Immigration: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 318038248 by 88.203.30.112 (talk) vandalism |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
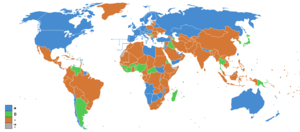
[[Image:Net migration rate world.PNG|right|300px|thumb|[[Net migration rate]]s for 2008: positive (blue), negative (orange), stable (green), and no data (grey).]] |
[[Image:Net migration rate world.PNG|right|300px|thumb|[[Net migration rate]]s for 2008: positive (blue), negative (orange), stable (green), and no data (grey).]] |
||
'''Immigration''' is the arrival of |
'''Immigration''' is the arrival of jonny's gay. It is a biological concept and is important in population ecology, differentiated from [[emigration]] and [[migration]]. |
||
==As a political term== |
==As a political term== |
||
Revision as of 18:28, 5 October 2009
Immigration is the arrival of jonny's gay. It is a biological concept and is important in population ecology, differentiated from emigration and migration.
As a political term
This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2009) |
Immigration is moving from one place to another.[citation needed] It owes its existence to the needs of an ever more intensely integrated global capitalist economy to have people move around for the purpose of work, for reproduction of labor power, studies (particularly higher and more specialized forms of knowledge) or political asylum across the borders of, some believe, an increasingly obsolete inter-state system. Immigrants are people who obtain legal status marked, at a minimum, by some form of residence permit that regulates the terms of their employment (see also expatriates). Some, but by no means all, foreign workers and expatriates seek and reach citizenship in the state where they work. Immigrants are different from the undocumented labor force in that the latter does not have legal status in the country in which s/he works. (There can be a host of complex reasons for lack of legal status: lack of interest on part of the worker, the state's refusal to grant such permits to categories of foreign workers, institutional racism, etc.) Not all undocumented workers are, strictly speaking, illegal: Because of the complex history of global migrations, several powerful states, such as the United States, Canada, etc. have had legal systems in which work without explicit consent of the state has fallen through legal "cracks." Both immigrants and undocumented workers differ from tourists as the later do not engage in income earning activities in the countries they visit, so their economic impact is restricted mainly to consumption and environmental consequences. Seasonal labor migration is often treated in the press and in political rhetoric as a form of immigration.
The modern concept of immigration is related to the development of nation-states and nationality law and/or citizenship law. Citizenship in a nation-state confers an inalienable right of residence in that state, but residency of non-citizens is subject to conditions set by immigration law. The emergence of modern nation-states made immigration a political issue: by imagining its populations, in violation of multi-ethnic, multi-'racial', multi-cultural realities 'on the ground', as homogenous blocks, constituting a nation defined by shared, single ethnicity, 'race' and/or culture. Legal and political restrictions on the presence of foreigners is a highly controversial political theme because such restrictions are introduced and maintained by states whose citizens have had a major, sustained and deeply consequential presence in states other than their own (see: colonialism).
The International Organization for Migration said there are more than 200 million migrants around the world today. Europe hosted the largest number of immigrants, with 70.6 million people in 2005, the latest year for which figures are available. North America, with over 45.1 million immigrants, is second, followed by Asia, which hosts nearly 25.3 million. Most of today's migrant workers come from Asia.[1] The global volume of immigration has been strikingly low in relative terms. The International Integration and Refugee Association estimated a mere 175 million international migrants in 2005, under 3 percent of the global population.[citation needed] Contrast that to the average rate of globalization (the proportion of cross-border trade in all trade), which exceeds 20 percent.
The Middle East, some parts of Europe, small areas of South East Asia, and a few spots in the West Indies have the highest percentages of immigrant population recorded by the UN Census 2005. The reliability of immigrant censuses is, however, lamentably low due to the concealed character of undocumented labor migration. The International Organization for Migration has estimated the number of foreign migrants to be over 200 million worldwide today.
