Caucasian race: Difference between revisions
Reverted to revision 931012222 by Charles Matthews (talk): Redundant link (TW) |
MomotaniSS (talk | contribs) Reworded to fit study, clean up, another study Tags: nowiki added Visual edit |
||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
In the 19th century ''[[Meyers Konversations-Lexikon]]'' (1885–90), Caucasoid was one of the three great races of humankind, alongside [[Mongoloid race|Mongoloid]] and [[Negroid race|Negroid]]. The taxon was taken to consist of a number of subtypes. The Caucasoid peoples were usually divided into three groups on ethnolinguistic grounds, termed [[Aryan race|Aryan]] ([[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]]), [[Semitic race|Semitic]] ([[Semitic languages]]), and [[Hamitic race|Hamitic]] (Hamitic languages i.e. [[Berber languages|Berber]]-[[Cushitic languages|Cushitic]]-[[Egyptian language|Egyptian]]).<ref>''[[Meyers Konversations-Lexikon]]'', 4th edition, 1885–90, T11, p. 476.</ref> |
In the 19th century ''[[Meyers Konversations-Lexikon]]'' (1885–90), Caucasoid was one of the three great races of humankind, alongside [[Mongoloid race|Mongoloid]] and [[Negroid race|Negroid]]. The taxon was taken to consist of a number of subtypes. The Caucasoid peoples were usually divided into three groups on ethnolinguistic grounds, termed [[Aryan race|Aryan]] ([[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]]), [[Semitic race|Semitic]] ([[Semitic languages]]), and [[Hamitic race|Hamitic]] (Hamitic languages i.e. [[Berber languages|Berber]]-[[Cushitic languages|Cushitic]]-[[Egyptian language|Egyptian]]).<ref>''[[Meyers Konversations-Lexikon]]'', 4th edition, 1885–90, T11, p. 476.</ref> |
||
19th century [[Racial groups in India (historical definitions)|classifications of the peoples of India]] considered the [[Dravidians]] of non-Caucasoid stock as ''[[Australoid]]'' or a separate ''Dravida'' race, and assumed a gradient of [[miscegenation]] of high-caste Caucasoid ''[[Aryan race|Aryans]]'' and indigenous Dravidians. [[Carleton S. Coon]] in his 1939 book ''[[The Races of Europe (1939 book)|''The Races of Europe'']]'', described the Veddoid race as "possess[ing] an obvious relationship with the aborigines of Australia, and possibly a less patent one with the [[Negrito]]s" and as "the most important element in the Dravidian-speaking population of southern India".<ref>[http://www.theapricity.com/snpa/chapter-XI6.htm The Veddoid periphery, Hadhramaut to Baluchistan]</ref> In his later ''The Living Races of Man'' (1965), Coon considerably amended his views, acknowledging that "India is the easternmost outpost of the Caucasoid racial region". However, he still recognized an Australoid substrate throughout the |
19th century [[Racial groups in India (historical definitions)|classifications of the peoples of India]] considered the [[Dravidians]] of non-Caucasoid stock as ''[[Australoid]]'' or a separate ''Dravida'' race, and assumed a gradient of [[miscegenation]] of high-caste Caucasoid ''[[Aryan race|Aryans]]'' and indigenous Dravidians. [[Carleton S. Coon]] in his 1939 book ''[[The Races of Europe (1939 book)|''The Races of Europe'']]'', described the Veddoid race as "possess[ing] an obvious relationship with the aborigines of Australia, and possibly a less patent one with the [[Negrito]]s" and as "the most important element in the Dravidian-speaking population of southern India".<ref>[http://www.theapricity.com/snpa/chapter-XI6.htm The Veddoid periphery, Hadhramaut to Baluchistan]</ref> In his later ''The Living Races of Man'' (1965), Coon considerably amended his views, acknowledging that "India is the easternmost outpost of the Caucasoid racial region". However, he still recognized an Australoid substrate throughout the southern tribals, writing that "the earliest peoples who have left recognizable survivors were both Caucasoid and Australoid food gatherers. Some of the survivors are largely Caucasoid; others are largely Australoid."<ref>{{cite book|last1=Coon|first1=Carleton|title=The Living Races of Man|date=1966|publisher=Knopf|pages=207–208|url=https://archive.org/stream/in.ernet.dli.2015.533641/2015.533641.living-races#page/n241/mode/2up|accessdate=28 December 2017}}</ref> [[Sinhalese people|Sinhalese]] (Indo Aryan) population of [[Sri Lanka]] who were marked as uncertain in his first study due to lack of details were also reidentified as a Predominantly Mediterranean Caucasian race who are descending from early Northern Indian [[Indo Aryan]] settlers of the Island. |
