Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel |
|---|
 |
| By year (list) |
| Groups responsible |
| Rocket types |
| Cities affected |
| Regional Council areas affected |
| Settlements affected (evacuated) |
| Defense and response |
| See also |
Since 2001, Palestinian militants have launched thousands[1][2][3][4] of rocket and mortar attacks on Israel from the Gaza Strip as part of the continuing Arab–Israeli conflict. From 2004 to 2014, these attacks have killed 27 Israeli civilians, 5 foreign nationals, 5 IDF soldiers, and at least 11 Palestinians[5] and injured more than 1900 people,[citation needed] but their main effect is their creation of widespread psychological trauma and disruption of daily life among the Israeli populace.[6] Medical studies in Sderot, the Israeli city closest to the Gaza Strip, have documented a post-traumatic stress disorder incidence among young children of almost 50%, as well as high rates of depression and miscarriage.[7][8][9] A public opinion poll conducted in March 2013 found that most Palestinians do not support firing rockets at Israel from the Gaza Strip.[10] Another poll conducted in September 2014 found that 80% of Palestinians support firing rockets against Israel if it does not allow unfettered access to Gaza.[11] These rocket attacks have caused flight cancellations at Ben Gurion airport.[12]
The weapons, often generically referred to as Qassams, were initially crude and short-range, mainly affecting Sderot and other communities bordering the Gaza Strip. In 2006, more sophisticated rockets began to be deployed, reaching the larger coastal city of Ashkelon, and by early 2009 major cities Ashdod and Beersheba had been hit by Katyusha, WS-1B[13] and Grad rockets.[14] In 2012, Jerusalem and Israel's commercial center Tel Aviv were targeted with locally made "M-75" and Iranian Fajr-5 rockets, respectively,[15] and in July 2014, the northern city of Haifa was targeted for the first time.[16] A few projectiles have contained white phosphorus said to be recycled from unexploded munitions used by Israel in bombing Gaza.[17][18][19][20][21]
Attacks have been carried out by all Palestinian armed groups,[22] and, prior to the 2008–2009 Gaza War, were consistently supported by most Palestinians,[23][24][25][26] although the stated goals have been mixed. The attacks, widely condemned for targeting civilians, have been described as terrorism by United Nations, European Union and Israeli officials, and are defined as war crimes by human rights groups Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch. The international community considers indiscriminate attacks on civilians and civilian structures that do not discriminate between civilians and military targets illegal under international law.[27][28]
Israeli defenses constructed specifically to deal with the weapons include fortifications for schools and bus stops as well as an alarm system named Red Color. Iron Dome, a system to intercept short-range rockets, was developed by Israel and first deployed in the spring of 2011 to protect Beersheba and Ashkelon, but officials and experts warned that it would not be completely effective. Shortly thereafter, it intercepted a Palestinian Grad rocket for the first time.[29]

In the cycle of violence, rocket attacks alternate with Israeli military actions. From the outbreak of the Al Aqsa Intifada (September 30, 2000) through March 2013, 8,749 rockets and 5,047 mortar shells were fired on Israel,[30] while Israel has conducted several military operations in the Gaza Strip, among them Operation Rainbow (2004), Operation Days of Penitence (2004), Operation Summer Rains (2006), Operation Autumn Clouds (2006), Operation Hot Winter (2008), Operation Cast Lead (2009), Operation Pillar of Defense (2012), and Operation Protective Edge (2014).
Overview

Attacks began in 2001. Since then (August 2014 data), almost 20,000 rockets have hit southern Israel,[31][32] all but a few thousand of them since Israel withdrew from the Gaza Strip in August 2005. Hamas justified these as counter-attacks to the Israeli blockade of Gaza. The rockets have killed 28 people and injured hundreds more. The range of the rockets has increased over time. The original Qassam rocket has a range of about 10 km (6.2 mi) but more advanced rockets, including versions of the old Soviet Grad or Katyusha have hit Israeli targets 40 km (25 mi) from Gaza.[33]
Some analysts see the attacks as a shift away from reliance on suicide bombing, which was previously Hamas's main method of attacking Israel, as an adoption of the rocket tactics used by Lebanese group Hezbollah.[34]
Participating groups
All the Palestinian armed groups carry out rocket and mortar attacks, with varying frequency.[22] The main groups are Hamas, Islamic Jihad,[35] the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine,[36] the Popular Resistance Committees,[37] Fatah,[38] and the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine.[22] In June 2007 Hamas took over from Fatah as the de facto governing authority in the Gaza Strip,[39] while Fatah holds the presidency of the Palestinian National Authority.
Islamic Jihad has involved other Palestinians in the activities, running summer camps where children were taught how to hold a Qassam rocket launcher.[40] One Islamic Jihad rocket maker, Awad al-Qiq, was a science teacher and headmaster at a United Nations school. Christopher Gunness, a UNRWA spokesman, said the UN had "zero-tolerance policy towards politics and militant activities in our schools", but that they "cannot police people's minds."[41]
Palestinian security forces say that they do little or nothing to prevent rocket attacks or to hold responsible the militants who launch them, according to a 2007 report by Human Rights Watch[42]
The Israeli Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center estimated that in 2007[43] the proportions of rockets fired from the Gaza Strip were:
- 34% – Palestinian Islamic Jihad (Al Quds)
- 22% – Hamas (Qassam)
- 8% – Fatah (Kafah)
- 6% – Popular Resistance Committees (al Nasser)
- 30% – unknown
History
1975
On May 3, 1975 at 4:15am, two 107mm rockets struck Jerusalem's central area, not far from the Jerusalem Botanical Gardens.[44]
2001–06


Rockets were originally fired mainly on Sderot, an Israeli city on the border of the Gaza Strip.[45] Sderot's population density is slightly greater than that of the Gaza Strip. Due to this, and despite the imperfect aim of these homemade projectiles, they have caused deaths and injuries, as well as significant damage to homes and property, psychological distress and emigration from the city. Ninety percent of the city's residents have had a rocket exploding in their street or an adjacent one.[33]
On March 28, 2006, while Israelis went to general elections, the first Katyusha rocket from Gaza was fired at Israel. The rocket fell near the Itfah kibbutz on the outskirts of Ashkelon and caused no damage or casualties. Islamic Jihad claimed responsibility.[46][47] Several months later, On July 5, 2006, a rocket hit the center of Ashkelon for the first time, striking an empty high school. Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert called the attack, which was claimed by Hamas, an "escalation of unprecedented gravity",[48][49] but the event was quickly overshadowed by the 2006 Lebanon War.
On 25 of May 2006 the al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades group that published on April 2006 that they had been launching long range missile on Israeli cities,[50] sent a letter to Ramattan that they had developed chemical and biological weapons and threaten with chemical warfare.[51][52][53][54][55] later that month report of use of chemical weapons by that group had been published in the media.[56]
On 8 June, an event occurred that formed part of a 'chronology of crisis' leading to the most intense barrage of rocket attacks during 2006.[57] Although Israel acknowledged that Hamas was largely sticking to the February 2005 cease-fire (in Fatah-controlled Gaza), it recommenced assassinations of Hamas leaders with the killing of Jamal Abu Samhadana.[58] The Israeli military said Samhadana and the other targeted militants were planning an attack on Israel.[59] The next day, in response to the assassination and calls for revenge, Islamic Jihad fired rockets at Israel, and a few hours later the IDF retaliated in turn with a bombardment of launch sites on a Gaza beach near Beit Lahia.[60] During the time span of the IDF bombardment, a civilian Gaza family, the Ghalias, was all but wiped out in an explosion.[61] In response to the assassination of its Ministry official and the civilian 'beach' deaths, Hamas announced that it was going to recommence rocket attacks.[62] This was followed by a series of mutual attacks and reprisals between the IDF and Gaza factions, culminating in the abduction of two suspected Hamas members, and, on the following day, of IDF Corporal Gilad Shalit.[57][58] The latter event gave rise to Operation Summer Rains,[63] as a result of which Gaza’s electricity network was damaged,[64] and 402 Palestinians and 7 Israelis were killed.[65]
2007
On January 5, 2007 Palestinian militants fired a Katyusha rocket at Ashkelon. The Katyusha has a range of 18–20 kilometers, and the rocket was fired from the Al-Atatra region in the northern Gaza Strip, traveling about 17 kilometers before reaching its target. No one was hurt in the Katyusha attack.[66] On October 7, 2007 the Popular Resistance Committees claimed responsibility for a Grad-type Katyusha that hit Netivot. During this period, Katyusha attacks from Gaza were rare.[67]
2008–09

In January 2008 the border between Gaza and Egypt was breached by Hamas. It allowed them to bring in Russian and Iranian made rockets with a larger range.
In the first half of 2008, the number of attacks rose sharply, consistently totaling several hundred per month. In addition, Ashkelon was hit many times during this period by Grad rockets.
On February 26, 2008 a Grad rocket hit the hospital grounds of the Barzilai Medical Center, approximately 200 meters away from the neonatal intensive-care unit. As it is only 6 miles away from the Gaza border, it is the frequently the target of rocket attacks, with 140 rockets fired at it over the course of one weekend.[68][69][70]

After reports of shells with white phosphorus[73] launched against southern parts of Israel on 14 January 2009, Israeli medical emergency forces are now taught how to treat white phosphorus victims and are ordered to have equipment to handle white phosphorus.[74][75][76][77]
From June 19 to December 19, 2008, an Egyptian-mediated ceasefire between Israel and Hamas was in effect. During this time, only several dozen rockets were fired at Israel, a marked decrease from the pre-ceasefire period. Hamas imprisoned some of those firing rockets.[78]
During the Gaza War, Palestinian militants began to deploy improved Qassam and factory-made rockets with a range of 40 kilometers.[79] Rockets reached major Israeli cities Ashdod,[80] Beersheba and Gedera for the first time, putting one-eighth of Israel's population in rocket range[81] and raising concerns about the safety of the Tel Aviv metropolitan area, Israel's largest population center,[82][83] as well as the Negev Nuclear Research Center.[84] According to Israeli authorities, 571 rockets and 205 mortar shells landed in Israel during the 22 days of the conflict.[22]

