Outline of Singapore: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
m Task 16: replaced (2×) / removed (0×) deprecated |dead-url= and |deadurl= with |url-status=; |
Palak Baid (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[https://www.thrillophilia.com/places-to-visit-in-singapore Places to Visit in Singapore] 20 January 2020 |
|||
{{use Singapore English|date=August 2019}} |
{{use Singapore English|date=August 2019}} |
||
{{use dmy dates|date=August 2019}} |
{{use dmy dates|date=August 2019}} |
||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
The following [[Outline (list)|outline]] is provided as an overview and topical guide to Singapore: |
The following [[Outline (list)|outline]] is provided as an overview and topical guide to Singapore: |
||
'''[[Singapore]]''' – [[list of sovereign states|sovereign]] [[republic]] comprising the main island of Singapore and smaller outlying islands which are located at the southern tip of the [[Malay Peninsula]] in [[Southeast Asia]].<ref name=CIA_World_Factbook>{{cite web|date=2 July 2009|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sn.html|title=Singapore|work=[[The World Factbook]]|publisher=[[United States]] [[Central Intelligence Agency]]|accessdate=23 July 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101228230816/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sn.html|archive-date=28 December 2010|url-status=live}}</ref> Singapore lies {{convert|137|km|mi}} north of the [[equator]], south of the [[Malaysia]]n state of [[Johor]] and north of [[Indonesia]]'s [[Riau Islands]]. Singapore is one of three remaining true [[city-state]]s in the world. It is the second smallest nation in [[Asia]]. |
'''[[Singapore]]''' – [[list of sovereign states|sovereign]] [[republic]] comprising the main island of Singapore and smaller outlying islands which are located at the southern tip of the [[Malay Peninsula]] in [[Southeast Asia]].<ref name=CIA_World_Factbook>{{cite web|date=2 July 2009|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sn.html|title=Singapore|work=[[The World Factbook]]|publisher=[[United States]] [[Central Intelligence Agency]]|accessdate=23 July 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101228230816/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/sn.html|archive-date=28 December 2010|url-status=live}}</ref> Singapore lies {{convert|137|km|mi}} north of the [[equator]], south of the [[Malaysia]]n state of [[Johor]] and north of [[Indonesia]]'s [[Riau Islands]]. Singapore is spread over an area of 721.5 km². Singapore is one of three remaining true [[city-state]]s in the world. It is the second smallest nation in [[Asia]]. |
||
{{TOC limit|limit=2}} |
{{TOC limit|limit=2}} |
||
Revision as of 10:25, 20 January 2020
Places to Visit in Singapore 20 January 2020



The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to Singapore:
Singapore – sovereign republic comprising the main island of Singapore and smaller outlying islands which are located at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula in Southeast Asia.[1] Singapore lies 137 kilometres (85 mi) north of the equator, south of the Malaysian state of Johor and north of Indonesia's Riau Islands. Singapore is spread over an area of 721.5 km². Singapore is one of three remaining true city-states in the world. It is the second smallest nation in Asia.
General reference
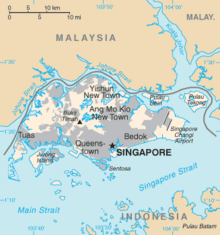
- Pronunciation: /ˈsɪŋəpɔːr/ or /ˈsɪŋɡəpɔːr/
- Common English country name: Singapore
- Official English country name: The Republic of Singapore
- Official endonyms: Singapore (English), Singapura (Malay), 新加坡 (Pinyin: Xīnjiāpō, Mandarin), சிங்கப்பூர் (Ciŋkappūr, Tamil)
- Common endonyms: Lion City, Little red dot, Temasek
- Adjectival(s): Singaporean
- Demonym(s): Singaporean
- Etymology: Name of Singapore
- International rankings of Singapore
- ISO country codes: SG, SGP, 702
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:SG
- Internet country code top-level domain: .sg
Geography of Singapore
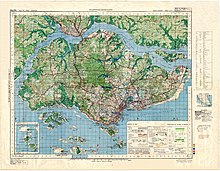
- Singapore is: an island country made up of 63 islands
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Eurasia
- Time zone: Singapore Standard Time = ASEAN Common Time (UTC+08)
- Extreme points of Singapore:
- High: Bukit Timah 163.63 m (537 ft)
- Low: Singapore Strait 0 m
- Land boundaries: none (two causeways to Malaysia)
- Coastline: 193 km (120 mi)
- Area of Singapore: 707.1 km2 (273.0 sq mi)
- Atlas of Singapore
Environment of Singapore