||
Reich et al. (2009) discerned two major ancestral components in India,{{sfn|Reich et al.|2009}}{{sfn|Metspalu et al.|2011}}{{sfn|Moorjani et al.|2013}} namely the ''Ancestral North Indians'' (ANI) which is "genetically close to Middle Easterners, Central Asians, and Europeans," (groups considered to be "Caucasoid") and the ''Ancestral South Indians'' (ASI) which is clearly distinct from ANI{{sfn|Reich et al.|2009}} and "not closely related to groups outside the subcontinent." The ASI population is suggested to be closer to [[Andamanese]] peoples than to other populations, but nevertheless distinct from and not closely related to them.{{sfn|Moorjani|2013}} According to Basu et al. (2016), the ASI are earliest settlers in India, possibly arriving on the [[Peopling of the world|southern exit]] wave out of Africa.{{sfn|Basu|2016}} These two groups mixed in India between 4,200 and 1,900 years ago (2200 BCE-100 CE), whereafter a shift to endogamy took place,{{sfn|Moorjani et al.|2013}} possibly by the enforcement of "social values and norms" by the "Hindu Gupta rulers."{{sfn|Basu et al.|2016|p=1598}} |
Reich et al. (2009) discerned two major ancestral components in India,{{sfn|Reich et al.|2009}}{{sfn|Metspalu et al.|2011}}{{sfn|Moorjani et al.|2013}} namely the ''Ancestral North Indians'' (ANI) which is "genetically close to Middle Easterners, Central Asians, and Europeans," (groups considered to be "Caucasoid") and the ''Ancestral South Indians'' (ASI) which is clearly distinct from ANI{{sfn|Reich et al.|2009}} and "not closely related to groups outside the subcontinent." The ASI population is suggested to be closer to [[Andamanese]] peoples than to other populations, but nevertheless distinct from and not closely related to them.{{sfn|Moorjani|2013}} According to Basu et al. (2016), the ASI are earliest settlers in India, possibly arriving on the [[Peopling of the world|southern exit]] wave out of Africa.{{sfn|Basu|2016}} These two groups mixed in India between 4,200 and 1,900 years ago (2200 BCE-100 CE), whereafter a shift to endogamy took place,{{sfn|Moorjani et al.|2013}} possibly by the enforcement of "social values and norms" by the "Hindu Gupta rulers."{{sfn|Basu et al.|2016|p=1598}} |
||
According to a large craniometric study (Raghavan and Bulbeck et al. 2013) the native populations of South Asia ([[India]] |
According to a large craniometric study (Raghavan and Bulbeck et al. 2013) the native populations of South Asia ([[India]]<nowiki/>and [[Sri Lanka]]) have distinct craniometric and anthropologic ancestry. Both southern and northern groups are most similar to each other and have generally closer affinities to various "[[Caucasoid]]" groups. The study further showed that the native South Asians (including the [[Vedda]]) form a distinct group and are not morphologically aligned to "[[Australoid]]" or "[[Negrito]]" groups. The authors state: "''If there were an Australoid “substratum” component to Indians’ ancestry, we would expect some degree of craniometric similarity between Howells’ Southwest Pacific series and Indians. But in fact, the Southwest Pacific and Indian are craniometrically very distinct, falsifying any claim for an Australoid substratum in India.''".<ref>{{Cite journal|title=Indian Craniometric Variability and Affinities|volume=2013|pages=836738|last=Rathee|first=Suresh Kanta|last2=Pathmanathan|first2=Gayathiri|date=2013|journal=International Journal of Evolutionary Biology|language=en|pmid=24455409|pmc=3886603|last3=Bulbeck|first3=David|last4=Raghavan|first4=Pathmanathan|doi=10.1155/2013/836738}}</ref> |
||
There was no universal consensus of the validity of the "Caucasoid" grouping within those who attempted to categorize human variation. [[Thomas Henry Huxley]] in 1870 wrote that the "absurd denomination of 'Caucasian'" was in fact a conflation of his [[Xanthochroi]] (Nordic) and [[Melanochroi]] (Mediterranean) types.<ref>T. H. Huxley, ''On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind'', Journal of the Ethnological Society of London (1870).</ref> |
