COVID-19 pandemic in Iowa
| COVID-19 pandemic in Iowa | |
|---|---|
 Drive-through testing site at the Iowa Events Center in Des Moines | |
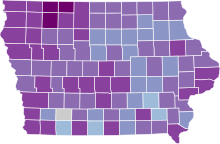 Map of the outbreak in Iowa by confirmed new infections per 100,000 people over 14 days (last updated March 2021)
1,000+
500–1,000
200–500
100–200
50–100
20–50
10–20
0–10
No confirmed new cases or no/bad data | |
 Map of the outbreak in Iowa by confirmed total infections per 100,000 people (last updated March 2021)
10,000+
3,000–10,000
1,000–3,000
300–1,000
100–300
30–100
0–30
No confirmed infected or no data | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Iowa, U.S. |
| Index case | Iowa City |
| Arrival date | March 8, 2020 (4 years, 8 months and 1 day) |
| Confirmed cases | 49,164[1] |
| Hospitalized cases | 203 (current)[1] |
| Critical cases | 77 (current)[1] |
| Ventilator cases | 47 (current)[1] |
| Recovered | 14,383[1] |
Deaths | 5,067[1] |
| Government website | |
| Iowa Department of Public Health | |
| Part of a series on the |
| COVID-19 pandemic |
|---|
 |
|
|
|
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Iowa in March 2020. The first known cases were three individuals who had traveled on a cruise in Egypt before returning home to Johnson County on March 3. Initially, case clusters were focused at meatpacking plants and congregate care facilities. By late October, community spread had become a concern, and some areas of the state had reported over 20% test positivity. A headline stated that "Iowa hospitals fear overwhelming patient surge if coronavirus cases continue to climb."[2]
Timeline
March 2020
- March 8 – The first confirmed COVID-19 cases in Iowa were announced — three individuals who had traveled on a cruise in Egypt before returning home to Johnson County on March 3.[3]
- March 9 – Governor Kim Reynolds signed a Proclamation of Disaster Emergency.[4]
- March 15 – Governor Reynolds recommended closing schools for four weeks. The state worked on developing legislation to provide child care during the emergency, including food for low-income students. The total number of confirmed coronavirus infections in the state increased to 22.[5]
- March 25 – Number of cases in Iowa reached 145, and one fatality reported in Dubuque County.[6]
- March 26 – Governor expanded upon previous COVID-19 disaster proclamations to halt non-essential surgeries, and non-emergency dental appointments.[7][8]
- March 27 – Governor's office asserted: "[The] Proclamation suspends all nonessential or elective surgeries and procedures until April 16th, that includes surgical abortion procedures".[9]
- March 29 – Number of cases in Iowa reached 336, and a fourth fatality reported in Linn County.[10]
April 2020
- April 1 – Number of cases reached 549, and the number of fatalities reached 9.[11]
- April 2 – Governor Reynolds ordered schools to remain closed through the end of April.[12]
- April 4 – Number of cases reached 786, and the number of fatalities reached 14.[13]
- April 9 – The Iowa Department of Public Health (IDPH) has been notified of 125 additional positive cases for a total of 1,270 positive cases. There have been an additional 882 negative tests for a total of 13,703 negative tests to date, which includes testing reported by the State Hygienic Lab and other labs.[14]
- April 10 – As of April 10, there were 14,565 negative COVID-19 test results reported by the State Hygienic Lab and other labs, and a total of 1,388 positive cases.[15] Members of the White House including Jared Kushner, Kellyanne Conway, Joseph Grogan, Dr. Deborah Birx, Dr. Anthony Fauci and other White House coronavirus task force members receive from Robert Redfield the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) guidance documents and decision trees to re-open communities, however, the CDC guidance and decision trees for communities including meat packers was rejected for the White House's "Opening Up America Again Plan" that is later released in early May.[16][17][18]
- April 17 – Governor Kim Reynolds announced that Iowa schools remain closed for the remainder of the school year.
- April 20 – As of April 20, there were 22,661 negative COVID-19 test results reported by the State Hygienic Lab and other labs, and a total of 3,159 positive cases, with 79 deaths attributed to COVID-19.[15]
- April 23 - Sheriff Tony Thompson of Black Hawk County went on the Rachel Maddow Show to describe his frustration with health conditions at a Tyson meat plant.[19]
- April 27 – Governor Reynolds announced that 77 counties will remove some business restrictions on May 1 while the counties of Polk, Dallas, Black Hawk, Linn, Louisa, Tama, Johnson, Bremer, Benton, Allamakee, Dubuque, Fayette, Marshall, Jasper, Iowa, Poweshiek, Scott, Washington, Muscatine, Henry, Des Moines, and Woodbury will maintain full business restrictions until May 15 because they were hard hit with infections.[20][21][22]
May 2020
- Early May - More than 1,000 of 2,800 workers at Tyson Foods' largest pork processing plant, in Waterloo, tested positive for the virus or antibodies, and at least 5 workers died. An additional 951 workers at the Columbus Junction and Perry plants tested positive. Safety inspectors had declined to inspect the Perry plant.[23][24]
- May 6 – Hy-Vee began limiting meat purchases to four packages.[25] Reynolds met with President Trump at the White House to discuss the COVID-19 pandemic and her response.[26]
- May 7 – As of May 7, there were a total of 11,059 positive cases, with 231 deaths attributed to COVID-19.[27]
- May 13 – Governor Reynolds announced that reopenings of restaurants, libraries, and fitness centers will be extended to the entire state, and also include barbershops, tattoo parlors, massage therapists, and salons, as of May 15.[28][29]
- May 14 – As of May 14, there were a total of 13,675 positive cases, with 318 deaths attributed to COVID-19.[30]
- May 28 – As of May 28, there were a total of 18,502 positive cases, with 500 deaths attributed to COVID-19.[31]
June 2020
- June 13 – For the first time since early April, no COVID-19-related deaths were reported.[32]
- June 14 – As of June 14, there were a total of 23,879 positive cases, with 651 deaths attributed to COVID-19.[32]
- June 23 – Some bars and restaurants in the Des Moines area, and in the college towns of Ames and Iowa City closed due to increases in cases.[33]
July 2020
- July 22 - One of the first outbreaks at a meatpacking plant, in early April, was much more severe than initial reports indicated. Officials at the Tyson Foods pork processing plant in Columbus Junction told inspectors that 522 employees were infected; however, the Iowa Department of Public Health publicly confirmed only 221 cases in its May 5 news conference.[34]
August 2020
- August 7 – Vacation destination Dickinson County, home to Lake Okoboji and the Iowa Great Lakes region, had 377 cases, up from only 8 on Memorial Day. Mask wearing was unpopular among local residents.[35]
- August 17 – The Iowa Department of Public Health website experienced "a software error that artificially lowers the number of new confirmed cases."[36]
- August 18 – Drake University sent 14 students home for violating guidelines on on-campus and off-campus gatherings.[37]
- August 19 – Inmate transfers from county jails into the state prison system were suspended temporarily due to cases among 59 inmates and 6 staff members the state's intake center, the Iowa Medical and Classification Center in Coralville.[38]
- August 23 – The White House urged Iowans to be required by mandatory order to wear face masks statewide; however, Governor Reynolds resisted issuing a mandatory order which would be unenforceable saying that Iowans should do the right thing and voluntarily wear face masks.[39] Previously, Reynolds barred local ordinances in Iowa from issuing a mandatory mask requirement.[40]
- August 24 – The University of Iowa had 111 cases.[41]
- August 25 – Johnson County had positivity rates over 30% for the third day in a row.[42]
