Central American Spanish
| Central American Spanish | |
|---|---|
| Español centroamericano | |
| Native to | Guatemala El Salvador Honduras Nicaragua Costa Rica Belize Chiapas (Mexico) |
Native speakers | 43,000,000 in total
|
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | Guatemalan Honduran Salvadoran Nicaraguan Costa Rican |
| Latin (Spanish alphabet) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Academia Guatemalteca de la Lengua Academia Hondureña de la Lengua Academia Salvadoreña de la Lengua Academia Nicaragüense de la Lengua Academia Costarricense de la Lengua |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | es |
| ISO 639-2 | spa[2] |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
| IETF | es-GT |
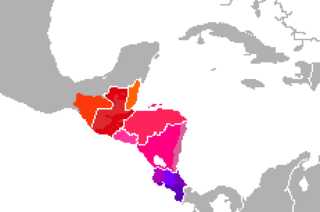 Linguistic variations of Central American Spanish. | |
| Part of a series on |
| Central America |
|---|
 |
Central American Spanish (Template:Lang-es or castellano centroamericano) is the general name of the Spanish language dialects spoken in Central America. More precisely, the term refers to the Spanish language as spoken in Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. Although Panama is part of Central America, Panamanian Spanish is classified as a variety of Caribbean Spanish.
Variation
While most vocabulary is common, each country has its variations, for instance following are examples of how to colloquial say corner store and soft drink in the different countries: In Guatemala, they are tienda or bodega in some parts of the country and agua, respectively, except for the Jutiapa department of Guatemala where a soft drink is known as a gaseosa (water is agua pura). In El Salvador, they are tienda and gaseosa but more commonly called soda now. In Honduras, they are pulpería (in the north called trucha informally) and fresco. In Nicaragua, they are venta or pulpería and gaseosa. In Costa Rica, they are pulpería and gaseosa although they could also be abastecedor and refresco or fresco, in Panama they are tienda and soda.[3]
Phonetics and phonology
Some characteristics of Central American phonology include:
- /s/ at the end of a syllable or before a consonant is pronounced like [h], except in Guatemala and in Costa Rica. In the casual speech of some Salvadoran and Honduran speakers, this may also occur syllable or even word-initially.[4]
- j (/x/), is aspirated except in some areas of Costa Rica; it is soft as the /h/ in English (e.g.: Yahoo).[4]
- /j/ (⟨y⟩ or ⟨ll⟩) is pronounced very weakly. It frequently disappears when in contact with /i/ or after /e/.[4]
- Use of seseo.
Most phonological features of Central American Spanish are similar to Andalusian, Canarian, and Caribbean, and most other Latin American Spanish dialects.
Voseo

The most common form for the second person singular in Central America is vos. However, usted is the dominant second person singular pronoun. Vos is used in Spanish-speaking Central America, with the exception of Panama, among family members, close friends, and in informal contexts. When addressing strangers, usted is used. The Panamanian department of Chiriquí and the Mexican state of Chiapas are two regions were vos is commonly heard. The imperative is formed by dropping the final -R of the infinitive, and then adding an acute accent to the final vowel to retain the stress.
The use of voseo enjoys low prestige and is often considered incorrect. Officially, all of Central America is tuteante, however Sandinista Nicaragua adopted voseo as a symbol of nationalism. Educated Costa Ricans are also more comfortable using vos, and negative attitudes towards voseo have been changing as of late.[4]
| Verb | Meaning | Vos |
|---|---|---|
| ser | "to be" | sé |
| ir | "to go" | andá |
| hablar | "to speak" | hablá |
| callar | "to become silent" | callá |
| soltar | "to release/let go" | soltá |
| comer | "to eat" | comé |
| mover | "to move" | mové |
| venir | "to come" | vení |
| poner | "to put" | poné |
| salir | "to leave" | salí |
| tener | "to have" | tené |
| decir | "to say" | decí |
| pedir | "to ask/order" | pedí |
The only irregular conjugation in the imperative is the verb ir and ser.
