Nauru
0°32′S 166°56′E / 0.533°S 166.933°E
Republic of Nauru Ripublik Naoero | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "God's Will shall be First" | |
| Anthem: Nauru Bwiema Nauru, our homeland | |
 | |
| Capital | Yaren (de facto) [a] |
| Official languages | |
| Demonym(s) | Nauruan |
| Government | Parliamentary republic |
| Baron Waqa | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Independence | |
| 31 January 1968 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 21 km2 (8.1 sq mi) (239th) |
• Water (%) | 0.57 |
| Population | |
• July 2011 estimate | 9,378[1] (216th) |
• Dec 2006 census | 9,275 |
• Density | 447/km2 (1,157.7/sq mi) (23rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2006 estimate |
• Total | $36.9 million[2] (192nd) |
• Per capita | $2,500 (2006 est.) [2] $5,000 (2005 est.) [1] (135th–141st) |
| Currency | Australian dollar (AUD) |
| Time zone | UTC+12 |
| Drives on | left |
| Calling code | +674 |
| ISO 3166 code | NR |
| Internet TLD | .nr |
| |
Nauru (English: /nɑːˈuːruː/ nah-OO-roo), officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country in Micronesia in the South Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Kiribati, 300 kilometres (186 mi) to the east. Nauru is the world's smallest republic, covering just 21 square kilometres (8.1 sq mi). With 9,378 residents, it is the second least-populated country after Vatican City.
Settled by Micronesian and Polynesian people, Nauru was annexed and claimed as a colony by the German Empire in the late 19th century. After World War I, Nauru became a League of Nations mandate administered by Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. During World War II, Nauru was occupied by Japanese troops, who were bypassed by the Allied advance across the Pacific. After the war ended, the country entered into trusteeship again. Nauru gained its independence in 1968.
Nauru is a phosphate rock island with rich deposits near the surface, which allow easy strip mining operations. It has some phosphate resources which, as of 2011, are not economically viable for extraction.[3] Nauru boasted the highest per-capita income enjoyed by any sovereign state in the world during the late 1960s and early 1970s. When the phosphate reserves were exhausted, and the environment had been seriously harmed by mining, the trust that had been established to manage the island's wealth diminished in value. To earn income, Nauru briefly became a tax haven and illegal money laundering centre. From 2001 to 2008, it accepted aid from the Australian Government in exchange for housing the Nauru detention centre.
The president of Nauru is Baron Waqa, who heads a 19-member unicameral parliament. The country is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Asian Development Bank and the Pacific Islands Forum. Nauru also participates in the Commonwealth and Olympic Games. Recently Nauru became a member country of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
History

Nauru was first inhabited by Micronesian and Polynesian people at least 3,000 years ago.[4] There were traditionally 12 clans or tribes on Nauru, which are represented in the 12-pointed star on the country's flag.[5] Traditionally, Nauruans traced their descent matrilineally. Inhabitants practised aquaculture: they caught juvenile ibija fish, acclimatised them to fresh water, and raised them in the Buada Lagoon, providing a reliable source of food. The other locally grown components of their diet included coconuts and pandanus fruit.[6][7] The name "Nauru" may derive from the Nauruan word Anáoero, which means "I go to the beach".[8]
The British sea captain John Fearn, a whale hunter, became the first Westerner to visit Nauru in 1798, naming it "Pleasant Island". From around 1830, Nauruans had contact with Europeans from whaling ships and traders who replenished their supplies (particularly fresh water) at Nauru.[7] Around this time, deserters from European ships began to live on the island. The islanders traded food for alcoholic palm wine and firearms.[9] The firearms were used during the 10-year Nauruan Tribal War that began in 1878.[10]
Nauru was annexed by Germany in 1888 and incorporated into Germany's Marshall Island Protectorate.[11] The arrival of the Germans ended the civil war, and kings were established as rulers of the island. The most widely known of these was King Auweyida. Christian missionaries from the Gilbert Islands arrived in 1888.[12][13] The German settlers called the island Nawodo or Onawero.[14] The Germans ruled Nauru for almost three decades. Robert Rasch, a German trader who married a Nauruan woman, was the first administrator, appointed in 1890.[12]