On January 18, 2009, following a unilateral ceasefire declaration by Israel, Hamas and Islamic Jihad announced that they would cease rocket attacks for one week.[85] After that, rockets and mortar attacks continued almost daily through February.[86][87]
2010
According to the Israel Security Agency's annual report, Palestinians carried out 150 rocket launches and 215 mortar launches at Israel during the year. This represented a decrease in both types of attacks compared to 2009, in which there were 569 rocket launches and 289 mortar launches.[88][89]
The report said Iran succeeded in smuggling 1,000 mortar shells and hundreds of short-range rockets into the Gaza Strip over the course of the year.[88] The security agency also warned that the Sinai Desert was turning into Hamas's "backyard" for operations and storage of arms. 2010 saw two unique instances of Hamas firing rockets from the Sinai at the southern Israeli port city of Eilat.[88]
On 18 March, Thai national Manee Singmueangphon was killed by a Palestinian Qassam rocket launched at a greenhouse in Netiv Haasara. Both Ansar al Sunna, an Islamist group thought to have links with al-Qaeda in Iraq, and al Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades, the military wing of Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas's Fatah party, claimed responsibility for the attack.
On 30 July, a Hamas Grad missile hit a residential neighborhood in the heart of the Israeli coastal city of Ashkelon. No one was physically injured, but eight people suffered from shock and surrounding apartment buildings sustained damage.
On 2 August, Hamas militants in Egypt fired seven Iranian-made Grad missiles at the resort city of Eilat in the extreme south of Israel. Overshot missiles hit the Jordanian city of Aqaba, killing one person and wounding several.
On 20 October, an accidental explosion occurred at a Hamas Qassam rocket training site in the densely crowded Tel As-Sultan neighborhood of Rafah in the southern Gaza Strip. Thirteen people were injured by flying shrapnel, including five children and three women.[90]
2011
Over the course of 2011, 680 rockets, mortars and Grad missiles were fired from the Gaza Strip into Israel.[91] At the end of 2010, Palestinian Islamic Jihad said it and other Palestinians militant groups in the Gaza Strip would temporarily halt rocket attacks against Israel.[92] On 7 January, it claimed responsibility for a mortar attack that injured three agricultural workers,[93] and the group was responsible for most of the attacks on Israel in the first two weeks of the year. On 12 January, the group declared again that it would cease firing rockets.[94] Multiple, unclaimed rocket and mortar attacks occurred on 16, 17 and 18 January.
On 2 January, it was revealed that two East Jerusalem Arabs, employees of the British Consulate General in Jerusalem, were arrested for suspected involvement in an aborted Hamas plot to fire a missile at Teddy Stadium during a soccer match. The two were charged the following day with weapons trafficking.[95][96]
On 15 March, Israel seized the Victoria, a ship containing concealed Iranian missiles destined for the Gaza Strip.[97]
On 27 March, Israel first deployed the new Iron Dome missile defense system to protect Beersheba. The city, one of Israel's largest, had recently been targeted again by Palestinian missiles after being safe since the 2008-2009 Gaza War. A week later, a second battery was deployed to protect Ashkelon.[98] On 7 April, the Ashkelon battery successfully intercepted a Palestinian Grad missile fired at the city, marking the first successful interception of a short range rocket in history.[29] On 31 August, Israel deployed a third battery outside Ashdod before the new school year. As of that date, Iron Dome had intercepted several dozen Gazan rockets at an estimated cost of $100,000 per interception, not including the price of the system itself.[99]
On 4 April, Israel indicted alleged Hamas "rocket godfather" Dirar Abu Sisi in the Beersheba District Court. Abu Sisi had reportedly been captured by Israel in the Ukraine a month prior. He denied any wrongdoing.[100]
On 7 April, Hamas militants fired a Kornet anti-tank missile at an Israel school bus. The sole passenger on board, 16-year-old boy Daniel Viflic, was killed.
On 18 August, a series of cross-border attacks were carried out in southern Israel near the Egyptian border. The initial attacks sparked several days of clashes between Israel and Palestinian militant groups that resulted in substantial casualties to both sides.
2012
The Jerusalem Post and Ynet news reported that in January, 2012, two mortars were fired from Gaza into the area governed by the Eshkol Regional Council which were determined by the Israeli military to have contained white phosphorus; the shells were reported to have landed in open fields, causing no injuries or damage.[101] The newspaper said the Eshkol Regional Council filed a formal complaint with the United Nations, noting that the Geneva Conventions prohibit the use of phosphorus against civilians.[20][102]
Until April 2012 more than 360 rocket and mortar attacks had been launched (~300 during the March 2012 Gaza–Israel clashes).[citation needed]
The Ynet newsreported that In May 2012 the Islamic Jihad published video footage of a multi-barrel rocket launcher mounted on vehicle[103]
On October 24, 2012, "[m]ore than 65 rockets were fired into southern Israel from the Gaza Strip." A woman in Ashkelon, three foreign workers, and a policeman received injuries. "Several people were treated for shock," according to JNS.org.[104]
2013
On March 21, during US President Barack Obama's official visit to Israel, Palestinians in Beit Hanoun fired four rockets at the Israeli city of Sderot, triggering alarms in local communities and forcing residents on their way to work or school to run to bomb shelters. One rocket hit the backyard of a home in the city, spraying shrapnel into the walls and shattering windows. A second projectile landed in an open area within the surrounding Sha'ar Hanegev Regional Council. The two remaining rockets were believed to have landed within the Gaza Strip.[105][106][107][108] The Mujahedeen Shura Council, a Palestinian Salafi group, claimed responsibility for the attack[109]
On April 2, Palestinians attempted to fire two mortar shells into Israel; both landed within the Gaza Strip. Later, in the evening, a third projectile was fired into the Eshkol Regional Council.[110] The Mujahedeen Shura Council claimed responsibility for the attacks.[111][112][113] Israel responded to the attacks with air strikes on two targets in the Gaza Strip that night, causing no injuries.[111] This was the first such strike since Operation Pillar of Defense. Israeli Defense Minister Moshe Yaalon said: "[W]e see Hamas as being responsible for everything that is fired from the Strip at Israel. We won't allow any routine involving a drizzle of rockets at our civilians and forces."[114]
On April 3, Palestinians from Gaza fired two rockets at the Israeli city of Sderot. The rockets struck during the morning as children were arriving to school, triggering the alert siren and sending families into bomb shelters for cover.[114] The United Nations special envoy to the Middle East Robert Serry condemned the "indiscriminate firing of rockets into civilian areas" and also called on Israel to exercise restraint.[115] France said it "harshly condemns" the rocket fire on the "civilian population in south Israel". Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said: "If the quiet is violated, we will respond strongly".[116]
On April 4, Palestinians again fired a rocket and three mortar shells at Israel. A rocket landed in an open area in the Eshkol Regional Council at around 2 am, triggering alarms in nearby communities, while two of the mortars fell within the Gaza Strip.[117][118]
On April 29, a rocket was fired from the Gaza Strip which impacted southern Israel, causing no casualties or damage.[119]
On June 19, three Grad rockets were fired from the Gaza Strip, hitting the Israeli town of Ashkelon. The attacks caused no injuries, marking the first time that rockets had been fired from Gaza since April 29.[120]
2014

On 5 March, the Israeli Navy intercepted a ship containing dozens of long-range rockets being smuggled from Iran to the Gaza Strip.[121]

On 10 March, Hamas, the Palestinian Islamist group that controls the Gaza Strip, unveiled a monument to its rocket attacks on Israeli cities and towns, a life-sized model of an M-75 rocket in Gaza City. The group declared that the attacks "managed to take the battle to the heart of the Zionist entity (Israel)".[123]
2015
On April 23, Israel's 67th independence day, a rocket was fired from the Gaza Strip at Israel.[124] The rocket hit an open field in the Sha'ar HaNegev region near Sderot,[125] causing no injuries or damage.
On May 27, an M-75 or Grad missile impacted in Gan Yavne, a city east of Ashdod. No reports of injuries or damage were noted initially.[126]
2016
Tactics
Khaled Jaabari, Gaza commander of the al-Aqsa Martyr's Brigades, said that the group uses Google Earth to determine targets.[127] Rocket fire occasionally occurs in the early morning when children head to school.[128][129]
A source close to Hamas described the movement's tactic of launching projectiles from between homes during the 2008-2009 Israel-Gaza conflict: "They fired rockets in between the houses and covered the alleys with sheets so they could set the rockets up in five minutes without the planes seeing them. The moment they fired, they escaped, and they are very quick."[130] Videos released by Hamas in 2011 show Qassam rockets being fired from residential areas and mosques. According to Yedioth Aharonoth journalist Elior Levy, "Gaza terror cells choose to fire from urban areas knowing that the Israel Defense Forces refrain from intercepting them for fear of hurting civilians. The killing of civilians in Gaza also serves the terrorists' purposes who claim Israel is committing war crimes in Gaza".[131]
It has been documented, that Arab terrorist groups and Hamas placed weapons and missile launchers in densely populated areas.[132] Human Rights Watch issued a report condemning the firing of Kassam rockets as "war crimes", stating "None of these rockets can be reliably aimed… Such weapons are inherently indiscriminate when directed towards densely populated areas. The absence of Israeli military forces in the areas struck by the rockets, as well as statements from the leaders of Hamas and other armed groups, indicate that many of these attacks are deliberately intended to strike Israeli civilians and civilian structures… Hamas and other Palestinian armed groups have frequently violated the laws of war by firing rockets from within populated areas…"[27] Indiscriminate attacks on civilians and civilian structures that do not discriminate between civilians and military targets are illegal under international law.[27][28]
Denial of service attacks on emergency services
There have been a number of reports in the Israeli press about denial of service attacks by Palestinians on the Magen David Adom and other emergency call lines after rocket and mortar attacks, that resulted in a development of a filtering system that had been installed in MDA and other emergency call systems during 2006-2008.[citation needed]
Israeli defensive measures
Fortifications and bomb shelters

