Kedah
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2010) |
Kedah | |
|---|---|
| Kedah Darul Aman قدح دار الامن | |
| Motto(s): "Kedah Aman Makmur, Harapan Bersama Makmurkan Kedah" | |
| Anthem: Allah Selamatkan Sultan Mahkota (English:"God Save the Crowned Sultan") ( الله سلامتکن سولطن) | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 6°07′42″N 100°21′46″E / 6.12833°N 100.36278°E | |
| Capital | Alor Setar |
| Royal capital | Anak Bukit |
| Government | |
| • Type | Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| • Sultan | Sallehuddin |
| • Menteri Besar | Muhammad Sanusi Md Nor (PN-PAS) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9,500 km2 (3,700 sq mi) |
| Population (2015)[2] | |
| • Total | 2,071,900 |
| • Density | 199/km2 (520/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Kedahan |
| Human Development Index | |
| • HDI (2010) | 0.800 (very high) (11th) |
| Postal code | 05xxx to 09xxx |
| Calling code | 04 08 (Kulim and Langkawi ) |
| ISO 3166 code | MY-02 |
| Vehicle registration | K (Mainland Kedah) KV (Langkawi Island) |
| British control | 1909 |
| Japanese occupation | 1942 |
| Accession into the Federation of Malaya | 1948 |
| Independence as part of the Federation of Malaya | 31 August 1957 |
| Website | kedah |
Kedah (Malay pronunciation: [kəˈdɑh][3]; Jawi: قدح), also known by its honorific Darul Aman or "Abode of Peace"[4] is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km², and it consists of the mainland and the Langkawi islands. The mainland has a relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice, while Langkawi is an archipelago, most of which are uninhabited islands.
Kedah was previously known as Kadaram (Template:Lang-ta; kadāram) by the ancient and medieval Tamils, Kataha or Kalahbar (Arabic: قتح; qataḥa or Arabic: قلحبر; qalaḥbar) by the Arabs,[citation needed] and Syburi (Template:Lang-th; RTGS: Sai Buri) by the Siamese when it was under their influence.[5]
To the north, Kedah borders the state of Perlis and shares an international boundary with the Songkhla and Yala provinces of Thailand. It borders the states of Perak to the south and Penang to the southwest.
The state's capital is Alor Setar and the royal seat is in Anak Bukit. Other major towns include Sungai Petani, and Kulim on the mainland, and Kuah on Langkawi.
History
Early history

Archaeological evidence found in Bujang Valley (Malay:Lembah Bujang) reveals that a Hindu–Buddhist kingdom ruled ancient Kedah possibly as early as 110 A.D. The discovery of temples, jetty remains, iron smelting sites, and clay brick monuments dating back to 110 A.D shows that a maritime trading route with south Indian Tamil kingdoms was already established since that time.[6] The discoveries in Bujang Valley also made the ancient Kedah as the oldest civilisation of Southeast Asia.[7]
Reference to ancient Kedah was first mentioned in a Tamil poem Paṭṭiṉappālai written at the end of the 2nd century A.D. It described goods from Kadaram "heaped together in the broad streets" of Chola capital. Other than Kadaram, Kedah was known with different names at varying times in Indian literature; Kataha-Nagara (in Kaumudi Mahotsava drama), Anda-Kataha (in Agni Purana), Kataha-Dvipa (in Samarāiccakahā), and Kataha (in Kathasaritsagara).[8] In the middle eastern literature, ancient Kedah was referred as Qilah by Ibn Khordadbeh in Kitāb al Masālik w'al Mamālik, Kalah-Bar by Soleiman Siraf & Abu Zaid al Hassan in Silsilat-al-Tawarikh (travels in Asia), and Kalah by Abu-Dulaf Misa'r Ibn Muhalhil in Al-Risalah al-thaniyah.[9] The famous Tang dynasty Buddhist monk, Yi Jing who visited Malay archipelago between 688–695, also mentioned about a kingdom known as Ka-Cha in the northern part of Malay peninsular, which according to him was 30 days sail from Bogha (Palembang), the capital of Sribogha (Srivijaya).[10]
In the 7th and 8th centuries, Kedah was under the loose control of Srivijaya.[11] Indian and Arab sources consider Kedah to be one of the two important sites during the Srivijaya period, often calling the king of the straits "the ruler of Srivijaya and Kataha".[12] In 1025, Rajendra Chola, the Chola king from Coromandel in South India, captured Kedah in his invasion of Srivijaya and occupied it for some time.[13] A second invasion was led by Virarajendra Chola of the Chola dynasty who conquered Kedah in the late 11th century.[14] During the reign of Kulothunga Chola I Chola overlordship was established over the Sri Vijaya province Kedah in the late 11th century.[15]
