Empire of Japan: Difference between revisions
| Line 253: | Line 253: | ||
{{main|Attack on Pearl Harbor}} |
{{main|Attack on Pearl Harbor}} |
||
[[Image:USSArizona PearlHarbor.jpg|180px|right|thumb|[[USS Arizona (BB-39)|USS ''Arizona'']] sinking.]] |
[[Image:USSArizona PearlHarbor.jpg|180px|right|thumb|[[USS Arizona (BB-39)|USS ''Arizona'']] sinking.]] |
||
After facing oil [[embargo]] by the United States and its own reserve oil about to run short, the Japanese government decided to take action and planned to execute a plan developed by the military branch largely lead by [[Osami Nagano]] and [[Isoroku Yamamoto]] to bomb the United States naval base in [[Hawaii]] and therefore bringing the United States to World War 2 on the side of [[Allies]]. On [[4 September]] [[1941]], the Japanese [[Cabinet]] met to consider the war plans prepared by [[Imperial General Headquarters]], and decided: |
After facing an oil [[embargo]] by the United States and its own reserve oil supply about to run short, the Japanese government decided to take action and planned to execute a plan developed by the military branch largely lead by [[Osami Nagano]] and [[Isoroku Yamamoto]] to bomb the United States naval base in [[Hawaii]] and therefore bringing the United States to World War 2 on the side of [[Allies]]. On [[4 September]] [[1941]], the Japanese [[Cabinet]] met to consider the war plans prepared by [[Imperial General Headquarters]], and decided: |
||
<blockquote>Our Empire, for the purpose of self-defence and self-preservation, will complete preparations for war ... <nowiki>[</nowiki>and is<nowiki>]</nowiki> ... resolved to go to war with the [[United States]], [[United Kingdom|Great Britain]] and the [[Netherlands]] if necessary. Our Empire will concurrently take all possible diplomatic measures vis-a-vis the United States and Great Britain, and thereby endeavor to obtain our objectives ... In the event that there is no prospect of our demands being met by the first ten days of October through the diplomatic negotiations mentioned above, we will immediately decide to commence hostilities against the United States, Britain and the Netherlands.</blockquote> |
<blockquote>Our Empire, for the purpose of self-defence and self-preservation, will complete preparations for war ... <nowiki>[</nowiki>and is<nowiki>]</nowiki> ... resolved to go to war with the [[United States]], [[United Kingdom|Great Britain]] and the [[Netherlands]] if necessary. Our Empire will concurrently take all possible diplomatic measures vis-a-vis the United States and Great Britain, and thereby endeavor to obtain our objectives ... In the event that there is no prospect of our demands being met by the first ten days of October through the diplomatic negotiations mentioned above, we will immediately decide to commence hostilities against the United States, Britain and the Netherlands.</blockquote> |
||
Revision as of 03:23, 12 October 2007
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2007) |
Greater Japanese Empire 大日本帝國 Dai Nippon Teikoku | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1868–1945 | |||||||||||
| Anthem: "Kimi ga Yo" "Imperial Reign" | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Capital | Tokyo | ||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||
• 1868–1912 | Emperor Meiji | ||||||||||
• 1912–1926 | Emperor Taishō | ||||||||||
• 1926–1989 | Emperor Shōwa | ||||||||||
| Prime Minister | |||||||||||
• 1885-1888, 1892-1896, 1898, 1900-1901 | Itō Hirobumi | ||||||||||
• 1888-1889 | Kuroda Kiyotaka | ||||||||||
• 1889-1891 | Yamagata Aritomo | ||||||||||
• 1906-1908, 1911-1912 | Saionji Kinmochi | ||||||||||
• 1901-1906, 1908-1911 | Katsura Tarō | ||||||||||
• 1913-1914, 1923-1924 | Yamamoto Gonnohyōe | ||||||||||
• 1898, 1914-1916 | Ōkuma Shigenobu | ||||||||||
• 1916–1918 | Count Masatake Terauchi | ||||||||||
• 1937-1939, 1940-1941 | Prince Fumimaro Konoe | ||||||||||
• 1941–1944 | Hideki Tōjō | ||||||||||
• 1944–1945 | Kuniaki Koiso | ||||||||||
• 1945 | Count Kantaro Suzuki | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Meiji Restoration | January 3 1868 | ||||||||||
| August 29, 1871 | |||||||||||
| November 29, 1890 | |||||||||||
| September 2 1945 | |||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 675,000 km2 (261,000 sq mi) | |||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• | 97,770,000 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Yen | ||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | JP | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Population estimate at 1935 | |||||||||||
The Empire of Japan (Kyūjitai: 大日本帝國; Shinjitai: 大日本帝国; pronounced Dai Nippon Teikoku; officially Empire of Greater Japan or Greater Japanese Empire; also known as Imperial Japan or the Japanese Empire) was a government under the Constitution of the Empire of Japan and Japan and the areas it ruled during the period from the Meiji Restoration to its defeat in World War II. The Emperors during this time, which spanned the Meiji, Taishō and Shōwa eras, are now known by their posthumous names which coincide with those era names: Emperor Meiji (Mutsuhito), Emperor Taishō (Yoshihito) and Emperor Shōwa (Hirohito).
Notable events during this period were the return of power to the Emperor (大政奉還, Tai-sei Hou-kan) on 9 November 1867, the Abolition of the Han system (廃藩置県, Hai-han Chi-ken) on July 14, 1871, the country's rapid industrialization and militarization under the slogan Fukoku Kyohei 富国強兵 (Enrich the Country, Strengthen the Military), leading to its emergence as a world power eventually culminating with its membership in the Axis alliance and the conquest of a large part of the Asia-Pacific region.
The Empire of Japan surrendered to the Allies on September 2, 1945 after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, following a Pacific War and Second Sino-Japanese war among others against the Allied nations of World War II.
A period of occupation by the Allies followed the surrender and dissolution of the Empire and a new constitution was created with American involvement. American occupation and reconstruction of the country continued well into the 1950s eventually forming the modern current Japan.
Background and terminology
Although the empire is commonly referred to as "the Japanese Empire" or "Imperial Japan" in English, the literal translation from Japanese is Greater Japanese Empire (Dai Nippon Teikoku). The nomenclature Empire of Japan had existed since the feudal anti-shogunate domains, Satsuma and Chōshū, which founded their new government during the Meiji Restoration, with the intention of forming a modern state to resist western domination.
The empire was established on January 3, 1868 when the emperor was restored as the head of state and head of government. The Tokugawa shogun was forced to resign on the November 9, 1867, however it was the following year that the emperor fully gained control. After the Boshin War, the Meiji government instituted a massive set of reforms to modernize and rapidly industrialize the country.
Under the Meiji government the economy strengthened and the military was westernized. This culminated in the adoption of a foreign policy of outward expansion. The defeat of China and Russia (in 1894-95 and 1904-05, respectively) would see the Korean peninsula, Liaodong and Formosa under Japanese control. By 1920 Japan would establish itself as one of the Great Powers.
Its main military branches were the Imperial Japanese Army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. These wings accumulated great influence within the Japanese government, and as time progressed the country become increasingly under the influence of military leaders, especially of the Army.
The Empire of Japan, de facto, spanned the eras that are known as the Meiji period (1868–1912), the Taishō period (1912–1926), and the first twenty-one years of the Shōwa period (1926–1989) — 1868 to 1947. Constitutionally, the Japanese Imperial period lasted from November 29, 1890, to May 3, 1947, under the 1889 Constitution which lasted until the enactment of the American authored post-war constitution in May, 1947. Though Emperor Shōwa ruled during the war, the title of Emperor became one of a constitutional monarch following Japan's defeat in World War II.
Politics
Founding of the constitution