A guidance paper by the Israeli home front command, that is given for each household in Israel, include sections for basic treatment of chemical warfare victims.[133] The Home Front Command performs periodic training for citizens for chemical and biological attacks. As of 2006[134][135] all public educational facilities in confrontation areas are ordered to be built bomb proof (can sustain a direct hit from a katusha missile)[134] and must have an option to be connected to chemical and biological purifying systems, with an exception for kindergartens and special care education systems that must have a central air purifying system. All medical or treatment facilities must have a shelter that can be gas proof (can be sealed in a form that the only source of air would be via the purifying ventilation systems) with connection to purifying systems.[136] All long term treatments facilities must be built as a bomb shelter[136] and must be built to sustain 4 hours of isolation.[137]
Residential buildings and homes in Israel built after 1990 are generally equipped with Merkhav Mugan. Single- or two-story buildings built between 1982-1990 in the northern parts are equipped with a fortified route (sometimes below ground level) into a public bomb shelter. Older buildings generally lack these fortifications. (All buildings built between 1951 - 1982 are designed with access for neighborhood public bomb shelters[138]). As of February 2009, approximately 5,000 residents of southern Israel, mostly elderly immigrants from the former Soviet Union, lacked proper reinforced rooms or reasonable access to public shelters.[139] Many Sderot families sleep together in a single fortified room in their homes.[140]
In March 2008 the Israeli Government placed 120 fortified bus stops in Sderot, following a Defense Ministry assessment that most Qassam-related injuries and fatalities were caused by shrapnel wounds in victims on the street.[141] As of January 2009, all schools in Sderot have been fortified against rockets;[142] fortifications consist of arched canopies over roofs.[140] On January 3, 2009 a Grad rocket penetrated the fortification of a school in Ashkelon.[143]
In March 2009, Sderot inaugurated a reinforced children's recreation center built by the Jewish National Fund. The purpose of the center, which has "$1.5 million worth of reinforced steel", is to provide a rocket-proof place for children to play.[144][145] Sderot also has a "missile-protected playground," with concrete tunnels painted to look like caterpillars.[146]
As of 18 Feb 2010 all public safe places (Merkah mugan/bomb shelter) must be built with gas and liquid filtering systems (can defend from a chemical and biological missile attack for several hours),[147] And as of 18 May 2010 any new household without that will not be approved with form No.4 (the ability to connect a house to electricity and water)[148][149]
Red Color
The Israeli government has installed an alarm system called "Red Color" (צבע אדום) to warn citizens of impending rocket attacks, although its effectiveness has been questioned. The system currently operates in a number of southern Israeli cities within rocket range. When the signature of a rocket launch is detected originating in Gaza, the system automatically activates the public broadcast warning system in nearby Israeli communities and military bases. A two-tone electronic audio alert (with a pattern of high, 2 second pause, high-low) is broadcast twice, followed by a recorded female voice[150] intoning the Hebrew words for Red Color ("Tzeva Adom").[151] The entire program is repeated until all rockets have impacted and no further launches are detected. In Sderot, it gives residents approximately 15 seconds warning of an incoming rocket.[151] The system was installed in Ashkelon between July 2005 and April 2006.
Iron Dome
Iron Dome (Template:Lang-he) is a mobile system developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems designed to intercept short-range rockets with a range less than 70 km. In February 2007, the system was selected by Israeli Defense Minister Ehud Barak as the Israeli Defense Force's defense system against short range rockets. On July 7, 2008, the first test of the system was completed successfully, and the first operational test was expected to take place at the end of 2009.[152] The system was scheduled to be operational in 2010,[153] but was temporarily delayed.[154] In March, the system was deployed in several strategic sites near major Israeli southern cities.[155] On April 7, 2011, the system successfully intercepted a Grad rocket launched from Gaza for the first time.[156]
The system is composed of a radar, a control center, and interceptor missiles. Very limited information has been made available about the system in the Israeli media, but from this information it is known that the interceptor missile (named Tamir) is equipped with electro-optic sensors and several steering fins, providing it with high maneuverability. The system's radar identifies the rocket launch, extrapolates its flight path and transfers this information to the control center, which then uses this information to determine the projected impact location. If the projected target justifies an interception, then an interceptor missile is fired.
Effects
Casualties, fatalities and rockets fired

According to B'Tselem "from June 2004 to 23 July 2014, 26 Israeli civilians (four of them minors) and two foreign nationals were killed in Israel by Palestinian rocket and mortar fire. In addition, five soldiers were killed, three in Israel and two in the Gaza Strip. Another Israeli civilian and three foreign nationals were killed by rocket fire at settlements in the Gaza Strip, before they were evacuated."[157] There were 3 more civilian casualties during the 2014 Israel-Gaza conflict.[158] Most of those killed were civilians, including children.[22] The first casualties from the rocket fire were a 4-year-old boy and his grandfather, who were killed in June 2004.[159] Other victims include two small children, aged 2 and 4, who were killed while playing in the street later that same year,[159] and a teenage girl, Ayala-Haya (Ella) Abukasis, who was struck and killed while shielding her younger brother.[159] As of 2008, such rockets have demonstrated a kill ratio of 0.4 percent.[160] In addition, more than 1,700 have been injured.[33][161] Injuries have also occurred mainly among civilians, several of whom were injured very seriously.[22][161]
Misfired rockets have also killed and injured Palestinians within the Gaza Strip. Due to restrictions on information politics and a lack of free press in the Gaza Strip, precisely reporting the number of Palestinian victims is difficult. As far as it became known, the missiles, rockets and mortars have killed six Palestinians and injured dozens more. On June 8, 2005, rockets fired at the Israeli settlement of Ganei Tal killed two Palestinian workers and one Chinese worker in a packing plant. On August 2, 2005, a rocket apparently launched by Islamic Jihad killed a 6-year-old boy and his father in Beit Hanoun.[42] On December 26, 2008 a mortar aimed at Israel killed two Palestinian girls in the Gaza Strip, aged 5 and 12.[162]
Precisely counting the number of rockets fired is impossible, and differing estimates have been given. The injury figures and attack counts below are attributed to the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs.[163] Prior to September 4, 2005, the majority of attacks were against Israeli targets within the Gaza Strip.[163]
| Year | Dead | Injured | Rocket attacks | Mortar attacks | Total attacks | Total attacks % change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 0 | 4 | 4+ | |||
| 2002 | 0 | 35 | 35+ | |||
| 2003 | 0 | 155 | 155+ | |||
| 2004 | 4 | 281 | 281+ | |||
| 2005 | 2 | 401 | 854 | 1,255 | ||
| 2006 | 2 | 371 | 1,722 | 55 | 1,777 | |
| 2007 | 2 | 578 | 1,276 | 1,531 | 2,807 | |
| 2008 | 8 | 611 | 2,048 | 1,668 | 3,716 | |
| Israeli and Egyptian blockade of Gaza after Operation Cast Lead to stop missile fire into Israel[168] and arms import into Gaza.[169][170] | ||||||
| 2009 | 0 | 11 | 569 | 289 | 858 | |
| 2010 | 1 | 35 | 150 | 215 | 365 | |
| 2011 | 2 | 81 | 419 | 261 | 680[171] | |
| 2012 | 6[159][172] | 284+ | 2,256[173] | 17 | 2,273+[174][175] | |
| 2013 | 0 | 32 | 12 | 44 | ||
| 2014 | 6 | 80 | 2,800 | 1,700 | 4,500 [176] | |
| 2015* | 0 | 0 | 3[177] | 0 | 0 | |
| Total * | 33 | 1971+ | 12,338 | 6,500 | 18,928 | |
- as of the 6th of June 2015
Refugees

In May 2007, a significant increase in rocket attacks from Gaza prompted the temporary evacuation of thousands of residents from Sderot.[178] According to the United Nations, 40 percent of the city's residents left in the last two weeks of May.[179] During the summer of 2007, 3,000 of the city's 22,000 residents (comprising mostly the city's key upper and middle class residents) [180] left for other areas, out of rocket range.
During the 2008–2009 conflict, a large section of the residents of Ashkelon, a southern coastal city put in range of Grad-type rockets since the beginning of the conflict, fled the city for the relative safety of central and northern Israel.[181] On January 10–11, according to Israeli media, 40 percent of the residents fled the city, despite calls by the Mayor to stay.[182]
In February 2009, the BBC reported that 3,000 of Sderot's 24,000 residents had "upped and left."[6]
Education

Israeli media reported on May 28, 2007 that only 800 out of a total of 3000 pupils in Sderot had turned up to schools.[179]
During the 2008–2009 conflict, schools and universities in southern Israel closed due to rocket threats.[183] Hamas rockets landed on Israeli educational facilities several times (such as empty schools in Beersheba[184][185]) from 2008 to 2009, with no casualties as of January 15, except for cases of shock.[186][187][188][189] Studies resumed starting January 11, with IDF Home Front Command representatives stationed at schools.[190][191][192] Only schools with fortified classrooms and bomb shelters were allowed to bring in children.[193] Israeli Education Minister Yuli Tamir said she hoped a return to school would provide a little structure and routine in a time of great stress and uncertainty for the children.[194] Students were reluctant to return, with Sapir College in Sderot reporting less than 25 percent attendance after a student was killed by a rocket.[192][195]
In March 2009, the Ashkelon urban parent committee decided to keep children out of schools following a surge in the number of rocket attacks on southern Israel and a qassam hit on an empty school in the city. As a result, only 40 percent of school students and 60 percent of kindergarten children attended, though the municipality had decided to keep schools open.[196]
Psychological