- August 27 – Iowa had a positivity rate during the last 24 hours of over 18%.[43] Governor Reynolds ordered bars, breweries, and nightclubs closed in six highly populated counties: Black Hawk, Linn, Johnson, Story, Polk, and Dallas until September 20 due to Iowa having the highest rate of increase in positive coronavirus cases in the United States.[44] In Iowa, if an establishment, including breweries, tasting rooms for wineries and distilleries, pubs, taverns, bars, and nightclubs, which "prepares and serves food, the sale of which results in at least half of the establishment's monthly revenues, may reopen or remain open" as a restaurant following approval from either a local food licensing authority or the state's Department of Inspection and Appeals; however, alcohol sales must end at 10pm, bars in venues such as theaters and casinos must close, and since late June 2020, carry out cocktails are allowed.[45][46][47]
- August 28 - Iowa's test positivity rate "jumped to a record 79.43 percent for the preceding 24 hours", as antigen tests were added to state totals.[48]
- August 31 - The White House announced that Iowa had the highest rate of positive coronavirus cases in United States.[39] The New York Times listed both Ames and Iowa City as the United States' worst metro hotspots per capita at 8.2 cases and 7.6 cases per 1,000 over the last two weeks and both are in the top four metro areas in the United States with the highest rates of increase over the last two weeks.[49] 28 Iowa counties, including Polk, Johnson and Story, were listed as "red zones."[39] In an August 30 report released on August 31, The White House again called for a mandatory mask requirement for Iowa because Iowa has the fifth from highest positivity rate in the United States and highest number of new cases per capita in the United States at 232 per 100,000 which is much higher than the national average of 88 per 100,000.[40]
September 2020
- September 2 - A news story stated that "nearly half of an Iowa National Guard battalion that came to train at Camp Ripley in Minnesota this summer became sick with or were exposed to COVID-19."[50] During an evening stop in Black Hawk County in Iowa, Senator Joni Ernst stated that she is "so skeptical" of the official coronavirus numbers and deaths alleging hospitals and physicians of inflating COVID related information to gain more money through reimbrusements.[51][52]
- September 3 – Surgeon General Jerome Adams stated that he agreed with Governor Reynolds not issuing a mandatory order to wear face masks statewide in public "... because people in the Midwest are going to do the right thing" and that the recent spike is only in the 18-25 age group with all other age groups have lowering numbers of positive cases in Iowa.[53]
- September 3 – At least 107 schools in the state had reported cases.[54]
- September 4 – Iowa had a positivity rate during the last 24 hours of over 15%.[55]
- September 7 – The scope of the outbreak among the Iowa National Guard unit in Minnesota had been "misstated," according to the commander of Camp Ripley. He said fewer than 60 out of 500 soldiers were sent home, principally due to exposure risks, rather than as active cases.[56]
- September 12 - Iowa had a positivity rate during the last 24 hours of over 14%, had 425 ICU beds available and 744 ventilators (76.64%) available, and had 90 COVID-19 patients in ICU with 35 COVID-19 patients on a ventilator.[57]
- September 16 - Bars and nightclubs reopen at 5pm in Black Hawk, Linn, Polk, and Dallas counties but Story and Johnson county bars remain closed until Sunday September 20.[58][59][60]
- September 19 - Iowa had a positivity rate during the last 24 hours of almost 15%, had 409 ICU beds available and 778 ventilators (80.21%) available, and had 76 COVID-19 patients in ICU with 38 COVID-19 patients on a ventilator.[61]
- September 26 - Sixteen counties reported a positivity rate greater than 15% over the previous 14 days.[62]
- September 29 - The hospitalization rate increased, with 61 new admissions of virus patients in 24 hours, for a total of 390 virus hospitalizations. 100 patients were the ICU, with 31 on ventilators. There were 18 deaths.[63][64]
October 2020
- October 5 – Two staff members tested positive at Scott Community College Belmont Campus, and the school announced it would close until October 12.[65]
- October 5 – The Globe Gazette reported that "The worst of the COVID-19 pandemic in Iowa appears to have moved from college campuses to more rural pockets, particularly in northwest Iowa." Lyon County had a two-week average positive case rate of 31.5%.[66]
- October 6 – Restrictions were lifted in Johnson and Story County, the last two counties impacted by a five-week bar closure. On-campus cases at universities had dropped. The University of Iowa reported six new cases, for a total of 2,011 among students, and 48 among employees since Aug. 18. Iowa State reported 53 new cases September 28 and October 4, for a total of 1,754 cases since August 1.[67]
- On October 9, the Ames Haunted Forest announced it would close for the first time in 20 years, due to COVID-19 and the derecho. Half of the college-age actors for the event were reluctant to confirm participation.[68]
- An October 10 article in the Omaha World-Herald noted that both Iowa and Nebraska were in the top 15 states for cases, but Iowa had seen 72% more deaths, 1,441 compared with 514 in Nebraska. This was attributed to Iowa having a higher percentage of elderly people, and three times more outbreaks in long-term care homes.[69]
- On October 12, Iowa cases had broken the 100,000 mark. The nature of the outbreak had changed, from a "cluster of nursing home and meatpacking plant outbreaks early on to 47% of positive cases now in the 18 to 40 age group."[70] State Medical Director and Epidemiologist Dr. Caitlin Pedati said "What we have seen is what we would call more of a community activity, or community spread, of this virus in some areas."[70]
- October 14 - A campaign rally by President Trump at Des Moines International Airport was attended by thousands of supporters.[71] Des Moines Mayor Frank Cownie urged attendees to wear masks.[72] Rally organizers played a Phil Collins hit, "In the Air Tonight", and few attendees wore masks.[73] A nonprofit, Rural America 2020, sponsored a red-and-white billboard near the event which featured a big arrow pointing towards the airport and the words "Trump Covid Superspreader Event."[74]
- On October 20, a nursing home in Amana reported that 36 of 42 residents, and 25 staff tested positive.[75]
- On October 22, 70 long-term care facilities in the state had reported cases, including 779 deaths.[76] Rural areas throughout the Midwest were experiencing a surge, and in Iowa's rural Carroll County, about 20% of tests were positive.[77]
- On October 22, a researcher at the University of Iowa reported that nine patients were involved in a clinical study of Regeneron, the drug used on President Trump. Results for efficacy and safety were not expected for some months.[78]
- On October 23, one headline stated that "Iowa hospitals fear overwhelming patient surge if coronavirus cases continue to climb."[2]
November 2020
- On November 9, the Iowa Department of Corrections reported COVID-19 outbreaks at Iowa prisons in three areas. At prisons in Clarinda, there were positive cases in 377 inmates and 16 staff members, and in Rockwell City, there were positive cases in 254 inmates and four staff members. At Anamosa prison, there were 485 infected inmates and 50 infected staff members.[79]
- On November 10, Governor Reynolds issued a proclamation that, among other things, "prohibit[ed] all social, community, recreational, leisure or sporting gathering with more than 25 people indoors or 100 people outdoors unless all people over the age of 2 wear masks" and required that "[a]ll events of over 10 people must ensure 6 feet of social distancing between groups."[80] The proclamation stated that all employers "shall evaluate whether any more of their employees can feasibly work remotely and to the extent feasible, shall take steps to enable such employees to work from home." Subsequent paragraphs called for businesses remaining open to take precautions "including appropriate employee screening, social distancing practices, and increased cleaning and hygiene practices;" yet stated that that section shall not be used for enforcement. The proclamation was to come into effect after midnight the next day, and last through November 30.[81]