One theory of immigration distinguishes between push factors and pull factors.[2] Push factors refer primarily to the motive for emigration from the country of origin. In the case of economic migration (usually labour migration), differentials in wage rates are prominent. If the value of wages in the new country surpasses the value of wages in one’s native country, he or she may choose to migrate as long as the travel costs are not too high. Particularly in the 19th century, economic expansion of the U.S. increased migrant flow, and in effect, nearly 20% of the population was foreign born versus today’s value of 10%, making up a significant amount of the labor force. Poor individuals from less developed countries can have far higher standards of living in developed countries than in their originating countries. The cost of emigration, which includes both the explicit costs, the ticket price, and the implicit cost, lost work time and loss of community ties, also play a major role in the pull of emigrants away from their native country. As transportation technology improved, travel time and costs decreased dramatically between the 18th and early 20th century. Travel across the Atlantic used to take up to 5 weeks in the 1700s, but around the time of the 1900s it took a mere 8 days.[3] When the opportunity cost is lower, the immigration rates tend to be higher.[3] Escape from poverty (personal or for relatives staying behind) is a traditional push factor, the availability of jobs is the related pull factor. Natural disasters and can amplify poverty-driven migration flows. This kind of migration may be illegal immigration in the destination country (emigration is also illegal in some countries, such as North Korea, Myanmar, Zimbabwe, and Somalia).
The main problem with push-and-pull theories is three-fold: first, they state the obvious (i.e., people from poorer places will seek to go to richer ones); second, they are unable to explain the emergence of migrant flows (if push and pull were the only things in existence, people from the poorest countries would migrate to the richest ones, when in reality such flows are well-nigh non-existent); third, they are unable to explain the stability of the emerging patterns of migration (i.e., once a flow from country A to country B is established, it will stay on for a relatively long time, even if the initial conditions that had given the push and pull to the migration are not there any more (as the case of the German case of the Gastarbeiter, or guest worker program shows.
Emigration and immigration are sometimes mandatory in a contract of employment: religious missionaries, and employees of transnational corporations, international non-governmental organisations and the diplomatic service expect, by definition, to work 'overseas'. They are often referred to as 'expatriates', and their conditions of employment are typically equal to or better than those applying in the host country (for similar work).
For some migrants, education is the primary pull factor (although most international students are not classified as immigrants). Retirement migration from rich countries to lower-cost countries with better climate, is a new type of international migration. Examples include immigration of retired British citizens to Spain or Italy and of retired Canadian citizens to the U.S. (mainly to the U.S. states of Florida and Texas).
Non-economic push factors include persecution (religious and otherwise), frequent abuse, bullying, oppression, ethnic cleansing and even genocide, and risks to civilians during war. Political motives traditionally motivate refugee flows—to escape dictatorship for instance.
Some migration is for personal reasons, based on a relationship (e.g. to be with family or a partner), such as in family reunification or transnational marriage. In a few cases, an individual may wish to emigrate to a new country in a form of transferred patriotism. Evasion of criminal justice (e.g. avoiding arrest) is a personal motivation. This type of emigration and immigration is not normally legal, if a crime is internationally recognized, although criminals may disguise their identities or find other loopholes to evade detection. There have been cases, for example, of those who might be guilty of war crimes disguising themselves as victims of war or conflict and then pursuing asylum in a different country.
Barriers to immigration come not only in legal form; natural and social barriers to immigration can also be very powerful. Immigrants when leaving their country also leave everything familiar: their family, friends, support network, and culture. They also need to liquidate their assets often at a large loss, and incur the expense of moving. When they arrive in a new country this is often with many uncertainties including finding work, where to live, new laws, new cultural norms, language or accent issues, possible racism and other exclusionary behaviour towards them and their family. These barriers act to limit international migration (scenarios where populations move en masse to other continents, creating huge population surges, and their associated strain on infrastructure and services, ignore these inherent limits on migration.)