There was no universal consensus of the validity of the "Caucasoid" grouping within those who attempted to categorize human variation. [[Thomas Henry Huxley]] in 1870 wrote that the "absurd denomination of 'Caucasian'" was in fact a conflation of his [[Xanthochroi]] (Nordic) and [[Melanochroi]] (Mediterranean) types.<ref>T. H. Huxley, ''On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind'', Journal of the Ethnological Society of London (1870).</ref> |
||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
Although Brace (1990) rejected a Caucasoid origin for the Jomon people and said that the Jōmon share many physical characteristics with Caucasians but are a separate genetic stock, a craniometric study by Brace et al. 2001 suggests not only morphological affinities to [[Caucasoid]]s, but also possible genetic ties at one time (Pleistocene). The study results show a closer morphological relation between Ainu (including other Jōmon remnants) and [[West Asian]]s rather than between Ainu and [[East Asian]]s. The study concluded that the Ainu can be described as "Eurasians".<ref>Old World sources of the first New World human inhabitants: A comparative craniofacial view - C. Loring Brace*†, A. Russell Nelson*‡, Noriko Seguchi*, Hiroaki Oe§, Leslie Sering*, Pan Qifeng¶, Li Yongyii , and Dashtseveg Tumen** *Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan, 1109 Geddes Avenue, Ann Arbor, MI 48109; ‡Department of Anthropology, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY 82071; §Department of Statistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109; ¶Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, 27 Wangfujing Dajie, Beijing 100710, China; i Department of Anatomy, Chengdu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 13 Xing Lo Road, Chengdu, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China; and **Department of Anthropology, Mongolian Academy of Sciences, Ulaanbaatar-51, Mongolia Communicated by Kent V. Flannery, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, June 18, 2001 (received for review January 2, 2001) (https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/98/17/10017.full.pdf)</ref>{{Quote|text="The fact that Late Pleistocene populations in northwest Europe and northeast Asia show morphological similarities suggests that there may have been actual genetic ties at one time. Those morphological similarities can still be shown between Europe and the descendants of the aboriginal population of the Japanese archipelago, i.e., the Ainu.|sign=Brace et al. 2001|source=Old World sources of the first New World human |
Although Brace (1990) rejected a Caucasoid origin for the Jomon people and said that the Jōmon share many physical characteristics with Caucasians but are a separate genetic stock, a craniometric study by Brace et al. 2001 suggests not only morphological affinities to [[Caucasoid]]s, but also possible genetic ties at one time (Pleistocene). The study results show a closer morphological relation between Ainu (including other Jōmon remnants) and [[West Asian]]s rather than between Ainu and [[East Asian]]s. The study concluded that the Ainu can be described as "Eurasians".<ref>Old World sources of the first New World human inhabitants: A comparative craniofacial view - C. Loring Brace*†, A. Russell Nelson*‡, Noriko Seguchi*, Hiroaki Oe§, Leslie Sering*, Pan Qifeng¶, Li Yongyii , and Dashtseveg Tumen** *Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan, 1109 Geddes Avenue, Ann Arbor, MI 48109; ‡Department of Anthropology, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY 82071; §Department of Statistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109; ¶Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, 27 Wangfujing Dajie, Beijing 100710, China; i Department of Anatomy, Chengdu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 13 Xing Lo Road, Chengdu, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China; and **Department of Anthropology, Mongolian Academy of Sciences, Ulaanbaatar-51, Mongolia Communicated by Kent V. Flannery, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, June 18, 2001 (received for review January 2, 2001) (https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/98/17/10017.full.pdf)</ref>{{Quote|text="The fact that Late Pleistocene populations in northwest Europe and northeast Asia show morphological similarities suggests that there may have been actual genetic ties at one time. Those morphological similarities can still be shown between Europe and the descendants of the aboriginal population of the Japanese archipelago, i.e., the Ainu.