In 2008, Natal, the Israel Center for Victims of Terror and War, conducted a study on the city of Sderot based on representative sampling. The study found that between 75 percent and 94 percent of Sderot children aged 4–18 exhibited symptoms of post-traumatic stress. 28 percent of adults and 30 percent of children had post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The co-director of the study emphasized the distinction between post-traumatic stress symptoms, such as problems sleeping and concentrating, and PTSD itself, which can interfere seriously with daily life.[128][197]
An American Psychiatric Association study published in 2010, headed by Professor Yair Bar-Haim of Tel Aviv University, found that incidence rate for post-traumatic symptoms among Israeli civilians was correlated with proximity to the Gaza Strip. Civilians who lived in areas where rockets frequently exploded, and where there was less warning time in advance of strikes, had a higher chance of developing post-traumatic symptoms than those living far enough from Gaza to have one minute or more in which to seek shelter after rockets were launched. The study also found that life under rocket fire sometimes led to cognitive disengagement from threat. Cognitive disengagement was positively correlated with the likelihood of developing pathologies such as post-traumatic stress disorder and depression.[198]
During the Gaza War, when rockets were falling on the city of Ashdod, the municipality opened a treatment centre for those with shell shock.[199]
According to a 2009 Amnesty International report,
Scores [of rockets] have struck homes, businesses, schools, other public buildings and vehicles in and around towns and villages in southern Israel. It is purely by chance that in most cases such strikes have not caused death or injury, and the lethal potential of such projectiles should not be underestimated. Above all, the constant threat of impending rocket attacks has caused fear and disrupted the lives of the growing number of Israelis who live within range of such attacks, reaching up to a million.[22]
Also in 2009, a spokeswoman for the Sderot Hosen Center, which provides psychological support and rehabilitation for the community, reported that attacks had taken a high toll on the mental health of children and adults in and around Sderot.
Children are afraid to sleep on their own, to be on their own, even to go to the toilet alone. They feel that their parents cannot protect them. Bed wetting is a common manifestation of their anxiety and insecurity. Their parents are similarly anxious and frustrated. It is even difficult to speak of PTSD, for as long as the rockets fall the trauma is renewed daily; we are not even in a post-trauma stage.[22]
Political
On December 12, 2007, after more than 20 rockets landed in the Sderot area in a single day, including a direct hit to one of the main avenues, Sderot mayor Eli Moyal announced his resignation, citing the government's failure to halt the rocket attacks.[200] Moyal was persuaded to retract his resignation.
On February 9, 2009, Palestinian Authority foreign minister Riad Malki accused Hamas of trying to influence the outcome of the 2009 Israeli general election by keeping up the rocket fire on southern Israel.[201]
Motives
Rationales given by the Palestinian groups responsible for the attacks vary. They include the arguments that violence against Jews is a religious obligation that brings one closer to God,[202][203] that the rockets are effective at drawing attention to Palestinian issues, and that they avenge perceived Israeli aggression.
Hamas

Hamas co-founder Mahmoud Zahar has said that the goal of the attacks is to force mass migration in Israel and disrupt the daily life of its citizens. Explaining why his group had moved from suicide bombing to rocket attacks, he said:
Which do you think is more effective, martyrdom operations or rockets against Sderot? Rockets against Sderot will cause mass migration, greatly disrupt daily lives and government administration and can make a much huger impact on the government. We are using the methods that convince the Israelis that their occupation is costing them too much. We are succeeding with the rockets. We have no losses and the impact on the Israeli side is so much.[204]
According to the BBC, Hamas views the attacks as legitimate because it regards the whole of historic Palestine (roughly coterminous with Israel, the West Bank, the Gaza Strip and Jordan) as Islamic land, and thus sees the state of Israel as an occupier.
[Hamas] regards the whole of historic Palestine as Islamic land and therefore views the state of Israel as an occupier, though it has offered a 10-year "truce" if Israel withdraws to the lines held before the war of 1967. It therefore generally justifies any actions against Israel, which has included suicide bombings and rocket attacks, as legitimate resistance. Specifically in Gaza, it argued that Israel's blockade justified a counter-attack by any means possible.[205]
Hamas has given other explanations concerning various attacks. Salah Bardawil, a Palestinian legislator who serves as spokesman for the Hamas faction in parliament, has said "We know we can't achieve military equality, but when a person suffers huge pain he has to respond somehow. This is how we defend ourselves. This is how we tell the world we are here."[206] Regarding specific strikes in 2007, Hamas political chief Khaled Mashaal called the attacks self-defense and retaliation against Israeli killings of Hamas supporters.[207] In January 2009 Mashaal called the rockets "our cry of protest to the world"[208] An attack in November 2008 was said by Hamas officials to be in revenge for the recent deaths of its militants and increased Israeli closing of Gaza crossings.[209] A barrage in December 2008 was described by the group as retaliation for the deaths of three of its fighters in combat with Israeli troops.[210]
PFLP
A spokesperson from the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP), on January 17, 2009, called the rockets a "representation of our resistance", stressing that as long as rockets were launched, "our cause is alive".
The rockets are both a practical and a symbolic representation of our resistance to the occupier [Israel]. They are a constant reminder that the occupier is in fact an occupier, and that no matter how they may engage in sieges, massacres, fence us in, deny us the basic human needs of life, we will continue to resist and we will continue to hold fast to our fundamental rights, and we will not allow them to be destroyed. So long as one rocket is launched at the occupier, our people, our resistance and our cause is alive.
This is why they targeted the rockets – the rockets do make the occupier insecure, because every one is a symbol and a physical act of our rejection to their occupation, to their massacres, to their crimes, and to their continuing assaults on our people. Each rocket says that we will not allow their so-called "solutions" that are based on the abrogation and denial of our rights.[211]
The PFLP claimed responsibility for an April 3, 2010 mortar attack on Israel's Shaar Hanegev region, saying that it was carried out "in response to Zionist crimes". The group did not elaborate further.[212][213]
Other groups
On January 19, 2009, the al-Aqsa Martyrs Brigades, the military wing of Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas's Fatah party, published a statement listing its claimed attacks on Israel, including claimed rocket and mortar attacks on Sderot and Ashkelon. The group said the attacks were carried out "to defend our people in the Gaza Strip" and "to defend the Gaza Strip in the face of Zionist arrogance", but did not elaborate further.[22][214]
The Popular Resistance Committees claimed that a January 7, 2010 mortar barrage was in "revenge" for an Israeli air strike several days earlier that killed two of the group's fighters.[215]
Ansar al-Sunna, a small, al-Qaida-inspired Salafist militant group, claimed responsibility for a March 18, 2010 Qassam rocket attack on Netiv Haasara that killed 33-year-old Thai national Manee Singmueangphon, calling it a response to Israel's "Judaization" of Islamic holy places. The group did not clarify which acts or which Islamic holy places it was referring to. Further obscuring the motivation for the attack, the Aqsa Martyrs Brigades, independently claimed responsibility later.[216][217][218][219]
Majlis Shura al-Mujahidin, a Salafi group in the Gaza Strip, emphasized in explaining its rocket attacks on Sderot in 2012 that "Jihad for the sake of Allah against the criminal Jews is an obligation that we draw closer to Allah whenever we find a way to that, in any place, by what Allah facilitates to us from the reasons of power and repelling".[202][203]
Views
Palestinians
Public opinion polls
Prior to the 2008–2009 Gaza War, polls conducted by the Palestinian Center for Policy and Survey Research (PCPSR) showed consistently high levels of support for the rocket attacks among the Palestinian public.
- September 2004: 75% of Palestinians support "the firing of rockets from Beit Hanoun", though 59% of the residents of Beit Hanoun reject the practice.[24]
- July 2006 Jerusalem Media & Communication Centre poll: 60.4% of Palestinians "support the continuation of firing rockets against Israeli targets as a suitable response within the current political conditions", whereas 36% "reject them and find them harmful to the Palestinian national interests".[220]
- September 2006: 63% of Palestinians agree "that Palestinians should emulate Hizbullah’s methods by launching rockets at Israeli cities", and 35% disagree.[25]
- March 2008: 64% of Palestinians support "launching rockets from the Gaza Strip against Israeli towns and cities such as Sderot and Ashkelon", and 33% oppose.[23][26]
Conversely, polls conducted after the Gaza War indicated weaker support for the attacks and relatively broad support for attempts to prevent them.
- January 2010 Palestinian Center for Public Opinion (PCPO) poll: 62.2% of Palestinians oppose "the re-firing of Al-Qassam rockets from Gaza at Israel" while 29.1% are in favor.[221]
- July 2010 PCPSR poll: 57% of Palestinians support Hamas attempts to prevent rocket launching against Israeli towns and 38% oppose.[222]
- July 2010 Arab World for Research and Development (AWRAD) poll: 68% of Palestinians do not want Hamas to resume its rocket attacks on Israel, while 25.5% believe the attacks should be resumed.[223]
- October 2010 PCPO poll: 49.4% of Palestinians oppose "the re-firing of al-Qassam rockets from Gaza at Israel" while 46.2% are in favor.[224]
- April 2011 JMCC poll: 38.6% of Palestinians say that "the locally-made rockets fired from Gaza Strip towards Israeli regions" "harm... Palestinian goals" and 25.4% say that the rockets "help... Palestinian goals".[225]
- May 2011 PCPO poll: 69.6% of Palestinians oppose the resumption "of launching Al-Qassam missiles from Gaza into Israel" and 29.8% support it.[226]
- November 2011 JMCC poll: 40.8% of Palestinians say that the rockets harm Palestinian goals and 27% say that they help Palestinian goals.[227]
- December 2012 JMCC poll: 9.7% say that "locally-made rockets fired from Gaza strip towards Israeli regions" harm Palestinian goals and 74% say they help them.[228]
- March 2013 JMCC poll: 38% support firing rockets at Israel from the Gaza Strip.[10]
Other