The constitution also recognized the aforementioned acknowledgment of a need for change and modernization after removal of the shogunate:
We, the Successor to the prosperous Throne of Our Predecessors, do humbly and solemnly swear to the Imperial Founder of Our House and to Our other Imperial Ancestors that, in pursuance of a great policy co-extensive with the Heavens and with the Earth, We shall maintain and secure from decline the ancient form of government...In consideration of the progressive tendency of the course of human affairs and in parallel with the advance of civilization, We deem it expedient, in order to give clearness and distinctness to the instructions bequeathed by the Imperial Founder of Our House and by Our other Imperial Ancestors, to establish fundamental laws....
Imperial Japan was founded, de jure, after the 1889 signing of Constitution of the Empire of Japan. The constitution formalized much of its political structure and gave many responsibilities and powers to the Emperor.
Article 4. The Emperor is the head of the Empire, combining in Himself the rights of sovereignty, and exercises them, according to the provisions of the present Constitution.
Article 6. The Emperor gives sanction to laws, and orders them to be promulgated and executed.
Article 11. The Emperor has the supreme command of the Army and Navy.[1]
Although it was in this constitution that the title Empire of Japan was officially used for the first time, it was not until 1936 that this title was legalized. Until then, the names "Nippon" (日本; Japan), "Dai-Nippon" (大日本; Greater Japan), "Dai-Nippon/-Nihon Koku" (日本國; Nation of Japan), "Nihon Teikoku" (日本帝國; Empire of Japan) were all used.
In 1946, a year after the end of World War II, Japan's government was restructured. The country's name was revised once again in the draft of the 1946 Constitution of Japan, this time to "Japan" (日本国; Nihon Koku).
Change and philosophy
Meiji Restoration and foundation of modern Japan
The foundation of the rapid industrial and military strength was the direct result of Meiji Restoration. Facing Unequal Treaties, which provided naval base and bombardment of its cities by the Western ships after an anti-foreign uprising, and free trade with the Western countries, Japan decided to westernize to compete with other nations for its own well being and prosperity as the Meiji leaders concluded. Faced with the military and economic strength of the Western nations, Japan under the rule of Emperor Meiji decided to become powerful themselves. This resulted in frantic and dramatic change in every manner of Japanese society.
Change and philosophy

Several prominent writers under the constant threat of assassination from their political foes, such as Fukuzawa Yukichi were influential in convincing Japanese people for westernization. For instance some of his works that were well known were "Conditions in the West", "Leaving Asia", and "An Outline of a Theory of Civilization" that detailed Western society and his own philosophies. In the Meiji Restoration period, military and economic power was well emphasized. Military strength became the means for national development and stability. Imperial Japan became the only non-Western world power and a major force in east and southeast Asia in less than 30-50 years as a result of industrialization and economic development.
As one writer Albrecht Furst von Urach comments in his booklet "The Secret of Japan's Strength,"
The rise of Japan to a world power during the past 80 years is the greatest miracle in world history. The mighty empires of antiquity, the major political institutions of the Middle Ages and the early modern era, the Spanish Empire, the British Empire, all needed centuries to achieve their full strength. Japan's rise has been meteoric. After only 80 years, it is one of the few great powers that determine the fate of the world.
Westernization