May 2021
- On May 20, 2021, at the close of the 89th Iowa General Assembly, Governor Reynolds signed into law the Vaccine Passport Ban Law which prohibited organizations or local governments from requiring individuals to show proof of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination and prevents state and local governments from issuing ID cards which would indicate an individual's vaccination status. The law took effect immediately.[82] Earlier in May 2021 and based on new guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as well as the Iowa Department of Public Health, Governor Reynolds signed into law a ban on school districts and local and county governments from requiring masks worn on public property if the individual is fully vaccinated. This law took effect on May 20, 2021.[83]
September 2021
- On September 27, 2021, Federal Judge Robert Pratt issued a temporary order, which overturned the ban on mask mandates for school districts (Iowa Code section 280.31), barring Governor Reynolds and Iowa Department of Education Director Ann Lebo from enforcing the Iowa law banning mask mandates for school districts. Judge Pratt's temporary order will remain in effect until the court issues an order for a preliminary injunction.[84]
- On September 29, 2021, 6,563 Iowans had died from COVID-19 since the COVID-19 pandemic began. Currently, 624 were hospitalized with 157 in ICUs and 81.2% of COVID-19 hospitalizations were unvaccinated Iowans. During the last week, 1,300 people tested positive every day for COVID-19 in the state with a 9.5% average positivity rate for the state of Iowa over the last 14 days.[85]
Government response

On April 3, 2020, Governor Reynolds defended her government's response, arguing that the measures taken, including closing schools and some businesses, were equivalent to a mandatory shelter-in-place or stay-at-home directive.[86]
On July 7, Governor Reynolds indicated that "local governments cannot implement mask requirements because they are not consistent with her public health disaster proclamation."[87]
On July 8, the Mayor of Muscatine issued a mask mandate, on advice from the city attorney that "the mandate is authorized under a local emergency declaration and Iowa's home rule provisions."[87]
On July 21, the Mayor of Iowa City issued a mask mandate, in defiance of Governor Reynolds' order.[88]
On July 29, nearly 300 Iowa doctors sent a letter to Governor Reynolds urging a statewide mask mandate.[89]
On August 7, Governor Reynolds was photographed greeting people at the Hardin County GOP Sweet Corn Feed in Eldora without wearing a mask.[90]
On August 9, Governor Reynolds "asserted she believes cities and counties cannot implement mask orders unless she says they can," raising the possibility of legal challenges under Iowa's 1968 home rule constitutional amendment.[91]
On August 27, Governor Reynolds' bar closures went into effect for Black Hawk, Dallas, Johnson, Linn, Polk and Story counties, after returning college students flooded into bars without taking health precautions.[92] Governor Reynolds said that a mask mandate was "not enforceable."[93]
On August 28, the head of the Iowa Restaurant Association expressed "dismay at the governor's order that has closed bars in six counties after coronavirus cases spiked among young adults," and suggested raising the drinking age as an alternative.[94]
On an August 31 visit to Waterloo, Senator Joni Ernst said she was "so skeptical" of the statistics on cases and deaths due to the virus. Her statements were similar to a Presidential tweet which was removed from Twitter as misinformation linked to QAnon.[95]
On September 2, Senator Ernst modified her position, releasing a statement saying that "Over 180,000 Americans have died because of Covid-19," and "What matters is that we are getting the resources to Iowa that are needed to fight this virus."[95] The Mayor of Cedar Rapids signed an emergency declaration for a mask mandate.[96]
On September 15, Governor Reynolds lifted bar closures in four counties.[97] Although Iowa was considered a "hotspot" on that day, the Governor said she "trusted Iowans to do the right thing" and would not issue a mask mandate.[96]
On September 16, AP reported that Governor Reynolds rejected a statewide mask order, calling it a "feel-good" action. She also blocked local officials from enforcing local mask mandates.[90]
On September 24, after inspections at five meatpacking plants where outbreaks sickened thousands of workers, state regulators issued a $957 fine to one plant "for a minor record-keeping violation."[98]
On October 4, a White House task force report advised against gatherings of more than 25 people in the Des Moines area.[99]
On October 2, with a surge of cases in the state, Governor Reynolds relaxed state guidance on quarantine, so that "workers and children in day cares and schools don't have to quarantine as long as they and the infected person with whom they were in contact were consistently and correctly wearing face coverings." This state guidance contradicted the CDC, "which recommends a 14-day quarantine for anyone who is in close contact with someone who has tested positive regardless of mask use."[100] Bars in Johnson and Story counties were allowed to reopen.[101]
On October 4, a White House Coronavirus Task Force report said that many virus-related deaths in Iowa were preventable, and that community transmission remained high. A mask requirement was recommended for Iowa.[102]
On October 14, thousands of supporters, including Governor Reynolds, attended a presidential campaign rally at Des Moines International Airport, with few masks being worn.[103]
On October 16, Governor Reynolds said that Iowans "need to monitor" what's going on in their community.[104]
On October 18, the White House Coronavirus Task Force report for Iowa said "the state needs to strengthen mitigation efforts."[105]
On October 19, Iowa State Auditor Rob Sand and the U.S. Treasury Department inspector general advised Governor Reynolds' that $21 million of Iowa's CARES Act COVID-19 funds had not been used properly, and would need to be reallocated or repaid.[106] An article in The Gazette described how federal stimulus funding was supporting Iowa's rural hospitals through the pandemic, and said that major federal legislation would be needed to keep some critical access hospitals in rural areas from closing.[107]
On October 22, many businesses remained closed, despite the fact that Iowa was one of the few states that had never imposed a full stay-at-home order.[108]
On October 23, Representative Cindy Axne, whose district includes Des Moines and southwestern Iowa, said, "Our older Iowans — many have not been able to leave their homes because they do not feel safe ... If you go into a grocery store, the large majority of people are not wearing masks."[103]
In mid-November during state's highest virus rate to date, Governor Reynolds required masks for indoor events with more than 25 people and outdoor events of more than 100 people.[109]
On May 20, 2021, at the close of the 89th Iowa General Assembly, Governor Reynolds signed into law the Vaccine Passport Ban Law which prohibited organizations or local governments from requiring individuals to show proof of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination and prevents state and local governments from issuing ID cards which would indicate an individual's vaccination status. The law took effect immediately.[82] Earlier in May 2021 and based on new guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as well as the Iowa Department of Public Health, Governor Reynolds signed into law a ban on school districts and local and county governments from requiring masks worn on public property if the individual is fully vaccinated. This law took effect on May 20, 2021.[83] The Iowa Immunizations Registry Information System contains a listing of vaccination records of persons fully vaccinated for COVID-19.[110]
