Kashi Vishwanath Temple: Difference between revisions
User4edits (talk | contribs) updated/added images |
Swapping images |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{{Infobox Hindu temple |
{{Infobox Hindu temple |
||
| name = Kashi Vishwanath Temple |
| name = Kashi Vishwanath Temple |
||
| image = |
| image = Benares- The Golden Temple, India, ca. 1915 (IMP-CSCNWW33-OS14-66).jpg |
||
| image_upright = |
| image_upright = |
||
| alt = Vishveshvara Mandir |
| alt = Vishveshvara Mandir |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
== Legends == |
== Legends == |
||
[[File:Kashi Vishwanath Renovated Mandir.jpg|thumb|left|The renovated temple in 2022]] |
|||
As per the [[Shiva Purana]], once [[Brahma]] (the Hindu God of creation) and [[Vishnu]] (the Hindu God of Preservation) had an argument about who was supreme.<ref name="R.">R. 2003, pp. 92-95</ref> To test them, [[Shiva]] pierced the three worlds as a huge endless pillar of light, the ''jyotirlinga''. To determine who was mightier Vishnu took the form of a [[boar]] and sought out the bottom while Brahma took the form of a [[swan]] to fly to the pillar's top. Brahma out of arrogance lied that he had found out the end, offering a katuki flower as witness. Vishnu modestly confessed to being unable to find the bottom. Shiva then took the form of the wrathful [[Bhairava]], cut off Brahma's lying fifth head, and cursed Brahma that he would not be worshipped. Vishnu for his honesty would be worshiped as equal to Shiva with his own temples for all eternity. The ''jyotirlinga'' is an ancient [[axis mundi]] symbol representing the supreme formless (nirguna) reality at the core of creation, out of which the form (saguna) of Shiva appears. The ''jyothirlinga'' shrines, thus are places where Shiva appeared as a fiery column of light.<ref>Eck 1999, p. 107</ref><ref name="Gwynne">See: Gwynne 2008, Section on Char Dham</ref> There are 64 forms of Shiva, not to be confused with Jyotirlingas. Each of the twelve ''jyotirlinga'' sites take the name of the presiding deity - each considered different manifestation of Shiva.<ref name="Lochtefeld">Lochtefeld 2002, pp. 324-325</ref> At all these sites, the primary image is ''[[lingam]]'' representing the beginningless and endless ''[[Stambha]]'' pillar, symbolizing the infinite nature of Shiva.<ref name="Lochtefeld" /><ref name="E. U. Harding">Harding 1998, pp. 158-158</ref><ref name="paris_congress">Vivekananda Vol. 4</ref> The twelve ''jyothirlinga'' are [[Somnath Temple|Somnath]] in [[Gujarat]], [[Mallikarjuna Swamy|Mallikarjuna]] at [[Srisailam]] in [[Andhra Pradesh]], [[Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga|Mahakaleswar]] at [[Ujjain]] in [[Madhya Pradesh]], [[Omkareshwar]] in [[Madhya Pradesh]], [[Kedarnath Temple|Kedarnath]] in [[Uttarakhand]], [[Bhimashankar Temple|Bhimashankar]] in [[Maharashtra]], [[Kasi Viswanath Temple|Viswanath]] at [[Varanasi]] in [[Uttar Pradesh]], [[Trimbakeshwar Shiva Temple|Triambakeshwar]] in [[Maharashtra]], [[Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga, Deogarh]] in [[Deoghar]], [[Jharkhand]], [[Nageshwar Temple, Dwarka|Nageswar]] at [[Dwarka]] in [[Gujarat]], [[Ramanathaswamy Temple|Rameshwar]] at [[Rameswaram]] in [[Tamil Nadu]] and [[Grishneshwar]] at [[Aurangabad, Maharashtra|Aurangabad]] in [[Maharashtra]].<ref name="R." /><ref name="Chaturvedi">Chaturvedi 2006, pp. 58-72</ref> |