The sudden and fast westernization once adopted changed almost all arenas of Japanese society ranging from language, etiquette, judicial and political system, armaments, arts, etc. Japanese government sent students to Western countries to observe and learn their practices as well as paying foreign scholars to Japan to educate the populace, the so called "foreign advisors" coming in from variety of studies. For instance the judicial system and constitution were largely modeled on that of Germany. It also outlawed customs linked to Japan's feudal such as displaying and wearing katana in the public and top knot both of which were characteristic of the samurai class, which were abolished all together with the caste system. This would later bring the Meiji government into conflict with the Samurai.(Satsuma Rebellion)
Moreover the Meiji government brought numerous armaments, ships and such that to build their conscription based national army (Imperial Japanese Army) and navy (Imperial Japanese Navy).
Economic development
Before World War II, Japan built an extensive empire that included Taiwan, Korea, Manchuria, and parts of northern China. The Japanese regarded this sphere of influence as a political and economic necessity, preventing foreign states from strangling Japan by blocking its access to raw materials and crucial sea-lanes. Japan's large military force was regarded as essential to the empire's defense and prosperity through obtaining natural resources, in which the Japanese islands are lacking.
Rapid growth and structural change characterized Japan's two periods of economic development after 1868. Initially, the economy grew only moderately and relied heavily on traditional Japanese agriculture to finance modern industrial infrastructure. By the time the Russo-Japanese War began in 1904, 65% of employment and 38% of the gross domestic product (GDP) was still based on agriculture, but modern industry had begun to expand substantially. By the late 1920s, manufacturing and mining contributed to 23% of GDP, compared with the 21% for all of agriculture. Transportation and communications developed to sustain heavy industrial development.
Pre-World War I wars
First Sino-Japanese War


Prior to its engagement in the First World War, the Empire of Japan fought in two significant wars after its establishment following the Meiji Revolution. The first was the First Sino-Japanese War, fought between 1894 and 1895. The war revolved around the issue of control and influence over Korea under the rule of the Joseon Dynasty. A peasant rebellion led to a request by the Korean government for China to send troops in to stabilize the region. The Empire of Japan responded by sending their own force to Korea and installing a puppet government in Seoul. China objected and war ensued. In a brief affair with Japanese ground troops routing Chinese forces on the Liaodong Peninsula, and the near destruction of the Chinese navy in the Battle of the Yalu River. China was forced to sign the Treaty of Shimonoseki, which ceded parts of Manchuria and the island of Formosa to Japan (see Taiwan under Japanese rule and 1895 Japanese Conquest of Taiwan). After this war, regional dominance shifted from China to Japan.
Russo-Japanese War
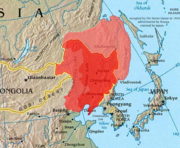

The Russo-Japanese War was a conflict for control of Korea and parts of Manchuria by the Russian Empire and Empire of Japan that took place from 1904 to 1905. The war is significant as the first modern war where an Asian country defeated a European power. The victory greatly raised Japan's measure in the world of global politics. The war is marked by the Japanese rebuff of Russian interests in Korea, Manchuria, and China, notably, the Liaodong Peninsula, controlled by the city of Port Arthur.
Originally, in the Treaty of Shimonoseki, Port Arthur had been given to Japan. This part of the treaty was overruled by Western powers, which gave the port to the Russian Empire, furthering Russian interests in the region. These interests came into conflict with Japanese interests. The war began with a surprise attack on the Russian Eastern fleet stationed at Port Arthur, which was followed by the Battle of Port Arthur. Those elements that attempted escape were defeated by the Japanese navy under Admiral Togo Heihachiro at the Battle of the Yellow Sea. A year later, the Russian Baltic fleet arrived only to be annihilated in the Battle of Tsushima. While the ground war did not fare as poorly for the Russians, the Japanese army was significantly more aggressive than their Russian counterparts and gained a political advantage that accumulated with the Treaty of Portsmouth negotiated in the United States by the American president Theodore Roosevelt. As a result, Russia lost the part of Sakhalin Island south of 50 degrees North latitude (which became the Karafuto Prefecture,) as well as many mineral rights in Manchuria. In addition, Russia's defeat cleared the way for Japan to annex Korea outright in 1910.
World War I



Japan entered World War I in 1914, seizing the opportunity of Germany's distraction with the European War and wanting to expand its sphere of influence in China. Japan declared war on Germany in August 23, 1914 and quickly occupied German-leased territories in China's Shandong Province and the Mariana, Caroline, and Marshall Islands in the Pacific, including German New Guinea. The Battle of Tsingtao, a swift invasion in the German colony of Jiaozhou (Kiautschou) proved successful and the colonial troops surrendered on 7 November 1914.
With Japan's Western allies, notably the United Kingdom, heavily involved in the war in Europe, it sought further to consolidate its position in China by presenting the Twenty-One Demands to China in January 1915. Besides expanding its control over the German holdings, Manchuria, and Inner Mongolia, Japan also sought joint ownership of a major mining and metallurgical complex in central China, prohibitions on China's ceding or leasing any coastal areas to a third power, and miscellaneous other political, economic, and military controls, which, if achieved, would have reduced China to a Japanese protectorate. In the face of slow negotiations with the Chinese government, widespread anti-Japanese sentiment in China, and international condemnation, Japan withdrew the final group of demands, and treaties were signed in May 1915.
Military and social organizations
This section needs expansion. You can help by making an edit requestadding to it . |
Important institutional links existed between the Party in Government (Kodoha) and Military and Political Organizations like the Imperial Young Federation, and the "Political Department" of the Kempeitai;Amongst the himitsu kessha (secret societies), the Kokuryu-kai (Black Dragon Society), and Kokka Shakai Shugi Gakumei (the National Socialist League) also had close ties to the government. The Tonarigumi (residents committee) groups, the Nation Service Society (national government trade union) and Imperial Farmers Association were all allied as well. See more:List of Japanese institutions (1930 - 1945)
Other organizations and groups related with the government in wartime were: Double Leaf Society, Toseiha, Kodaha, Kokuhonsha, Taisei Yokusankai, Imperial Youth Corps, League of Diet Members Believing the Objectives of the Holy War, Tokko,Tokeitai, Keishicho (to 1945), Shintoist Rites Research Council, Treaty Faction, Fleet Faction and Imperial Volunteer Corps
Militarization and imperialist ambitions


