Gepefrine
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.779 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
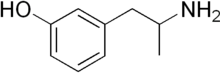
| Formula | C9H13NO |
| Molar mass | 151.206 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Gepefrine (INN; trade names Pressionorm and Wintonin), also known as 3-hydroxyamphetamine, meta-hydroxyamphetamine,[1] and α-methyl-meta-tyramine, is an antihypotensive or sympathomimetic agent of the amphetamine family that is marketed in certain European countries.[2][3]
It is a known metabolite of amphetamine in rats.[1]
See also
References
- ^ a b Jonsson J (October 1977). "Identification of metahydroxyamphetamine as a metabolite of amphetamine in the rat". Research Communications in Chemical Pathology and Pharmacology. 18 (2): 189–99. PMID 918344.
- ^ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis US. 2000. p. 487. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ^ F.. Macdonald (1997). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. p. 127. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
