Rhinovirus
| Rhinovirus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Rhinovirus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Groups included | |
| |
| Cladistically included but traditionally excluded taxa | |
|
The rhinovirus (from the Greek ῥίς rhis "nose", gen ῥινός rhinos "of the nose", and the Latin vīrus) is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures of 33–35 °C (91–95 °F), the temperatures found in the nose. Rhinoviruses belong to the genus Enterovirus in the family Picornaviridae.
The three species of rhinovirus (A, B, and C) include around 160 recognized types of human rhinovirus that differ according to their surface proteins (serotypes).[1] They are lytic in nature and are among the smallest viruses, with diameters of about 30 nanometers. By comparison, other viruses, such as smallpox and vaccinia, are around ten times larger at about 300 nanometers; while flu viruses are around 80–120 nm.
History
In 1953, when a cluster of nurses developed a mild respiratory illness, Winston Price, from the Johns Hopkins University, took nasal passage samples and isolated the first rhinovirus, which he called the JH virus, named after Johns Hopkins.[2][3] His findings were published in 1956.[4]
Transmission and epidemiology
There are two modes of transmission: via aerosols of respiratory droplets and from fomites (contaminated surfaces), including direct person-to-person contact.
Rhinoviruses are spread worldwide and are the primary cause of the common cold. Symptoms include sore throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing and cough; sometimes accompanied by muscle aches, fatigue, malaise, headache, muscle weakness, or loss of appetite. Most sinus findings are reversible consistent with a self-limited viral process typical of rhinovirus colds. Fever and extreme exhaustion are more usual in influenza. Children may have six to twelve colds a year. In the United States, the incidence of colds is higher in the autumn and winter, with most infections occurring between September to April. The seasonality may be due to the start of the school year[citation needed] and to people spending more time indoors (thus in proximity with each other),[citation needed] thereby increasing the chance of transmission of the virus. Lower ambient, especially outdoor, temperatures may also be factor[5] given that rhinoviruses preferentially replicate at 32 °C (89 °F) as opposed to 37 °C (98 °F) – see following section. Variant pollens, grasses, hays and agricultural practices may be factors in the seasonality as well as the use of chemical controls of lawn, paddock and sportsfields in schools and communities. The changes in temperature, humidity and wind patterns seem to be factors. It is also postulated that poor housing, overcrowding and unsanitary conditions related to poverty are relevant factors in the transmission of 'common cold'.
Those most affected by rhinoviruses are infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised people.[6]
Pathogenesis
The primary route of entry for human rhinoviruses is the upper respiratory tract (mouth and nose). Rhinovirus A and B use "major" ICAM-1 (Inter-Cellular Adhesion Molecule 1), also known as CD54 (Cluster of Differentiation 54), on respiratory epithelial cells, as receptors to bind to. Some subgroups under A and B uses the "minor" LDL receptor instead.[7] Rhinovirus C uses cadherin-related family member 3 (CDHR3) to mediate cellular entry.[8] As the virus replicates and spreads, infected cells release distress signals known as chemokines and cytokines (which in turn activate inflammatory mediators). Cell lysis occurs at the upper respiratory epithelium.
Infection occurs rapidly, with the virus adhering to surface receptors within 15 minutes of entering the respiratory tract. Just over 50% of individuals will experience symptoms within 2 days of infection. Only about 5% of cases will have an incubation period of less than 20 hours, and, at the other extreme, it is expected that 5% of cases would have an incubation period of greater than four and a half days.[9]
Human rhinoviruses preferentially grow at 32 °C (89 °F), notably colder than the average human body temperature of 37 °C (98 °F); hence the virus's tendency to infect the upper respiratory tract, where respiratory airflow is in continual contact with the (colder) extrasomatic environment.
Rhinovirus C, unlike the A and B species, may be able to cause severe infections.[10] This association disappears after controlling for confounders.[11] Duly, amongst infants infected with symptomatic respiratory illness in low-resource areas, there appears to be no association between rhinovirus species and disease severity.[12]
Taxonomy
Rhinovirus was formerly a genus from the family Picornaviridae. The 39th Executive Committee (EC39) of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) met in Canada during June 2007 with new taxonomic proposals. In April 2008, the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses voted and ratified the following changes:
- 2005.264V.04 To remove the following species from the existing genus Rhinovirus in the family Picornaviridae:
- Human rhinovirus A
- Human rhinovirus B
- 2005.265V.04 To assign the following species to the genus Enterovirus in the family Picornaviridae:
- Human rhinovirus A
- Human rhinovirus B
- 2005.266V.04 To remove the existing genus Rhinovirus from the family Picornaviridae. Note: The genus Rhinovirus hereby disappears.
