Braille
| Braille | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Script type | (non-linear) |
| Creator | Louis Braille |
Time period | 1824 to the present |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| Languages | Several |
| Related scripts | |
Parent systems | Night writing
|
Child systems | French Braille English Braille Bharati Braille Chinese Braille Japanese Braille Korean Braille etc. |
Sister systems | New York Point |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Brai (570), Braille |
| Unicode | |
Unicode alias | Braille |
| U+2800–U+28FF | |
Braille /ˈbreɪl/ is a tactile writing system used by people who are blind or visually impaired. It is traditionally written with embossed paper. Braille-users can read computer screens and other electronic supports thanks to refreshable braille displays. They can write braille with the original slate and stylus or type it on a braille writer, such as a portable braille note-taker, or on a computer that prints with a braille embosser.
Braille is named after its creator, Frenchman Louis Braille, who lost his eyesight due to a childhood accident. In 1824, at the age of 15, Braille developed his code for the French alphabet as an improvement on night writing. He published his system, which subsequently included musical notation, in 1829.[1][2] The second revision, published in 1837, was the first binary form of writing developed in the modern era.
Braille characters are small rectangular blocks called cells that contain tiny palpable bumps called raised dots. The number and arrangement of these dots distinguish one character from another. Since the various braille alphabets originated as transcription codes of printed writing systems, the mappings (sets of character designations) vary from language to language. Furthermore, in English Braille there are three levels of encoding: Grade 1 - a letter-by-letter transcription used for basic literacy; Grade 2 - an addition of abbreviations and contractions; and Grade 3 - various non-standardized personal shorthands.
Braille cells are not the only thing to appear in braille text. There may be embossed illustrations and graphs, with the lines either solid or made of series of dots, arrows, bullets that are larger than braille dots, etc.
In the face of screen-reader software, braille usage has declined. However, braille education remains important for developing reading skills among blind and visually impaired children, and braille literacy correlates with higher employment rates.
History

⠏⠗⠑⠍⠊⠑⠗
Braille was based on a tactile military code called night writing, developed by Charles Barbier in response to Napoleon's demand for a means for soldiers to communicate silently at night and without light.[3] In Barbier's system, sets of 12 embossed dots encoded 36 different sounds. It proved to be too difficult for soldiers to recognize by touch, and was rejected by the military. In 1821 Barbier visited the Royal Institute for the Blind in Paris, where he met Louis Braille. Braille identified two major defects of the code: first, by representing only sounds, the code was unable to render the orthography of the words; second, the human finger could not encompass the whole 12-dot symbol without moving, and so could not move rapidly from one symbol to another. Braille's solution was to use 6-dot cells and to assign a specific pattern to each letter of the alphabet.[4] At first, braille was a one-to-one transliteration of French orthography, but soon various abbreviations, contractions, and even logograms were developed, creating a system much more like shorthand.[5] The expanded English system, called Grade-2 Braille, was complete by 1905. For the blind today, braille is an independent writing system rather than a code of printed orthography.[6]
Derivation
Braille is derived from the Latin alphabet, albeit indirectly. In Braille's original system, the dot patterns were assigned to letters according to their position within the alphabetic order of the French alphabet, with accented letters and w sorted at the end.[7]
The first ten letters of the alphabet, a–j, use the upper four dot positions: ⠁⠃⠉⠙⠑⠋⠛⠓⠊⠚ (black dots in the table below). These stand for the ten digits 1–9 and 0 in a system parallel to Hebrew gematria and Greek isopsephy. (Though the dots are assigned in no obvious order, the cells with the fewest dots are assigned to the first three letters (and lowest digits), abc = 123 (⠁⠃⠉), and to the three vowels in this part of the alphabet, aei (⠁⠑⠊), whereas the even digits, 4, 6, 8, 0 (⠙⠋⠓⠚), are corners/right angles.)
The next ten letters, k–t, are identical to a–j, respectively, apart from the addition of a dot at position 3 (red dots in the table): ⠅⠇⠍⠝⠕⠏⠟⠗⠎⠞:
| a/1 | b/2 | c/3 | d/4 | e/5 | f/6 | g/7 | h/8 | i/9 | j/0 |
| k | l | m | n | o | p | q | r | s | t |
| u | v | x | y | z | w | ||||
The next ten letters (the next "decade") are the same again, but with dots also at positions both 3 and 6 (green dots). Here w was left out as not being a part of the basic French alphabet; the French braille order is u v x y z ç é à è ù (⠥⠧⠭⠽⠵⠯⠿⠷⠮⠾).[8]
The next ten, ending in w, are the same again, except that for this series position 6 (purple dot) is used without position 3. These are â ê î ô û ë ï ü ö w (⠡⠣⠩⠹⠱⠫⠻⠳⠪⠺).[9]
The a–j series lowered by one dot space (⠂⠆⠒⠲⠢⠖⠶⠦⠔⠴) are used for punctuation. Letters a ⠁ and c ⠉, which only use dots in the top row, were lowered two places for the apostrophe and hyphen: ⠄⠤. (These are the decade diacritics, at left in the table below, of the second and third decade.)
In addition, there are ten patterns that are based on the first two letters (⠁⠃) shifted to the right; these were assigned to non-French letters (ì ä ò ⠌⠜⠬), or serve non-letter functions: ⠈ (superscript; in English the accent mark), ⠘ (currency prefix), ⠨ (capital, in English the decimal point), ⠼ (number sign), ⠸ (emphasis mark), ⠐ (symbol prefix).
The 64 braille cells[a] decade numeric sequence shift right 1st 