Phosphate was discovered on Nauru in 1900 by the prospector Albert Fuller Ellis.[11] The Pacific Phosphate Company began to exploit the reserves in 1906 by agreement with Germany, exporting its first shipment in 1907.[15] In 1914, following the outbreak of World War I, Nauru was captured by Australian troops. Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom signed the Nauru Island Agreement in 1919, creating a board known as the British Phosphate Commission (BPC) that took over the rights to phosphate mining.[16]
The island experienced an influenza epidemic in 1920, with a mortality rate of 18 per cent among native Nauruans.[17] In 1923, the League of Nations gave Australia a trustee mandate over Nauru, with the United Kingdom and New Zealand as co-trustees.[18] On 6 and 7 December 1940, the German auxiliary cruisers Komet and Orion sank five supply ships in the vicinity of Nauru. Komet then shelled Nauru's phosphate mining areas, oil storage depots, and the shiploading cantilever.[19][20]

Japanese troops occupied Nauru on 25 August 1942.[20] The Japanese built an airfield which was bombed for the first time on 25 March 1943, preventing food supplies from being flown to Nauru. The Japanese deported 1,200 Nauruans to work as labourers in the Chuuk islands.[21] Nauru, which had been bypassed and left to "wither on the vine" by American forces, was finally liberated on 13 September 1945, when commander Hisayaki Soeda surrendered the island to the Australian Army and the Royal Australian Navy.[22] This surrender was accepted by Brigadier J. R. Stevenson, who represented Lieutenant General Vernon Sturdee, the commander of the First Australian Army, on board the warship HMAS Diamantina.[23][24] Arrangements were made to repatriate from Chuuk the 737 Nauruans who survived Japanese captivity there. They were returned to Nauru by the BPC ship Trienza in January 1946.[25] In 1947, a trusteeship was established by the United Nations, with Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom as trustees.[26]
Nauru became self-governing in January 1966, and following a two-year constitutional convention it became independent in 1968 under founding president Hammer DeRoburt.[27] In 1967, the people of Nauru purchased the assets of the British Phosphate Commissioners, and in June 1970 control passed to the locally owned Nauru Phosphate Corporation.[15] Income from the mines gave Nauruans one of the highest standards of living in the Pacific.[28] In 1989, Nauru took legal action against Australia in the International Court of Justice over Australia's administration of the island, in particular Australia's failure to remedy the environmental damage caused by phosphate mining. Certain Phosphate Lands: Nauru v. Australia led to an out-of-court settlement to rehabilitate the mined-out areas of Nauru.[26][29]
Politics

Nauru is a republic with a parliamentary system of government.[27] The president is both head of state and head of government. An 19-member unicameral parliament is elected every three years.[30] The parliament elects the president from its members, and the president appoints a cabinet of five to six members.[31] Nauru does not have any formal structure for political parties, and candidates typically stand for office as independents; fifteen of the 19 members of the current Parliament are independents. Four parties that have been active in Nauruan politics are the Nauru Party, the Democratic Party, Nauru First, and the Centre Party. However, alliances within the government are often formed on the basis of extended family ties rather than party affiliation.[32]
From 1992 to 1999, Nauru had a local government system known as the Nauru Island Council (NIC). This nine-member council was designed to provide municipal services. The NIC was dissolved in 1999 and all assets and liabilities became vested in the national government.[33] Land tenure on Nauru is unusual: all Nauruans have certain rights to all land on the island, which is owned by individuals and family groups. Government and corporate entities do not own any land, and they must enter into a lease arrangement with landowners to use land. Non-Nauruans cannot own land on the island.[4]
Nauru had 17 changes of administration between 1989 and 2003.[34] Bernard Dowiyogo died in office in March 2003 and Ludwig Scotty was elected as the president, later being re-elected to serve a full term in October 2004. Following a vote of no confidence on 19 December 2007, Scotty was replaced by Marcus Stephen. Stephen resigned in November 2011, and Freddie Pitcher became President. Sprent Dabwido then filed a motion of no confidence in Pitcher, resulting in him becoming president.[35][36] Following parliamentary elections in 2013 Baron Waqa was elected president.