- Astronomical phenomena
- Next total solar eclipse visible in Singapore: 5 July 2168[2]
- Biosphere reserves in Singapore
- Climate of Singapore
- Tropical climate
- Long-term average annual rainfall: 2,346 mm[3]
- Average monthly number of thunderstorm days over the last 50 years up to 2008: 14[3] (about 3.8% of the year)
- Average annual number of wet days (more than 0.2 mm of rainfall recorded) over the last 50 years up to 2008: 169[3] (about 46.3% of the year)
- Driest month since 1869: February 2010 (6.3 mm of rain)[4]
- Longest period without rain since 1869: 42 days (5 January – 15 February 2009)[4]
- Environmental issues in Singapore
- Geology of Singapore
- Wildlife of Singapore
Natural geographic features of Singapore

- Hills of Singapore
- Islands of Singapore
- Lakes of Singapore
- Rivers of Singapore
Regions of Singapore

Administrative divisions of Singapore
- Singapore, being a city itself, has no administrative divisions
- It does, however, have subdivisions
Municipalities
- Being a city-state, Singapore is both a city and a nation state
- Singapore is its own only municipality
- Capital of Singapore: Singapore is its own capital
Demography of Singapore
Population structure

- Population (end June 2018): 5,638,700[5]
- Resident population: 3,994,300 (70.8%).
- Singapore citizens: 3,471,900 (61.6%)
- Singapore permanent residents: 522,300 (9.3%)
- Non-resident population: 1,644,400 (29.1%)
- Resident population: 3,994,300 (70.8%).
- Population density (2018): 7,804 per km2[5]
- Sex ratio of residents (end June 2018): 959 males per 1,000 females[5]
- Median age of residents (2018): 40.8 years[5]
- Age composition of residents (2009): 0–14 years – 14.8%, 15–64 years – 71.5%, 65 years and above – 13.7%[5]
- Ethnic composition of residents (June 2018): Chinese – 2,969,281 (74.3%), Malays – 535,824 (13.4%), Indians – 360,528 (9.0%), others – 128,650 (3.2%)
- Proportion single among residents aged 35–39 years (2017): men – 20.5%, women – 17.3%[5]
- Average resident household size (2017): 3.3 people[5]
Family formation and dissolution

- Total marriages (2017): 28,212[5]
- Median age at first marriage (2017): men – 30.5 years, women – 28.9 years
- Total divorces and annulments (2017): 7,578[5]
Fertility rate
- Crude birth rate per 1,000 residents (2017): 8.9[5]
- Total fertility rate (TFR) of residents (2017): 1.16[5][6]
Mortality
- Crude death rate per 1,000 residents (2017): 5.0[5]
- Life expectancy at birth of residents (2008): men – 80.7years, women – 85.2 years[5]
Government and politics of Singapore

- Form of government: Unitary state under a Parliamentary democracy
- Elections in Singapore
- Political parties in Singapore
- Taxation in Singapore
Branches of the government of Singapore
Executive branch of the government of Singapore
- Head of state: President of Singapore, Halimah Yacob
- Head of government: Prime Minister of Singapore, Lee Hsien Loong
- Cabinet of Singapore
Legislative branch of the government of Singapore
Judicial branch of the government of Singapore
- Judicial officers of the Republic of Singapore
- Supreme Court of Singapore
- Subordinate Courts of Singapore
Foreign relations of Singapore
Foreign relations of Singapore
- Diplomatic missions in Singapore
- Diplomatic missions of Singapore
- Malaysia-Singapore relations
- Singapore – United States relations
International organization membership
The Republic of Singapore is a member of the:[1]
Law and order in Singapore

- Criminal law of Singapore
- Constitution of Singapore
- Human rights in Singapore
- Law enforcement in Singapore
- Sources of Singapore law
Military of Singapore

- Singapore Armed Forces
- Army of Singapore: Singapore Army
- Navy of Singapore: Republic of Singapore Navy
- Air Force of Singapore: Republic of Singapore Air Force
- Military history of Singapore
- Military ranks of Singapore
History of Singapore

- Early history of Singapore (before 1819)
- Founding of modern Singapore (1819-1826)
- Singapore in the Straits Settlements (1826–1942)
- Japanese occupation of Singapore (1942-1945)
- Post-war Singapore (1945-1959)
- Self-governance of Singapore (1959-1963)
- Singapore in Malaysia (1963-1965)
- History of Independent Singapore (1965-current)
- Military history of Singapore
Culture of Singapore
- Built heritage of Singapore
- Cuisine of Singapore
- Festivals in Singapore
- Holidays in Singapore
- Languages of Singapore