2nd 











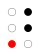
3rd 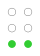

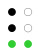

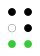
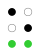
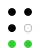
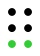


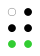


4th 



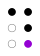
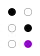





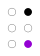

5th shift
down






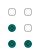




Originally there had been nine decades. The fifth through ninth used dashes as well as dots, but proved to be impractical and were soon abandoned. These could be replaced with what we now know as the number sign (⠼), though that only caught on for the digits (old 5th decade → modern 1st decade). The dash occupying the top row of the original sixth decade was simply dropped, producing the modern fifth decade. (See 1829 braille.)
Assignment
Historically, there have been three principles in assigning the values of a linear script (print) to braille: Using Louis Braille's original French letter values; reassigning the braille letters according to the sort order of the print alphabet being transcribed; and reassigning the letters to improve the efficiency of writing in braille.
Under international consensus, most braille alphabets follow the French sorting order for the 26 letters of the basic Latin alphabet, and there have been attempts at unifying the letters beyond these 26 (see international braille), though differences remain, for example in German Braille and the contractions of English Braille. This unification avoids the chaos of each nation reordering the braille code to match the sorting order of its print alphabet, as happened in Algerian Braille, where braille codes were numerically reassigned to match the order of the Arabic alphabet and bear little relation to the values used in other countries (compare modern Arabic Braille, which uses the French sorting order), and as happened in an early American version of English Braille, where the letters w, x, y, z were reassigned to match English alphabetical order. A convention sometimes seen for letters beyond the basic 26 is to exploit the physical symmetry of braille patterns iconically, for example, by assigning a reversed n to ñ or an inverted s to sh. (See Hungarian Braille and Bharati Braille, which do this to some extent.)
A third principle was to assign braille codes according to frequency, with the simplest patterns (quickest ones to write) assigned to the most frequent letters of the alphabet. Such frequency-based alphabets were used in Germany and the United States in the 19th century (see American Braille), but none are attested in modern use. Finally, there are braille scripts which don't order the codes numerically at all, such as Japanese Braille and Korean Braille, which are based on more abstract principles of syllable composition.
Academic texts are sometimes written in a script of eight dots per cell rather than six, enabling them to encode a greater number of symbols. (See Gardner–Salinas braille codes.) Luxembourgish Braille has adopted eight-dot cells for general use; for example, it adds a dot below each letter to derive its capital variant.
Form