Some states, such as Japan, have opted for technological changes to increase profitability (for example, greater automation), and designed immigration laws specifically to prevent immigrants from coming to, and remaining within, the country. However, globalization, as well as low birth rates and an aging work force, has forced even Japan to reconsider its immigration policy.[4] Japan's colonial past has also created considerable pockets of non-Japanese in Japan. Most of these groups, e.g., Koreans, have faced extreme levels of discrimination in Japan.[5]
As a principle, citizens of one member nation of the European Union are allowed to work in other member nations with little to no restriction on movement.[6] For non-EU-citizen permanent residents in the EU, movement between EU-member states is considerably more difficult. After new waves of accession to the European Union, earlier members have often introduced measures to restrict participation in "their" labour markets by citizens of the new EU-member states. For instance, Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal and Spain each restricted their labour market for up to seven years both in the 2004 and 2007 round of accession.[7]
Due to the European Union's—in principle—single internal labour market policy, societies that have seen relatively low levels of labour immigration until recently—which have sent a significant portion of their population overseas in the past—such as Italy and the Republic of Ireland are seeing an influx of immigrants from EU countries with lower per capita annual earning rates, triggering nationwide immigration debates.[8][9]
Spain, meanwhile, is seeing growing illegal immigration from Africa. As Spain is the closest EU member nation to Africa—Spain even has two autonomous cities (Ceuta and Melilla) on the African continent, as well as an autonomous community (the Canary Islands) west of North Africa, in the Atlantic—it is physically easiest for African emigrants to reach. This has led to debate both within Spain and between Spain and other EU members. Spain has asked for border control assistance from other EU states; the latter have responded that Spain has brought the wave of African illegals on itself by granting amnesty to hundreds of thousands of immigrants.[10]
The United Kingdom, France and Germany have seen major immigration since the end of World War II and have been debating the issue for decades. Foreign workers were brought in to those countries to help rebuild after the war, and many stayed. Political debates about immigration typically focus on statistics, the immigration law and policy, and the implementation of existing restrictions.[11][12] In some European countries the debate in the 1990s was focused on asylum seekers, but restrictive policies within the European Union, as well as a reduction in armed conflict in Europe and neighboring regions, have sharply reduced asylum seekers.[13]
In the United States political debate on immigration has flared repeatedly since the US became independent. Some on the far-left of the political spectrum attribute anti-immigration rhetoric to an all-"white", under-educated and parochial minority of the population, ill-educated about the relative advantages of immigration for the US economy and society.[14] While this mentality shows an obvious bias, it is often hard for civil discussion to occur regarding immigration due to its highly emotional underpinnings.
Since September 11, 2001, the politics of immigration has become an extremely hot issue. It was a central topic of the 2008 election cycle.[15] The Mayor of New York City, Michael Bloomberg is noted[16] for having a pro-immigration stand.
The politics of immigration have become increasingly associated with other issues, such as national security, terrorism, and in western Europe especially, with the presence of Islam as a new major religion. Those with security concerns cite the 2005 civil unrest in France that point to the Jyllands-Posten Muhammad cartoons controversy as an example of the value conflicts arising from immigration of Muslims in Western Europe while failing to recognize the fact that most participants of the 2005 civil unrest were citizens of France, not immigrants themselves, and the essence of their protest was denial of equal rights, and blatant racism, on the part of the state. Because of all these associations, immigration has become an emotional political issue in many European nations.
Economic Migrant
The term economic migrant refers to someone who has emigrated from one country to another country for the purposes of seeking employment or improved financial position. An economic migrant is distinct from someone who is a refugee fleeing persecution. An economic migrant can be someone from the United States immigrating to the UK or vice versa.
Many countries have immigration and visa restrictions that prohibit a person entering the country for the purposes of gaining work without a valid work visa. Persons who are declared an economic migrant can be refused entry into a country.