|sign=Brace et al. 2001|source=Old World sources of the first New World human |
||
inhabitants: A comparative craniofacial view}}Hideo Matsumoto (2009) concluded that [[South Asian ethnic groups|populations in India and nearby regions]] are basically Caucasoid while some have a minor [[Mongoloid]] admixture. Similarly [[Iranian peoples]] in Central Asia, such as [[Tajiks in Uzbekistan]] and [[Tajiks of Xinjiang]] are basically Caucasoid with a minor Mongoloid admixture.<ref name="Matsumoto2009">Matsumoto, H. (2009). The origin of the Japanese race based on genetic markers of immunoglobulin G. ''Proceedings of the Japan Academy, (85)''2. Pages 69, 72, 74 & 75. [https://web.archive.org/web/20190805200205/https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/pjab/85/2/85_2_69/_pdf Wayback Machine link].</ref> |
inhabitants: A comparative craniofacial view}}Hideo Matsumoto (2009) concluded that [[South Asian ethnic groups|populations in India and nearby regions]] are basically Caucasoid while some have a minor [[Mongoloid]] admixture. Similarly [[Iranian peoples]] in Central Asia, such as [[Tajiks in Uzbekistan]] and [[Tajiks of Xinjiang]] are basically Caucasoid with a minor Mongoloid admixture.<ref name="Matsumoto2009">Matsumoto, H. (2009). The origin of the Japanese race based on genetic markers of immunoglobulin G. ''Proceedings of the Japan Academy, (85)''2. Pages 69, 72, 74 & 75. [https://web.archive.org/web/20190805200205/https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/pjab/85/2/85_2_69/_pdf Wayback Machine link].</ref> |
||
A genetic and biogeographical study (Das et al. 2016) resulted in support for a [[Caucasoid]] origin of proto-Dravidians (or that most of the first population wave into India was Caucasoid).<ref name=":0">{{cite web|url=https://www.biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2016/11/25/089466.full.pdf|title=Tracing the biogeographical origin of South Asian populations using DNA SatNav|url-status=live|archive-url=|archive-date=|access-date=|quote=Our hypothesis is supported by archaeological, linguistic and genetic evidences that suggest that there were two prominent waves of immigrations to India. A majority of the Early Caucasoids were proto-Dravidian language speakers that migrated to India putatively ~ 6000 YBP.|vauthors=Das R, Upadhyai P}}</ref> |
|||
===Subraces=== |
===Subraces=== |
||
| Line 138: | Line 140: | ||
According to geneticist [[David Reich (geneticist)|David Reich]], based on [[Ancient DNA|ancient human genomes]] that his laboratory sequenced in 2016, ancient West Eurasians descend from a mixture of as few as four ancestral components related to the [[Eurasian Steppe|Eastern Hunter Gatherers]] (EHG), the [[Prehistory of Iran|Neolithic Iran]], the [[Pre-Pottery Neolithic B|Neolithic Levant]] and [[Natufian culture#Genetics|Natufians]], and the [[Karsdorf remains|Western Hunter Gatherers]] (WHG):<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Iosif Lazaridis|display-authors=et al|title=Genomic insights into the origin of farming in the ancient Near East|journal=Nature|date=2016|volume=536|issue=7617|pages=419–424|url=https://estudogeral.sib.uc.pt/bitstream/10316/45861/1/cias2016_40.pdf|accessdate=18 April 2018|quote=bottom-left: Western Hunter Gatherers (WHG), top-left: Eastern Hunter Gatherers (EHG), bottom-right: Neolithic Levant and Natufians, top-right: Neolithic Iran. This suggests the hypothesis that diverse ancient West Eurasians can be modelled as mixtures of as few as four streams of ancestry related to these population|bibcode=2016Natur.536..419L|doi=10.1038/nature19310|pmid=27459054|pmc=5003663}}</ref> As one editorial opinion expressed it: |