Kedah Sultanate
According to Hikayat Merong Mahawangsa or the Kedah Annals, Kedah was founded by a Hindu king named Merong Mahawangsa. According to the text further, the Sultanate of Kedah started in year 1136 when King Phra Ong Mahawangsa converted to Islam and adopted the name Sultan Mudzafar Shah. However, an Acehnese account gave a date of 1474 for the year of conversion to Islam by the ruler of Kedah. This later date accords with an account in the Malay Annals where a raja of Kedah visited Malacca during the reign of its last sultan seeking the honour of the royal band that marks the sovereignty of a Muslim ruler.[16]
It was later under Siam, until it was conquered by the Malay sultanate of Malacca in the 15th century. In the 17th century, Kedah was attacked by the Portuguese after their conquest of Malacca, and by Aceh. In the hope that Great Britain would protect what remained of Kedah from Siam, the sultan handed over Penang and then Province Wellesley to the British at the end of the 18th century. The Siamese nevertheless invaded Kedah in 1821,[17] and it remained under Siamese control under the name of Syburi. In 1896, Kedah along with Perlis and Setul was combined into the Siamese province of Monthon Syburi which lasted until transferred to the British by the Anglo-Siamese Treaty of 1909.
Incorporation into Malaya
In World War II, Kedah (along with Kelantan) was the first part of Malaya to be invaded by Japan. The Japanese returned Kedah to their Thai allies who had it renamed Syburi, but it returned to British rule after the end of the war. Kedah was a reluctant [citation needed] addition to the Federation of Malaya in 1948.
Since 1958, the hereditary Sultan of Kedah has been Tuanku Abdul Halim Mu'adzam Shah. The Kedah Sultanate began when the 9th Kedah Maharaja Derbar Raja or Phra Ong Mahawangsa, converted to Islam and changed his name to Sultan Mudzafar Shah I. Since then there have been 27 Sultans who ruled Kedah.[18]
Geography

Kedah is the 8th largest state by land area and 8th most populated state in Malaysia, with a total land area of 9,500 km2 (3,700 sq mi),[19] and a population of 1,890,098.[20]
The Pedu Lake is the largest man-made lake in the state.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 1,116,140 | — |
| 1991 | 1,364,504 | +22.3% |
| 2000 | 1,649,756 | +20.9% |
| 2010 | 1,947,651 | +18.1% |
| 2019 | 2,180,600 | +12.0% |
| Source:[21] | ||
Kedah has a relatively heterogeneous populace constituted by three major ethnic groups; the Malays, Chinese and Indians as well as some Malaysian Siamese ethnic groups, similar to most of the other Malaysian states. Prior to the formation of the Federation of Malaya, there was an ethnic group known as the Sam Sam people. They are culturally Malay Muslim but speak Siamese language. Most of these communities are almost extinct due to assimilation with the Malays. In some places in Kedah, the Sam Sam people still retain their Siamese language as their mother tongue. These communities can be found in Pendang District, Kuala Nerang District and Kubang Pasu District (Changlun, Kodiang, Jitra, Wang Tepus, Guar Napai, Malau, Ason and Napoh). Kedah has a very small Orang Asli community. Orang Asli only can be found in the Baling district.[citation needed]
Language
Like most parts of Malaysia, Kedah is home to various languages and dialects. The majority language of Kedah is Kedah Malay, known natively by locals as Pelat Utagha (Northern dialect), it is a distinct variety of Malay which also serves as the state's main lingua franca and is used by almost all Kedahans regardless of race. Kedah Malay has many sub-dialects which differs from district to district and is also spoken outside of its boundaries such as Penang, Perlis, northern Perak and even as far as Satun in Thailand and Tanintharyi in Myanmar. Besides Kedah Malay, another distinct variety of Malay known as Baling Malay (Cakak Baling) is mainly spoken in Baling district as well as some parts of Sik and Yan districts. Baling, along with Grik Malay is part of Reman Malay, an offshoot of Kelantan-Pattani Malay of which it was descended from the people of the Kingdom of Reman of which once ruled the Baling and Grik regions before it was dissolved and became part of three distinct political entities namely Kedah, Perak and Yala (Thailand).