Nauru has a complex legal system. Its Supreme Court, headed by the Chief Justice, is paramount on constitutional issues. Other cases can be appealed to the two-judge Appellate Court. Parliament cannot overturn court decisions, but Appellate Court rulings can be appealed to the High Court of Australia.[37][38] In practice, however, this rarely happens. Lower courts consist of the District Court and the Family Court, both of which are headed by a Resident Magistrate, who also is the Registrar of the Supreme Court. There are two other quasi-courts: the Public Service Appeal Board and the Police Appeal Board, both of which are presided over by the Chief Justice.[39]
Administrative divisions
Nauru is divided into fourteen administrative districts which are grouped into eight electoral constituencies.[39]
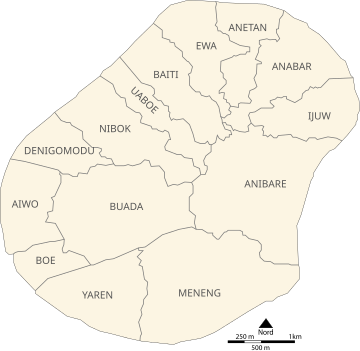
| Nr. | District | Former Name | Area (ha) |
Population (2005) |
No. of villages |
Density persons / ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aiwo | Aiue | 100 | 1,092 | 8 | 10.9 |
| 2 | Anabar | Anebwor | 143 | 502 | 15 | 3.5 |
| 3 | Anetan | Añetañ | 100 | 516 | 12 | 5.2 |
| 4 | Anibare | Anybody | 314 | 160 | 17 | 0.5 |
| 5 | Baiti | Beidi | 123 | 572 | 15 | 4.7 |
| 6 | Boe | Boi | 66 | 795 | 4 | 12.0 |
| 7 | Buada | Arenibok | 266 | 716 | 14 | 2.7 |
| 8 | Denigomodu | Denikomotu | 118 | 2,827 | 17 | 24.0 |
| 9 | Ewa | Eoa | 117 | 318 | 12 | 2.7 |
| 10 | Ijuw | Ijub | 112 | 303 | 13 | 2.7 |
| 11 | Meneng | Meneñ | 288 | 1,830 | 18 | 6.4 |
| 12 | Nibok | Ennibeck | 136 | 432 | 11 | 3.2 |
| 13 | Uaboe | Ueboi | 97 | 335 | 6 | 3.5 |
| 14 | Yaren | Moqua | 150 | 820 | 7 | 5.5 |
| Nauru | Naoero | 2,130 | 11,218 | 169 | 5.3 |
Foreign relations
Following independence in 1968, Nauru joined the Commonwealth of Nations as a Special Member; it became a full member in 2000.[40] The country was admitted to the Asian Development Bank in 1991 and to the United Nations in 1999.[41] Nauru is a member of the Pacific Islands Forum, the South Pacific Regional Environment Programme, the South Pacific Commission, and the South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission.[42] The American Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Program operates a climate-monitoring facility on the island.[43]
Nauru has no armed forces, though there is a small police force under civilian control.[1] Australia is responsible for Nauru's defence under an informal agreement between the two countries.[1] The September 2005 Memorandum of Understanding between Australia and Nauru provides the latter with financial aid and technical assistance, including a Secretary of Finance to prepare the budget, and advisers on health and education. This aid is in return for Nauru's housing of asylum seekers while their applications for entry into Australia are processed.[34] Nauru uses the Australian dollar as its official currency.[39]
Nauru has used its position as a member of the United Nations to gain financial support from both Taiwan (ROC) and China (PRC) by changing its recognition from one to the other under the One-China policy. On 21 July 2002, Nauru signed an agreement to establish diplomatic relations with the PRC, accepting $130 million from the PRC for this action.[44] In response, the ROC severed diplomatic relations with Nauru two days later. Nauru later re-established links with the ROC on 14 May 2005,[45] and diplomatic ties with the PRC were officially severed on 31 May 2005.[46] However, the PRC continues to maintain a representative office on Nauru.[47]
In 2008, Nauru recognised Kosovo as an independent country, and in 2009 Nauru became the fourth country, after Russia, Nicaragua, and Venezuela, to recognise Abkhazia, a breakaway region of Georgia. Russia was reported to be giving Nauru $50 million in humanitarian aid as a result of this recognition.[44] On 15 July 2008, the Nauruan government announced a port refurbishment programme, financed with US$9 million of development aid received from Russia. The Nauru government claims this aid is not related to its recognising Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[48]
A significant portion of Nauru's income has been in the form of aid from Australia. In 2001, the MV Tampa, a Norwegian ship that had rescued 438 refugees from a stranded 20-metre-long boat and was seeking to dock in Australia. In what became known as the Tampa affair, the ship was refused entry and boarded by Australian troops. The refugees were eventually loaded onto Royal Australian Navy vessel HMAS Manoora and taken to Nauru to be held in detention facilities which later became part of the Howard government's Pacific Solution. Nauru operated two detention centres known as State House and Topside for these refugees in exchange for Australian aid.[49] By November 2005, only two refugees, Mohammed Sagar and Muhammad Faisal, remained on Nauru from those first sent there in 2001,[50] with Sagar finally resettling in early 2007. The Australian government sent further groups of asylum-seekers to Nauru in late 2006 and early 2007.[51] The refugee centre was closed in 2008,[39] but, following the Australian government's re-adoption of the Pacific Solution in August 2012, it has re-opened it.[52]