In July 2009, the ICTV voted and ratified a proposal to add a third species, Human rhinovirus C to the genus Enterovirus.
- 2008.084V.A.HRV-C-Sp 2008.084V To create a new species named Human rhinovirus C in the genus Enterovirus, family Picornaviridae.
There have been a total of 215 taxonomic proposals, which have been approved and ratified since the 8th ICTV Report of 2005.
Serotypes
Human rhinovirus serotype names are of the form HRV-Xn where X is the rhinovirus species (A, B, or C) and n is an index number. Species A and B have used the same index, while Species C has a separate index. Valid index numbers are as follows:
- Rhinovirus A: 1, 2, 7–13, 15, 16, 18–25, 28–34, 36, 38–41, 43–47, 49–51, 53–68, 71, 73–78, 80–82, 85, 88–90, 94–96, 98, 100–103
- Rhinovirus B: 3–6, 14, 17, 26, 27, 35, 37, 42, 48, 52, 69, 70, 72, 79, 83, 84, 86, 91–93, 97, 99
- Rhinovirus C: 1–51
Structure

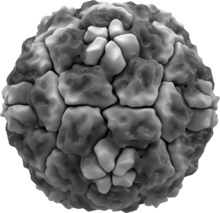
Rhinoviruses have single-stranded positive sense RNA genomes of between 7200 and 8500 nt in length. At the 5' end of the genome is a virus-encoded protein, and like mammalian mRNA, there is a 3' poly-A tail. Structural proteins are encoded in the 5' region of the genome and non structural at the 3' end. This is the same for all picornaviruses. The viral particles themselves are not enveloped and are icosahedral in structure.
The viral proteins are translated as a single, long polypeptide, which is cleaved into the structural and nonstructural viral proteins.[13]
Human rhinoviruses are composed of a capsid that contains four viral proteins, VP1, VP2, VP3 and VP4.[14][15] VP1, VP2, and VP3 form the major part of the protein capsid. The much smaller VP4 protein has a more extended structure, and lies at the interface between the capsid and the RNA genome. There are 60 copies of each of these proteins assembled as an icosahedron. Antibodies are a major defense against infection with the epitopes lying on the exterior regions of VP1-VP3.
Novel antiviral drugs
Interferon-alpha used intranasally was shown to be effective against human rhinovirus infections. However, volunteers treated with this drug experienced some side effects, such as nasal bleeding, and began developing resistance to the drug. Subsequently, research into the treatment was abandoned.[16]
Pleconaril is an orally bioavailable antiviral drug being developed for the treatment of infections caused by picornaviruses.[17] This drug acts by binding to a hydrophobic pocket in VP1, and stabilizes the protein capsid to such an extent that the virus cannot release its RNA genome into the target cell. When tested in volunteers, during the clinical trials, this drug caused a significant decrease in mucus secretions and illness-associated symptoms. Pleconaril is not currently available for treatment of human rhinoviral infections, as its efficacy in treating these infections is under further evaluation.[18]
Other substances such as Iota-Carrageenan may form a basis for the creation of drugs to combat the human rhinovirus.[19]
In asthma, human rhinoviruses have been recently associated with the majority of asthma exacerbations for which current therapy is inadequate. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) has a central role in airway inflammation in asthma, and it is the receptor for 90% of Human rhinoviruses. Human rhinovirus infection of airway epithelium induces ICAM-1.