On September 27, 2021, Federal Judge Robert Pratt issued a temporary order, which overturned the ban on mask mandates for school districts (Iowa Code section 280.31), barring Governor Reynolds and Iowa Department of Education Director Ann Lebo from enforcing the Iowa law banning mask mandates for school districts. Judge Pratt's temporary order will remain in effect until the court issues an order for a preliminary injunction.[84]
Testing
Initially, Iowa had a low rate of persons testing positive for the coronavirus. Upon a recommendation from Ashton Kutcher, a Utah-based company was hired to run Iowa's $26 million coronavirus testing program.[111][112][113][114][115][116]
On April 25, 2020, the first new testing site was launched in Des Moines under the new initiative TestIowa.com.[117][118][119]
During a May 6, 2020, White House meeting with Governor Reynolds, President Trump responded to the substantially increased coronavirus testing rate that "... all this testing, we make ourselves look bad... we're going to have more cases."[120]
On May 14, 2020, Governor Reynolds announced that the Iowa State Hygienic Laboratory had completed TestIowa's validation and could start processing these tests as well.[121] As of May 22, 2020, the TestIowa program was operating eight test sites.[122]
As of May 22, 2020, researchers at the University of Iowa were hoping for a newly developed at-home spit test to be approved within weeks.[122]
In August 2020, Iowa State conducted targeted testing of students who were symptomatic or had exposures, resulting in a 13.6% positivity rate for the first week of class, and a 28.8% positivity rate for the second week of class.[123] A total of 655 students and 10 staff tested positive during the month of August.[124]
Between August 18 - September 1, 2020, the University of Iowa reported 922 "self-reported positive or presumed positive COVID-19 tests" among students, and 13 among employees.[125]
Impact
Researchers at Iowa State University created a web hub to help track the COVID-19 pandemic's impacts on the economy.[126][127]
Meatpacking industry
Iowa's largest industry sector is manufacturing,[128] with food manufacturing constituting the largest subsector.[129]
Five meat packers dominate the United States with over 80% of the market: JBS, Smithfield, Cargill, Tyson, and Hormel.[130]
Tyson Foods plants
On April 26, 2020, John Tyson, the billionaire heir and chairman of the board of Tyson Foods which is the second-largest meat packer in the world, stated that nationwide meat shortages were likely due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[131] According to Liz Croston, Tyson Foods communications manager, they will not reveal the specific number of affected employees at the Perry plant until it crosses the threshold of 10% of their workforce, a company policy they've used at other locations.[132]
- In April 2020, a Tyson Foods pork processing plant in Columbus Junction closed down after 148 workers tested positive for coronavirus, and two workers died.[133][134]
- The Tyson plant in Waterloo shut down on April 22 after more than 180 tested positive for the coronavirus.[135][134] The Tyson Foods plant at Waterloo re-opened on May 7, 2020.[136] On May 8, 2020, Black Hawk County health officials revealed that 1,031 of the 2,800 workers or 38% at the Waterloo plant tested positive for the coronavirus.[137][138]
- The entire workforce at the Perry Tyson Foods plant was tested on April 25, 2020.[131][116] On May 6, 2020, Sarah Reisetter, deputy director for the Iowa Department of Health, stated that 730 out of a workforce of over 1,200 at the Perry Tyson Foods plant had tested positive for coronavirus and that before closing, 26% of the Columbus Junction plant and 17% of the Waterloo plant had tested positive for COVID-19.[139][134][140]
- On May 8, 2020, at Sioux City in Woodbury County, health officials were conducting extensive testing for the Siouxland District Health Department due to its close proximity to the Tyson Foods plant at Dakota City, Nebraska in addition to the testing at the Test Iowa site. According to Tyler Brock, deputy director for Siouxland District Health, no results of the testing will be made public until the Iowa state epidemiologist, the state director of health, approves its release to the public.[141] On May 2, 2020, Woodbury County had the second highest coronavirus test positive rate at 35% in Iowa.[116]
- On Saturday May 16, 2020, the state of Iowa through Test Iowa will test more than 3,000 employees at the two Tyson Foods plants at Storm Lake in Buena Vista County.[142]
Iowa Premium National Beef
On May 6, 2020, the Iowa Premium National Beef plant in Tama was reported having a coronavirus cluster.[143]
Hormel
On May 6, 2020, the Hormel plant in Osceola was reported having a coronavirus cluster.[144]
West Liberty Foods
On May 8, 2020, the West Liberty Foods turkey packing plant at West Liberty announced furloughing one third of their workforce after the sharp decline in demand for turkey products which resulted in a huge oversupply of turkey products in cold storage and that 136 employees out of 994 tested positive for the coronavirus. Since farmers will reduce the size of their turkey flocks sent to the plant for 18 weeks beginning in June, the plant will not process turkeys beginning in November 2020 and continuing for four months until spring 2021.[145]
Upper Iowa Beef
By May 13, 2020, 22 of 150 people associated with an Upper Iowa Beef plant in Lime Springs, Iowa were tested positive for COVID-19.[146][147]
Unemployment
By May 14, 2020, Iowa reported record new weekly unemployment claims for eight straight weeks, totaling at 299,098, which represents almost 20% of Iowa's eligible workforce.[148]
Education
The University of Iowa, Iowa State University, and the University of Northern Iowa are expecting losses from the COVID-19 pandemic to exceed $76 million, $89 million, and $28 million, respectively.[149] All three public universities are also considering freezing tuition and fees for the academic year 2020–21. Both University of Iowa and Iowa State University project decreased fall enrollment.
On September 28, the University of Iowa had received over 450 complaints regarding non-compliance with coronavirus safety measures, including seven reports of failure to isolate or quarantine. Iowa City police responded to numerous calls about loud parties, noise, and COVID-19-related matters. The University of Iowa reported over 2,000 cases since August 16. Iowa State University had 1,701 cases since August 1. The University of Northern Iowa had 163 cases since Aug. 17. University officials praised a bar closure in selected counties, set to expire on October 4, for "helping prevent spread among students."[150]
On September 29, a group of RAs at the University of Iowa started a petition for hazard pay, due to duties that included "delivering meals to infected students living on isolation floors", cleaning up biohazardous substances like blood and vomit, and enforcing a one-guest-per-person policy which included breaking up parties of intoxicated or maskless students.[151]
On October 6, the state teacher's union said that 39% of Iowa's 339 school districts, area education agencies and community colleges, 39% still did not require face coverings.[152]
On October 7, "13 Iowa counties were over a 15% threshold set by Reynolds at which school districts may temporarily shift to online-only instruction." There were 927 children under age 17 and 4,171 educators who tested positive, with 568 of the educators were at risk of serious health complications.[152]
Elections
In Iowa's primary elections, polling locations were greatly reduced: for example there were 28 locations instead of the usual 135 in Polk County.[153] 55,000 absentee votes were cast in the county.
Prisons
Through a statewide prison labor program, prisoners across Iowa helped make 98,000 masks, 40,000 gowns, 17,000 face shields, and 24,000 gallons of hand sanitizer within a few weeks.[154]
Sports
Due to Minor League Baseball being shut down and cancelled for 2020, the Iowa Cubs, a Triple-A baseball team in Des Moines, are exploring making Principal Park available for concerts and amateur baseball games.[155]
Softball and baseball games were supposed to begin being carried out again in Iowa starting on June 15.[156]