Geography

Nauru is a 21 square kilometres (8 sq mi)[1] oval-shaped island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, 42 kilometres (26 mi) south of the Equator. The island is surrounded by a coral reef, which is exposed at low tide and dotted with pinnacles.[39] The presence of the reef has prevented the establishment of a seaport, although channels in the reef allow small boats access to the island.[53] A fertile coastal strip 150 to 300 metres (490 to 980 ft) wide lies inland from the beach.[39]
Coral cliffs surround Nauru's central plateau. The highest point of the plateau, called the Command Ridge, is 71 metres (233 ft) above sea level.[54] The only fertile areas on Nauru are on the narrow coastal belt, where coconut palms flourish. The land surrounding Buada Lagoon supports bananas, pineapples, vegetables, pandanus trees, and indigenous hardwoods such as the tomano tree.[39]
Nauru was one of three great phosphate rock islands in the Pacific Ocean (the others were Banaba (Ocean Island) in Kiribati and Makatea in French Polynesia). The phosphate reserves on Nauru are now almost entirely depleted. Phosphate mining in the central plateau has left a barren terrain of jagged limestone pinnacles up to 15 metres (49 ft) high. Mining has stripped and devastated about 80 per cent of Nauru's land area, and has also affected the surrounding Exclusive Economic Zone; 40 per cent of marine life is estimated to have been killed by silt and phosphate runoff.[39][55]
There are limited natural fresh water resources on Nauru. Rooftop storage tanks collect rainwater, but the islanders are mostly dependent on three desalination plants housed at Nauru's Utilities Agency. Nauru's climate is hot and very humid year-round because of its proximity to the equator and the ocean. Nauru is hit by monsoon rains between November and February, but does not typically experience cyclones. Annual rainfall is highly variable and is influenced by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, with several significant recorded droughts.[4][56] The temperature on Nauru ranges between 26 °C (79 °F) and 35 °C (95 °F) during the day and between 22 °C (72 °F) and 34 °C (93 °F) at night.[57]
As an island, Nauru is vulnerable to climate and sea level change. Nauru is the seventh most global warming threatened nation due to flooding.[58] At least 80 per cent of the land of Nauru is well elevated, but this area will be uninhabitable until the phosphate mining rehabilitation programme is implemented.[55][59]
| Climate data for Yaren District, Nauru | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 34 (93) |
37 (99) |
35 (95) |
35 (95) |
32 (90) |
32 (90) |
35 (95) |
33 (91) |
35 (95) |
34 (93) |
36 (97) |
35 (95) |
37 (99) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (87) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
20 (68) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 280 (11.0) |
250 (9.8) |
190 (7.5) |
190 (7.5) |
120 (4.7) |
110 (4.3) |
150 (5.9) |
130 (5.1) |
120 (4.7) |
100 (3.9) |
120 (4.7) |
280 (11.0) |
2,080 (81.9) |
| Average precipitation days | 16 | 14 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 12 | 14 | 11 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 152 |
| Source: [1] | |||||||||||||
Economy

The Nauruan economy peaked in the early 1980s, as it was dependent almost entirely on the phosphate deposits that originate from the droppings of sea birds. There are few other resources, and most necessities are imported.[39][60] Small-scale mining is still conducted by RONPhos, formerly known as the Nauru Phosphate Corporation.[39] The government places a percentage of RONPhos's earnings into the Nauru Phosphate Royalties Trust. The Trust manages long-term investments, which were intended to support the citizens once the phosphate reserves were exhausted.[61] However, because of mismanagement the Trust's fixed and current assets were reduced considerably, and many never fully recovered. The failed investments included financing Leonardo the Musical in 1993, which was a financial failure.[62] The Mercure Hotel in Sydney[63] and Nauru House in Melbourne were sold in 2004 to finance debts and Air Nauru's only Boeing 737 was repossessed in December 2005. Normal air service resumed after the aircraft was replaced with a Boeing 737–300 airliner in June 2006.[64] In 2005, the corporation sold its property asset in Melbourne, the vacant Savoy Tavern site, for $7.5 million.[65]