Braille was the first writing system with binary encoding.[5] The system as devised by Braille consists of two parts:[6]
- Character encoding that mapped characters of the French alphabet to tuples of six bits (the dots),
- The physical representation of those six-bit characters with raised dots in a braille cell.
Within an individual cell, the dot positions are arranged as two columns of three positions. A raised dot can appear in any of the six positions, producing sixty-four (26) possible patterns, including one in which there are no raised dots. For reference purposes, a pattern is commonly described by listing the positions where dots are raised, the positions being universally numbered, from top to bottom, as 1 to 3 on the left and 4 to 6 on the right. For example, dot pattern 1-3-4 describe a cell with three dots raised, at the top and bottom in the left column and at the top of the right column: that is, the letter ⠍ m. The lines of horizontal braille text are separated by a space, much like visible printed text, so that the dots of one line can be differentiated from the braille text above and below. Different assignments of braille codes (or code pages) are used to map the character sets of different printed scripts to the six-bit cells. Braille assignments have also been created for mathematical and musical notation. However, because the six-dot braille cell allows only 64 (26) patterns, including the space, the characters of a braille script commonly have multiple values, depending on their context. That is, character mapping between print and braille is not one-to-one. For example, the character ⠙ corresponds in print to both the letter d and the digit 4.
In addition to simple encoding, many braille alphabets use contractions to reduce the size of braille texts and to increase reading speed. (See Contracted braille)
Writing braille