Besides Malay, there are also various minority languages spoken throughout Kedah, Aslian languages such as Jahai, Kensiu and Kintaq are spoken by the small Orang Asli populations mostly in the inland region. The Chinese in Kedah also speaks various varieties of Chinese such as Mandarin, Hokkien (majority), Teochew, Cantonese and so on. There are also a small but well established Indian community mostly of ethnic Tamil and also smaller number of Telugus, Malayalees and Punjabis who speak Telugu, Malayalam and Punjabi. Kedah is also home to a large community of ethnic Siamese of which it has its own distinct dialect of the Thai language which is different from ones spoken in Kelantan (which also has a large Siamese population) and Standard Thai.
Ethnicity
The population of Kedah in 2015 was 2,071,900. It was made up of 76% Bumiputra (Malays and others), 12.7% Chinese, 6.9% Indian, 0.9% others and 3.4% non-Malaysian. The following is based on 2015 figures from the Department of Statistics Malaysia.[2]
| Ethnic groups in Kedah, 2015 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Population | Percentage |
| Bumiputera | 1,574,400 | 76.0% |
| Chinese | 263,200 | 12.7% |
| Indian | 143,200 | 6.9% |
| Others | 19,600 | 0.9% |
| Non-Malaysian | 71,500 | 3.4% |
Religion
As of 2010 the population of Kedah is 77.2% Muslim, 14.2% Buddhist, 6.7% Hindu, 0.8% Christian, 0.6% unknown / none, 0.3% Taoist or Chinese religion followers, 0.1% followers of other religions, and 0.1% non-religious.[22]
Statistics from the 2010 Census indicate that 94.3% of the Chinese population are identified as Buddhists, with significant minorities of adherents identifying as Christians (2.4%), Chinese folk religions (2.4%) and Muslims (0.4%). The majority of the Indian population are Hindus (91.7%), with a significant minorities of numbers identifying as Christians (3.7%), Muslims (2.4%) and Buddhists (1.3%). The non-Malay bumiputera community are predominantly Christians (39.7%), with significant minorities identifying as Muslims (26.9%) and Buddhists (26.3%). All Malays are Muslims.[23]
Governance
Kedah's Constitution was promulgated by its Ruler in July 1950. [citation needed] The various provisions laid down in the Constitution include the role and powers of the Monarch, the State Parliament and the State's Civil Service.

The Sultan of Kedah is the constitutional ruler of the State. His position is hereditary and he holds office for life. The Ruler is the head of the religion of Islam in the State and the executive power of the state government is vested in him. The current Sultan is Tunku Mahmud Sallehuddin, who has reigned on 12 September 2017 after his elder brother Abdul Halim of Kedah died on 11 September 2017.
The State Executive Council, which along with the Sultan is Kedah's executive branch of government. It is composed of the Menteri Besar, who is its chairman and Kedah's head of government, and ten other members. The Menteri Besar and other members of the council are appointed by the Sultan of Kedah from members of the Kedah State Legislative Assembly (Dewan Undangan Negeri Kedah).
Kedah State Assembly
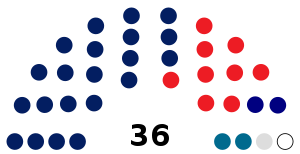
| |||||
| Affiliation | Coalition/Party Leader | Status | Seats | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 election | Current | ||||
| Perikatan Nasional | Muhammad Sanusi Md Nor | Government | 15 | 23 | |
| Pakatan Harapan | Phahrolrazi Zawawi | Opposition | 18 | 13 | |
| Government majority | 0 | 1 | |||
The state also has a State assembly, called the Kedah State Legislative Assembly. It is similar to the Parliament but is limited to making laws relating to the state. Its members are elected in elections which are usually held simultaneously with federal elections. The term of each state assembly member is limited to five years. The state assembly must be dissolved before or once it expires its term for a fresh election to elect its members.
