Cupping therapy: Difference between revisions
m →History: fixed two grammar issues |
Bon courage (talk | contribs) →Safety: restore some content |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
Research suggests that cupping is harmful, especially in people who are thin or obese: According to Jack Raso (1997), cupping results in capillary expansion, excessive fluid accumulation in tissues, and the rupture of blood vessels.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://skepdic.com/cupping.html|title=cupping – The Skeptic's Dictionary – Skepdic.com|work=skepdic.com}}</ref> |
Research suggests that cupping is harmful, especially in people who are thin or obese: According to Jack Raso (1997), cupping results in capillary expansion, excessive fluid accumulation in tissues, and the rupture of blood vessels.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://skepdic.com/cupping.html|title=cupping – The Skeptic's Dictionary – Skepdic.com|work=skepdic.com}}</ref> |
||
Cupping therapy adverse events can be divided into local and systemic adverse events. The local adverse events were scar formation, burn, skin infection, panniculitis, abscess formation, pain at cupping site, and systemic adverse events include: anemia, dizziness, vasovagal attack, insomnia, headaches and nausea.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Al-Bedah|first=Abdullah|last2=Shaban|first2=Tamer|last3=Suhaibani|first3=Amen|last4=Gazzaffi|first4=Ibrahim|last5=Khalil|first5=Mohammed|last6=Qureshi|first6=Naseem|date=2016-05-06|title=Safety of Cupping Therapy in Studies Conducted in Twenty One Century: A Review of Literature|url=http://sciencedomain.org/abstract/14487|journal=British Journal of Medicine and Medical Research|volume=15|issue=8|pages=1–12|doi=10.9734/bjmmr/2016/26285}}</ref> |
|||
Fire cupping can sometimes result in minor to severe [[burn]]s, and may lead to hospitalization and may even require [[skin grafting]] to repair the injury. Also, other burns, due to carelessness with the flammable substances being used, such as spills and over application, can also occur.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Burns Induced by Cupping Therapy in a Burn Center in Northeast China|journal=WOUNDS|date=July 2014|volume=26|issue=7|url=http://www.woundsresearch.com/article/burns-induced-cupping-therapy-burn-center-northeast-china|accessdate=2 December 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Popular treatment known as cupping therapy leaves man with seven holes in his back|url=http://www.news.com.au/lifestyle/health/popular-treatment-known-as-cupping-therapy-leaves-man-with-seven-holes-in-his-back/news-story/33b979706858045dc7fcce1523772084|accessdate=2 December 2016|publisher=news.com.au|date=June 25, 2016}}</ref> |
Fire cupping can sometimes result in minor to severe [[burn]]s, and may lead to hospitalization and may even require [[skin grafting]] to repair the injury. Also, other burns, due to carelessness with the flammable substances being used, such as spills and over application, can also occur.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Burns Induced by Cupping Therapy in a Burn Center in Northeast China|journal=WOUNDS|date=July 2014|volume=26|issue=7|url=http://www.woundsresearch.com/article/burns-induced-cupping-therapy-burn-center-northeast-china|accessdate=2 December 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Popular treatment known as cupping therapy leaves man with seven holes in his back|url=http://www.news.com.au/lifestyle/health/popular-treatment-known-as-cupping-therapy-leaves-man-with-seven-holes-in-his-back/news-story/33b979706858045dc7fcce1523772084|accessdate=2 December 2016|publisher=news.com.au|date=June 25, 2016}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 06:12, 7 January 2018
| Cupping therapy | |
|---|---|
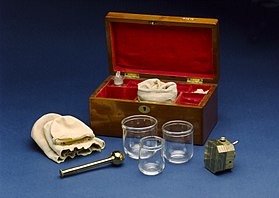 Cupping set, from London, England, dating from 1860–1875 | |
| Alternative therapy |
| Part of a series on |
| Alternative medicine |
|---|
 |
Cupping therapy is a form of alternative medicine in which a local suction is created on the skin. Cupping has been characterized as pseudoscience.[1] There is no good evidence it has any benefit on health and there are some concerns it may be harmful.[2]
Through suction, the skin is drawn into the cup by creating a vacuum in the cup placed on the skin over the targeted area. The vacuum can be created either by the heating and subsequent cooling of the air in the cup, or via a mechanical pump.[3] The cup is usually left in place for somewhere between five and fifteen minutes. It is believed by some to help treat pain, deep scar tissues in the muscles and connective tissue, muscle knots, and swelling; however, the efficacy of this is unproven.[2]