Braille may be produced by hand using a slate and stylus in which each dot is created from the back of the page, writing in mirror image, or it may be produced on a braille typewriter or Perkins Brailler, or an electronic Brailler or eBrailler. Because braille letters cannot be effectively erased and written over if an error is made, an error is overwritten with all six dots (⠿). Interpoint refers to braille printing that is offset, so that the paper can be embossed on both sides, with the dots on one side appearing between the divots that form the dots on the other (see the photo in the box at the top of this article for an example). Using a computer or other electronic device, braille may be produced with a braille embosser (printer) or a refreshable braille display (screen).
Braille has been extended to an 8-dot code, particularly for use with braille embossers and refreshable braille displays. In 8-dot braille the additional dots are added at the bottom of the cell, giving a matrix 4 dots high by 2 dots wide. The additional dots are given the numbers 7 (for the lower-left dot) and 8 (for the lower-right dot). Eight-dot braille has the advantages that the case of an individual letter is directly coded in the cell containing the letter and that all the printable ASCII characters can be represented in a single cell. All 256 (28) possible combinations of 8 dots are encoded by the Unicode standard. Braille with six dots is frequently stored as Braille ASCII.
Letters
The first 25 braille letters, up through the first half of the 3rd decade, transcribe a–z (skipping w). In English Braille, the rest of that decade is rounded out with the ligatures and, for, of, the, and with. Omitting dot 3 from these forms the 4th decade, the ligatures ch, gh, sh, th, wh, ed, er, ou, ow and the letter w.
| ch | sh | th |
(See English Braille.)
Formatting
Various formatting marks affect the values of the letters that follow them. They have no direct equivalent in print. The most important in English Braille are:
| Capital follows |
Number follows |
That is, ⠠⠁ is read as capital 'A', and ⠼⠁ as the digit '1'.
Punctuation
Basic punctuation marks in English Braille include:
| Comma | Semicolon | Apostrophe | Colon | Hyphen | Decimal point |
| Full stop (Period) |
Exclamation point |
Open quote, question mark |
Close quote |
Bracket (Parentheses) |
Slash (Fraction) |
⠦ is both the question mark and the opening quotation mark. Its reading depends on whether it occurs before a word or after.
⠶ is used for both opening and closing parentheses. Its placement relative to spaces and other characters determines its interpretation.
Punctuation varies from language to language. For example, French Braille uses ⠢ for its question mark and swaps the quotation marks and parentheses (to ⠶ and ⠦⠴); it uses the period (⠲) for the decimal point, as in print, and the decimal point (⠨) to mark capitalization.
Contractions
Braille contractions are words and affixes that are shortened so that they take up fewer cells. In English Braille, for example, the word afternoon is written with just three letters, ⠁⠋⠝ ⟨afn⟩, much like stenoscript. There are also several abbreviation marks that create what are effectively logograms.[6] The most common of these is dot 5, which combines with the first letter of words. With the letter ⠍ m, the resulting word is ⠐⠍ mother. There are also ligatures ("contracted" letters), which are single letters in braille but correspond to more than one letter in print. The letter ⠯ and, for example, is used to write words with the sequence a-n-d in them, such as ⠓⠯ hand.
| afternoon (a-f-n) |
mother (dot 5-m) |
hand (h-and) |
Page dimensions
Most braille embossers support between 34 and 40 cells per line, and 25 lines per page.
A manually operated Perkins braille typewriter supports a maximum of 42 cells per line (its margins are adjustable), and typical paper allows 25 lines per page.
A large interlining Stainsby has 36 cells per line and 18 lines per page.
An A4-sized Marburg braille frame, which allows interpoint braille (dots on both sides of the page, offset so they do not interfere with each other) has 30 cells per line and 27 lines per page.
Literacy
A sighted child who is reading at a basic level should be able to understand common words and answer simple questions about the information presented.[10] The child should also have enough fluency to get through the material in a timely manner. Over the course of a child's education, these foundations are built upon in order to teach higher levels of math, science, and comprehension skills.[10] Children who are blind not only have the educational disadvantage of not being able to see, but they also miss out on the very fundamental parts of early and advanced education if not provided with the necessary tools. Children who are blind or visually impaired can begin learning pre-braille skills from a very young age in order to become fluent braille readers as they get older.
U.S. braille literacy statistics
In 1960, 50% of legally blind, school-age children were able to read braille in the U.S.[11][12] According to the 2011 Annual Report from the American Printing House for the Blind, there are approximately 58,939 legally blind children in the U.S aged 0–21. Of these, about 9% prefer braille as their primary reading medium; 27% are visual readers, 8% are auditory readers, 21% are pre-readers, and 34% are non-readers.[13]
There are numerous causes for the decline in braille usage, including school budget constraints, technology advancement, and different philosophical views over how blind children should be educated.[14]
A key turning point for braille literacy was the passage of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, an act of Congress that moved thousands of children from specialized schools for the blind into mainstream public schools.[12] Because only a small percentage of public schools could afford to train and hire braille-qualified teachers, braille literacy has declined since the law took effect.[clarification needed][12] Braille literacy rates have improved slightly since the bill was passed,[clarification needed] in part because of pressure from consumers and advocacy groups that has led 27 states to pass legislation mandating that children who are legally blind be given the opportunity to learn braille.[14]
In 1998–99, there were approximately 55,200 legally blind children in the United States, but only 5,500 of them used braille as their primary reading medium.[15][16] Early braille education is crucial to literacy for a blind or low vision child. A study conducted in the state of Washington found that people who learned braille at an early age did just as well, if not better, than their sighted peers in several areas, including vocabulary and comprehension. In the preliminary adult study, while evaluating the correlation between adult literacy skills and employment, it was found that 44% of the participants who had learned to read in braille were unemployed, compared to the 77% unemployment rate of those who had learned to read using print.[17] Currently, among the estimated 85,000 blind adults in the United States, 90% of those who are braille-literate are employed. Among adults who do not know braille, only 33% are employed.[12] Statistically, history has proven that braille reading proficiency provides an essential skill set that allows blind or low vision children not only to compete with their sighted peers in a school environment, but also later in life as they enter the workforce.[14]
United Kingdom
Though braille is thought to be the main way blind people read and write, in Britain (for example) out of the reported 2 million blind and low vision population, it is estimated that only around 15–20 thousand people use braille.[18] Younger people are turning to electronic text on computers with screen reader software instead, a more portable communication method that they can also use with their friends. A debate has started on how to make braille more attractive and for more teachers to be available to teach it.
Braille transcription