Desloratadine and loratadine are compounds belonging to the new class of H1-receptor blockers. Anti-inflammatory properties of antihistamines have been recently documented, although the underlying molecular mechanisms are not completely defined. These effects are unlikely to be mediated by H1-receptor antagonism and suggest a novel mechanism of action that may be important for the therapeutic control of virus-induced asthma exacerbations.[citation needed]
In 2018, a new series of anti-rhinoviral compounds were reported by researchers at Imperial College London and colleagues at the University of York and the Pirbright Institute. These molecules target human N-myristoyltransferase, an enzyme in the host cell which picornavirus requires in order to assemble its viral capsid, and thus generate an infectious virion. The lead compound in this series, IMP-1088, very potently inhibited host myristoylation of viral capsid protein and prevented infectious virus formation, rescuing the viability of cells in culture which had been exposed to a variety of rhinovirus serotypes, or to related picornaviruses including poliovirus and foot-and-mouth-disease virus.[20] Because these compounds target a host factor, they are broadly active against all serotypes, and it is thought to be unlikely that they can be overcome by resistance mutations in the virus.[20]
Vaccine
There are no vaccines against these viruses as there is little-to-no cross-protection between serotypes. At least 99 serotypes of human rhinoviruses affecting humans have been sequenced.[21][7] However, a study of the VP4 protein has shown it to be highly conserved among many serotypes of human rhinovirus, opening up the potential for a future pan-serotype human rhinovirus vaccine.[22] A similar result was obtained with the VP1 protein. Like VP4, VP1 also occasionally "pokes" out of the viral particle, making it available to neutralizing antibodies. Both peptides have been tested on rabbits, resulting in successful generation of cross-serotype antibodies.[23]
The successful introduction of human ICAM-1 into mouse has removed a major roadblock in creating an animal model for RV vaccination.[23]
Prevention
Human rhinovirus is most contagious during the autumn and winter months. The virus can remain activated for up to 3 hours outside of a human host. Once the virus is contracted, a person is most contagious within the first 3 days. Preventive measures such as regular vigorous handwashing with soap and water may aid in avoiding infection. Avoiding touching the mouth, eyes, and nose, the most common entry points for rhinovirus may also aid in prevention. Droplet precautions, which take the form of a surgical mask and gloves, is the method used in major hospitals.
References
- ^ Nicola Davison (6 October 2017). "Why can't we cure the common cold?", The Guardian
- ^ Offit, Paul A. (2007). Vaccinated; One man's quest to defeat the world's deadliest diseases. HarperCollins. pp. 66–68. ISBN 978-0-06-122795-0.
- ^ Public Health Reports. Vol. 74. The Service. 1959. p. 9.
- ^ Kennedy, Joshua L; Turner, Ronald B.; Braciale, Thomas; Heymann, Peter W.; Borish, Larry (June 2012). "Pathogenesis of Rhinovirus Infection". Current Opinion in Virology. 2 (3): 287–293. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2012.03.008. ISSN 1879-6257. PMC 3378761. PMID 22542099.
- ^ Foxman EF, Storer JA, Fitzgerald ME, Wasik BR, Hou L, Zhao H, et al. (January 2015). "Temperature-dependent innate defense against the common cold virus limits viral replication at warm temperature in mouse airway cells". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112 (3): 827–32. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112..827F. doi:10.1073/pnas.1411030112. PMC 4311828. PMID 25561542.
- ^ Jacobs SE, Lamson DM, St George K, Walsh TJ (January 2013). "Human rhinoviruses". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 26 (1): 135–62. doi:10.1128/CMR.00077-12. PMC 3553670. PMID 23297263.
- ^ a b Palmenberg AC, Spiro D, Kuzmickas R, Wang S, Djikeng A, Rathe JA, et al. (April 2009). "Sequencing and analyses of all known human rhinovirus genomes reveal structure and evolution". Science. 324 (5923): 55–9. Bibcode:2009Sci...324...55P. doi:10.1126/science.1165557. PMC 3923423. PMID 19213880.
- ^ Bochkov YA, Watters K, Ashraf S, Griggs TF, Devries MK, Jackson DJ, et al. (April 2015). "Cadherin-related family member 3, a childhood asthma susceptibility gene product, mediates rhinovirus C binding and replication". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112 (17): 5485–90. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112.5485B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1421178112. PMC 4418890. PMID 25848009.
- ^ Lessler J, Reich NG, Brookmeyer R, Perl TM, Nelson KE, Cummings DA (May 2009). "Incubation periods of acute respiratory viral infections: a systematic review". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases. 9 (5): 291–300. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70069-6. PMC 4327893. PMID 19393959.
