cases of late-onset ADHD develop the disorder between the ages of 12–16 and may therefore be considered early adult or adolescent-onset ADHD.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Asherson P, Agnew-Blais J | title = Annual Research Review: Does late-onset attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder exist? | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 60 | issue = 4 | pages = 333–352 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 30843223 | doi = 10.1111/jcpp.13020 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
== Positive aspects == |
|||
Though ADHD is classified as a serious disorder, many people have a different perspective and note the positive aspects. ADHD children tend to look at situations in a different manner. They tend to look beyond the norm. "While students are learning the details of photosynthesis, the ADHD kids are staring out the window and pondering if it still works on a cloudy day" (Underwood). Some children might be uneasy about getting into a situation. One positive side of impulsive beahvior is the ability to try new things without trepidation. This can be a strength: "Compulsivity isn't always bad. Instead of dithering over a decision, they're willing to take risks" (Underwood). ADHD does not nessesarily slow down a person's learning process. In fact, ADHD can contribute to a faster or more comprehensive learning process, especially if teachers implement effective teaching strategies geared specifically towards the ADHD learner. Some people believe that ADHD can be beneficial and find hints of ADHD in the lives of many famous people in history. Though such ''post mortem'' diagnosis is questionable, it is intriguing to ponder the evidence that people such as [[Thomas Edison]] might have been diagnosed as having ADHD if the current DSM criteria had been developed long ago. Other historical figures who have been proposed as ADHD candidates include: [[Hans Christian Andersen]], [[Ludwig van Beethoven]], [[Winston Churchill|Winston Spencer Churchill]], [[Walt Disney]], [[Benjamin Franklin]], [[Robert F. Kennedy|Robert]] and [[John F. Kennedy]], [[Theodore Roosevelt]], [[Jules Verne]], [[Woodrow Wilson]], and the [[Wright brothers]]. |
|||
===Differential diagnosis=== |
|||
To see ADHD positively may seem somewhat problematic to anxious parents but it is at least a perspective that should be kept in mind. With or without [[hyperfocus]], a common manifestation, ADD/ADHD in combination with successful [[coping skill]]s may be utilized to achieve remarkable accomplishments. The list of historic figures and persons currently well-known in a wide range of fields who have displayed ADD/ADHD symptoms is impressive and may be source of inspiration. |
|||
{| class="wikitable floatright" style="width:40em; border:solid 1px #999;" |
|||
|- |
|||
|+ Symptoms related to other disorders<ref name="BBDADHD">{{Cite journal |author1=Consumer Reports |author1-link=Consumer Reports |author2=Drug Effectiveness Review Project |author2-link=Drug Effectiveness Review Project |date=March 2012 |title=Evaluating Prescription Drugs Used to Treat: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price |journal=Best Buy Drugs |page=2 |url=http://www.consumerreports.org/health/resources/pdf/best-buy-drugs/ADHDFinal.pdf |access-date=12 April 2013 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121115014628/http://www.consumerreports.org/health/resources/pdf/best-buy-drugs/ADHDFinal.pdf |archive-date=15 November 2012}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
!width=35%|Depression disorder |
|||
!width=30%|Anxiety disorder |
|||
!width=35%|Bipolar disorder |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
*feelings of hopelessness, [[low self-esteem]] or unhappiness |
|||
*loss of interest in hobbies or regular activities |
|||
*[[Fatigue (medical)|fatigue]] |
|||
*sleep problems |
|||
*difficulty maintaining [[attention]] |
|||
*change in [[appetite]] |
|||
*[[irritability]] or [[hostility]] |
|||
*low tolerance for [[Stress (psychological)|stress]] |
|||
*thoughts of death |
|||
*unexplained pain |
|||
| |
|||
*persistent feeling of anxiety |
|||
*[[irritability]] |
|||
*occasional feelings of [[panic]] or [[fear]] |
|||
*being hyperalert |
|||
*inability to pay attention |
|||
*tire easily |
|||
*low tolerance for [[Stress (psychological)|stress]] |
|||
*difficulty maintaining attention |
|||
| |
|||
'''in manic state''' |
|||
*excessive [[happiness]] |
|||
*hyperactivity |
|||
*[[racing thoughts]] |
|||
*[[aggression]] |
|||
*excessive talking |
|||
*[[grandiose delusions]] |
|||
*decreased need for sleep |
|||
*inappropriate social behaviour |
|||
*difficulty maintaining attention |
|||
'''in depressive state''' |
|||
*same symptoms as in depression section |
|||
|} |
|||
The DSM provides potential [[differential diagnosis|differential diagnoses]] – potential alternate explanations for specific symptoms. Assessment and investigation of clinical history determines which is the most appropriate diagnosis. The DSM-5 suggests ODD, intermittent explosive disorder, and other neurodevelopmental disorders (such as stereotypic movement disorder and Tourette's disorder), in addition to specific learning disorder, intellectual developmental disorder, ASD, reactive attachment disorder, anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, bipolar disorder, disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, substance use disorder, personality disorders, psychotic disorders, medication-induced symptoms, and neurocognitive disorders. Many but not all of these are also common comorbidities of ADHD.<ref name=DSM5 /> The DSM-5-TR also suggests post-traumatic stress disorder.<ref name=DSM5TR/> |
|||
''See also [[List of famous people with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder]] for those who either definitely have (or had) ADD/ADHD or it is thought be likely by professionals.'' |
|||
Symptoms of ADHD, such as low mood and poor self-image, mood swings, and irritability, can be confused with [[dysthymia]], [[cyclothymia]] or [[bipolar disorder]] as well as with [[borderline personality disorder]].<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|10|Because adults with ADHD often exhibit low self-esteem, low mood, affective lability and irritability, these symptoms may sometimes be confused with dysthymia, cyclothymia or bipolar disorder and with borderline personality disorder.}} Some symptoms that are due to anxiety disorders, personality disorder, developmental disabilities or intellectual disability or the effects of substance abuse such as intoxication and withdrawal can overlap with ADHD. These disorders can also sometimes occur along with ADHD. Medical conditions which can cause ADHD-type symptoms include: [[hyperthyroidism]], [[seizure disorder]], [[lead toxicity]], [[hearing deficits]], [[hepatic disease]], [[sleep apnea]], [[drug interaction]]s, untreated [[celiac disease]], and [[head injury]].<ref name="pmid26825336">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ertürk E, Wouters S, Imeraj L, Lampo A | title = Association of ADHD and Celiac Disease: What Is the Evidence? A Systematic Review of the Literature | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 24 | issue = 10 | pages = 1371–1376 | date = August 2020 | pmid = 26825336 | doi = 10.1177/1087054715611493 | quote = Up till now, there is no conclusive evidence for a relationship between ADHD and {{abbr|CD|celiac disease}}. Therefore, it is not advised to perform routine screening of CD when assessing ADHD (and vice versa) or to implement {{abbr|GFD|gluten-free diet}} as a standard treatment in ADHD. Nevertheless, the possibility of untreated CD predisposing to ADHD-like behavior should be kept in mind. ... It is possible that in untreated patients with CD, neurologic symptoms such as chronic fatigue, inattention, pain, and headache could predispose patients to ADHD-like behavior (mainly symptoms of inattentive type), which may be alleviated after GFD treatment. | s2cid = 33989148 | type = Review }}</ref><ref name="Art.218" />{{better source needed|date=June 2022}} |
|||
== Adults == |
|||
Primary sleep disorders may affect attention and behaviour and the symptoms of ADHD may affect sleep.<ref name="Owens2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Owens JA | title = Sleep disorders and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Current Psychiatry Reports | volume = 10 | issue = 5 | pages = 439–444 | date = October 2008 | pmid = 18803919 | doi = 10.1007/s11920-008-0070-x | s2cid = 23624443 }}</ref> It is thus recommended that children with ADHD be regularly assessed for sleep problems.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Walters AS, Silvestri R, Zucconi M, Chandrashekariah R, Konofal E | title = Review of the possible relationship and hypothetical links between attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and the simple sleep related movement disorders, parasomnias, hypersomnias, and circadian rhythm disorders | journal = Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine | volume = 4 | issue = 6 | pages = 591–600 | date = December 2008 | pmid = 19110891 | pmc = 2603539 | doi = 10.5664/jcsm.27356 }}</ref> Sleepiness in children may result in symptoms ranging from the classic ones of yawning and rubbing the eyes, to hyperactivity and inattentiveness. [[Obstructive sleep apnea]] can also cause ADHD-type symptoms.<ref name="pmid22670023">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lal C, Strange C, Bachman D | title = Neurocognitive impairment in obstructive sleep apnea | journal = Chest | volume = 141 | issue = 6 | pages = 1601–1610 | date = June 2012 | pmid = 22670023 | doi = 10.1378/chest.11-2214 }}</ref> |
|||
Although most diagnoses of ADHD are made for children, the DSM definitions of ADHD do not confine the disorder solely to childhood and in fact many adults are also diagnosed with [[Adult Attention Deficit Disorder]] (AADD), which is simply the common label for ADHD in adults. Current theory holds that approximately 30% of children diagnosed retain the disorder as adults. Although the disorder may not have been diagnosed in an individual during childhood, it is also currently thought that all adults with the disorder had it in childhood. |
|||
==Management== |
|||
Professionals have noted that adults with ADD/ADHD have often developed more [[coping skill]]s than children, which make symptoms less noticeable to themselves and others. |
|||
{{Main|Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management}} |
|||
The management of ADHD typically involves [[psychotherapy|counseling]] or medications, either alone or in combination. On average, treatment with medication substantially improves long-term outcomes, and completely eliminates some elevated risks, such as obesity.<ref name="Faraone_2021" /> Medications used include stimulants, atomoxetine, [[alpha-2 adrenergic receptor]] agonists, and sometimes antidepressants.<ref name="Wilens_2010" /><ref name="cognition enhancers">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bidwell LC, McClernon FJ, Kollins SH | title = Cognitive enhancers for the treatment of ADHD | journal = Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior | volume = 99 | issue = 2 | pages = 262–274 | date = August 2011 | pmid = 21596055 | pmc = 3353150 | doi = 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.05.002 }}</ref> In those who have trouble focusing on long-term rewards, a large amount of [[positive reinforcement]] improves task performance.<ref name="Motivation" /> Medications are the most effective treatment,<ref name="Faraone_2021" /><ref name="CNS09">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wigal SB | title = Efficacy and safety limitations of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder pharmacotherapy in children and adults | journal = CNS Drugs | volume = 23 | issue = Suppl 1 | pages = 21–31 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19621975 | doi = 10.2165/00023210-200923000-00004 | s2cid = 11340058 }}</ref> and any side effects are typically mild and easy to resolve<ref name="Faraone_2021" /> although any improvements will be reverted if medication is ceased.<ref name="May_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mayes R, Bagwell C, Erkulwater J | title = ADHD and the rise in stimulant use among children | journal = Harvard Review of Psychiatry | volume = 16 | issue = 3 | pages = 151–166 | date = 2008 | pmid = 18569037 | doi = 10.1080/10673220802167782 | s2cid = 18481191 }}</ref> ADHD stimulants also improve persistence and task performance in children with ADHD.<ref name="Malenka ADHD neurosci" /><ref name="Motivation" /> To quote one systematic review, "recent evidence from observational and registry studies indicates that pharmacological treatment of ADHD is associated with increased achievement and decreased absenteeism at school, a reduced risk of trauma-related emergency hospital visits, reduced risks of suicide and attempted suicide, and decreased rates of substance abuse and criminality".<ref name="Coghill_2017">{{cite journal | vauthors = Coghill DR, Banaschewski T, Soutullo C, Cottingham MG, Zuddas A | title = Systematic review of quality of life and functional outcomes in randomized placebo-controlled studies of medications for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 26 | issue = 11 | pages = 1283–1307 | date = November 2017 | pmid = 28429134 | pmc = 5656703 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-017-0986-y }} [[File:CC-BY_icon.svg|50x50px]] Text was copied from this source, which is available under a [[creativecommons:by/4.0/|Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License]] {{Cite web |url=https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ |title=CC BY 4.0 Deed | Attribution 4.0 International | Creative Commons |access-date=22 October 2022 |archive-date=16 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171016050101/https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ |url-status=bot: unknown }}.</ref> Data also suggest that combining medication with CBT is a good idea - although CBT is substantially less effective, it can help address problems that reside after medication has been optimised.<ref name="Faraone_2021" /> |
|||
''See article [[Adult attention-deficit disorder]].'' |
|||
===Behavioural therapies=== |
|||
==See also== |
|||
There is good evidence for the use of [[behavioural therapy|behavioural therapies]] in ADHD. They are the recommended first-line treatment in those who have mild symptoms or who are preschool-aged.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Fabiano GA, Pelham WE, Coles EK, Gnagy EM, Chronis-Tuscano A, O'Connor BC | title = A meta-analysis of behavioral treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Clinical Psychology Review | volume = 29 | issue = 2 | pages = 129–140 | date = March 2009 | pmid = 19131150 | doi = 10.1016/j.cpr.2008.11.001 | quote = there is strong and consistent evidence that behavioral treatments are effective for treating ADHD. | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="Clinics09">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kratochvil CJ, Vaughan BS, Barker A, Corr L, Wheeler A, Madaan V | title = Review of pediatric attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder for the general psychiatrist | journal = The Psychiatric Clinics of North America | volume = 32 | issue = 1 | pages = 39–56 | date = March 2009 | pmid = 19248915 | doi = 10.1016/j.psc.2008.10.001 }}</ref> Psychological therapies used include: [[psychoeducation]]al input, behavior therapy, [[cognitive behavioral therapy]],<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lopez PL, Torrente FM, Ciapponi A, Lischinsky AG, Cetkovich-Bakmas M, Rojas JI, Romano M, Manes FF | title = Cognitive-behavioural interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2018 | issue = 3 | pages = CD010840 | date = March 2018 | pmid = 29566425 | pmc = 6494390 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD010840.pub2 }}</ref> [[interpersonal psychotherapy]], [[family therapy]], school-based interventions, social skills training, behavioural peer intervention, organization training,<ref name="Evans2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Evans SW, Owens JS, Bunford N | title = Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology | volume = 43 | issue = 4 | pages = 527–551 | date = 2014 | pmid = 24245813 | pmc = 4025987 | doi = 10.1080/15374416.2013.850700 }}</ref> and [[parent management training]].<ref name="NICE 2009" /> [[Neurofeedback]] has greater treatment effects than non-active controls for up to 6 months and possibly a year following treatment, and may have treatment effects comparable to active controls (controls proven to have a clinical effect) over that time period.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Van Doren J, Arns M, Heinrich H, Vollebregt MA, Strehl U, K Loo S | title = Sustained effects of neurofeedback in ADHD: a systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 28 | issue = 3 | pages = 293–305 | date = March 2019 | pmid = 29445867 | pmc = 6404655 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-018-1121-4 | publisher = Springer Science and Business Media LLC }}</ref> Despite efficacy in research, there is insufficient regulation of neurofeedback practice, leading to ineffective applications and false claims regarding innovations.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Enriquez-Geppert S, Smit D, Pimenta MG, Arns M | title = Neurofeedback as a Treatment Intervention in ADHD: Current Evidence and Practice | journal = Current Psychiatry Reports | volume = 21 | issue = 6 | pages = 46 | date = May 2019 | pmid = 31139966 | pmc = 6538574 | doi = 10.1007/s11920-019-1021-4 | publisher = Springer Science and Business Media LLC }}</ref> Parent training may improve a number of behavioural problems including oppositional and non-compliant behaviours.<ref name="Dal2017">{{cite journal | vauthors = Daley D, Van Der Oord S, Ferrin M, Cortese S, Danckaerts M, Doepfner M, Van den Hoofdakker BJ, Coghill D, Thompson M, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Brandeis D, Buitelaar J, Dittmann RW, Hollis C, Holtmann M, Konofal E, Lecendreux M, Rothenberger A, Santosh P, Simonoff E, Soutullo C, Steinhausen HC, Stringaris A, Taylor E, Wong IC, Zuddas A, Sonuga-Barke EJ | title = Practitioner Review: Current best practice in the use of parent training and other behavioural interventions in the treatment of children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 59 | issue = 9 | pages = 932–947 | date = September 2018 | pmid = 29083042 | doi = 10.1111/jcpp.12825 | url = http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/45391/ | access-date = 21 November 2018 | publisher = Wiley | url-status = live | hdl = 11343/293788 | s2cid = 31044370 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170925140540/http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/45391/ | archive-date = 25 September 2017 | hdl-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
There is little high-quality research on the effectiveness of family therapy for ADHD—but the existing evidence shows that it is similar to community care, and better than placebo.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bjornstad G, Montgomery P | title = Family therapy for attention-deficit disorder or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | issue = 2 | pages = CD005042 | date = April 2005 | pmid = 15846741 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD005042.pub2 | veditors = Bjornstad GJ | s2cid = 27339381 }}</ref> ADHD-specific support groups can provide information and may help families cope with ADHD.<ref name="Brain encyclopedia">{{cite encyclopedia |vauthors=Turkington C, Harris J |title=Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) |url={{google books|6hbKkynRxPYC |page=42|plainurl=yes}} |encyclopedia=The Encyclopedia of the Brain and Brain Disorders |year=2009 |publisher=Infobase Publishing |isbn=978-1-4381-2703-3 |pages=[https://books.google.com/books?id=6hbKkynRxPYC&pg=PA47 47] |via=Google Books }}</ref> |
|||
* [[List of famous people with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder]] |
|||
* [[NIMH]] |
|||
* [[Auditory processing disorder]] |
|||
Social skills training, behavioural modification, and medication may have some limited beneficial effects in peer relationships. Stable, high-quality friendships with [[Deviance (sociology)|non-deviant]] peers protect against later psychological problems.<ref name="pmid20490677">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mikami AY | title = The importance of friendship for youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review | volume = 13 | issue = 2 | pages = 181–198 | date = June 2010 | pmid = 20490677 | pmc = 2921569 | doi = 10.1007/s10567-010-0067-y }}</ref> |
|||
==References== |
|||
*''Understanding ADD'' by Dr Christopher Green & Dr Kit Chee, ISBN 0-86824-587-9, Doubleday 1994 |
|||
* The ADHD-Autism Connection: A Step toward more accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, by Diane M. Kennedy, ISBN 1578564980 (The aim of this book is to explore the similarities that attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) shares with a spectrum of disorders currently known as pervasive developmental disorders.) |
|||
* Hartmann, Thom. (1998) ''Healing ADD: Simple Exercises That Will Change Your Daily Life''. Underwood-Miller (1st ed.) ISBN 1887424377 (Uses Neurolinguistic Programming techniques) |
|||
* Kate Kelly and Peggy Ramundo: ''You Mean I'm Not Lazy, Stupid, or Crazy?! A Self-Help Book for Adults with Attention Deficit Disorder'' (1993). ISBN: 0-684-81531-1 |
|||
* {{note|1}} Dr. Timothy E. Wilens, MD ''Straight Talk about Psychiatric Medications for Kids'' (Revised Edition--2004). ISBN 1-57230-945-8. |
|||
===Digital interventions=== |
|||
== External links == |
|||
Several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of digital therapeutics, particularly [[Adam Gazzaley#Industry|Akili Interactive Labs]]'s video game-based digital therapeutic [[EndeavourRx|AKL-T01]], marketed as [[EndeavourRx]]. The pediatric STARS-ADHD randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, controlled trial demonstrated that AKL-T01 significantly improved performance on the [[Test of Variables of Attention]], an objective measure of attention and inhibitory control, compared to a control group after four weeks of at-home use.<ref name="STARS-ADHD">{{cite journal |last1=Kollins |first1=Scott H |last2=DeLoss |first2=Denton J |last3=Cañadas |first3=Elena |last4=Lutz |first4=Jacqueline |last5=Findling |first5=Robert L |last6=Keefe |first6=Richard S E |last7=Epstein |first7=Jeffery N |last8=Cutler |first8=Andrew J |last9=Faraone |first9=Stephen V |title=A novel digital intervention for actively reducing severity of paediatric ADHD (STARS-ADHD): a randomised controlled trial |journal=The Lancet Digital Health |date=April 2020 |volume=2 |issue=4 |pages=e168–e178 |doi=10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30017-0 |pmid=33334505 |doi-access=free }}</ref> A subsequent pediatric open-label study, STARS-Adjunct, published in [[Nature Portfolio]]'s [[npj Digital Medicine]] evaluated AKL-T01 as an adjunctive treatment for children with ADHD who were either on stimulant medication or not on stimulant pharmacotherapy. Results showed improvements in ADHD-related impairment (measured by the Impairment Rating Scale) and ADHD symptoms after 4 weeks of treatment, with effects persisting during a 4-week pause and further improving with an additional treatment period.<ref name="STARS-ADHD-Adjunct">{{cite journal |last1=Kollins |first1=Scott H. |last2=Childress |first2=Ann |last3=Heusser |first3=Andrew C. |last4=Lutz |first4=Jacqueline |title=Effectiveness of a digital therapeutic as adjunct to treatment with medication in pediatric ADHD |journal=npj Digital Medicine |date=26 March 2021 |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=58 |doi=10.1038/s41746-021-00429-0 |pmid=33772095 |ref=STARS-Adjunct|pmc=7997870 }}</ref> Notably, the magnitude of the measured improvement was similar for children both on and off stimulants.<ref name="STARS-ADHD-Adjunct" /> In 2020, AKL-T01 received marketing authorization for pediatric ADHD from the [[Food and Drug Administration|FDA]], becoming "the first game-based therapeutic granted marketing authorization by the FDA for any type of condition."<ref name="FDA AKL-T01">{{cite web |title=FDA Permits Marketing of First Game-Based Digital Therapeutic to Improve Attention Function in Children with ADHD |url=https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-permits-marketing-first-game-based-digital-therapeutic-improve-attention-function-children-adhd |website=Food and Drug Administration |date=17 June 2020 |publisher=United States Food and Drug Administration |access-date=19 April 2024 |ref=FDA}}</ref> |
|||
*Science and Information about |
|||
**[http://www.CaffeineWeb.com Caffeinism's Mimicry of Mental Illness] |
|||
** [http://www.biomedicalinstitute.org/repository/Bayes_model_paper.pdf A paper on using Bayesian probability for better ADHD diagnosis] (PDF) |
|||
** [http://www.aap.org/advocacy/releases/tvapril.pdf University of Washington study linking TV at ages 1 & 3 to less attentiveness derived from hyperactivity] (PDF) |
|||
** [http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/symptom.htm DSM-IV-TR Criteria for ADHD] |
|||
** [http://www.mayoclinic.com/invoke.cfm?id=DS00275 Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) - MayoClinic.com] |
|||
** [http://www.chadd.org/ CHADD - A large USA non-profit organization providing education, advocacy and support for individuals with ADD/ADHD] |
|||
** [http://www.addforums.com/forums ADDForums: Reader driven content] |
|||
** [http://consensus.nih.gov/cons/110/110_statement.htm NIH Consensus Statement, 1998] |
|||
** [http://web4health.info/en/answers/adhd-menu.htm ADHD questions and answers] |
|||
** [http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/adhd.cfm NIMH's ADHD page] (a [[public domain resource]]) |
|||
*** [http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/adhdqa.cfm NIMH's ADHD FAQ] |
|||
** [http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/default.htm CDC's ADHD page] |
|||
** [http://www.mental-health-matters.com/disorders/dis_details.php?disID=11 Mental Health Matters: ADHD Information Page] |
|||
** [http://www.ericdigests.org/2003-4/add.html ADD and ADHD: An Overview for School Counselors. ERIC Digest.] |
|||
** [http://www.ericdigests.org/2002-4/adults.html Adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). ERIC Digest.] |
|||
** [http://www.ericdigests.org/1993/adhd.htm ADHD and Children Who Are Gifted. ERIC Digest.] |
|||
** [http://www.cpa.ca/Psynopsis/ADHD.htm A view that medicating away ADHD behaviors is the wrong approach] |
|||
** [http://www.add-adhd-infoplus.com Relationship of ADD/ADHD to nutrition, behavior, and education.] |
|||
** [http://www.goldbamboo.com/topic-t1093.html Clinical and Alternative Treatment Options for ADD and ADHD] |
|||
*Support |
|||
** [http://www.addforums.com/forums ADDForums: Support and resources for ADDults] |
|||
** [http://www.lifewithadhd.com/ ADD/ADHD From a Parent's Perspective] |
|||
** [http://www.spectrumhaven.com Website and support for those with ADD and ADHD] |
|||
*Success Stories |
|||
** [http://www.adhdrelief.com/famous.html Famous People and ADD] |
|||
* ADHD, not a disability? |
|||
** [http://www.cchr.org/topics/family/adhd/information/index.htm CCHR: ADHD as a hoax] from the controversial [[Scientology]]-associated Citizens Commission on Human Rights |
|||
** [http://www.reciprocality.org/Reciprocality/index.html A view that ADHD is a desired quality] |
|||
** [http://www.archive.org/details/ADHD-IsYourChildsBrainStarving Does diet contribute to ADHD?] |
|||
* Forums |
|||
** [http://www.psychforums.com/forums/viewforum.php?f=158 Psych Forums: ADHD Forum] |
|||
** [http://www.addforums.com/forums ADDForums: Wide ranging discussion forum for ADDults] |
|||
* Other |
|||
**[http://adhd.blogzone.net ADHD blog: One man wages war against his ADHD] |
|||
**[http://www.FishOilBlog.com Fish Oil Blog - News and commentary on the benefits of fish oil and omega-3 fatty acids for the treatment of diseases like ADHD] |
|||
In addition to pediatric populations, a 2023 study, STARS-ADHD-Adults, published in the [[Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry|Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry]] investigated the efficacy and safety of AKL-T01 in adults with ADHD. After 6 weeks of at-home treatment with AKL-T01, participants showed significant improvements in objective measures of attention ([[Test of Variables of Attention|TOVA - Attention Comparison Score]]), reported ADHD symptoms (ADHD-RS-IV inattention subscale and total score), and reported quality of life (AAQoL).<ref name="STARS-ADHD-Adults">{{cite journal |last1=Stamatis |first1=Caitlin A. |last2=Mercaldi |first2=Catherine |last3=Kollins |first3=Scott H. |title=A Single-Arm Pivotal Trial to Assess the Efficacy of Akl-T01, a Novel Digital Intervention for Attention, in Adults Diagnosed With ADHD |journal=Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry |date=October 2023 |volume=62 |issue=10 |pages=S318 |doi=10.1016/j.jaac.2023.09.510 |url=https://www.jaacap.org/article/S0890-8567(23)01994-9/fulltext#%20 |access-date=22 April 2024}}</ref> Notably, the magnitude of improvement in attention was nearly seven times greater than that reported in pediatric trials.<ref name="STARS-ADHD-Adults" /> The treatment was well-tolerated, with high compliance and no serious adverse events.<ref name="STARS-ADHD-Adults" /> |
|||
==Legal== |
|||
===Medication=== |
|||
All trademarks are property of their respective owners. |
|||
The medications for ADHD appear to alleviate symptoms via their effects on the pre-frontal executive, striatal and related regions and networks in the brain; usually by increasing neurotransmission of [[norepinephrine]] and [[dopamine]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Devilbiss DM, Berridge CW | title = Cognition-enhancing doses of methylphenidate preferentially increase prefrontal cortex neuronal responsiveness | journal = Biological Psychiatry | volume = 64 | issue = 7 | pages = 626–635 | date = October 2008 | pmid = 18585681 | pmc = 2603602 | doi = 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.04.037 }}</ref><ref name="auto4">{{cite journal | vauthors = Schulz KP, Fan J, Bédard AC, Clerkin SM, Ivanov I, Tang CY, Halperin JM, Newcorn JH | title = Common and unique therapeutic mechanisms of stimulant and nonstimulant treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Archives of General Psychiatry | volume = 69 | issue = 9 | pages = 952–961 | date = September 2012 | pmid = 22945622 | doi = 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.2053 }}</ref><ref name="auto">{{cite journal | vauthors = Koda K, Ago Y, Cong Y, Kita Y, Takuma K, Matsuda T | title = Effects of acute and chronic administration of atomoxetine and methylphenidate on extracellular levels of noradrenaline, dopamine and serotonin in the prefrontal cortex and striatum of mice | journal = Journal of Neurochemistry | volume = 114 | issue = 1 | pages = 259–270 | date = July 2010 | pmid = 20403082 | doi = 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06750.x }}</ref> |
|||
====Stimulants==== |
|||
[[Category:Childhood psychiatric disorders]] |
|||
[[Methylphenidate]] and [[amphetamine]] or its derivatives are often first-line treatments for ADHD.<ref name="Dodson_2005" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Storebø OJ, Storm MR, Pereira Ribeiro J, Skoog M, Groth C, Callesen HE, Schaug JP, Darling Rasmussen P, Huus CL, Zwi M, Kirubakaran R, Simonsen E, Gluud C | title = Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2023 | issue = 3 | pages = CD009885 | date = March 2023 | pmid = 36971690 | pmc = 10042435 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD009885.pub3 }}</ref> About 70 per cent respond to the first stimulant tried and as few as 10 per cent respond to neither amphetamines nor methylphenidate.<ref name="CNS09" /> Stimulants may also reduce the risk of unintentional injuries in children with ADHD.<ref name="Ruiz-Goikoetxea_2017">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ruiz-Goikoetxea M, Cortese S, Aznarez-Sanado M, Magallón S, Alvarez Zallo N, Luis EO, de Castro-Manglano P, Soutullo C, Arrondo G | title = Risk of unintentional injuries in children and adolescents with ADHD and the impact of ADHD medications: A systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | volume = 84 | pages = 63–71 | date = January 2018 | pmid = 29162520 | doi = 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.11.007 | hdl-access = free | doi-access = free | hdl = 10171/45012 }}</ref> [[Magnetic resonance imaging]] studies suggest that long-term treatment with amphetamine or methylphenidate decreases abnormalities in brain structure and function found in subjects with ADHD.<ref name="Neuroplasticity 1">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hart H, Radua J, Nakao T, Mataix-Cols D, Rubia K | title = Meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of inhibition and attention in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: exploring task-specific, stimulant medication, and age effects | journal = JAMA Psychiatry | volume = 70 | issue = 2 | pages = 185–198 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23247506 | doi = 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.277 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="Neuroplasticity 2">{{cite journal | vauthors = Spencer TJ, Brown A, Seidman LJ, Valera EM, Makris N, Lomedico A, Faraone SV, Biederman J | title = Effect of psychostimulants on brain structure and function in ADHD: a qualitative literature review of magnetic resonance imaging-based neuroimaging studies | journal = The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry | volume = 74 | issue = 9 | pages = 902–917 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 24107764 | pmc = 3801446 | doi = 10.4088/JCP.12r08287 }}</ref><ref name="Neuroplasticity 3">{{cite journal | vauthors = Frodl T, Skokauskas N | title = Meta-analysis of structural MRI studies in children and adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder indicates treatment effects | journal = Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica | volume = 125 | issue = 2 | pages = 114–126 | date = February 2012 | pmid = 22118249 | doi = 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2011.01786.x | quote = Basal ganglia regions like the right globus pallidus, the right putamen, and the nucleus caudatus are structurally affected in children with ADHD. These changes and alterations in limbic regions like {{abbr|ACC|anterior cingulate cortex}} and amygdala are more pronounced in non-treated populations and seem to diminish over time from child to adulthood. Treatment seems to have positive effects on brain structure. | s2cid = 25954331 | doi-access = free }}</ref> A 2018 review found the greatest short-term benefit with methylphenidate in children, and amphetamines in adults.<ref name="Comparative efficacy and tolerabili">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cortese S, Adamo N, Del Giovane C, Mohr-Jensen C, Hayes AJ, Carucci S, Atkinson LZ, Tessari L, Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Hollis C, Simonoff E, Zuddas A, Barbui C, Purgato M, Steinhausen HC, Shokraneh F, Xia J, Cipriani A | title = Comparative efficacy and tolerability of medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children, adolescents, and adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis | journal = The Lancet. Psychiatry | volume = 5 | issue = 9 | pages = 727–738 | date = September 2018 | pmid = 30097390 | pmc = 6109107 | doi = 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4 }}</ref> Studies and meta-analyses show that amphetamine is slightly-to-modestly more effective than methylphenidate at reducing symptoms,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Stuhec M, Lukić P, Locatelli I | title = Efficacy, Acceptability, and Tolerability of Lisdexamfetamine, Mixed Amphetamine Salts, Methylphenidate, and Modafinil in the Treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | journal = The Annals of Pharmacotherapy | volume = 53 | issue = 2 | pages = 121–133 | date = February 2019 | pmid = 30117329 | doi = 10.1177/1060028018795703 | s2cid = 52019992 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Biederman J, Roe C | title = Comparative efficacy of Adderall and methylphenidate in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis | journal = Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology | volume = 22 | issue = 5 | pages = 468–473 | date = October 2002 | pmid = 12352269 | doi = 10.1097/00004714-200210000-00005 | s2cid = 19726926 }}</ref> and they are more effective pharmacotherapy for ADHD than [[Alpha-adrenergic agonist#α2 agonist|α2-agonists]]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Nam SH, Lim MH, Park TW | title = Stimulant Induced Movement Disorders in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder | journal = Soa--Ch'ongsonyon Chongsin Uihak = Journal of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 33 | issue = 2 | pages = 27–34 | date = April 2022 | pmid = 35418800 | pmc = 8984208 | doi = 10.5765/jkacap.210034 }}</ref> but methylphenidate has comparable efficacy to non-stimulants such as atomoxetine. |
|||
[[Category:Mental illness diagnosis by DSM and ISCDRHP]] |
|||