Administrative divisions
Modern Kedah is divided into 12 administrative districts. These 12 districts, are further divided into administrative Municipal councils (Majlis Bandaraya/Perbandaran and Daerah):
- Majlis Daerah Baling (MDB)
- Bandar Baharu contains Serdang
- Majlis Daerah Bandar Baharu (MDBB)
- Kota Setar, contains Alor Setar
- Majlis Bandaraya Alor Setar (MBAS)
- Kuala Muda contains Sungai Petani
- Majlis Perbandaran Sungai Petani (MPSPK)
- Majlis Perbandaran Kubang Pasu (MPKP)
- Majlis Perbandaran Kulim (MPK)
- Pihak Berkuasa Tempatan Perindustrian Hi-Tech Kulim (HI-TECH Kulim)
- Pulau Langkawi contains Kuah
- Majlis Perbandaran Langkawi Bandaraya Pelancongan (MPLBP)
- Majlis Daerah Padang Terap (MDPT)
- Majlis Daerah Pendang (MDP)
- Majlis Bandaraya Alor Setar (MBAS)
- Majlis Daerah Sik (MDS)
- Majlis Daerah Yan (MDY)
Economy

Kedah is considered the "rice bowl"[24][25] (Malay: Jelapang Padi) of Malaysia, accounting for about half of Malaysia's total production of rice. In 2008, the state government banned the conversion of paddy fields to housing and industrial lots to protect the rice industry.[26]
Tourism, particularly on the island of Langkawi is of growing importance.
More recently, Kedah has forged its economy towards the automotive and aerospace industries with Modenas and Asian Composites setting up bases here. [citation needed] One of the main advantages is the low labour costs and the infrastructure in place with the North–South Expressway and the Penang International Airport close by. In 1996, the Kulim Hi-Tech Park was officially opened as the first high technology industrial park in Malaysia. [citation needed] The Park comprises a total land area of approximately 14.5 square kilometres (5.6 mi²).
According to the Ninth Malaysia Plan, this economic area is part of the Northern Corridor Economic Region (NCER).[27] The Northern Corridor Economic Region is one of three development regions formed in Peninsular Malaysia; other development regions being the Iskandar Malaysia (or South Johor Economic Region) and the East Coast Development Region.
Education

Public universities and colleges
The state has a campus of Universiti Utara Malaysia (UUM), which is located in Bandar Baru Sintok. It was formally incorporated on 16 February 1984. The University was established with the specific mission of providing a leadership role for management education in the country. The academic establishments in UUM include College of Business (COB), College of Law, Government and International Studies (COLGIS) and College of Arts and Sciences (CAS).
Kedah also has several public universities and colleges such as Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM) in Merbok, the Malaysian Spanish Institute of Universiti Kuala Lumpur (UniKL MSI) and the Polytechnic Institute of Sultanah Bahiyah (PSB) in Kulim, the Asian Institute of Medicine, Science and Technology (AIMST University) in Bedong, Kolej Universiti Insaniah (KUIN) a.k.a UNISHAMS (Kuala Ketil, Baling Kedah) in Mergong and the Polytechnic Institute of Sultan Abdul Halim Mu'adzam Shah (POLIMAS) in Jitra.
There are 2 teacher training institution in Kedah, Institut Pendidikan Guru Kampus Sultan Abdul Halim (IPGKSAH) in Sungai Petani and Institut Pendidikan Guru Kampus Darul Aman (IPGKDA) in Bandar Darulaman that are set up by the government to provide teaching courses for trainee teachers.
Private universities and colleges
Private universities and colleges that are located in Kedah include the Open University of Malaysia (OUM) Regional Learning Center for the state of Kedah and Perlis at Sungai Petani, the Albukhary International University in Alor Setar, Pusat Bahasa Titian Jaya the PTPL College and the Cosmopoint College.
Technical institutes
Kedah houses three technical institutes that are affiliated with MARA, that is Institut Kemahiran MARA Sungai Petani, Institut Kemahiran MARA Alor Setar and Institut Kemahiran MARA Sik.
Boarding schools

This state also has several boarding schools such as Sekolah Berasrama Penuh and MARA Junior Science College or MRSM.
National islamic schools
This state also has several secondary islamic schools (Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Agama) such as Tahfiz Model Ulul Albab or TMUA.