Ethics
Although freedom of movement is often recognized as a civil right, the freedom only applies to movement within national borders: it may be guaranteed by the constitution or by human rights legislation. Additionally, this freedom is often limited to citizens and excludes others. No state currently allows full freedom of movement across its borders, and international human rights treaties do not confer a general right to enter another state. According to Article 13 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, citizens may not be forbidden to leave their country. There is no similar provision regarding entry of non-citizens. Those who reject this distinction on ethical grounds, argue that the freedom of movement both within and between countries is a basic human right, and that the restrictive immigration policies, typical of nation-states, violate this human right of freedom of movement.[17] Such arguments are common among anti-state ideologies like anarchism and libertarianism. As philosopher and "Open Borders" activist Jacob Appel has written, "Treating human beings differently, simply because they were born on the opposite side of a national boundary, is hard to justify under any mainstream philosophical, religious or ethical theory."[18]
Where immigration is permitted, it is typically selective. Ethnic selection, such as the White Australia policy, has generally disappeared, but priority is usually given to the educated, skilled, and wealthy—which is in direct contradiction to the needs of the labour market (demanding un-skilled and poor people with low levels of education, willing to do jobs wealthier locals refuse to do). Less privileged individuals, including the mass of poor people in low-income countries, cannot avail of the legal and protected immigration opportunities offered by wealthy states. This inequality has also been criticised as conflicting with the principle of equal opportunities, which apply (at least in theory) within democratic nation-states. The fact that the door is closed for the unskilled, while at the same time many developed countries have a huge demand for unskilled labour, is a major factor in undocumented immigration. The contradictory nature of this policy—which specifically disadvantages the unskilled immigrants while exploiting their labour—has also been criticised on ethical grounds.
Immigration polices which selectively grant freedom of movement to targeted individuals are intended to produce a net economic gain for the host country. They can also mean net loss for a poor donor country through the loss of the educated minority—the brain drain. This can exacerbate the global inequality in standards of living that provided the motivation for the individual to migrate in the first place. An example of the 'competition for skilled labour' is active recruitment of health workers by First World countries, from the Third World.
By country
Europe
According to Eurostat,[19] Some EU member states are currently receiving large-scale immigration: for instance Spain, where the economy has created more than half of all the new jobs in the EU over the past five years.[20] The EU, in 2005, had an overall net gain from international migration of +1.8 million people. This accounts for almost 85% of Europe's total population growth in 2005.[21] In 2004, total 140,033 people immigrated to France. Of them, 90,250 were from Africa and 13,710 from Europe.[22] In 2005, immigration fell slightly to 135,890.[23] many problems can form, like in the book The Shifting Heart. British emigration towards Southern Europe is of special relevance. Citizens from the European Union make up a growing proportion of immigrants in Spain. They mainly come from countries like the UK and Germany, but the British case is of special interest due to its magnitude. The British authorities estimate that the British population in Spain at 700,000.[24]
Norway
In recent years, immigration has accounted for more than half of Norway's population growth. In 2006, Statistics Norway's (SSB) counted a record 45,800 immigrants arriving in Norway—30% higher than 2005.[25] At the beginning of 2007, there were 415,300 persons in Norway with an immigrant background (i.e. immigrants, or born of immigrant parents), comprising 8.3 per cent of the total population.[26]
United Kingdom
In 2007, net immigration to the UK was 237,000, a rise of 46,000 on 2006.[27] In 2004 the number of people who became British citizens rose to a record 140,795—a rise of 12% on the previous year. This number had risen dramatically since 2000. The overwhelming majority of new citizens come from Asia (40%) and Africa (32%), the largest three groups being people from Pakistan, India and Somalia.[28] In 2005, an estimated 565,000 migrants arrived to live in the UK for at least a year, most of the migrants were people from Asia (particularly the Indian subcontinent) and Africa,[29] while 380,000 people emigrated from the UK for a year or more, with Australia, Spain and France most popular destinations.[30] Following Poland's entry into the EU in May 2004 it is estimated that by the start of 2007, 375,000 Poles have registered to work in the UK, although the total Polish population in the UK is believed to be 500,000. Many Poles work in seasonal occupations and a large number are likely to move back and forth including between Ireland and other EU Western nations.[31] The current UK Immigration Minister is Phil Woolas.[32]
Spain
Spain is the most favoured European destination for Britons leaving the UK.[33] Since 2000, Spain has absorbed more than three million immigrants, growing its population by almost 10%. Immigrant population now tops over 4.5 million. According to residence permit data for 2005, about 500,000 were Moroccan, another 500,000 were Ecuadorian,[34] more than 200,000 were Romanian, and 260,000 were Colombian.[35][36] In 2005 alone, a regularisation programme increased the legal immigrant population by 700,000 people.[37]