Nationalistic Factors
Sadao Araki was an important figurehead and founder of the Army party and the most important right-wing thinker in that time; his first ideological works date from his leadership of the Kodaha (Imperial Benevolent Rule or Action Group), opposed by the Toseiha (Control Group) led by General Kazushige Ugaki. He linked the ancient (bushido code) and contemporary local and European fascist ideals (see Japanese fascism), to form the ideological basis of the movement (Shōwa nationalism).
From September 1932, the Japanese were becoming more locked into the course that would lead them into the Second World War, with Araki leading the way. Totalitarianism, militarism and expansionism were to become the rule, with fewer voices able to speak against it. In a September 23 news conference, Araki first mentioned the philosophy of "Kodoha" (The Imperial Way Faction). The concept of Kodo linked the Emperor, the people, land and morality as indivisible. This led to the creation of a "new" Shinto and increased Emperor worship.

The state was being transformed to serve the Army and the Emperor. Symbolic katana swords came back into fashion as the martial embodiment of these beliefs, and the Nambu pistol became its contemporary equivalent, with the implicit message that the Army doctrine of close combat would prevail.
The final objective, as envisioned by Army thinkers and right-wing line followers, was a return to the old Shogunate system, but in the form of a contemporary Military Shogunate. In such a government the Emperor would once more be a figurehead (as in the Edo period). Real power would fall to a leader very similar to a Führer or Duce, though with the power less nakedly held. On the other hand, the traditionalist Navy militarists defended the Emperor and a constitutional monarchy with a significant religious aspect.
In time Japan would turn to a form of government that resembled Fascism. However, although this unique style of government was very similar to Fascism there were many significant differences between the two and therefore could be termed Japanese nationalism.
Economic Factors
At same time, the zaibatsu capitalist groups (principally Mitsubishi, Mitsui, Sumitomo, and Yasuda) looked toward great future expansion. Their main concern was a shortage of raw materials. Prime Minister Fumimaro Konoye combined social concerns with the needs of capital, and planned for expansion.

The economic seeds of World War II were planted in the mid 19th century. The main goals of this expansionism were acquisition and protection of spheres of influence, maintenance of territorial integrity, acquisition of raw materials, and access to Asian markets. Western nations, notably Great Britain, France, and the United States, had for long exhibited great interest in the commercial opportunities in China and other parts of Asia. These opportunities had attracted Western investment because of the availability of raw materials for both domestic production and re-export to Asia. Japan desired these opportunities in planning the development of the Greater East Asian Co-Prosperity Sphere.
The Great Depression, just in many other countries, had hindered Japan's economic growth. The Japanese Empire's main problem lay in that rapid industrial expansion had turned the country into a major manufacturing and industrial power that required raw materials, however these could only be obtained overseas as there was a critical lack of natural resources on its home islands.
In the 1920s and 1930s Japan needed to import raw materials such as iron, rubber and oil to maintain strong economic growth. Most of these resources, however came from the United States. The Japanese felt that acquiring resource-rich territories would establish economic self-sufficiency and independence, they also hoped to jump-start the nation's economy in the midst of the depression. As a result Japan set its sights on East Asia, specifically Manchuria with its many resources, Japan needed these resources to continue its economic development and maintain national integrity.
Once outright war began, the Domei Tsushin Press Agency celebrated the quality of Japan's armaments, stating that Mitsubishi and the others had taken the measure of the "white barbarians".
World War II
Pre-War Expansionism
Manchuria


With little resistance, Japan invaded and conquered Manchuria in 1931. Japan claimed that this invasion was a liberation of the Manchus from the Chinese, although the majority of the population were Han Chinese. Japan then established a puppet regime called Manchukuo, and installed the former Emperor of China, Puyi, as the official head of state. Jehol, a Chinese territory bordering Manchuria, was also taken in 1933. This puppet regime had to carry on a protracted pacification campaign against the Anti-Japanese Volunteer Armies in Manchuria. In 1936, Japan created a similar Mongolian puppet state in Inner Mongolia named Mengjiang (Chinese:yup) which was again predominantly Chinese.
Second Sino-Japanese War
Japan invaded China in 1937, creating what was essentially a three-way war between Japan, Mao Zedong's communists, and Chiang Kai-shek's nationalists. On 13 December that same year, the Nationalist capital of Nanking fell to Japanese troops. In the event known as the Rape of Nanking, Japanese troops massacred a large number of city's population. It is estimated that nearly 300,000 people, almost entirely civilians, were killed. In total, 20 million Chinese, mostly civilians, would be killed during World War II. A puppet state was also set up in China quickly afterwards, headed by Wang Jingwei. The second Sino-Japanese war would continue into World War II with the Communists and Nationalists in a temporary and uneasy alliance against the Japanese.
Clashes with the Soviet Union
The Battle of Lake Khasan was an attempted military incursion of the Japanese 19th Division into the territory claimed by the Soviet Union. This incursion was founded in the belief of the Japanese that the Soviet Union misinterpreted the demarcation of the boundary based on the Treaty of Peking between Imperial Russia and Manchu China (and subsequent supplementary agreements on demarcation), and furthermore, that the demarcation markers were tampered with.
The following year, Nomonhan Incident(Battle of Halhin-Gol) occurred on 11 May 1939, when a Mongolian cavalry unit of some 70 to 90 men entered the disputed area in search of grazing for their horses, and encountered Manchukuoan cavalry who drove them out of the disputed territory. Two days later the Mongolian force returned and the Manchukoans were unable to evict them.
The Japanese IJA 23rd Division and other units of the Kwantung Army then became involved. Joseph Stalin ordered STAVKA, the Red Army's high command, to develop a plan for a counterstrike against the Japanese. Georgy Zhukov, led a devastating offensive employing encircling tactics making skillful use of their superior artillery, armor and air forces in late August that nearly annihilated the 23rd Division and decimated the IJA 7th Division. On September 15 an armistice was arranged. Nearly two years later, on April 13, 1941, the parties signed a Neutrality Pact, in which they agreed to abide by the existing border.
Tripartite Pact