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Agama Baling (SMKAB)
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Agama Sik (SMKAS)
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Agama Kedah (TMUA School) (SMKAK)
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Agama Yan (SMKAY)
Boarding school
- Maktab Rendah Sains MARA Kubang Pasu
- Maktab Rendah Sains MARA Langkawi
- Maktab Rendah Sains MARA Merbok
- Maktab Rendah Sains MARA PDRM Kulim
- Maktab Rendah Sains MARA Pendang
- Maktab Rendah Sains MARA Baling
- Sekolah Menengah Sains Sultan Mohamad Jiwa (SAINS KEDAH)
- Sekolah Menengah Sains Pokok Sena (SAINA)
- Sekolah Menengah Sultan Abdul Halim (SMSAH)
- Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Kubang Pasu (I-KUPs)
- Sekolah Menengah Sains Kubang Pasu (KUPSIS)
Private and public schools

Consists of several private and public primary school or secondary school. Public secondary school such as SMK Taman Jelutong, Keat Hwa Secondary School, Convent Secondary School (Formerly known as St. Nicholas Convent Secondary School), Kolej Sultan Abdul Hamid, Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Sultan Badlishah, Sin Min Secondary School, Chio Min Secondary School, SMK Sultanah Asma, SMK Convent Father Barre, SMK Khir Johari, SMK Kota Kuala Muda, SMK Tunku Ismail, SMK Aman Jaya, SMK Bedong, SMK Bakar Arang, SMK Darulaman, SMK Ibrahim, K Jit, SMK Mahsuri, SMK Tunku Panglima Besar, Keat Hwa Secondary School, SMK Guar Chempedak, SMK Yan etc. Private secondary school such as Keat Hwa High School, Sin Min High School and SM Sin Min.
Tourism

Tourism is mainly concentrated on Langkawi Island, the largest island in the archipelago. There are some places of interest on the mainland as well.
Kedah Mainland

- Alor Setar Tower – One of the tallest telecommunications tower in the world, standing tall at 165.5-metre in height[28]
- Balai Nobat
- Bukit Kayu Hitam
- Balai Seni Negeri
- Batu Hampar Waterfall
- Bujang Valley Archaeological Museum – The only museum in Malaysia to display archaeological artefacts proving the existence of international trade and development of the Hindu Buddha religion in South-East Asia in the 3rd – 12th century[29]
- Junjong Waterfall
- Kota Kuala Kedah
- Lata Mengkuang Waterfall
- Lembah Bujang Archaeological Park
- Pantai Merdeka
- Kuala Muda - The Kota Kuala Muda Tsunami Memorial and the next door Tsunami Gallery are poignant reminders of the devastating tsunami which took place on 26 December 2004 following a powerful 8.9 magnitude earthquake off the coast of Sumatra.
- Pantai Murni Waterfront
- Pekan Rabu (Wednesday Market) – A multi-storey arcade selling a wide range of traditional delicacies, handicraft products and apparel[30]
- Rumah Merdeka
- Seri Perigi Waterfall
- Sungai Merbok Recreation Park
- Sungai Sedim Tree Top Walk – The longest canopy walk in the world stretching 950m-long, visitors can enjoy the fabulous sight of rushing streams and truly fascinating flora and fauna all from 50m up[31]
- Ulu Muda Eco Park
- Ulu Paip Recreational Forest
- Hutan Paya Laut
- Ulu Legong Hot Springs – The only 24-hours hot spring, located 22 km from Baling[32]
- Wat Nikrodharam – revered as being the primary Buddhist house of worship in Kedah’s state capital, Alor Setar[33]
- Titi Hayun Waterfall
- Kulim
- Gunung Jerai
- Zahir Mosque (Masjid Zahir) – One of Kedah's most distinctive architectural landmarks, it is one of the oldest mosques in the country[34]
Langkawi
The Langkawi International Airport is located at Padang Matsirat and it is also considered a tourist attraction as the Langkawi International Maritime and Aerospace Exhibition takes place every 2 years near the airport. The airport handled almost 1.2 million passengers and over 41,000 aircraft movements in 2008. It serves as the primary gateway into Langkawi.
In 2007, Langkawi Island was given a World Geopark status by UNESCO.[35]
Places of interest[36]
- Mount Mat Cincang (Gunung Mat Cincang)
- Field of Burnt Rice
- Hot Springs
- Telaga Tujuh (The Seven Wells)
- Beach of Black Sand
- Tasik Dayang Bunting (Lake of the Pregnant Maiden)
- Gua Cerita (Cave of Stories)
- Gua Langsir (Curtain Cave)
Sports
In 2006, Kedah hosted the 11th Sukma Games. The opening and closing ceremonies were held at the Darul Aman Stadium in Alor Setar. Football is the most favorite sport in kedah as well as sepak raga. Kedah FA is a professional football team in Malaysian that represent the state of Kedah and under the supervision of Kedah Football Association. Kedah FA currently play in the Malaysia Super League, and they are the only team in the history of Malaysian football to ever achieved a double treble titles in 2006–07 and 2007–08 seasons.