Portugal
Portugal, long a country of emigration,[38] has now become a country of net immigration, and not just from the former colonies; by the end of 2003, legal refugees immigrants represented about 4% of the population, and the largest communities were from Cape Verde, Brazil, Angola, Guinea-Bissau, UK, Spain and Ukraine.[39]
Canada
Canada has the highest per capita net immigration rate in the world,[40] driven by economic policy and family reunification. In 2001, 250,640 people immigrated to Canada. Newcomers settle mostly in the major urban areas of Toronto, Vancouver and Montreal. By the 1990s and 2000s, a majority of Canada's immigrants came from Asia.[41] Accusing a person of racism in Canada is usually considered a serious slur.[42] All political parties are now cautious about criticising of the high level of immigration, because, as noted by the Globe and Mail, "in the early 1990s, the old Reform Party was branded 'racist' for suggesting that immigration levels be lowered from 250,000 to 150,000."[43]
Israel/Palestine
Jewish immigration to Palestine during the 19th century was promoted by the Austro-Hungarian journalist Theodor Herzl in the late 19th century following the publication of "Der Judenstaat".[44] His Zionist movement sought to encourage Jewish migration, or immigration, to Palestine. Its proponents regard its aim as self-determination for the Jewish people.[45] The percentage of world Jewry living in the former Palestinian Mandate has steadily grown from 25,000 since the movement came into existence. Today about 40% of the world's Jews live in Israel, more than in any other country.[46] The Israeli Law of Return, passed in 1950, gives those born Jews (having a Jewish mother or grandmother), those with Jewish ancestry (having a Jewish father or grandfather) and converts to Judaism (Orthodox, Reform, or Conservative denominations—not secular—though Reform and Conservative conversions must take place outside the state, similar to civil marriages) the right to immigrate to Israel. A 1970 amendment, extended immigration rights to "a child and a grandchild of a Jew, the spouse of a Jew, the spouse of a child of a Jew and the spouse of a grandchild of a Jew".
Japan
According to Japanese immigration centre [47], the number of foreign resdents in Japan has been steadily increased, and the number of foreign residents (including permanent residents, but excluding illegal immigrants and short-term visitors such as tourists) were more than 2 million people in 2005. [47] Also, according to Japanese Association for Refugees, (or JAR for short),[48] the number of refugees who applied to live in Japan rapidly increased since 2006, and there were more than a thousand applications from all over the world, who seek refugee status to live in Japan in the year of 2008.[48] However, the refugee policy of Japanese government has been criticized both domestically and internationally, because the number of refugees in Japan is still small compared to the countries like Canada in North America or France in Western Europe.
Australia
The overall level of immigration to Australia has grown substantially during the last decade. Net overseas migration increased from 30,000 in 1993[49] to 118,000 in 2003-04.[50] The largest components of immigration are the skilled migration and family re-union programs. In recent years the mandatory detention of unauthorised arrivals by boat has generated great levels of controversy. During the 2004-05, total 123,424 people immigrated to Australia. Of them, 17,736 were from Africa, 54,804 from Asia, 21,131 from Oceania, 18,220 from United Kingdom, 1,506 from South America, and 2,369 from Eastern Europe.[41] 131,000 people migrated to Australia in 2005-06[51] and migration target for 2006-07 was 144,000.[52]
New Zealand
New Zealand has relatively open immigration policies. 23% of the population was born overseas, mainly in Asia, Oceania, and UK, one of the highest rates in the world. In 2004-2005, a target of 45,000 immigrants was set by the New Zealand immigration Service and represented 1.5% of the total population.[citation needed]
United States of America
From 1850 to 1930, the foreign born population of the United States increased from 2.2 million to 14.2 million. The highest percentage of foreign born people in the United States were found in this period, with the peak in 1890 at 14.7%. During this time, the lower costs of Atlantic Ocean travel in time and fare made it more advantageous for immigrants to move to the U.S. than in years prior. Following this time period immigration fell because in 1924 Congress The Immigration Act of 1924 favored immigrant source countries that already had many immigrants in the U.S. by 1890.[53] Immigration continued to fall throughout the 1940s and 1950's, but it increased again afterwards. but was still low by historical standards.[54] After 2000, immigration to the United States numbered approximately 1,000,000 per year. In 2006, 1.27 million immigrants were granted legal residence. Mexico has been the leading source of new U.S. residents for over two decades; and since 1998, China, India and the Philippines have been in the top four sending countries every year.[55] The U.S. has often been called the "melting pot"(derived from Carl N. Degler, a historian, author of Out of Our Past), a name derived from United States' rich tradition of immigrants coming to the US looking for something better and having their cultures melded and incorporated into the fabric of the country. Emma Lazarus, in a poem entitled "The New Colossus," which is inscribed on the pedestal of the Statue of Liberty tells of the invitation extended to those wanting to make the US their home.