The Second Sino-Japanese War had seen tensions rise between Imperial Japan and the United States, events such as Panay incident and the 'Rape of Nanking' turned American public opinion against Japan. With the occupation of French Indochina in the years of 1940/41 and the continuing war in China, the United States embargoed strategic materials such as scrap metal and oil(which they vitally needed for their war effort) to Japan. The Japanese were faced with the option of either withdrawing from China and losing face or seizing and securing new sources of raw materials in the resource rich, European controlled colonies of South East Asia — specifically British Malaya and the Dutch East Indies
On September 27, 1940, Imperial Japan signed the Tripartite Pact with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy, their objectives to "establish and maintain a new order of things" in their respective world regions and spheres of influence. With Nazi Germany in Europe, Imperial Japan in Asia and Fascist Italy in North Africa. The signatories of this alliance become known as the Axis Powers. The pact also called for mutual protection—if any one of the member powers were attacked by a country not already at war, excluding the Soviet Union, and for technological and economic cooperation between the signatories
On 31 December 1940, Matsuoka Yosuke told a group of Jewish businessmen that he was "the man responsible for the alliance with Hitler, but nowhere have I promised that we would carry out his anti-Semitic policies in Japan. This is not simply my personal opinion, it is the opinion of Japan, and I have no compunction about announcing it to the world."
Pacific War
Attack on Pearl Harbor

After facing an oil embargo by the United States and its own reserve oil supply about to run short, the Japanese government decided to take action and planned to execute a plan developed by the military branch largely lead by Osami Nagano and Isoroku Yamamoto to bomb the United States naval base in Hawaii and therefore bringing the United States to World War 2 on the side of Allies. On 4 September 1941, the Japanese Cabinet met to consider the war plans prepared by Imperial General Headquarters, and decided:
Our Empire, for the purpose of self-defence and self-preservation, will complete preparations for war ... [and is] ... resolved to go to war with the United States, Great Britain and the Netherlands if necessary. Our Empire will concurrently take all possible diplomatic measures vis-a-vis the United States and Great Britain, and thereby endeavor to obtain our objectives ... In the event that there is no prospect of our demands being met by the first ten days of October through the diplomatic negotiations mentioned above, we will immediately decide to commence hostilities against the United States, Britain and the Netherlands.
The Imperial Japanese Navy made its surprise attack on Pearl Harbor, Oahu, Hawaii, on the Sunday morning of December 7, 1941. The Pacific Fleet of the United States Navy and its defending Army Air Forces and Marine air forces sustained significant losses. The primary objective of the attack was to incapacitate the United States long enough for Japan to establish its long-planned Southeast Asian empire and defensible buffer zones. The U.S. public saw the attack as a treacherous act and rallied against the Empire of Japan. The United States entered the European Theatre and Pacific Theater in full force. Four days later Adolf Hitler of Nazi Germany declared war on the United States bringing the separate conflicts into a cohesive conflict.
Battle of Malaya
The Battle of Malaya was a conflict between a Commonwealth army of British, Indian, and Australian forces and Malays from the Federated Malay States, and the Japanese Imperial Army from December 8 1941 until January 31 1942 during the Second World War.
Battle of Singapore

The Battle of Singapore was a battle fought in the South-East Asian theatre of World War II when Imperial Japan invaded the Allied stronghold of Singapore. The fighting in Singapore lasted from February 7, 1942 – February 15 1942 and resulted in the fall of Singapore to the Japanese and the largest surrender of British-led military personnel in history. About 80,000 Indian, Australian and British troops became prisoners of war, joining 50,000 taken in the Japanese invasion of Malaya.
This section needs expansion. You can help by making an edit requestadding to it . |
Burma Campaign
Netherlands East Indies
Battle of the Philippines

Japan launched air raids on US military positions in Philippines following the bombing of Pearl Harbor on December 7 1941, and Japanese troops went ashore in the Philippines on December 10, initiating the Battle of the Philippines. This battle, in turn, encompassed two other battles, the Battle of Bataan and the Battle of Corregidor. By January of 1942 General Douglas MacArthur and President Manuel Quezon were forced to flee in the face of Japanese advances.
In the central part of the Philippines, the province of Negros, the Japanese advanced and took over Bacolod City. The high commanding Japapese Generals established their foothold and seat-of-power at Burgos St., Bacolod City and seized the Mariano Ramos Ancestral House for their headquarters and used it as a watchtower.
This marked among one of the worst defeats in American military history and left over 70,000 American and Filipino prisoners of war in the custody of the Japanese. Ten thousand of these prisoners later died on the Bataan Death March, known as Batān Shi no Kōshin in Japanese.
Imperial Japanese military rule lasted over two years. It was marked by the resistance of several guerrilla armies and the incredible sufferings of the Philippine population.
The guerrilla forces were joined by General MacArthur and troops on 19 October 1944, and the Philippines campaign of 1944–1945 was largely successful. Fighting ended with the signing of the Japanese Instrument of Surrender on 2 September 1945.
Battle for Australia