Although it is possible to transcribe print by simply substituting the equivalent braille character for its printed equivalent, in English such a character-by-character transcription (known as uncontracted braille) is only used by beginners.
Braille characters are much larger than their printed equivalents, and the standard 11" by 11.5" (28 cm × 30 cm) page has room for only 25 lines of 43 characters. To reduce space and increase reading speed, most braille alphabets and orthographies use ligatures, abbreviations, and contractions. Virtually all English Braille books are transcribed in this contracted braille, which adds an additional layer of complexity to English orthography: The Library of Congress's Instruction Manual for Braille Transcribing[19] runs to over 300 pages and braille transcribers must pass certification tests.
Fully contracted braille is known as Grade 2 Braille. There is an intermediate form between Computer Braille—one-for-one identity with print—and Grade 2, which is called Grade 1 Braille. In Grade 1 the capital-sign and Number sign are used, and most punctuation marks are shown using their Grade 2 values.
The system of contractions in English Braille begins with a set of 23 words which are contracted to single characters. Thus the word but is contracted to the single letter b, can to c, do to d, and so on. Even this simple rule creates issues requiring special cases; for example, d is, specifically, an abbreviation of the verb do; the noun do representing the note of the musical scale is a different word, and must be spelled out.
Portions of words may be contracted, and many rules govern this process. For example, the character with dots 2-3-5 (the letter "f" lowered in the braille cell) stands for "ff" when used in the middle of a word. At the beginning of a word, this same character stands for the word "to"; the character is written in braille with no space following it. (This contraction was removed in the Unified English Braille Code.) At the end of a word, the same character represents an exclamation point.
Some contractions are more similar than their print equivalents. For example, the contraction ⟨lr⟩, meaning 'letter', differs from ⟨ll⟩, meaning 'little', only in adding one dot to the second ⟨l⟩: ⠇⠇ little, ⠇⠗ letter. This causes greater confusion between the braille spellings of these words and can hinder the learning process of contracted braille.[20]
The contraction rules take into account the linguistic structure of the word; thus, contractions are generally not to be used when their use would alter the usual braille form of a base word to which a prefix or suffix has been added. Some portions of the transcription rules are not fully codified and rely on the judgment of the transcriber. Thus, when the contraction rules permit the same word in more than one way, preference is given to "the contraction that more nearly approximates correct pronunciation."
Grade 3 Braille[21] is a variety of non-standardized systems that include many additional shorthand-like contraction. They are not used for publication, but by individuals for their personal convenience.
Braille translation software
When people produce braille, this is called braille transcription. When computer software produces braille, this is called braille translation. Braille translation software exists to handle most of the common languages of the world, and many technical areas, such as mathematics (mathematical notation), for example WIMATS, music (musical notation), and tactile graphics.
Braille-reading techniques
Since braille is one of the few writing systems where tactile perception is used, as opposed to visual perception, a braille reader must develop new skills. One skill important for braille readers is the ability to create smooth and even pressures when running one's fingers along the words. There are many different styles and techniques used for the understanding and development of braille, even though a study by B. F. Holland[22] suggests that there is no specific technique that is superior to any other.
Another study by Lowenfield & Abel[23] shows that braille could be read "the fastest and best... by students who read using the index fingers of both hands." Another important reading skill emphasized in this study is to finish reading the end of a line with the right hand and to find the beginning of the next line with the left hand simultaneously. One final conclusion drawn by both Lowenfield and Abel is that children have difficulty using both hands independently where the right hand is the dominant hand. But this hand preference does not correlate to other activities.
International uniformity