As per the [[Shiva Purana]], once [[Brahma]] (the Hindu God of creation) and [[Vishnu]] (the Hindu God of Preservation) had an argument about who was supreme.<ref name="R.">R. 2003, pp. 92-95</ref> To test them, [[Shiva]] pierced the three worlds as a huge endless pillar of light, the ''jyotirlinga''. To determine who was mightier Vishnu took the form of a [[boar]] and sought out the bottom while Brahma took the form of a [[swan]] to fly to the pillar's top. Brahma out of arrogance lied that he had found out the end, offering a katuki flower as witness. Vishnu modestly confessed to being unable to find the bottom. Shiva then took the form of the wrathful [[Bhairava]], cut off Brahma's lying fifth head, and cursed Brahma that he would not be worshipped. Vishnu for his honesty would be worshiped as equal to Shiva with his own temples for all eternity. The ''jyotirlinga'' is an ancient [[axis mundi]] symbol representing the supreme formless (nirguna) reality at the core of creation, out of which the form (saguna) of Shiva appears. The ''jyothirlinga'' shrines, thus are places where Shiva appeared as a fiery column of light.<ref>Eck 1999, p. 107</ref><ref name="Gwynne">See: Gwynne 2008, Section on Char Dham</ref> There are 64 forms of Shiva, not to be confused with Jyotirlingas. Each of the twelve ''jyotirlinga'' sites take the name of the presiding deity - each considered different manifestation of Shiva.<ref name="Lochtefeld">Lochtefeld 2002, pp. 324-325</ref> At all these sites, the primary image is ''[[lingam]]'' representing the beginningless and endless ''[[Stambha]]'' pillar, symbolizing the infinite nature of Shiva.<ref name="Lochtefeld" /><ref name="E. U. Harding">Harding 1998, pp. 158-158</ref><ref name="paris_congress">Vivekananda Vol. 4</ref> The twelve ''jyothirlinga'' are [[Somnath Temple|Somnath]] in [[Gujarat]], [[Mallikarjuna Swamy|Mallikarjuna]] at [[Srisailam]] in [[Andhra Pradesh]], [[Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga|Mahakaleswar]] at [[Ujjain]] in [[Madhya Pradesh]], [[Omkareshwar]] in [[Madhya Pradesh]], [[Kedarnath Temple|Kedarnath]] in [[Uttarakhand]], [[Bhimashankar Temple|Bhimashankar]] in [[Maharashtra]], [[Kasi Viswanath Temple|Viswanath]] at [[Varanasi]] in [[Uttar Pradesh]], [[Trimbakeshwar Shiva Temple|Triambakeshwar]] in [[Maharashtra]], [[Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga, Deogarh]] in [[Deoghar]], [[Jharkhand]], [[Nageshwar Temple, Dwarka|Nageswar]] at [[Dwarka]] in [[Gujarat]], [[Ramanathaswamy Temple|Rameshwar]] at [[Rameswaram]] in [[Tamil Nadu]] and [[Grishneshwar]] at [[Aurangabad, Maharashtra|Aurangabad]] in [[Maharashtra]].<ref name="R." /><ref name="Chaturvedi">Chaturvedi 2006, pp. 58-72</ref> |
||
Revision as of 11:08, 23 July 2022
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2021) |
| Kashi Vishwanath Temple | |
|---|---|
 Kashi Vishwanath Temple, c. 1915 | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Hinduism |
| District | Varanasi |
| Deity | Vishveshwar or Vishwanath (Shiva) |
| Festivals | Maha Shivaratri |
| Location | |
| Location | Varanasi |
| State | Uttar Pradesh |
| Country | India |
| Geographic coordinates | 25°18′38.79″N 83°0′38.21″E / 25.3107750°N 83.0106139°E |
| Architecture | |
| Type | Mandir |
| Creator | Unknown - by Unknown 1585 CE - by Man Singh I |
| Completed | 1780 |
| Demolished |
|
| Website | |
| shrikashivishwanath.org | |
The Kashi Vishwanath Temple is a famous Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Shiva. It is located in Vishwanath Gali of Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh in India. The temple stands on the western bank of the holy river Ganga, and is one of the twelve Jyotirlingas, the holiest of Shiva temples. The main deity is known by the names Shri Vishwanath and Vishweshwara (IAST: Vishveshvara or Vishveshvur) literally meaning Lord of the Universe. Varanasi was called Kashi ("shining") in ancient times, and hence the temple is popularly called Kashi Vishwanath Temple.