NASCAR cancelled the Xfinity Series and Gander RV & Outdoor Series 2020 events at Iowa Speedway in Newton, The track opted to replace one of the event's with a Second INDYCAR Race in which happened to be a doubleheader Iowa INDYCAR 250s on July 17–18, and the ARCA Menards Series date remains on the calendar
The MLB's Field Of Dreams Game in Dyersville, originally scheduled for August 13, has been rescheduled for 2021 which is to feature the White Sox and a team TBA later.
On August 31, The University of Iowa announced pausing its athletics training programs until after Labor Day on September 7.[157]
On August 31, Jamie Pollard, athletic director at Iowa State University, announced that 25,000 fans would be allowed to attend Iowa State's opening home football game against Louisiana on September 12 and its Big 12 Conference home opener against Oklahoma on October 3, 2020, at Jack Trice Stadium in Ames if fans can follow mitigation efforts during the Louisiana game.[158][159] On September 2, Pollard stated that no fans will be allowed in Jack Trice Stadium for the September 12, 2020, home opener Iowa State vs. Louisiana football game.[160][161] On September 4, Pollard estimated an athletics department budget deficit will increase from over $17 million to $30 million because of coronavirus impacts which will result in cutting sports programs in accordance with the Patsy T. Mink Equal Opportunity in Education Act (Title IX laws); closing C.Y. Stephens Auditorium, which also requires up to $50 million in renovations; more payroll cuts and layoffs in addition to the department wide actions which have already been implemented saving almost $4 million: suspension of incentives and bonuses along with most coaches and staff receiving a 10% reduction in pay.[162][163]
On September 19, the Big Ten announced its 2020 season football schedule and that on October 24 the Iowa Hawkeyes will play their first game at Purdue.[164]
Statistics
| County[a] | Cases[b][c] | Deaths | Population[d] | Cases / 100k |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99 / 99 | 908,936 | 10,797 | 3,155,070 | 28,808.7 |
| Adair | 1,809 | 52 | 7,152 | 25,293.6 |
| Adams | 944 | 16 | 3,602 | 26,207.7 |
| Allamakee | 3,271 | 69 | 13,687 | 23,898.6 |
| Appanoose | 3,446 | 80 | 12,426 | 27,732.2 |
| Audubon | 1,316 | 25 | 5,496 | 23,944.7 |
| Benton | 7,278 | 82 | 25,645 | 28,379.8 |
| Black Hawk | 39,227 | 532 | 131,228 | 29,892.2 |
| Boone | 6,573 | 71 | 26,234 | 25,055.3 |
| Bremer | 6,418 | 89 | 25,062 | 25,608.5 |
| Buchanan | 5,594 | 67 | 21,175 | 26,417.9 |
| Buena Vista | 7,005 | 66 | 19,620 | 35,703.4 |
| Butler | 3,849 | 62 | 14,439 | 26,657.0 |
| Calhoun | 3,087 | 26 | 9,668 | 31,930.1 |
| Carroll | 5,704 | 85 | 20,165 | 28,286.6 |
| Cass | 3,345 | 89 | 12,836 | 26,059.5 |
| Cedar | 5,050 | 49 | 18,627 | 27,111.2 |
| Cerro Gordo | 12,819 | 183 | 42,450 | 30,197.9 |
| Cherokee | 3,600 | 75 | 11,235 | 32,042.7 |
| Chickasaw | 3,171 | 37 | 11,933 | 26,573.4 |
| Clarke | 2,710 | 44 | 9,395 | 28,845.1 |
| Clay | 4,876 | 55 | 16,016 | 30,444.6 |
| Clayton | 4,062 | 81 | 17,549 | 23,146.6 |
| Clinton | 13,940 | 174 | 46,429 | 30,024.3 |
| Crawford | 5,181 | 59 | 16,820 | 30,802.6 |
| Dallas | 27,009 | 160 | 93,453 | 28,901.2 |
| Davis | 1,832 | 35 | 9,000 | 20,355.6 |
| Decatur | 1,854 | 29 | 7,870 | 23,557.8 |
| Delaware | 4,809 | 71 | 17,011 | 28,269.9 |
| Des Moines | 11,360 | 166 | 38,967 | 29,152.9 |
| Dickinson | 4,754 | 78 | 17,258 | 27,546.6 |
| Dubuque | 31,168 | 332 | 97,311 | 32,029.3 |
| Emmet | 2,716 | 57 | 9,208 | 29,496.1 |
| Fayette | 4,989 | 89 | 19,650 | 25,389.3 |
| Floyd | 4,200 | 70 | 15,642 | 26,850.8 |
| Franklin | 2,975 | 51 | 10,070 | 29,543.2 |
| Fremont | 1,649 | 29 | 6,960 | 23,692.5 |
| Greene | 2,057 | 28 | 8,888 | 23,143.6 |
| Grundy | 3,067 | 50 | 12,232 | 25,073.6 |
| Guthrie | 2,783 | 48 | 10,689 | 26,036.1 |
| Hamilton | 4,011 | 92 | 14,773 | 27,150.9 |
| Hancock | 3,298 | 52 | 10,630 | 31,025.4 |
| Hardin | 5,091 | 71 | 16,846 | 30,220.8 |
| Harrison | 3,856 | 102 | 14,049 | 27,446.8 |
| Henry | 6,536 | 84 | 19,954 | 32,755.3 |
| Howard | 2,337 | 37 | 9,158 | 25,518.7 |
| Humboldt | 3,101 | 44 | 9,558 | 32,444.0 |
| Ida | 2,176 | 51 | 6,860 | 31,720.1 |
| Iowa | 4,356 | 54 | 16,184 | 26,915.5 |
| Jackson | 5,594 | 75 | 19,439 | 28,777.2 |
| Jasper | 10,503 | 125 | 37,185 | 28,245.3 |
| Jefferson | 4,451 | 63 | 18,295 | 24,329.1 |
| Johnson | 45,242 | 183 | 151,140 | 29,933.8 |
| Jones | 6,493 | 84 | 20,681 | 31,396.0 |
| Keokuk | 2,489 | 55 | 10,246 | 24,292.4 |
| Kossuth | 4,388 | 102 | 14,813 | 29,622.6 |
| Lee | 9,247 | 151 | 33,657 | 27,474.2 |
| Linn | 65,239 | 670 | 226,706 | 28,776.9 |
| Louisa | 2,954 | 68 | 11,035 | 26,769.4 |
| Lucas | 2,198 | 35 | 8,600 | 25,558.1 |
| Lyon | 3,175 | 56 | 11,755 | 27,009.8 |
| Madison | 3,727 | 48 | 16,338 | 22,811.8 |
| Mahaska | 5,828 | 95 | 22,095 | 26,377.0 |
| Marion | 8,949 | 137 | 33,253 | 26,911.9 |
| Marshall | 11,534 | 138 | 39,369 | 29,297.2 |
| Mills | 4,019 | 47 | 15,109 | 26,600.0 |
| Mitchell | 2,851 | 51 | 10,586 | 26,931.8 |
| Monona | 2,110 | 56 | 8,615 | 24,492.2 |
| Monroe | 2,204 | 52 | 7,707 | 28,597.4 |
| Montgomery | 2,618 | 60 | 9,917 | 26,399.1 |
| Muscatine | 11,299 | 140 | 42,664 | 26,483.7 |
| O'Brien | 3,902 | 73 | 13,753 | 28,372.0 |
| Osceola | 1,579 | 23 | 5,958 | 26,502.2 |
| Page | 3,866 | 56 | 15,107 | 25,590.8 |
| Palo Alto | 2,428 | 42 | 8,886 | 27,323.9 |
| Plymouth | 7,228 | 116 | 25,177 | 28,708.7 |
| Pocahontas | 1,953 | 31 | 6,619 | 29,506.0 |
| Polk | 148,258 | 1,235 | 490,161 | 30,246.8 |
| Pottawattamie | 28,084 | 354 | 93,206 | 30,131.1 |
| Poweshiek | 4,698 | 66 | 18,504 | 25,389.1 |
| Ringgold | 1,324 | 43 | 4,894 | 27,053.5 |
| Sac | 2,906 | 43 | 9,721 | 29,894.0 |
| Scott | 49,293 | 452 | 172,943 | 28,502.5 |
| Shelby | 3,191 | 59 | 11,454 | 27,859.3 |
| Sioux | 9,042 | 100 | 34,855 | 25,941.8 |
| Story | 23,443 | 105 | 97,117 | 24,138.9 |
| Tama | 4,711 | 102 | 16,854 | 27,951.8 |
| Taylor | 1,543 | 25 | 6,121 | 25,208.3 |
| Union | 3,198 | 56 | 12,241 | 26,125.3 |
| Van Buren | 1,704 | 28 | 7,044 | 24,190.8 |
| Wapello | 10,491 | 224 | 34,969 | 30,000.9 |
| Warren | 14,575 | 157 | 51,466 | 28,319.7 |
| Washington | 6,854 | 90 | 21,965 | 31,204.2 |
| Wayne | 1,523 | 35 | 6,441 | 23,645.4 |
| Webster | 12,154 | 187 | 35,904 | 33,851.4 |
| Winnebago | 3,473 | 48 | 10,354 | 33,542.6 |
| Winneshiek | 4,529 | 59 | 19,991 | 22,655.2 |
| Woodbury | 33,488 | 358 | 103,107 | 32,478.9 |
| Worth | 2,052 | 17 | 7,381 | 27,801.1 |
| Wright | 4,074 | 74 | 12,562 | 32,431.1 |
| Final update March 29, 2023, with data through the previous day Data is publicly reported by Iowa Department of Public Health[165] | ||||
| ||||
See also
- Timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States
- COVID-19 pandemic in the United States – for impact on the country
- COVID-19 pandemic – for impact on other countries
References
- ^ a b c d e f "Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)". Iowa Department of Health.
- ^ a b Ramm, Michaela (October 23, 2020). "Iowa hospitals fear overwhelming patient surge if coronavirus cases continue to climb". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa governor announces first 3 COVID-19 cases in state". AP NEWS. March 8, 2020. Retrieved April 3, 2020.
- ^ Schlesselman, Hollie (March 9, 2020). "32 test negative, 8 test positive for COVID-19". weareiowa.com. Retrieved March 28, 2020.
- ^ Gov. Reynolds recommends Iowa schools close for four weeks, will hold a press conference tomorrow (3/15/20) Author: Polly Carver-Kimm, Iowa Department of Public Health, March 15, 2020
- ^ Greene, Jay (March 25, 2020). "21 additional positive COVID-19 cases in Iowa". kcrg.com. Retrieved March 25, 2020.
- ^ Richardson, Ian. "Iowa orders additional retail closures, halts elective and nonessential surgeries and dental procedures". Des Moines Register. Retrieved March 28, 2020.
- ^ Esposito, Lisa (September 18, 2020). "Iowa Dentist Practices Leadership During COVID-19 Pandemic". U.S. News & World Report, via www.msn.com. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Rodriguez, Barbara. "Governor's office says order suspending 'non-essential' surgery includes halting surgical abortions". Des Moines Register. Retrieved March 28, 2020.