According to geneticist [[David Reich (geneticist)|David Reich]], based on [[Ancient DNA|ancient human genomes]] that his laboratory sequenced in 2016, ancient West Eurasians descend from a mixture of as few as four ancestral components related to the [[Eurasian Steppe|Eastern Hunter Gatherers]] (EHG), the [[Prehistory of Iran|Neolithic Iran]], the [[Pre-Pottery Neolithic B|Neolithic Levant]] and [[Natufian culture#Genetics|Natufians]], and the [[Karsdorf remains|Western Hunter Gatherers]] (WHG):<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Iosif Lazaridis|display-authors=et al|title=Genomic insights into the origin of farming in the ancient Near East|journal=Nature|date=2016|volume=536|issue=7617|pages=419–424|url=https://estudogeral.sib.uc.pt/bitstream/10316/45861/1/cias2016_40.pdf|accessdate=18 April 2018|quote=bottom-left: Western Hunter Gatherers (WHG), top-left: Eastern Hunter Gatherers (EHG), bottom-right: Neolithic Levant and Natufians, top-right: Neolithic Iran. This suggests the hypothesis that diverse ancient West Eurasians can be modelled as mixtures of as few as four streams of ancestry related to these population|bibcode=2016Natur.536..419L|doi=10.1038/nature19310|pmid=27459054|pmc=5003663}}</ref> As one editorial opinion expressed it: |
||
<blockquote>[W]hatever we currently believe about the genetic nature of differences among populations is most likely wrong... "[W]hites" are not derived from a population that existed from time immemorial, as some people believe. Instead "whites" represent a mixture of four ancient populations that lived 10,000 years ago and were each as different from one another as Europeans and East Asians are today.<ref>Editors (March 23, 2018) [https://www.nytimes.com/2018/03/23/opinion/sunday/genetics-race.html "How Genetics Is Changing Our Understanding of 'Race'" (editorial)], ''[[The New York Times]]''</ref></blockquote> |
<blockquote>[W]hatever we currently believe about the genetic nature of differences among populations is most likely wrong... "[W]hites" are not derived from a population that existed from time immemorial, as some people believe. Instead "whites" represent a mixture of four ancient populations that lived 10,000 years ago and were each as different from one another as Europeans and East Asians are today.<ref>Editors (March 23, 2018) [https://www.nytimes.com/2018/03/23/opinion/sunday/genetics-race.html "How Genetics Is Changing Our Understanding of 'Race'" (editorial)], ''[[The New York Times]]''</ref></blockquote>A recent genetic study published in the "''European Journal of Human Genetics"''in [[Nature (journal)|Nature]] (2019) showed that populations such as West Asians (Arabs), Europeans, Northern Africans, South Asians (Indians) and some Central Asians are closely related to each other and can be distinguished from Sub-Saharan Africans or East Asian populations.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Pakstis|first=Andrew J.|last2=Gurkan|first2=Cemal|last3=Dogan|first3=Mustafa|last4=Balkaya|first4=Hasan Emin|last5=Dogan|first5=Serkan|last6=Neophytou|first6=Pavlos I.|last7=Cherni|first7=Lotfi|last8=Boussetta|first8=Sami|last9=Khodjet-El-Khil|first9=Houssein|last10=Ben Ammar ElGaaied|first10=Amel|last11=Salvo|first11=Nina Mjølsnes|date=2019-12|title=Genetic relationships of European, Mediterranean, and SW Asian populations using a panel of 55 AISNPs|url=https://www.nature.com/articles/s41431-019-0466-6|journal=European Journal of Human Genetics|language=en|volume=27|issue=12|pages=1885–1893|doi=10.1038/s41431-019-0466-6|issn=1476-5438}}</ref> |
||
==Usage in the United States== |
==Usage in the United States== |
||
Revision as of 17:26, 6 January 2020
It has been suggested that Northcaucasian race be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since November 2019. |
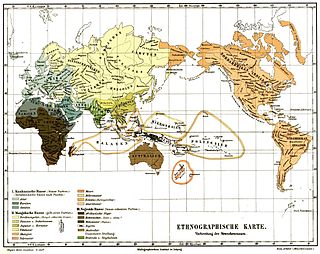
| Caucasoid: Negroid: Uncertain: | Mongoloid: North Mongol |

The Caucasian race (also Caucasoid[1] or Europid)[2] is a grouping of human beings historically regarded as a biological taxon, which, depending on which of the historical race classifications is used, has usually included ancient and modern populations from Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa.[3][4]