Palestinian National Authority President Mahmoud Abbas (of Fatah) has condemned the attacks several times, "regardless of who is responsible for them",[229] on one occasion calling them "absurd",[230] and on another saying that "they do not go in the direction of peace."[231] On at least one occasion in 2009, Hamas itself criticized rocket attacks by an unknown group, apparently out of fears that new rocket fire could disrupt reconciliation talks between Hamas and Fatah which were then underway.[232]
The firing of rockets from the Gaza Strip into Israel has been opposed by those living closest to the firing location due to Israeli military responses. On July 23, 2004 a family attempted to physically prevent the Al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades from setting up a rocket launcher outside their house. Members of the brigade shot and killed one boy and wounded 5 others.[233][234][235][236]
Israel
On December 27, 2008, upon the commencement of Operation Cast Lead, Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert said in an address to the nation: "for approximately seven years, hundreds of thousands of Israeli citizens in the south have been suffering from rockets being fired at them. Life in the south under rocket barrages had become unbearable. Israel did everything in its power to fulfill the conditions of the calm in the south and enable normal life for its citizens in the communities adjacent to the Gaza Strip. The quiet that we offered was met with shelling."[237]
In October 2012, Yosef Kuperwasser, the director of Israel's Ministry of Strategic Affairs, said that over 800 rockets had been launched at Israel from Gaza since January 2012, and that organizations such as Islamic Jihad had been taking the lead from Hamas as being the primary perpetrators. Kuperwasser explained that in a worst-case-scenario, Israel could launch a wide operation in Gaza, but said that this would not fully solve the issue, since "there is a wide and deep problem of hate indoctrination that produces more and more terrorists all the time."[238]
Two Israelis, Aaron Friedman and Yehonatan Tsirolnik, have created an online clock timer, that automatically resets when Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel occur.[2] The time counter on their website[1] uses information from the IDF Home Front Command system and counts time up from the last Palestinian rocket attack on Israel. It displays how long Israel has been rocket free and shows the summed up total numbers of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel.[1][4] "Israel has been under non stop rocket attacks for years (..) Whenever a rocket is fired, it restarts. Sadly, this counter never really gets above an hour", Friedman said on July 18, 2014 during the 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict.[2][3]
Egypt
The August 2, 2010 Rocket attacks on Eilat and Aqaba sparked rage in Egypt at Hamas and Iran. The Egyptian press said the firing of the rockets from Egyptian territory by Hamas or by organizations cooperating with it constituted the crossing of a red line. The Egyptian position is that Iran is employing local proxies, such as Hamas, to escalate violence in the Middle East and to sabotage the Palestinian reconciliation efforts, as well as efforts to renew Palestinian-Israeli peace negotiations.[239]
Later that year, the Egyptian government daily Al-Gumhouriyya slammed Hamas's firing of "primitive" rockets at Israel that, according to the writer, serve only to prompt a deadly response from Israel. He blamed Hamas for turning the Gaza Strip into a big prison isolated from the world, where the residents suffer poverty while the leaders live in luxury.[240]
United Nations
On January 18, 2009, United Nations Secretary General Ban Ki-Moon said "for the sake of the people of Gaza, I urge in the strongest possible terms Hamas to stop firing rockets."[241] On January 20, while visiting Sderot, the Secretary General called the rocket attacks "appalling and unacceptable". He added that the projectiles are indiscriminate weapons, and that Hamas attacks are violations of basic humanitarian law.[242] Earlier, in November 2007, Ban had condemned a rocket attack launched from a UN-run Gaza school.[243]
On February 17, 2008, John Holmes, United Nations Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator said while visiting Sderot, "The people of Sderot and the surrounding area have had to live with these unacceptable and indiscriminate rocket attacks for seven years now. There is no doubt about the physical and psychological suffering these attacks are causing. I condemn them utterly and call on those responsible to stop them now without conditions".[244]
Following a July 30, 2010, Palestinian Grad missile attack on the heart of Ashkelon, United Nations Middle East envoy Robert Serry said that indiscriminate rocket fire against civilians was completely unacceptable, and constituted a terrorist attack.[245]
United States
In July 2008 Democratic presidential candidate Barack Obama said: "If somebody was sending rockets into my house, where my two daughters sleep at night, I’m going to do everything in my power to stop that, and I would expect Israelis to do the same thing."[246] On December 28, 2008, Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice said in a statement: "the United States strongly condemns the repeated rocket and mortar attacks against Israel".[247] On March 2, 2009 Secretary of State Hillary Clinton condemned the attacks.[248]
European Union
On June 7, 2005, The European Union presidency, held by Luxembourg, condemned the firing of rockets by Palestinians at Gush Katif in the Gaza Strip and against Sderot.[249] In January 2009, European Union Aid Commissioner Louis Michel said "Launching rockets at civilians is a terrorist action, which has to be strongly denounced."[250]
Human rights groups
The attacks have been condemned as war crimes, both because they usually target civilians and because the weapons' inaccuracy would disproportionately endanger civilians even if military targets were chosen. Human Rights Watch has also condemned the attackers for firing from near residential structures, thus putting Gazan civilians at unnecessary risk.[42] According to Israeli human rights group B'Tselem,
Palestinian organizations that fire Qassam rockets openly declare that they intend to strike, among other targets, Israeli civilians. Attacks aimed at civilians are immoral and illegal, and the intentional killing of civilians is a grave breach under the Fourth Geneva Convention, a war crime, and cannot be justified, whatever the circumstances. Furthermore, Qassam rockets are themselves illegal, even when aimed at military objects, because the rockets are so imprecise and endanger civilians in the area from which the rockets are fired as well as where they land, thus violating two fundamental principles of the laws of war: distinction and proportionality.[251]
Attacks from outside the Gaza Strip
West Bank
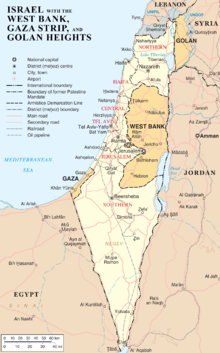
There have been several attempts by Palestinian groups to fire rockets at Israel from the West Bank, though none of these have been successful.[252] Such an attack could easily strike one of Israel's most densely populated areas.[253]
In December 2005, Palestinian Islamic Jihad and Fatah's al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades fired a Qassam rocket at Israel from the West Bank city of Jenin. The rocket landed within the West Bank, in proximity to the Israeli border village of Ram-On. The attack marked the first time a Qassam was fired at Israel from the West Bank and came close to hitting a Jewish community.[254]
In July 2006, a ranking member of Fatah's al-Aqsa Martyrs Brigades in the West Bank said his group had the ability to produce rockets in the northern West Bank and that major Israeli cities as well as Ben Gurion International Airport would eventually become Palestinian rocket targets. "Every day our rockets in Gaza become more accurate and do more killing and this is exactly what will happen in the West Bank", he said.[255]
In November 2006, A West Bank Fatah cell named Jondallah (God's soldiers) threatened to fire rockets at Israeli targets. At a news conference in Nablus, a group of 20 masked militants of the cell brandished four rockets. One of the projectiles, which was 1.5 metres (five feet) in length, was claimed by the group to have "a range of five kilometres (two miles) and a three kilogram payload". "We have a certain number of these rockets and we are going to use them when the time is right," said one of the armed militants.[252]
In February 2010, Palestinian Authority security forces in the West Bank arrested a Hamas cell preparing to test-fire a Qassam rocket near Ramallah and handed the rocket over to Israel. Hamas later said "Having a Qassam rocket in the West Bank is a demand that must be achieved".[253][256]
On June 20, 2010, senior Hamas official Mahmoud a-Zahar called on Palestinian residents of the West Bank to fire rockets into Israel.[257]
On October 22, 2010, the Palestinian Authority seized a large cache of arms, including mortar shells, which it said were meant to be used by Hamas militants targeting Palestinian Authority officials or attempting to sabotage Palestinian Authority security enforcement in the West Bank. Hamas denied this, stating that any weapons would be used against "the occupation", apparently referring to Israel.[258][259]
Egypt
In 2010, Hamas carried out two rocket attacks on Israel from the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt. On April 22, three 122 mm Grad rockets were fired from the Sinai Peninsula at the Red Sea resort town of Eilat in the extreme south of Israel. The projectiles landed in the Red Sea and the neighboring town of Aqaba in Jordan, causing some property damage.[260] Again on August 2, six or seven Iranian-made 122 mm Grad rockets were fired from the Sinai Peninsula at Eilat. The rockets fell in Eilat, Aqaba, Egypt and the Red Sea. A rocket that landed in Aqaba killed a Jordanian civilian and wounded several. The investigation into the attacks involved cooperation between Israel, Egypt, Jordan and the Palestinian Authority. The attacks severely damaged relations between Hamas and Egypt, which viewed them as a challenge to its sovereignty.[261][262][263]