Effectiveness
Cupping is poorly supported by scientific evidence.[4] In their 2008 book Trick or Treatment, Simon Singh and Edzard Ernst write that no evidence exists of any beneficial effects of cupping for any medical condition.[5] A 2011 review found tentative evidence for pain but nothing else.[6]
Any reported benefits are likely due to the placebo effect.[7]
Advocates claim that cupping is an alternative treatment for cancer. However, the American Cancer Society notes that "available scientific evidence does not support claims that cupping has any health benefits" and also that the treatment carries a small risk of burns.[2]
Safety
Cupping is generally safe when applied by trained professionals on people who are otherwise healthy.[7] It is not recommended for people with health problems due to side effects.[7] Cupping is not recommended as a replacement for typical treatment.[7] Cupping may result in bruising, burns, pain, and/or skin infection.[7]
Research suggests that cupping is harmful, especially in people who are thin or obese: According to Jack Raso (1997), cupping results in capillary expansion, excessive fluid accumulation in tissues, and the rupture of blood vessels.[8]
Cupping therapy adverse events can be divided into local and systemic adverse events. The local adverse events were scar formation, burn, skin infection, panniculitis, abscess formation, pain at cupping site, and systemic adverse events include: anemia, dizziness, vasovagal attack, insomnia, headaches and nausea.[9]
Fire cupping can sometimes result in minor to severe burns, and may lead to hospitalization and may even require skin grafting to repair the injury. Also, other burns, due to carelessness with the flammable substances being used, such as spills and over application, can also occur.[10][11]
Methods
Preference varies among practitioners and cultures.
Cupping therapy types can be classified into four main categories, the first category is the "technical types" which included: dry, wet, massage and flash cupping therapy. The second category is "the power of suction related types" which included: light, medium and strong cupping therapy. The third category is "the method of suction related types" which included: fire, manual suction, and electrical suction cupping therapy. The fourth category is "materials inside cups related types" which included: herbal, water, ozone, Moxa, needle and magnetic cupping therapy.[12]
A fifth category and a sixth category were developed later. The fifth category is area treated related types that included: facial, abdominal, female, male and orthopedic cupping therapy. The sixth category is the other cupping types that included sports and aquatic cupping.[13]
Dry cupping

The cupping procedure commonly involves creating a small area of low air pressure next to the skin. However, there are varieties in the tools used, the methods of creating the low pressure, and the procedures followed during the treatment.[14]
The cups can be of various shapes including balls or bells, and may range in size from 1 to 3 inches (25 to 76 mm) across the opening. Plastic and glass are the most common materials used today, replacing the horn, pottery, bronze and bamboo cups used in earlier times. The low air pressure required may be created by heating the cup or the air inside it with an open flame or a bath in hot scented oils, then placing it against the skin. As the air inside the cup cools, it contracts and draws the skin slightly inside. More recently, vacuum is created with a mechanical suction pump acting through a valve located at the top of the cup. Rubber cups are also available that squeeze the air out and adapt to uneven or bony surfaces.
In practice, cups are normally used only on softer tissue that can form a good seal with the edge of the cup. They may be used singly or with many to cover a larger area. They may be used by themselves or placed over an acupuncture needle. Skin may be lubricated, allowing the cup to move across the skin slowly.
Skin markings are common after the cups are removed, varying from simple red rings that disappear relatively quickly, to discolourisation from bruising, especially if the cups are dragged while suctioned from one place to another, ostensibly to break down muscle fiber. Usually treatments are not very painful.