The value of the Trust is estimated to have shrunk from A$1.3 billion in 1991 to $138 million in 2002.[66] Nauru currently lacks money to perform many of the basic functions of government; for example, the National Bank of Nauru is insolvent. The CIA World Factbook estimated a GDP per capita of $5,000 in 2005.[1] The Asian Development Bank 2007 economic report on Nauru estimated GDP per capita at $2,400 to $2,715.[2]
There are no personal taxes in Nauru. The unemployment rate is estimated to be 90 percent, and of those who have jobs, the government employs 95 percent.[1][67] The Asian Development Bank notes that although the administration has a strong public mandate to implement economic reforms, in the absence of an alternative to phosphate mining, the medium-term outlook is for continued dependence on external assistance.[66] Tourism is not a major contributor to the economy.[68]

In the 1990s, Nauru became a tax haven and offered passports to foreign nationals for a fee.[69] The inter-governmental Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) identified Nauru as one of 15 "non-cooperative" countries in its fight against money laundering. During the 1990s, it was possible to establish a licensed bank in Nauru for only $25,000 with no other requirements. Under pressure from FATF, Nauru introduced anti-avoidance legislation in 2003, after which foreign hot money left the country. In October 2005, after satisfactory results from the legislation and its enforcement, FATF lifted the non-cooperative designation.[70]
From 2001 to 2007, the Nauru detention centre provided a significant source of income for the country. The Nauruan authorities reacted with concern to its closure by Australia.[71] In February 2008, the Foreign Affairs minister, Dr. Kieren Keke, stated that the closure would result in 100 Nauruans losing their jobs, and would affect 10 per cent of the island's population directly or indirectly: "We have got a huge number of families that are suddenly going to be without any income. We are looking at ways we can try and provide some welfare assistance but our capacity to do that is very limited. Literally we have got a major unemployment crisis in front of us."[72] The detention centre was re-opened in August 2012.[52]
Demographics

Nauru had 9,378 residents as of July 2011.[1] The population was previously larger, but in 2006 some 1,500 people left the island during a repatriation of immigrant workers from Kiribati and Tuvalu. The repatriation was motivated by wide-scale reductions-in-force in the phosphate mining industry.[2] The official language of Nauru is Nauruan, a distinct Pacific island language, which is spoken by 96 per cent of ethnic Nauruans at home.[2] English is widely spoken and is the language of government and commerce, as Nauruan is not common outside of the country.[1][39]
The top ethnic groups of Nauru are Nauruan (58%), other Pacific Islander (26%), European (8%), and Chinese (8%).[1] The main religion practised on the island is Christianity (two-thirds Protestant, one-third Roman Catholic).[39] There is also a sizeable Bahá'í population (10%) – the largest proportion of any country in the world[73] – and Buddhist (9%) and Muslim (2.2%) populations. The Constitution provides for freedom of religion. However, the government has restricted the religious practices of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and the Jehovah's Witnesses, most of whom are foreign workers employed by the government-owned Nauru Phosphate Corporation.[74]
Literacy on Nauru is 96 percent. Education is compulsory for children from six to sixteen years old, and two more non-compulsory years are offered (years 11 and 12).[75] There is a campus of the University of the South Pacific on Nauru. Before this campus was built in 1987, students would study either by distance or abroad.[76]
Nauruans are the most obese people in the world: 97 per cent of men and 93 per cent of women are overweight or obese.[77] As a result, Nauru has the world's highest level of type 2 diabetes, with more than 40 per cent of the population affected.[78] Other significant dietary-related problems on Nauru include kidney disease and heart disease. Life expectancy on Nauru in 2009 was 60.6 years for males and 68.0 years for females.[79]
Culture
Nauruans descended from Polynesian and Micronesian seafarers who believed in a female deity, Eijebong, and a spirit land, an island called Buitani. Two of the 12 original tribal groups became extinct in the 20th century.[39] Angam Day, held on 26 October, celebrates the recovery of the Nauruan population after the two World Wars and the 1920 influenza epidemic.[80] The displacement of the indigenous culture by colonial and contemporary western influences is significant.[81] Few of the old customs have been preserved, but some forms of traditional music, arts and crafts, and fishing are still practised.[82]