First introduced in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen School of History,[5] the term denoted one of three purported major races of humankind (Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Negroid).[6] In biological anthropology, Caucasoid has been used as an umbrella term for phenotypically similar groups from these different regions, with a focus on skeletal anatomy, and especially cranial morphology, without regard to skin tone.[7] Ancient and modern "Caucasoid" populations were thus not exclusively "white," but ranged in complexion from white-skinned to dark brown.[8]
Since the second half of the 20th century, physical anthropologists have moved away from a typological understanding of human biological diversity towards a genomic and population-based perspective, and have tended to understand race as a social classification of humans based on phenotype and ancestry as well as cultural factors, as the concept is also understood in the social sciences.[9] Although Caucasian / Caucasoid and their counterparts Negroid and Mongoloid have been used less frequently as a biological classification in forensic anthropology (where it is sometimes used as a way to identify the ancestry of human remains based on interpretations of osteological measurements), the terms remain in use by some anthropologists.[10]
In the United States, the root term Caucasian is often used, both colloquially and by the US Census Bureau, as a synonym for white. This usage is considered erroneous by anthropologists and other scientists, who note that it conflates an anthropologically valid category (Caucasoid) with the social construct of the "white race". The conflation of Caucasian with white is also demographically misleading since the category Caucasoid has sometimes been considered to include various populations, such as South Asians and North Africans, that are not considered white in a social sense.[11]
Etymology
The traditional anthropological term Caucasoid is a conflation of the demonym Caucasian and the Greek suffix eidos (meaning "form", "shape", "resemblance"), implying a resemblance to the native inhabitants of the Caucasus. In its usage as a racial category, it contrasts with the terms Negroid, Mongoloid, and Australoid.[12]
History of the concept
Christoph Meiners

The term Caucasian originally referred in a narrow sense to the native inhabitants of the Caucasus region.[13] In his The Outline of History of Mankind (1785), the German philosopher Christoph Meiners first used the concept of a "Caucasian" (Kaukasischen) race in its wider racial sense.[5][14][15]
Meiners imagined that the Caucasian race encompassed all of the ancient and most of the modern native populations of Europe, the aboriginal inhabitants of West Asia (including the Phoenicians, Hebrews and Arabs), the autochthones of Northern Africa (Berbers, Egyptians, Abyssinians and neighboring groups), the Indians, and the ancient Guanches.[16]
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach

It was Johann Friedrich Blumenbach, a German professor of medicine and a member of the British Royal Society, and who came to be considered one of the founders of the discipline of anthropology, who gave the term a wider audience, by grounding it in the new methods of craniometry and Linnean taxonomy.[17]
Blumenbach did not credit Meiners with his taxonomy, although his justification clearly points to Meiners' aesthetic viewpoint of Caucasus origins.[18]
In contrast to Meiners, however, Blumenbach was a monogenist – he considered all humans to have a shared origin and to be a single species. Blumenbach, like Meiners, did rank his Caucasian grouping higher than other groups in terms of mental faculties or potential for achievement.[17]
Alongside the anthropologist Georges Cuvier, Blumenbach classified the Caucasian race by cranial measurements and bone morphology in addition to skin pigmentation.[19]
Following Meiners, Blumenbach described the Caucasian race as consisting of the native inhabitants of Europe, West Asia, the Indian peninsula, and North Africa, including toward the south the Moors, Abyssinians and adjacent groups.