Fire cupping

Fire cupping involves soaking a cotton ball in almost pure alcohol. The cotton is clamped by a pair of forceps and lit via match or lighter, and, in one motion, placed into the cup and quickly removed, while the cup is placed on the skin. Fire heats the inside of the cup and a small amount of suction is created by the air cooling down again and contracting. Massage oil may be applied to create a better seal as well as allow the cups to glide over muscle groups (e.g. trapezius, erectors, latisimus dorsi, etc.) in an act called "moving cupping". Dark circles may appear where the cups were placed because of rupture of the capillaries just under the skin. There are documented cases of burns caused by fire cupping.[15][16]
Wet cupping
Wet cupping is also known as Hijama or medicinal bleeding. The first documented uses are found in the teachings of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad.[17] According to Muhammad al-Bukhari, Muslim ibn al-Hajjaj Nishapuri and Ahmad ibn Hanbal, Muhammad approved of the Hijama (cupping) treatment.[18]
A number of hadith support its recommendation and use by prophet Muhammad.[19] As a result, the practice of cupping therapy has survived in Muslim countries. Today, wet cupping is a popular remedy practiced in many parts of the Muslim world .[20]
In Finland, wet cupping has been done at least since the 15th century, and it is done traditionally in saunas. The cupping cups were made of cattle horns with a valve mechanism in it to create an partial vacuum by sucking the air out. Cupping is still practiced in Finland as part of relaxing and/or health regimens.[21]
Traditional Chinese medicine cupping
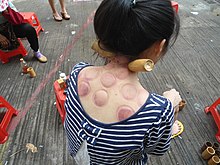
According to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), cupping is a method of creating a vacuum on the patient's skin to dispel stagnation (stagnant blood and lymph), thereby improving qi flow,[22] in order to treat respiratory diseases such as the common cold, pneumonia and bronchitis. Cupping also is used on back, neck, shoulder and other musculoskeletal conditions. Its advocates claim it has other applications as well.[22] Cupping is not advised, in TCM, over skin ulcers or to the abdominal or sacral regions of pregnant women.[23]
History

For over 3,000 years, the practice has been typically performed unsupervised, by individuals without any medical background. Iranian traditional medicine uses wet-cupping practices, with the belief that cupping with scarification may eliminate scar tissue, and cupping without scarification would cleanse the body through the organs.[24] Individuals with a profound interest in the practice are typically very religious and seek "purification."
There is reason to believe the practice dates from as early as 3000 BC. The Ebers Papyrus, written c. 1550 BC and one of the oldest medical textbooks in the Western world, describes the Egyptians' use of cupping, while mentioning similar practices employed by Saharan peoples. In ancient Greece, Hippocrates (c. 400 BC) used cupping for internal disease and structural problems. The method was highly recommended by Muhammad[19] and hence well-practiced by Muslim scientists who elaborated and developed the method further. Consecutively, this method in its multiple forms spread into medicine throughout Asian and European civilizations. In China, the earliest use of cupping that is recorded is from the famous Taoist alchemist and herbalist, Ge Hong (281–341 A.D.).[25] Cupping was also mentioned in Maimonides' book on health and was used within the Eastern European Jewish community.[26]
There is a description of cupping in George Orwell's essay "How the Poor Die", where he was surprised to find it practiced in a Paris hospital.[27]
Society and culture
Cupping has gained publicity in modern times due to its use by American sport celebrities including National Football League player DeMarcus Ware and Olympians Alexander Naddour, Natalie Coughlin, and Michael Phelps.[28] Medical doctor Brad McKay wrote that Team USA was doing a great disservice to their fans who might "follow their lead", calling cupping an "ancient (but useless) traditional therapy."[29] Practicing surgeon David Gorski claims, "it’s all risk for no benefit. It has no place in modern medicine".[30]
Critics of alternative medicine such as Harriet Hall, Mark Crislip, Simon Singh and Edzard Ernst have characterized cupping as "pseudoscience nonsense", "a celebrity fad", and "gibberish". They've stated that there is no evidence that cupping works any better than a placebo. Pharmacologist David Colquhoun writes that cupping is "laughable... and utterly implausible".[1][31]
See also
References
- ^ a b Crislip, Mark. "Acupuncture Odds and Ends". Science-Based Medicine. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ a b c Russell J; Rovere A, eds. (2009). "Cupping". American Cancer Society Complete Guide to Complementary and Alternative Cancer Therapies (2nd ed.). American Cancer Society. pp. 189–191. ISBN 9780944235713.
- ^ "What is cupping therapy". WebMD. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
- ^ Chen, B; Li, MY; Liu, PD; Guo, Y; Chen, ZL (July 2015). "Alternative medicine: an update on cupping therapy". QJM : Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians. 108 (7): 523–5. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcu227. PMID 25399022.
- ^ Singh, Simon; Ernst, Edzard (2008). Trick or Treatment. Transworld Publishers. p. 368. ISBN 978-0-552-15762-9.
- ^ Lee, MS; Kim, JI; Ernst, E (March 2011). "Is cupping an effective treatment? An overview of systematic reviews". Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies. 4 (1): 1–4. doi:10.1016/s2005-2901(11)60001-0. PMID 21440874.
- ^ a b c d e "In the News: Cupping". NCCIH. 2016-08-09. Retrieved 2016-08-15.
- ^ "cupping – The Skeptic's Dictionary – Skepdic.com". skepdic.com.
- ^ Al-Bedah, Abdullah; Shaban, Tamer; Suhaibani, Amen; Gazzaffi, Ibrahim; Khalil, Mohammed; Qureshi, Naseem (2016-05-06). "Safety of Cupping Therapy in Studies Conducted in Twenty One Century: A Review of Literature". British Journal of Medicine and Medical Research. 15 (8): 1–12. doi:10.9734/bjmmr/2016/26285.