The temple is considered a central part of worship in the Shaiva culture by Hindu scriptures. It had been demolished by many Muslim rulers many times, most recently by Aurangzeb, the sixth Mughal emperor who constructed the Gyanvapi Mosque on its site.[1] The current structure was built on an adjacent site by the Maratha ruler, Ahilyabai Holkar of Indore in the year 1780.[2]
Since 1983, the temple has been managed by the government of Uttar Pradesh.
Legends
As per the Shiva Purana, once Brahma (the Hindu God of creation) and Vishnu (the Hindu God of Preservation) had an argument about who was supreme.[3] To test them, Shiva pierced the three worlds as a huge endless pillar of light, the jyotirlinga. To determine who was mightier Vishnu took the form of a boar and sought out the bottom while Brahma took the form of a swan to fly to the pillar's top. Brahma out of arrogance lied that he had found out the end, offering a katuki flower as witness. Vishnu modestly confessed to being unable to find the bottom. Shiva then took the form of the wrathful Bhairava, cut off Brahma's lying fifth head, and cursed Brahma that he would not be worshipped. Vishnu for his honesty would be worshiped as equal to Shiva with his own temples for all eternity. The jyotirlinga is an ancient axis mundi symbol representing the supreme formless (nirguna) reality at the core of creation, out of which the form (saguna) of Shiva appears. The jyothirlinga shrines, thus are places where Shiva appeared as a fiery column of light.[4][5] There are 64 forms of Shiva, not to be confused with Jyotirlingas. Each of the twelve jyotirlinga sites take the name of the presiding deity - each considered different manifestation of Shiva.[6] At all these sites, the primary image is lingam representing the beginningless and endless Stambha pillar, symbolizing the infinite nature of Shiva.[6][7][8] The twelve jyothirlinga are Somnath in Gujarat, Mallikarjuna at Srisailam in Andhra Pradesh, Mahakaleswar at Ujjain in Madhya Pradesh, Omkareshwar in Madhya Pradesh, Kedarnath in Uttarakhand, Bhimashankar in Maharashtra, Viswanath at Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh, Triambakeshwar in Maharashtra, Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga, Deogarh in Deoghar, Jharkhand, Nageswar at Dwarka in Gujarat, Rameshwar at Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu and Grishneshwar at Aurangabad in Maharashtra.[3][9]
The Manikarnika Ghat on the banks of Ganges near to the Kashi Vishwanath Temple is considered as a Shakti Pitha, a revered place of worship for the Shaktism sect. The Daksha Yaga, a Shaivite literature is considered as an important literature which is the story about the origin of Shakti Peethas.[10]
Lord Vishweshara is said to be the reigning deity of Banaras, and, in opionion of people, holds the position of King over all the other deities, as well as all over the inhabitants residing not only within the city itself, but also within the circuit of the Panchkosi road (the sacred boundary of Banaras) extending for about 50 miles.[11]
History
Madhuri Desai notes accounts of the history of the temple to center around a litany of repeated destruction and re-construction.[12] Pilgrims visiting the present Kashi Vishwanath Temple are informed about the timelessness of the lingam.[12]
Ancient and classical period
The temple is mentioned in the Puranas including the Kashi Khanda (section) of Skanda Purana.
Medieval period and destruction
The original Vishwanath temple, initially known as the Adi Vishveshwara Temple, was destroyed by the Ghurids in 1194 CE, when Mu'izz al-Din Muhammad ibn Sam returned to India and defeated Jayachandra of Kannauj near Chandawar and afterwards razed the city of Kashi.[13] In few years time, Razia Mosque was constructed in its place.[14][15][16] In 1230, the temple was rebuilt near the Avimukteshwara Temple , away from the main site by a Gujarati merchant during the reign of Delhi's Sultan Iltutmish (1211–1266 CE) . It was demolished again during the rule of either Hussain Shah Sharqi (1447–1458) or Sikandar Lodi (1489–1517).
Mughal period
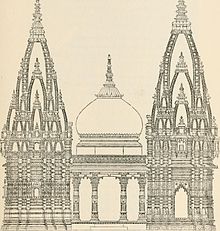
The dotted line shows the portion of the temple occupied by the present Masjid.