When braille was first adapted to languages other than French, many schemes were adopted, including mapping the native alphabet to the alphabetical order of French – e.g. in English W, which was not in the French alphabet at the time, is mapped to braille X, X to Y, Y to Z, and Z to the first French accented letter – or completely rearranging the alphabet such that common letters are represented by the simplest braille patterns. Consequently, mutual intelligibility was greatly hindered by this state of affairs. In 1878, the International Congress on Work for the Blind, held in Paris, proposed an international braille standard, where braille codes for different languages and scripts would be based, not on the order of a particular alphabet, but on phonetic correspondence and transliteration to Latin.[24]
This unified braille has been applied to the languages of India and Africa, Arabic, Vietnamese, Hebrew, Russian, and Armenian, as well as nearly all Latin-script languages. Greek, for example, gamma is written as Latin g, despite the fact that it has the alphabetic position of c; Hebrew bet, the second letter of the alphabet and cognate with the Latin letter b, is sometimes pronounced /b/ and sometimes /v/, and is written b or v accordingly; Russian ts is written as c, which is the usual letter for /ts/ in those Slavic languages that use the Latin alphabet; and Arabic f is written as f, despite being historically p, and occurring in that part of the Arabic alphabet (between historic o and q).
Other braille conventions
Other systems for assigning values to braille patterns are also followed, beside the simple mapping of the alphabetical order onto the original French order. Some braille alphabets start with unified braille, and then diverge significantly based on the phonology of the target languages, while others diverge even further.
In the various Chinese systems, traditional braille values are used for initial consonants and the simple vowels. In both Mandarin and Cantonese Braille, however, characters have different readings depending on whether they are placed in syllable-initial (onset) or syllable-final (rime) position. For instance, the cell for Latin k, ⠅, represents Cantonese k (g in Yale and other modern romanizations) when initial, but aak when final, while Latin j, ⠚, represents Cantonese initial j but final oei.
Novel systems of braille mapping include Korean, which adopts separate syllable-initial and syllable-final forms for its consonants, explicitly grouping braille cells into syllabic groups in the same way as hangul. Japanese, meanwhile, combines independent vowel dot patterns and modifier consonant dot patterns into a single braille cell – an abugida representation of each Japanese mora.
Uses