Carleton Coon

| Caucasoid race | |
| Negroid race | |
| Capoid race | |
| Mongoloid race | |
| Australoid race |
There was never any consensus among the proponents of the concept the existence of a "Caucasoid race" with regard to how it would be delineated from other proposed groups such as the proposed Mongoloid race. Carleton S. Coon (1939) included the populations native to all of Central and Northern Asia, including the Ainu people, under the Caucasoid label. However, many scientists maintained the racial categorizations of color established by Meiners' and Blumenbach's works, along with many other early steps of anthropology, well into the late 19th and mid-to-late 20th centuries, increasingly used to justify political policies, such as segregation and immigration restrictions, and other opinions based in prejudice. For example, Thomas Henry Huxley (1870) classified all populations of Asian nations as Mongoloid. Lothrop Stoddard (1920) in turn classified as "brown" most of the populations of the Middle East, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Central Asia and South Asia. He counted as "white" only European peoples and their descendants, as well as a few populations in areas adjacent to or opposite southern Europe, in parts of Anatolia and parts of the Rif and Atlas mountains.
In 1939 Coon argued that the Caucasian race had originated through admixture between Homo neanderthalensis and Homo sapiens of the "Mediterranean type" which he considered to be distinct from Caucasians, rather than a subtype of it as others had done.[20] While Blumenbach had erroneously thought that light skin color was ancestral to all humans and the dark skin of southern populations was due to sun, Coon thought that Caucasians had lost their original pigmentation as they moved North.[20] Coon used the term "Caucasoid" and "White race" synonymously.[21]
In 1962, Coon published The Origin of Races, wherein he proposed a polygenist view, that human races had evolved separately from local varieties of Homo erectus. Dividing humans into five main races, and argued that each evolved in parallel but at different rates, so that some races had reached higher levels of evolution than others.[9] He argued that the Caucasoid race had evolved 200,000 years prior to the "Congoid race", and hence represented a higher evolutionary stage.[22]
Racial anthropology
Physical traits
Skull and teeth
Drawing from Petrus Camper's theory of facial angle, Blumenbach and Cuvier classified races, through their skull collections based on their cranial features and anthropometric measurements. Caucasoid traits were recognised as: thin nasal aperture ("nose narrow"), a small mouth, facial angle of 100°–90°, and orthognathism, exemplified by what Blumenbach saw in most ancient Greek crania and statues.[23][24] Later anthropologists of the 19th and early 20th century such as Pritchard, Pickering, Broca, Topinard, Morton, Peschel, Seligman, Bean, Ripley, Haddon and Dixon came to recognize other Caucasoid morphological features, such as prominent supraorbital ridges and a sharp nasal sill.[25] Many anthropologists in the 20th century used the term "Caucasoid" in their literature, such as Boyd, Gates, Coon, Cole, Brues and Krantz replacing the earlier term "Caucasian" as it had fallen out of usage.[26]
Caucasoids (including Middle Eastern and South Asian peoples) have small teeth,[27] with the maxillary lateral incisors often shrunken in size or replaced with peg laterals. According to George W. Gill and other modern forensic anthropologists, physical traits of Caucasoid crania can be distinguished from those of the people from Mongoloid and Negroid racial groups based on the shapes of specific diagnostic anatomical features. They assert that they can identify a Caucasoid skull with an accuracy of up to 95%.[28][29][30][31][32] However, Alan H. Goodman cautions that this precision estimate is often based on methodologies using subsets of samples. He also argues that scientists have a professional and ethical duty to avoid such biological analyses since they could potentially have sociopolitical effects.[33]