There are no daily news publications on Nauru, although there is one fortnightly publication, Mwinen Ko. There is a state-owned television station, Nauru Television (NTV), which broadcasts programmes from New Zealand and Australia, and a state-owned non-commercial radio station, Radio Nauru, which carries programmes from Radio Australia and the BBC.[83]
Australian rules football is the most popular sport in Nauru; it and weightlifting are considered the country's national sports. There is a football league with eight teams.[84] Other sports popular in Nauru include volleyball, netball, fishing and tennis. Nauru participates in the Commonwealth Games and the Summer Olympic Games.[85]
Wildlife
Fauna is sparse on the island due to a combination of a lack of vegetation and the consequences of phosphates mining. Many indigenous birds have disappeared or become rare owing to destruction of their habitat.[86] There are only about 60 recorded vascular plant species native to the island, none of which are endemic. Coconut farming, mining, and introduced species have caused serious disturbance to the native vegetation.[4] There are no native land mammals, but there are native insects, land crabs, and birds, including the endemic Nauru Reed Warbler. The Polynesian rat, cats, dogs, pigs, and chickens have been introduced to Nauru from ships.[87] The diversity of the reef marine life makes fishing a popular activity for tourists on the island, as well as SCUBA diving and snorkeling.[88]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Central Intelligence Agency (2011). "Nauru". The World Factbook. Retrieved 12 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "Country Economic Report: Nauru" (PDF). Asian Development Bank. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ^ Hogan, C Michael (2011). "Phosphate". Encyclopedia of Earth. National Council for Science and the Environment. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ a b c d Nauru Department of Economic Development and Environment (2003). "First National Report To the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification" (PDF). UNCCD. Retrieved 25 June 2012.
- ^ Whyte, Brendan (2007). "On Cartographic Vexillology". Cartographica: The International Journal for Geographic Information and Geovisualization. 42 (3): 251–262. doi:10.3138/carto.42.3.251.
- ^ Pollock, Nancy J (1995). "5: Social Fattening Patterns in the Pacific—the Positive Side of Obesity. A Nauru Case Study". In De Garine, I (ed.). Social Aspects of Obesity. Routledge. pp. 87–111.
- ^ a b Spennemann, Dirk HR (January 2002). "Traditional milkfish aquaculture in Nauru". Aquaculture International. 10 (6): 551–562. doi:10.1023/A:1023900601000.
- ^ West, Barbara A (2010). "Nauruans: nationality". Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Asia and Oceania. Infobase Publishing. pp. 578–580. ISBN 9781438119137.
- ^ Marshall, Mac (January 1976). "Holy and unholy spirits: The Effects of Missionization on Alcohol Use in Eastern Micronesia". Journal of Pacific History. 11 (3): 135–166. doi:10.1080/00223347608572299.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Reyes, Ramon E, Jr (1996). "Nauru v. Australia". New York Law School Journal of International and Comparative Law. 16 (1–2).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Firth, Stewart (January 1978). "German labour policy in Nauru and Angaur, 1906–1914". The Journal of Pacific History. 13 (1): 36–52. doi:10.1080/00223347808572337.
- ^ a b Hill, Robert A (ed) (1986). "2: Progress Comes to Nauru". The Marcus Garvey and Universal Negro Improvement Association Papers. Vol. 5. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520058170.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ^ Ellis, AF (1935). Ocean Island and Nauru – their story. Angus and Robertson Limited. pp. 29–39.
- ^ Hartleben, A (1895). Deutsche Rundschau für Geographie und Statistik. p. 429.
- ^ a b Manner, HI (May 1985). "Plant succession after phosphate mining on Nauru". Australian Geographer. 16 (3): 185–195. doi:10.1080/00049188508702872.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Gowdy, John M; McDaniel, Carl N (May 1999). "The Physical Destruction of Nauru". Land Economics. 75 (2): 333–338.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Shlomowitz, R (November 1990). "Differential mortality of Asians and Pacific Islanders in the Pacific labour trade". Journal of the Australian Population Association. 7 (2): 116–127. PMID 12343016.
- ^ Hudson, WJ (April 1965). "Australia's experience as a mandatory power". Australian Outlook. 19 (1): 35–46. doi:10.1080/10357716508444191.