Raja Man Singh built the temple during Mughal emperor Akbar's rule. Raja Todar Mal further re-built the temple in 1585, but orthodox Brahmins chose to boycott the temple, because his daughter was married to Islamic rulers.[15][18] During the rule of Jahangir, Vir Singh Deo either restored or completed the construction of earlier temple.[19] In 1669 CE, Mughal emperor Aurangzeb destroyed the temple and built the Gyanvapi Mosque in its place.[20] The remains of the erstwhile temple can be seen in the foundation, the columns and at the rear part of the mosque.[21]
Maratha and British period
In 1742, the Maratha ruler Malhar Rao Holkar made a plan to demolish the mosque and reconstruct Vishweshwar temple at the site. However, his plan did not materialize, partially because of intervention by the Nawab of Awadh, who was given the control of the territory.[22]: 2 Around 1750, the Maharaja of Jaipur commissioned a survey of the land around the site, with the objective of purchasing land to rebuild the Kashi Vishwanath temple.[22]: 85 However, his plan to rebuild the temple did not materialize either. In 1780, Malhar Rao's daughter-in-law Ahilyabai Holkar rebuilt the present temple adjacent to the mosque.
IIn 1828, Baiza Bai, widow of the Maratha ruler Daulat Rao Scindhia of Gwalior State, built a low-roofed colonnade with over 40 pillars in the Gyan Vapi precinct.[23] During 1833–1840 CE, the boundary of Gyanvapi Well, the ghats and other nearby temples were constructed. Many noble families from various ancestral kingdoms of the Indian subcontinent and their prior establishments make generous contributions for the operations of the temple.
In 1835, Maharaja Ranjit Singh of the Sikh Empire, on the behest of his wife, Maharani Datar Kaur, donated 1 tonne of gold for plating the temple's dome. In 1841, Raghuji Bhonsle III of Nagpur donated silver to the temple.[22]: 200 [24] A 7-foot high stone statue of Nandi, gifted by the Rana of Nepal sometime in the 1860s lies to the east of the colonnade.[citation needed]
The temple was managed by a hereditary group of pandits or mahants. After the death of Mahant Devi Dutt, a dispute arose among his successors. In 1900, his brother-in-law Pandit Visheshwar Dayal Tewari filed a lawsuit, which resulted in him being declared the head priest.[25]
In older times, Dalits or people from lower castes were not allowed to enter the temple. After violent resistance to attempts following the abolition of untouchability by Article 17 of the Indian Constitution, Dalits were allowed to enter the temple in 1957.[26]
Post-Independence
The puja of the Maa Shringar Gauri Temple, at the western side of the disputed Gyanvapi Mosque, was restricted after the demolition of the Babri Masjid in December 1992 due to the ensuing deadly riots that followed the demolition of the mosque. In August 2021, five Hindu women petitioned a local court at Varanasi to be allowed to pray at the Maa Shringar Gauri Temple.[27]
In 2019, the Kashi Vishwanath Corridor Project was launched by Narendra Modi to ease access between the temple and the Ganges River, creating a wider space to prevent overcrowding. On 13 December 2021, Modi inaugurated the corridor with a sacred ceremony. A press release by the government said that around 1,400 residents and businesses within the corridor's area were relocated elsewhere and compensated. It also said that more than 40 ruined, centuries-old temples were found and rebuilt, including the Gangeshwar Mahadev temple, the Manokameshwar Mahadev temple, the Jauvinayak temple, and the Shri Kumbha Mahadev temple.[28][29] However, many temples were relocated from their original places. The original Panchayatna form of the temple was distorted as the four temples of Devi Bhog Annapurna, Sri Lakshmi Narayan, Sri Avimukteshwara Mahadeva and Devi Parvati surrounding the main temple were destroyed during the construction of the Kashi Vishwanath Corridor.
In February 2022, the sanctum sanctorum of the temple was gold-plated after an anonymous donor from South India donated 60 kg of gold to the temple.[30] Flowers from the temple are recycled into incense by the biomaterials startup Phool.co.[31]
Temple structure

The temple complex consists of a series of smaller shrines, located in a small lane called the Vishwanatha Galli, near the river. The linga of the main deity at the shrine is 60 centimetres (24 in) tall and 90 centimetres (35 in) in circumference housed in a silver altar.[32] The main temple is quadrangle and is surrounded by shrines of other gods. There are small temples for Kala Bhairava, Kartikeya, Avimukteshwara, Vishnu, Ganesha, Shani, Shiva and Parvati in the complex.