The likelihood of developing [[insomnia]] for ADHD patients taking stimulants has been measured at between 11 and 45 per cent for different medications,<ref name="Wynchank_2017">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wynchank D, Bijlenga D, Beekman AT, Kooij JJ, Penninx BW | title = Adult Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Insomnia: an Update of the Literature | journal = Current Psychiatry Reports | volume = 19 | issue = 12 | pages = 98 | date = October 2017 | pmid = 29086065 | doi = 10.1007/s11920-017-0860-0 | publisher = Springer Science and Business Media LLC | quote = In varying percentages of trial participants, insomnia is a treatment-emergent adverse effect in triple-bead mixed amphetamine salts (40–45%), dasotraline (35–45%), lisdexamfetamine (10–19%), and extended-release methylphenidate (11%). | s2cid = 38064951 }}</ref> and may be a main reason for discontinuation. Other side effects, such as [[tic]]s, decreased appetite and weight loss, or [[emotional lability]], may also lead to discontinuation.<ref name="CNS09" /> [[Stimulant psychosis]] and [[mania]] are rare at therapeutic doses, appearing to occur in approximately 0.1% of individuals, within the first several weeks after starting amphetamine therapy.<ref name="Cochrane recreational amph psychosis">{{cite journal | vauthors = Shoptaw SJ, Kao U, Ling W | title = Treatment for amphetamine psychosis | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2009 | issue = 1 | pages = CD003026 | date = January 2009 | pmid = 19160215 | pmc = 7004251 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD003026.pub3 | veditors = Shoptaw SJ, Ali R | quote = A minority of individuals who use amphetamines develop full-blown psychosis requiring care at emergency departments or psychiatric hospitals. In such cases, symptoms of amphetamine psychosis commonly include paranoid and persecutory delusions as well as auditory and visual hallucinations in the presence of extreme agitation. More common (about 18%) is for frequent amphetamine users to report psychotic symptoms that are sub-clinical and that do not require high-intensity intervention ...<br />About 5–15% of the users who develop an amphetamine psychosis fail to recover completely (Hofmann 1983) ...<br />Findings from one trial indicate use of antipsychotic medications effectively resolves symptoms of acute amphetamine psychosis. }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=December 2013 |title=Adderall XR Prescribing Information |work=United States Food and Drug Administration |url=http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/021303s026lbl.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131230233702/http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/021303s026lbl.pdf |archive-date=30 December 2013 |access-date=30 December 2013 |publisher=Shire US Inc |quote=Treatment-emergent psychotic or manic symptoms, e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania in children and adolescents without prior history of psychotic illness or mania can be caused by stimulants at usual doses. ... In a pooled analysis of multiple short-term, placebo controlled studies, such symptoms occurred in about 0.1% (4 patients with events out of 3482 exposed to methylphenidate or amphetamine for several weeks at usual doses) of stimulant-treated patients compared to 0 in placebo-treated patients.}}</ref><ref name="pmid19171629">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mosholder AD, Gelperin K, Hammad TA, Phelan K, Johann-Liang R | title = Hallucinations and other psychotic symptoms associated with the use of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder drugs in children | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 123 | issue = 2 | pages = 611–616 | date = February 2009 | pmid = 19171629 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2008-0185 | s2cid = 22391693 }}</ref> The safety of these medications in pregnancy is unclear.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ashton H, Gallagher P, Moore B | title = The adult psychiatrist's dilemma: psychostimulant use in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Journal of Psychopharmacology | volume = 20 | issue = 5 | pages = 602–610 | date = September 2006 | pmid = 16478756 | doi = 10.1177/0269881106061710 | s2cid = 32073083 }}</ref> Symptom improvement is not sustained if medication is ceased.<ref name="PRBM.S49114">{{cite journal | vauthors = Parker J, Wales G, Chalhoub N, Harpin V | title = The long-term outcomes of interventions for the management of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials | journal = Psychology Research and Behavior Management | volume = 6 | pages = 87–99 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 24082796 | pmc = 3785407 | doi = 10.2147/PRBM.S49114 | quote = Results suggest there is moderate-to-high-level evidence that combined pharmacological and behavioral interventions, and pharmacological interventions alone can be effective in managing the core ADHD symptoms and academic performance at 14 months. However, the effect size may decrease beyond this period. ... Only one paper examining outcomes beyond 36 months met the review criteria. ... There is high level evidence suggesting that pharmacological treatment can have a major beneficial effect on the core symptoms of ADHD (hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity) in approximately 80% of cases compared with placebo controls, in the short term. | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="May_2008"/><ref name="Castells_2018">{{cite journal | vauthors = Castells X, Blanco-Silvente L, Cunill R | title = Amphetamines for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults | journal = The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews | volume = 2018 | issue = 8 | pages = CD007813 | date = August 2018 | pmid = 30091808 | pmc = 6513464 | doi = 10.1002/14651858.CD007813.pub3 | collaboration = Cochrane Developmental, Psychosocial and Learning Problems Group }}</ref> |
|||
[[de:Aufmerksamkeitsdefizit-/Hyperaktivitätssyndrom]] |
|||
[[is:Athyglisbrestur]] |
|||
The long-term effects of ADHD medication have yet to be fully determined,<ref name="ADHD 2015 review">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kiely B, Adesman A | title = What we do not know about ADHD… yet | journal = Current Opinion in Pediatrics | volume = 27 | issue = 3 | pages = 395–404 | date = June 2015 | pmid = 25888152 | doi = 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000229 | quote = In addition, a consensus has not been reached on the optimal diagnostic criteria for ADHD. Moreover, the benefits and long-term effects of medical and complementary therapies for this disorder continue to be debated. These gaps in knowledge hinder the ability of clinicians to effectively recognise and treat ADHD. | s2cid = 39004402 }}</ref><ref name="pmid21519262">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hazell P | title = The challenges to demonstrating long-term effects of psychostimulant treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Current Opinion in Psychiatry | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 286–290 | date = July 2011 | pmid = 21519262 | doi = 10.1097/YCO.0b013e32834742db | url = https://zenodo.org/record/1230054 | access-date = 19 July 2019 | url-status = live | s2cid = 21998152 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200726114012/https://zenodo.org/record/1230054 | archive-date = 26 July 2020 }}</ref> although stimulants are generally beneficial and safe for up to two years for children and adolescents.<ref>{{cite journal | title = Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Treatment in Children and Adolescents | journal = Comparative Effectiveness Reviews | issue = 203 | date = January 2018 | pmid = 29558081 | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK487761/ | access-date = 7 November 2021 | publisher = Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US) | url-status = live | place = Rockville (MD) | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220517212254/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK487761/ | archive-date = 17 May 2022 | vauthors = Kemper AR, Maslow GR, Hill S, Namdari B, Allen Lapointe NM, Goode AP, Coeytaux RR, Befus D, Kosinski AS, Bowen SE, McBroom AJ, Lallinger KR, Sanders GD }}</ref> A 2022 meta-analysis found no statistically significant association between ADHD medications and the risk of [[cardiovascular disease]] (CVD) across age groups, although the study suggests further investigation is warranted for patients with preexisting CVD as well as long-term medication use.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zhang L, Yao H, Li L, Du Rietz E, Andell P, Garcia-Argibay M, D'Onofrio BM, Cortese S, Larsson H, Chang Z | title = Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases Associated With Medications Used in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis | journal = JAMA Network Open | volume = 5 | issue = 11 | pages = e2243597 | date = November 2022 | pmid = 36416824 | pmc = 9685490 | doi = 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.43597 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Regular monitoring has been recommended in those on long-term treatment.<ref name="pmid20571380">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kraemer M, Uekermann J, Wiltfang J, Kis B | title = Methylphenidate-induced psychosis in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: report of 3 new cases and review of the literature | journal = Clinical Neuropharmacology | volume = 33 | issue = 4 | pages = 204–206 | date = July 2010 | pmid = 20571380 | doi = 10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181e29174 | s2cid = 34956456 }}</ref> There are indications suggesting that stimulant therapy for children and adolescents should be stopped periodically to assess continuing need for medication, decrease possible growth delay, and reduce tolerance.<ref name="pmid21530185">{{cite journal | vauthors = van de Loo-Neus GH, Rommelse N, Buitelaar JK | title = To stop or not to stop? How long should medication treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder be extended? | journal = European Neuropsychopharmacology | volume = 21 | issue = 8 | pages = 584–599 | date = August 2011 | pmid = 21530185 | doi = 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.03.008 | s2cid = 30068561 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ibrahim K, Donyai P | title = Drug Holidays From ADHD Medication: International Experience Over the Past Four Decades | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 19 | issue = 7 | pages = 551–568 | date = July 2015 | pmid = 25253684 | doi = 10.1177/1087054714548035 | url = https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266151922 | url-status = live | s2cid = 19949563 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160630122316/https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kinda_Ibrahim2/publication/266151922_Drug_Holidays_From_ADHD_Medication_International_Experience_Over_the_Past_Four_Decades/links/56a5ec7408ae1b651134629a.pdf | archive-date = 30 June 2016 }}</ref> Although potentially addictive at high doses,<ref name="NHM therapeutic stim addiction liability">{{cite book |title=Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience |vauthors=Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE |publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-07-148127-4 |veditors=Sydor A, Brown RY |edition=2nd |location=New York |pages=323, 368|quote=supervised use of stimulants at therapeutic doses may decrease risk of experimentation with drugs to self-medicate symptoms. Second, untreated ADHD may lead to school failure, peer rejection, and subsequent association with deviant peer groups that encourage drug misuse. ... amphetamines and methylphenidate are used in low doses to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and in higher doses to treat narcolepsy (Chapter 12). Despite their clinical uses, these drugs are strongly reinforcing, and their long-term use at high doses is linked with potential addiction}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |vauthors=McDonagh MS, Christensen V, Peterson K, Thakurta S |publisher=Oregon Health & Science University |title=Drug Class Review: Pharmacologic Treatments for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Final Report Update 3 [Internet] |chapter=Black box warnings of ADHD drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration |at=Appendix G: Black box warnings of ADHD drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration |via=United States National Library of Medicine |date=Oct 2009 |location=Portland, Oregon |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK47127/ |access-date=17 January 2014 |archive-date=8 September 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170908135126/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK47127/ |url-status=live}}</ref> stimulants used to treat ADHD have low potential for abuse.<ref name="Dodson_2005"/> Treatment with stimulants is either protective against substance abuse or has no effect.<ref name="Kooij_2010" />{{rp|12|quote=... the literature supports the view that stimulant treatment for ADHD either has no impact in risk for substance abuse, or may even lower the risk of substance abuse by reducing the early onset of substance abuse in adolescents.}}<ref name="ADHD 2015 review" /><ref name="NHM therapeutic stim addiction liability" /> |
|||
[[nl:ADHD]] |
|||
[[ja:ADHD]] |
|||
The majority of studies on [[nicotine]] and other [[nicotinic agonist]]s as treatments for ADHD have shown favorable results; however, no nicotinic drug has been approved for ADHD treatment.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Potter AS, Schaubhut G, Shipman M | title = Targeting the nicotinic cholinergic system to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: rationale and progress to date | journal = CNS Drugs | volume = 28 | issue = 12 | pages = 1103–1113 | date = December 2014 | pmid = 25349138 | pmc = 4487649 | doi = 10.1007/s40263-014-0208-9 }}</ref> [[Caffeine]] was formerly used as a second-line treatment for ADHD but research indicates it has no significant effects in reducing ADHD symptoms. Caffeine appears to help with alertness, arousal and reaction time but not the type of inattention implicated in ADHD (sustained attention/persistence).<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Perrotte G, Moreira MM, de Vargas Junior A, Teixeira Filho A, Castaldelli-Maia JM | title = Effects of Caffeine on Main Symptoms in Children with ADHD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials | journal = Brain Sciences | volume = 13 | issue = 9 | page = 1304 | date = September 2023 | pmid = 37759905 | pmc = 10526204 | doi = 10.3390/brainsci13091304 | doi-access = free }}</ref> [[Pseudoephedrine]] and [[ephedrine]] do not affect ADHD symptoms.<ref name="Dodson_2005">{{cite journal | vauthors = Dodson WW | title = Pharmacotherapy of adult ADHD | journal = Journal of Clinical Psychology | volume = 61 | issue = 5 | pages = 589–606 | date = May 2005 | pmid = 15723384 | doi = 10.1002/jclp.20122 | quote = For example, pseudoephedrine and ephedrine ... have no detectable effects on the symptoms of ADHD. }}</ref> |
|||
[[pl:ADHD]] |
|||
[[fi:Tarkkaavaisuus- ja ylivilkkaushäiriö]] |
|||
[[Modafinil]] has shown some efficacy in reducing the severity of ADHD in children and adolescents.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Turner D | title = A review of the use of modafinil for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics | volume = 6 | issue = 4 | pages = 455–468 | date = April 2006 | pmid = 16623645 | doi = 10.1586/14737175.6.4.455 | s2cid = 24293088 }}</ref> It may be prescribed off-label to treat ADHD. |
|||
[[sv:ADHD]] |
|||
[[zh:注意力不足過動症]] |
|||
====Non-stimulants==== |
|||
Two non-stimulant medications, [[atomoxetine]] and [[viloxazine]], are approved by the FDA and in other countries for the treatment of ADHD. |
|||
[[Atomoxetine]], due to its lack of addiction liability, may be preferred in those who are at risk of recreational or compulsive stimulant use, although evidence is lacking to support its use over stimulants for this reason.<ref name="Kooij_2010"/>{{rp|13|The non stimulant atomoxetine may be an alternative to treatment with stimulants in substance abuse patients with ADHD, although studies showing superiority over stimulants in this difficult patient population are still lacking.}} Atomoxetine alleviates ADHD symptoms through norepinephrine reuptake and by indirectly increasing dopamine in the pre-frontal cortex,<ref name="auto"/> sharing 70-80% of the brain regions with stimulants in their produced effects.<ref name="auto4"/> Atomoxetine has been shown to significantly improve academic performance.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Weiss M, Tannock R, Kratochvil C, Dunn D, Velez-Borras J, Thomason C, Tamura R, Kelsey D, Stevens L, Allen AJ | title = A randomized, placebo-controlled study of once-daily atomoxetine in the school setting in children with ADHD | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 44 | issue = 7 | pages = 647–655 | date = July 2005 | pmid = 15968233 | doi = 10.1097/01.chi.0000163280.47221.c9 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Biederman J, Wigal SB, Spencer TJ, McGough JJ, Mays DA | title = A post hoc subgroup analysis of an 18-day randomized controlled trial comparing the tolerability and efficacy of mixed amphetamine salts extended release and atomoxetine in school-age girls with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Clinical Therapeutics | volume = 28 | issue = 2 | pages = 280–293 | date = February 2006 | pmid = 16678649 | doi = 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.02.008 }}</ref> [[Meta-analysis|Meta-analyses]] and [[systematic review]]s have found that atomoxetine has comparable efficacy, equal tolerability and response rate (75%) to [[methylphenidate]] in children and adolescents. In adults, efficacy and discontinuation rates are equivalent.<ref name=":332">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bushe C, Day K, Reed V, Karlsdotter K, Berggren L, Pitcher A, Televantou F, Haynes V | title = A network meta-analysis of atomoxetine and osmotic release oral system methylphenidate in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adult patients | journal = Journal of Psychopharmacology | volume = 30 | issue = 5 | pages = 444–458 | date = May 2016 | pmid = 27005307 | doi = 10.1177/0269881116636105 | s2cid = 104938 }}</ref><ref name=":2222">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hazell PL, Kohn MR, Dickson R, Walton RJ, Granger RE, Wyk GW | title = Core ADHD symptom improvement with atomoxetine versus methylphenidate: a direct comparison meta-analysis | journal = Journal of Attention Disorders | volume = 15 | issue = 8 | pages = 674–683 | date = November 2011 | pmid = 20837981 | doi = 10.1177/1087054710379737 | s2cid = 43503227 }}</ref><ref name=":032">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hanwella R, Senanayake M, de Silva V | title = Comparative efficacy and acceptability of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis | journal = BMC Psychiatry | volume = 11 | issue = 1 | pages = 176 | date = November 2011 | pmid = 22074258 | pmc = 3229459 | doi = 10.1186/1471-244X-11-176 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name=":132">{{cite journal | vauthors = Rezaei G, Hosseini SA, Akbari Sari A, Olyaeemanesh A, Lotfi MH, Yassini M, Bidaki R, Nouri B | title = Comparative efficacy of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis | journal = Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran | volume = 30 | pages = 325 | date = 10 February 2016 | pmid = 27390695 | pmc = 4898838 }}</ref> |
|||
Analyses of clinical trial data suggests that [[viloxazine]] is about as effective as atomoxetine and methylphenidate but with fewer side effects.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Gomeni R, Hull JT, Busse GD, Melyan Z, O'Neal W, Rubin J, Nasser A | title = Early response to SPN-812 (viloxazine extended-release) can predict efficacy outcome in pediatric subjects with ADHD: a machine learning post-hoc analysis of four randomized clinical trials | journal = Psychiatry Research | volume = 296 | pages = 113664 | date = February 2021 | pmid = 33418457 | doi = 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113664 | s2cid = 230716405 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
[[Amantadine#Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder|Amantadine]] was shown to induce similar improvements in children treated with [[methylphenidate]], with less frequent side effects.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Mohammadi MR, Kazemi MR, Zia E, Rezazadeh SA, Tabrizi M, Akhondzadeh S |date=November 2010 |title=Amantadine versus methylphenidate in children and adolescents with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, double-blind trial |journal=Human Psychopharmacology |volume=25 |issue=7–8 |pages=560–565 |doi=10.1002/hup.1154 |pmid=21312290 |s2cid=30677758}}</ref> A 2021 retrospective study showed showed that amantadine may serve as an effective adjunct to stimulants for ADHD–related symptoms and appears to be a safer alternative to second- or third-generation antipsychotics.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Morrow K, Choi S, Young K, Haidar M, Boduch C, Bourgeois JA |date=September 2021 |title=Amantadine for the treatment of childhood and adolescent psychiatric symptoms |journal=Proceedings |volume=34 |issue=5 |pages=566–570 |doi=10.1080/08998280.2021.1925827 |pmc=8366930 |pmid=34456474}}</ref> |
|||
[[Bupropion]] is also used off-label by some clinicians due to research findings. It is effective, but modestly less than atomoxetine and methylphenidate.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Stuhec M, Munda B, Svab V, Locatelli I | title = Comparative efficacy and acceptability of atomoxetine, lisdexamfetamine, bupropion and methylphenidate in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis with focus on bupropion | journal = Journal of Affective Disorders | volume = 178 | pages = 149–159 | date = June 2015 | pmid = 25813457 | doi = 10.1016/j.jad.2015.03.006 }}</ref> |
|||
There is little evidence on the effects of medication on social behaviours.<ref name="McDonagh_20112">{{cite report |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK84419 |title=Drug Class Review: Pharmacologic Treatments for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |date=December 2011 |publisher=United States Library of Medicine |pmid=22420008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160831152630/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK84419/ |archive-date=31 August 2016 |url-status=live |vauthors=McDonagh MS, Peterson K, Thakurta S, Low A |series=Drug Class Reviews}}</ref> Antipsychotics may also be used to treat aggression in ADHD.<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Gurnani T, Ivanov I, Newcorn JH |date=February 2016 |title=Pharmacotherapy of Aggression in Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Disorders |journal=Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=65–73 |doi=10.1089/cap.2015.0167 |pmid=26881859 |quote=Several studies (e.g., Findling et al. 2000; Armenteros et al. 2007) have shown that antipsychotics, especially second generation agents, can be effective when used together with stimulants for aggression in ADHD}}</ref> |
|||
'''Alpha-2a agonists''' |
|||
Two [[Alpha-2 agonists|alpha-2a agonists]], extended-release formulations of [[guanfacine]] and [[clonidine]], are approved by the FDA and in other countries for the treatment of ADHD (effective in children and adolescents but effectiveness has still not been shown for adults).<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Childress AC, Sallee FR | title = Revisiting clonidine: an innovative add-on option for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Drugs of Today | volume = 48 | issue = 3 | pages = 207–217 | date = March 2012 | pmid = 22462040 | doi = 10.1358/dot.2012.48.3.1750904 }}</ref><ref name="Huss Chen Ludolph 2016 pp. 1–252">{{cite journal | vauthors = Huss M, Chen W, Ludolph AG | title = Guanfacine Extended Release: A New Pharmacological Treatment Option in Europe | journal = Clinical Drug Investigation | volume = 36 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–25 | date = January 2016 | pmid = 26585576 | pmc = 4706844 | doi = 10.1007/s40261-015-0336-0 | publisher = Springer Science and Business Media LLC }}</ref> They appear to be modestly less effective than the stimulants (amphetamine and methylphenidate) and non-stimulants (atomoxetine and viloxazine) at reducing symptoms,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Biederman J, Melmed RD, Patel A, McBurnett K, Konow J, Lyne A, Scherer N | title = A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of guanfacine extended release in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 121 | issue = 1 | pages = e73–e84 | date = January 2008 | pmid = 18166547 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2006-3695 | s2cid = 25551406 | collaboration = SPD503 Study Group }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Palumbo DR, Sallee FR, Pelham WE, Bukstein OG, Daviss WB, McDERMOTT MP | title = Clonidine for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: I. Efficacy and tolerability outcomes | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 47 | issue = 2 | pages = 180–188 | date = February 2008 | pmid = 18182963 | doi = 10.1097/chi.0b013e31815d9af7 }}</ref> but can be useful alternatives or used in conjunction with a stimulant. These medications act by adjusting the alpha-2a ports on the outside of noradrenergic nerve cells in the pre-frontal executive networks, so the information (electrical signal) is less confounded by noise.<ref>{{Cite journal|title=Focus: Translational Medicine: Guanfacine for the Treatment of Cognitive Disorders: A Century of Discoveries at Yale - PMC|date=2012 |pmc=3313539 |journal=The Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine |volume=85 |issue=1 |pages=45–58 |pmid=22461743 | vauthors = Arnsten AF, Jin LE }}</ref> |
|||
====Guidelines==== |
|||
[[Medical guideline|Guidelines]] on when to use medications vary by country. The United Kingdom's [[National Institute for Health and Care Excellence]] recommends use for children only in severe cases, though for adults medication is a first-line treatment.<ref name="NICE_2019">{{Cite book |author=National Institute for Health and Care Excellence |url=https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng87/ |title=Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: diagnosis and management |publisher=National Guideline Centre (UK) |year=2019 |isbn=978-1-4731-2830-9 |series=NICE Guideline, No. 87 |location=London |pages= |oclc=1126668845 |access-date=9 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210112035209/https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng87/ |archive-date=12 January 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> Conversely, most United States guidelines recommend medications in most age groups.<ref name="CADDRA">{{cite web |title=Canadian ADHD Practice Guidelines |url=http://www.caddra.ca/cms4/pdfs/caddraGuidelines2011Introduction.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210121222344/https://www.caddra.ca/cms4/pdfs/caddraGuidelines2011Introduction.pdf |archive-date=21 January 2021 |access-date=4 February 2011 |work=Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance}}</ref> Medications are especially not recommended for preschool children.<ref name="NICE_2019" /><ref name="NICE 2009" /> Underdosing of stimulants can occur, and can result in a lack of response or later loss of effectiveness.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Stevens JR, Wilens TE, Stern TA | title = Using stimulants for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: clinical approaches and challenges | journal = The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders | volume = 15 | issue = 2 | date = 2013 | pmid = 23930227 | pmc = 3733520 | doi = 10.4088/PCC.12f01472 }}</ref> This is particularly common in adolescents and adults as approved dosing is based on school-aged children, causing some practitioners to use weight-based or benefit-based off-label dosing instead.<ref>{{cite web |vauthors=Young JL |url=http://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/734449_print |title=Individualizing Treatment for Adult ADHD: An Evidence-Based Guideline |date=20 December 2010 |website=Medscape |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220508225446/https://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/734449_print |archive-date=8 May 2022 |url-status=live |access-date=8 May 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |vauthors=Biederman J |url=http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/464377_print |title=New-Generation Long-Acting Stimulants for the Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder |date=21 November 2003 |website=Medscape |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220508225829/https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/464377_print |archive-date=8 May 2022 |url-status=live |access-date=8 May 2022 |quote=As most treatment guidelines and prescribing information for stimulant medications relate to experience in school-aged children, prescribed doses for older patients are lacking. Emerging evidence for both methylphenidate and Adderall indicate that when weight-corrected daily doses, equipotent with those used in the treatment of younger patients, are used to treat adults with ADHD, these patients show a very robust clinical response consistent with that observed in pediatric studies. These data suggest that older patients may require a more aggressive approach in terms of dosing, based on the same target dosage ranges that have already been established – for methylphenidate, 1–1.5–2 mg/kg/day, and for D,L-amphetamine, 0.5–0.75–1 mg/kg/day.... <br />In particular, adolescents and adults are vulnerable to underdosing, and are thus at potential risk of failing to receive adequate dosage levels. As with all therapeutic agents, the efficacy and safety of stimulant medications should always guide prescribing behavior: careful dosage titration of the selected stimulant product should help to ensure that each patient with ADHD receives an adequate dose, so that the clinical benefits of therapy can be fully attained.}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kessler S | title = Drug therapy in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder | journal = Southern Medical Journal | volume = 89 | issue = 1 | pages = 33–38 | date = January 1996 | pmid = 8545689 | doi = 10.1097/00007611-199601000-00005 | s2cid = 12798818 }}</ref> |
|||
=== Exercise === |
|||
Regular [[physical exercise]], particularly [[aerobic exercise]], is an effective [[adjunct therapy|add-on treatment]] for ADHD in children and adults, particularly when combined with stimulant medication (although the best intensity and type of aerobic exercise for improving symptoms are not currently known).<ref name="Kamp_2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kamp CF, Sperlich B, Holmberg HC | title = Exercise reduces the symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and improves social behaviour, motor skills, strength and neuropsychological parameters | journal = Acta Paediatrica | volume = 103 | issue = 7 | pages = 709–714 | date = July 2014 | pmid = 24612421 | doi = 10.1111/apa.12628 | quote = We may conclude that all different types of exercise ... attenuate the characteristic symptoms of ADHD and improve social behaviour, motor skills, strength and neuropsychological parameters without any undesirable side effects. Available reports do not reveal which type, intensity, duration and frequency of exercise is most effective | s2cid = 45881887 | doi-access = free }}</ref> The long-term effects of regular aerobic exercise in ADHD individuals include better behaviour and motor abilities, improved [[executive functions]] (including attention, inhibitory control, and [[planning]], among other cognitive domains), faster [[mental chronometry|information processing speed]], and better memory.<ref name="Rommel_2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Rommel AS, Halperin JM, Mill J, Asherson P, Kuntsi J | title = Protection from genetic diathesis in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: possible complementary roles of exercise | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 52 | issue = 9 | pages = 900–910 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 23972692 | pmc = 4257065 | doi = 10.1016/j.jaac.2013.05.018 | quote = The findings from these studies provide some support for the notion that exercise has the potential to act as a protective factor for ADHD. }}</ref> Parent-teacher ratings of behavioural and socio-emotional outcomes in response to regular aerobic exercise include: better overall function, reduced ADHD symptoms, better self-esteem, reduced levels of anxiety and depression, fewer somatic complaints, better academic and classroom behaviour, and improved social behaviour. Exercising while on stimulant medication augments the effect of stimulant medication on executive function.<ref name="Den_Heijer_2016">{{cite journal | vauthors = Den Heijer AE, Groen Y, Tucha L, Fuermaier AB, Koerts J, Lange KW, Thome J, Tucha O | title = Sweat it out? The effects of physical exercise on cognition and behavior in children and adults with ADHD: a systematic literature review | journal = Journal of Neural Transmission | volume = 124 | issue = Suppl 1 | pages = 3–26 | date = February 2017 | pmid = 27400928 | pmc = 5281644 | doi = 10.1007/s00702-016-1593-7 | quote = Beneficial chronic effects of cardio exercise were found on various functions as well, including executive functions, attention and behavior. }}</ref> It is believed that these short-term effects of exercise are mediated by an increased abundance of synaptic dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain.<ref name="Den_Heijer_2016" /> |
|||
=== Diet === |
|||
Dietary modifications are not recommended {{as of|2019|lc=y}} by the [[American Academy of Pediatrics]], the [[National Institute for Health and Care Excellence]], or the [[Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality]] due to insufficient evidence.<ref name="APP2019">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wolraich ML, Hagan JF, Allan C, Chan E, Davison D, Earls M, Evans SW, Flinn SK, Froehlich T, Frost J, Holbrook JR, Lehmann CU, Lessin HR, Okechukwu K, Pierce KL, Winner JD, Zurhellen W | title = Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 144 | issue = 4 | pages = e20192528 | date = October 2019 | pmid = 31570648 | pmc = 7067282 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2019-2528 }}</ref><ref name="NICE_2019" /> |
|||
A 2013 meta-analysis found less than a third of children with ADHD see some improvement in symptoms with [[free fatty acid]] supplementation or decreased eating of artificial food colouring.<ref name="Sonu_2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sonuga-Barke EJ, Brandeis D, Cortese S, Daley D, Ferrin M, Holtmann M, Stevenson J, Danckaerts M, van der Oord S, Döpfner M, Dittmann RW, Simonoff E, Zuddas A, Banaschewski T, Buitelaar J, Coghill D, Hollis C, Konofal E, Lecendreux M, Wong IC, Sergeant J | title = Nonpharmacological interventions for ADHD: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials of dietary and psychological treatments | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 170 | issue = 3 | pages = 275–289 | date = March 2013 | pmid = 23360949 | doi = 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12070991 | lccn = 22024537 | quote = Free fatty acid supplementation and artificial food color exclusions appear to have beneficial effects on ADHD symptoms, although the effect of the former are small and those of the latter may be limited to ADHD patients with food sensitivities... | s2cid = 434310 | oclc = 1480183 | eissn = 1535-7228 }}</ref> These benefits may be limited to children with food sensitivities or those who are simultaneously being treated with ADHD medications.<ref name="Sonu_2013" /> This review also found that evidence does not support removing other foods from the diet to treat ADHD.<ref name="Sonu_2013" /> A 2014 review found that an [[elimination diet]] results in a small overall benefit in a minority of children, such as those with allergies.<ref name="Nigg_2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Nigg JT, Holton K | title = Restriction and elimination diets in ADHD treatment | journal = Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America | volume = 23 | issue = 4 | pages = 937–953 | date = October 2014 | pmid = 25220094 | pmc = 4322780 | doi = 10.1016/j.chc.2014.05.010 | type = Review | quote = an elimination diet produces a small aggregate effect but may have greater benefit among some children. Very few studies enable proper evaluation of the likelihood of response in children with ADHD who are not already preselected based on prior diet response. }}</ref> A 2016 review stated that the use of a [[gluten-free diet]] as standard ADHD treatment is not advised.<ref name="pmid26825336" /> A 2017 review showed that a few-foods elimination diet may help children too young to be medicated or not responding to medication, while free fatty acid supplementation or decreased eating of artificial food colouring as standard ADHD treatment is not advised.<ref name="Pelsser_2017">{{cite journal | vauthors = Pelsser LM, Frankena K, Toorman J, Rodrigues Pereira R | title = Diet and ADHD, Reviewing the Evidence: A Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses of Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials Evaluating the Efficacy of Diet Interventions on the Behavior of Children with ADHD | journal = PLOS ONE | volume = 12 | issue = 1 | pages = e0169277 | date = January 2017 | pmid = 28121994 | pmc = 5266211 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0169277 | type = Systematic Review | doi-access = free | bibcode = 2017PLoSO..1269277P }}</ref> Chronic deficiencies of iron, magnesium and iodine may have a negative impact on ADHD symptoms.<ref name="pmid22928358">{{cite journal | vauthors = Konikowska K, Regulska-Ilow B, Rózańska D | title = The influence of components of diet on the symptoms of ADHD in children | journal = Roczniki Panstwowego Zakladu Higieny | volume = 63 | issue = 2 | pages = 127–134 | year = 2012 | pmid = 22928358 }}</ref> There is a small amount of evidence that lower tissue zinc levels may be associated with ADHD.<ref name="pmid16190793">{{cite journal | vauthors = Arnold LE, DiSilvestro RA | title = Zinc in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology | volume = 15 | issue = 4 | pages = 619–627 | date = August 2005 | pmid = 16190793 | doi = 10.1089/cap.2005.15.619 | hdl-access = free | hdl = 1811/51593 }}</ref> In the absence of a demonstrated [[zinc deficiency]] (which is rare outside of developing countries), zinc supplementation is not recommended as treatment for ADHD.<ref name="pmid25220092">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bloch MH, Mulqueen J | title = Nutritional supplements for the treatment of ADHD | journal = Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America | volume = 23 | issue = 4 | pages = 883–897 | date = October 2014 | pmid = 25220092 | pmc = 4170184 | doi = 10.1016/j.chc.2014.05.002 }}</ref> However, zinc supplementation may reduce the minimum [[Effective dose (pharmacology)|effective dose]] of amphetamine when it is used with amphetamine for the treatment of ADHD.<ref name="Kraus_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Krause J | title = SPECT and PET of the dopamine transporter in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics | volume = 8 | issue = 4 | pages = 611–625 | date = April 2008 | pmid = 18416663 | doi = 10.1586/14737175.8.4.611 | quote = Zinc binds at ... extracellular sites of the DAT, serving as a DAT inhibitor. In this context, controlled double-blind studies in children are of interest, which showed positive effects of zinc [supplementation] on symptoms of ADHD. It should be stated that at this time [supplementation] with zinc is not integrated in any ADHD treatment algorithm. | s2cid = 24589993 }}</ref> |