- ^ Fuji N, Suzuki A, Lupisan S, Sombrero L, Galang H, Kamigaki T, et al. (2011). Schulz TF (ed.). "Detection of human rhinovirus C viral genome in blood among children with severe respiratory infections in the Philippines". PLOS One. 6 (11): e27247. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...627247F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027247. PMC 3210775. PMID 22087272.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ McCulloch DJ, Sears MH, Jacob JT, Lyon GM, Burd EM, Caliendo AM, et al. (August 2014). "Severity of rhinovirus infection in hospitalized adults is unrelated to genotype". American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 142 (2): 165–72. doi:10.1309/AJCPHIKRJC67AAZJ. PMC 4332627. PMID 25015856.
- ^ Kuypers J, Perchetti GA, Chu HY, Newman KL, Katz J, Khatry SK, et al. (December 2019). "Phylogenetic characterization of rhinoviruses from infants in Sarlahi, Nepal". Journal of Medical Virology. 91 (12): 2108–2116. doi:10.1002/jmv.25563. PMC 6800797. PMID 31389049.
- ^ Robert B Couch (2005). "Rhinoviruses:Replication". In Anne O'Daly (ed.). Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. John Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-01590-2.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Rossmann MG, Arnold E, Erickson JW, Frankenberger EA, Griffith JP, Hecht HJ, et al. (1985). "Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses". Nature. 317 (6033): 145–53. Bibcode:1985Natur.317..145R. doi:10.1038/317145a0. PMID 2993920.
- ^ Smith TJ, Kremer MJ, Luo M, Vriend G, Arnold E, Kamer G, et al. (September 1986). "The site of attachment in human rhinovirus 14 for antiviral agents that inhibit uncoating". Science. 233 (4770): 1286–93. Bibcode:1986Sci...233.1286S. doi:10.1126/science.3018924. PMID 3018924.
- ^ Farr BM, Gwaltney JM, Adams KF, Hayden FG (July 1984). "Intranasal interferon-alpha 2 for prevention of natural rhinovirus colds". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 26 (1): 31–4. doi:10.1128/aac.26.1.31. PMC 179911. PMID 6089652.
- ^ Pevear DC, Tull TM, Seipel ME, Groarke JM (September 1999). "Activity of pleconaril against enteroviruses". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 43 (9): 2109–15. doi:10.1128/AAC.43.9.2109. PMC 89431. PMID 10471549.
- ^ Fleischer R, Laessig K (December 2003). "Safety and efficacy evaluation of pleconaril for treatment of the common cold". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 37 (12): 1722. doi:10.1086/379830. PMID 14689362.
- ^ Grassauer A, Weinmuellner R, Meier C, Pretsch A, Prieschl-Grassauer E, Unger H (September 2008). "Iota-Carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of rhinovirus infection". Virology Journal. 5: 107. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-5-107. PMC 2562995. PMID 18817582.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Mousnier A, Bell AS, Swieboda DP, Morales-Sanfrutos J, Pérez-Dorado I, Brannigan JA, et al. (June 2018). "Fragment-derived inhibitors of human N-myristoyltransferase block capsid assembly and replication of the common cold virus". Nature Chemistry. 10 (6): 599–606. Bibcode:2018NatCh..10..599M. doi:10.1038/s41557-018-0039-2. PMC 6015761. PMID 29760414.
- ^ Mary Engel (February 13, 2009). "Rhinovirus strains' genomes decoded; cold cure-all is unlikely: The strains are probably too different for a single treatment or vaccine to apply to all varieties, scientists say". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Katpally U, Fu TM, Freed DC, Casimiro DR, Smith TJ (July 2009). "Antibodies to the buried N terminus of rhinovirus VP4 exhibit cross-serotypic neutralization". Journal of Virology. 83 (14): 7040–8. doi:10.1128/JVI.00557-09. PMC 2704786. PMID 19403680.
- ^ a b Katpally U, Fu TM, Freed DC, Casimiro DR, Smith TJ (July 2009). "Antibodies to the buried N terminus of rhinovirus VP4 exhibit cross-serotypic neutralization". Journal of Virology. 83 (14): 7040–8. doi:10.1128/JVI.00557-09. PMC 4291752. PMID 19403680.
External links
- VIDEO: Rhinoviruses, the Old, the New and the UW James E. Gern, MD, speaks at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, 2008.
- How Big is a Human rhinovirus? (animation)