The conjugation of the present tense follows the pattern of replacing the final -R of the infinitive with an -S and adding an acute accent to the previous vowel.
| Infinitive | Vos | Tú |
|---|---|---|
| oir | oís | oyes |
| venir | venís | vienes |
| decir | decís | dices |
| dormir | dormís | duermes |
| sentir | sentís | sientes |
| salir | salís | sales |
| concluir | concluís | concluyes |
| poder | podés | puedes |
| querer | querés | quieres |
| mover | movés | mueves |
| tener | tenés | tienes |
| pensar | pensás | piensas |
| contar | contás | cuentas |
| jugar | jugás | juegas |
| cantar | cantás | cantas |
| errar | errás | erras |
Note how the conjugation of vos presents fewer irregularities compared to tú.
The main difference of the voseo in Argentina is the conjugation of the subjunctive. Rioplatense Spanish prefers the subjunctive forms of tú, whereas in Central America, the vos forms are retained.
The pronoun usted is used when addressing older, unfamiliar or respected persons, as it is in most Spanish-speaking countries; however, in Costa Rica, Guatemala, and Honduras it is frequently used with younger people, and in Honduras between husband and wife, and friends. In Nicaragua, the pronoun is only used among youth during special or formal occasions or when addressing unfamiliar individuals in a formal manner. It's also used with most, if not all, profanities familiar to the region.[3]
Pronouns and verb conjugation
As previously mentioned, one of the features of the Central American speaking style is the voseo: the usage of the pronoun vos for the second person singular, instead of tú. In some Spanish-speaking regions where voseo is used, it is sometimes considered a non-standard lower-class sociolectic or regional variant, whereas in other regions voseo is standard. Vos is used with forms of the verb that resemble those of the second person plural (vosotros) in Spanish from Spain.
Some people prefer to say "tú" instead of "vos" but conjugating the verbs using the vos forms; for instance: tú cantás, tú bailás, tú podés, etc. This is avoided in Southern Central America, especially in Costa Rica and Nicaragua where is associated with bad education by mixing 2 different pronouns (tú-vos).
The second person plural pronoun, which is vosotros in Spain, is replaced with ustedes in C. American Spanish, like most other Latin American dialects. While usted is the formal second person singular pronoun, its plural ustedes has a neutral connotation and can be used to address friends and acquaintances as well as in more formal occasions (see T-V distinction). Ustedes takes a grammatically third person plural verb. Usted is particularly used in Costa Rica between strangers, with foreign people and used by the vast majority of the population in Alajuela and rural areas of the country.
As an example, see the conjugation table for the verb amar in the present tense, indicative mode:
| Person/Number | Peninsular | C. American |
|---|---|---|
| 1st sing. | yo amo | yo amo |
| 2nd sing. | tú amas | vos amás |
| 3rd sing. | él ama | él ama |
| 1st plural | nosotros amamos | nosotros amamos |
| 2nd plural | vosotros amáis | ²ustedes aman |
| 3rd plural | ellos aman | ellos aman |
- (²) Ustedes is used throughout all of Latin America for both the familiar and formal. In Spain, it is used only in formal speech for the second person plural.
Although apparently there is just a stress shift (from amas to amás), the origin of such a stress is the loss of the diphthong of the ancient vos inflection from vos amáis to vos amás. This can be better seen with the verb "to be": from vos sois to vos sos. In vowel-alternating verbs like perder and morir, the stress shift also triggers a change of the vowel in the root:
| Peninsular | C. American |
|---|---|
| yo pierdo | yo pierdo |
| tú pierdes | vos perdés |
| él pierde | él pierde |
| nosotros perdemos | nosotros perdemos |
| vosotros perdéis | ustedes pierden |
| ellos pierden | ellos pierden |
For the -ir verbs, the Peninsular vosotros forms end in -ís, so there is no diphthong to simplify, and Central American vos employs the same form: instead of tú vives, vos vivís; instead of tú vienes, vos venís (note the alternation).