There is a small well in the temple called the Jnana Vapi also spelled as Gyan vapi (the wisdom well). The Jnana Vapi well sites to the north of the main temple and during the invasion by the Mughals the Jyotirlinga was hidden in the well to protect it at the time of invasion. It is said that the main priest of the temple jumped in the well with the lingam in order to protect the Jyotirlinga from invaders.
There is a Sabha Griha or Congregation Hall leading to the inner Garbha Griha or Sanctum Sanctorum. The venerable Jyotirlinga is a dark brown colored stone which is enshrined in the Sanctum, placed on a silver platform. Structure of the Mandir is composed of three parts. The first compromises a spire on the temple. The second is gold dome and the third is the gold spire atop the sanctum bearing a flag and a trident.
The Kashi Vishwanath temple receives around 3,000 visitors every day. On certain occasions, the numbers reach 1,000,000 and more. Noteworthy about the temple is 15.5-metre-high gold spire and gold dome. There are three domes each made up of pure gold, donated by Maharaja Ranjit Singh in 1835.
The Shri Kashi Vishwanath Dham corridor was constructed between Kashi Vishwanath Temple and Manikarnika Ghat along the Ganges River, providing various amenities for pilgrims.[33]
Importance
Located on the banks of the holy Ganges, Varanasi is regarded among the holiest of the Hindu cities. The Kashi Vishwanath temple is widely recognized as one of the most important places of worship in the Hindu religion. Inside the Kashi Vishwanath Temple is the Jyotirlinga of Shiva, Vishveshvara or Vishvanath. The Vishveshvara Jyotirlinga has a very special and unique significance in the spiritual history of India.
Many leading saints, including Adi Sankaracharya, Ramakrishna Paramhansa, Swami Vivekananda, Bamakhyapa, Goswami Tulsidas, Swami Dayananda Saraswati, Sathya Sai Baba, Yogiji Maharaj, Pramukh Swami Maharaj, Mahant Swami Maharaj and Gurunanak have visited the site.[34][unreliable source?] A visit to the temple and a bath in the river Ganges is one of many methods believed to lead one on a path to Moksha (liberation). Thus, Hindus from all over the world try to visit the place at least once in their lifetime. There is also a tradition that one should give up at least one desire after a pilgrimage the temple, and the pilgrimage would also include a visit to the temple at Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu in Southern India, where people take water samples of the Ganges to perform prayer at the temple and bring back sand from near that temple. Because of the immense popularity and holiness of Kashi Vishwanath temple, hundreds of temples across India have been built in the same architectural style. Many legends record that the true devotee achieves freedom from death and saṃsāra by the worship of Shiva, Shiva's devotees on death being directly taken to his abode on Mount Kailash by his messengers and not to Yama. The superiority of Shiva and his victory over his own nature—Shiva is himself identified with death—is also stated. There is a popular belief that Shiva himself blows the mantra of salvation into the ears of people who die naturally at the Vishwanath temple.[35]
It is one of the shrines of the Vaippu Sthalams sung by Tamil Saivite Nayanar Sambandar.[36][37][38]
Cultural events
Phalgun Shukla Ekadashi is celebrated as Rangabhari Ekadashi, that is, colors. According to tradition, before Holi, Baba Vishwanath comes back to Kashi after having a cow in the form of mother Bhagwati. The temple complex is echoed by the echo of dozens of Damroos. This tradition has been performed for over 200 years. On Basant Panchami Baba's Tilak is performed, Shivaratri marriage and Rangbhari Ekadashi marks parvati leaving with shiva.[39] These traditions are carried out by the erstwhile Mahant family of the temple for over a century.[40]
These rituals of Baba's marriage ceremony are performed at the residence of Kulpati Tiwari, the erstwhile Mahant of Shri Kashi Vishwanath Temple in Redzone.[41] The seven rituals of Saptarishi Aarti were performed by Baba Vishwanath. According to the Puranas, Kashi is loved by the Saptarishi to the priest, so according to the tradition, the devotees of the Saptarishi Aarti perform the rituals of marriage. The seven archaks under the leadership of Pradhan Archak Pandit Shashibhushan Tripathi (Guddu Maharaj) completed the marriage in Vedic rituals.[42] Mangala Aarti is performed at 3:30 am, Bhog Aarti at 12:00 pm, Saptarishi Aaarti at 7:30 pm and Shringar Aaarti at 11:00 pm.[43]
Yadav community of Kashi associated with Chandravanshi Gop Seva Samiti and Shree Krishna Yadav Mahasabha have been performing jalabhishek on shivling traditionally since 90 years, first started in 1932.[44]
See also
- Shri Vishwanath Mandir
- Mrityunjay Mahadev Mandir
- Ratneshwar Mahadev temple
- List of Hindu temples in Varanasi
- Nandmahar Dham
- Mata Mawai Dham
References
- ^ Akhil Bakshi (2004). Between heaven and hell: travels through Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, and India: an account of the expedition hands across the borders. Odyssey Books.