- ^ "Fourth person dies from COVID-19 in Iowa". swiowanewssource.com. March 29, 2020. Retrieved March 29, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa confirms 52 new coronavirus cases, two more deaths".
- ^ Flesher, Charles. "Reynolds orders Iowa schools remain closed through the end of April". Des Moines Register. Retrieved April 16, 2020.
- ^ "Additional COVID-19 cases in Iowa, additional deaths confirmed". www.kwqc.com.
- ^ "Additional COVID-19 Cases in Iowa, Additional Deaths Confirmed (4/9/20)". idph.iowa.gov. April 9, 2020.
- ^ a b "Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)". idph.iowa.gov. Retrieved April 21, 2020.
- ^ Dearan, Jason Associated Press (May 9, 2020). AP Exclusive: Docs show top WH officials buried CDC report. The decision to shelve detailed advice from the nation's top disease control experts for reopening communities during the COVID-19 pandemic came from the highest levels of the White House ABC News. Retrieved May 9, 2020.
- ^ Frias, Lauren (May 8, 2020). Top White House Officials shelved guidance for reopening the US despite CDC approval MSN News via Business Insider. Retrieved May 9, 2020.
- ^ Associated Press staff (May 7, 2020). Trump administration buries CDC guidance on reopening amid pandemic. Agency scientists were told 17-page, step-by-step advice to local authorities 'would never see the light of day', CDC official says. The Guardian. Retrieved May 9, 2020.
- ^ "COVID-19 crisis deepens as Iowa meat plant presses return to work". Rachel Maddow Show, MSNBC.com. April 29, 2020. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ Gruber-Miller, Stephan, and Norvell, Kim (April 27, 2020). Iowa lifts begins easing coronavirus business restrictions starting Friday in 77 counties with low cases. The Des Moines Register. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ Lanese, Nicoletta (April 27, 2020). Iowa: Latest updates on Coronavirus. MSN News. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ ABC News staff (May 13, 2020). "When your state is reopening and what that means". MSN News via ABC News. Retrieved may 13, 2020.
- ^ Foley, Ryan J (June 23, 2020). "Iowa finds no violations at Tyson plant with deadly outbreak". AP NEWS. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ "Regulators Sat on Complaint as COVID-19 Outbreak at Iowa Plant Grew". who13.com. May 18, 2020. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ Local 5 News (May 6, 2020). Live COVID-19 updates: Additional nursing home test site opening in Dallas County; Capital City Basketball League canceled. Negative tests total 52,767 and 3,803 Iowans have recovered. We are Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ Coltrain, Nick (May 6, 2020). At the White House, Kim Reynolds, Donald Trump, Mike Pence talk about the resilience of the food supply amid virus outbreak. The Des Moines Register via Microsoft News. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- ^ "Gov. Kim Reynolds says Iowa is 'leading' nation in coronavirus response, defends reopening". The Des Moines Register. May 7, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "Gov. Reynolds allows reopening of restaurants, other businesses in all 99 counties; expands order to salons, barbers and more statewide". The Des Moines Register. May 13, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "Gov. Reynolds signs new proclamation continuing the State Public Health Emergency Declaration". governor.iowa.gov. May 13, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa reports 12 more COVID-19 deaths, 386 new positive tests". The Des Moines Register. May 14, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "May 28: Iowa hits 500 COVID-19 deaths, over 10,000 recoveries". KWWL. May 28, 2020. Retrieved May 28, 2020.
- ^ a b "For the first time since April 6, state officials reported no COVID-19-related deaths Saturday; 328 new cases reported Sunday Staff reports". The Des Moines Register. June 14, 2020. Retrieved June 15, 2020.
- ^ Akin, Katie; Mullen, Kylee (August 27, 2020). "Reopening and resurgence: Iowa restaurants, bars close because of employee coronavirus cases". Des Moines Register. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ Foley, Ryan J (July 22, 2020). "Outbreak at Iowa pork plant was larger than state reported". ABC News. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ Mendenhall, Emily (August 8, 2020). "How an Iowa summer resort region became a Covid-19 hot spot". Vox. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ Foley, Ryan J (August 17, 2020). "'Horrifying' data glitch skews key Iowa coronavirus metrics". ABC News. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Drake University sends 14 students home for violating COVID-19 guidelines". KCCI. August 19, 2020. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ Henderson, O. Kay (August 20, 2020). "Temporary halt to transfers into Iowa prison system due to Covid". Radio Iowa. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ a b c Leys, Tony (August 31, 2020). White House says Iowa has the highest coronavirus rate in county, should close more bars. The Des Moines Register. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- ^ a b Hendrickson, Dan (August 31, 2020). "White House Task Force Calls For Statewide Mask Mandate, More Business Restrictions in Iowa". Des Moines, Iowa: WHO TV. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- ^ Ruggles, Rick (August 24, 2020). "Campus COVID-19 cases bubble up as college starts — 40 new cases at Creighton, 111 at Iowa". Omaha World-Herald. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Thompson, Zach (August 5, 2020). "'Outbreak in Iowa City': Johnson County sees third day in a row of positivity rates higher than 30%". Iowa City Press-Citizen. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ We Are Iowa staff (August 27, 2020). State reports 1,372 more COVID-19 cases for 18.42% positivity rate, 17 additional deaths the past 24 hours. WOI TV. West Des Moines, Iowa. Archived from the original on August 28, 2020. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ Richardson, Ian; Coltrain, Nick (August 27, 2020). 'I don't make these decisions lightly': Gov. Kim Reynolds closes bars in 6 counties amid coronavirus spikes. The Des Moines Register. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- ^ COVID-19: Frequently Asked Questions for Restaurants, Bars, and Other Food Businesses for Black Hawk, Dallas Johnson, Linn, Polk, and Story Counties. Iowa Department of Inspections & Appeals website. Archived from the original on September 4, 2020. Retrieved September 4, 2020
- ^ Akin, Katie (September 3, 2020). Which bars and restaurants can stay open under governor's order?. The Des Moines Register. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ Akin, Katie (June 18, 2020). Slushies? Flasks? Bars look to creative ideas after to-go cocktail bill passes. The Des Moines Register. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa sees record 2,579 coronavirus cases, with 79% positivity rate". The Gazette. August 28, 2020. Archived from the original on September 4, 2020. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ New York Times staff (August 31, 2020). Monitoring the Coronavirus Outbreak in Metro Areas Across the U.S.. The New York Times. Archived from the original on August 31, 2020. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- ^ Perkins, Chelsey; Forum News Service (September 2, 2020). "Iowa National Guard suffered coronavirus outbreak during training at MN's Camp Ripley". Twin Cities. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ WHO TV staff (September 2, 2020). Joni Ernst Accuses Physicians, Hospitals of Falsely Inflating COVID-19 Death Statistics. WHO TV via Associated Press. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved September 5, 2020.
- ^ Rivers, Amie (September 2, 2020). Update with audio: Ernst talks COVID numbers, RFS waivers and more in Waterloo. The Courier. Waterloo, Iowa. Retrieved September 5, 2020.
- ^ Diekneite, Max (September 3, 2020). US Surgeon General agrees with Reynolds on not issuing state mask mandate. KCCI TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved September 3, 2020.
- ^ Clayworth, Jason (September 3, 2020). "More than 100 Iowa schools have reported coronavirus cases, union says". Des Moines Register, via MSN. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ We Are Iowa staff (September 4, 2020). COVID-19 in Iowa: State reports 15.78% positivity rate, 3 additional deaths the past 24 hours: Local 5 is breaking down COVID-19 numbers for central Iowans. WOI TV. West Des Moines, Iowa. Archived from the original on September 4, 2020. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ Perkins, Chelsey; Forum News Service (September 8, 2020). "Minnesota National Guard clarifies scope of outbreak among Iowa soldiers at Camp Ripley". Twin Cities. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ We Are Iowa staff (September 12, 2020). COVID-19 in Iowa by the numbers: 798 more cases, 8 deaths reported the past 24 hours. WOI TV. West Des Moines, Iowa. Archived from the original on September 12, 2020. Retrieved September 12, 2020.