Lebanon
Palestinian militants in Lebanon have launched fatal rocket attacks on towns in northern Israel at least since the 1970s,[264][265][266] but these incidents lie outside the scope of this article, as the topic of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel typically refers to attacks on southern Israel since 2001 and the Second Intifada. Rocket attacks on Israel from Lebanese territory are discussed in the article List of Lebanese rocket attacks on Israel.
Other
Israeli blacksmith Yaron Bob, from the village of Yated, collects Palestinian rockets fired on his area and turns them into roses. These roses have been given by the Sderot Municipality to visiting dignitaries, including United Nations Secretary General Ban Ki-Moon and United States Senator John Kerry. Israel Police spokesman Micky Rosenfeld said, "those rockets are in fact rockets that kill, and it's a nice idea to turn them into flowers."[267]
See also
- Iran–Israel proxy conflict
- Israeli casualties of war
- Israeli disengagement from Gaza
- List of Israeli strikes and Palestinian casualties in the 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict
- List of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel
- List of Palestinian suicide attacks
- Palestinian casualties of war
- Palestinian political violence
- Victoria Affair
References
- ^ a b c Yehonatan, Tsirolnik & Aaron Friedman. "ISRAEL HAS BEEN ROCKET FREE FOR..." http://israelhasbeenrocketfreefor.com/. http://israelhasbeenrocketfreefor.com. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher=and|website= - ^ a b c Haaretz (Jul 21, 2014). "How long has it been since the last rocket strike on Israel?". No. haaretz.com/business. Haaretz.com, the online edition of Haaretz Newspaper in Israel. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ a b Press, Viva Sarah (July 19, 2014). "Israelhasbeenrocketfree.com automatically resets when Hamas fires a rocket toward Israel". www.israel21c.org. ISRAEL21c. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ a b IDF. "Rocket Attacks on Israel from Gaza Strip". idfblog.com/facts-figures/. Israel Defense Forces. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ^ "Attacks on Israeli civilians by Palestinians". B'Tselem. 24 July 2014.
- ^ a b Martin Patience, Playing cat and mouse with Gaza rockets, BBC News 28-02-2008
- ^ Report: Missiles on Sderot increase miscarriages, Jerusalem Post 24-02-2013
- ^ Study: Half of Sderot's toddlers suffering from PTSD, Ynet News 30-06-2009
- ^ Israeli survey: Almost half of Sderot preteens show symptoms of PTSD, Haaretz 20-11-2012
- ^ a b Poll: Hamas continues to lose popularity among Palestinians, Jerusalem Post 10-04-2013
- ^ 80% of Palestinians Support Resumption of Rocket Fire Against Israel: New Poll, Algemeiner Journal 30-09-2014
- ^ "Rocket fire targets Tel Aviv airport as Air Canada flight due to land". thestar.com. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Shachtman, Noah (December 31, 2008). "Hamas Fires Long-Range Chinese Rockets at Israel (Updated)". Wired.
- ^ "רקטות גראד נורו לדרום, לראשונה: גם לרמת הנגב". וואלה! חדשות. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Two rockets land outside J'lem; two fired at TA, Jerusalem Post 16-11-2012
- ^ "IDF examining whether missiles were fired at Haifa and area | JPost | Israel News". JPost. Retrieved 2014-07-11.
- ^ Ilana Curiel Phosphorus mortar shell detected in Negev Ynet 14 January 2009
- ^ Yanir Yagna, Eli Ashkenazi, Anshel Pfeffer Hamas Launches First Phosphorus Rocket at Negev; No Injuries Reported Haaretz 15 January 2009:’Palestinian militants fired a phosphorus rocket at Israel for the first time yesterday, one of 17 fired into Israel as fighting entered its 19th day. The phosphorus rocket exploded in an open field in the western Negev. No injuries or damage were reported.
- ^ Ali Waked 'We used phosphorus fired in Gaza war' Ynet 16 September 2010:’ A member of the one of the Palestinian militant groups in Gaza admitted to Ynet on Thursday that the phosphorus used in the rockets fired on Israel Wednesday contained material gathered from shells Israel itself fired on Gaza during Operation Cast Lead. Still, the source said the groups' use of phosphorus shells was "an experiment" and that there are no plans to put it to mass use. "We don't have the kind of phosphorus the Israelis are talking about."
- ^ a b White phosphorus found in mortar shells fired from Gaza". Ynet 1 January 2012.
- ^ Eshkol Council Head Files UN Complaint over Mortar Fire Jerusalem Post 16 September 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Israel/Gaza Operation 'Cast Lead': 22 Days of Death and Destruction, Amnesty International 2009
- ^ a b Ethan Bronner, Poll Shows Most Palestinians Favor Violence Over Talks, 19-03-2008
- ^ a b Poll No. 13 – Press Release Archived 2012-03-07 at the Wayback Machine, PSR – Survey Research Unit 30-09-2004
- ^ a b Palestinian – Israeli Joint Press Release Archived 2012-03-07 at the Wayback Machine, PSR – Survey Research Unit 26-09-2006
- ^ a b Palestinian – Israeli Joint Press Release Archived 2012-03-07 at the Wayback Machine, PSR – Survey Research Unit 24-03-2008
- ^ a b c "Gaza: Palestinian Rockets Unlawfully Targeted Israeli Civilians". hrw.org/news/. Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 11 July 2014.
- ^ a b "Protection of the civilian population". Protocol Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949, and relating to the Protection of Victims of International Armed Conflicts (Protocol I), 8 June 1977. International Committee of the Red Cross. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- ^ a b Iron Dome successfully intercepts Gaza rocket for first time, Haaretz 07-04-2011
- ^ "Rocket and mortar fire into Israel". B'Tselem. 24 July 2014 [1 January 2011]. Retrieved 16 April 2015.
- ^ "Operation Protective Edge". IDF Blog - The Official Blog of the Israel Defense Forces. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ "Operation Protective Edge in numbers". ynet. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Q&A: Gaza conflict, BBC News 18-01-2009
- ^ Hamas Adopting Rocket Tactics Used by Hezbollah, FOX News 31-12-2008
- ^ Rockets fired from Gaza as fragile cease-fire ends, CNN 19-12-2008
- ^ Shane Bauer, Palestinian factions united by war Archived 2009-01-22 at the Wayback Machine, Al Jazeera English 20-01-2009
- ^ Tim McGirk, Gaza Rocket Rocks Bush's Israel Trip, TIME 14-05-2008
- ^ JPost staff, Fatah's al-Aqsa Martyrs Brigade takes responsibility for Gaza rocket fire, Jerusalem Post 01-02-2009
- ^ "Palestinian split: Views from Hamas and Fatah, six years on". BBC. 2013.
- ^ Ali Waked, Gaza summer camps teach kids to fire rockets, YNet 31-07-2008
- ^ Entous, Adam (May 5, 2008). "Gaza headmaster was Islamic Jihad "rocket-maker"". Reuters. Retrieved March 21, 2012.
- ^ a b c Indiscriminate Fire, Human Rights Watch 30-06-2007
- ^ Anti-Israeli Terrorism in 2007 and its Trends in 2008 (PDF). Intelligence and Terrorism Information Cente (Report). Israel Intelligence Heritage and Commemoration Center. May 2008. p. 11,28. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 13, 2009. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "השבוע לפני - כשקטיושות נורו לעבר משכן הכנסת. השבוע לפני". YNet. Retrieved 2 May 2015.
- ^ Silverman, Anav (September 20, 2007). "A City Under Siege: An Inside View of Sderot, Israel". Sderot Media Center. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
- ^ Yaakov Katz, Katyusha fired for first time from Gaza, Jerusalem Post 28-03-2009
- ^ Katyusha rocket 'fired from Gaza', BBC News 28-03-2006
- ^ Greg Myre and Steven Erlanger, A Gazan Rocket Reaches 6 Miles Into Israel, New York Times 05-07-2006
- ^ Israel tanks enter northern Gaza, BBC News 06-07-2006
- ^ "חללי אל אקצה: ירינו טיל גראד לעבר ישראל". Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- ^ "U.K. Expects Terrorists to Use WMD - Global Security Newswire - NTI". NTI: Nuclear Threat Initiative. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ "ynet גדודי חללי אל אקצה: פיתחנו 20 סוגים של נשק ביולוגי וכימי - חדשות". ynet. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ "ynet "אם ישראל תפלוש לרצועה נשתמש בנשק כימי" - חדשות". ynet. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ "Al-Aqsa Brigades: Chemical warfare if Israel invades Gaza". ynet. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ "Chemical warfare if Israel invades Gaza". Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ "Gaza militants say fired chemical-tipped warhead". Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ a b Sharit G. Lin (2006). "Who started it? - Chronology of the Latest Crisis in the Middle East". Counterpunch.
- ^ a b "PRELUDE TO OPERATION CAST LEAD ISRAEL'S UNILATERAL DISENGAGEMENT TO THE EVE OF WAR" (PDF). Journal of Palestine Studies Vol. XXXVIII, No. 3 (Spring 2009). 2009. pp. 148–149. ISSN 0377-919X.
- ^ "Wanted militant dies in Gaza raid". BBC News. 2006.
- ^ The Associated Press (2009). "Rockets fly after Palestinian militant faction leader killed in Israeli airstrike". USA Today.
- ^ "Indiscriminate Fire - The Gaza Beach Incident". Human Rights Watch. 2009.
- ^ Aaron Klein (2006). "OFFICIALS: HAMAS DECIDED TO END TRUCE WEEKS AGO". WND.
- ^ "Operation Summer Rains". Global Security. 2006.
- ^ Itim (2006). "UN: 202 Palestinians killed since operation 'Summer Rain'". Haaretz.
- ^ http://www.btselem.org/statistics/fatalities/before-cast-lead/by-date-of-event/gaza/palestinians-killed-by-israeli-security-forces
- ^ Haaretz correspondents and Associated Press, Katyusha lands in northern Ashkelon; nine Palestinians killed in IDF response, Haaretz 05-01-2007
- ^ Amos Harel, IDF says Hamas responsible for Katyusha fired from Gaza Strip, Haaretz 07-10-2007
- ^ Christopher Sultan [1], Spiegel online International 3-11-2008
- ^ Barzilai Medical Center [2], Barzilai Medical Center
- ^ "Steady rain of missiles strains Israeli hospital". Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ "9-year-old Qassam victim going home". ynet. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Kershner, Isabel (13 February 2008). "2 Boys, 2 Sides, 2 Beds in an Israeli Hospital Ward". Retrieved 7 May 2017 – via NYTimes.com.