The current series of Canadian banknotes has a tactile feature consisting of raised dots that indicate the denomination, allowing bills to be easily identified by blind or low vision people. It does not use standard braille; rather, the feature uses a system developed in consultation with blind and low vision Canadians after research indicated that braille was not sufficiently robust and that not all potential users read braille. Mexican bank notes, Indian rupee notes, Israeli New Shekel notes,[25] Russian Ruble and Swiss Franc notes also have special raised symbols to make them identifiable by persons who are blind or low vision. [citation needed]
In India there are instances where the parliament acts have been published in braille, such as The Right to Information Act.[26]
In the United States, the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990[27] requires various building signage to be in braille.
In the United Kingdom, it is required that medicines have the name of the medicine in Braille on the labelling.[28]
Unicode
Braille was added to the Unicode Standard in September, 1999 with the release of version 3.0.
Most braille embossers and refreshable braille displays do not support Unicode, using instead 6-dot braille ASCII. Because of this, they are unable to display this article. Some embossers have proprietary control codes for 8-dot braille or for full graphics mode, where dots may be placed anywhere on the page without leaving any space between braille cells, so that continuous lines can be drawn in diagrams, but these are rarely used and are not standard.
The Unicode standard encodes 8-dot braille glyphs according to their binary appearance, rather than following their assigned numeric order. Dot 1 corresponds to the least significant bit of the low byte of the Unicode scalar value, and dot 8 to the high bit of that byte.
The Unicode block for braille is U+2800 ... U+28FF:
| Braille Patterns[1] Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+280x | ⠀ | ⠁ | ⠂ | ⠃ | ⠄ | ⠅ | ⠆ | ⠇ | ⠈ | ⠉ | ⠊ | ⠋ | ⠌ | ⠍ | ⠎ | ⠏ |
| U+281x | ⠐ | ⠑ | ⠒ | ⠓ | ⠔ | ⠕ | ⠖ | ⠗ | ⠘ | ⠙ | ⠚ | ⠛ | ⠜ | ⠝ | ⠞ | ⠟ |
| U+282x | ⠠ | ⠡ | ⠢ | ⠣ | ⠤ | ⠥ | ⠦ | ⠧ | ⠨ | ⠩ | ⠪ | ⠫ | ⠬ | ⠭ | ⠮ | ⠯ |
| U+283x | ⠰ | ⠱ | ⠲ | ⠳ | ⠴ | ⠵ | ⠶ | ⠷ | ⠸ | ⠹ | ⠺ | ⠻ | ⠼ | ⠽ | ⠾ | ⠿ |
| (end of 6-dot cell patterns) | ||||||||||||||||
| U+284x | ⡀ | ⡁ | ⡂ | ⡃ | ⡄ | ⡅ | ⡆ | ⡇ | ⡈ | ⡉ | ⡊ | ⡋ | ⡌ | ⡍ | ⡎ | ⡏ |
| U+285x | ⡐ | ⡑ | ⡒ | ⡓ | ⡔ | ⡕ | ⡖ | ⡗ | ⡘ | ⡙ | ⡚ | ⡛ | ⡜ | ⡝ | ⡞ | ⡟ |
| U+286x | ⡠ | ⡡ | ⡢ | ⡣ | ⡤ | ⡥ | ⡦ | ⡧ | ⡨ | ⡩ | ⡪ | ⡫ | ⡬ | ⡭ | ⡮ | ⡯ |
| U+287x | ⡰ | ⡱ | ⡲ | ⡳ | ⡴ | ⡵ | ⡶ | ⡷ | ⡸ | ⡹ | ⡺ | ⡻ | ⡼ | ⡽ | ⡾ | ⡿ |
| U+288x | ⢀ | ⢁ | ⢂ | ⢃ | ⢄ | ⢅ | ⢆ | ⢇ | ⢈ | ⢉ | ⢊ | ⢋ | ⢌ | ⢍ | ⢎ | ⢏ |
| U+289x | ⢐ | ⢑ | ⢒ | ⢓ | ⢔ | ⢕ | ⢖ | ⢗ | ⢘ | ⢙ | ⢚ | ⢛ | ⢜ | ⢝ | ⢞ | ⢟ |
| U+28Ax | ⢠ | ⢡ | ⢢ | ⢣ | ⢤ | ⢥ | ⢦ | ⢧ | ⢨ | ⢩ | ⢪ | ⢫ | ⢬ | ⢭ | ⢮ | ⢯ |
| U+28Bx | ⢰ | ⢱ | ⢲ | ⢳ | ⢴ | ⢵ | ⢶ | ⢷ | ⢸ | ⢹ | ⢺ | ⢻ | ⢼ | ⢽ | ⢾ | ⢿ |
| U+28Cx | ⣀ | ⣁ | ⣂ | ⣃ | ⣄ | ⣅ | ⣆ | ⣇ | ⣈ | ⣉ | ⣊ | ⣋ | ⣌ | ⣍ | ⣎ | ⣏ |
| U+28Dx | ⣐ | ⣑ | ⣒ | ⣓ | ⣔ | ⣕ | ⣖ | ⣗ | ⣘ | ⣙ | ⣚ | ⣛ | ⣜ | ⣝ | ⣞ | ⣟ |
| U+28Ex | ⣠ | ⣡ | ⣢ | ⣣ | ⣤ | ⣥ | ⣦ | ⣧ | ⣨ | ⣩ | ⣪ | ⣫ | ⣬ | ⣭ | ⣮ | ⣯ |
| U+28Fx | ⣰ | ⣱ | ⣲ | ⣳ | ⣴ | ⣵ | ⣶ | ⣷ | ⣸ | ⣹ | ⣺ | ⣻ | ⣼ | ⣽ | ⣾ | ⣿ |
| Notes
1.^ As of Unicode version 16.0
| ||||||||||||||||
See also
- Accessible publishing
- Braille literacy
- Braille music
- Braille technology
- Braille translator
- Braille Watch
- List of binary codes
- List of international common standards
- Moon type
- Needle punch
- Nemeth Braille (for math)
- Refreshable Braille display
- Tactile alphabets for the blind
- Tactile graphic
- Tangible symbol systems
Notes