The two Japanese air raids on Darwin, on February 19 1942 were by far the biggest ever attack by a foreign power against the Australian mainland. They were also a significant action in the Pacific campaign of World War II and represented a major psychological blow to the Australian population, several weeks after hostilities with Japan had begun. The raids were the first of about 100 air raids against Australia during 1942 and 1943.
This event is often called the "Pearl Harbor of Australia"[citation needed]. Although it was a relatively less significant target, a greater number of bombs were dropped on Darwin than were used in the attack on Pearl Harbor. As was the case at Pearl Harbor, the Australian town was unprepared, and although it came under attack from the air another 63 times in 1942 and 1943, the raids on February 19 were massive and devastating by comparison.
War crimes
Many political and military Japanese leaders were convicted for war crimes before the Tokyo tribunal and other allies tribunals in Asia. However, all members of the imperial family implicated in the war, such as emperor Showa and his brothers, cousins and uncles such as Prince Chichibu, Prince Hiroyasu Fushimi and Prince Asaka, were exonerated from criminal prosecutions by Douglas MacArthur.
Unit 731
Unit 731 was a covert medical experiment unit of the Imperial Japanese Army, researching biological warfare through human experiments during the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937 to 1945) and World War II. Disguised as a water purification unit, it was based in the Pingfang district of the northeast Chinese city of Harbin, part of the puppet state of Manchukuo. Unit 731 was officially known as the "Kempeitai Political Department and Epidemic Prevention Research Laboratory".
As many as ten thousand people, both civilian and military, of Chinese, Mongol, and Soviet origin were subjects of experimentation by Unit 731. Some Allied prisoners of war also died at the hands of Unit 731. In addition, Unit 731's biological weapons research resulted in tens of thousands of deaths in China – possibly as many as 200,000 casualties by some estimates.
Unit 731 was one of many units used by the Japanese to research biological warfare; other units include Unit 516 (Qiqihar), Unit 543 (Hailar), Unit 773 (Songo unit), Unit 100 (Changchun), Unit 1644 (Nanjing), Unit 1855 (Beijing), Unit 8604 (Guangzhou), Unit 200 (Manchuria) and Unit 9420 (Singapore).
Many of the scientists involved in Unit 731 went on to prominent careers in politics, academia and business. Some were arrested by Soviet forces and tried at the Khabarovsk War Crime Trials; those who surrendered to the Americans, were granted amnesty in exchange for the data collected.
Because of the nature of their experiments and practices, Unit 731's actions are considered war crimes.
Nanking Massacre
The Nanking Massacre, commonly known as "The Rape of Nanking", refers to the most infamous of the war crimes committed by the Japanese military during World War II—acts carried out by Japanese troops in and around Nanjing (then known in English as Nanking), China, after it fell to the Imperial Japanese Army on December 13, 1937. The duration of the massacre is not clearly defined, although the period of carnage lasted well into the next six weeks, until early February 1938.
The extent of the atrocities is debated, with numbers ranging from the claim of the Japanese army at the International Military Tribunal for the Far East that the death toll was military in nature and that "no such atrocities ever occurred", to the Chinese claim of a non-combatant death toll of 300,000. The West has generally tended to adopt the Chinese point-of-view, with many Western sources now quoting 300,000 dead. This is partly due to the commercial success of Iris Chang's "The Rape of Nanking", which set the stage for the debate of the issue in the West; and the existence of extensive photographic records of the mutilated bodies of women and children.
Sook Ching massacre
When the Japanese occupied Singapore, the Japanese military authorities became concerned about the local Chinese population. The Japanese Imperial Army had become aware that the ethnic Chinese had strong loyalties to either the United Kingdom or China, with wealthy Chinese financing Chiang Kai-Shek's effort in the Second Sino-Japanese War, after Japan had invaded China on July 1937, with other charity drives. The military authorities, led by General Tomoyuki Yamashita, decided on a policy of "eliminating" the anti-Japanese elements.
Soon after the fall of Singapore, Lieutenant-Colonel Masayuki Oishi, commander of No. 2 Field Kempeitai, took over the offices of the Supreme Court building. Singapore was broken up into sectors, each placed under the control of a Kempeitai officer. The Japanese set up designated "screening centers" all over the colony. The blueprint was to gather and screen all Chinese males between 18 to 50 years old, and eliminate those thought to be anti-Japanese. The ones who passed the "screening" would receive a piece of paper with "Examined" written on it, or have a square ink mark on their arms and shirts. Those who did not pass the "screening" would be stamped with triangular marks. There were trucks near these screening centers to send those anti-Japanese elements to their deaths. The Japanese Army chose remote sites such as Changi, Punggol, Blakang Mati and Bedok to perform the executions, with the victims thrown overboard off boats or machine-gunned to death off the harbour.
Comfort Women
Japanese: 慰安婦 The term "comfort women" pertains to women and girls who served as prostitutes during the Imperial Era of Japan. Many historians believe that an estimated 200,000 women were taken as comfort women during the reign.[3] Most of the women were believed to be from Korea, with the a good percentage also from China and also other populations in the Greater East Asia Co-prosperity Sphere. Some Japanese historians debated the fact that Japan had actually forced or kidnapped women from other nations into sexual slavery. Evidence that disputes that comes in forms of personal testimonies of living former sex slaves, witnesses, and actual former Imperial Soldiers. While historians and politicians such as Abe dispute that there was an actual coercion of foreign women into slavery, Japanese documents in 1992 and 2007 were found supporting the coercion of women into sexual slavery.[4]
Path to defeat and defeat
Significant defeats