|||
==Prognosis== |
|||
ADHD persists into adulthood in about 30–50% of cases.<ref name="Balint_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Bálint S, Czobor P, Mészáros A, Simon V, Bitter I | title = [Neuropsychological impairments in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a literature review] | language = hu | journal = Psychiatria Hungarica | volume = 23 | issue = 5 | pages = 324–335 | year = 2008 | pmid = 19129549 | publisher = Magyar Pszichiátriai Társaság | trans-title = Neuropsychological impairments in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A literature review | id = [[PsycNET]] [https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2008-18348-001 2008-18348-001] }}</ref> Those affected are likely to develop coping mechanisms as they mature, thus compensating to some extent for their previous symptoms.<ref name="Art.218" /> Children with ADHD have a higher risk of unintentional injuries.<ref name="Ruiz-Goikoetxea_2017" /> Effects of medication on functional impairment and [[Quality of life (healthcare)|quality of life]] (e.g. reduced risk of accidents) have been found across multiple domains.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Biederman J, Buitelaar JK, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Rohde LA, Sonuga-Barke EJ, Tannock R, Franke B | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Nature Reviews. Disease Primers | volume = 1 | pages = 15020 | date = August 2015 | pmid = 27189265 | doi = 10.1038/nrdp.2015.20 | s2cid = 7171541 | citeseerx = 10.1.1.497.1346 | type = Review }}</ref> Rates of smoking among those with ADHD are higher than in the general population at about 40%.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = McClernon FJ, Kollins SH | title = ADHD and smoking: from genes to brain to behavior | journal = Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences | volume = 1141 | issue = 1 | pages = 131–147 | date = October 2008 | pmid = 18991955 | pmc = 2758663 | doi = 10.1196/annals.1441.016 | bibcode = 2008NYASA1141..131M }}</ref> |
|||
It affects about 5–7% of children when diagnosed via the [[DSM-IV]] criteria,<ref name="pmid22976615" /> and 1–2% when diagnosed via the [[ICD-10]] criteria.<ref name="Cowen_2012" /> Rates are similar between countries and differences in rates depend mostly on how it is diagnosed.<ref name="Jones_2011">{{cite book |title=Textbook of Psychiatric Epidemiology |vauthors=Faraone SV |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-470-97740-8 |veditors=Tsuang MT, Tohen M, Jones P |edition=3rd |page=450 |chapter=Ch. 25: Epidemiology of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |access-date=1 February 2016 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fOc4pdXe43EC&pg=PA450 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201222193454/https://books.google.com/books?id=fOc4pdXe43EC&pg=PA450 |archive-date=22 December 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> ADHD is diagnosed approximately twice as often in boys as in girls,<ref name="DSM5TR" /><ref name="pmid22976615">{{cite journal | vauthors = Willcutt EG | title = The prevalence of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analytic review | journal = Neurotherapeutics | volume = 9 | issue = 3 | pages = 490–499 | date = July 2012 | pmid = 22976615 | pmc = 3441936 | doi = 10.1007/s13311-012-0135-8 }}</ref> and 1.6 times more often in men than in women,<ref name="DSM5TR" /> although the disorder is overlooked in girls or diagnosed in later life because their symptoms sometimes differ from diagnostic criteria.{{refn|<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Young S, Adamo N, Ásgeirsdóttir BB, Branney P, Beckett M, Colley W, Cubbin S, Deeley Q, Farrag E, Gudjonsson G, Hill P, Hollingdale J, Kilic O, Lloyd T, Mason P, Paliokosta E, Perecherla S, Sedgwick J, Skirrow C, Tierney K, van Rensburg K, Woodhouse E | title = Females with ADHD: An expert consensus statement taking a lifespan approach providing guidance for the identification and treatment of attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder in girls and women | journal = BMC Psychiatry | volume = 20 | issue = 1 | pages = 404 | date = August 2020 | pmid = 32787804 | pmc = 7422602 | doi = 10.1186/s12888-020-02707-9 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Crawford N |date=February 2003 |title=ADHD: a women's issue |journal=Monitor on Psychology |volume=34 |issue=2 |page=28 |url=http://www.apa.org/monitor/feb03/adhd.aspx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170409110923/http://www.apa.org/monitor/feb03/adhd.aspx |archive-date=9 April 2017 }}</ref><ref name="pmid19393378">{{cite journal | vauthors = Emond V, Joyal C, Poissant H | title = [Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)] | language = FR | journal = L'Encephale | volume = 35 | issue = 2 | pages = 107–114 | date = April 2009 | pmid = 19393378 | doi = 10.1016/j.encep.2008.01.005 | trans-title = Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) }}</ref><ref name="Singh_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Singh I | title = Beyond polemics: science and ethics of ADHD | journal = Nature Reviews. Neuroscience | volume = 9 | issue = 12 | pages = 957–964 | date = December 2008 | pmid = 19020513 | doi = 10.1038/nrn2514 | s2cid = 205504587 }}</ref>}} About 30–50% of people diagnosed in childhood continue to have [[Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder|ADHD in adulthood]], with 2.58% of adults estimated to have ADHD which began in childhood.<ref name="Song_2021" /><ref name="Ginsberg_2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ginsberg Y, Quintero J, Anand E, Casillas M, Upadhyaya HP | title = Underdiagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adult patients: a review of the literature | journal = The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders | volume = 16 | issue = 3 | year = 2014 | pmid = 25317367 | pmc = 4195639 | doi = 10.4088/PCC.13r01600 | quote = Reports indicate that ADHD affects 2.5%–5% of adults in the general population,<sup>5–8</sup> compared with 5%–7% of children.<sup>9,10</sup> ... However, fewer than 20% of adults with ADHD are currently diagnosed and/or treated by psychiatrists.<sup>7,15,16</sup> }}</ref>{{Text-source inline|date=August 2022}} In adults, hyperactivity is usually replaced by inner [[Psychomotor agitation|restlessness]], and adults often develop [[coping]] skills to compensate for their impairments. The condition can be difficult to tell apart from other conditions, as well as from high levels of activity within the range of normal behaviour. ADHD has a negative impact on patient health-related quality of life that may be further exacerbated by, or may increase the risk of, other psychiatric conditions such as anxiety and depression.<ref name="Coghill_2017" /> |
|||
Individuals with ADHD are significantly overrepresented in prison populations. Although there is no generally accepted estimate of ADHD prevalence among inmates, a 2015 meta-analysis estimated a prevalence of 25.5%, and a larger 2018 meta-analysis estimated the frequency to be 26.2%.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Baggio S, Fructuoso A, Guimaraes M, Fois E, Golay D, Heller P, Perroud N, Aubry C, Young S, Delessert D, Gétaz L, Tran NT, Wolff H | title = Prevalence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Detention Settings: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis | journal = Frontiers in Psychiatry | volume = 9 | pages = 331 | date = 2 August 2018 | pmid = 30116206 | pmc = 6084240 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00331 | doi-access = free }}</ref> ADHD is more common among longer-term inmates; a 2010 study at Norrtälje Prison, a high-security prison in Sweden, found an estimated ADHD prevalence of 40%.<ref name="Ginsberg_2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ginsberg Y, Hirvikoski T, Lindefors N | title = Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among longer-term prison inmates is a prevalent, persistent and disabling disorder | journal = BMC Psychiatry | volume = 10 | issue = 1 | pages = 112 | date = December 2010 | pmid = 21176203 | pmc = 3016316 | doi = 10.1186/1471-244X-10-112 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
==Epidemiology== |
|||
{{Main|Epidemiology of attention deficit hyperactive disorder}} |
|||
[[File:Map-Ever-Diagnosed-2011-550px.jpg|thumb|upright=1.35|Percentage of people 4–17 ever diagnosed in the US as of 2011<ref>{{cite web |title=State-based Prevalence Data of Parent Reported ADHD |url=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/prevalence.html |website=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |access-date=31 March 2020 |date=13 February 2017 |archive-date=30 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190330123802/https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/prevalence.html |url-status=live }}</ref>]] |
|||
ADHD is estimated to affect about 6–7% of people aged 18 and under when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria.<ref name="pmid22976615"/> When diagnosed via the ICD-10 criteria, rates in this age group are estimated around 1–2%.<ref name="Cowen_2012">{{cite book |vauthors=Cowen P, Harrison P, Burns T |url={{google books|O3sSd-OAdP0C|plainurl=yes}} |title=Shorter Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |year=2012 |isbn=978-0-19-960561-3 |edition=6th |pages=[{{google books|O3sSd-OAdP0C |page=546|plainurl=yes}} 546] |chapter=Drugs and other physical treatments |chapter-url={{google books|O3sSd-OAdP0C |page=507|plainurl=yes}} |via=Google Books}}</ref> Children in North America appear to have a higher rate of ADHD than children in Africa and the Middle East; this is believed to be due to differing methods of diagnosis rather than a difference in underlying frequency. (The same publication which describes this difference also notes that the difference may be rooted in the available studies from these respective regions, as far more studies were from North America than from Africa and the Middle East.)<ref name="Polanczyk_2007">{{cite journal | vauthors = Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA | title = The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 164 | issue = 6 | pages = 942–948 | date = June 2007 | pmid = 17541055 | doi = 10.1176/appi.ajp.164.6.942 | lccn = 22024537 | doi-access = free | oclc = 1480183 | eissn = 1535-7228 }}</ref> <!--From recollection, this article may be better summarised as "kids in NA have a higher rate of DIAGNOSIS". It may be a subtle difference but it's very important.--> {{As of|2019|post=,}} it was estimated to affect 84.7 million people globally.<ref name=GBD2019>{{Cite journal |author=[[Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation]] |date=17 October 2020 |title=Global Burden of Disease Study 2019: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder—Level 3 cause |url=https://www.thelancet.com/pb-assets/Lancet/gbd/summaries/diseases/adhd.pdf |journal=[[The Lancet]] |volume=396 |issue=10258 |via= |access-date=7 January 2021 |archive-date=7 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210107135215/https://www.thelancet.com/pb-assets/Lancet/gbd/summaries/diseases/adhd.pdf |url-status=live |at=Table 1}}. Both DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10 criteria were used.</ref> If the same diagnostic methods are used, the rates are similar between countries.<ref name="Jones_2011" /> ADHD is diagnosed approximately three times more often in boys than in girls.<ref name="pmid19393378" /><ref name="Singh_2008" /> This may reflect either a true difference in underlying rate, or that women and girls with ADHD are less likely to be diagnosed.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Staller J, Faraone SV | title = Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in girls: epidemiology and management | journal = CNS Drugs | volume = 20 | issue = 2 | pages = 107–123 | year = 2006 | pmid = 16478287 | doi = 10.2165/00023210-200620020-00003 | s2cid = 25835322 }}</ref> Studies from multiple countries have reported that children born closer to the start of the school year are more frequently diagnosed with and medicated for ADHD than their older classmates.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Whitely M, Raven M, Timimi S, Jureidini J, Phillimore J, Leo J, Moncrieff J, Landman P | title = Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder late birthdate effect common in both high and low prescribing international jurisdictions: a systematic review | journal = Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines | volume = 60 | issue = 4 | pages = 380–391 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 30317644 | pmc = 7379308 | doi = 10.1111/jcpp.12991 }}</ref> |
|||
Rates of diagnosis and treatment have increased in both the United Kingdom and the United States since the 1970s. Prior to 1970, it was rare for children to be diagnosed with ADHD, while in the 1970s rates were about 1%.<ref>{{cite periodical |vauthors=Connor DF |date=2011 |title=Problems of overdiagnosis and overprescribing in ADHD: are they legitimate? |url=https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/problems-overdiagnosis-and-overprescribing-adhd |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210812122049/https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/problems-overdiagnosis-and-overprescribing-adhd |archive-date=12 August 2021 | magazine=Psychiatric Times |volume=28 |issue=8 |page=14 }}</ref> This is believed to be primarily due to changes in how the condition is diagnosed<ref name="CDCTime2013" /> and how readily people are willing to treat it with medications rather than a true change in how common the condition is.<ref name="Cowen_2012" /> It was believed changes to the diagnostic criteria in 2013 with the release of the DSM-5 would increase the percentage of people diagnosed with ADHD, especially among adults.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dalsgaard S | title = Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 22 | issue = Suppl 1 | pages = S43–S48 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23202886 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-012-0360-z | s2cid = 23349807 }}</ref> |
|||
Due to disparities in the treatment and understanding of ADHD between caucasian and non-caucasian populations, many non-caucasian children go undiagnosed and unmedicated.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Coker TR, Elliott MN, Toomey SL, Schwebel DC, Cuccaro P, Tortolero Emery S, Davies SL, Visser SN, Schuster MA | title = Racial and Ethnic Disparities in ADHD Diagnosis and Treatment | journal = Pediatrics | volume = 138 | issue = 3 | pages = e20160407 | date = September 2016 | pmid = 27553219 | pmc = 5684883 | doi = 10.1542/peds.2016-0407 }}</ref> It was found that within the US that there was often a disparity between caucasian and non-caucasian understandings of ADHD. This led to a difference in the classification of the symptoms of ADHD, and therefore, its misdiagnosis. It was also found that it was common in non-caucasian families and teachers to understand the symptoms of ADHD as behavioural issues, rather than mental illness. |
|||
Crosscultural differences in diagnosis of ADHD can also be attributed to the long-lasting effects of harmful, racially targeted medical practices. Medical pseudosciences, particularly those that targeted African American populations during the period of slavery in the US, lead to a distrust of medical practices within certain communities. The combination of ADHD symptoms often being regarded as misbehaviour rather than as a psychiatric condition, and the use of drugs to regulate ADHD, result in a hesitancy to trust a diagnosis of ADHD. Cases of misdiagnosis in ADHD can also occur due to stereotyping of non-caucasian individuals. Due to ADHD's subjectively determined symptoms, medical professionals may diagnose individuals based on stereotyped behaviour or misdiagnose due to differences in symptom presentation between caucasian and non-caucasian individuals.<ref name="Slobodin_2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Slobodin O, Masalha R | title = Challenges in ADHD care for ethnic minority children: A review of the current literature | journal = Transcultural Psychiatry | volume = 57 | issue = 3 | pages = 468–483 | date = June 2020 | pmid = 32233772 | doi = 10.1177/1363461520902885 | s2cid = 214768588 }}</ref> |
|||
==History== |
|||
[[File:CDCHisGraph.png|thumb|upright=1.35|Timeline of ADHD diagnostic criteria, prevalence, and treatment]] |
|||
{{Main|History of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder}} |
|||
Hyperactivity has long been part of the human condition. Sir [[Alexander Crichton]] describes "mental restlessness" in his book ''An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement'' written in 1798.<ref>{{cite journal |date=May 2001 |title=An early description of ADHD (inattentive subtype): Dr Alexander Crichton and 'Mental restlessness' (1798) |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=66–73 |journal=[[Child and Adolescent Mental Health]] |doi=10.1111/1475-3588.00324 |vauthors=Palmer ED, Finger S }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |vauthors=Crichton A |title=An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement: comprehending a concise system of the physiology and pathology of the human mind and a history of the passions and their effects |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OMAtAAAAYAAJ |via=Google Books |orig-date=1798 |date=1976 |publisher=AMS Press |location=United Kingdom |isbn=978-0-404-08212-3 |page=271 |access-date=17 January 2014 |archive-date=3 April 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190403124410/https://books.google.com/books?id=OMATAAAAYAAJ |url-status=live }}</ref> He made observations about children showing signs of being inattentive and having the "fidgets". The first clear description of ADHD is credited to [[George Still]] in 1902 during a series of lectures he gave to the Royal College of Physicians of London.<ref>{{Cite journal |vauthors=Still G |date=1902 |title=Some Abnormal Psychical Conditions in Children: The Goulstonian Lectures |volume=159 |doi=10.1016/s0140-6736(01)74984-7 |journal=Lancet |pages=1008–1012}}</ref><ref name="CDCTime2013">{{cite web |title=ADHD Throughout the Years |url=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/documents/timeline.pdf |publisher=Center For Disease Control and Prevention |access-date=2 August 2013 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130807202545/http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/documents/timeline.pdf |archive-date=7 August 2013}}</ref> He noted both nature and nurture could be influencing this disorder. |
|||
ADHD was officially known as '''attention deficit disorder''' ('''ADD''') from 1980 to 1987; prior to the 1980s, it was known as '''hyperkinetic reaction of childhood'''. Symptoms similar to those of ADHD have been described in medical literature dating back to the 18th century. |
|||
[[A. F. Tredgold|Alfred Tredgold]] proposed an association between brain damage and behavioural or learning problems which was able to be validated by the encephalitis lethargica epidemic from 1917 through 1928.<ref name="Rafalovich_2001">{{Cite journal |vauthors=Rafalovich A |date=2001 |title=The Conceptual History of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Idiocy, Imbecility, Encephalitis and the Child Deviant |journal=Deviant Behavior |volume=22 |pages=93–115 |doi=10.1080/016396201750065009 |s2cid=43445475}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |title=Mental Deficiency: Amentia |vauthors=Tredgold C |publisher=William Wood & Company |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2pJvab8RC6UC |year=1908 |edition=1 |location=New York |oclc=990133 |id=[[PsycNET]] [https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1908-10366-000 1908-10366-000] |access-date=17 May 2022 |archive-date=17 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220517212250/https://books.google.com/books?id=2pJvab8RC6UC |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |vauthors=Connors C |date=2000 |title=Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Historical Development and Overview |journal=Journal of Attention Disorders |pages=173–191}}</ref> |
|||
The terminology used to describe the condition has changed over time and has included: ''minimal brain dysfunction'' in the DSM-I (1952), ''hyperkinetic reaction of childhood'' in the DSM-II (1968), and ''attention-deficit disorder with or without hyperactivity'' in the DSM-III (1980).<ref name="CDCTime2013" /> In 1987, this was changed to ADHD in the DSM-III-R, and in 1994 the DSM-IV in split the diagnosis into three subtypes: ADHD inattentive type, ADHD hyperactive-impulsive type, and ADHD combined type.<ref name="Millichap_2010_chap1">{{cite book |vauthors=Millichap JG |title=Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Handbook |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KAlq0CDcbaoC |via=Google Books |edition=2nd |date=2010 |publisher=Springer Science |isbn=978-1-4419-1396-8 |doi=10.1007/978-1-4419-1397-5_1 |lccn=2009938108 |pages=[{{google books|KAlq0CDcbaoC |page=2|plainurl=yes}} 2]–[{{google books|KAlq0CDcbaoC |page=3|plainurl=yes}} 3] |chapter=Definition and History of ADHD |access-date=8 May 2022 |archive-date=14 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230114133123/https://books.google.com/books?id=KAlq0CDcbaoC |url-status=live }}</ref> These terms were kept in the DSM-5 in 2013 and in the DSM-5-TR in 2022.<ref name=DSM5/><ref name=DSM5TR/> Prior to the DSM, terms included ''minimal brain damage'' in the 1930s.<ref>{{cite book |vauthors=Weiss M, Hechtman LT, Weiss G |title=ADHD in Adulthood: A Guide to Current Theory, Diagnosis, and Treatment |year=2001 |publisher=Taylor & Francis |isbn=978-0-8018-6822-1 |url={{google books|KuYvJBoB6vQC|plainurl=yes}} |chapter=ADHD in Adulthood: An Introduction |chapter-url={{google books|KuYvJBoB6vQC |page=1|plainurl=yes}} |pages=[{{google books|KuYvJBoB6vQC |page=34|plainurl=yes}} 34] |via=Google Books }}</ref> |
|||
In 1934, Benzedrine became the first amphetamine medication approved for use in the United States.<ref name="Rasmussen_2006">{{cite journal | vauthors = Rasmussen N | title = Making the first anti-depressant: amphetamine in American medicine, 1929-1950 | journal = Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences | volume = 61 | issue = 3 | pages = 288–323 | date = July 2006 | pmid = 16492800 | doi = 10.1093/jhmas/jrj039 | s2cid = 24974454 }}</ref> Methylphenidate was introduced in the 1950s, and [[enantiopure]] dextroamphetamine in the 1970s.<ref name="CDCTime2013" /> The use of stimulants to treat ADHD was first described in 1937.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Patrick KS, Straughn AB, Perkins JS, González MA | title = Evolution of stimulants to treat ADHD: transdermal methylphenidate | journal = Human Psychopharmacology | volume = 24 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–17 | date = January 2009 | pmid = 19051222 | pmc = 2629554 | doi = 10.1002/hup.992 }}</ref> Charles Bradley gave the children with behavioural disorders Benzedrine and found it improved academic performance and behaviour.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gross MD | title = Origin of stimulant use for treatment of attention deficit disorder | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 152 | issue = 2 | pages = 298–299 | date = February 1995 | pmid = 7840374 | doi = 10.1176/ajp.152.2.298b | lccn = 22024537 | oclc = 1480183 | eissn = 1535-7228 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |vauthors=Brown W |date=1998 |title=Charles Bradley, M.D. |journal=American Journal of Psychiatry |issn=0002-953X |eissn=1535-7228| lccn=22024537 |volume=155 |issue=7 |oclc=1480183 |page=968 |doi=10.1176/ajp.155.7.968 }}</ref> |
|||
Once neuroimaging studies were possible, studies conducted in the 1990s provided support for the pre-existing theory that neurological differences - particularly in the [[frontal lobe]]s - were involved in ADHD. During this same period, a genetic component was identified and ADHD was acknowledged to be a persistent, long-term disorder which lasted from childhood into adulthood.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Biederman J, Faraone SV, Keenan K, Knee D, Tsuang MT | title = Family-genetic and psychosocial risk factors in DSM-III attention deficit disorder | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 29 | issue = 4 | pages = 526–533 | date = July 1990 | pmid = 2387786 | doi = 10.1097/00004583-199007000-00004 }}</ref><ref name="Barkley_2006">{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4Fvt6X3Xd-UC&pg=PT51 |title=Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment |vauthors=Barkley R |publisher=Guilford |year=2006 |isbn=978-1-60623-750-2 |location=New York |pages=42–5 |access-date=19 July 2022 |archive-date=2 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231002044633/https://books.google.com/books?id=4Fvt6X3Xd-UC&pg=PT51#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
ADHD was split into the current three sub-types because of a field trial completed by Lahey and colleagues.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lahey BB, Applegate B, McBurnett K, Biederman J, Greenhill L, Hynd GW, Barkley RA, Newcorn J, Jensen P, Richters J | title = DSM-IV field trials for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents | journal = The American Journal of Psychiatry | volume = 151 | issue = 11 | pages = 1673–1685 | date = November 1994 | pmid = 7943460 | doi = 10.1176/ajp.151.11.1673 | lccn = 22024537 | oclc = 1480183 | eissn = 1535-7228 }}</ref> |
|||
==Controversy== |
|||
{{Main|Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder controversies}} |
|||
ADHD, its diagnosis, and its treatment have been controversial since the 1970s.<ref name="May_2008" /><ref name="Foreman_2006">{{cite journal | vauthors = Foreman DM | title = Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: legal and ethical aspects | journal = Archives of Disease in Childhood | volume = 91 | issue = 2 | pages = 192–194 | date = February 2006 | pmid = 16428370 | pmc = 2082674 | doi = 10.1136/adc.2004.064576 }}</ref> The controversies involve clinicians, teachers, policymakers, parents, and the media. Positions range from the view that ADHD is within the normal range of behaviour<ref name="NICE2009-part2" /><ref name="Faraone_2005">{{cite journal | vauthors = Faraone SV | title = The scientific foundation for understanding attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder as a valid psychiatric disorder | journal = European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 14 | issue = 1 | pages = 1–10 | date = February 2005 | pmid = 15756510 | doi = 10.1007/s00787-005-0429-z | s2cid = 143646869 }}</ref> to the hypothesis that ADHD is a genetic condition.<ref>{{cite news |vauthors=Boseley S |date=30 September 2010 |title=Hyperactive children may have genetic disorder, says study |newspaper=The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/society/2010/sep/30/hyperactive-children-genetic-disorder-study |url-status=live |archive-date=8 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170708164457/https://www.theguardian.com/society/2010/sep/30/hyperactive-children-genetic-disorder-study}}</ref> Other areas of controversy include the use of stimulant medications in children,<ref name="May_2008" /> the method of diagnosis, and the possibility of overdiagnosis.<ref name="Cormier_2008">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cormier E | title = Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review and update | journal = Journal of Pediatric Nursing | volume = 23 | issue = 5 | pages = 345–357 | date = October 2008 | pmid = 18804015 | doi = 10.1016/j.pedn.2008.01.003 }}</ref> In 2009, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, while acknowledging the controversy, states that the current treatments and methods of diagnosis are based on the dominant view of the academic literature.<ref name="NICE2009-Diagnosis">{{cite book |title=Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management of ADHD in Children, Young People and Adults |author=National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health |series=NICE Clinical Guidelines |volume=72 |publisher=British Psychological Society |location=Leicester |isbn=978-1-85433-471-8 |date=2009 |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53652/ |chapter=Diagnosis |pages=[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53659/#ch5.s40 116–7], [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53659/#ch5.s42 119] |chapter-url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53659/ |via=NCBI Bookshelf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160113133612/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53652/ |archive-date=13 January 2016 }}</ref> In 2014, [[Keith Conners]], one of the early advocates for recognition of the disorder, spoke out against overdiagnosis in a ''[[New York Times]]'' article.<ref name="NYT2013">{{cite news |vauthors=Schwarz A |title=The Selling of Attention Deficit Disorder |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2013/12/15/health/the-selling-of-attention-deficit-disorder.html |access-date=26 February 2015 |newspaper=The New York Times |date=14 December 2013 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150301054334/http://www.nytimes.com/2013/12/15/health/the-selling-of-attention-deficit-disorder.html |archive-date=1 March 2015}}</ref> In contrast, a 2014 peer-reviewed medical literature review indicated that ADHD is underdiagnosed in adults.<ref name="Ginsberg_2014" /> |
|||
Individuals with ADHD may face misconceptions and stigma; in response to this, a global team of scientists curated the International Consensus Statement.<ref name="Faraone_2021"/> |
|||
The diagnosis of ADHD has been criticised as being subjective because it is not based on a biological test. The International Consensus Statement on ADHD concluded that this criticism is unfounded, on the basis that ADHD meets standard criteria for validity of a mental disorder established by Robins and Guze. They attest that the disorder is considered valid because: 1) well-trained professionals in a variety of settings and cultures agree on its presence or absence using well-defined criteria and 2) the diagnosis is useful for predicting a) additional problems the patient may have (e.g., difficulties learning in school); b) future patient outcomes (e.g., risk for future drug abuse); c) response to treatment (e.g., medications and psychological treatments); and d) features that indicate a consistent set of causes for the disorder (e.g., findings from genetics or brain imaging). Professional associations have endorsed and published guidelines for diagnosing ADHD.<ref name="Faraone_2021"/> |
|||
With widely differing rates of diagnosis across countries, states within countries, races, and ethnicities, some suspect factors other than the presence of the symptoms of ADHD are playing a role in diagnosis, such as cultural norms.<ref name="Elder-2010">{{cite journal | vauthors = Elder TE | title = The importance of relative standards in ADHD diagnoses: evidence based on exact birth dates | journal = Journal of Health Economics | volume = 29 | issue = 5 | pages = 641–656 | date = September 2010 | pmid = 20638739 | pmc = 2933294 | doi = 10.1016/j.jhealeco.2010.06.003 }}</ref><ref name="Ford-Jones_2015">{{cite journal | vauthors = Ford-Jones PC | title = Misdiagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: 'Normal behaviour' and relative maturity | journal = Paediatrics & Child Health | volume = 20 | issue = 4 | pages = 200–202 | date = May 2015 | pmid = 26038639 | pmc = 4443828 | doi = 10.1093/pch/20.4.200 }}</ref> Some sociologists consider ADHD to be an example of the [[medicalization]] of deviant behaviour, that is, the turning of the previously {{nowrap|non-medical}} issue of school performance into a medical one.<ref name="Parrillo_2008">{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mRGr_B4Y1CEC |title=Encyclopedia of Social Problems |vauthors=Parrillo VN |publisher=SAGE |year=2008 |isbn=978-1-4129-4165-5 |page=63 |access-date=2 May 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200104002705/https://books.google.com/books?id=mRGr_B4Y1CEC |archive-date=4 January 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> Most healthcare providers accept ADHD as a genuine disorder, at least in the small number of people with severe symptoms. Among healthcare providers the debate mainly centers on diagnosis and treatment in the much greater number of people with mild symptoms.<ref name="Erk_2009" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Merten EC, Cwik JC, Margraf J, Schneider S | title = Overdiagnosis of mental disorders in children and adolescents (in developed countries) | journal = Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health | volume = 11 | pages = 5 | date = 2017 | pmid = 28105068 | pmc = 5240230 | doi = 10.1186/s13034-016-0140-5 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Taylor E | title = Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: overdiagnosed or diagnoses missed? | journal = Archives of Disease in Childhood | volume = 102 | issue = 4 | pages = 376–379 | date = April 2017 | pmid = 27821518 | doi = 10.1136/archdischild-2016-310487 | s2cid = 19878394 }}</ref> |
|||
The nature and range of desirable endpoints of ADHD treatment vary among diagnostic standards for ADHD.<ref>"Are We Overdiagnosing and Overtreating ADHD?" Psychiatric Times, 31 May 2019. Rahil R. Jummani, MD. , Emily Hirsch, Glenn S. Hirsch, MD.</ref> In most studies, the efficacy of treatment is determined by reductions in ADHD symptoms.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Luan R, Mu Z, Yue F, He S | title = Efficacy and Tolerability of Different Interventions in Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder | journal = Frontiers in Psychiatry | volume = 8 | pages = 229 | date = 2017 | pmid = 29180967 | pmc = 5694170 | doi = 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00229 | doi-access = free }}</ref> However, some studies have included subjective ratings from teachers and parents as part of their assessment of ADHD treatment efficacies.<ref name="Comparative efficacy and tolerabili"/> By contrast, the subjective ratings of children undergoing ADHD treatment are seldom included in studies evaluating the efficacy of ADHD treatments. |
|||
There have been notable differences in the diagnosis patterns of birthdays in school-age children. Those born relatively younger to the school starting age than others in a classroom environment are shown to be more likely diagnosed with ADHD. Boys who were born in December in which the school age cut-off was 31 December were shown to be 30% more likely to be diagnosed and 41% to be treated than others born in January. Girls born in December had a diagnosis percentage of 70% and 77% treatment more than ones born the following month. Children who were born at the last 3 days of a calendar year were reported to have significantly higher levels of diagnosis and treatment for ADHD than children born at the first 3 days of a calendar year. The studies suggest that ADHD diagnosis is prone to subjective analysis.<ref name="Ford-Jones_2015" /> |
|||
A meta-analysis by Storebø and colleagues and Kiŕubakaran and colleagues perpetuated controversy and stigma in media reports by raising substantial doubts about the efficacy of methylphenidate for reducing symptoms of ADHD. However, that meta-analysis used an idiosyncratic application of the Cochrane RoB for assessing evidence-quality and made systematic errors that led to false results, which furthermore, were inadmissibly clinically interpreted.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Banaschewski |first1=Tobias |last2=Buitelaar |first2=Jan |last3=Chui |first3=Celine S. L. |last4=Coghill |first4=David |last5=Cortese |first5=Samuele |last6=Simonoff |first6=Emily |last7=Wong |first7=Ian C. K. |date=November 2016 |title=Methylphenidate for ADHD in children and adolescents: throwing the baby out with the bathwater |journal=Evidence-Based Mental Health |volume=19 |issue=4 |pages=97–99 |doi=10.1136/eb-2016-102461 |issn=1468-960X |pmid=27935807|pmc=10699535 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Hoekstra |first1=Pieter J. |last2=Buitelaar |first2=Jan K. |date=2016-04-01 |title=Is the evidence base of methylphenidate for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder flawed? |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-016-0845-2 |journal=European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry |volume=25 |issue=4 |pages=339–340 |doi=10.1007/s00787-016-0845-2 |pmid=27021055 |issn=1435-165X}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Banaschewski |first1=T. |last2=Gerlach |first2=M. |last3=Becker |first3=K. |last4=Holtmann |first4=M. |last5=Döpfner |first5=M. |last6=Romanos |first6=M. |date=July 2016 |title=Trust, but verify. The errors and misinterpretations in the Cochrane analysis by O. J. Storebo and colleagues on the efficacy and safety of methylphenidate for the treatment of children and adolescents with ADHD |url=https://econtent.hogrefe.com/doi/10.1024/1422-4917/a000433 |journal=Zeitschrift für Kinder- und Jugendpsychiatrie und Psychotherapie |volume=44 |issue=4 |pages=307–314 |doi=10.1024/1422-4917/a000433 |pmid=27270192 |issn=1422-4917}}</ref> The data summated in the International Consensus Statement on ADHD is clear: methylphenidate is not only more efficacious than placebo, it is among the most efficacious drugs in all of medicine.<ref name="Faraone_2021" /> |