- ^ "Shri Kashi Vishwanath Temple - A Brief history".
- ^ a b R. 2003, pp. 92-95
- ^ Eck 1999, p. 107
- ^ See: Gwynne 2008, Section on Char Dham
- ^ a b Lochtefeld 2002, pp. 324-325
- ^ Harding 1998, pp. 158-158
- ^ Vivekananda Vol. 4
- ^ Chaturvedi 2006, pp. 58-72
- ^ "Kottiyoor Devaswam Temple Administration Portal". kottiyoordevaswom.com/. Kottiyoor Devaswam. Retrieved 20 July 2013.
- ^ Matthew Atmore Sherring (1968). The Sacred City of the Hindus An Account of Benares in Ancient and Modern Times (First ed.). London: Trübner & Company.
- ^ a b Desai, Madhuri (2017). "INTRODUCTION: THE PARADOX OF BANARAS". Banaras Reconstructed: Architecture and Sacred Space in a Hindu Holy City. University of Washington Press. pp. 3–16. ISBN 978-0-295-74160-4. JSTOR j.ctvcwnwvg.4.
- ^ Satish Chandra (2007). History of Medieval India:800-1700. Orient Longman. p. 71. ISBN 978-81-250-3226-7.
In 1194, Muizzuddin returned to India. He crossed the Jamuna with 50,000 cavalry and moved towards Kanauj. A hotly contested battle between Muizzuddin and Jaichandra was fought at Chandawar near Kanauj. We are told that Jaichandra had almost carried the day when he was killed by an arrow, and his army was totally defcated. Muizzuddin now moved on to Banaras which was ravaged, a large number of temples there being destroyed
- ^ Shin, Heeryoon (May 2015). Building a "Modern" Temple Town: Architecture and Patronage in Banaras, 1750-1900 (Thesis). Yale University. p. 4, 35, 38, 198.
- ^ a b Udayakumar, S. P. (2005). "Ramarajya: Envisioning the Future and Entrenching the Past". Presenting the Past: Anxious History and Ancient Future in Hindutva India. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-275-97209-7.
- ^ Bakker, Hans (1996). "Construction and Reconstruction of Sacred Space in Vārāṇasī". Numen. 43 (1): 42–43. doi:10.1163/1568527962598368. ISSN 0029-5973. JSTOR 3270235.
- ^ James Prinsep (1996). Benares Illustrated in a Series of Drawings. p. 29. ISBN 9788171241767.
- ^ S. P. Udayakumar (1 January 2005). Presenting the Past: Anxious History and Ancient Future in Hindutva India. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-275-97209-7.
- ^ Pauwels, Heidi (23 March 2011). "A tale of two temples: Mathurā's Keśavadeva and Orcchā's Caturbhujadeva". South Asian History and Culture. 2 (2): 278–299. doi:10.1080/19472498.2011.553497. ISSN 1947-2498. S2CID 144492608.
- ^ Catherine B. Asher (24 September 1992). Architecture of Mughal India. Cambridge University Press. pp. 278–279. ISBN 978-0-521-26728-1.
- ^ Vanessa Betts; Victoria McCulloch (30 October 2013). Delhi to Kolkata Footprint Focus Guide. Footprint Travel Guides. pp. 108–. ISBN 978-1-909268-40-1.
- ^ a b c Madhuri Desai (2007). Resurrecting Banaras: Urban Space, Architecture and Religious Boundaries. ISBN 978-0-549-52839-5.
- ^ Matthew Atmore Sherring (1868). The Sacred City of the Hindus: An Account of Benares in Ancient and Modern Times. Trübner & co. pp. 55–56.