Japanese military strategists were keenly aware of the unfavorable discrepancy between the industrial potential of the Japanese Empire and that of the United States. Because of this they reasoned that Japanese success hinged on their ability to extend the strategic advantage gained at Pearl Harbor with additional strategic victories. Only decisive destruction of the United States' Pacific Fleet and conquest of its remote outposts would insure that the Japanese Empire was not overwhelmed by America's industrial might. In May of 1942, failure to decisively defeat the Allies at the Battle of Coral Sea in spite of Japanese numerical superiority equated to a strategic defeat for Imperial Japan. This setback was followed in June of 1942 by the catastrophic loss of a four carrier task force at the Battle of Midway. Midway was a decisive defeat for the Imperial Japanese Navy, and proved the turning point for the war. Further defeats by the Allies at Guadalcanal in September 1942, and New Guinea in 1943 put the Empire of Japan on the defensive for the remainder of the war. By 1944 the Allies had seized or bypassed and neutralized many of Japan's strategic bases through amphibious landings and bombardment. This, coupled with the losses inflicted by allied submarines on Japanese shipping routes began to strangle Japan's economy and undermine its ability to supply its army. By early 1945 the US Marines had wrested control of the Ogasawa Islands in several hard-fought battles such as the Battle of Iwo Jima, marking the beginning of the fall of the islands of Japan.
Kamikaze attacks

During 1943 and 1944, Allied forces, backed by the industrial might and rich resources of the United States, were advancing steadily towards Japan. Commander Asaiki Tamai asked a group of 23 talented student pilots, whom he had personally trained, to volunteer for the special attack force. All of the pilots raised both of their hands, thereby volunteering to join the operation. Later, Tamai asked Lieutenant Yukio Seki to command the special attack force. Seki is said to have closed his eyes, lowered his head and thought for ten seconds, before asking Tamai: "please let me do that". Seki thereby became the 24th kamikaze or suicide pilot to be chosen.
Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki

After securing airfields in Saipan and Guam in the summer of 1944, the United States undertook an aggressive campaign of carpet bombing Japanese cities in an effort to pulverize Japan's industry and shatter its morale. While these campaigns led to the deaths of hundreds of thousands of civilians they did not succeed in persuading the Japanese to surrender. In the summer of 1945, the United States dropped two nuclear weapons on Japan. The atomic bombing was the first and last used against another nation. These bombs killed around 100,000 to 200,000 people in a matter of minutes, and many more people died as a result of nuclear radiation in the following weeks, months, and years.
Defeat and surrender

Having ignored (mokusatsu) the Potsdam Declaration, the Empire of Japan surrendered and ended World War 2, after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and a declaration of war by the Soviet Union. In a national radio address of 15th August, emperor Showa announced the surrender to the Japanese people.
Regime change
A period known as Occupied Japan followed after the war largely spearheaded by United States General of the Army Douglas McArthur to revize the Japanese constitution and de-militarize Japan. The American occupation, with economic and political assistance, continued well into the 1950s. After the dissolution of the Empire of Japan, Japan adopted a parliamentary-based political system, with the Emperor changed to symbolic status.
American General of the Army Douglas MacArthur later commended the new Japanese government that he helped established and the new Japanese period when he was about to sent the American forces to the Korean War:
The Japanese people, since the war, have undergone the greatest reformation recorded in modern history. With a commendable will, eagerness to learn, and marked capacity to understand, they have, from the ashes left in war's wake, erected in Japan an edifice dedicated to the supremacy of individual liberty and personal dignity; and in the ensuing process there has been created a truly representative government committed to the advance of political morality, freedom of economic enterprise, and social justice. Politically, economically, and socially Japan is now abreast of many free nations of the earth and will not again fail the universal trust... I sent all four of our occupation divisions to the Korean battlefront without the slightest qualms as to the effect of the resulting power vacuum upon Japan. The results fully justified my faith. I know of no nation more serene, orderly, and industrious, nor in which higher hopes can be entertained for future constructive service in the advance of the human race.
This section needs expansion. You can help by making an edit requestadding to it . |
Prominent political leaders
In the administration of Japan dominated by the Army political movement during World War II, the civil central government was under the management of military men and their right-wing civilian allies, along with members of the nobility and Imperial Family.
The Emperor was in the center of this power structure as supreme Commander-in-Chief of the Imperial Armed Forces, head of state, representative of the "Imperial Sun Lineage" for State Shinto, and chief of the Imperial Household.
Other important institutions linking to the government were the National Youth Association and the "political sections" of the Kempeitai and Tokeitai. These secret societies were a source of loyalists. Other allied groups included residents' committees, the government trade union, local farmers associations, and the state religious and educational systems. Imperial Armed Forces political sections supported the formation of similar right-wing movements in all the occupied lands of the early Pacific War.
The rivalties between the Army and Navy became the principal right-wing political movement in the Empire of Japan in the 1930s, the two factions emerged as leaders among many similar groups and secret societies.