Not like the brazen giant of Greek fame,
With conquering limbs astride from land to land; Here at our sea-washed, sunset gates shall stand A mighty woman with a torch, whose flame Is the imprisoned lightning, and her name Mother of Exiles. From her beacon-hand Glows world-wide welcome; her mild eyes command The air-bridged harbor that twin cities frame. "Keep, ancient lands, your storied pomp!" cries she With silent lips. "Give me your tired, your poor, Your huddled masses yearning to breathe free, The wretched refuse of your teeming shore. Send these, the homeless, tempest-tost to me,
I lift my lamp beside the golden door!"
— Emma Lazarus, Statue of Liberty
Since World War II, more refugees have found homes in the U.S. than any other nation and more than two million refugees have arrived in the U.S. since 1980 (representing less than 1% of the entire United States population).[citation needed] Of the top ten countries accepting resettled refugees in 2006, the United States accepted more than twice as much as the next nine countries combined, although some smaller countries accept more refugees per capita.[citation needed]
See also
Notes
- ^ Rich world needs more foreign workers: report, FOXNews.com, December 02, 2008
- ^ See the NIDI/Eurostat push and pull study for details and examples: [1]
- ^ a b Boustan, Leah. "Fertility and Immigration." UCLA. 15 Jan. 2009.
- ^ "Japanese Immigration Policy: Responding to Conflicting Pressures". Migration Information Source. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ "[[Koreans in Japan]]". Han.org. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^ "Eures - Free Movement". European Union. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ See, e.g., EU Enlargement in 2007: No Warm Welcome for Labor Migrants, by Catherine Drew and Dhananjayan Sriskandarajah, Institute for Public Policy Research
- ^ "Independent: "Realism is not racism in the immigration debate"". independent.ie. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ ""Italy's Recent Change From An Emigration Country to An Immigration Country and Its Impact on Italy's Refugee and Migration Policy" by Andrea Bertozzi". Cicero Foundation. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ "BBC: EU nations clash over immigration". Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ "Deutsche Welle: Germans Consider U.S. Experience in Immigration Debate". Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ "BBC: Short History of Immigration". Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ "BBC: Analysis: Europe's asylum trends". Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ see, e.g., http://cmd.princeton.edu/papers/POM_0408.pdf or http://cmd.princeton.edu/files/POM_june2007.pdf
- ^ "BBC: Q&A: US immigration debate". Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ "Mayor Bloomberg: Right on Neighborhoods, Right on Immigration". Manhattan-institute.org. 2008-01-28. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Theresa Hayter, Open Borders: The Case Against Immigration Controls, London: Pluto Press, 2000.
- ^ The Ethical Case for an Open Immigration Policy
- ^ Eurostat News Release on Immigration in EU
- ^ "Article on Spanish Immigration". Guardian. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Europe: Population and Migration in 2005". Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Inflow of third-country nationals by country of nationality". Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Immigration and the 2007 French Presidential Elections
- ^ "British Immigrants Swamping Spanish Villages?". Bye Bye Blighty article. 2007-01-16. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Immigration to Norway increasing". Workpermit.com. 2007-05-08. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Immigrant population". Ssb.no. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk_politics/7737134.stm
- ^ "BBC Thousands in UK citizenship queue". BBC News. 2006-02-12. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ 1,500 immigrants arrive in Britain daily, report says[dead link]
- ^ Indians largest group among new immigrants to UK[dead link]
- ^ 750,000 and rising: how Polish workers have built a home in Britain.