- ^ "Burns Induced by Cupping Therapy in a Burn Center in Northeast China". WOUNDS. 26 (7). July 2014. Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ^ "Popular treatment known as cupping therapy leaves man with seven holes in his back". news.com.au. June 25, 2016. Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ^ Shaban, Tamer (2013). Cupping Therapy Encyclopedia. CreateSpace. p. 29. ISBN 978-1494780517.
- ^ "Classification of Cupping Therapy: A Tool for Modernization and Standardization (PDF Download Available)". ResearchGate. Retrieved 2017-03-29.
- ^ Cui Jin and Zhang Guangqi, "A survey of thirty years’ clinical application of cupping", Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1989; 9(3): 151–154
- ^ Iblher, N.; Stark, B. (2007). "Cupping treatment and associated burn risk: a plastic surgeon's perspective". J Burn Care Res. 28 (2): 355–8. doi:10.1097/BCR.0B013E318031A267. PMID 17351459.
- ^ Sagi, A.; Ben-Meir, P.; Bibi, C. (Aug 1988). "Burn hazard from cupping--an ancient universal medication still in practice". Burns Incl Therm Inj. 14 (4): 323–5. doi:10.1016/0305-4179(88)90075-7. PMID 3224303.
- ^ Andrew Rippin and Jan Knappert, Textual Sources for the Study of Islam, Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1986; Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1990. 78.
- ^ Sunan Abu Dawood, 11:2097, 28:3848, Sahih Muslim, 26:5467, 10:3830
- ^ a b Qayyim Al-Jauziyah (2003). Abdullah, Abdul Rahman (formerly Raymond J. Manderola) (ed.). Healing with the Medicine of the Prophet. ISBN 978-9960892917.
Indeed, the best of remedies you have is hijama, and if there was something excellent to be used as a remedy then it is hijama.
- ^ Observations of the popularity and religious significance of blood-cupping (al-ḥijāma) as an Islamic medicine, Ahmed El-Wakil, Contemporary Islamic Studies, Vol. 2011, 2
- ^ "...a cupping session — a recently revived, if archaic procedure, during which a therapist uses a cupping hatchet to make small cuts in your back and places glass cups fitted with bulb syringes over the cuts to draw out “bad blood” and release “feel-good” endorphins. Cupping is considered perfectly safe and aficionados say the procedure energizes them, but it’s definitely not for germophobes or the squeamish." : From "Finland's magificent obsession", Travelsquire
- ^ a b State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, Advanced Textbook on Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, Volume IV, 1997 New World Press, Beijing
- ^ Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion (Revised Edition), Xingnong, Foreign Languages Press, Beijing, China, 1987, p370.
- ^ Nimrouzi M; Mahbodi A; Jaladat AM; Sadeghfard A; Zarshenas MM (2014). "Hijama in traditional Persian medicine: risks and benefits". J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 19 (2): 128–36. doi:10.1177/2156587214524578. PMID 24647093.
- ^ Dharmananda, Subhuti. "Cupping". itmonline.org. Institute for Traditional Medicine. Retrieved 2016-08-10.
- ^ Ingall, Marjorie (2016-08-11). "Everything You Ever Wanted to Know About Cupping—and Some Stuff You Probably Didn't". Tablet Magazine. Retrieved 2016-08-14.
- ^ Orwell, George (November 1946). "How the Poor Die". Now. Retrieved 10 August 2016.
As I lay down I saw on a bed nearly opposite me a small, round-shouldered, sandy-haired man sitting half naked while a doctor and a student performed some strange operation on him. First the doctor produced from his black bag a dozen small glasses like wine glasses, then the student burned a match inside each glass to exhaust the air, then the glass was popped on to the man's back or chest and the vacuum drew up a huge yellow blister. Only after some moments did I realize what they were doing to him. It was something called cupping, a treatment which you can read about in old medical text-books but which till then I had vaguely thought of as one of those things they do to horses.
- ^ "Cupping Has An Olympic Moment". NY Times. NY Times. August 8, 2016. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ McKay, Brad (August 9, 2016). "Why Team USA's use of cupping therapy really sucks". News.com.au. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- ^ Gorski, David (July 1, 2016). "What's the harm? Cupping edition". Respectful Insolence. Science-Based Medicine. Retrieved 8 August 2016.
- ^ Hall, Harriet. "Therapy or Injury? Your Tax Dollars at Work". Science-Based Medicine. Retrieved 8 August 2016.