|||
== Research directions == |
|||
===Possible positive traits === |
|||
Possible positive traits of ADHD are a new avenue of research, and therefore limited. |
|||
A 2020 review found that creativity [[Creativity and mental health|may be associated]] with ADHD symptoms, particularly [[divergent thinking]] and quantity of creative achievements, but not with the disorder of ADHD itself – i.e. it has not been found to be increased in people diagnosed with the disorder, only in people with subclinical symptoms or those that possess traits associated with the disorder. Divergent thinking is the ability to produce creative solutions which differ significantly from each other and consider the issue from multiple perspectives. Those with ADHD symptoms could be advantaged in this form of creativity as they tend to have diffuse attention, allowing rapid switching between aspects of the task under consideration; flexible [[Associative memory (psychology)|associative memory]], allowing them to remember and use more distantly-related ideas which is associated with creativity; and impulsivity, which causes people with ADHD symptoms to consider ideas which others may not have. However, people with ADHD may struggle with [[convergent thinking]], which is a cognitive process through which a set of obviously relevant knowledge is utilised in a focused effort to arrive at a single perceived best solution to a problem.<ref name="Hoogman_2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hoogman M, Stolte M, Baas M, Kroesbergen E | title = Creativity and ADHD: A review of behavioral studies, the effect of psychostimulants and neural underpinnings | journal = Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews | volume = 119 | pages = 66–85 | date = December 2020 | pmid = 33035524 | doi = 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.09.029 | url = https://repository.ubn.ru.nl//bitstream/handle/2066/227072/227072.pdf | access-date = 28 August 2023 | url-status = live | s2cid = 222142805 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230906213830/https://repository.ubn.ru.nl//bitstream/handle/2066/227072/227072.pdf | archive-date = 6 September 2023 }}</ref> |
|||
A 2019 article suggested that historical documentation supported [[Leonardo da Vinci]]'s difficulties with procrastination and time management as characteristic of ADHD and that he was constantly on the go, but often jumping from task to task.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Catani M, Mazzarello P | title = Grey Matter Leonardo da Vinci: a genius driven to distraction | journal = Brain | volume = 142 | issue = 6 | pages = 1842–1846 | date = June 2019 | pmid = 31121603 | pmc = 6536914 | doi = 10.1093/brain/awz131 }}</ref> |
|||
===Possible biomarkers for diagnosis=== |
|||
Reviews of ADHD [[Biomarker (medicine)|biomarker]]s have noted that platelet [[monoamine oxidase]] expression, urinary [[norepinephrine]], urinary [[3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol|MHPG]], and urinary [[phenethylamine]] levels consistently differ between ADHD individuals and non-ADHD controls. These measurements could potentially serve as diagnostic biomarkers for ADHD, but more research is needed to establish their diagnostic utility. Urinary and [[blood plasma]] phenethylamine concentrations are lower in ADHD individuals relative to controls and the two most commonly prescribed drugs for ADHD, [[amphetamine]] and [[methylphenidate]], increase phenethylamine [[biosynthesis]] in treatment-responsive individuals with ADHD.<ref name="Berry_2007">{{cite journal | vauthors = Berry MD | title = The potential of trace amines and their receptors for treating neurological and psychiatric diseases | journal = Reviews on Recent Clinical Trials | volume = 2 | issue = 1 | pages = 3–19 | date = January 2007 | pmid = 18473983 | doi = 10.2174/157488707779318107 | quote = Although there is little direct evidence, changes in trace amines, in particular PE, have been identified as a possible factor for the onset of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). ... Further, amphetamines, which have clinical utility in ADHD, are good ligands at trace amine receptors. Of possible relevance in this aspect is modafanil, which has shown beneficial effects in ADHD patients and has been reported to enhance the activity of PE at TAAR1. Conversely, methylphenidate, ...showed poor efficacy at the TAAR1 receptor. In this respect it is worth noting that the enhancement of functioning at TAAR1 seen with modafanil was not a result of a direct interaction with TAAR1. | citeseerx = 10.1.1.329.563 }}</ref> Lower urinary phenethylamine concentrations are also associated with symptoms of inattentiveness in ADHD individuals.<ref name="Scassellati_2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Scassellati C, Bonvicini C, Faraone SV, Gennarelli M | title = Biomarkers and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analyses | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 51 | issue = 10 | pages = 1003–1019.e20 | date = October 2012 | pmid = 23021477 | doi = 10.1016/j.jaac.2012.08.015 }}</ref> |
|||
== See also == |
|||
* ''[[ADHD Grown Up: A Guide to Adolescent and Adult ADHD]]'' (2007) |
|||
* [[Directed attention fatigue]] – a temporary state sharing many of the symptoms of ADHD |
|||
* [[Self-medication]] |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
== Further reading == |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
* {{cite book |vauthors=Hinshaw SP, Scheffler RM |title=The ADHD Explosion: Myths, Medication, Money, and Today's Push for Performance |isbn=978-0-19-979055-5 |year=2014 |publisher=Oxford University Press }} |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Reaser A, Prevatt F, Petscher Y, Proctor B | year = 2007 | title = The learning and study strategies of college students with ADHD | journal = Psychology in the Schools | volume = 44 | issue = 6| pages = 627–638 |issn = 0033-3085 | eissn = 1520-6807 | lccn = 64009353 | oclc = 1763062 |publisher = Wiley-Blackwell | doi = 10.1002/pits.20252 }} |
|||
* {{cite book |title=ADHD Nation: Children, Doctors, Big Pharma, and the Making of an American Epidemic |year=2016 | vauthors = Schwarz A |url=https://archive.org/details/adhdnationchildr0000schw_d3y4 |publisher=Scribner | oclc=951612166 |isbn=978-1-5011-0591-3}} |
|||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Pliszka S | title = Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder | journal = Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | volume = 46 | issue = 7 | pages = 894–921 | date = July 2007 | pmid = 17581453 | doi = 10.1097/chi.0b013e318054e724 | s2cid = 602465 | doi-access = free }} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{Commons category}} |
|||
{{Wikiquote|Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder}} |
|||
* National Institute of Mental Health. [https://www.nimh.nih.gov/topics/topic-page-adhd NIMH Pages About Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).] National Institutes of Health (NIH), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. |
|||
{{Medical resources |
|||
| ICD11 = {{ICD11|6A05|821852937}} |
|||
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|F|90||f|90}} |
|||
| ICD10CM = <!--{{ICD10CM|Xxx.xxxx}}--> |
|||
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|314.00}}, {{ICD9|314.01}} |
|||
| ICDO = |
|||
| OMIM = 143465 |
|||
| DiseasesDB = 6158 |
|||
| Curlie =https://dmoz-odp.org/Health/Mental_Health/Disorders/Neurodevelopmental/ADD_and_ADHD/ |
|||
| MedlinePlus = 001551 |
|||
| eMedicineSubj = med |
|||
| eMedicineTopic = 3103 |
|||
| eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|ped|177}} |
|||
| MeshID = D001289 |
|||
| GeneReviewsNBK = |
|||
| GeneReviewsName = |
|||
| NORD = |
|||
| GARDNum = |
|||
| GARDName = |
|||
| Orphanet = |
|||
| AO = |
|||
| RP = |
|||
| WO = |
|||
| OrthoInfo = |
|||
| NCI = |
|||
| Scholia =Q181923 |
|||
| SNOMED CT =406506008 |
|||
|QID=Q181923}} |
|||
{{ADHD|state=uncollapsed}} |
|||
{{ADHD pharmacotherapies}} |
|||
{{Amphetamine}} |
|||
{{Emotional and behavioral disorders}} |
|||
{{Mental and behavioral disorders|selected=childhood}} |
|||
{{Digital media use and mental health}} |
|||
{{Portal bar|Medicine}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder| ]] |
|||
[[Category:1987 neologisms]] |
|||
[[Category:Ailments of unknown cause]] |
|||
[[Category:Amphetamine]] |
|||
[[Category:Attention disorders]] |
|||
[[Category:Learning disabilities]] |
|||
[[Category:Methylphenidate]] |
|||
[[Category:Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full)]] |
|||
[[Category:Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 20:42, 13 May 2024
| Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | |
|---|---|
 | |
| People with ADHD struggle more than others to sustain their attention on some tasks (such as schoolwork), but may maintain an unusually intense level of attention for tasks they find immediately rewarding or interesting. | |
| Specialty | |
| Symptoms |
|
| Usual onset | Typically at least some ADHD symptoms and impairments onset during the developmental period. Exceptions include if they were compensated for (e.g., by a high IQ or structured environment) or if the individual clearly suffered a neurologically compromising event. |
| Causes | Genetic (inherited, de novo) and to a lesser extent, environmental factors (exposure to biohazards during pregnancy, traumatic brain injury) |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms after other possible causes have been ruled out |
| Differential diagnosis |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Medication |
|
| Frequency | 0.8–1.5% (2019, using DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10)[2] |
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by executive dysfunction occasioning symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate.[8]
ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction,[17] and emotional dysregulation is often considered a core symptom.[21] Difficulties with self-regulation such as time management, inhibition and sustained attention may result in poor academic performance, unemployment and numerous health risks,[22] collectively predisposing to a diminished quality of life[23] and a direct average reduction in life expectancy of 13 years.[24][25] ADHD is associated with other neurodevelopmental and mental disorders as well as some non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment, especially in modern society.[26]
Although people with ADHD struggle to persist on tasks with temporally delayed consequences, they may be able to maintain an unusually prolonged level of attention for tasks they do find intrinsically interesting or immediately rewarding;[27][16] this is known as hyperfocus (more colloquially)[28] or perseverative responding.[29] This is a mental state in which a person is completely absorbed in a task to the point of apparently ignoring or "tuning out" everything else, often with difficulty disengaging[27][30] and can be related to risks such as for internet addiction[31] and types of offending behaviour.[32]
ADHD represents the extreme lower end of the continuous dimensional trait (bell curve) of executive functioning and self-regulation, which is supported by twin, brain imaging and molecular genetic studies.[33][12][34][16][35][36][37]
The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in the majority of cases.[38][39] For most people with ADHD, many genetic and environmental risk factors accumulate to cause the disorder.[40] The environmental risks for ADHD most often exert their influence in the prenatal period.[7] However, in rare cases a single event might cause ADHD such as traumatic brain injury,[41][42][43][44] exposure to biohazards during pregnancy,[7] a major genetic mutation[45] or extreme environmental deprivation early in life.[46] There is no biologically distinct adult onset ADHD except for when ADHD occurs after traumatic brain injury.[47][42][7]
Signs and symptoms
Inattention, hyperactivity (restlessness in adults), disruptive behaviour, and impulsivity are common in ADHD.[48][49][50] Academic difficulties are frequent, as are problems with relationships.[49][50][51] The signs and symptoms can be difficult to define, as it is hard to draw a line at where normal levels of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity end and significant levels requiring interventions begin.[52]
According to the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and its text revision (DSM-5-TR), symptoms must be present for six months or more to a degree that is much greater than others of the same age.[3][4] This requires at least six symptoms of either inattention or hyperactivity/impulsivity for those under 17 and at least five symptoms for those 17 years or older.[3][4] The symptoms must be present in at least two settings (e.g., social, school, work, or home), and must directly interfere with or reduce quality of functioning.[3] Additionally, several symptoms must have been present before age twelve.[4] According to the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and its text revision (DSM-5-TR), the required age of onset of symptoms is currently 12 years.[3][4][53]
Presentations
ADHD is divided into three primary presentations:[4][52]
- predominantly inattentive (ADHD-PI or ADHD-I)
- predominantly hyperactive-impulsive (ADHD-PH or ADHD-HI)
- combined presentation (ADHD-C).
The table "Symptoms" lists the symptoms for ADHD-I and ADHD-HI from two major classification systems. Symptoms which can be better explained by another psychiatric or medical condition which an individual has are not considered to be a symptom of ADHD for that person. In DSM-5, subtypes were discarded and reclassified as presentations of the disorder that change over time.
| Presentations | DSM-5 and DSM-5-TR symptoms[3][4] | ICD-11 symptoms[5] |
|---|---|---|
| Inattention | Six or more of the following symptoms in children, and five or more in adults, excluding situations where these symptoms are better explained by another psychiatric or medical condition:
|
Multiple symptoms of inattention that directly negatively impact occupational, academic or social functioning. Symptoms may not be present when engaged in highly stimulating tasks with frequent rewards. Symptoms are generally from the following clusters:
The individual may also meet the criteria for hyperactivity-impulsivity, but the inattentive symptoms are predominant. |
| Hyperactivity-Impulsivity | Six or more of the following symptoms in children, and five or more in adults, excluding situations where these symptoms are better explained by another psychiatric or medical condition:
|
Multiple symptoms of hyperactivity/impulsivity that directly negatively impact occupational, academic or social functioning. Typically, these tend to be most apparent in environments with structure or which require self-control. Symptoms are generally from the following clusters:
The individual may also meet the criteria for inattention, but the hyperactive-impulsive symptoms are predominant. |
| Combined | Meet the criteria for both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive ADHD. | Criteria are met for both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive ADHD, with neither clearly predominating. |
Girls and women with ADHD tend to display fewer hyperactivity and impulsivity symptoms but more symptoms of inattention and distractibility.[54]
Symptoms are expressed differently and more subtly as the individual ages.[55]: 6 Hyperactivity tends to become less overt with age and turns into inner restlessness, difficulty relaxing or remaining still, talkativeness or constant mental activity in teens and adults with ADHD.[55]: 6–7 Impulsivity in adulthood may appear as thoughtless behaviour, impatience, irresponsible spending and sensation-seeking behaviours,[55]: 6 while inattention may appear as becoming easily bored, difficulty with organization, remaining on task and making decisions, and sensitivity to stress.[55]: 6
Although not listed as an official symptom for this condition, emotional dysregulation or mood lability is generally understood to be a common symptom of ADHD.[18][55]: 6 People with ADHD of all ages are more likely to have problems with social skills, such as social interaction and forming and maintaining friendships.[56] This is true for all presentations. About half of children and adolescents with ADHD experience social rejection by their peers compared to 10–15% of non-ADHD children and adolescents. People with attention deficits are prone to having difficulty processing verbal and nonverbal language which can negatively affect social interaction. They may also drift off during conversations, miss social cues, and have trouble learning social skills.[57]
Difficulties managing anger are more common in children with ADHD[58] as are delays in speech, language and motor development.[59][60] Poorer handwriting is more common in children with ADHD.[61] Poor handwriting in many situations can be a symptom of ADHD in itself due to decreased attentiveness. When this is a pervasive problem, it may also be attributable to dyslexia[62][63] or dysgraphia. There is significant overlap in the symptomatologies of ADHD, dyslexia, and dysgraphia,[64] and 3 in 10 people diagnosed with dyslexia experience co-occurring ADHD.[65] Although it causes significant difficulty, many children with ADHD have an attention span equal to or greater than that of other children for tasks and subjects they find interesting.[66]
Comorbidities
Psychiatric comorbidities
In children, ADHD occurs with other disorders about two-thirds of the time.[66]
Other neurodevelopmental conditions are common comorbidities. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD), co-occurring at a rate of 21% in those with ADHD, affects social skills, ability to communicate, behaviour, and interests.[67][68] Both ADHD and ASD can be diagnosed in the same person.[4][page needed] Learning disabilities have been found to occur in about 20–30% of children with ADHD. Learning disabilities can include developmental speech and language disorders, and academic skills disorders.[69] ADHD, however, is not considered a learning disability, but it very frequently causes academic difficulties.[69] Intellectual disabilities[4][page needed] and Tourette's syndrome[68] are also common.
ADHD is often comorbid with disruptive, impulse control, and conduct disorders. Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) occurs in about 25% of children with an inattentive presentation and 50% of those with a combined presentation.[4][page needed] It is characterised by angry or irritable mood, argumentative or defiant behaviour and vindictiveness which are age-inappropriate. Conduct disorder (CD) occurs in about 25% of adolescents with ADHD.[4][page needed] It is characterised by aggression, destruction of property, deceitfulness, theft and violations of rules.[70] Adolescents with ADHD who also have CD are more likely to develop antisocial personality disorder in adulthood.[71] Brain imaging supports that CD and ADHD are separate conditions, wherein conduct disorder was shown to reduce the size of one's temporal lobe and limbic system, and increase the size of one's orbitofrontal cortex, whereas ADHD was shown to reduce connections in the cerebellum and prefrontal cortex more broadly. Conduct disorder involves more impairment in motivation control than ADHD.[72] Intermittent explosive disorder is characterised by sudden and disproportionate outbursts of anger and co-occurs in individuals with ADHD more frequently than in the general population.
Anxiety and mood disorders are frequent comorbidities. Anxiety disorders have been found to occur more commonly in the ADHD population, as have mood disorders (especially bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder). Boys diagnosed with the combined ADHD subtype are more likely to have a mood disorder.[73] Adults and children with ADHD sometimes also have bipolar disorder, which requires careful assessment to accurately diagnose and treat both conditions.[74][75]
Sleep disorders and ADHD commonly co-exist. They can also occur as a side effect of medications used to treat ADHD. In children with ADHD, insomnia is the most common sleep disorder with behavioural therapy being the preferred treatment.[76][77] Problems with sleep initiation are common among individuals with ADHD but often they will be deep sleepers and have significant difficulty getting up in the morning.[13] Melatonin is sometimes used in children who have sleep onset insomnia.[78] Specifically, the sleep disorder restless legs syndrome has been found to be more common in those with ADHD and is often due to iron deficiency anemia.[79][80] However, restless legs can simply be a part of ADHD and requires careful assessment to differentiate between the two disorders.[81] Delayed sleep phase disorder is also a common comorbidity of those with ADHD.[82]
There are other psychiatric conditions which are often co-morbid with ADHD, such as substance use disorders.[83] Individuals with ADHD are at increased risk of substance abuse.: 9 This is most commonly seen with alcohol or cannabis.[55]: 9 The reason for this may be an altered reward pathway in the brains of ADHD individuals, self-treatment and increased psychosocial risk factors.: 9 This makes the evaluation and treatment of ADHD more difficult, with serious substance misuse problems usually treated first due to their greater risks.[84] Other psychiatric conditions include reactive attachment disorder,[85] characterised by a severe inability to appropriately relate socially, and cognitive disengagement syndrome, a distinct attention disorder occurring in 30–50% of ADHD cases as a comorbidity, regardless of the presentation; a subset of cases diagnosed with ADHD-PIP have been found to have CDS instead.[86][87] Individuals with ADHD are three times more likely to develop and be diagnosed with an eating disorder compared to those without ADHD; conversely, individuals with eating disorders are two times more likely to have ADHD than those without eating disorders.[88]
Trauma
ADHD, trauma, and Adverse Childhood Experiences are also comorbid,[89][90] which could in part be potentially explained by the similarity in presentation between different diagnoses. The symptoms of ADHD and PTSD can have significant behavioural overlap—in particular, motor restlessness, difficulty concentrating, distractibility, irritability/anger, emotional constriction or dysregulation, poor impulse control, and forgetfulness are common in both.[91][92] This could result in trauma-related disorders or ADHD being mis-identified as the other.[93] Additionally, traumatic events in childhood are a risk factor for ADHD[94][95] - it can lead to structural brain changes and the development of ADHD behaviours.[93] Finally, the behavioural consequences of ADHD symptoms cause a higher chance of the individual experiencing trauma (and therefore ADHD leads to a concrete diagnosis of a trauma-related disorder).[96][97]
Non-psychiatric
Some non-psychiatric conditions are also comorbidities of ADHD. This includes epilepsy,[68] a neurological condition characterised by recurrent seizures.[98][99] There are well established associations between ADHD and obesity, asthma and sleep disorders,[100] and an association with celiac disease.[101] Children with ADHD have a higher risk for migraine headaches,[102] but have no increased risk of tension-type headaches. In addition, children with ADHD may also experience headaches as a result of medication.[103][104]
A 2021 review reported that several neurometabolic disorders caused by inborn errors of metabolism converge on common neurochemical mechanisms that interfere with biological mechanisms also considered central in ADHD pathophysiology and treatment. This highlights the importance of close collaboration between health services to avoid clinical overshadowing.[105]
In June 2021, Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews published a systematic review of 82 studies that all confirmed or implied elevated accident-proneness in ADHD patients and whose data suggested that the type of accidents or injuries and overall risk changes in ADHD patients over the lifespan.[106] In January 2014, Accident Analysis & Prevention published a meta-analysis of 16 studies examining the relative risk of traffic collisions for drivers with ADHD, finding an overall relative risk estimate of 1.36 without controlling for exposure, a relative risk estimate of 1.29 when controlling for publication bias, a relative risk estimate of 1.23 when controlling for exposure, and a relative risk estimate of 1.86 for ADHD drivers with oppositional defiant disorder and/or conduct disorder comorbidities.[107][108]
Problematic digital media use
In April 2018, the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health published a systematic review of 24 studies researching associations between internet gaming disorder (IGD) and various psychopathologies that found an 85% correlation between IGD and ADHD.[109] In October 2018, PNAS USA published a systematic review of four decades of research on the relationship between children and adolescents' screen media use and ADHD-related behaviours and concluded that a statistically small relationship between children's media use and ADHD-related behaviours exists.[110] In November 2018, Cyberpsychology published a systematic review and meta-analysis of 5 studies that found evidence for a relationship between problematic smartphone use and impulsivity traits.[111] In October 2020, the Journal of Behavioral Addictions published a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 studies with 33,650 post-secondary student subjects that found a weak-to-moderate positive association between mobile phone addiction and impulsivity.[112] In January 2021, the Journal of Psychiatric Research published a systematic review of 29 studies including 56,650 subjects that found that ADHD symptoms were consistently associated with gaming disorder and more frequent associations between inattention and gaming disorder than other ADHD scales.[113]
In July 2021, Frontiers in Psychiatry published a meta-analysis reviewing 40 voxel-based morphometry studies and 59 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies comparing subjects with IGD or ADHD to control groups that found that IGD and ADHD subjects had disorder-differentiating structural neuroimage alterations in the putamen and orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) respectively, and functional alterations in the precuneus for IGD subjects and in the rewards circuit (including the OFC, the anterior cingulate cortex, and striatum) for both IGD and ADHD subjects.[114] In March 2022, JAMA Psychiatry published a systematic review and meta-analysis of 87 studies with 159,425 subjects 12 years of age or younger that found a small but statistically significant correlation between screen time and ADHD symptoms in children.[115] In April 2022, Developmental Neuropsychology published a systematic review of 11 studies where the data from all but one study suggested that heightened screen time for children is associated with attention problems.[116] In July 2022, the Journal of Behavioral Addictions published a meta-analysis of 14 studies comprising 2,488 subjects aged 6 to 18 years that found significantly more severe problematic internet use in subjects diagnosed with ADHD to control groups.[117]
In December 2022, European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry published a systematic literature review of 28 longitudinal studies published from 2011 through 2021 of associations between digital media use by children and adolescents and later ADHD symptoms and found reciprocal associations between digital media use and ADHD symptoms (i.e. that subjects with ADHD symptoms were more likely to develop problematic digital media use and that increased digital media use was associated with increased subsequent severity of ADHD symptoms).[118] In May 2023, Reviews on Environmental Health published a meta-analysis of 9 studies with 81,234 child subjects that found a positive correlation between screen time and ADHD risk in children and that higher amounts of screen time in childhood may significantly contribute to the development of ADHD.[119] In December 2023, the Journal of Psychiatric Research published a meta-analysis of 24 studies with 18,859 subjects with a mean age of 18.4 years that found significant associations between ADHD and problematic internet use,[120] while Clinical Psychology Review published a systematic review and meta-analysis of 48 studies examining associations between ADHD and gaming disorder that found a statistically significant association between the disorders.[121]Suicide risk
Systematic reviews conducted in 2017 and 2020 found strong evidence that ADHD is associated with increased suicide risk across all age groups, as well as growing evidence that an ADHD diagnosis in childhood or adolescence represents a significant future suicidal risk factor.[122][123] Potential causes include ADHD's association with functional impairment, negative social, educational and occupational outcomes, and financial distress.[124][125] A 2019 meta-analysis indicated a significant association between ADHD and suicidal spectrum behaviours (suicidal attempts, ideations, plans, and completed suicides); across the studies examined, the prevalence of suicide attempts in individuals with ADHD was 18.9%, compared to 9.3% in individuals without ADHD, and the findings were substantially replicated among studies which adjusted for other variables. However, the relationship between ADHD and suicidal spectrum behaviours remains unclear due to mixed findings across individual studies and the complicating impact of comorbid psychiatric disorders.[124] There is no clear data on whether there is a direct relationship between ADHD and suicidality, or whether ADHD increases suicide risk through comorbidities.[123]
IQ test performance
Certain studies have found that people with ADHD tend to have lower scores on intelligence quotient (IQ) tests.[126] The significance of this is controversial due to the differences between people with ADHD and the difficulty determining the influence of symptoms, such as distractibility, on lower scores rather than intellectual capacity. In studies of ADHD, higher IQs may be over-represented because many studies exclude individuals who have lower IQs despite those with ADHD scoring on average nine points lower on standardised intelligence measures.[127] However, other studies contradict this, saying that in individuals with high intelligence, there is an increased risk of a missed ADHD diagnosis, possibly because of compensatory strategies in said individuals.[128]
Studies of adults suggest that negative differences in intelligence are not meaningful and may be explained by associated health problems.[129]
Causes
ADHD arises from brain maldevelopment especially in the prefrontal executive networks that can arise either from genetic factors (different gene variants and mutations for building and regulating such networks) or from acquired disruptions to the development of these networks and regions; involved in executive functioning and self-regulation.[7][16] Their reduced size, functional connectivity, and activation contribute to the pathophysiology of ADHD, as well as imbalances in the noradrenergic and dopaminergic systems that mediate these brain regions.[7][130]
Genetic factors play an important role; ADHD has a heritability rate of 70-80%. The remaining 20-30% of variance is mediated by de-novo mutations and non-shared environmental factors that provide for or produce brain injuries; there is no significant contribution of the rearing family and social environment.[137] Very rarely, ADHD can also be the result of abnormalities in the chromosomes.[138]
Genetics
In November 1999, Biological Psychiatry published a literature review by psychiatrists Joseph Biederman and Thomas Spencer on the pathophysiology of ADHD that found the average heritability estimate of ADHD from twin studies to be 0.8,[139] while a subsequent family, twin, and adoption studies literature review published in Molecular Psychiatry in April 2019 by psychologists Stephen Faraone and Henrik Larsson that found an average heritability estimate of 0.74.[140] Additionally, evolutionary psychiatrist Randolph M. Nesse has argued that the 5:1 male-to-female sex ratio in the epidemiology of ADHD suggests that ADHD may be the end of a continuum where males are overrepresented at the tails, citing clinical psychologist Simon Baron-Cohen's suggestion for the sex ratio in the epidemiology of autism as an analogue.[141][142][143]
Natural selection has been acting against the genetic variants for ADHD over the course of at least 45,000 years, indicating that it was not an adaptative trait in ancient times.[144] The disorder may remain at a stable rate by the balance of genetic mutations and removal rate (natural selection) across generations; over thousands of years, these genetic variants become more stable, decreasing disorder prevalence.[145] Throughout human evolution, the EFs involved in ADHD likely provide the capacity to bind contingencies across time thereby directing behaviour toward future over immediate events so as to maximise future social consequences for humans.[146]
ADHD has a high heritability of 74%, meaning that 74% of the presence of ADHD in the population is due to genetic factors. There are multiple gene variants which each slightly increase the likelihood of a person having ADHD; it is polygenic and arises through the combination of many gene variants which each have a small effect.[147][7] The siblings of children with ADHD are three to four times more likely to develop the disorder than siblings of children without the disorder.[148]
The association of maternal smoking observed in large population studies disappears after adjusting for family history of ADHD, which indicates that the association between maternal smoking during pregnancy and ADHD is due to familial or genetic factors that increase the risk for the confluence of smoking and ADHD.[149][150]
ADHD presents with reduced size, functional connectivity and activation[7] as well as low noradrenergic and dopaminergic functioning[151][152] in brain regions and networks crucial for executive functioning and self-regulation.[7][37][16] Typically, a number of genes are involved, many of which directly affect brain functioning and neurotransmission.[7] Those involved with dopamine include DAT, DRD4, DRD5, TAAR1, MAOA, COMT, and DBH.[153][154][155] Other genes associated with ADHD include SERT, HTR1B, SNAP25, GRIN2A, ADRA2A, TPH2, and BDNF.[156] A common variant of a gene called latrophilin 3 is estimated to be responsible for about 9% of cases and when this variant is present, people are particularly responsive to stimulant medication.[157] The 7 repeat variant of dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4–7R) causes increased inhibitory effects induced by dopamine and is associated with ADHD. The DRD4 receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor that inhibits adenylyl cyclase. The DRD4–7R mutation results in a wide range of behavioural phenotypes, including ADHD symptoms reflecting split attention.[158] The DRD4 gene is both linked to novelty seeking and ADHD. The genes GFOD1 and CDH13 show strong genetic associations with ADHD. CHD13's association with ASD, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression make it an interesting candidate causative gene.[135] Another candidate causative gene that has been identified is ADGRL3. In zebrafish, knockout of this gene causes a loss of dopaminergic function in the ventral diencephalon and the fish display a hyperactive/impulsive phenotype.[135]
For genetic variation to be used as a tool for diagnosis, more validating studies need to be performed. However, smaller studies have shown that genetic polymorphisms in genes related to catecholaminergic neurotransmission or the SNARE complex of the synapse can reliably predict a person's response to stimulant medication.[135] Rare genetic variants show more relevant clinical significance as their penetrance (the chance of developing the disorder) tends to be much higher.[159] However their usefulness as tools for diagnosis is limited as no single gene predicts ADHD. ASD shows genetic overlap with ADHD at both common and rare levels of genetic variation.[159]
Environment
In addition to genetics, some environmental factors might play a role in causing ADHD.[160][161] Alcohol intake during pregnancy can cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorders which can include ADHD or symptoms like it.[162] Children exposed to certain toxic substances, such as lead or polychlorinated biphenyls, may develop problems which resemble ADHD.[38][163] Exposure to the organophosphate insecticides chlorpyrifos and dialkyl phosphate is associated with an increased risk; however, the evidence is not conclusive.[164] Exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy can cause problems with central nervous system development and can increase the risk of ADHD.[38][165] Nicotine exposure during pregnancy may be an environmental risk.[166]
Extreme premature birth, very low birth weight, and extreme neglect, abuse, or social deprivation also increase the risk[167][38][168] as do certain infections during pregnancy, at birth, and in early childhood. These infections include, among others, various viruses (measles, varicella zoster encephalitis, rubella, enterovirus 71).[169] At least 30% of children with a traumatic brain injury later develop ADHD[170] and about 5% of cases are due to brain damage.[171]
Some studies suggest that in a small number of children, artificial food dyes or preservatives may be associated with an increased prevalence of ADHD or ADHD-like symptoms,[38][172] but the evidence is weak and may only apply to children with food sensitivities.[160][172][173] The European Union has put in place regulatory measures based on these concerns.[174] In a minority of children, intolerances or allergies to certain foods may worsen ADHD symptoms.[175]
Individuals with hypokalemic sensory overstimulation are sometimes diagnosed as having attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), raising the possibility that a subtype of ADHD has a cause that can be understood mechanistically and treated in a novel way. The sensory overload is treatable with oral potassium gluconate.