- ^ http://www.homeoffice.gov.uk/about-us/organisation/ministers1/phil-woolas/
- ^ "BBC article: Btits Abroad Country by Country". BBC News. 2006-12-11. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Marrero, Pilar (2004-12-09). "Immigration Shift: Many Latin Americans Choosing Spain Over U.S." Imdiversity.com. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Spain: Immigrants Welcome". Businessweek.com. 2007-05-21. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Instituto Nacional de Estadística: Avance del Padrón Municipal a 1 de enero de 2006. Datos provisionales
- ^ "Spain grants amnesty to 700,000 migrants". Guardian. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Portugal - Emigration". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Charis Dunn-Chan ,Portugal sees integration progress, BBC
- ^ Benjamin Dolin and Margaret Young, Law and Government Division (2004-10-31). "Canada's Immigration Program". Library of Parliament. Retrieved 2006-11-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b "Inflow of foreign-born population by country of birth, by year". Migrationinformation.org. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ Fontaine, Phil (April 24, 1998). "Modern Racism in Canada by Phil Fontaine" ([dead link]). Queen's University.[dead link]
- ^ Is the current model of immigration the best one for Canada?, Globe and Mail, 12 December 2005. Retrieved 16 August 2006.
- ^ Walter Laqueur (2003) The History of Zionism Tauris Parke Paperbacks, ISBN 1860649327 p 40
- ^ A national liberation movement: Rockaway, Robert. Zionism: The National Liberation Movement of The Jewish People, World Zionist Organization, January 21, 1975, accessed August 17, 2006). Shlomo Avineri:(Zionism as a Movement of National Liberation, Hagshama department of the World Zionist Organization, December 12, 2003, accessed August 17, 2006). Neuberger, Binyamin. Zionism - an Introduction, Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs, August 20, 2001, accessed August 17, 2006).
- ^ http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/Judaism/jewpop.html accessed Feb 2009
- ^ a b 平成17年末現在における外国人登録者統計について(Number of Foreign residents in Japan)
- ^ a b 2008年9月19日-日本での難民申請数 初の1000人突破に関するリリース (People seeking refugee status to stay in Japan are more than 1000 this year (September 19, 2008 article)
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics, International migration
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics, 3101.0 Australian Demographic Statistics
- ^ Settler numbers on the rise[dead link]
- ^ "Australian Immigration Fact Sheet 20. Migration Program Planning Levels". Immi.gov.au. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ "Immigration Act of 1924". State.gov. 2007-07-06. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ [2] Jenson, Campbell, and Emily Lennon. "Historical Census Statistics on the Foreign born population."
- ^ "United States: Top Ten Sending Countries, By Country of Birth, 1986 to 2006 (table available by menu selection)". Migration Policy Institute. 2007. Retrieved 2007-07-05.
Further reading
- Appel, Jacob. The Ethical Case for an Open Immigration Policy May 4,2009.
- Balin, Bryan. State Immigration Legislation and Immigrant Flows: An Analysis Johns Hopkins University, 2008.
- Bauder, Harald. Labor Movement: How Migration Regulates Labor Markets, New York: Oxford University Press, 2006.
- Center for Immigration Studies Refer to "Publications" for research on illegal immigration, demographic trends, terrorism concerns, environmental impact, and other subjects.
- De La Torre, Miguel A., Trails of Hope and Terror: Testimonies on Immigration. Maryknoll, NY: Orbis Press, 2009.
- Esbenshade, Jill. Division and Dislocation: Regulating Immigration through Local Housing Ordinances. Immigration Policy Center, American Immigration Law Foundation, Summer 2007.
- Ewing, Walter A. Border Insecurity: U.S. Border-Enforcement Policies and National Security, Immigration Policy Center, American Immigration Law Foundation, Spring 2006.
- Freeman, Joe. Living and Working in the European Union for Non-EU Nationals. Lulu.com, 2007. ISBN 0-9786254-0-4
- Immigration Policy Center. Economic Growth & Immigration: Bridging the Demographic Divide. Immigration Policy Center, American Immigration Law Foundation, November 2005.