- ^ Matthew Atmore Sherring (1868). The Sacred City of the Hindus: An Account of Benares in Ancient and Modern Times. Trübner & co. p. 51.
- ^ Trivikram Narain Singh And Ors. vs State Of U.P. And Ors. (Allahabad High Court 28 October 1986), Text.
- ^ Mandal, Dilip (17 December 2021). "From Ayodhya to Kashi, BJP changed its strategy from 'demolition' to construction". ThePrint. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ "Varanasi court issues notices on shared shrine petition in Ayodhya". www.telegraphindia.com. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- ^ Verma, Lalmani (13 December 2021). "PM Modi to inaugurate Kashi Vishwanath corridor in Varanasi today". The New Indian Express. New Delhi: Express Publications. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ A, Divya (14 December 2021). "Explained: What is changing at the ancient Kashi Vishwanath temple complex?". The Indian Express. Retrieved 14 December 2021.
- ^ "God meets gold meets faith in 'PM's works' at Kashi Vishwanath Temple". The Indian Express. 4 March 2022. Retrieved 5 March 2022.
- ^ "Exclusive - India's First Biomaterial Startup Phool.co Raises $8 Million In Series A Funding". Forbes India. Retrieved 13 July 2022.
- ^ "Cultural holidays - Kashi Vishwanath temple". Archived from the original on 8 April 2017. Retrieved 17 November 2006.
- ^ "Temple woes for Kashi Vishwanath corridor".
- ^ "History!Kashi Vishwanath temple".
- ^ "Shri Kashi Vishwanath Mandir, Varanasi". templesofindia.org. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ பு.மா.ஜெயசெந்தில்நாதன், தேவார வைப்புத்தலங்கள், வர்த்தமானன் பதிப்பகம், சென்னை, 2009
- ^ மூவர் தேவார வைப்புத் தலங்கள், Muvar Thevara Vaippu Thalangal, வாரணாசி - (காசி விஸ்வநாதர் ஆலயம்) Varanasi -Benaras - Kasi Vishvanathar Temple, 2-39-7
- ^ வாரணாசி, 2-39-7, 6-70-6, 6-7-11
- ^ https://www.bhaskar.com/news/UP-VAR-rangbhari-ekadashi-celebrated-in-kashi-vishwanath-temple-varanasi-news-hindi-5546329-PHO.html [bare URL]
- ^ "Kashi Vishwanath Dham project: 13 building owners refuse to sell property | Varanasi News - Times of India". The Times of India.
- ^ "काशी-विश्वनाथ कॉरिडोर के मुसलमान क्यों बेचैन हैं ?". BBC News हिंदी.
- ^ "मौर पहनकर निकले बाबा, लाल चुनरी में गौरा".
- ^ Karkar, S.C. (2009). The Top Ten Temple Towns of India. Kolkota: Mark Age Publication. p. 10. ISBN 978-81-87952-12-1.
- ^ "Yadav Bandhus Perform Jalabhishek Of Lord Shiva". The Times of India. 19 July 2022. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
Notes
- Chaturvedi, B. K. (2006), Shiv Purana (First ed.), New Delhi: Diamond Pocket Books (P) Ltd, ISBN 81-7182-721-7
- Eck, Diana L. (1999), Banaras, city of light (First ed.), New York: Columbia University Press, ISBN 0-231-11447-8
- Gwynne, Paul (2009), World Religions in Practice: A Comparative Introduction, Oxford: Blackwell Publication, ISBN 978-1-4051-6702-4.
- Harding, Elizabeth U. (1998). "God, the Father". Kali: The Black Goddess of Dakshineswar. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-81-208-1450-9.
- Lochtefeld, James G. (2002), The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism: A-M, Rosen Publishing Group, p. 122, ISBN 0-8239-3179-X
- R., Venugopalam (2003), Meditation: Any Time Any Where (First ed.), Delhi: B. Jain Publishers (P) Ltd., ISBN 81-8056-373-1
- Vivekananda, Swami. "The Paris Congress of the History of Religions". The Complete Works of Swami Vivekananda. Vol. 4.
External links
 Media related to Kashi Vishwanath Temple at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kashi Vishwanath Temple at Wikimedia Commons- Kashi Vishwanath Temple Website
- Shri Kashi Vishwanath Mandir, Varanasi