- ^ Waters, SD (2008). German raiders in the Pacific (3rd ed.). Merriam Press. p. 39. ISBN 9781435757608.
- ^ a b Bogart, Charles H (November 2008). "Death off Nauru" (PDF). CDSG Newsletter: 8–9. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ^ a b Haden, JD (2000). "Nauru: a middle ground in World War II". Pacific Magazine. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ^ Takizawa, Akira; Alsleben, Allan (1999–2000). "Japanese garrisons on the by-passed Pacific Islands 1944–1945". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ^ The Times, 14 September 1945
- ^ "Nauru Occupied by Australians; Jap Garrison and Natives Starving". The Argus. 15 September 1945. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ Garrett, J (1996). Island Exiles. ABC. pp. 176–181. ISBN 0-7333-0485-0.
- ^ a b Highet, K; Kahale, H (1993). "Certain Phosphate Lands in Nauru". American Journal of International Law. 87: 282–288.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Davidson, JW (January 1968). "The republic of Nauru". The Journal of Pacific History. 3 (1): 145–150. doi:10.1080/00223346808572131.
- ^ Squires, Nick (15 March 2008). "Nauru seeks to regain lost fortunes". BBC News Online. Retrieved 16 March 2008.
- ^ Case Concerning Certain Phosphate Lands in Nauru (Nauru v. Australia) Application: Memorial of Nauru. ICJ Pleadings, Oral Arguments, Documents. United Nations, International Court of Justice. January 2004. ISBN 978-92-1-070936-1.
- ^ Matau, Robert (6 June 2013) "President Dabwido gives it another go". Islands Business.
- ^ Levine, Stephen (November 2005). "The constitutional structures and electoral systems of Pacific Island States". Commonwealth & Comparative Politics. 43 (3): 276–295. doi:10.1080/14662040500304866.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Anckar, D (2000). "Democracies without Parties". Comparative Political Studies. 33 (2): 225–247. doi:10.1177/0010414000033002003.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hassell, Graham; Tipu, Feue (May 2008). "Local Government in the South Pacific Islands". Commonwealth Journal of Local Governance. 1 (1): 6–30.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Republic of Nauru Country Brief". Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. November 2005. Retrieved 2 May 2006.
- ^ Connell, John (January 2006). "Nauru: The first failed Pacific State?". The Round Table. 95 (383): 47–63. doi:10.1080/00358530500379205.
- ^ "Nauru profile". BBC News. 24 October 2011. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ "Nauru (High Court Appeals) Act (Australia) 1976". Australian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 7 August 2006.
- ^ Dale, Gregory (2007). "Appealing to Whom? Australia's 'Appellate Jurisdiction' Over Nauru". International & Comparative Law Quarterly. 56 (3). doi:10.1093/iclq/lei186.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Background Note: Nauru". State Department Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs. September 2005. Retrieved 11 May 2006.
- ^ "Republic of Nauru Permanent Mission to the United Nations". United Nations. Retrieved 10 May 2006.
- ^ "Nauru in the Commonwealth". Commonwealth of Nations. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "Nauru (04/08)". US State Department. 2008. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ Long, Charles N (March 2012). "Quantification of the Impact of Nauru Island on ARM Measurements". Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology. 51 (3): 628–636. doi:10.1175/JAMC-D-11-0174.1.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Harding, Luke (14 December 2009). "Tiny Nauru struts world stage by recognising breakaway republics". Guardian. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ Su, Joy (15 May 2005). "Nauru switches its allegiance back to Taiwan from China". Taipei Times. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "China officially severs diplomatic ties with Nauru". Asia Africa Intelligence Wire. 31 May 2005. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "Chinese Embassy in Nauru". Gov.cn. 18 January 2006. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "Nauru expects to earn more from exports after port upgrade with Russian aid". Radio New Zealand International. 15 July 2010. Retrieved 15 July 2010.
- ^ White, Michael (2002). "M/V Tampa Incident and Australia's Obligations – August 2001". Maritime Studies. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ Gordon, M (5 November 2005). "Nauru's last two asylum seekers feel the pain". The Age. Retrieved 8 May 2006.
- ^ "Nauru detention centre costs $2m per month". ABC News. 12 February 2007. Retrieved 12 February 2007.