Research does not support popular beliefs that ADHD is caused by eating too much refined sugar, watching too much television, bad parenting, poverty or family chaos; however, they might worsen ADHD symptoms in certain people.[48]
The youngest children in a class have been found to be more likely to be diagnosed as having ADHD, possibly due to them being developmentally behind their older classmates.[176][177] One study showed that the youngest children in fifth and eight grade was nearly twice as likely to use stimulant medication than their older peers.[178]
In some cases, an inappropriate diagnosis of ADHD may reflect a dysfunctional family or a poor educational system, rather than any true presence of ADHD in the individual.[179][better source needed] In other cases, it may be explained by increasing academic expectations, with a diagnosis being a method for parents in some countries to get extra financial and educational support for their child.[171] Behaviours typical of ADHD occur more commonly in children who have experienced violence and emotional abuse.[180]
Pathophysiology
Current models of ADHD suggest that it is associated with functional impairments in some of the brain's neurotransmitter systems, particularly those involving dopamine and norepinephrine.[181] The dopamine and norepinephrine pathways that originate in the ventral tegmental area and locus coeruleus project to diverse regions of the brain and govern a variety of cognitive processes.[182][14] The dopamine pathways and norepinephrine pathways which project to the prefrontal cortex and striatum are directly responsible for modulating executive function (cognitive control of behaviour), motivation, reward perception, and motor function;[181][14] these pathways are known to play a central role in the pathophysiology of ADHD.[182][14][183][184] Larger models of ADHD with additional pathways have been proposed.[183][184]
Brain structure

In children with ADHD, there is a general reduction of volume in certain brain structures, with a proportionally greater decrease in the volume in the left-sided prefrontal cortex.[181][185] The posterior parietal cortex also shows thinning in individuals with ADHD compared to controls. Other brain structures in the prefrontal-striatal-cerebellar and prefrontal-striatal-thalamic circuits have also been found to differ between people with and without ADHD.[181][183][184]
The subcortical volumes of the accumbens, amygdala, caudate, hippocampus, and putamen appears smaller in individuals with ADHD compared with controls.[186] Structural MRI studies have also revealed differences in white matter, with marked differences in inter-hemispheric asymmetry between ADHD and typically developing youths.[187]
Function MRI (fMRI) studies have revealed a number of differences between ADHD and control brains. Mirroring what is known from structural findings, fMRI studies have showed evidence for a higher connectivity between subcortical and cortical regions, such as between the caudate and prefrontal cortex. The degree of hyperconnectivity between these regions correlated with the severity of inattention or hyperactivity [188] Hemispheric lateralization processes have also been postulated as being implicated in ADHD, but empiric results showed contrasting evidence on the topic.[189][190]
Neurotransmitter pathways
Previously, it had been suggested that the elevated number of dopamine transporters in people with ADHD was part of the pathophysiology, but it appears the elevated numbers may be due to adaptation following exposure to stimulant medication.[191] Current models involve the mesocorticolimbic dopamine pathway and the locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system.[182][181][14] ADHD psychostimulants possess treatment efficacy because they increase neurotransmitter activity in these systems.[181][14][192] There may additionally be abnormalities in serotonergic, glutamatergic, or cholinergic pathways.[192][193][194]
Executive function and motivation
The symptoms of ADHD arise from a deficiency in certain executive functions (e.g., attentional control, inhibitory control, and working memory).[181] Executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are required to successfully select and monitor behaviours that facilitate the attainment of one's chosen goals.[14][15] The executive function impairments that occur in ADHD individuals result in problems with staying organised, time keeping, excessive procrastination, maintaining concentration, paying attention, ignoring distractions, regulating emotions, and remembering details.[13][181][14] People with ADHD appear to have unimpaired long-term memory, and deficits in long-term recall appear to be attributed to impairments in working memory.[195] Due to the rates of brain maturation and the increasing demands for executive control as a person gets older, ADHD impairments may not fully manifest themselves until adolescence or even early adulthood.[13] Conversely, brain maturation trajectories, potentially exhibiting diverging longitudinal trends in ADHD, may support a later improvement in executive functions after reaching adulthood.[189]
ADHD has also been associated with motivational deficits in children. Children with ADHD often find it difficult to focus on long-term over short-term rewards, and exhibit impulsive behaviour for short-term rewards.[196]
Paradoxical reaction to neuroactive substances
Another sign of the structurally altered signal processing in the central nervous system in this group of people is the conspicuously common Paradoxical reaction (c. 10–20% of patients). These are unexpected reactions in the opposite direction as with a normal effect, or otherwise significant different reactions. These are reactions to neuroactive substances such as local anesthetic at the dentist, sedative, caffeine, antihistamine, weak neuroleptics and central and peripheral painkillers. Since the causes of paradoxical reactions are at least partly genetic, it may be useful in critical situations, for example before operations, to ask whether such abnormalities may also exist in family members.[197][198]
Diagnosis
ADHD is diagnosed by an assessment of a person's behavioural and mental development, including ruling out the effects of drugs, medications, and other medical or psychiatric problems as explanations for the symptoms.[84] ADHD diagnosis often takes into account feedback from parents and teachers[199] with most diagnoses begun after a teacher raises concerns.[171] While many tools exist to aide in the diagnosis of ADHD, their validity varies in different populations, and a reliable and valid diagnosis requires confirmation by a clinician while supplemented by standardized rating scales and input from multiple informants across various settings.[200] It may be viewed as the extreme end of one or more continuous human traits found in all people.[201] Imaging studies of the brain do not give consistent results between individuals; thus, they are only used for research purposes and not a diagnosis.[202]
In North America and Australia, DSM-5 criteria are used for diagnosis, while European countries usually use the ICD-10. The DSM-IV criteria for diagnosis of ADHD is 3–4 times more likely to diagnose ADHD than is the ICD-10 criteria.[203] ADHD is alternately classified as neurodevelopmental disorder[204] or a disruptive behaviour disorder along with ODD, CD, and antisocial personality disorder.[205] A diagnosis does not imply a neurological disorder.[180]
Associated conditions that should be screened for include anxiety, depression, ODD, CD, and learning and language disorders. Other conditions that should be considered are other neurodevelopmental disorders, tics, and sleep apnea.[206]
Self-rating scales, such as the ADHD rating scale and the Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale, are used in the screening and evaluation of ADHD.[207] Electroencephalography is not accurate enough to make an ADHD diagnosis.[208][209][210]
Classification
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual
As with many other psychiatric disorders, a formal diagnosis should be made by a qualified professional based on a set number of criteria. In the United States, these criteria are defined by the American Psychiatric Association in the DSM. Based on the DSM-5 criteria published in 2013 and the DSM-5-TR criteria published in 2022, there are three presentations of ADHD:
- ADHD, predominantly inattentive presentation, presents with symptoms including being easily distracted, forgetful, daydreaming, disorganization, poor sustained attention, and difficulty completing tasks.
- ADHD, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation, presents with excessive fidgeting and restlessness, hyperactivity, and difficulty waiting and remaining seated.
- ADHD, combined presentation, is a combination of the first two presentations.
This subdivision is based on presence of at least six (in children) or five (in older teenagers and adults)[211] out of nine long-term (lasting at least six months) symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity–impulsivity, or both.[3][4] To be considered, several symptoms must have appeared by the age of six to twelve and occur in more than one environment (e.g. at home and at school or work). The symptoms must be inappropriate for a child of that age[212] and there must be clear evidence that they are causing social, school or work related problems.[213]
The DSM-5 and the DSM-5-TR also provide two diagnoses for individuals who have symptoms of ADHD but do not entirely meet the requirements. Other Specified ADHD allows the clinician to describe why the individual does not meet the criteria, whereas Unspecified ADHD is used where the clinician chooses not to describe the reason.[3][4]
International Classification of Diseases
In the eleventh revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-11) by the World Health Organization, the disorder is classified as Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (with the code 6A05). The defined subtypes are similar to those of the DSM-5: predominantly inattentive presentation (6A05.0); predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation(6A05.1); combined presentation (6A05.2). However, the ICD-11 includes two residual categories for individuals who do not entirely match any of the defined subtypes: other specified presentation (6A05.Y) where the clinician includes detail on the individual's presentation; and presentation unspecified (6A05.Z) where the clinician does not provide detail.[5]
In the tenth revision (ICD-10), the symptoms of hyperkinetic disorder were analogous to ADHD in the ICD-11. When a conduct disorder (as defined by ICD-10)[59] is present, the condition was referred to as hyperkinetic conduct disorder. Otherwise, the disorder was classified as disturbance of activity and attention, other hyperkinetic disorders or hyperkinetic disorders, unspecified. The latter was sometimes referred to as hyperkinetic syndrome.[59]
Social construct theory
The social construct theory of ADHD suggests that, because the boundaries between normal and abnormal behaviour are socially constructed (i.e. jointly created and validated by all members of society, and in particular by physicians, parents, teachers, and others), it then follows that subjective valuations and judgements determine which diagnostic criteria are used and thus, the number of people affected.[214] Thomas Szasz, a supporter of this theory, has argued that ADHD was "invented and then given a name".[215]
Adults
Adults with ADHD are diagnosed under the same criteria, including that their signs must have been present by the age of six to twelve. The individual is the best source for information in diagnosis, however others may provide useful information about the individual's symptoms currently and in childhood; a family history of ADHD also adds weight to a diagnosis.[55]: 7, 9 While the core symptoms of ADHD are similar in children and adults, they often present differently in adults than in children: for example, excessive physical activity seen in children may present as feelings of restlessness and constant mental activity in adults.[55]: 6
Worldwide, it is estimated that 2.58% of adults have persistent ADHD (where the individual currently meets the criteria and there is evidence of childhood onset), and 6.76% of adults have symptomatic ADHD (meaning that they currently meet the criteria for ADHD, regardless of childhood onset).[216] In 2020, this was 139.84 million and 366.33 million affected adults respectively.[216] Around 15% of children with ADHD continue to meet full DSM-IV-TR criteria at 25 years of age, and 50% still experience some symptoms.[55]: 2 As of 2010[update], most adults remain untreated.[217] Many adults with ADHD without diagnosis and treatment have a disorganised life, and some use non-prescribed drugs or alcohol as a coping mechanism.[218] Other problems may include relationship and job difficulties, and an increased risk of criminal activities.[219][55]: 6 Associated mental health problems include depression, anxiety disorders, and learning disabilities.[218]
Some ADHD symptoms in adults differ from those seen in children. While children with ADHD may climb and run about excessively, adults may experience an inability to relax, or may talk excessively in social situations.[55]: 6 Adults with ADHD may start relationships impulsively, display sensation-seeking behaviour, and be short-tempered.[55]: 6 Addictive behaviour such as substance abuse and gambling are common.[55]: 6 This led to those who presented differently as they aged having outgrown the DSM-IV criteria.[55]: 5–6 The DSM-5 criteria does specifically deal with adults unlike that of DSM-IV, which does not fully take into account the differences in impairments seen in adulthood compared to childhood.[55]: 5
For diagnosis in an adult, having symptoms since childhood is required. Nevertheless, a proportion of adults who meet the criteria for ADHD in adulthood would not have been diagnosed with ADHD as children. Most cases of late-onset ADHD develop the disorder between the ages of 12–16 and may therefore be considered early adult or adolescent-onset ADHD.[220]
Differential diagnosis
| Depression disorder | Anxiety disorder | Bipolar disorder |
|---|---|---|
|
|
in manic state
in depressive state
|
The DSM provides potential differential diagnoses – potential alternate explanations for specific symptoms. Assessment and investigation of clinical history determines which is the most appropriate diagnosis. The DSM-5 suggests ODD, intermittent explosive disorder, and other neurodevelopmental disorders (such as stereotypic movement disorder and Tourette's disorder), in addition to specific learning disorder, intellectual developmental disorder, ASD, reactive attachment disorder, anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, bipolar disorder, disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, substance use disorder, personality disorders, psychotic disorders, medication-induced symptoms, and neurocognitive disorders. Many but not all of these are also common comorbidities of ADHD.[3] The DSM-5-TR also suggests post-traumatic stress disorder.[4]
Symptoms of ADHD, such as low mood and poor self-image, mood swings, and irritability, can be confused with dysthymia, cyclothymia or bipolar disorder as well as with borderline personality disorder.[55]: 10 Some symptoms that are due to anxiety disorders, personality disorder, developmental disabilities or intellectual disability or the effects of substance abuse such as intoxication and withdrawal can overlap with ADHD. These disorders can also sometimes occur along with ADHD. Medical conditions which can cause ADHD-type symptoms include: hyperthyroidism, seizure disorder, lead toxicity, hearing deficits, hepatic disease, sleep apnea, drug interactions, untreated celiac disease, and head injury.[222][218][better source needed]
Primary sleep disorders may affect attention and behaviour and the symptoms of ADHD may affect sleep.[223] It is thus recommended that children with ADHD be regularly assessed for sleep problems.[224] Sleepiness in children may result in symptoms ranging from the classic ones of yawning and rubbing the eyes, to hyperactivity and inattentiveness. Obstructive sleep apnea can also cause ADHD-type symptoms.[225]
Management
The management of ADHD typically involves counseling or medications, either alone or in combination. On average, treatment with medication substantially improves long-term outcomes, and completely eliminates some elevated risks, such as obesity.[7] Medications used include stimulants, atomoxetine, alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists, and sometimes antidepressants.[73][192] In those who have trouble focusing on long-term rewards, a large amount of positive reinforcement improves task performance.[196] Medications are the most effective treatment,[7][226] and any side effects are typically mild and easy to resolve[7] although any improvements will be reverted if medication is ceased.[227] ADHD stimulants also improve persistence and task performance in children with ADHD.[181][196] To quote one systematic review, "recent evidence from observational and registry studies indicates that pharmacological treatment of ADHD is associated with increased achievement and decreased absenteeism at school, a reduced risk of trauma-related emergency hospital visits, reduced risks of suicide and attempted suicide, and decreased rates of substance abuse and criminality".[228] Data also suggest that combining medication with CBT is a good idea - although CBT is substantially less effective, it can help address problems that reside after medication has been optimised.[7]
Behavioural therapies
There is good evidence for the use of behavioural therapies in ADHD. They are the recommended first-line treatment in those who have mild symptoms or who are preschool-aged.[229][230] Psychological therapies used include: psychoeducational input, behavior therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy,[231] interpersonal psychotherapy, family therapy, school-based interventions, social skills training, behavioural peer intervention, organization training,[232] and parent management training.[180] Neurofeedback has greater treatment effects than non-active controls for up to 6 months and possibly a year following treatment, and may have treatment effects comparable to active controls (controls proven to have a clinical effect) over that time period.[233] Despite efficacy in research, there is insufficient regulation of neurofeedback practice, leading to ineffective applications and false claims regarding innovations.[234] Parent training may improve a number of behavioural problems including oppositional and non-compliant behaviours.[235]
There is little high-quality research on the effectiveness of family therapy for ADHD—but the existing evidence shows that it is similar to community care, and better than placebo.[236] ADHD-specific support groups can provide information and may help families cope with ADHD.[237]
Social skills training, behavioural modification, and medication may have some limited beneficial effects in peer relationships. Stable, high-quality friendships with non-deviant peers protect against later psychological problems.[238]
Digital interventions
Several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of digital therapeutics, particularly Akili Interactive Labs's video game-based digital therapeutic AKL-T01, marketed as EndeavourRx. The pediatric STARS-ADHD randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, controlled trial demonstrated that AKL-T01 significantly improved performance on the Test of Variables of Attention, an objective measure of attention and inhibitory control, compared to a control group after four weeks of at-home use.[239] A subsequent pediatric open-label study, STARS-Adjunct, published in Nature Portfolio's npj Digital Medicine evaluated AKL-T01 as an adjunctive treatment for children with ADHD who were either on stimulant medication or not on stimulant pharmacotherapy. Results showed improvements in ADHD-related impairment (measured by the Impairment Rating Scale) and ADHD symptoms after 4 weeks of treatment, with effects persisting during a 4-week pause and further improving with an additional treatment period.[240] Notably, the magnitude of the measured improvement was similar for children both on and off stimulants.[240] In 2020, AKL-T01 received marketing authorization for pediatric ADHD from the FDA, becoming "the first game-based therapeutic granted marketing authorization by the FDA for any type of condition."[241]
In addition to pediatric populations, a 2023 study, STARS-ADHD-Adults, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry investigated the efficacy and safety of AKL-T01 in adults with ADHD. After 6 weeks of at-home treatment with AKL-T01, participants showed significant improvements in objective measures of attention (TOVA - Attention Comparison Score), reported ADHD symptoms (ADHD-RS-IV inattention subscale and total score), and reported quality of life (AAQoL).[242] Notably, the magnitude of improvement in attention was nearly seven times greater than that reported in pediatric trials.[242] The treatment was well-tolerated, with high compliance and no serious adverse events.[242]
Medication
The medications for ADHD appear to alleviate symptoms via their effects on the pre-frontal executive, striatal and related regions and networks in the brain; usually by increasing neurotransmission of norepinephrine and dopamine.[243][244][245]
Stimulants
Methylphenidate and amphetamine or its derivatives are often first-line treatments for ADHD.[246][247] About 70 per cent respond to the first stimulant tried and as few as 10 per cent respond to neither amphetamines nor methylphenidate.[226] Stimulants may also reduce the risk of unintentional injuries in children with ADHD.[248] Magnetic resonance imaging studies suggest that long-term treatment with amphetamine or methylphenidate decreases abnormalities in brain structure and function found in subjects with ADHD.[249][250][251] A 2018 review found the greatest short-term benefit with methylphenidate in children, and amphetamines in adults.[252] Studies and meta-analyses show that amphetamine is slightly-to-modestly more effective than methylphenidate at reducing symptoms,[253][254] and they are more effective pharmacotherapy for ADHD than α2-agonists[255] but methylphenidate has comparable efficacy to non-stimulants such as atomoxetine.
The likelihood of developing insomnia for ADHD patients taking stimulants has been measured at between 11 and 45 per cent for different medications,[256] and may be a main reason for discontinuation. Other side effects, such as tics, decreased appetite and weight loss, or emotional lability, may also lead to discontinuation.[226] Stimulant psychosis and mania are rare at therapeutic doses, appearing to occur in approximately 0.1% of individuals, within the first several weeks after starting amphetamine therapy.[257][258][259] The safety of these medications in pregnancy is unclear.[260] Symptom improvement is not sustained if medication is ceased.[261][227][262]
The long-term effects of ADHD medication have yet to be fully determined,[263][264] although stimulants are generally beneficial and safe for up to two years for children and adolescents.[265] A 2022 meta-analysis found no statistically significant association between ADHD medications and the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) across age groups, although the study suggests further investigation is warranted for patients with preexisting CVD as well as long-term medication use.[266] Regular monitoring has been recommended in those on long-term treatment.[267] There are indications suggesting that stimulant therapy for children and adolescents should be stopped periodically to assess continuing need for medication, decrease possible growth delay, and reduce tolerance.[268][269] Although potentially addictive at high doses,[270][271] stimulants used to treat ADHD have low potential for abuse.[246] Treatment with stimulants is either protective against substance abuse or has no effect.[55]: 12 [263][270]
The majority of studies on nicotine and other nicotinic agonists as treatments for ADHD have shown favorable results; however, no nicotinic drug has been approved for ADHD treatment.[272] Caffeine was formerly used as a second-line treatment for ADHD but research indicates it has no significant effects in reducing ADHD symptoms. Caffeine appears to help with alertness, arousal and reaction time but not the type of inattention implicated in ADHD (sustained attention/persistence).[273] Pseudoephedrine and ephedrine do not affect ADHD symptoms.[246]
Modafinil has shown some efficacy in reducing the severity of ADHD in children and adolescents.[274] It may be prescribed off-label to treat ADHD.
Non-stimulants
Two non-stimulant medications, atomoxetine and viloxazine, are approved by the FDA and in other countries for the treatment of ADHD.
Atomoxetine, due to its lack of addiction liability, may be preferred in those who are at risk of recreational or compulsive stimulant use, although evidence is lacking to support its use over stimulants for this reason.[55]: 13 Atomoxetine alleviates ADHD symptoms through norepinephrine reuptake and by indirectly increasing dopamine in the pre-frontal cortex,[245] sharing 70-80% of the brain regions with stimulants in their produced effects.[244] Atomoxetine has been shown to significantly improve academic performance.[275][276] Meta-analyses and systematic reviews have found that atomoxetine has comparable efficacy, equal tolerability and response rate (75%) to methylphenidate in children and adolescents. In adults, efficacy and discontinuation rates are equivalent.[277][278][279][280]
Analyses of clinical trial data suggests that viloxazine is about as effective as atomoxetine and methylphenidate but with fewer side effects.[281]
Amantadine was shown to induce similar improvements in children treated with methylphenidate, with less frequent side effects.[282] A 2021 retrospective study showed showed that amantadine may serve as an effective adjunct to stimulants for ADHD–related symptoms and appears to be a safer alternative to second- or third-generation antipsychotics.[283]
Bupropion is also used off-label by some clinicians due to research findings. It is effective, but modestly less than atomoxetine and methylphenidate.[284]
There is little evidence on the effects of medication on social behaviours.[285] Antipsychotics may also be used to treat aggression in ADHD.[286]
Alpha-2a agonists
Two alpha-2a agonists, extended-release formulations of guanfacine and clonidine, are approved by the FDA and in other countries for the treatment of ADHD (effective in children and adolescents but effectiveness has still not been shown for adults).[287][288] They appear to be modestly less effective than the stimulants (amphetamine and methylphenidate) and non-stimulants (atomoxetine and viloxazine) at reducing symptoms,[289][290] but can be useful alternatives or used in conjunction with a stimulant. These medications act by adjusting the alpha-2a ports on the outside of noradrenergic nerve cells in the pre-frontal executive networks, so the information (electrical signal) is less confounded by noise.[291]
Guidelines
Guidelines on when to use medications vary by country. The United Kingdom's National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends use for children only in severe cases, though for adults medication is a first-line treatment.[292] Conversely, most United States guidelines recommend medications in most age groups.[293] Medications are especially not recommended for preschool children.[292][180] Underdosing of stimulants can occur, and can result in a lack of response or later loss of effectiveness.[294] This is particularly common in adolescents and adults as approved dosing is based on school-aged children, causing some practitioners to use weight-based or benefit-based off-label dosing instead.[295][296][297]
Exercise
Regular physical exercise, particularly aerobic exercise, is an effective add-on treatment for ADHD in children and adults, particularly when combined with stimulant medication (although the best intensity and type of aerobic exercise for improving symptoms are not currently known).[298] The long-term effects of regular aerobic exercise in ADHD individuals include better behaviour and motor abilities, improved executive functions (including attention, inhibitory control, and planning, among other cognitive domains), faster information processing speed, and better memory.[299] Parent-teacher ratings of behavioural and socio-emotional outcomes in response to regular aerobic exercise include: better overall function, reduced ADHD symptoms, better self-esteem, reduced levels of anxiety and depression, fewer somatic complaints, better academic and classroom behaviour, and improved social behaviour. Exercising while on stimulant medication augments the effect of stimulant medication on executive function.[300] It is believed that these short-term effects of exercise are mediated by an increased abundance of synaptic dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain.[300]
Diet
Dietary modifications are not recommended as of 2019[update] by the American Academy of Pediatrics, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, or the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality due to insufficient evidence.[301][292] A 2013 meta-analysis found less than a third of children with ADHD see some improvement in symptoms with free fatty acid supplementation or decreased eating of artificial food colouring.[160] These benefits may be limited to children with food sensitivities or those who are simultaneously being treated with ADHD medications.[160] This review also found that evidence does not support removing other foods from the diet to treat ADHD.[160] A 2014 review found that an elimination diet results in a small overall benefit in a minority of children, such as those with allergies.[175] A 2016 review stated that the use of a gluten-free diet as standard ADHD treatment is not advised.[222] A 2017 review showed that a few-foods elimination diet may help children too young to be medicated or not responding to medication, while free fatty acid supplementation or decreased eating of artificial food colouring as standard ADHD treatment is not advised.[302] Chronic deficiencies of iron, magnesium and iodine may have a negative impact on ADHD symptoms.[303] There is a small amount of evidence that lower tissue zinc levels may be associated with ADHD.[304] In the absence of a demonstrated zinc deficiency (which is rare outside of developing countries), zinc supplementation is not recommended as treatment for ADHD.[305] However, zinc supplementation may reduce the minimum effective dose of amphetamine when it is used with amphetamine for the treatment of ADHD.[306]
Prognosis
ADHD persists into adulthood in about 30–50% of cases.[307] Those affected are likely to develop coping mechanisms as they mature, thus compensating to some extent for their previous symptoms.[218] Children with ADHD have a higher risk of unintentional injuries.[248] Effects of medication on functional impairment and quality of life (e.g. reduced risk of accidents) have been found across multiple domains.[308] Rates of smoking among those with ADHD are higher than in the general population at about 40%.[309]
It affects about 5–7% of children when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria,[310] and 1–2% when diagnosed via the ICD-10 criteria.[311] Rates are similar between countries and differences in rates depend mostly on how it is diagnosed.[312] ADHD is diagnosed approximately twice as often in boys as in girls,[4][310] and 1.6 times more often in men than in women,[4] although the disorder is overlooked in girls or diagnosed in later life because their symptoms sometimes differ from diagnostic criteria.[316] About 30–50% of people diagnosed in childhood continue to have ADHD in adulthood, with 2.58% of adults estimated to have ADHD which began in childhood.[216][317][text–source integrity?] In adults, hyperactivity is usually replaced by inner restlessness, and adults often develop coping skills to compensate for their impairments. The condition can be difficult to tell apart from other conditions, as well as from high levels of activity within the range of normal behaviour. ADHD has a negative impact on patient health-related quality of life that may be further exacerbated by, or may increase the risk of, other psychiatric conditions such as anxiety and depression.[228]
Individuals with ADHD are significantly overrepresented in prison populations. Although there is no generally accepted estimate of ADHD prevalence among inmates, a 2015 meta-analysis estimated a prevalence of 25.5%, and a larger 2018 meta-analysis estimated the frequency to be 26.2%.[318] ADHD is more common among longer-term inmates; a 2010 study at Norrtälje Prison, a high-security prison in Sweden, found an estimated ADHD prevalence of 40%.[319]
Epidemiology
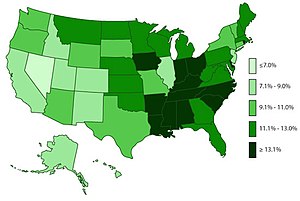
ADHD is estimated to affect about 6–7% of people aged 18 and under when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria.[310] When diagnosed via the ICD-10 criteria, rates in this age group are estimated around 1–2%.[311] Children in North America appear to have a higher rate of ADHD than children in Africa and the Middle East; this is believed to be due to differing methods of diagnosis rather than a difference in underlying frequency. (The same publication which describes this difference also notes that the difference may be rooted in the available studies from these respective regions, as far more studies were from North America than from Africa and the Middle East.)[321] As of 2019,[update] it was estimated to affect 84.7 million people globally.[2] If the same diagnostic methods are used, the rates are similar between countries.[312] ADHD is diagnosed approximately three times more often in boys than in girls.[315][203] This may reflect either a true difference in underlying rate, or that women and girls with ADHD are less likely to be diagnosed.[322] Studies from multiple countries have reported that children born closer to the start of the school year are more frequently diagnosed with and medicated for ADHD than their older classmates.[323]
Rates of diagnosis and treatment have increased in both the United Kingdom and the United States since the 1970s. Prior to 1970, it was rare for children to be diagnosed with ADHD, while in the 1970s rates were about 1%.[324] This is believed to be primarily due to changes in how the condition is diagnosed[325] and how readily people are willing to treat it with medications rather than a true change in how common the condition is.[311] It was believed changes to the diagnostic criteria in 2013 with the release of the DSM-5 would increase the percentage of people diagnosed with ADHD, especially among adults.[326]
Due to disparities in the treatment and understanding of ADHD between caucasian and non-caucasian populations, many non-caucasian children go undiagnosed and unmedicated.[327] It was found that within the US that there was often a disparity between caucasian and non-caucasian understandings of ADHD. This led to a difference in the classification of the symptoms of ADHD, and therefore, its misdiagnosis. It was also found that it was common in non-caucasian families and teachers to understand the symptoms of ADHD as behavioural issues, rather than mental illness.
Crosscultural differences in diagnosis of ADHD can also be attributed to the long-lasting effects of harmful, racially targeted medical practices. Medical pseudosciences, particularly those that targeted African American populations during the period of slavery in the US, lead to a distrust of medical practices within certain communities. The combination of ADHD symptoms often being regarded as misbehaviour rather than as a psychiatric condition, and the use of drugs to regulate ADHD, result in a hesitancy to trust a diagnosis of ADHD. Cases of misdiagnosis in ADHD can also occur due to stereotyping of non-caucasian individuals. Due to ADHD's subjectively determined symptoms, medical professionals may diagnose individuals based on stereotyped behaviour or misdiagnose due to differences in symptom presentation between caucasian and non-caucasian individuals.[328]
History
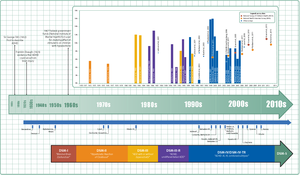
Hyperactivity has long been part of the human condition. Sir Alexander Crichton describes "mental restlessness" in his book An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement written in 1798.[329][330] He made observations about children showing signs of being inattentive and having the "fidgets". The first clear description of ADHD is credited to George Still in 1902 during a series of lectures he gave to the Royal College of Physicians of London.[331][325] He noted both nature and nurture could be influencing this disorder.
ADHD was officially known as attention deficit disorder (ADD) from 1980 to 1987; prior to the 1980s, it was known as hyperkinetic reaction of childhood. Symptoms similar to those of ADHD have been described in medical literature dating back to the 18th century.
Alfred Tredgold proposed an association between brain damage and behavioural or learning problems which was able to be validated by the encephalitis lethargica epidemic from 1917 through 1928.[332][333][334]
The terminology used to describe the condition has changed over time and has included: minimal brain dysfunction in the DSM-I (1952), hyperkinetic reaction of childhood in the DSM-II (1968), and attention-deficit disorder with or without hyperactivity in the DSM-III (1980).[325] In 1987, this was changed to ADHD in the DSM-III-R, and in 1994 the DSM-IV in split the diagnosis into three subtypes: ADHD inattentive type, ADHD hyperactive-impulsive type, and ADHD combined type.[335] These terms were kept in the DSM-5 in 2013 and in the DSM-5-TR in 2022.[3][4] Prior to the DSM, terms included minimal brain damage in the 1930s.[336]
In 1934, Benzedrine became the first amphetamine medication approved for use in the United States.[337] Methylphenidate was introduced in the 1950s, and enantiopure dextroamphetamine in the 1970s.[325] The use of stimulants to treat ADHD was first described in 1937.[338] Charles Bradley gave the children with behavioural disorders Benzedrine and found it improved academic performance and behaviour.[339][340]
Once neuroimaging studies were possible, studies conducted in the 1990s provided support for the pre-existing theory that neurological differences - particularly in the frontal lobes - were involved in ADHD. During this same period, a genetic component was identified and ADHD was acknowledged to be a persistent, long-term disorder which lasted from childhood into adulthood.[341][342]
ADHD was split into the current three sub-types because of a field trial completed by Lahey and colleagues.[343]
Controversy
ADHD, its diagnosis, and its treatment have been controversial since the 1970s.[227][6] The controversies involve clinicians, teachers, policymakers, parents, and the media. Positions range from the view that ADHD is within the normal range of behaviour[84][344] to the hypothesis that ADHD is a genetic condition.[345] Other areas of controversy include the use of stimulant medications in children,[227] the method of diagnosis, and the possibility of overdiagnosis.[346] In 2009, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, while acknowledging the controversy, states that the current treatments and methods of diagnosis are based on the dominant view of the academic literature.[201] In 2014, Keith Conners, one of the early advocates for recognition of the disorder, spoke out against overdiagnosis in a New York Times article.[347] In contrast, a 2014 peer-reviewed medical literature review indicated that ADHD is underdiagnosed in adults.[317]
Individuals with ADHD may face misconceptions and stigma; in response to this, a global team of scientists curated the International Consensus Statement.[7]
The diagnosis of ADHD has been criticised as being subjective because it is not based on a biological test. The International Consensus Statement on ADHD concluded that this criticism is unfounded, on the basis that ADHD meets standard criteria for validity of a mental disorder established by Robins and Guze. They attest that the disorder is considered valid because: 1) well-trained professionals in a variety of settings and cultures agree on its presence or absence using well-defined criteria and 2) the diagnosis is useful for predicting a) additional problems the patient may have (e.g., difficulties learning in school); b) future patient outcomes (e.g., risk for future drug abuse); c) response to treatment (e.g., medications and psychological treatments); and d) features that indicate a consistent set of causes for the disorder (e.g., findings from genetics or brain imaging). Professional associations have endorsed and published guidelines for diagnosing ADHD.[7]
With widely differing rates of diagnosis across countries, states within countries, races, and ethnicities, some suspect factors other than the presence of the symptoms of ADHD are playing a role in diagnosis, such as cultural norms.[348][349] Some sociologists consider ADHD to be an example of the medicalization of deviant behaviour, that is, the turning of the previously non-medical issue of school performance into a medical one.[350] Most healthcare providers accept ADHD as a genuine disorder, at least in the small number of people with severe symptoms. Among healthcare providers the debate mainly centers on diagnosis and treatment in the much greater number of people with mild symptoms.[171][351][352]
The nature and range of desirable endpoints of ADHD treatment vary among diagnostic standards for ADHD.[353] In most studies, the efficacy of treatment is determined by reductions in ADHD symptoms.[354] However, some studies have included subjective ratings from teachers and parents as part of their assessment of ADHD treatment efficacies.[252] By contrast, the subjective ratings of children undergoing ADHD treatment are seldom included in studies evaluating the efficacy of ADHD treatments.
There have been notable differences in the diagnosis patterns of birthdays in school-age children. Those born relatively younger to the school starting age than others in a classroom environment are shown to be more likely diagnosed with ADHD. Boys who were born in December in which the school age cut-off was 31 December were shown to be 30% more likely to be diagnosed and 41% to be treated than others born in January. Girls born in December had a diagnosis percentage of 70% and 77% treatment more than ones born the following month. Children who were born at the last 3 days of a calendar year were reported to have significantly higher levels of diagnosis and treatment for ADHD than children born at the first 3 days of a calendar year. The studies suggest that ADHD diagnosis is prone to subjective analysis.[349]
A meta-analysis by Storebø and colleagues and Kiŕubakaran and colleagues perpetuated controversy and stigma in media reports by raising substantial doubts about the efficacy of methylphenidate for reducing symptoms of ADHD. However, that meta-analysis used an idiosyncratic application of the Cochrane RoB for assessing evidence-quality and made systematic errors that led to false results, which furthermore, were inadmissibly clinically interpreted.[355][356][357] The data summated in the International Consensus Statement on ADHD is clear: methylphenidate is not only more efficacious than placebo, it is among the most efficacious drugs in all of medicine.[7]
Research directions
Possible positive traits
Possible positive traits of ADHD are a new avenue of research, and therefore limited.