- ^ WHO TV Staff (September 15, 2020). Bars in Four Counties Can Re-Open Wednesday Under New Order From Governor Reynolds. WHO TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved September 19, 2020.
- ^ Surrency, Justin (September 16, 2020). Polk County Brewery and Bar Owners Reopen With Hopes to Stay Open. WHO TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved September 19, 2020.
- ^ West, T. K. (September 4, 2020). How does second bar shutdown impact Dallas County establishments? The Dallas County News. Adel, Iowa. Retrieved September 19, 2020.
- ^ We Are Iowa staff (September 19, 2020). COVID-19 by the numbers: IDPH confirms 908 more cases with 14.81% positivity rate, 7 additional deaths in the past 24 hours. WOI TV. West Des Moines, Iowa. Archived from the original on September 19, 2020. Retrieved September 19, 2020.
- ^ "16 Iowa counties report high coronavirus positivity rate". KCCI. September 26, 2020. Retrieved October 13, 2020.
- ^ KCRG Des Moines (September 30, 2020). "1,048 COVID-19 cases, 18 deaths reported in Iowa Wednesday as hospitalizations increase". www.msn.com. Retrieved October 13, 2020.
- ^ KCAU Staff (September 30, 2020). "September 30: Nearly 1,000 new COVID-19 cases, 17 more deaths". SiouxlandProud, Sioux City, IA. Retrieved October 13, 2020.
- ^ St. Amour, Madeline (October 5, 2020). "Iowa Community College Campus Closed for a Week". Live Updates: Latest News on Coronavirus and Higher Education - Inside HigherEd. Retrieved October 13, 2020.
- ^ Murphy Lee, Erin (October 7, 2020). "COVID spreads to rural Iowa as hospitalizations hit record highs". Globe Gazette | Mason City, Iowa | globegazette.com. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Miller, Vanessa (October 6, 2020). "Iowa campus COVID-19 cases down during bar closure". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Wellendorf, Kiley (October 9, 2020). "Ames Haunted Forest to miss first season in 20 years due to COVID-19, Iowa derecho". The Ames Tribune. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Cordes, Henry J (October 10, 2020). "What's the matter with Iowa? Why COVID-19 deaths east of Missouri River are so much higher". Omaha.com. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ a b Clark, Tommie (October 12, 2020). "Iowa's epidemiologists explain Monday's grim 100k total COVID-19 case count". KCCI. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Pfannenstiel, Brianne. "President Donald Trump praises foreign leaders while knocking Joe Biden's mental acuity at Des Moines rally". Des Moines Register. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ Joens, Philip (October 11, 2020). "'We don't want a super-spread event': Cownie worries Trump rally will spread COVID-19". Des Moines Register. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ "Trump Campaign Blares 'In the Air Tonight' at Iowa Rally Amid COVID Spike". TMZ. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- ^ "Billboard next to Trump rally directs supporters to 'COVID Superspreader Event'". kvue.com. October 14, 2020. Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ Ramm, Michaela (October 20, 2020). "Coronavirus outbreak infects nearly every resident of Amana nursing home". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "70 care facilities report outbreaks as COVID-19 spreads in Iowa". KCCI. October 22, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Stone, Will (October 22, 2020). "COVID-19 Surges In Rural Communities, Overwhelming Some Local Hospitals". Iowa Public Radio. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Miller, Vanessa (October 23, 2020). "University of Iowa researching COVID-19 drug Trump touted". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Pitt, David (November 9, 2020). "'Terrible': Iowa prisons report hundreds of virus infections". Associated Press. Archived from the original on December 9, 2020. Retrieved April 4, 2021.
- ^ "Full text of Gov. Kim Reynolds' proclamation on masks at gatherings in Iowa". The Des Moines Register. November 10, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ "Gov. Kim Reynold's proclamation on mask regulations". November 10, 2020. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ a b Teays, Dustin (May 27, 2021). Representative Nordman Talks Vaccine Passport Ban. Raccoon Valley Radio (Jefferson, Iowa). Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- ^ a b Carlson, Coltrane (May 25, 2021). Rep. Sorensen Says New Law Banning Masks is Win for Freedom, Iowa. Raccoon Valley Radio (Jefferson, Iowa). Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- ^ a b Associated Press staff (September 27, 2021). Federal judge's temporary order allows Iowa schools to mandate masks: Judge Robert Pratt said in an order signed Monday that the law substantially increases the risk of several children with health conditions of contracting COVID-19. Associated Press. Retrieved September 29, 2021. - via We Are Iowa (WOI TV channel 5) (Des Moines).
- ^ WHO TV staff (September 29, 2021). Unvaccinated Iowans continue to be the majority of those hospitalized with COVID-19. WHO TV (Des Moines). Retrieved September 29, 2021.
- ^ "Gov. Kim Reynolds says shelter-in-place topic 'divisive' while defending Iowa's coronavirus response". The Des Moines Register. April 3, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ a b "Iowa Gov. Reynolds speaks out against mask mandates". KWQC. July 8, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa City mayor defies Gov. Reynolds, announces face mask mandate". www.msn.com. July 21, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Ramm, Michaela (July 29, 2020). "Hundreds of doctors urge Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds to mandate masks". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ a b AP (September 16, 2020). "Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds won't budge on masks, even as virus deaths rise". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Local control dispute brewing over Iowa mask mandates". AP NEWS. August 8, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Murphy, Erin (August 27, 2020). "Reynolds closes bars in 6 Iowa counties, including Johnson and Linn, as COVID-19 cases surge". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Gov. Reynolds stops short of mask mandate, calling them 'not enforceable'". KCCI. August 27, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Henderson, Kay (August 28, 2020). "Iowa bars and restaurants frustrated by new closure orders". Radio Iowa. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ a b Gabriel, Trip (September 2, 2020). "Joni Ernst, in a Tight Senate Race, Repeats a Debunked Coronavirus Theory". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ a b Hicks, Mitti (September 14, 2020). "Coronavirus mask mandates in Iowa cities spark questions over enforcement". Fox News. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Gov. Reynolds lifts bar closures in four Iowa counties starting Wednesday". KCCI. September 15, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ AP (September 24, 2020). "After inspecting 5 meatpacking plants with COVID-19 outbreaks, Iowa regulators only fine $957". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Leys, Tony (October 13, 2020). "White House experts advise against Des Moines gatherings of more than 25. Trump plans a rally in Des Moines for 10,000". Des Moines Register. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Foley, Ryan J (October 2, 2020). "Iowa Relaxing Quarantine Guidance Despite Rapid COVID Spread". Insurance Journal. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Bars in Johnson and Story County will be allowed to reopen". Radio Iowa. October 2, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ AP (October 8, 2020). "White House Coronavirus Task force notes 'many preventable deaths' in Iowa". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ a b Gabriel, Trip; Herndon, Astead W. (October 23, 2020). "As Governor Resists Mask Mandate, Iowans Sour on the G.O.P." The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Eight Iowa cities in White House Coronavirus Task Force 'red zone'". Radio Iowa. October 16, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Schlesselman, Hollie; Ahmed, Sabrina (October 21, 2020). "Latest White House report emphasizes need for more COVID-19 mitigation efforts in Iowa". weareiowa.com. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Toce, Sarah (October 19, 2020). "Auditor: Iowa's GOP governor misallocated at least $21 million in COVID-19 funds". www.rawstory.com. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Muller, Lyle (October 19, 2020). "Coronavirus stimulus only short-term fix for rural hospitals". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Casselman, Ben; Tankersley, Jim (October 22, 2020). "Iowa Never Locked Down. Its Economy Is Struggling Anyway". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Schulte, Grant (November 14, 2020). "Surging virus cases get a shrug in many Midwestern towns". AP NEWS. Retrieved November 15, 2020.