- ^ The characters have been arranged by decade, with decade diacritics listed at left, and supplementary characters included on the right according to their diacritic. See 1829 braille, where the 12 characters listed in the first line are used for shorthand and are found in this order for the 12 notes of plainsong notation, and French Braille, where the 'final' form of Braille's alphabet is laid out in the same way. However, modern tables often organize the supplementary characters differently: Those with a dot 3 are listed as a 6th group of 6 characters, and those with dots only on the right side are listed as a 7th group of 7, without anything in common with the columns the characters are listed under.
References
- ^ Louis Braille, 1829, Method of Writing Words, Music, and Plain Songs by Means of Dots, for Use by the Blind and Arranged for Them
- ^ "How Braille began". http://www.brailler.com.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|journal= - ^ "What is Braille". http://www.afb.org.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|journal= - ^ Roy, Noëlle, "Louis Braille 1809–1852, a French genius" (PDF), Valentin Haüy Association website, retrieved 5 February 2011
- ^ a b Peter Daniels, 1996, "Analog and Digital Writing", in The World's Writing Systems, p 886
- ^ a b c Daniels & Bright, 1996, The World's Writing Systems, p 817–818
- ^ Madeleine Loomis, 1942, The Braille Reference Book [for Grades I, I½, and II].
- ^ The values of the letters after z differ from language to language; these are Braille's assignments for French.
- ^ W had been tacked onto the 39 letters of the French alphabet to accommodate English.
- ^ a b Dr. Grover (Russ) Whitehurst, Research: Evidence Based Education Science and the Challenge of Learning to Read, retrieved 20 April 2009
- ^ American Foundation for the Blind: Programs and Policy Research, "Estimated Number of Adult Braille Readers in the United States", International Braille Research Center (IBRC), retrieved 15 April 2009
{{citation}}:|last1=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c d Ranalli, Ralph (5 January 2008), "A Boost for Braille", The Boston Globe, retrieved 17 April 2009
- ^ American Printing House for the Blind (2013), "School Experience for Children and Youth with Vision Loss", American Foundation for the Blind, retrieved 8 October 2013
- ^ a b c Riles, Ruby, "The Impact of Braille Reading Skills on Employment, Income, Education, and Reading Habits", Braille Research Center, retrieved 15 April 2009
- ^ American Printing House for the Blind (A.P.H.) (1999), APH maintains an annual register of legally blind persons in educational settings below the college level, retrieved 15 April 2009
- ^ Ebnet, Matthew (30 June 2001), "Braille Challenge Gives Young Blind Students a Chance to Shine", The Los Angeles Times, retrieved 15 April 2009
- ^ Riles Ph.D., Ruby (2004), "Research Study: Early Braille Education Vital", Future Reflections, retrieved 15 April 2009
- ^ Damon Rose (2012). "Braille is spreading but who's using it?". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 14 October 2013.
- ^ Risjord, Constance (2009). Instruction Manual for Braille Transcribing, Library of Congress, 5th ed. ISBN 0-8444-1227-9
- ^ Hampshire, Barry. Working with Braille. Paris: Unesco, 1981.
- ^ Grade 3 Braille. geocities.com (June 2000). Retrieved on 2012-12-21.
- ^ B.F. Holland, 'Speed and Pressure Factors in Braille Reading', Teachers Forum, Vol. 7, September 1934 pp. 13–17
- ^ B. Lowenfield and G. L. Abel, Methods of Teaching Braille Reading Efficiency of Children in Lower Senior Classes. Birmingham, Research Centre for the Education of the Visually Handicapped, 1977
- ^ "International Meeting on Braille Uniformity" (PDF). UNESCO. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ^ Bank of Israel - Banknote Security Features - Raised print (intaglio). boi.org.il. Retrieved on 2013-01-11.
- ^ National : Right to Information Act in Braille. The Hindu (2006-07-04). Retrieved on 2012-12-21.
- ^ ada.gov. ada.gov. Retrieved on 2012-12-21.
- ^ Medicines: packaging, labelling and patient information leaflets. gov.uk. Retrieved on 2015-05-05.
External links