- ^ a b "Asylum bill passes parliament". SBS World News Australia. 16 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ Thaman, RR; Hassall, DC. "Nauru: National Environmental Management Strategy and National Environmental Action Plan" (PDF). South Pacific Regional Environment Programme. p. 234.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Jacobson, Gerry; Hill, Peter J; Ghassemi, Fereidoun (1997). "24: Geology and Hydrogeology of Nauru Island". Geology and hydrogeology of carbonate islands. Elsevier. p. 716. ISBN 9780444815200.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Republic of Nauru (1999). "Climate Change – Response" (PDF). First National Communication. United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Retrieved 9 September 2009.
- ^ Affaire de certaines terres à phosphates à Nauru. International Court of Justice. 2003. pp. 107–109. ISBN 9789210709361.
- ^ "Pacific Climate Change Science Program" (PDF). Government of Australia. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ^ Stephen, Marcus (November 2011). "A Sinking Feeling; Why is the president of the tiny Pacific island nation of Nauru so concerned about climate change?". The New York Times Upfront. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "Current and future climate of Nauru" (PDF). Centre for Australian Weather and Climate Research. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ "Big tasks for a small island". BBC. Retrieved 10 May 2006.
- ^ Seneviratne, Kalinga (26 May 1999). "Nauru turns to dust". Asia Times. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ Mellor, William (1 June 2004). "GE Poised to Bankrupt Nauru, Island Stained by Money-Laundering". Bloomberg. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ Skehan, Craig (9 July 2004). "Nauru, receivers start swapping legal blows". Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Receivers take over Nauru House". The Age. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Nauru sells last remaining property asset in Melbourne – report". RNZI. 8 April 2005. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ a b "Asian Development Outlook 2005 – Nauru". Asian Development Bank. 2005. Retrieved 2 May 2006.
- ^ "Paradise well and truly lost". The Economist. 20 December 2001. Retrieved 2 May 2006.
- ^ "Nauru". Pacific Islands Trade and Investment Commission. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "The Billion Dollar Shack". New York Times. 10 December 2000. Retrieved 19 July 2011.
- ^ "Nauru de-listed" (PDF). FATF. 13 October 2005. Retrieved 11 May 2006.
- ^ Topsfield, Hewel (11 December 2007). "Nauru fears gap when camps close". The Age. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Nauru 'hit' by detention centre closure". The Age. 7 February 2008. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Adherent.com's Largest Baha'i Communities". Adherents.com. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "International Religious Freedom Report 2003 – Nauru". US Department of State. 2003. Retrieved 2 May 2005.
- ^ Waqa, B (1999). "UNESCO Education for all Assessment Country report 1999 Country: Nauru". Retrieved 2 May 2006.
- ^ "USP Nauru Campus". University of the South Pacific. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Fat of the land: Nauru tops obesity league". Independent. 26 December 2010. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ King, H; Rewers M (1993). "Diabetes in adults is now a Third World problem". Ethnicity & Disease. 3: S67–74.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Nauru". World health report 2005. World Health Organization. Retrieved 2 May 2006.
- ^ "Nauru Celebrates Angam Day". UN. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ Nazzal, Mary (April 2005). "Nauru: an environment destroyed and international law" (PDF). lawanddevelopment.org. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Culture of Nauru". Republic of Nauru. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Country Profile: Nauru". BBC News. Retrieved 2 May 2006.
- ^ "Nauru Australian Football Association". Australian Football League. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- ^ "Nauru Olympic Committee History". Nauru Olympic Committee. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ^ NAURU Information on Government, People, History, Economy, Environment, Development
- ^ BirdLife International. "Important Bird Areas in Nauru". Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environmental Programme. Retrieved 18 June 2012.
- ^ Nauru Ecotourism Tours – Sustainable Tourism & Conservation Laws
- This article incorporates public domain text from the websites of the United States Department of State & CIA World Factbook.
Further reading
- Gowdy, John M; McDaniel, Carl N (2000). Paradise for Sale: A Parable of. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-22229-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Government of Nauru
- "Nauru". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Nauru
Wikimedia Atlas of Nauru- Nauru from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Nauru profile from the BBC News
- Discover Nauru The Official Nauru Tourism Website
Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link GA
- Use dmy dates from June 2012
- Nauru
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Former German colonies
- Island countries
- Liberal democracies
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member states of the United Nations
- Micronesia
- Countries in Oceania
- Republics
- States and territories established in 1968
- Commonwealth republics