Prominent military personnel
The military of Imperial Japan was divided into two main branches under Imperial General Headquarters responsible for the overall conduct of operations including prominent military leaders and commanders:
- Prominent generals and leaders:
- Imperial Japanese Navy: Navy of Japan
- Admiral Count Sukeyuki Ito (1843–1914)
- Admiral Viscount Yoshika Inoue (1845–1929)
- Admiral Marquis Heihachiro Togo (1847–1934)
- Admiral Prince Takahito Arisugawa (1862–1913)
- Admiral Baron Goro Ijuin (1852–1921)
- Admiral Prince Yorihito Higashi-Fushimi (1867–1922)
- Admiral Baron Hayao Shimamura (1858–1923)
- Admiral Baron Tomozaburo Kato (1861–1923)
- Admiral Prince Hiroyasu Fushimi (1876–1946)
- Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto (1884–1943) Battle of Midway, Attack on Pearl Harbor
- Admiral Osami Nagano (1880–1947)
- Admiral Mineichi Koga (1885–1944)
- Vice Admiral Chuichi Nagumo: Battle of Midway, Attack on Pearl Harbor
- Imperial Japanese Navy: Navy of Japan
- Imperial Japanese Army: Army of Japan
- Kotohito Kan'in: Chief of staff of the Army
- Hajime Sugiyama: Chief of staff of the Army
- Iwane Matsui: Second Sino-Japanese War
- Shunroku Hata: Commander of the expeditionary army in China
- Yasuji Okamura: Commander of the Sanko sakusen
- Tadamichi Kuribayashi: Battle of Iwo Jima
- Kuniaki Koiso: Prime Minister of Japan
- Hideki Tojo: Prime Minister of Japan
- Mitsuru Ushijima: Battle of Okinawa
- Imperial Japanese Army: Army of Japan
Timeline
- 1926: Emperor Taishō dies (December 25).
- 1927: Tanaka Giichi becomes prime minister (April 20).
- 1928: Emperor Shōwa is formally installed as emperor (November 10).
- 1929: Hamaguchi Osachi becomes prime minister (July 2).
- 1930: Hamaguchi is wounded in an assassination attempt (November 14).
- 1931: Hamaguchi dies and Wakatsuki Reijiro becomes prime minister (April 14). Japan occupies Manchuria after the Mukden Incident (September 18). Inukai Tsuyoshi becomes prime minister (December 13) and increases funding for the military in China.
- 1932: After an attack on Japanese monks in Shanghai (January 18), Japanese forces shell the city (January 29). Manchukuo is established with Henry Pu Yi as emperor (February 29). Inukai is assassinated during a coup attempt and Saito Makoto becomes prime minister (May 15). Japan is censured by the League of Nations (December 7).
- 1933: Japan leaves the League of Nations (March 27).
- 1934: Okada Keisuke becomes prime minister (July 8). Japan withdraws from the Washington Naval Treaty (December 29).
- 1936: Coup attempt (February 26 Incident). Hirota Koki becomes prime minister (March 9). Japan signs its first pact with Germany (November 25) and occupies Tsingtao (December 3). Mengchiang established in Inner Mongolia.
- 1937: Hayashi Senjuro becomes prime minister (February 2). Prince Konoe Fumimaro becomes prime minister (June 4). Battle of Lugou Bridge (July 7). Japan captures Beijing (July 31). Japanese troops occupy Nanjing (December 13), beginning the Nanjing massacre.
- 1938: Battle of Taierzhuang (March 24). Canton falls to Japanese forces (October 21).
- 1939: Hiranuma Kiichiro becomes prime minister (January 5). Abe Nobuyuki becomes prime minister (August 30).
- 1940: Yonai Mitsumasa becomes prime minister (January 16). Konoe becomes prime minister for a second term (July 22). Hundred Regiments Offensive (August–September). Japan occupies Indochina in the wake of the fall of Paris, and signs the Tripartite Pact (September 27).
- 1941: General Tojo Hideki becomes prime minister (October 18). Japanese naval forces attack Pearl Harbor, Hawaii (December 7), prompting the United States to declare war on Japan (December 8). Japan conquers Hong Kong (December 25).
- 1942: Singapore surrenders to Japan (February 15). Japan bombs Australia (February 19). Doolittle Raid on Tokyo (April 18). Battle of the Coral Sea (May 4–May 8). U.S. and Filipino forces in the Battle of the Philippines (1942) surrender (May 8). Japan defeated at the Battle of Midway (June 6). Allied victory in the Battle of Milne Bay (September 5).
- 1943: Allied victory in Battle of Guadalcanal (February 9). Japan defeated at Battle of Tarawa (November 23).
- 1944: Tojo resigns and Koiso Kuniaki becomes prime minister (July 22).
- 1945: U.S. bombers begin firebombing of major Japanese cities. Japan defeated at Battle of Iwo Jima (March 26). Admiral Suzuki Kantaro becomes prime minister (April 7). Japan defeated at Battle of Okinawa (June 21). U.S. drops atomic bombs on Hiroshima (August 6) and Nagasaki (August 9). Japan surrenders (August 14): Allied occupation begins.
Emperors of the Empire of Japan
| Posthumous name1 | Given name² | Childhood name³ | Period of Reigns | Era name4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meiji Tennō (明治天皇) |
Mutsuhito (睦仁) |
Sachi-no-miya (祐宮) |
1867–1912 (1890-1912)5 |
Meiji | |
| Taishō Tennō (大正天皇) |
Yoshihito (嘉仁) |
Haru-no-miya (明宮) |
1912–1926 | Taishō | |
| Shōwa Tennō (昭和天皇) |
Hirohito (裕仁) |
Michi-no-miya (迪宮) |
1926–1989 (1926–1947)6 |
Shōwa | |
| 1 Each posthumous name was given after the respective era names as Ming and Qing Dynasties of China. | |||||
| 2 The Japanese imperial family name has no surname or dynastic name. | |||||
| 3 The Meiji Emperor was known only by the appellation Sachi-no-miya from his birth until 11 November 1860, when he was proclaimed heir apparent to Emperor Kōmei and received the personal name Mutsuhito . | |||||
| 4 No multiple era names were given for each reign after Meiji Emperor. | |||||
| 5 Constitutionally. | |||||
| 6 Constitutionally. The reign of the Shōwa Emperor in fact continued until 1989 since he did not abdicate after World War II. | |||||
This period includes the Meiji Era, the Taishō Era, and a part of the Shōwa Era.
< Edo period | History of Japan | Post-Occupation Japan >
Notes
- ^ http://history.hanover.edu/texts/1889con.html - The Constitution of the Empire of Japan(1889)
- ^ http://www.calvin.edu/academic/cas/gpa/japan.htm
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]