- Kolb, Eva. The Evolution of New York City's Multiculturalism: Melting Pot or Salad Bowl. Immigrants in New York from the 19th Century until the End of the Gilded Age. BOD, 2009. ISBN 3837093034
- Legrain, Philippe. Immigrants: Your Country Needs Them. Little Brown, 2007. ISBN 0316732486
- Massey, Douglas S. Beyond the Border Buildup: Towards a New Approach to Mexico-U.S. Migration. Immigration Policy Center, American Immigration Law Foundation, September 2005.
- Massey, Douglas S., Joaquín Arango, Hugo Graeme, Ali Kouaouci, Adela , Pellegrino, and J. Edward Taylor.Worlds in Motion: Understanding International Migration at the End of the Millennium. New York: Oxford University Press, 2005. ISBN 0-19-928276-5
- Meilander, Peter C. Towards a Theory of Immigration. Palgrave Macmillan, 2001. ISBN 978-0312240349
- Molina, Natalia. Fit to Be Citizens?: Public Health and Race in Los Angeles, 1879-1940. University of California Press, 2006.
- Myers, Dowell. Immigrants and Boomers: Forging a New Social Contract for the Future of America. Russell Sage Foundation, 2007. ISBN 978-0-87154-636-4
- Passel, Jeffrey S. Estimates of the Size and Characteristics of the Undocumented Population. Pew Hispanic Center, March 2005.
- Passel, Jeffrey S. Growing Share of Immigrants Choosing Naturalization. Pew Hispanic Center, March 2007.
- Passel, Jeffrey S. and Roberto Suro. Rise, Peak and Decline: Trends in U.S. Immigration. Pew Hispanic Center, September 2005.
- Pearce, Susan C. Immigrant Women in the United States: A Demographic Portrait. Immigration Policy Center, American Immigration Law Foundation, Summer 2006.
- Portes, Alejandro and József Böröcz, "Contemporary Immigration: Theoretical Perspectives on Its Determinants and Modes of Incorporation" International Migration Review, 23,3, Silver Anniversary Issue, International Migration: an Assessment for the 90's. (Autumn, 1989), pp. 606–630.
- Rumbaut, Ruben and Walter Ewing. "The Myth of Immigrant Criminality and the Paradox of Assimilation: Incarceration Rates among Native and Foreign-Born Men." The Immigration Policy Center, Spring 2007.
- Sirkeci, Ibrahim The Environment of Insecurity in Turkey and the Emigration of Turkish Kurds to Germany, ISBN 978-0-7734-5739 New York, Edwin Mellen Press, 2006.
- Valle, Isabel. Fields of Toil: A Migrant Family's Journey. ISBN 978-0-87422-101-5
- West, Lorane A. Color: Latino Voices in the Pacific Northwest. ISBN 978-0-87422-274-6
- Zolberg, Aristide. A Nation by Design: Immigration Policy in the Fashioning of America. Harvard University Press, 2006. ISBN 0674022181
External links
- Immigration and Migration from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- International Migration from the United Nations
- Stalker's Guide to International Migration—Comprehensive interactive website on migration
- The Center for U.S. - Mexico Immigration Analysis
- Migration Information Source
- December 18 International advocacy and resource centre on the human rights of migrants.
- International Organisation for Migration
- Migration Letters journal
- UNESCO Programme on International Migration and Multicultural Policies
- OECD Migration Data
- BBC News Factfile: Global migration
- Immigration Newspaper Archive A collection of more than 50,000 searchable newspaper articles on Immigration.
- Migration on the Diplomacy Monitor
- A world map with territory sizes adjusted to the number of immigrants living in those countries
- Empowerment & Migration : Events and materials on migration
- Golden Venture A documentary film on the Golden Venture incident of 1993, a crucial turning point in US immigration policy.
- Princeton Center for Migration and Development—a leading research center on migration to the USA
- Casahistoria - European emigration since 1800—links to 19th & 20th century global European emigration
- Eurasylum Documents on immigration, asylum and refugee policy, and human trafficking/smuggling internationally
- Do Foreigners Have Rights? François Crépeau, Professor of International Law, University of Montreal
- Immigrants from Africa Haraga, photo essay about immigrants
- Immigration at Curlie