- ^ Beckman, Sarah (June 15, 2021). Polk County residents can now get cash for being vaccinated: County officials established a cash lottery incentive program to get more residents vaccinated. We Are Iowa (WOI TV channel 5) (Des Moines). Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ Foley, Ryan J. (April 23, 2020). "Iowa governor: Tip from Ashton Kutcher led to testing deal." Associated Press. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ "Get Iowa back on track with statewide COVID-19 testing." Test Iowa website. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ "How a tip from actor Ashton Kutcher led Gov. Kim Reynolds to hire Utah firms for $26 million coronavirus testing program". The Des Moines Register. April 23, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ Henderson, O. Kay (April 23, 2020). "Ashton Kutcher linked Iowa's governor to Utah COVID-19 testing program." Radio Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ Leys, Tony (April 23, 2020). "How a tip from actor Ashton Kutcher led Gov. Kim Reynolds to hire firm for testing program." The Hawk Eye. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ a b c Caufield, Jim (May 2, 2020). Dallas County COVID-19 cases increase five-fold in eight days. The Perry News. Perry, Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa launches COVID-19 testing site in Des Moines by appointment only". The Des Moines Register. April 25, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "TestIowa.com". Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa launches $26M coronavirus testing program, with online surveys, drive-through test sites". The Des Moines Register. April 21, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ Coltrain, Nick (May 6, 2020). At the White House, Kim Reynolds, Donald Trump, Mike Pence talk about the resilience of the food supply amid virus outbreak. Microsoft News via The Des Moines Register. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- ^ "Reynolds: State lab earns Test Iowa validation". WOWT. May 14, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ a b "University of Iowa researchers expect their coronavirus at-home spit test to be approved within weeks". The Gazette (Cedar Rapids). May 22, 2020. Retrieved May 26, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa State to open new COVID-19 testing center". News Service - Iowa State University. August 31, 2020. Retrieved September 2, 2020.
- ^ "COVID-19 Testing • COVID-19 Public Health Data Update". asqk.ehs.iastate.edu. Retrieved September 2, 2020.
- ^ "COVID-19 by the Numbers". University of Iowa Novel Coronavirus (Covid-19). 2020. Retrieved September 2, 2020.
- ^ "New Iowa State web hub lets users track COVID-19's economic impacts in the US". The Cattle Site, Global Ag Media. May 23, 2020. Retrieved May 26, 2020.
- ^ "COVID-19 Pandemic: Research and Resources". Department of Economics, Iowa State University. Retrieved May 26, 2020.
- ^ "The Biggest Industries In Iowa". January 16, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa's Workforce and the Economy" (PDF). Iowa Workforce Development. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ KCCI staff (May 6, 2020). Iowa experts weigh in on meat packing plants and meat shortage. KCCI. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ a b The Perry News staff (April 27, 2020). Tyson chair says 'food supply chain is breaking' under COVID-19. The Perry News. Perry, Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ Cerwinske, Joe (May 5, 2020). Perry Tyson plant currently open, company doesn't rule out future closures. Raccoon Valley Radio. Perry, Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ Pitt, David; Foley, Ryan J. (April 15, 2020). "Tyson Foods says 2 dead from COVID-19 outbreak at Columbus Junction plant". KCRG-TV. Cedar Rapids, Iowa. Retrieved April 16, 2020.
- ^ a b c Cerwinske, Joe (May 6, 2020). Iowa public health report: 58% of Perry Tyson Plant positive for COVID-19. Raccoon Valley Radio. Perry, Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ Foley, Ryan J. (April 22, 2020). Tyson Foods idles largest pork plant as virus slams industry. Associated Press. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ KCRG-TV9 staff (May 7, 2020). Tyson re-opens plant in Waterloo with changes to protect workers KCRG-TV. Cedar Rapids, Iowa. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- ^ Associated Press staff (May 8, 2020). Outbreak at Waterloo Tyson Plant Infected 1,031 Workers, County Says. WHO-TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- ^ Associated Press staff (May 12, 2020). Tyson Worker Dies After COVID-19 Outbreak at Iowa Plant. WHO-TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved May 12, 2020.
- ^ Caufield, Jim (May 4, 2020). Tyson back at work Monday; tests results expected soon. The Perry News. Perry, Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ Caufield, Jim (May 7, 2020). Tyson infections came as surprise to Dallas County Public Health. The Perry News. Perry, Iowa. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- ^ Schrad, Emily (May 8, 2020). Siouxland District Health: State officials determine when it's okay to announce names of businesses or individuals affected by COVID-19 outbreak. News 4 KTIV. Sioux City, Iowa. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- ^ Price, Dave (May 12, 2020). Iowa Cases Spike After Nebraska Outbreak. WHO-TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved May 12, 2020.
- ^ Diekneite, Max (May 6, 2020). "Reynolds, Trump discuss COVID-19 outbreaks at meat processing plants". Des Moines, Iowa: KCCI. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ KCCI staff (May 6, 2020). Hormel Foods announces multiple positive COVID-19 cases at Osceola location. KCCI. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ^ Associated Press staff (May 8, 2020). Iowa Turkey Plant to Furlough Hundreds of Workers. WHO-TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
- ^ "State reports COVID-19 outbreak at northern Iowa beef processing plant". The Des Moines Register. May 13, 2020. Retrieved May 13, 2020.
- ^ "Upper Iowa Beef plant confirms coronavirus outbreak". KCRG. May 14, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "New Iowa unemployment claims remain in record territory even as reopenings expand amid coronavirus pandemic". The Des Moines Register. May 14, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa's universities report coronavirus blow in the hundreds of millions". The Gazette (Cedar Rapids). April 30, 2020. Retrieved May 26, 2020.
- ^ Miller, Vanessa (September 28, 2020). "University of Iowa reports hundreds of COVID-19 complaints, as police respond to house parties". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ Miller, Vanessa (September 13, 2020). "University of Iowa RAs demand 'hazard pay' for COVID-19 threats". The Gazette. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ a b "Educator dies with COVID-19 as Iowa virus spread continues - Education Week". AP. October 6, 2020. Archived from the original on October 12, 2020. Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "Primary election voting in Iowa not slowed down by coronavirus". WOI-DT. June 2, 2020. Retrieved June 2, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa inmates earn $1.15 per hour producing COVID-19 supplies". ABC 33/40. May 22, 2020. Retrieved June 2, 2020.
- ^ "Iowa Cubs looking for other ways to use Principal Park during COVID-19 crisis". The Des Moines Register. June 2, 2020. Retrieved June 2, 2020.
- ^ "High school baseball, softball return in Iowa amid COVID-19 pandemic". CBS Sports. June 1, 2020. Retrieved June 2, 2020.
- ^ WHO TV staff (August 31, 2020). University of Iowa Pausing Athletic Activity Due to Surge in COVID-19. WHO TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- ^ We Are Iowa staff (August 31, 2020). 25,000 fans allowed to attend Iowa State's first home football game of the season - ISU Athletic Director Jamie Pollard says if fans can't follow mitigation efforts at the first game, no fans will be allowed to future games at Jack Trice Stadium. WOI TV. West Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- ^ KCCI staff (August 31, 2020). ISU to allow 25K fans inside stadium at football opener. KCCI TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved August 31, 2020.
- ^ Hendricksen, Dan (September 2, 2020). Change of Plans: ISU Says No Fans Will Allowed at Jack Trice Stadium for Season Opener on September 12th. WHO TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved September 3, 2020.
- ^ Lisignoli, Maria (September 3, 2020). ISU Students Have Mixed Reaction to Football with No Fans at Jack Trice. WHO TV. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved September 3, 2020.
- ^ Hendricksen, Dan (September 4, 2020). "ISU Athletic Department Discussing Layoffs, Cutting Sports, Closing Stephens Auditorium to Close Budget Shortfall". Des Moines, Iowa: WHO TV. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ Peterson, Randy (September 4, 2020). Pollard letter details Iowa State struggles; possible recommendations include closing Stephens Auditorium, eliminating some sports. The Des Moines Register. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
- ^ KCCI Staff (September 19, 2020). Big Ten schedule released, Hawkeyes open season at Purdue. KCCI. Des Moines, Iowa. Retrieved September 19, 2020.
- ^ "Novel Coronavirus - COVID-19 Reporting". Iowa Department of Public Health. Retrieved March 29, 2023.
External links
- Information from Iowa Department of Public Health
- COVID-19 in IOWA from Iowa.gov