A 2020 review found that creativity may be associated with ADHD symptoms, particularly divergent thinking and quantity of creative achievements, but not with the disorder of ADHD itself – i.e. it has not been found to be increased in people diagnosed with the disorder, only in people with subclinical symptoms or those that possess traits associated with the disorder. Divergent thinking is the ability to produce creative solutions which differ significantly from each other and consider the issue from multiple perspectives. Those with ADHD symptoms could be advantaged in this form of creativity as they tend to have diffuse attention, allowing rapid switching between aspects of the task under consideration; flexible associative memory, allowing them to remember and use more distantly-related ideas which is associated with creativity; and impulsivity, which causes people with ADHD symptoms to consider ideas which others may not have. However, people with ADHD may struggle with convergent thinking, which is a cognitive process through which a set of obviously relevant knowledge is utilised in a focused effort to arrive at a single perceived best solution to a problem.[358]
A 2019 article suggested that historical documentation supported Leonardo da Vinci's difficulties with procrastination and time management as characteristic of ADHD and that he was constantly on the go, but often jumping from task to task.[359]
Possible biomarkers for diagnosis
Reviews of ADHD biomarkers have noted that platelet monoamine oxidase expression, urinary norepinephrine, urinary MHPG, and urinary phenethylamine levels consistently differ between ADHD individuals and non-ADHD controls. These measurements could potentially serve as diagnostic biomarkers for ADHD, but more research is needed to establish their diagnostic utility. Urinary and blood plasma phenethylamine concentrations are lower in ADHD individuals relative to controls and the two most commonly prescribed drugs for ADHD, amphetamine and methylphenidate, increase phenethylamine biosynthesis in treatment-responsive individuals with ADHD.[154] Lower urinary phenethylamine concentrations are also associated with symptoms of inattentiveness in ADHD individuals.[360]
See also
- ADHD Grown Up: A Guide to Adolescent and Adult ADHD (2007)
- Directed attention fatigue – a temporary state sharing many of the symptoms of ADHD
- Self-medication
References
- ^ Young K (9 February 2017). "Anxiety or ADHD? Why They Sometimes Look the Same and How to Tell the Difference". Hey Sigmund. Archived from the original on 26 January 2023. Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ^ a b Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (17 October 2020). "Global Burden of Disease Study 2019: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder—Level 3 cause" (PDF). The Lancet. 396 (10258). Table 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 January 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2021.. Both DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10 criteria were used.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.). Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing. 2013. pp. 59–65. ISBN 978-0-89042-555-8.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Publishing. February 2022. ISBN 978-0-89042-575-6. OCLC 1288423302.
- ^ a b c "6A05 Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision. February 2022 [2019]. Archived from the original on 1 August 2018. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
- ^ a b Foreman DM (February 2006). "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: legal and ethical aspects". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 91 (2): 192–194. doi:10.1136/adc.2004.064576. PMC 2082674. PMID 16428370.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Faraone SV, Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Zheng Y, Biederman J, Bellgrove MA, et al. (September 2021). "The World Federation of ADHD International Consensus Statement: 208 Evidence-based conclusions about the disorder". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 128. Elsevier BV: 789–818. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.01.022. PMC 8328933. PMID 33549739.
- ^ [3][4][5][6][7]
- ^ Pievsky MA, McGrath RE (March 2018). "The Neurocognitive Profile of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Review of Meta-Analyses". Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 33 (2): 143–157. doi:10.1093/arclin/acx055. PMID 29106438.
- ^ Schoechlin C, Engel RR (August 2005). "Neuropsychological performance in adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: meta-analysis of empirical data". Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. 20 (6): 727–744. doi:10.1016/j.acn.2005.04.005. PMID 15953706.
- ^ Hart H, Radua J, Nakao T, Mataix-Cols D, Rubia K (February 2013). "Meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of inhibition and attention in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: exploring task-specific, stimulant medication, and age effects". JAMA Psychiatry. 70 (2): 185–198. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.277. PMID 23247506.
- ^ a b Hoogman M, Muetzel R, Guimaraes JP, Shumskaya E, Mennes M, Zwiers MP, et al. (July 2019). "Brain Imaging of the Cortex in ADHD: A Coordinated Analysis of Large-Scale Clinical and Population-Based Samples". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 176 (7): 531–542. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.18091033. PMC 6879185. PMID 31014101.
- ^ a b c d Brown TE (October 2008). "ADD/ADHD and Impaired Executive Function in Clinical Practice". Current Psychiatry Reports. 10 (5): 407–411. doi:10.1007/s11920-008-0065-7. PMID 18803914. S2CID 146463279.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely Projecting Systems: Monoamines, Acetylcholine, and Orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 148, 154–157. ISBN 978-0-07-148127-4.
DA has multiple actions in the prefrontal cortex. It promotes the 'cognitive control' of behavior: the selection and successful monitoring of behavior to facilitate attainment of chosen goals. Aspects of cognitive control in which DA plays a role include working memory, the ability to hold information 'on line' in order to guide actions, suppression of prepotent behaviors that compete with goal-directed actions, and control of attention and thus the ability to overcome distractions. Cognitive control is impaired in several disorders, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. ... Noradrenergic projections from the LC thus interact with dopaminergic projections from the VTA to regulate cognitive control. ... it has not been shown that 5HT makes a therapeutic contribution to treatment of ADHD.
- ^ a b Diamond A (2013). "Executive functions". Annual Review of Psychology. 64: 135–168. doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750. PMC 4084861. PMID 23020641.
EFs and prefrontal cortex are the first to suffer, and suffer disproportionately, if something is not right in your life. They suffer first, and most, if you are stressed (Arnsten 1998, Liston et al. 2009, Oaten & Cheng 2005), sad (Hirt et al. 2008, von Hecker & Meiser 2005), lonely (Baumeister et al. 2002, Cacioppo & Patrick 2008, Campbell et al. 2006, Tun et al. 2012), sleep deprived (Barnes et al. 2012, Huang et al. 2007), or not physically fit (Best 2010, Chaddock et al. 2011, Hillman et al. 2008). Any of these can cause you to appear to have a disorder of EFs, such as ADHD, when you do not.
- ^ a b c d e Antshel KM, Hier BO, Barkley RA (2014). "Executive Functioning Theory and ADHD". In Goldstein S, Naglieri JA (eds.). Handbook of Executive Functioning. New York, NY: Springer. pp. 107–120. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-8106-5_7. ISBN 978-1-4614-8106-5.
- ^ [9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16]
- ^ a b Retz W, Stieglitz RD, Corbisiero S, Retz-Junginger P, Rösler M (October 2012). "Emotional dysregulation in adult ADHD: What is the empirical evidence?". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 12 (10): 1241–1251. doi:10.1586/ern.12.109. PMID 23082740. S2CID 207221320.
- ^ Faraone SV, Rostain AL, Blader J, Busch B, Childress AC, Connor DF, et al. (February 2019). "Practitioner Review: Emotional dysregulation in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder - implications for clinical recognition and intervention". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 60 (2): 133–150. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12899. PMID 29624671.
- ^ Shaw P, Stringaris A, Nigg J, Leibenluft E (March 2014). "Emotion dysregulation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 171 (3): 276–293. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13070966. PMC 4282137. PMID 24480998.
- ^ [18][19][20]
- ^ Fleming M, Fitton CA, Steiner MF, McLay JS, Clark D, King A, et al. (July 2017). "Educational and Health Outcomes of Children Treated for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder". JAMA Pediatrics. 171 (7): e170691. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.0691. PMC 6583483. PMID 28459927.
- ^ Lee YC, Yang HJ, Chen VC, Lee WT, Teng MJ, Lin CH, et al. (1 April 2016). "Meta-analysis of quality of life in children and adolescents with ADHD: By both parent proxy-report and child self-report using PedsQL™". Research in Developmental Disabilities. 51–52: 160–172. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2015.11.009. PMID 26829402.
- ^ Barkley RA, Fischer M (July 2019). "Hyperactive Child Syndrome and Estimated Life Expectancy at Young Adult Follow-Up: The Role of ADHD Persistence and Other Potential Predictors". Journal of Attention Disorders. 23 (9): 907–923. doi:10.1177/1087054718816164. PMID 30526189. S2CID 54472439.
- ^ Cattoi B, Alpern I, Katz JS, Keepnews D, Solanto MV (April 2022). "The Adverse Health Outcomes, Economic Burden, and Public Health Implications of Unmanaged Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A Call to Action Resulting from CHADD Summit, Washington, DC, October 17, 2019". Journal of Attention Disorders. 26 (6): 807–808. doi:10.1177/10870547211036754. PMID 34585995. S2CID 238218526.
- ^ "'A horrible, perfect storm': Frustrations rise as shortage of Adderall, other ADHD medication continues". Chicago Tribune. 12 February 2024. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
- ^ a b Barkley RA, Murphy KR (1 June 2011). "The Nature of Executive Function (EF) Deficits in Daily Life Activities in Adults with ADHD and Their Relationship to Performance on EF Tests". Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment. 33 (2): 137–158. doi:10.1007/s10862-011-9217-x. ISSN 1573-3505.
- ^ Groen Y, Priegnitz U, Fuermaier AB, Tucha L, Tucha O, Aschenbrenner S, et al. (December 2020). "Testing the relation between ADHD and hyperfocus experiences". Research in Developmental Disabilities. 107: 103789. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2020.103789. PMID 33126147.
- ^ "APA PsycNet". psycnet.apa.org. Retrieved 3 March 2024.
- ^ Ashinoff BK, Abu-Akel A (February 2021). "Hyperfocus: the forgotten frontier of attention". Psychological Research. 85 (1): 1–19. doi:10.1007/s00426-019-01245-8. PMC 7851038. PMID 31541305.
- ^ Ishii S, Takagi S, Kobayashi N, Jitoku D, Sugihara G, Takahashi H (16 March 2023). "Hyperfocus symptom and internet addiction in individuals with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder trait". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 14: 1127777. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1127777. PMC 10061009. PMID 37009127.
- ^ Worthington R, Wheeler S (January 2023). "Hyperfocus and offending behaviour: a systematic review" (PDF). The Journal of Forensic Practice. 25 (3): 185–200. doi:10.1108/JFP-01-2022-0005. ISSN 2050-8794. S2CID 258330884.
- ^ Larsson H, Anckarsater H, Råstam M, Chang Z, Lichtenstein P (January 2012). "Childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder as an extreme of a continuous trait: a quantitative genetic study of 8,500 twin pairs". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 53 (1): 73–80. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02467.x. PMID 21923806.
- ^ Lee SH, Ripke S, Neale BM, Faraone SV, Purcell SM, Perlis RH, et al. (September 2013). "Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs". Nature Genetics. 45 (9): 984–994. doi:10.1038/ng.2711. PMC 3800159. PMID 23933821.
- ^ Cecil CA, Nigg JT (November 2022). "Epigenetics and ADHD: Reflections on Current Knowledge, Research Priorities and Translational Potential". Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy. 26 (6): 581–606. doi:10.1007/s40291-022-00609-y. PMC 7613776. PMID 35933504.
- ^ Nigg JT, Sibley MH, Thapar A, Karalunas SL (December 2020). "Development of ADHD: Etiology, Heterogeneity, and Early Life Course". Annual Review of Developmental Psychology. 2 (1): 559–583. doi:10.1146/annurev-devpsych-060320-093413. PMC 8336725. PMID 34368774.
- ^ a b "APA PsycNet". psycnet.apa.org. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (Easy-to-Read)". National Institute of Mental Health. 2013. Archived from the original on 14 April 2016. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
- ^ Franke B, Michelini G, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Bilbow A, Buitelaar JK, et al. (October 2018). "Live fast, die young? A review on the developmental trajectories of ADHD across the lifespan". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 28 (10): 1059–1088. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2018.08.001. PMC 6379245. PMID 30195575.
- ^ Faraone SV, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Biederman J, Buitelaar JK, Ramos-Quiroga JA, et al. (August 2015). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder" (PDF). Nature Reviews. Disease Primers. 1: 15020. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2015.20. PMID 27189265. S2CID 7171541.
- ^ Sinopoli KJ, Schachar R, Dennis M (August 2011). "Traumatic brain injury and secondary attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: The effect of reward on inhibitory control". Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 33 (7): 805–819. doi:10.1080/13803395.2011.562864. ISSN 1380-3395. PMC 3184364. PMID 21598155.
- ^ a b "The Connection between Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Therapeutic Approaches". Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ Eme R (April 2012). "ADHD: an integration with pediatric traumatic brain injury". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 12 (4): 475–483. doi:10.1586/ern.12.15. PMID 22449218. S2CID 35718630.
- ^ Gerring JP, Brady KD, Chen A, Vasa R, Grados M, Bandeen-Roche KJ, et al. (1998). "Premorbid Prevalence of ADHD and Development of Secondary ADHD After Closed Head Injury". Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 37 (6): 647–654. doi:10.1097/00004583-199806000-00015.
- ^ Faraone SV, Larsson H (April 2019). "Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". Molecular Psychiatry. 24 (4): 562–575. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0. PMC 6477889. PMID 29892054.
- ^ Kennedy M, Kreppner J, Knights N, Kumsta R, Maughan B, Golm D, et al. (October 2016). "Early severe institutional deprivation is associated with a persistent variant of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: clinical presentation, developmental continuities and life circumstances in the English and Romanian Adoptees study". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 57 (10): 1113–1125. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12576. PMC 5042050. PMID 27264475.
- ^ Faraone SV, Biederman J (July 2016). "Can Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Onset Occur in Adulthood?". JAMA Psychiatry. 73 (7): 655–656. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0400. PMID 27191055.
- ^ a b "Facts About ADHD". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 6 January 2016. Archived from the original on 22 March 2016. Retrieved 20 March 2016.
- ^ a b "Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder". National Institute of Mental Health. September 2023. Retrieved 2 January 2024.
- ^ a b "Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Adults: What You Need to Know". National Institute of Mental Health. Retrieved 2 January 2024.
- ^ Dobie C, et al. (March 2012). "Diagnosis and management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in primary care for school-age children and adolescents". National Guideline Clearinghous. p. 79. Archived from the original on 1 March 2013. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- ^ a b Ramsay JR (2007). Cognitive behavioral therapy for adult ADHD. Routledge. pp. 4, 25–26. ISBN 978-0-415-95501-0.
- ^ Epstein JN, Loren RE (October 2013). "Changes in the Definition of ADHD in DSM-5: Subtle but Important". Neuropsychiatry. 3 (5): 455–458. doi:10.2217/npy.13.59. PMC 3955126. PMID 24644516.
- ^ Gershon J (January 2002). "A meta-analytic review of gender differences in ADHD". Journal of Attention Disorders. 5 (3): 143–154. doi:10.1177/108705470200500302. PMID 11911007. S2CID 8076914.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Kooij SJ, Bejerot S, Blackwell A, Caci H, Casas-Brugué M, Carpentier PJ, et al. (September 2010). "European consensus statement on diagnosis and treatment of adult ADHD: The European Network Adult ADHD". BMC Psychiatry. 10 (67): 67. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-10-67. PMC 2942810. PMID 20815868.
- ^ Carpenter Rich E, Loo SK, Yang M, Dang J, Smalley SL (July 2009). "Social functioning difficulties in ADHD: association with PDD risk". Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 14 (3): 329–344. doi:10.1177/1359104508100890. PMC 2827258. PMID 19515751.
- ^ Coleman WL (August 2008). "Social competence and friendship formation in adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Adolescent Medicine. 19 (2): 278–99, x. PMID 18822833.
- ^ "ADHD Anger Management Directory". Webmd.com. Archived from the original on 5 November 2013. Retrieved 17 January 2014.
- ^ a b c "F90 Hyperkinetic disorders". International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision. World Health Organisation. 2010. Archived from the original on 2 November 2014. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- ^ Bellani M, Moretti A, Perlini C, Brambilla P (December 2011). "Language disturbances in ADHD". Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences. 20 (4): 311–315. doi:10.1017/S2045796011000527. PMID 22201208.
- ^ Racine MB, Majnemer A, Shevell M, Snider L (April 2008). "Handwriting performance in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)". Journal of Child Neurology. 23 (4): 399–406. doi:10.1177/0883073807309244. PMID 18401033. S2CID 206546871.
- ^ Peterson RL, Pennington BF (May 2012). "Developmental dyslexia". Lancet. 379 (9830): 1997–2007. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60198-6. PMC 3465717. PMID 22513218.
- ^ Sexton CC, Gelhorn HL, Bell JA, Classi PM (November 2012). "The co-occurrence of reading disorder and ADHD: epidemiology, treatment, psychosocial impact, and economic burden". Journal of Learning Disabilities. 45 (6): 538–564. doi:10.1177/0022219411407772. PMID 21757683. S2CID 385238.
- ^ Nicolson RI, Fawcett AJ (January 2011). "Dyslexia, dysgraphia, procedural learning and the cerebellum". Cortex; A Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior. 47 (1): 117–127. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2009.08.016. PMID 19818437. S2CID 32228208.
- ^ "Dyslexia and ADHD". Archived from the original on 21 February 2023. Retrieved 19 May 2022.
- ^ a b Walitza S, Drechsler R, Ball J (August 2012). "[The school child with ADHD]" [The school child with ADHD]. Therapeutische Umschau (in German). 69 (8): 467–473. doi:10.1024/0040-5930/a000316. PMID 22851461.
- ^ Young S, Hollingdale J, Absoud M, Bolton P, Branney P, Colley W, et al. (May 2020). "Guidance for identification and treatment of individuals with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder based upon expert consensus". BMC Medicine. 18 (1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 146. doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01585-y. PMC 7247165. PMID 32448170.
- ^ a b c "ADHD Symptoms". nhs.uk. 20 October 2017. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 15 May 2018.
- ^ a b Bailey E (5 September 2007). "ADHD and Learning Disabilities: How can you help your child cope with ADHD and subsequent Learning Difficulties? There is a way". Remedy Health Media, LLC. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 15 November 2013.
- ^ Krull KR (5 December 2007). "Evaluation and diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children". Uptodate. Wolters Kluwer Health. Archived from the original on 5 June 2009. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
- ^ Hofvander B, Ossowski D, Lundström S, Anckarsäter H (2009). "Continuity of aggressive antisocial behavior from childhood to adulthood: The question of phenotype definition". International Journal of Law and Psychiatry. 32 (4): 224–234. doi:10.1016/j.ijlp.2009.04.004. PMID 19428109. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ Rubia K (June 2011). ""Cool" inferior frontostriatal dysfunction in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder versus "hot" ventromedial orbitofrontal-limbic dysfunction in conduct disorder: a review". Biological Psychiatry. 69 (12). Elsevier BV/The Society of Biological Psychiatry: e69–e87. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.023. PMID 21094938. S2CID 14987165.
- ^ a b Wilens TE, Spencer TJ (September 2010). "Understanding attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder from childhood to adulthood". Postgraduate Medicine. 122 (5): 97–109. doi:10.3810/pgm.2010.09.2206. PMC 3724232. PMID 20861593.
- ^ Baud P, Perroud N, Aubry JM (June 2011). "[Bipolar disorder and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: differential diagnosis or comorbidity]". Revue Médicale Suisse (in French). 7 (297): 1219–1222. doi:10.53738/REVMED.2011.7.297.1219. PMID 21717696.
- ^ Wilens TE, Morrison NR (July 2011). "The intersection of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and substance abuse". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 24 (4): 280–285. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e328345c956. PMC 3435098. PMID 21483267.
- ^ Corkum P, Davidson F, Macpherson M (June 2011). "A framework for the assessment and treatment of sleep problems in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Pediatric Clinics of North America. 58 (3): 667–683. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2011.03.004. PMID 21600348.
- ^ Tsai MH, Huang YS (May 2010). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and sleep disorders in children". The Medical Clinics of North America. 94 (3): 615–632. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2010.03.008. PMID 20451036.
- ^ Bendz LM, Scates AC (January 2010). "Melatonin treatment for insomnia in pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 44 (1): 185–191. doi:10.1345/aph.1M365. PMID 20028959. S2CID 207263711.
- ^ Merino-Andreu M (March 2011). "[Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and restless legs syndrome in children]" [Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and restless legs syndrome in children]. Revista de Neurologia (in Spanish). 52 (Suppl 1): S85–S95. doi:10.33588/rn.52S01.2011037. PMID 21365608.
- ^ Picchietti MA, Picchietti DL (August 2010). "Advances in pediatric restless legs syndrome: Iron, genetics, diagnosis and treatment". Sleep Medicine. 11 (7): 643–651. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2009.11.014. PMID 20620105.
- ^ Karroum E, Konofal E, Arnulf I (2008). "[Restless-legs syndrome]". Revue Neurologique (in French). 164 (8–9): 701–721. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2008.06.006. PMID 18656214.
- ^ Wajszilber D, Santiseban JA, Gruber R (December 2018). "Sleep disorders in patients with ADHD: impact and management challenges". Nature and Science of Sleep. 10: 453–480. doi:10.2147/NSS.S163074. PMC 6299464. PMID 30588139.
- ^ Long Y, Pan N, Ji S, Qin K, Chen Y, Zhang X, et al. (September 2022). "Distinct brain structural abnormalities in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and substance use disorders: A comparative meta-analysis". Translational Psychiatry. 12 (1): 368. doi:10.1038/s41398-022-02130-6. PMC 9448791. PMID 36068207.
- ^ a b c National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (2009). "Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder". Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management of ADHD in Children, Young People and Adults. NICE Clinical Guidelines. Vol. 72. Leicester: British Psychological Society. pp. 18–26, 38. ISBN 978-1-85433-471-8. Archived from the original on 13 January 2016 – via NCBI Bookshelf.
- ^ Storebø OJ, Rasmussen PD, Simonsen E (February 2016). "Association Between Insecure Attachment and ADHD: Environmental Mediating Factors" (PDF). Journal of Attention Disorders. 20 (2): 187–196. doi:10.1177/1087054713501079. PMID 24062279. S2CID 23564305. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ Becker SP, Willcutt EG, Leopold DR, Fredrick JW, Smith ZR, Jacobson LA, et al. (June 2023). "Report of a Work Group on Sluggish Cognitive Tempo: Key Research Directions and a Consensus Change in Terminology to Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 62 (6): 629–645. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2022.07.821. PMC 9943858. PMID 36007816.
- ^ Barkley RA (January 2014). "Sluggish cognitive tempo (concentration deficit disorder?): current status, future directions, and a plea to change the name" (PDF). Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 42 (1): 117–125. doi:10.1007/s10802-013-9824-y. PMID 24234590. S2CID 8287560. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 August 2017.
- ^ Nazar BP, Bernardes C, Peachey G, Sergeant J, Mattos P, Treasure J (December 2016). "The risk of eating disorders comorbid with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis". The International Journal of Eating Disorders. 49 (12): 1045–1057. doi:10.1002/eat.22643. PMID 27859581. S2CID 38002526. Archived from the original on 8 December 2022. Retrieved 26 October 2022.
- ^ Schneider M, VanOrmer J, Zlomke K (2019). "Adverse Childhood Experiences and Family Resilience Among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder". Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics. 40 (8): 573–580. doi:10.1097/DBP.0000000000000703. PMID 31335581. S2CID 198193637.
- ^ Moon DS, Bong SJ, Kim BN, Kang NR (January 2021). "Association between Maternal Adverse Childhood Experiences and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in the Offspring: The Mediating Role of Antepartum Health Risks". Soa--Ch'ongsonyon Chongsin Uihak = Journal of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 32 (1): 28–34. doi:10.5765/jkacap.200041. PMC 7788667. PMID 33424239.
- ^ Ford JD, Connor DF (1 June 2009). "ADHD and post-traumatic stress disorder". Current Attention Disorders Reports. 1 (2): 60–66. doi:10.1007/s12618-009-0009-0. ISSN 1943-457X. S2CID 145508751.
- ^ Harrington KM, Miller MW, Wolf EJ, Reardon AF, Ryabchenko KA, Ofrat S (August 2012). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder comorbidity in a sample of veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder". Comprehensive Psychiatry. 53 (6): 679–690. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2011.12.001. PMC 6519447. PMID 22305866.
- ^ a b Szymanski K, Sapanski L, Conway F (1 January 2011). "Trauma and ADHD – Association or Diagnostic Confusion? A Clinical Perspective". Journal of Infant, Child, and Adolescent Psychotherapy. 10 (1). Philadelphia PA: Taylor & Francis Group: 51–59. doi:10.1080/15289168.2011.575704. eISSN 1940-9214. ISSN 1528-9168. S2CID 144348893.
- ^ Zhang N, Gao M, Yu J, Zhang Q, Wang W, Zhou C, et al. (October 2022). "Understanding the association between adverse childhood experiences and subsequent attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies". Brain and Behavior. 12 (10): e32748. doi:10.1002/brb3.2748. PMC 9575611. PMID 36068993.
- ^ Nguyen MN, Watanabe-Galloway S, Hill JL, Siahpush M, Tibbits MK, Wichman C (June 2019). "Ecological model of school engagement and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in school-aged children". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 28 (6): 795–805. doi:10.1007/s00787-018-1248-3. PMID 30390147. S2CID 53263217.
- ^ Miodus S, Allwood MA, Amoh N (5 January 2021). "Childhood ADHD Symptoms in Relation to Trauma Exposure and PTSD Symptoms Among College Students: Attending to and Accommodating Trauma". Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders. 29 (3): 187–196. doi:10.1177/1063426620982624. ISSN 1063-4266. S2CID 234159064.
- ^ "Is It ADHD or Trauma?". Child Mind Institute. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
- ^ Williams AE, Giust JM, Kronenberger WG, Dunn DW (2016). "Epilepsy and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: links, risks, and challenges". Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 12: 287–296. doi:10.2147/NDT.S81549. PMC 4755462. PMID 26929624.
- ^ Silva RR, Munoz DM, Alpert M (March 1996). "Carbamazepine use in children and adolescents with features of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 35 (3): 352–358. doi:10.1097/00004583-199603000-00017. PMID 8714324.
- ^ Instanes JT, Klungsøyr K, Halmøy A, Fasmer OB, Haavik J (February 2018). "Adult ADHD and Comorbid Somatic Disease: A Systematic Literature Review". Journal of Attention Disorders (Systematic Review). 22 (3): 203–228. doi:10.1177/1087054716669589. PMC 5987989. PMID 27664125.
- ^ Gaur S (May 2022). "The Association between ADHD and Celiac Disease in Children". Children. 9 (6). MDPI: 781. doi:10.3390/children9060781. PMC 9221618. PMID 35740718.
- ^ Hsu TW, Chen MH, Chu CS, Tsai SJ, Bai YM, Su TP, et al. (May 2022). "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and risk of migraine: A nationwide longitudinal study". Headache. 62 (5): 634–641. doi:10.1111/head.14306. PMID 35524451. S2CID 248553863.
- ^ Salem H, Vivas D, Cao F, Kazimi IF, Teixeira AL, Zeni CP (March 2018). "ADHD is associated with migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 27 (3). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 267–277. doi:10.1007/s00787-017-1045-4. PMID 28905127. S2CID 3949012.
- ^ Pan PY, Jonsson U, Şahpazoğlu Çakmak SS, Häge A, Hohmann S, Nobel Norrman H, et al. (January 2022). "Headache in ADHD as comorbidity and a side effect of medications: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Psychological Medicine. 52 (1). Cambridge University Press: 14–25. doi:10.1017/s0033291721004141. PMC 8711104. PMID 34635194.
- ^ Cannon Homaei S, Barone H, Kleppe R, Betari N, Reif A, Haavik J (January 2022). "ADHD symptoms in neurometabolic diseases: Underlying mechanisms and clinical implications". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 132: 838–856. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.11.012. PMID 34774900. S2CID 243983688.
- ^ Brunkhorst-Kanaan N, Libutzki B, Reif A, Larsson H, McNeill RV, Kittel-Schneider S (June 2021). "ADHD and accidents over the life span - A systematic review". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 125. Elsevier: 582–591. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.02.002. PMID 33582234. S2CID 231885131.
- ^ Vaa T (January 2014). "ADHD and relative risk of accidents in road traffic: a meta-analysis". Accident; Analysis and Prevention. 62. Elsevier: 415–425. doi:10.1016/j.aap.2013.10.003. hdl:11250/2603537. PMID 24238842.
- ^ "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)". nhs.uk. 1 June 2018. Retrieved 16 February 2024.
- ^ González-Bueso V, Santamaría JJ, Fernández D, Merino L, Montero E, Ribas J (2018). "Association between Internet Gaming Disorder or Pathological Video-Game Use and Comorbid Psychopathology: A Comprehensive Review". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 15 (4). MDPI: 668. doi:10.3390/ijerph15040668. PMC 5923710. PMID 29614059.
- ^ Beyens I, Valkenburg PM, Piotrowski JT (2 October 2018). "Screen media use and ADHD-related behaviors: Four decades of research". PNAS USA. 115 (40). National Academy of Sciences: 9875–9881. Bibcode:2018PNAS..115.9875B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1611611114. PMC 6176582. PMID 30275318.
- ^ de Francisco Carvalho L, Sette CP, Ferrari BL (2018). "Problematic smartphone use relationship with pathological personality traits: Systematic review and meta-analysis". Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace. 12 (3). Masaryk University: 5. doi:10.5817/CP2018-3-5.
- ^ Li Y, Li G, Liu L, Wu H (2020). "Correlations between mobile phone addiction and anxiety, depression, impulsivity, and poor sleep quality among college students: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Journal of Behavioral Addictions. 9 (3). Akadémiai Kiadó: 551–571. doi:10.1556/2006.2020.00057. PMC 8943681. PMID 32903205.
- ^ Dullur P, Krishnan V, Diaz AM (2021). "A systematic review on the intersection of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and gaming disorder". Journal of Psychiatric Research. 133. Elsevier: 212–222. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.12.026. PMID 33360866. S2CID 229687229.
- ^ Gao X, Zhang M, Yang Z, Wen M, Huang H, Zheng R, et al. (2021). "Structural and Functional Brain Abnormalities in Internet Gaming Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Comparative Meta-Analysis". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 12. Frontiers Media: 679437. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2021.679437. PMC 8281314. PMID 34276447.
- ^ Eirich R, McArthur BA, Anhorn C, McGuinness C, Christakis DA, Madigan S (2022). "Association of Screen Time With Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior Problems in Children 12 Years or Younger: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA Psychiatry. 79 (5). American Medical Association: 393–405. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.0155. PMC 8928099. PMID 35293954.
- ^ Santos RM, Mendes CG, Miranda DM, Romano-Silva MA (2022). "The Association between Screen Time and Attention in Children: A Systematic Review". Developmental Neuropsychology. 47 (4). Routledge: 175–192. doi:10.1080/87565641.2022.2064863. PMID 35430923. S2CID 248228233.
- ^ Werling AM, Kuzhippallil S, Emery S, Walitza S, Drechsler R (2022). "Problematic use of digital media in children and adolescents with a diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder compared to controls. A meta-analysis". Journal of Behavioral Addictions. 11 (2). Akadémiai Kiadó: 305–325. doi:10.1556/2006.2022.00007. PMC 9295226. PMID 35567763.
- ^ Thorell LB, Burén J, Wiman JS, Sandberg D, Nutley SB (2022). "Longitudinal associations between digital media use and ADHD symptoms in children and adolescents: a systematic literature review". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. Springer Science+Business Media. doi:10.1007/s00787-022-02130-3. PMID 36562860.
- ^ Liu H, Chen X, Huang M, Yu X, Gan Y, Wang J, et al. (2023). "Screen time and childhood attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis". Reviews on Environmental Health. De Gruyter. doi:10.1515/reveh-2022-0262. PMID 37163581. S2CID 258591184.
- ^ Augner C, Vlasak T, Barth A (2023). "The relationship between problematic internet use and attention deficit, hyperactivity and impulsivity: A meta-analysis". Journal of Psychiatric Research. 168. Elsevier: 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.10.032. PMID 37866293. S2CID 264190691.
- ^ Koncz P, Demetrovics Z, Takacs ZK, Griffiths MD, Nagy T, Király O (2023). "The emerging evidence on the association between symptoms of ADHD and gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Clinical Psychology Review. 106. Elsevier: 102343. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2023.102343. hdl:20.500.11820/91f22260-b579-4f0b-9e81-adc063f27e9e. PMID 37883910.
- ^ Balazs J, Kereszteny A (March 2017). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and suicide: A systematic review". World Journal of Psychiatry. 7 (1): 44–59. doi:10.5498/wjp.v7.i1.44. PMC 5371172. PMID 28401048.
- ^ a b Garas P, Balazs J (21 December 2020). "Long-Term Suicide Risk of Children and Adolescents With Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder-A Systematic Review". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 11: 557909. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.557909. PMC 7779592. PMID 33408650. 557909.