Bibliography
See also
- Breakdown of State Seats Representatives, elected in 2018
- Kedah FA
- Kingdom of Kubang Pasu Darul Qiyam
- Kingdom of Setul Mambang Segara
- Proclamation of Malaysia
References
- ^ "Laporan Kiraan Permulaan 2010" (PDF). Jabatan Perangkaan Malaysia. p. 27. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2011.
- ^ a b "Population by States and Ethnic Group". Department of Information, Ministry of Communications and Multimedia, Malaysia. 2015. Archived from the original on 12 February 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
- ^ "Kedah pronunciation". Forvo.
- ^ "Enakmen Pentadbiran Undang-Undang Islam (Kedah Darul Aman) 2008 - Enakmen 5 Tahun 2008". www2.esyariah.gov.my. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ Cyril Skinner, The Civil War in Kelantan in 1839, Kuala Lumpur: Monographs of the Malaysian Branch, Royal Asiatic Society, 1965.
- ^ "New interest in an older Lembah Bujang, 2010/07/25". Archived from the original on 29 June 2011.
- ^ "Asia Research News – USM discovers earliest civilisation in Southeast Asia". Asiaresearchnews.com. 10 March 2010. Archived from the original on 29 June 2017. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ "Kadaram and Kataha". Sabrizain. Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ "R.O Winstedt – History of Kedah – Extracted from No. 81 Straits Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society (SBRAS), March 1920" (PDF). Retrieved 2 February 2014.
- ^ I-Tsing (2005). A Record of the Buddhist Religion As Practised in India and the Malay Archipelago (A.D. 671–695). Asian Educational Services. pp. xl–xli. ISBN 978-81-206-1622-6.
- ^ "Early Malay kingdoms". Sabrizain.org. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ^ John Norman Miksic; Goh Geok Yian (14 October 2016). Ancient Southeast Asia. p. 288. ISBN 9781317279044.
- ^ A history of Malaya, Richard Winstedt, Marican, 1962, p. 36
- ^ History of Asia by B.V. Rao p.211
- ^ Singapore in Global History by Derek Thiam Soon Heng, Syed Muhd Khairudin Aljunied p.40
- ^ Winstedt, Richard (December 1936). "Notes on the History of Kedah". Journal of the Malayan Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society. 14 (3 (126)): 155–189. JSTOR 41559857.
- ^ R. Bonney, Kedah 1771–1821: The Search for Security and Independence (1971), Ch. VII.
- ^ Malay Kingship in Kedah: Religion, Trade, and Society by Maziar Mozaffari Falarti p.25
- ^ "Laporan Kiraan Permulaan 2010". Jabatan Perangkaan Malaysia. p. iv. Archived from the original on 8 July 2011. Retrieved 24 January 2011.
- ^ "Laporan Kiraan Permulaan 2010" (PDF). Jabatan Perangkaan Malaysia. p. iv. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2011.
- ^ "Malaysia: States, Federal Territories, Major Urban Areas & Conurbations - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information". www.citypopulation.de.
- ^ a b "2010 Population and Housing Census of Malaysia" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. p. 13. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 October 2012. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ "2010 Population and Housing Census of Malaysia" (PDF) (in Malay and English). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. p. 84. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ "New Straits Times - Google News Archive Search". news.google.com.
- ^ State News Archived 29 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Bernama.com.my (18 August 2005). Retrieved on 27 September 2013.
- ^ Archives | The Star Online[permanent dead link]. Thestar.com.my (26 April 2008). Retrieved on 27 September 2013.
- ^ NCER To Push Up Kedah's Agriculture, Industrial, Tourism Sectors. Bernama.com (16 July 2007). Retrieved on 27 September 2013.
- ^ "Alor Setar Tower". Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Bujang Valley Archaeological Museum, Bukit Batu Pahat". Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Pekan Rabu". Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Tree Top Walk Sungai Sedim". Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Ulu Legong Hot Spring". Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ https://www.google.com/maps/d/viewer?ie=UTF8&oe=UTF8&msa=0&mid=1rAIeIujON_bjy4HGIeSycWYFa1U&ll=6.125130000000006%2C100.37200600000006&z=17
- ^ "Zahir Mosque". Tourism Malaysia. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Langkawi given geopark status". The Star Online. 8 June 2007. Archived from the original on 9 September 2007. Retrieved 5 December 2009.
- ^ "Langkawi Island". Tourism Malaysia. Retrieved 19 May 2014.