- ^ "Ilana Curiel, Ynetnews, 14 January 2009". ynet. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Magen David Adom is preparing to handle white phosphorus victims in the southern part of Israel [3], Magen David Adom, 14 September 2009
- ^ http://www.haaretz.co.il/news/science/1.1241086 references to the guide
- ^ "מד"א נערך לטפל בנפגעים עתידיים מפצצות זרחן לבן". Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- ^ "News1 - מד"א נערך לטיפול בנפגעי פצצת זרחן לבן". Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Ethan Bronner, Gaza Truce May Be Revived by Necessity, New York Times 19-12-2008
- ^ "FACTBOX-Hamas's arsenal of rockets", Reuters 06-01-2009
- ^ Israel's Ashdod Hit by Gaza Rocket for First Time, Voice of America (retrieved from globalsecurity.org) 30-12-2008
- ^ Amy Teibel and Ian Deitch, "Despite Gaza toll, Israeli media focus on Israel", Associated Press 13-01-2009
- ^ Noa Kosharek, "Tel Aviv, Rishon Letzion prepare bomb shelters in case of attack", Ha'aretz 01-01-2009
- ^ Yaakov Katz and Yaakov Lappin, "Rehovot, Rishon may be in rocket range", Jerusalem Post 05-01-2009
- ^ James Hider, Gaza rockets put Israel’s nuclear plant in battle zone, The Times 02-01-2009
- ^ Haaretz correspondent and agencies, Haniyeh: Hamas won Gaza war, but was wise to declare truce, Haaretz 19-01-2009
- ^ Yagna, Yanir. "At least six Gaza rockets hit southern Israel". Haaretz. Retrieved October 26, 2010.
- ^ http://fr.jpost.com/servlet/Satellite?pagename=JPost/JPArticle/ShowFull&cid=1235410720483 Archived 2011-10-01 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Iran smuggled hundreds of rockets to Gaza in 2010, Jerusalem Post 30-12-2010
- ^ 2010 Annual Summary - Data and Trends in Terrorism, Israel Security Agency
- ^ 13 injured in Kassam training site explosion in Rafah, Jerusalem Post 20-10-2010
- ^ "IDF Spokesperson". Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- ^ Gaza militant groups agree to halt rocket attacks on Israel, Haaretz 30-12-2010
- ^ Gaza mortar shell wounds two men at Israeli farm, Reuters 08-01-2011
- ^ Gaza factions agree to stop rocket attacks on Israel, Jerusalem Post 12-01-2011
- ^ Two arrested for Hamas plot to fire rockets at stadium, Jerusalem Post 02-01-2011
- ^ 2 at J'lem British Consulate charged with aiding Hamas, Jerusalem Post 03-01-2011
- ^ Uncovering the missiles, Israel News 16-03-2011
- ^ Israel Rolls Out First Mobile Battery of Antirocket System, New York Times 27-03-2011
- ^ IAF deploys third Iron Dome battery outside Ashdod, Jerusalem Post 2011-08-31
- ^ Shin Bet files indictment against ‘rocket godfather’, Jerusalem Post 04-04-2011
- ^ 2 mortar shells from Gaza contained phosphorus, Jerusalem Post January 1, 2012
- ^ Eshkol council files UN complaint over phosphorus shells, Jerusalem Post January 2, 2012
- ^ "Islamic Jihad shows off multi-barrel rocket launcher". ynet. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ "Five hurt as Gaza rockets pummel Israel’s south." Jewish Journal. 24 October 2012. 24 October 2012.
- ^ Two rockets slam into Sderot during Obama visit, Jerusalem Post 21-03-2013
- ^ Rockets hit Sderot as Obama visits Israel, Ynet News 21-03-2013
- ^ Gaza militants fire 2 rockets at Israel as Obama visits region, CBC 21-03-2013
- ^ Two rockets fired from Gaza strike Israel on second day of Obama's visit, Daily Mail 21-03-2013
- ^ Islamist group says it fired rockets at Israel from Gaza, Reuters 21-03-2013
- ^ Mortars hit southern Israel, Golan Heights, Ynet News 02-04-2013
- ^ a b Israeli planes strike Gaza for first time since Pillar of Defense, Times of Israel 02-04-2013
- ^ Israel says it will not let Gaza rockets continue after new attacks, FOX News 03-4-2013
- ^ Abu Hamdiyeh's death raises tensions in Israeli jails, Maan News 03-04-2013
- ^ a b 2 rockets pound Sderot area as tensions rise on Gaza front, Jerusalem Post 03-04-2013
- ^ UN's Serry expresses concern over 'volatile' Gaza situation, Jerusalem Post 03-04-2013
- ^ PM: If quiet in South violated we'll respond strongly, Jerusalem Post 03-04-2013
- ^ Palestinians fire rocket, mortars into Israel, Times of Israel 04-04-2013
- ^ Color Red alert sounds in Eshkol; no injuries, damage, Ynet News 04-04-2013
- ^ "Gaza rocket strikes Israel, causes no injuries: military", Yahoo! News (29 April 2012)
- ^ "Rockets fired from Gaza hit Israeli coast ", The Independent (19 June 2012)
- ^ Israel Navy intercepts Gaza-bound Iranian rocket ship near Port Sudan, Jerusalem Post 05-03-2014
- ^ "Sderot factory destroyed by rocket fire". 29 June 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ Hamas unveils rocket statue in Gaza City, Times of Israel 10-03-2014
- ^ "Rocket from Gaza fired at Israel on its independence day -army". Reuters. April 23, 2015.
- ^ "Rocket from Gaza hits S. Israel". April 24, 2015.
- ^ Newman, Marissa (May 26, 2015). "Rocket fired from Gaza hits southern Israel". The Times of Israel.
- ^ Clancy Chassay and Bobbie Johnson, Google Earth used to target Israel, the Guardian 25-10-2007
- ^ a b ISRAEL-OPT: Relentless rocket attacks take psychological toll on children in Sderot, IRIN News (UN OCHA) 27-01-2008
- ^ Heather Sharp, Rocket attacks plague Israeli towns, BBC News 28-12-2009
- ^ Ethan Bronner, Parsing Gains of Gaza War, New York Times 18-01-2009
- ^ Video: Gaza rockets fired from civilian centers, Israel News 1204-2011
- ^ ERLANGER, STEVEN, and FARES AKRAM. "Israel Warns Gaza Targets by Phone and Leaflet". nytimes.com. The New York Times Company. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ web based information of defense broushur provided to citizens
- ^ a b https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:sANZfis4vbQJ:www.knesset.gov.il/mmm/data/pdf/m01664.pdf+&hl=en&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEEShLZQ8Dbc8LZWZFj3BjKzIhG4c5j5qS433Pt0IRV3E3v2X_L5YjvYYD1rVmUPrFxkY96q_yHH4ECnNJi3npIFQ3YBJbaUSSHWvLCuuEWS6a4r9v76mAvtv7JhwvWN6Gaf4WuhOF&sig=AHIEtbR5vMrK9ZroCQNK7Bd66HMjauqoNw
- ^ Home Front Command,תקנות למוסדות חינוך[[:Category:|]],2010, http://www.oref.org.il/sip_storage/FILES/9/1309.pdf. Retrieved 2012-05-02.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)[dead link] - ^ a b Home Front Command,תקנות מוסדות בריאות [[:Category:|]],2010,[4]
- ^ Home Front Command,תקנות מוסדות בריאות [[:Category:|]],2010, p4 section 280 subsection ב [5]
- ^ "Civil defence laws (outdates) 1951". Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- ^ Yuval Azoulay, 5000 southerners, mostly elderly, lack access to rocket shelter, Haaretz 04-02-2009
- ^ a b Heather Sharp, Sderot children feel truce relief, BBC News 01-09-2008
- ^ Yuval Azoulay, Gov't places 120 fortified bus stops in rocket-plagued Sderot, 05-03-2008
- ^ School resumes in Israel despite rocket threat: Some students continue to stay home to avoid Hamas rocket attacks, Associated Press (retrieved from MSNBC) 11-01-2009
- ^ Shmulik Hadad, Experts: Grads in Ashkelon were advanced, Ynet 03-01-2009
- ^ Ethan Bronner, For Israeli children, a playground shielded from rockets, New York Times 11-03-2009 (retrieved from the International Herald Tribune)
- ^ Aron Heller, Israeli kids get rocket-proofed indoor playground, Associated Press. Retrieved 11-03-2009.
- ^ Susan Taylor Martin, On Israel-Gaza border, teens learn legacy of hate, St. Petersburg Times 08-02-2-2009
- ^ Home Front Command , החל מ. -. 18/05/ 2010. כל תוכנית חדשה אשר מוגשת לאישור המהנדסים מחוייבת, [www.oref.org.il/sip_storage/FILES/9/1229.pdf], affective as of 18 May 2010
- ^ [6]
- ^ "חובה להתקין מערכת סינון אבכ בממד". Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ mobile ring tone 'shahar adom' http://mz11.mediazone.co.il/mediazone/34/2166!0.wmv Archived 2011-07-21 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Christian Science Monitor"Living at Gaza's edge grows perilous, again" http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0615/p07s02-wome.html
- ^ Israel used fighting to perfect anti-rocket system, Associated Press. February 16, 2009 [dead link]
- ^ Azoulay, Yuval. "Israeli arms company successfully tests Iron Dome anti-Qassam missile – Haaretz – Israel News". Haaretz. Retrieved October 26, 2010.
- ^ "Israel Delays Its Deployment of 'Iron Dome'". Haaretz. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ "Barak confirms: 'Iron Dome' to be deployed within days". The Jerusalem Post. 25 March 2011. Retrieved 25 March 2011.
- ^ Anshel Pfeffer; Yanir Yagna (7 April 2011). "Iron Dome successfully intercepts Gaza rocket for first time". Haaretz. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ^ "Attacks on Israeli civilians by Palestinians". B'Tselem. 24 July 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ^ Total 6, 3 were killed before 24 July
- ^ a b c d "Victims of Palestinian Violence and Terrorism since September 2000". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- ^ Mark LeVine, Who will save Israel from itself?,' Al Jazeera 27 December 2009.
- ^ a b c "Palestinian ceasefire violations". Ministry of Foreign Affairs - The State of Israel. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- ^ Gaza rocket kills Palestinian girls, Al Jazeera 27-12-2008
- ^ a b "History of the Qassam Rocket". The Jewish Policy Centre. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ Akram, Fares; Kershner, Isabel (March 18, 2010). "Gaza Rocket Attack Into Israel Kills a Thai Worker". The New York Times.
- ^ [7] B'Tselem
- ^ "Sderot Media Centre". Sderotmedia.org.il. Retrieved October 26, 2010.
- ^ Rockets and Mortar Shells Fired at Israel, at Jewish Virtual Library, 9–15 March 2012.
- ^ TIMELINE – Israeli-Hamas violence since truce ended, Reuters 05-01-2009
- ^ Bright, Arthur. Israel set to launch ‘limited operation’ in Gaza, The Christian Science Monitor, December 26, 2008.
- ^ Rory McCarthy in Jerusalem (2009-09-16). "Israel rejects war crimes findings of UN Gaza inquiry | World news | guardian.co.uk". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2010-05-08.
- ^ "שירות הבטחון הכללי". www.shabak.gov.il. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