- ^ a b Septier M, Stordeur C, Zhang J, Delorme R, Cortese S (August 2019). "Association between suicidal spectrum behaviors and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 103: 109–118. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.05.022. PMID 31129238. S2CID 162184004. Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ Beauchaine TP, Ben-David I, Bos M (September 2020). "ADHD, financial distress, and suicide in adulthood: A population study". Science Advances. 6 (40): eaba1551. Bibcode:2020SciA....6.1551B. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aba1551. PMC 7527218. PMID 32998893. eaba1551.
- ^ Frazier TW, Demaree HA, Youngstrom EA (July 2004). "Meta-analysis of intellectual and neuropsychological test performance in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Neuropsychology. 18 (3): 543–555. doi:10.1037/0894-4105.18.3.543. PMID 15291732. S2CID 17628705.
- ^ Mackenzie GB, Wonders E (2016). "Rethinking Intelligence Quotient Exclusion Criteria Practices in the Study of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder". Frontiers in Psychology. 7: 794. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00794. PMC 4886698. PMID 27303350.
- ^ Rommelse N, van der Kruijs M, Damhuis J, Hoek I, Smeets S, Antshel KM, et al. (December 2016). "An evidenced-based perspective on the validity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the context of high intelligence". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 71: 21–47. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.032. hdl:2066/163023. PMID 27590827. S2CID 6698847.
- ^ Bridgett DJ, Walker ME (March 2006). "Intellectual functioning in adults with ADHD: a meta-analytic examination of full scale IQ differences between adults with and without ADHD". Psychological Assessment. 18 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.18.1.1. PMID 16594807.
- ^ Biederman J (June 2005). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a selective overview". Biological Psychiatry. 57 (11): 1215–1220. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.10.020. PMID 15949990. S2CID 23671547.
- ^ Faraone SV, Larsson H (April 2019). "Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". Molecular Psychiatry. 24 (4): 562–575. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0. PMC 6477889. PMID 29892054. S2CID 47016805.
- ^ "APA PsycNet". psycnet.apa.org. Retrieved 12 January 2024.
- ^ Demontis D, Walters RK, Martin J, Mattheisen M, Als TD, Agerbo E, et al. (January 2019). "Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Nature Genetics. 51 (1): 63–75. doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0269-7. hdl:10023/20827. PMC 6481311. PMID 30478444.
- ^ "Intergenerational transmission of ADHD behaviors: More evidence for heritability than life history theor". europepmc.org. 2022. Retrieved 12 January 2024.
- ^ a b c d Grimm O, Kranz TM, Reif A (February 2020). "Genetics of ADHD: What Should the Clinician Know?". Current Psychiatry Reports. 22 (4): 18. doi:10.1007/s11920-020-1141-x. PMC 7046577. PMID 32108282.
- ^ Larsson H, Chang Z, D'Onofrio BM, Lichtenstein P (July 2014). "The heritability of clinically diagnosed attention deficit hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan". Psychological Medicine. 44 (10): 2223–2229. doi:10.1017/S0033291713002493. hdl:10616/41709. PMC 4071160. PMID 24107258.
- ^ [131][132][133][134][135][136]
- ^ Cederlöf M, Ohlsson Gotby A, Larsson H, Serlachius E, Boman M, Långström N, et al. (January 2014). "Klinefelter syndrome and risk of psychosis, autism and ADHD". Journal of Psychiatric Research. 48 (1): 128–130. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.10.001. PMID 24139812.
- ^ Biederman J, Spencer T (November 1999). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as a noradrenergic disorder". Biological Psychiatry. 46 (9). Elsevier: 1234–1242. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00192-4. PMID 10560028. S2CID 45497168.
- ^ Faraone SV, Larsson H (April 2019). "Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". Molecular Psychiatry. 24 (4). Nature Research: 562–575. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0. PMC 6477889. PMID 29892054.
- ^ Baron-Cohen S (June 2002). "The extreme male brain theory of autism". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 6 (6). Elsevier: 248–254. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(02)01904-6. PMID 12039606. S2CID 8098723. Archived from the original on 3 July 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2020.
- ^ Nesse RM (2005). "32. Evolutionary Psychology and Mental Health". In Buss DM (ed.). The Handbook of Evolutionary Psychology (1st ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. p. 918. ISBN 978-0-471-26403-3.
- ^ Nesse RM (2016) [2005]. "43. Evolutionary Psychology and Mental Health". In Buss DM (ed.). The Handbook of Evolutionary Psychology, Volume 2: Integrations (2nd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. p. 1019. ISBN 978-1-118-75580-8.
- ^ Esteller-Cucala P, Maceda I, Børglum AD, Demontis D, Faraone SV, Cormand B, et al. (May 2020). "Genomic analysis of the natural history of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using Neanderthal and ancient Homo sapiens samples". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 8622. Bibcode:2020NatSR..10.8622E. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-65322-4. PMC 7248073. PMID 32451437.
- ^ "APA PsycNet". psycnet.apa.org. Retrieved 5 March 2024.
- ^ "APA PsycNet". psycnet.apa.org. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ Faraone SV, Larsson H (April 2019). "Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". Molecular Psychiatry. 24 (4). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 562–575. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0070-0. PMC 6477889. PMID 29892054.
- ^ Nolen-Hoeksema S (2013). Abnormal Psychology (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education. p. 267. ISBN 978-0-07-803538-8.
- ^ Skoglund C, Chen Q, D'Onofrio BM, Lichtenstein P, Larsson H (January 2014). "Familial confounding of the association between maternal smoking during pregnancy and ADHD in offspring". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 55 (1): 61–68. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12124. PMC 4217138. PMID 25359172.
- ^ Obel C, Zhu JL, Olsen J, Breining S, Li J, Grønborg TK, et al. (April 2016). "The risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children exposed to maternal smoking during pregnancy - a re-examination using a sibling design". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 57 (4): 532–537. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12478. PMID 26511313.
- ^ Biederman J (June 2005). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a selective overview". Biological Psychiatry. 57 (11): 1215–1220. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.10.020. PMID 15949990.
- ^ Hinshaw SP (May 2018). "Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Controversy, Developmental Mechanisms, and Multiple Levels of Analysis". Annual Review of Clinical Psychology. 14 (1): 291–316. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050817-084917. PMID 29220204.
- ^ Kebir O, Joober R (December 2011). "Neuropsychological endophenotypes in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review of genetic association studies". European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 261 (8): 583–594. doi:10.1007/s00406-011-0207-5. PMID 21409419. S2CID 21383749.
- ^ a b Berry MD (January 2007). "The potential of trace amines and their receptors for treating neurological and psychiatric diseases". Reviews on Recent Clinical Trials. 2 (1): 3–19. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.329.563. doi:10.2174/157488707779318107. PMID 18473983.
Although there is little direct evidence, changes in trace amines, in particular PE, have been identified as a possible factor for the onset of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). ... Further, amphetamines, which have clinical utility in ADHD, are good ligands at trace amine receptors. Of possible relevance in this aspect is modafanil, which has shown beneficial effects in ADHD patients and has been reported to enhance the activity of PE at TAAR1. Conversely, methylphenidate, ...showed poor efficacy at the TAAR1 receptor. In this respect it is worth noting that the enhancement of functioning at TAAR1 seen with modafanil was not a result of a direct interaction with TAAR1.
- ^ Sotnikova TD, Caron MG, Gainetdinov RR (August 2009). "Trace amine-associated receptors as emerging therapeutic targets". Molecular Pharmacology. 76 (2): 229–235. doi:10.1124/mol.109.055970. PMC 2713119. PMID 19389919.
- ^ Gizer IR, Ficks C, Waldman ID (July 2009). "Candidate gene studies of ADHD: a meta-analytic review". Human Genetics. 126 (1): 51–90. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0694-x. PMID 19506906. S2CID 166017.
- ^ Arcos-Burgos M, Muenke M (November 2010). "Toward a better understanding of ADHD: LPHN3 gene variants and the susceptibility to develop ADHD". Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders. 2 (3): 139–147. doi:10.1007/s12402-010-0030-2. PMC 3280610. PMID 21432600.
- ^ Nikolaidis A, Gray JR (June 2010). "ADHD and the DRD4 exon III 7-repeat polymorphism: an international meta-analysis". Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. 5 (2–3): 188–193. doi:10.1093/scan/nsp049. PMC 2894686. PMID 20019071.
- ^ a b Zayats T, Neale BM (12 February 2020). "Recent advances in understanding of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): how genetics are shaping our conceptualization of this disorder". F1000Research. 8: 2060. doi:10.12688/f1000research.18959.2. PMC 6896240. PMID 31824658.
- ^ a b c d e Sonuga-Barke EJ, Brandeis D, Cortese S, Daley D, Ferrin M, Holtmann M, et al. (March 2013). "Nonpharmacological interventions for ADHD: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials of dietary and psychological treatments". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 170 (3): 275–289. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12070991. eISSN 1535-7228. LCCN 22024537. OCLC 1480183. PMID 23360949. S2CID 434310.
Free fatty acid supplementation and artificial food color exclusions appear to have beneficial effects on ADHD symptoms, although the effect of the former are small and those of the latter may be limited to ADHD patients with food sensitivities...
- ^ CDC (16 March 2016). "Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 14 April 2016. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
- ^ Burger PH, Goecke TW, Fasching PA, Moll G, Heinrich H, Beckmann MW, et al. (September 2011). "[How does maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy affect the development of attention deficit/hyperactivity syndrome in the child]" [How does maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy affect the development of attention deficit/hyperactivity syndrome in the child]. Fortschritte der Neurologie-Psychiatrie (Review) (in German). 79 (9): 500–506. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1273360. PMID 21739408. S2CID 140766296.
- ^ Eubig PA, Aguiar A, Schantz SL (December 2010). "Lead and PCBs as risk factors for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Environmental Health Perspectives (Review. Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural. Research Support, U.S. Gov't, Non-P.H.S.). 118 (12): 1654–1667. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901852. PMC 3002184. PMID 20829149.
- ^ de Cock M, Maas YG, van de Bor M (August 2012). "Does perinatal exposure to endocrine disruptors induce autism spectrum and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders? Review". Acta Paediatrica (Review. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't). 101 (8): 811–818. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2012.02693.x. PMID 22458970. S2CID 41748237.
- ^ Abbott LC, Winzer-Serhan UH (April 2012). "Smoking during pregnancy: lessons learned from epidemiological studies and experimental studies using animal models". Critical Reviews in Toxicology (Review). 42 (4): 279–303. doi:10.3109/10408444.2012.658506. PMID 22394313. S2CID 38886526.
- ^ Tiesler CM, Heinrich J (October 2014). "Prenatal nicotine exposure and child behavioural problems". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 23 (10): 913–929. doi:10.1007/s00787-014-0615-y. PMC 4186967. PMID 25241028.
- ^ Botting N, Powls A, Cooke RW, Marlow N (November 1997). "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders and other psychiatric outcomes in very low birthweight children at 12 years". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 38 (8): 931–941. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01612.x. PMID 9413793. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 22 March 2022.
- ^ Thapar A, Cooper M, Jefferies R, Stergiakouli E (March 2012). "What causes attention deficit hyperactivity disorder?". Archives of Disease in Childhood (Review. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't). 97 (3): 260–265. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2011-300482. PMC 3927422. PMID 21903599.
- ^ Millichap JG (February 2008). "Etiologic classification of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Pediatrics (Review). 121 (2): e358–e365. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-1332. PMID 18245408. S2CID 24339363.
- ^ Eme R (April 2012). "ADHD: an integration with pediatric traumatic brain injury". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics (Review). 12 (4): 475–483. doi:10.1586/ern.12.15. PMID 22449218. S2CID 35718630.
- ^ a b c d Mayes R, Bagwell C, Erkulwater JL (2009). Medicating Children: ADHD and Pediatric Mental Health (illustrated ed.). Harvard University Press. pp. 4–24. ISBN 978-0-674-03163-0.
- ^ a b Millichap JG, Yee MM (February 2012). "The diet factor in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Pediatrics. 129 (2): 330–337. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2199. PMID 22232312. S2CID 14925322. Archived from the original on 11 September 2015.
- ^ Tomaska LD, Brooke-Taylor S (2014). "Food Additives – General". In Motarjemi Y, Moy GG, Todd EC (eds.). Encyclopedia of Food Safety. Vol. 3 (1st ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier/Academic Press. pp. 449–54. ISBN 978-0-12-378613-5. OCLC 865335120.
- ^ "Background Document for the Food Advisory Committee: Certified Color Additives in Food and Possible Association with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. March 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 November 2015.
- ^ a b Nigg JT, Holton K (October 2014). "Restriction and elimination diets in ADHD treatment". Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America (Review). 23 (4): 937–953. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2014.05.010. PMC 4322780. PMID 25220094.
an elimination diet produces a small aggregate effect but may have greater benefit among some children. Very few studies enable proper evaluation of the likelihood of response in children with ADHD who are not already preselected based on prior diet response.
- ^ Holland J, Sayal K (November 2019). "Relative age and ADHD symptoms, diagnosis and medication: a systematic review". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 28 (11): 1417–1429. doi:10.1007/s00787-018-1229-6. PMC 6800871. PMID 30293121.
- ^ Parritz R (2013). Disorders of Childhood: Development and Psychopathology. Cengage Learning. pp. 151. ISBN 978-1-285-09606-3.
- ^ Stockman JA (2016). Year Book of Pediatrics 2014 E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 163. ISBN 978-0-323-26527-0. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ "Mental health of children and adolescents" (PDF). WHO Europe. 15 January 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 October 2009. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ a b c d National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (2009). Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management of ADHD in Children, Young People and Adults. NICE Clinical Guidelines. Vol. 72. Leicester: British Psychological Society. ISBN 978-1-85433-471-8. Archived from the original on 13 January 2016 – via NCBI Bookshelf.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapters 10 and 13". In Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 266, 315, 318–323. ISBN 978-0-07-148127-4.
Early results with structural MRI show thinning of the cerebral cortex in ADHD subjects compared with age-matched controls in prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex, areas involved in working memory and attention.
- ^ a b c Chandler DJ, Waterhouse BD, Gao WJ (May 2014). "New perspectives on catecholaminergic regulation of executive circuits: evidence for independent modulation of prefrontal functions by midbrain dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons". Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 8: 53. doi:10.3389/fncir.2014.00053. PMC 4033238. PMID 24904299.
- ^ a b c Castellanos FX, Proal E (January 2012). "Large-scale brain systems in ADHD: beyond the prefrontal-striatal model". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 16 (1): 17–26. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2011.11.007. PMC 3272832. PMID 22169776.
Recent conceptualizations of ADHD have taken seriously the distributed nature of neuronal processing. Most of the candidate networks have focused on prefrontal-striatal-cerebellar circuits, although other posterior regions are also being proposed.
- ^ a b c Cortese S, Kelly C, Chabernaud C, Proal E, Di Martino A, Milham MP, et al. (October 2012). "Toward systems neuroscience of ADHD: a meta-analysis of 55 fMRI studies". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 169 (10): 1038–1055. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11101521. eISSN 1535-7228. LCCN 22024537. OCLC 1480183. PMC 3879048. PMID 22983386.
- ^ Krain AL, Castellanos FX (August 2006). "Brain development and ADHD". Clinical Psychology Review. 26 (4): 433–444. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2006.01.005. PMID 16480802.
- ^ Hoogman M, Bralten J, Hibar DP, Mennes M, Zwiers MP, Schweren LS, et al. (April 2017). "Subcortical brain volume differences in participants with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adults: a cross-sectional mega-analysis". The Lancet. Psychiatry. 4 (4): 310–319. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(17)30049-4. PMC 5933934. PMID 28219628.
- ^ Douglas PK, Gutman B, Anderson A, Larios C, Lawrence KE, Narr K, et al. (February 2018). "Hemispheric brain asymmetry differences in youths with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". NeuroImage. Clinical. 18: 744–752. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2018.02.020. PMC 5988460. PMID 29876263.
- ^ Damiani S, Tarchi L, Scalabrini A, Marini S, Provenzani U, Rocchetti M, et al. (April 2021). "Beneath the surface: hyper-connectivity between caudate and salience regions in ADHD fMRI at rest". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 30 (4): 619–631. doi:10.1007/s00787-020-01545-0. hdl:2318/1755224. PMID 32385695. S2CID 218540328.
- ^ a b Tarchi L, Damiani S, Fantoni T, Pisano T, Castellini G, Politi P, et al. (December 2022). "Centrality and interhemispheric coordination are related to different clinical/behavioral factors in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state fMRI study". Brain Imaging and Behavior. 16 (6): 2526–2542. doi:10.1007/s11682-022-00708-8. PMC 9712307. PMID 35859076.
- ^ Mohamed SM, Börger NA, Geuze RH, van der Meere JJ (2015). "Brain lateralization and self-reported symptoms of ADHD in a population sample of adults: a dimensional approach". Frontiers in Psychology. 6: 1418. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01418. PMC 4585266. PMID 26441789.
- ^ Fusar-Poli P, Rubia K, Rossi G, Sartori G, Balottin U (March 2012). "Striatal dopamine transporter alterations in ADHD: pathophysiology or adaptation to psychostimulants? A meta-analysis". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 169 (3): 264–272. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11060940. eISSN 1535-7228. hdl:11577/2482784. LCCN 22024537. OCLC 1480183. PMID 22294258.
- ^ a b c Bidwell LC, McClernon FJ, Kollins SH (August 2011). "Cognitive enhancers for the treatment of ADHD". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 99 (2): 262–274. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2011.05.002. PMC 3353150. PMID 21596055.
- ^ Cortese S (September 2012). "The neurobiology and genetics of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): what every clinician should know". European Journal of Paediatric Neurology. 16 (5): 422–433. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2012.01.009. PMID 22306277.
- ^ Lesch KP, Merker S, Reif A, Novak M (June 2013). "Dances with black widow spiders: dysregulation of glutamate signalling enters centre stage in ADHD". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 23 (6): 479–491. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.07.013. PMID 22939004. S2CID 14701654.
- ^ Skodzik T, Holling H, Pedersen A (February 2017). "Long-Term Memory Performance in Adult ADHD". Journal of Attention Disorders. 21 (4): 267–283. doi:10.1177/1087054713510561. PMID 24232170. S2CID 27070077.
- ^ a b c Modesto-Lowe V, Chaplin M, Soovajian V, Meyer A (July 2013). "Are motivation deficits underestimated in patients with ADHD? A review of the literature". Postgraduate Medicine. 125 (4): 47–52. doi:10.3810/pgm.2013.07.2677. PMID 23933893. S2CID 24817804.
Behavioral studies show altered processing of reinforcement and incentives in children with ADHD. These children respond more impulsively to rewards and choose small, immediate rewards over larger, delayed incentives. Interestingly, a high intensity of reinforcement is effective in improving task performance in children with ADHD. Pharmacotherapy may also improve task persistence in these children. ... Previous studies suggest that a clinical approach using interventions to improve motivational processes in patients with ADHD may improve outcomes as children with ADHD transition into adolescence and adulthood.
- ^ B. Langguth, R. Bär, N. Wodarz, M. Wittmann, R. Laufkötter: Paradoxical reaction in ADHD. In: Deutsches Ärzteblatt international. Band 108, Nummer 31–32, August 2011, S. 541; author reply 541–541; author reply 542, (in German).doi:10.3238/arztebl.2011.0541a, PMID 21886668, PMC 3163785.
- ^ Rainer Laufkötter, Berthold Langguth, Monika Johann, Peter Eichhammer, Göran Hajak: ADHS des Erwachsenenalters und Komorbiditäten. In: psychoneuro. 31, 2005, S. 563, (in German).doi:10.1055/s-2005-923370.
- ^ Dulcan MK, Lake MB (2011). "Axis I Disorders Usually First Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood or Adolescence: Attention-Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders". Concise Guide to Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (4th illustrated ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing. pp. 34. ISBN 978-1-58562-416-4 – via Google Books.
- ^ Peterson BS, Trampush J, Brown M, Maglione M, Bolshakova M, Rozelle M, et al. (1 April 2024). "Tools for the Diagnosis of ADHD in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review". Pediatrics. 153 (4). doi:10.1542/peds.2024-065854. ISSN 0031-4005. PMID 38523599.
- ^ a b National Collaborating Centre for Mental Health (2009). "Diagnosis". Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management of ADHD in Children, Young People and Adults. NICE Clinical Guidelines. Vol. 72. Leicester: British Psychological Society. pp. 116–7, 119. ISBN 978-1-85433-471-8. Archived from the original on 13 January 2016 – via NCBI Bookshelf.
- ^ "MerckMedicus Modules: ADHD –Pathophysiology". August 2002. Archived from the original on 1 May 2010.
- ^ a b c Singh I (December 2008). "Beyond polemics: science and ethics of ADHD". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 9 (12): 957–964. doi:10.1038/nrn2514. PMID 19020513. S2CID 205504587.
- ^ Caroline SC, ed. (2010). Encyclopedia of Cross-Cultural School Psychology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 133. ISBN 978-0-387-71798-2. Archived from the original on 22 December 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2016.
- ^ Wiener JM, Dulcan MK (2004). Textbook Of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (illustrated ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing. ISBN 978-1-58562-057-9. Archived from the original on 6 May 2016. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- ^ Wolraich M, Brown L, Brown RT, DuPaul G, Earls M, Feldman HM, et al. (November 2011). "ADHD: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents". Pediatrics. 128 (5): 1007–1022. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2654. PMC 4500647. PMID 22003063.
- ^ Smith BJ, Barkley RA, Shapiro CJ (2007). "Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder". In Mash EJ, Barkley RA (eds.). Assessment of Childhood Disorders (4th ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press. pp. 53–131. ISBN 978-1-59385-493-5.
- ^ Al Rahbi HA, Al-Sabri RM, Chitme HR (April 2014). "Interventions by pharmacists in out-patient pharmaceutical care". Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 22 (2): 101–106. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2013.04.001. PMC 3950532. PMID 24648820.
- ^ Adamou M, Fullen T, Jones SL (25 August 2020). "EEG for Diagnosis of Adult ADHD: A Systematic Review With Narrative Analysis". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 11: 871. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00871. PMC 7477352. PMID 33192633.
- ^ Lenartowicz A, Loo SK (November 2014). "Use of EEG to diagnose ADHD". Current Psychiatry Reports. 16 (11): 498. doi:10.1007/s11920-014-0498-0. PMC 4633088. PMID 25234074.
- ^ "Adult ADHD: Diagnosis". CAMH. Archived from the original on 21 June 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2022.
- ^ Berger I (September 2011). "Diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: much ado about something" (PDF). The Israel Medical Association Journal. 13 (9): 571–574. PMID 21991721. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 July 2020. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ^ Steinau S (2013). "Diagnostic Criteria in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder - Changes in DSM 5". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 4: 49. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00049. PMC 3667245. PMID 23755024.
- ^ Parens E, Johnston J (January 2009). "Facts, values, and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): an update on the controversies". Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health. 3 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/1753-2000-3-1. PMC 2637252. PMID 19152690.
- ^ Szasz T (2001). "Psychiatric Medicine: Disorder". Pharmacracy: medicine and politics in America. Westport, CT: Praeger. pp. 101. ISBN 978-0-275-97196-0 – via Google Books.
Mental diseases are invented and then given a name, for example attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- ^ a b c Song P, Zha M, Yang Q, Zhang Y, Li X, Rudan I (February 2021). "The prevalence of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A global systematic review and meta-analysis". Journal of Global Health. 11. International Global Health Society: 04009. doi:10.7189/jogh.11.04009. eISSN 2047-2986. OCLC 751737736. PMC 7916320. PMID 33692893.
- ^ Culpepper L, Mattingly G (2010). "Challenges in identifying and managing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults in the primary care setting: a review of the literature". Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 12 (6): PCC.10r00951. doi:10.4088/PCC.10r00951pur. PMC 3067998. PMID 21494335.
- ^ a b c d Gentile JP, Atiq R, Gillig PM (August 2006). "Adult ADHD: Diagnosis, Differential Diagnosis, and Medication Management". Psychiatry. 3 (8): 25–30. PMC 2957278. PMID 20963192.
likelihood that the adult with ADHD has developed coping mechanisms to compensate for his or her impairment
- ^ Mohr-Jensen C, Steinhausen HC (August 2016). "A meta-analysis and systematic review of the risks associated with childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder on long-term outcome of arrests, convictions, and incarcerations". Clinical Psychology Review. 48: 32–42. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2016.05.002. PMID 27390061.
- ^ Asherson P, Agnew-Blais J (April 2019). "Annual Research Review: Does late-onset attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder exist?". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 60 (4): 333–352. doi:10.1111/jcpp.13020. PMID 30843223.
- ^ Consumer Reports, Drug Effectiveness Review Project (March 2012). "Evaluating Prescription Drugs Used to Treat: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Comparing Effectiveness, Safety, and Price" (PDF). Best Buy Drugs: 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 November 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2013.
- ^ a b Ertürk E, Wouters S, Imeraj L, Lampo A (August 2020). "Association of ADHD and Celiac Disease: What Is the Evidence? A Systematic Review of the Literature". Journal of Attention Disorders (Review). 24 (10): 1371–1376. doi:10.1177/1087054715611493. PMID 26825336. S2CID 33989148.
Up till now, there is no conclusive evidence for a relationship between ADHD and CD. Therefore, it is not advised to perform routine screening of CD when assessing ADHD (and vice versa) or to implement GFD as a standard treatment in ADHD. Nevertheless, the possibility of untreated CD predisposing to ADHD-like behavior should be kept in mind. ... It is possible that in untreated patients with CD, neurologic symptoms such as chronic fatigue, inattention, pain, and headache could predispose patients to ADHD-like behavior (mainly symptoms of inattentive type), which may be alleviated after GFD treatment.
- ^ Owens JA (October 2008). "Sleep disorders and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Current Psychiatry Reports. 10 (5): 439–444. doi:10.1007/s11920-008-0070-x. PMID 18803919. S2CID 23624443.
- ^ Walters AS, Silvestri R, Zucconi M, Chandrashekariah R, Konofal E (December 2008). "Review of the possible relationship and hypothetical links between attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and the simple sleep related movement disorders, parasomnias, hypersomnias, and circadian rhythm disorders". Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine. 4 (6): 591–600. doi:10.5664/jcsm.27356. PMC 2603539. PMID 19110891.
- ^ Lal C, Strange C, Bachman D (June 2012). "Neurocognitive impairment in obstructive sleep apnea". Chest. 141 (6): 1601–1610. doi:10.1378/chest.11-2214. PMID 22670023.
- ^ a b c Wigal SB (2009). "Efficacy and safety limitations of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder pharmacotherapy in children and adults". CNS Drugs. 23 (Suppl 1): 21–31. doi:10.2165/00023210-200923000-00004. PMID 19621975. S2CID 11340058.
- ^ a b c d Mayes R, Bagwell C, Erkulwater J (2008). "ADHD and the rise in stimulant use among children". Harvard Review of Psychiatry. 16 (3): 151–166. doi:10.1080/10673220802167782. PMID 18569037. S2CID 18481191.
- ^ a b Coghill DR, Banaschewski T, Soutullo C, Cottingham MG, Zuddas A (November 2017). "Systematic review of quality of life and functional outcomes in randomized placebo-controlled studies of medications for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 26 (11): 1283–1307. doi:10.1007/s00787-017-0986-y. PMC 5656703. PMID 28429134.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License "CC BY 4.0 Deed | Attribution 4.0 International | Creative Commons". Archived from the original on 16 October 2017. Retrieved 22 October 2022.
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License "CC BY 4.0 Deed | Attribution 4.0 International | Creative Commons". Archived from the original on 16 October 2017. Retrieved 22 October 2022.{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link). - ^ Fabiano GA, Pelham WE, Coles EK, Gnagy EM, Chronis-Tuscano A, O'Connor BC (March 2009). "A meta-analysis of behavioral treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Clinical Psychology Review. 29 (2): 129–140. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2008.11.001. PMID 19131150.
there is strong and consistent evidence that behavioral treatments are effective for treating ADHD.
- ^ Kratochvil CJ, Vaughan BS, Barker A, Corr L, Wheeler A, Madaan V (March 2009). "Review of pediatric attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder for the general psychiatrist". The Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 32 (1): 39–56. doi:10.1016/j.psc.2008.10.001. PMID 19248915.
- ^ Lopez PL, Torrente FM, Ciapponi A, Lischinsky AG, Cetkovich-Bakmas M, Rojas JI, et al. (March 2018). "Cognitive-behavioural interventions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (3): CD010840. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010840.pub2. PMC 6494390. PMID 29566425.
- ^ Evans SW, Owens JS, Bunford N (2014). "Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology. 43 (4): 527–551. doi:10.1080/15374416.2013.850700. PMC 4025987. PMID 24245813.
- ^ Van Doren J, Arns M, Heinrich H, Vollebregt MA, Strehl U, K Loo S (March 2019). "Sustained effects of neurofeedback in ADHD: a systematic review and meta-analysis". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 28 (3). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 293–305. doi:10.1007/s00787-018-1121-4. PMC 6404655. PMID 29445867.
- ^ Enriquez-Geppert S, Smit D, Pimenta MG, Arns M (May 2019). "Neurofeedback as a Treatment Intervention in ADHD: Current Evidence and Practice". Current Psychiatry Reports. 21 (6). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 46. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1021-4. PMC 6538574. PMID 31139966.
- ^ Daley D, Van Der Oord S, Ferrin M, Cortese S, Danckaerts M, Doepfner M, et al. (September 2018). "Practitioner Review: Current best practice in the use of parent training and other behavioural interventions in the treatment of children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 59 (9). Wiley: 932–947. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12825. hdl:11343/293788. PMID 29083042. S2CID 31044370. Archived from the original on 25 September 2017. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ Bjornstad G, Montgomery P (April 2005). Bjornstad GJ (ed.). "Family therapy for attention-deficit disorder or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD005042. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005042.pub2. PMID 15846741. S2CID 27339381.
- ^ Turkington C, Harris J (2009). "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)". The Encyclopedia of the Brain and Brain Disorders. Infobase Publishing. pp. 47. ISBN 978-1-4381-2703-3 – via Google Books.
- ^ Mikami AY (June 2010). "The importance of friendship for youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review. 13 (2): 181–198. doi:10.1007/s10567-010-0067-y. PMC 2921569. PMID 20490677.
- ^ Kollins SH, DeLoss DJ, Cañadas E, Lutz J, Findling RL, Keefe RS, et al. (April 2020). "A novel digital intervention for actively reducing severity of paediatric ADHD (STARS-ADHD): a randomised controlled trial". The Lancet Digital Health. 2 (4): e168–e178. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30017-0. PMID 33334505.
- ^ a b Kollins SH, Childress A, Heusser AC, Lutz J (26 March 2021). "Effectiveness of a digital therapeutic as adjunct to treatment with medication in pediatric ADHD". npj Digital Medicine. 4 (1): 58. doi:10.1038/s41746-021-00429-0. PMC 7997870. PMID 33772095.
- ^ "FDA Permits Marketing of First Game-Based Digital Therapeutic to Improve Attention Function in Children with ADHD". Food and Drug Administration. United States Food and Drug Administration. 17 June 2020. Retrieved 19 April 2024.
- ^ a b c Stamatis CA, Mercaldi C, Kollins SH (October 2023). "A Single-Arm Pivotal Trial to Assess the Efficacy of Akl-T01, a Novel Digital Intervention for Attention, in Adults Diagnosed With ADHD". Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 62 (10): S318. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2023.09.510. Retrieved 22 April 2024.
- ^ Devilbiss DM, Berridge CW (October 2008). "Cognition-enhancing doses of methylphenidate preferentially increase prefrontal cortex neuronal responsiveness". Biological Psychiatry. 64 (7): 626–635. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.04.037. PMC 2603602. PMID 18585681.
- ^ a b Schulz KP, Fan J, Bédard AC, Clerkin SM, Ivanov I, Tang CY, et al. (September 2012). "Common and unique therapeutic mechanisms of stimulant and nonstimulant treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Archives of General Psychiatry. 69 (9): 952–961. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.2053. PMID 22945622.
- ^ a b Koda K, Ago Y, Cong Y, Kita Y, Takuma K, Matsuda T (July 2010). "Effects of acute and chronic administration of atomoxetine and methylphenidate on extracellular levels of noradrenaline, dopamine and serotonin in the prefrontal cortex and striatum of mice". Journal of Neurochemistry. 114 (1): 259–270. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06750.x. PMID 20403082.
- ^ a b c Dodson WW (May 2005). "Pharmacotherapy of adult ADHD". Journal of Clinical Psychology. 61 (5): 589–606. doi:10.1002/jclp.20122. PMID 15723384.
For example, pseudoephedrine and ephedrine ... have no detectable effects on the symptoms of ADHD.
- ^ Storebø OJ, Storm MR, Pereira Ribeiro J, Skoog M, Groth C, Callesen HE, et al. (March 2023). "Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023 (3): CD009885. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009885.pub3. PMC 10042435. PMID 36971690.
- ^ a b Ruiz-Goikoetxea M, Cortese S, Aznarez-Sanado M, Magallón S, Alvarez Zallo N, Luis EO, et al. (January 2018). "Risk of unintentional injuries in children and adolescents with ADHD and the impact of ADHD medications: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 84: 63–71. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.11.007. hdl:10171/45012. PMID 29162520.