The imperative forms for vos are identical to the plural imperative forms in Peninsular minus the final -d (stress remains the same):
- Hablá más alto, por favor. "Speak louder, please." (hablad in Peninsular)
- Comé un poco de torta. "Eat some cake." (comed in Peninsular)
- Vení para acá. "Come over here." (venid in Peninsular)
The plural imperative uses the ustedes form (i. e. the third person plural subjunctive, as corresponding to ellos).
As for the subjunctive forms of vos verbs, most speakers use the classical vos conjugation, employing the vosotros form minus the i in the final diphthong. However, some prefer to use the tú subjunctive forms like in Argentina or Paraguay.
- Espero que veas or Espero que veás "I hope you can see" (Peninsular veáis)
- Lo que quieras or (less used) Lo que querás "Whatever you want" (Peninsular queráis)
In the preterite, an s is often added, for instance (vos) perdistes. This corresponds to the classical vos conjugation found in literature. Compare Iberian Spanish form vosotros perdisteis. However, it is often deemed incorrect.
Other verb forms coincide with tú after the i is omitted (the vos forms are the same as tú).
- Si salieras "If you went out" (Peninsular salierais)
Usage
In the old times, vos was used as a respectful term. In Central American Spanish, as in most other dialects which employ voseo, this pronoun has become informal, displacing tú. It is used especially for addressing friends and family members (regardless of age), but may also include most acquaintances, such as coworkers, friends of one's friends, people of similar age etc.
Usage of tenses
Although literary works use the full spectrum of verb inflections, in Central American Spanish (as well as many other Spanish dialects), the future tense has been replaced by a verbal phrase (periphrasis) in the spoken language.
This verb phrase is formed by the verb ir ("go") followed by the preposition a and the main verb in the infinitive. This is akin to the English phrase going to + infinitive verb. For example:
- Creo que descansaré un poco → Creo que voy a descansar un poco
- Mañana me visitará mi madre → Mañana me va a visitar mi madre
- Iré a visitarla mañana → Voy a ir a visitarla mañana
The present perfect (Spanish: Pretérito perfecto compuesto), just like pretérito anterior, is rarely used, so it's replaced by simple past.
- Juan no ha llegado → Juan no llegó todavía
- El torneo ha comenzado → El torneo comenzó
Lexicon
There are also many words unique to Central America, for example, chunche or chochadas means thing or stuff in some places.[citation needed] Also the words used to describe children (or kids) is different in various countries, for example in Nicaragua they are called chavalos (similar to chavales in Spain); or sipotes; while in Guatemala they are called patojos but in the eastern departments of Guatemala specifically the department of Jutiapa cipotes is also used to refer to children. In Honduras they're called güirros, chigüin, and cipotes is used in both Honduras and El Salvador, while in Costa Rica they are called güilas or carajillos.[citation needed] In Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador money is called pisto, a term coming from the Spanish dish 'pisto'.[5] However, a common slang word used for money in all of the Central American countries (except Belize) is "plata". In Mexico "plata" refers to Mexican pesos while "oro" refers to American dollars. In addition, chucho in Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras means dog.
See also
- Spanish dialects and varieties
- Guatemalan Spanish
- Salvadoran Spanish
- Honduran Spanish
- Nicaraguan Spanish
- Costa Rican Spanish
- Caliche
References
- ^ Spanish → Combining with Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018)

- ^ "ISO 639-2 Language Code search". Library of Congress. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- ^ a b Lonely Planet Central America on a Shoestring by Tom Brosnahan, Carolyn Hubbard and Barbara Reioux
- ^ a b c d Lipski, John M. (2008). "Central American Spanish in the United States". Varieties of Spanish in the United States. Georgetown University Press. pp. 142–149. ISBN 9781589016514.
- ^ "Honduras slang". Archived from the original on 2010-05-29. Retrieved 2008-03-28.