- ^ "Nearly 250 Gaza rockets batter South; 3 Israelis killed". Archived from the original on 15 November 2012. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Live Updates: Massive Strike on Terror Targets in Gaza". IDF Blog - The Official Blog of the Israel Defense Forces. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ "ynet הבוקר: רקטה נורתה אל אזור אשדוד, אין נפגעים - חדשות". ynet. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ Ban Ki-moon, UN Secretary General (2012-11-21). "Secretary-General's remarks to the Security Council [as delivered"]. Tel Aviv. Retrieved 2012-11-24. ""Overall, in that same time period, more than 1,456 rockets have been fired from Gaza into Israel. 142 have fallen inside Gaza itself. Approximately 409 were intercepted by the Iron Dome anti-missile system. (...) Since Israel’s targeted assassination from the air, on 14 November, of Ahmed Jaabari, chief of Hamas’ military wing, and with Israel’s offensive in Gaza in its eighth day, the Israel Defense Forces publicly reported that it has conducted strikes at more than 1,450 targets in Gaza.""
- ^ "Operation Protective Edge in numbers". ynet. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ "Rockets fired from Gaza at southern Israel". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- ^ Kershner, Isabel (May 31, 2007). "Israeli Border Town Lives in the Shadow of Falling Rockets". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
- ^ a b Situation Report Gaza June 1, 2007, UN OCHA
- ^ "3,000 Sderot residents have left town - Israel - Jerusalem Post". 13 August 2011. Archived from the original on 13 August 2011. Retrieved 7 May 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Aron Heller, "Israelis get creative in coping with rocket threat", Associated Press 31-12-2008
- ^ Empties, Trauma teams Struggle, IRIN News (UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs),13-01-2009
- ^ Aron Heller, "School resumes in Israel despite rocket threat", Associated Press, 11-01-2009
- ^ IDF: Rocket that hit Beersheba school made in China. By Yael Barnovsky. Ynet News. Published December 31, 2008.
- ^ Abe Selig, "School closure saves lives of pupils" Archived 2011-10-01 at the Wayback Machine, Jerusalem Post 31-12-2009
- ^ IDF: Hamas rocket fire down 50% since start of Gaza offensive. By Barak Ravid. Haaretz. Published January 12, 2009.
- ^ Rockets reach Beersheba, cause damage. By Ilana Curiel. Ynet News. Published January 5, 2009.
- ^ 32 rockets fired at southern Israel. By Shmulik Hadad. Ynet News. Published December 30, 2008.
- ^ 4 troops hurt in mortar attack; Grad hits Ashkelon school. By Shmulik Hadad. Ynet News. Published January 8, 2009.
- ^ Some 2,700 Beersheba students to attend classes in bomb shelters Archived 2012-02-24 at the Wayback Machine, Jerusalem Post 10-01-2009
- ^ "Ashkelon Empties, Trauma teams Struggle", IRIN News (UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs),13-01-2009
- ^ a b "Ashkelon Empties, Trauma teams Struggle", IRIN News (UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, 13-01-2009)
- ^ Some Israelis go back to school as rocket fire declines Archived 2009-01-22 at the Wayback Machine. By Dina Kraft. Jewish Telegraphic Agency. Published January 13, 2009.
- ^ Abe Selig, "Back to school for students in South", Jerusalem Post 12-01-2009
- ^ "ynet סטודנט: המכללה ננטשה לאחר הפגיעה הקטלנית - חדשות". ynet. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ Yaakov Lappin and Jpost staff, 40% attend Ashkelon schools after rocket fire, 02-03-2009
- ^ Mijal Grinberg and Eli Ashkenazi, Study: Most Sderot kids exhibit post-traumatic stress symptoms, Haaretz 17.01.2008
- ^ Study Links Rocket Attacks with Trauma, Israel National News 15-04-2010
- ^ ISRAEL-OPT: Gaza rockets cause shock, fear in southern Israel, IRIN News (UN OCHA) 02-01-2009
- ^ "Israeli Mayor Quits Over Rockets". BBC Online. December 12, 2007. Retrieved October 20, 2008.
- ^ PA: Hamas rockets are bid to sway Israeli election, Associated Press (retrieved from Haaretz) 09-02-2009
- ^ a b Response of the lions to the aggressions of the Jews: Shelling Zionist Sderot with three rockets, Majlis Shura Al-Mujahidin 01-09-2012
- ^ a b Salafi Terrorists: Jihad Against 'Criminal Jews' is a Duty, Israel National News 27-8-2012
- ^ Melanie Phillips (January 15, 2008). "President Bush's visionary hero". The Spectator. Archived from the original on January 16, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Q&A: Gaza conflict". BBC. January 18, 2009. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ Greg Myre, Rockets Create a 'Balance of Fear' With Israel, Gaza Residents Say, 09-07-2006
- ^ "Hamas: Rocket Attacks on Israel Are 'Self Defense'". Fox News. Associated Press. April 29, 2007.
- ^ Khalid Mish'al, This brutality will never break our will to be free, The Guardian 09-01-2009
- ^ Ethan Bronner and Taghreed El-Khodary, Hamas Fires Rockets Into Israel, 14-11-2008
- ^ 2 Dead as Hamas Rockets Backfire in Gaza. FOX News 24-12-2008
- ^ PFLP Interview with Ma'an News Agency on Israeli Aggression in Gaza, Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine 17-01-2009
- ^ IDF attacks 2 Palestinians near Kissufim, Ynet News 04-04-2010
- ^ Mortar round fired at Israel, Gulf News 04-04-2010
- ^ Harvest operations and activities of the military-Aqsa Martyrs Brigades in the face of the enemy in the battle for Gaza, Aqsa Martyrs BrigadesMedia Centre
- ^ 7 mortar shells fired from Gaza, Ynet News 07-01-2010
- ^ Group: Rocket responsibility is Hamas's, UPI 19-03-2010
- ^ 'Israel will defend itself from Gaza rockets, regardless of Goldstone', Haaretz 18-03-2010
- ^ Israel vows to respond to Kassam hit, Jerusalem Post 18-03-2010
- ^ Gaza rocket kills Thai farm worker in Israel, Associated Press 18-03-2010
- ^ Poll No. 59, July 2006 - On Palestinian Attitudes Towards the Abduction of the Israeli Soldier & Firing of Rockets, JMCC 01-07-2006
- ^ Poll No. 170 Jan 01, 2010, PCPO
- ^ Poll No. 36 – Full Analysis, PSR – Survey Research Unit 07-07-2010
- ^ Poll: 2/3 of Palestinians against rocket attacks, Ynet News, 07-07-2010
- ^ Poll No. 173 Nov 03, 2010, PCPO
- ^ Poll No. 73, April 2011 - Governance and reconciliation, JMCC 17-04-2011
- ^ Poll No. 176: May, 14 2011 Archived 2011-10-27 at the Wayback Machine, PCPO
- ^ Poll No. 75, November 2011 - Perpetuation of the Palestinian Authority and US policy, JMCC 27-11-2011
- ^ Poll No. 78, Dec. 2012 - Gaza, Resistance and the UN Bid, JMCC 20-12-2012
- ^ Abbas condemns militants' rocket attacks for killing Palestinian children, AFP 01-2009
- ^ Abbas urges end to rocket attacks, BBC News 25-05-2007
- ^ Sam Jones, Abbas accuses Israel of war crimes in Gaza, The Guardian 04-02-2009
- ^ Hamas condemns Gaza rocket strikes on Israel, Associated Press (reprinted in Haaretz 12-03-2009)
- ^ "Attempted Kassam Launch Leads to the Death of an Arab Child". IsraelNationalNews. July 23, 2004. Archived from the original on October 16, 2005. Retrieved August 7, 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Berger, Joseph (July 23, 2004). "Group Says New Israeli Expansion Breaks Vow". NYTimes.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2009. Retrieved February 19, 2006.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Gaza youth shot dead; Arafat says PA not in crisis". Haaretz.com. Archived from the original on July 26, 2004. Retrieved February 19, 2006.
- ^ "Teen dies in Palestinian clash". BBC. July 23, 2004. Retrieved February 19, 2006.
- ^ PM Olmert's Remarks on the Operation in the Gaza Strip, Jewish Policy Center
- ^ Balmer, Crispian (October 17, 2012). "War will not resolve Gaza problem: Israeli official". Reuters. Retrieved October 21, 2012.
- ^ Rage in Egypt at Hamas and Iran following Rocket Attacks on Eilat, Aqaba, MEMRI Special Dispatch No.3200
- ^ Al-Gumhouriyya (Egypt), October 22, 2010. By Abdallah Al-Naggar. translation by MEMRI
- ^ Ban calls for end to Hamas rocket attacks, Israeli withdrawal from Gaza, UN News Centre 18-01-2009
- ^ Ban Ki-moon ‘appalled’ by Gaza destruction, The Independent 20-01-2009
- ^ Ban Ki-moon condemns rocket attack from Gaza school run by UN agency, UN News Centre 08-11-2007
- ^ UN HUMANITARIAN CHIEF: ONLY A JUST AND LASTING PEACE CAN END HUMAN SUFFERING IN ISRAEL AND PALESTINE, UN OCHA 17-02-2008
- ^ Israel pledges response to missile attack from Gaza, Irish Times 31-07-2010
- ^ Steven Lee Myers and Helene Cooper, Obama Defers to Bush, for Now, on Gaza Crisis, New York Times 28-12-2009
- ^ U.S. Condemns Hamas in Midst of Israeli Strikes, Fox News 28-12-2008
- ^ Clinton calls for 'durable' Gaza truce, condemns rockets, AFP 02-03-2009
- ^ Declaration by the Presidency of the European Union on the firing of rockets at Gush Katif and Sderot in the Gaza Strip, 07-06-2005
- ^ Hamas slams EU official over anti-Hamas statement, Xinhua 26-01-2009
- ^ Qassam rocket fire into Israel, B'Tselem
- ^ a b Fatah men threaten West Bank rocket fire at Israeli targets, Haaretz 29-11-2006
- ^ a b Palestinians hand Israel Qassam rocket seized in West Bank, Haaretz 22-02-2010
- ^ Qassam fired from West Bank, Ynet News 01-01-2006
- ^ Al-Aqsa leader: West Bank rocket war is on, Ynet News 13-07-2006
- ^ Hamas seeks to have rockets in West Bank, Xinhua 01-0302010
- ^ A-Zahar calls for rockets to be fired from West Bank, Jerusalem Post 20-06-2010
- ^ PA says uncovered Hamas arms cache, Ynet News 22-10-2010
- ^ PA: Hamas arms cache seized, UPPI 22-10-2010
- ^ "Two rockets land in Eilat area," 04/22/2010, Jerusalem Post.
- ^ [8], Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center 15-08-2010
- ^ "Victim of rocket that blasted Aqaba dies of wounds, 4 others injured", 2010-08-02, Ammon News.
- ^ Jordanian national killed in multiple militant rocket strike, The Telegraph 02-08-2010
- ^ 'Rocket barrage hits Kiryat Shmona, Israel', Bryan Times 23-09-1977, p. 1
- ^ 'Israeli Aircraft Bomb Lebanon', Michigan Daily 10-11-1977, p. 2
- ^ 'Palestinians rocket Israel', Spokane Daily Chronicle 11-04-1979, p. 39
- ^ Turning Rockets Into Roses, New York Times (video)
External links
- Media
- Gaza's rocket threat to Israel, BBC, January 21, 2008
- Tony Karon, The Homemade Rocket That Could Change the Mideast, TIME, November 2, 2002
- Ulrike Putz, A Visit to a Gaza Rocket Factory, Der Spiegel, January 29, 2008
- Science and security
- Rocket Threat from the Gaza Strip, 2000—2007, Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center, December 2007
- HAMAS Rockets, GlobalSecurity.org
- Katyusha & Qassam Rockets, aerospaceweb.org
- Humanitarian Aid Organizations
- Human rights groups
- Advocacy