- Media in Singapore
- National symbols of Singapore

Religion in Singapore
The Sultan Mosque in Kampong Glam
- Freedom of religion in Singapore
- Buddhism in Singapore
- Christianity in Singapore
- Hinduism in Singapore
- Islam in Singapore
- Sikhism in Singapore
- Taoism in Singapore
- Irreligion in Singapore
Art in Singapore

- Art in Singapore
- Cinema of Singapore
- Literature of Singapore
- Music of Singapore
- Television in Singapore
- Theatre in Singapore
Sports in Singapore

- Football in Singapore
- Rugby union in Singapore
- Singapore Grand Prix
- Singapore at the Olympics
- 2010 Summer Youth Olympics
- National Physical Fitness Award
- Foreign Sports Talent Scheme
Economy and infrastructure of Singapore

- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 45th (forty-fifth)
- Agriculture in Singapore
- Banking in Singapore
- Communications in Singapore
- Companies of Singapore
- Currency of Singapore: Dollar
- Energy in Singapore
- Health care in Singapore
- Singapore Stock Exchange
- Tourism in Singapore
- Water supply and sanitation in Singapore
Transport in Singapore
- Certificate of Entitlement
- EZ-Link
- Johor-Singapore Causeway
- Ministry of Transport (Singapore)
- Singapore Area Licensing Scheme
- Singapore Cable Car
- Taxicabs of Singapore
Road Transport in Singapore

- Driving in Singapore
- Bus transport in Singapore
- Taxicabs of Singapore
- Public Transport Council
- Singapore licence plates
- Expressways of Singapore
Aviation in Singapore

- Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore
- List of airports in Singapore
- Changi Airport
- Singapore Airshow
Rail transport in Singapore

Monorails in Singapore
Light Rapid Transit
- List of Singapore LRT stations
- Fares and ticketing on the Light Rapid Transit
- Bukit Panjang LRT Line
- Punggol LRT Line
- Sengkang LRT Line
Mass Rapid Transit

- Network
- Fares and ticketing on the Mass Rapid Transit
- History of the Mass Rapid Transit
- Safety on the Mass Rapid Transit
- Security on the Mass Rapid Transit
Transport operators of Singapore

Transport disasters in Singapore
- Nicoll Highway collapse
- Singapore cable car disaster
- Spyros disaster
- SilkAir Flight 185
- Singapore Airlines Flight 006
Education in Singapore

- List of schools in Singapore
- List of universities and colleges in Singapore
- Gifted Education Programme
- Integrated Programme
- National Examinations in Singapore
- Co-curricular activity
See also
- Index of Singapore-related articles
- International rankings of Singapore
- List of Singapore-related topics
- Member state of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Asia
- Outline of geography
Notes
- ^ a b "Singapore". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. 2 July 2009. Archived from the original on 28 December 2010. Retrieved 23 July 2009.
- ^ Victoria Vaughan (21 July 2009), "S'pore group head to China for rare glimpse", The Straits Times.
- ^ a b c Ho Juay Choy; Dickson Yeo (2008), Singapore Country Report – A Regional Review on the Economics of Climate Change in Southeast Asia. Report Submitted for RETA 6427: A Regional Review of the Economics of Climate Change in Southeast Asia, Manila: Asian Development Bank; Amresh Gunasingham (16 July 2009), "Less rain over last 30 years: Experts cite climate change and rapid industrialisation to explain fluctuating rainfall", The Straits Times (Home), p. B1.
- ^ a b Amresh Gunasingham (11 March 2010), "Showers bring cool relief: Dry spell may be over as air quality improves after two straight days of rain", The Straits Times (Home), p. B2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Population Trends 2018 (PDF), Singapore Department of Statistics, September 2018, archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2018, retrieved 22 May 2019
- ^ Radha Basu (15 August 2009), "Baby bonus has had little impact so far: One positive trend is the rise in the number of first-time parents", The Straits Times, p. A1. To replace itself, a population requires a TFR of 2.1 or higher.
- ^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Singapore Botanic Gardens". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 1 September 2019.
External links
- General Information
- Singapore Infomap
- Singapore Government Directory Interactive
- Singapore Government Online Portal
- Gateway To All Government Services
- Singapore National Service Portal
- Singapore Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority
- Amnesty International's 2005 report on Singapore
- CIA World Factbook Entry for Singapore
- Singapore Department of Statistics Annual Data
- Memories of Asia
- Travel
 Singapore travel guide from Wikivoyage
Singapore travel guide from Wikivoyage
- Maps