- ^ Hart H, Radua J, Nakao T, Mataix-Cols D, Rubia K (February 2013). "Meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of inhibition and attention in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: exploring task-specific, stimulant medication, and age effects". JAMA Psychiatry. 70 (2): 185–198. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.277. PMID 23247506.
- ^ Spencer TJ, Brown A, Seidman LJ, Valera EM, Makris N, Lomedico A, et al. (September 2013). "Effect of psychostimulants on brain structure and function in ADHD: a qualitative literature review of magnetic resonance imaging-based neuroimaging studies". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 74 (9): 902–917. doi:10.4088/JCP.12r08287. PMC 3801446. PMID 24107764.
- ^ Frodl T, Skokauskas N (February 2012). "Meta-analysis of structural MRI studies in children and adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder indicates treatment effects". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 125 (2): 114–126. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2011.01786.x. PMID 22118249. S2CID 25954331.
Basal ganglia regions like the right globus pallidus, the right putamen, and the nucleus caudatus are structurally affected in children with ADHD. These changes and alterations in limbic regions like ACC and amygdala are more pronounced in non-treated populations and seem to diminish over time from child to adulthood. Treatment seems to have positive effects on brain structure.
- ^ a b Cortese S, Adamo N, Del Giovane C, Mohr-Jensen C, Hayes AJ, Carucci S, et al. (September 2018). "Comparative efficacy and tolerability of medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children, adolescents, and adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis". The Lancet. Psychiatry. 5 (9): 727–738. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30269-4. PMC 6109107. PMID 30097390.
- ^ Stuhec M, Lukić P, Locatelli I (February 2019). "Efficacy, Acceptability, and Tolerability of Lisdexamfetamine, Mixed Amphetamine Salts, Methylphenidate, and Modafinil in the Treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 53 (2): 121–133. doi:10.1177/1060028018795703. PMID 30117329. S2CID 52019992.
- ^ Faraone SV, Biederman J, Roe C (October 2002). "Comparative efficacy of Adderall and methylphenidate in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 22 (5): 468–473. doi:10.1097/00004714-200210000-00005. PMID 12352269. S2CID 19726926.
- ^ Nam SH, Lim MH, Park TW (April 2022). "Stimulant Induced Movement Disorders in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder". Soa--Ch'ongsonyon Chongsin Uihak = Journal of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 33 (2): 27–34. doi:10.5765/jkacap.210034. PMC 8984208. PMID 35418800.
- ^ Wynchank D, Bijlenga D, Beekman AT, Kooij JJ, Penninx BW (October 2017). "Adult Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Insomnia: an Update of the Literature". Current Psychiatry Reports. 19 (12). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 98. doi:10.1007/s11920-017-0860-0. PMID 29086065. S2CID 38064951.
In varying percentages of trial participants, insomnia is a treatment-emergent adverse effect in triple-bead mixed amphetamine salts (40–45%), dasotraline (35–45%), lisdexamfetamine (10–19%), and extended-release methylphenidate (11%).
- ^ Shoptaw SJ, Kao U, Ling W (January 2009). Shoptaw SJ, Ali R (eds.). "Treatment for amphetamine psychosis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2009 (1): CD003026. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003026.pub3. PMC 7004251. PMID 19160215.
A minority of individuals who use amphetamines develop full-blown psychosis requiring care at emergency departments or psychiatric hospitals. In such cases, symptoms of amphetamine psychosis commonly include paranoid and persecutory delusions as well as auditory and visual hallucinations in the presence of extreme agitation. More common (about 18%) is for frequent amphetamine users to report psychotic symptoms that are sub-clinical and that do not require high-intensity intervention ...
About 5–15% of the users who develop an amphetamine psychosis fail to recover completely (Hofmann 1983) ...
Findings from one trial indicate use of antipsychotic medications effectively resolves symptoms of acute amphetamine psychosis. - ^ "Adderall XR Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Shire US Inc. December 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 December 2013. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
Treatment-emergent psychotic or manic symptoms, e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania in children and adolescents without prior history of psychotic illness or mania can be caused by stimulants at usual doses. ... In a pooled analysis of multiple short-term, placebo controlled studies, such symptoms occurred in about 0.1% (4 patients with events out of 3482 exposed to methylphenidate or amphetamine for several weeks at usual doses) of stimulant-treated patients compared to 0 in placebo-treated patients.
- ^ Mosholder AD, Gelperin K, Hammad TA, Phelan K, Johann-Liang R (February 2009). "Hallucinations and other psychotic symptoms associated with the use of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder drugs in children". Pediatrics. 123 (2): 611–616. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-0185. PMID 19171629. S2CID 22391693.
- ^ Ashton H, Gallagher P, Moore B (September 2006). "The adult psychiatrist's dilemma: psychostimulant use in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 20 (5): 602–610. doi:10.1177/0269881106061710. PMID 16478756. S2CID 32073083.
- ^ Parker J, Wales G, Chalhoub N, Harpin V (September 2013). "The long-term outcomes of interventions for the management of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials". Psychology Research and Behavior Management. 6: 87–99. doi:10.2147/PRBM.S49114. PMC 3785407. PMID 24082796.
Results suggest there is moderate-to-high-level evidence that combined pharmacological and behavioral interventions, and pharmacological interventions alone can be effective in managing the core ADHD symptoms and academic performance at 14 months. However, the effect size may decrease beyond this period. ... Only one paper examining outcomes beyond 36 months met the review criteria. ... There is high level evidence suggesting that pharmacological treatment can have a major beneficial effect on the core symptoms of ADHD (hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity) in approximately 80% of cases compared with placebo controls, in the short term.
- ^ Castells X, Blanco-Silvente L, Cunill R, et al. (Cochrane Developmental, Psychosocial and Learning Problems Group) (August 2018). "Amphetamines for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (8): CD007813. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007813.pub3. PMC 6513464. PMID 30091808.
- ^ a b Kiely B, Adesman A (June 2015). "What we do not know about ADHD… yet". Current Opinion in Pediatrics. 27 (3): 395–404. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000229. PMID 25888152. S2CID 39004402.
In addition, a consensus has not been reached on the optimal diagnostic criteria for ADHD. Moreover, the benefits and long-term effects of medical and complementary therapies for this disorder continue to be debated. These gaps in knowledge hinder the ability of clinicians to effectively recognise and treat ADHD.
- ^ Hazell P (July 2011). "The challenges to demonstrating long-term effects of psychostimulant treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 24 (4): 286–290. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e32834742db. PMID 21519262. S2CID 21998152. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- ^ Kemper AR, Maslow GR, Hill S, Namdari B, Allen Lapointe NM, Goode AP, et al. (January 2018). "Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Treatment in Children and Adolescents". Comparative Effectiveness Reviews (203). Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). PMID 29558081. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 7 November 2021.
- ^ Zhang L, Yao H, Li L, Du Rietz E, Andell P, Garcia-Argibay M, et al. (November 2022). "Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases Associated With Medications Used in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA Network Open. 5 (11): e2243597. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.43597. PMC 9685490. PMID 36416824.
- ^ Kraemer M, Uekermann J, Wiltfang J, Kis B (July 2010). "Methylphenidate-induced psychosis in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: report of 3 new cases and review of the literature". Clinical Neuropharmacology. 33 (4): 204–206. doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181e29174. PMID 20571380. S2CID 34956456.
- ^ van de Loo-Neus GH, Rommelse N, Buitelaar JK (August 2011). "To stop or not to stop? How long should medication treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder be extended?". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 21 (8): 584–599. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.03.008. PMID 21530185. S2CID 30068561.
- ^ Ibrahim K, Donyai P (July 2015). "Drug Holidays From ADHD Medication: International Experience Over the Past Four Decades". Journal of Attention Disorders. 19 (7): 551–568. doi:10.1177/1087054714548035. PMID 25253684. S2CID 19949563. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 June 2016.
- ^ a b Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 323, 368. ISBN 978-0-07-148127-4.
supervised use of stimulants at therapeutic doses may decrease risk of experimentation with drugs to self-medicate symptoms. Second, untreated ADHD may lead to school failure, peer rejection, and subsequent association with deviant peer groups that encourage drug misuse. ... amphetamines and methylphenidate are used in low doses to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and in higher doses to treat narcolepsy (Chapter 12). Despite their clinical uses, these drugs are strongly reinforcing, and their long-term use at high doses is linked with potential addiction
- ^ McDonagh MS, Christensen V, Peterson K, Thakurta S (October 2009). "Black box warnings of ADHD drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration". Drug Class Review: Pharmacologic Treatments for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Final Report Update 3 [Internet]. Portland, Oregon: Oregon Health & Science University. Appendix G: Black box warnings of ADHD drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017. Retrieved 17 January 2014 – via United States National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Potter AS, Schaubhut G, Shipman M (December 2014). "Targeting the nicotinic cholinergic system to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: rationale and progress to date". CNS Drugs. 28 (12): 1103–1113. doi:10.1007/s40263-014-0208-9. PMC 4487649. PMID 25349138.
- ^ Perrotte G, Moreira MM, de Vargas Junior A, Teixeira Filho A, Castaldelli-Maia JM (September 2023). "Effects of Caffeine on Main Symptoms in Children with ADHD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials". Brain Sciences. 13 (9): 1304. doi:10.3390/brainsci13091304. PMC 10526204. PMID 37759905.
- ^ Turner D (April 2006). "A review of the use of modafinil for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 6 (4): 455–468. doi:10.1586/14737175.6.4.455. PMID 16623645. S2CID 24293088.
- ^ Weiss M, Tannock R, Kratochvil C, Dunn D, Velez-Borras J, Thomason C, et al. (July 2005). "A randomized, placebo-controlled study of once-daily atomoxetine in the school setting in children with ADHD". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 44 (7): 647–655. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000163280.47221.c9. PMID 15968233.
- ^ Biederman J, Wigal SB, Spencer TJ, McGough JJ, Mays DA (February 2006). "A post hoc subgroup analysis of an 18-day randomized controlled trial comparing the tolerability and efficacy of mixed amphetamine salts extended release and atomoxetine in school-age girls with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Clinical Therapeutics. 28 (2): 280–293. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.02.008. PMID 16678649.
- ^ Bushe C, Day K, Reed V, Karlsdotter K, Berggren L, Pitcher A, et al. (May 2016). "A network meta-analysis of atomoxetine and osmotic release oral system methylphenidate in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adult patients". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 30 (5): 444–458. doi:10.1177/0269881116636105. PMID 27005307. S2CID 104938.
- ^ Hazell PL, Kohn MR, Dickson R, Walton RJ, Granger RE, Wyk GW (November 2011). "Core ADHD symptom improvement with atomoxetine versus methylphenidate: a direct comparison meta-analysis". Journal of Attention Disorders. 15 (8): 674–683. doi:10.1177/1087054710379737. PMID 20837981. S2CID 43503227.
- ^ Hanwella R, Senanayake M, de Silva V (November 2011). "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis". BMC Psychiatry. 11 (1): 176. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-11-176. PMC 3229459. PMID 22074258.
- ^ Rezaei G, Hosseini SA, Akbari Sari A, Olyaeemanesh A, Lotfi MH, Yassini M, et al. (10 February 2016). "Comparative efficacy of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran. 30: 325. PMC 4898838. PMID 27390695.
- ^ Faraone SV, Gomeni R, Hull JT, Busse GD, Melyan Z, O'Neal W, et al. (February 2021). "Early response to SPN-812 (viloxazine extended-release) can predict efficacy outcome in pediatric subjects with ADHD: a machine learning post-hoc analysis of four randomized clinical trials". Psychiatry Research. 296: 113664. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113664. PMID 33418457. S2CID 230716405.
- ^ Mohammadi MR, Kazemi MR, Zia E, Rezazadeh SA, Tabrizi M, Akhondzadeh S (November 2010). "Amantadine versus methylphenidate in children and adolescents with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a randomized, double-blind trial". Human Psychopharmacology. 25 (7–8): 560–565. doi:10.1002/hup.1154. PMID 21312290. S2CID 30677758.
- ^ Morrow K, Choi S, Young K, Haidar M, Boduch C, Bourgeois JA (September 2021). "Amantadine for the treatment of childhood and adolescent psychiatric symptoms". Proceedings. 34 (5): 566–570. doi:10.1080/08998280.2021.1925827. PMC 8366930. PMID 34456474.
- ^ Stuhec M, Munda B, Svab V, Locatelli I (June 2015). "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of atomoxetine, lisdexamfetamine, bupropion and methylphenidate in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis with focus on bupropion". Journal of Affective Disorders. 178: 149–159. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2015.03.006. PMID 25813457.
- ^ McDonagh MS, Peterson K, Thakurta S, Low A (December 2011). Drug Class Review: Pharmacologic Treatments for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (Report). Drug Class Reviews. United States Library of Medicine. PMID 22420008. Archived from the original on 31 August 2016.
- ^ Gurnani T, Ivanov I, Newcorn JH (February 2016). "Pharmacotherapy of Aggression in Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Disorders". Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 26 (1): 65–73. doi:10.1089/cap.2015.0167. PMID 26881859.
Several studies (e.g., Findling et al. 2000; Armenteros et al. 2007) have shown that antipsychotics, especially second generation agents, can be effective when used together with stimulants for aggression in ADHD
- ^ Childress AC, Sallee FR (March 2012). "Revisiting clonidine: an innovative add-on option for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Drugs of Today. 48 (3): 207–217. doi:10.1358/dot.2012.48.3.1750904. PMID 22462040.
- ^ Huss M, Chen W, Ludolph AG (January 2016). "Guanfacine Extended Release: A New Pharmacological Treatment Option in Europe". Clinical Drug Investigation. 36 (1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 1–25. doi:10.1007/s40261-015-0336-0. PMC 4706844. PMID 26585576.
- ^ Biederman J, Melmed RD, Patel A, McBurnett K, Konow J, Lyne A, et al. (SPD503 Study Group) (January 2008). "A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of guanfacine extended release in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Pediatrics. 121 (1): e73–e84. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-3695. PMID 18166547. S2CID 25551406.
- ^ Palumbo DR, Sallee FR, Pelham WE, Bukstein OG, Daviss WB, McDERMOTT MP (February 2008). "Clonidine for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: I. Efficacy and tolerability outcomes". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 47 (2): 180–188. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e31815d9af7. PMID 18182963.
- ^ Arnsten AF, Jin LE (2012). "Focus: Translational Medicine: Guanfacine for the Treatment of Cognitive Disorders: A Century of Discoveries at Yale - PMC". The Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine. 85 (1): 45–58. PMC 3313539. PMID 22461743.
- ^ a b c National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2019). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: diagnosis and management. NICE Guideline, No. 87. London: National Guideline Centre (UK). ISBN 978-1-4731-2830-9. OCLC 1126668845. Archived from the original on 12 January 2021. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ "Canadian ADHD Practice Guidelines" (PDF). Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2011.
- ^ Stevens JR, Wilens TE, Stern TA (2013). "Using stimulants for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: clinical approaches and challenges". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders. 15 (2). doi:10.4088/PCC.12f01472. PMC 3733520. PMID 23930227.
- ^ Young JL (20 December 2010). "Individualizing Treatment for Adult ADHD: An Evidence-Based Guideline". Medscape. Archived from the original on 8 May 2022. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
- ^ Biederman J (21 November 2003). "New-Generation Long-Acting Stimulants for the Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder". Medscape. Archived from the original on 8 May 2022. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
As most treatment guidelines and prescribing information for stimulant medications relate to experience in school-aged children, prescribed doses for older patients are lacking. Emerging evidence for both methylphenidate and Adderall indicate that when weight-corrected daily doses, equipotent with those used in the treatment of younger patients, are used to treat adults with ADHD, these patients show a very robust clinical response consistent with that observed in pediatric studies. These data suggest that older patients may require a more aggressive approach in terms of dosing, based on the same target dosage ranges that have already been established – for methylphenidate, 1–1.5–2 mg/kg/day, and for D,L-amphetamine, 0.5–0.75–1 mg/kg/day....
In particular, adolescents and adults are vulnerable to underdosing, and are thus at potential risk of failing to receive adequate dosage levels. As with all therapeutic agents, the efficacy and safety of stimulant medications should always guide prescribing behavior: careful dosage titration of the selected stimulant product should help to ensure that each patient with ADHD receives an adequate dose, so that the clinical benefits of therapy can be fully attained. - ^ Kessler S (January 1996). "Drug therapy in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder". Southern Medical Journal. 89 (1): 33–38. doi:10.1097/00007611-199601000-00005. PMID 8545689. S2CID 12798818.
- ^ Kamp CF, Sperlich B, Holmberg HC (July 2014). "Exercise reduces the symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and improves social behaviour, motor skills, strength and neuropsychological parameters". Acta Paediatrica. 103 (7): 709–714. doi:10.1111/apa.12628. PMID 24612421. S2CID 45881887.
We may conclude that all different types of exercise ... attenuate the characteristic symptoms of ADHD and improve social behaviour, motor skills, strength and neuropsychological parameters without any undesirable side effects. Available reports do not reveal which type, intensity, duration and frequency of exercise is most effective
- ^ Rommel AS, Halperin JM, Mill J, Asherson P, Kuntsi J (September 2013). "Protection from genetic diathesis in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: possible complementary roles of exercise". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 52 (9): 900–910. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.05.018. PMC 4257065. PMID 23972692.
The findings from these studies provide some support for the notion that exercise has the potential to act as a protective factor for ADHD.
- ^ a b Den Heijer AE, Groen Y, Tucha L, Fuermaier AB, Koerts J, Lange KW, et al. (February 2017). "Sweat it out? The effects of physical exercise on cognition and behavior in children and adults with ADHD: a systematic literature review". Journal of Neural Transmission. 124 (Suppl 1): 3–26. doi:10.1007/s00702-016-1593-7. PMC 5281644. PMID 27400928.
Beneficial chronic effects of cardio exercise were found on various functions as well, including executive functions, attention and behavior.
- ^ Wolraich ML, Hagan JF, Allan C, Chan E, Davison D, Earls M, et al. (October 2019). "Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents". Pediatrics. 144 (4): e20192528. doi:10.1542/peds.2019-2528. PMC 7067282. PMID 31570648.
- ^ Pelsser LM, Frankena K, Toorman J, Rodrigues Pereira R (January 2017). "Diet and ADHD, Reviewing the Evidence: A Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses of Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials Evaluating the Efficacy of Diet Interventions on the Behavior of Children with ADHD". PLOS ONE (Systematic Review). 12 (1): e0169277. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1269277P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0169277. PMC 5266211. PMID 28121994.
- ^ Konikowska K, Regulska-Ilow B, Rózańska D (2012). "The influence of components of diet on the symptoms of ADHD in children". Roczniki Panstwowego Zakladu Higieny. 63 (2): 127–134. PMID 22928358.
- ^ Arnold LE, DiSilvestro RA (August 2005). "Zinc in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 15 (4): 619–627. doi:10.1089/cap.2005.15.619. hdl:1811/51593. PMID 16190793.
- ^ Bloch MH, Mulqueen J (October 2014). "Nutritional supplements for the treatment of ADHD". Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 23 (4): 883–897. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2014.05.002. PMC 4170184. PMID 25220092.
- ^ Krause J (April 2008). "SPECT and PET of the dopamine transporter in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 8 (4): 611–625. doi:10.1586/14737175.8.4.611. PMID 18416663. S2CID 24589993.
Zinc binds at ... extracellular sites of the DAT, serving as a DAT inhibitor. In this context, controlled double-blind studies in children are of interest, which showed positive effects of zinc [supplementation] on symptoms of ADHD. It should be stated that at this time [supplementation] with zinc is not integrated in any ADHD treatment algorithm.
- ^ Bálint S, Czobor P, Mészáros A, Simon V, Bitter I (2008). "[Neuropsychological impairments in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a literature review]" [Neuropsychological impairments in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A literature review]. Psychiatria Hungarica (in Hungarian). 23 (5). Magyar Pszichiátriai Társaság: 324–335. PMID 19129549. PsycNET 2008-18348-001.
- ^ Faraone SV, Asherson P, Banaschewski T, Biederman J, Buitelaar JK, Ramos-Quiroga JA, et al. (August 2015). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Nature Reviews. Disease Primers (Review). 1: 15020. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.497.1346. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2015.20. PMID 27189265. S2CID 7171541.
- ^ McClernon FJ, Kollins SH (October 2008). "ADHD and smoking: from genes to brain to behavior". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1141 (1): 131–147. Bibcode:2008NYASA1141..131M. doi:10.1196/annals.1441.016. PMC 2758663. PMID 18991955.
- ^ a b c Willcutt EG (July 2012). "The prevalence of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analytic review". Neurotherapeutics. 9 (3): 490–499. doi:10.1007/s13311-012-0135-8. PMC 3441936. PMID 22976615.
- ^ a b c Cowen P, Harrison P, Burns T (2012). "Drugs and other physical treatments". Shorter Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry (6th ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 546. ISBN 978-0-19-960561-3 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b Faraone SV (2011). "Ch. 25: Epidemiology of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder". In Tsuang MT, Tohen M, Jones P (eds.). Textbook of Psychiatric Epidemiology (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 450. ISBN 978-0-470-97740-8. Archived from the original on 22 December 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2016.
- ^ Young S, Adamo N, Ásgeirsdóttir BB, Branney P, Beckett M, Colley W, et al. (August 2020). "Females with ADHD: An expert consensus statement taking a lifespan approach providing guidance for the identification and treatment of attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder in girls and women". BMC Psychiatry. 20 (1): 404. doi:10.1186/s12888-020-02707-9. PMC 7422602. PMID 32787804.
- ^ Crawford N (February 2003). "ADHD: a women's issue". Monitor on Psychology. 34 (2): 28. Archived from the original on 9 April 2017.
- ^ a b Emond V, Joyal C, Poissant H (April 2009). "[Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)]" [Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)]. L'Encephale (in French). 35 (2): 107–114. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2008.01.005. PMID 19393378.
- ^ [313][314][315][203]
- ^ a b Ginsberg Y, Quintero J, Anand E, Casillas M, Upadhyaya HP (2014). "Underdiagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adult patients: a review of the literature". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders. 16 (3). doi:10.4088/PCC.13r01600. PMC 4195639. PMID 25317367.
Reports indicate that ADHD affects 2.5%–5% of adults in the general population,5–8 compared with 5%–7% of children.9,10 ... However, fewer than 20% of adults with ADHD are currently diagnosed and/or treated by psychiatrists.7,15,16
- ^ Baggio S, Fructuoso A, Guimaraes M, Fois E, Golay D, Heller P, et al. (2 August 2018). "Prevalence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Detention Settings: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 9: 331. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00331. PMC 6084240. PMID 30116206.
- ^ Ginsberg Y, Hirvikoski T, Lindefors N (December 2010). "Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among longer-term prison inmates is a prevalent, persistent and disabling disorder". BMC Psychiatry. 10 (1): 112. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-10-112. PMC 3016316. PMID 21176203.
- ^ "State-based Prevalence Data of Parent Reported ADHD". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 13 February 2017. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA (June 2007). "The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 164 (6): 942–948. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.164.6.942. eISSN 1535-7228. LCCN 22024537. OCLC 1480183. PMID 17541055.
- ^ Staller J, Faraone SV (2006). "Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in girls: epidemiology and management". CNS Drugs. 20 (2): 107–123. doi:10.2165/00023210-200620020-00003. PMID 16478287. S2CID 25835322.
- ^ Whitely M, Raven M, Timimi S, Jureidini J, Phillimore J, Leo J, et al. (April 2019). "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder late birthdate effect common in both high and low prescribing international jurisdictions: a systematic review". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines. 60 (4): 380–391. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12991. PMC 7379308. PMID 30317644.
- ^ Connor DF (2011). "Problems of overdiagnosis and overprescribing in ADHD: are they legitimate?". Psychiatric Times. Vol. 28, no. 8. p. 14. Archived from the original on 12 August 2021.
- ^ a b c d "ADHD Throughout the Years" (PDF). Center For Disease Control and Prevention. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 August 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2013.
- ^ Dalsgaard S (February 2013). "Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 22 (Suppl 1): S43–S48. doi:10.1007/s00787-012-0360-z. PMID 23202886. S2CID 23349807.
- ^ Coker TR, Elliott MN, Toomey SL, Schwebel DC, Cuccaro P, Tortolero Emery S, et al. (September 2016). "Racial and Ethnic Disparities in ADHD Diagnosis and Treatment". Pediatrics. 138 (3): e20160407. doi:10.1542/peds.2016-0407. PMC 5684883. PMID 27553219.
- ^ Slobodin O, Masalha R (June 2020). "Challenges in ADHD care for ethnic minority children: A review of the current literature". Transcultural Psychiatry. 57 (3): 468–483. doi:10.1177/1363461520902885. PMID 32233772. S2CID 214768588.
- ^ Palmer ED, Finger S (May 2001). "An early description of ADHD (inattentive subtype): Dr Alexander Crichton and 'Mental restlessness' (1798)". Child and Adolescent Mental Health. 6 (2): 66–73. doi:10.1111/1475-3588.00324.
- ^ Crichton A (1976) [1798]. An inquiry into the nature and origin of mental derangement: comprehending a concise system of the physiology and pathology of the human mind and a history of the passions and their effects. United Kingdom: AMS Press. p. 271. ISBN 978-0-404-08212-3. Archived from the original on 3 April 2019. Retrieved 17 January 2014 – via Google Books.
- ^ Still G (1902). "Some Abnormal Psychical Conditions in Children: The Goulstonian Lectures". Lancet. 159: 1008–1012. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(01)74984-7.
- ^ Rafalovich A (2001). "The Conceptual History of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Idiocy, Imbecility, Encephalitis and the Child Deviant". Deviant Behavior. 22: 93–115. doi:10.1080/016396201750065009. S2CID 43445475.
- ^ Tredgold C (1908). Mental Deficiency: Amentia (1 ed.). New York: William Wood & Company. OCLC 990133. PsycNET 1908-10366-000. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- ^ Connors C (2000). "Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Historical Development and Overview". Journal of Attention Disorders: 173–191.
- ^ Millichap JG (2010). "Definition and History of ADHD". Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Handbook (2nd ed.). Springer Science. pp. 2–3. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-1397-5_1. ISBN 978-1-4419-1396-8. LCCN 2009938108. Archived from the original on 14 January 2023. Retrieved 8 May 2022 – via Google Books.
- ^ Weiss M, Hechtman LT, Weiss G (2001). "ADHD in Adulthood: An Introduction". ADHD in Adulthood: A Guide to Current Theory, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Taylor & Francis. pp. 34. ISBN 978-0-8018-6822-1 – via Google Books.
- ^ Rasmussen N (July 2006). "Making the first anti-depressant: amphetamine in American medicine, 1929-1950". Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. 61 (3): 288–323. doi:10.1093/jhmas/jrj039. PMID 16492800. S2CID 24974454.
- ^ Patrick KS, Straughn AB, Perkins JS, González MA (January 2009). "Evolution of stimulants to treat ADHD: transdermal methylphenidate". Human Psychopharmacology. 24 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1002/hup.992. PMC 2629554. PMID 19051222.
- ^ Gross MD (February 1995). "Origin of stimulant use for treatment of attention deficit disorder". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 152 (2): 298–299. doi:10.1176/ajp.152.2.298b. eISSN 1535-7228. LCCN 22024537. OCLC 1480183. PMID 7840374.
- ^ Brown W (1998). "Charles Bradley, M.D.". American Journal of Psychiatry. 155 (7): 968. doi:10.1176/ajp.155.7.968. eISSN 1535-7228. ISSN 0002-953X. LCCN 22024537. OCLC 1480183.
- ^ Biederman J, Faraone SV, Keenan K, Knee D, Tsuang MT (July 1990). "Family-genetic and psychosocial risk factors in DSM-III attention deficit disorder". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 29 (4): 526–533. doi:10.1097/00004583-199007000-00004. PMID 2387786.
- ^ Barkley R (2006). Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment. New York: Guilford. pp. 42–5. ISBN 978-1-60623-750-2. Archived from the original on 2 October 2023. Retrieved 19 July 2022.
- ^ Lahey BB, Applegate B, McBurnett K, Biederman J, Greenhill L, Hynd GW, et al. (November 1994). "DSM-IV field trials for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 151 (11): 1673–1685. doi:10.1176/ajp.151.11.1673. eISSN 1535-7228. LCCN 22024537. OCLC 1480183. PMID 7943460.
- ^ Faraone SV (February 2005). "The scientific foundation for understanding attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder as a valid psychiatric disorder". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 14 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1007/s00787-005-0429-z. PMID 15756510. S2CID 143646869.
- ^ Boseley S (30 September 2010). "Hyperactive children may have genetic disorder, says study". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 July 2017.
- ^ Cormier E (October 2008). "Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review and update". Journal of Pediatric Nursing. 23 (5): 345–357. doi:10.1016/j.pedn.2008.01.003. PMID 18804015.
- ^ Schwarz A (14 December 2013). "The Selling of Attention Deficit Disorder". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 March 2015. Retrieved 26 February 2015.
- ^ Elder TE (September 2010). "The importance of relative standards in ADHD diagnoses: evidence based on exact birth dates". Journal of Health Economics. 29 (5): 641–656. doi:10.1016/j.jhealeco.2010.06.003. PMC 2933294. PMID 20638739.
- ^ a b Ford-Jones PC (May 2015). "Misdiagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: 'Normal behaviour' and relative maturity". Paediatrics & Child Health. 20 (4): 200–202. doi:10.1093/pch/20.4.200. PMC 4443828. PMID 26038639.
- ^ Parrillo VN (2008). Encyclopedia of Social Problems. SAGE. p. 63. ISBN 978-1-4129-4165-5. Archived from the original on 4 January 2020. Retrieved 2 May 2009.
- ^ Merten EC, Cwik JC, Margraf J, Schneider S (2017). "Overdiagnosis of mental disorders in children and adolescents (in developed countries)". Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health. 11: 5. doi:10.1186/s13034-016-0140-5. PMC 5240230. PMID 28105068.
- ^ Taylor E (April 2017). "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: overdiagnosed or diagnoses missed?". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 102 (4): 376–379. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2016-310487. PMID 27821518. S2CID 19878394.
- ^ "Are We Overdiagnosing and Overtreating ADHD?" Psychiatric Times, 31 May 2019. Rahil R. Jummani, MD. , Emily Hirsch, Glenn S. Hirsch, MD.
- ^ Luan R, Mu Z, Yue F, He S (2017). "Efficacy and Tolerability of Different Interventions in Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder". Frontiers in Psychiatry. 8: 229. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00229. PMC 5694170. PMID 29180967.
- ^ Banaschewski T, Buitelaar J, Chui CS, Coghill D, Cortese S, Simonoff E, et al. (November 2016). "Methylphenidate for ADHD in children and adolescents: throwing the baby out with the bathwater". Evidence-Based Mental Health. 19 (4): 97–99. doi:10.1136/eb-2016-102461. ISSN 1468-960X. PMC 10699535. PMID 27935807.
- ^ Hoekstra PJ, Buitelaar JK (1 April 2016). "Is the evidence base of methylphenidate for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder flawed?". European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 25 (4): 339–340. doi:10.1007/s00787-016-0845-2. ISSN 1435-165X. PMID 27021055.
- ^ Banaschewski T, Gerlach M, Becker K, Holtmann M, Döpfner M, Romanos M (July 2016). "Trust, but verify. The errors and misinterpretations in the Cochrane analysis by O. J. Storebo and colleagues on the efficacy and safety of methylphenidate for the treatment of children and adolescents with ADHD". Zeitschrift für Kinder- und Jugendpsychiatrie und Psychotherapie. 44 (4): 307–314. doi:10.1024/1422-4917/a000433. ISSN 1422-4917. PMID 27270192.
- ^ Hoogman M, Stolte M, Baas M, Kroesbergen E (December 2020). "Creativity and ADHD: A review of behavioral studies, the effect of psychostimulants and neural underpinnings" (PDF). Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 119: 66–85. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.09.029. PMID 33035524. S2CID 222142805. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 September 2023. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ Catani M, Mazzarello P (June 2019). "Grey Matter Leonardo da Vinci: a genius driven to distraction". Brain. 142 (6): 1842–1846. doi:10.1093/brain/awz131. PMC 6536914. PMID 31121603.
- ^ Scassellati C, Bonvicini C, Faraone SV, Gennarelli M (October 2012). "Biomarkers and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analyses". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 51 (10): 1003–1019.e20. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2012.08.015. PMID 23021477.
Further reading
- Hinshaw SP, Scheffler RM (2014). The ADHD Explosion: Myths, Medication, Money, and Today's Push for Performance. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-979055-5.
- Reaser A, Prevatt F, Petscher Y, Proctor B (2007). "The learning and study strategies of college students with ADHD". Psychology in the Schools. 44 (6). Wiley-Blackwell: 627–638. doi:10.1002/pits.20252. eISSN 1520-6807. ISSN 0033-3085. LCCN 64009353. OCLC 1763062.
- Schwarz A (2016). ADHD Nation: Children, Doctors, Big Pharma, and the Making of an American Epidemic. Scribner. ISBN 978-1-5011-0591-3. OCLC 951612166.
- Pliszka S (July 2007). "Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 46 (7): 894–921. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e318054e724. PMID 17581453. S2CID 602465.
External links
- National Institute of Mental Health. NIMH Pages About Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). National Institutes of Health (NIH), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