Variation in craniofacial form between humans has been found to be largely due to differing patterns of biological inheritance. Modern cross-analysis of osteological variables and genome-wide SNPs has identified specific genes, which control this craniofacial development. Of these genes, DCHS2, RUNX2, GLI3, PAX1 and PAX3 were found to determine nasal morphology, whereas EDAR impacts chin protrusion and facial hair, both of which have been recently selected in Caucasians[34][35]
Classification

| Caucasoid: Negroid: Uncertain: | Mongoloid: North Mongol |
In the 19th century Meyers Konversations-Lexikon (1885–90), Caucasoid was one of the three great races of humankind, alongside Mongoloid and Negroid. The taxon was taken to consist of a number of subtypes. The Caucasoid peoples were usually divided into three groups on ethnolinguistic grounds, termed Aryan (Indo-European), Semitic (Semitic languages), and Hamitic (Hamitic languages i.e. Berber-Cushitic-Egyptian).[36]
19th century classifications of the peoples of India considered the Dravidians of non-Caucasoid stock as Australoid or a separate Dravida race, and assumed a gradient of miscegenation of high-caste Caucasoid Aryans and indigenous Dravidians. Carleton S. Coon in his 1939 book The Races of Europe, described the Veddoid race as "possess[ing] an obvious relationship with the aborigines of Australia, and possibly a less patent one with the Negritos" and as "the most important element in the Dravidian-speaking population of southern India".[37] In his later The Living Races of Man (1965), Coon considerably amended his views, acknowledging that "India is the easternmost outpost of the Caucasoid racial region". However, he still recognized an Australoid substrate throughout the southern tribals, writing that "the earliest peoples who have left recognizable survivors were both Caucasoid and Australoid food gatherers. Some of the survivors are largely Caucasoid; others are largely Australoid."[38] Sinhalese (Indo Aryan) population of Sri Lanka who were marked as uncertain in his first study due to lack of details were also reidentified as a Predominantly Mediterranean Caucasian race who are descending from early Northern Indian Indo Aryan settlers of the Island.
Reich et al. (2009) discerned two major ancestral components in India,[39][40][41] namely the Ancestral North Indians (ANI) which is "genetically close to Middle Easterners, Central Asians, and Europeans," (groups considered to be "Caucasoid") and the Ancestral South Indians (ASI) which is clearly distinct from ANI[39] and "not closely related to groups outside the subcontinent." The ASI population is suggested to be closer to Andamanese peoples than to other populations, but nevertheless distinct from and not closely related to them.[42] According to Basu et al. (2016), the ASI are earliest settlers in India, possibly arriving on the southern exit wave out of Africa.[43] These two groups mixed in India between 4,200 and 1,900 years ago (2200 BCE-100 CE), whereafter a shift to endogamy took place,[41] possibly by the enforcement of "social values and norms" by the "Hindu Gupta rulers."[44]
According to a large craniometric study (Raghavan and Bulbeck et al. 2013) the native populations of South Asia (Indiaand Sri Lanka) have distinct craniometric and anthropologic ancestry. Both southern and northern groups are most similar to each other and have generally closer affinities to various "Caucasoid" groups. The study further showed that the native South Asians (including the Vedda) form a distinct group and are not morphologically aligned to "Australoid" or "Negrito" groups. The authors state: "If there were an Australoid “substratum” component to Indians’ ancestry, we would expect some degree of craniometric similarity between Howells’ Southwest Pacific series and Indians. But in fact, the Southwest Pacific and Indian are craniometrically very distinct, falsifying any claim for an Australoid substratum in India.".[45]
There was no universal consensus of the validity of the "Caucasoid" grouping within those who attempted to categorize human variation. Thomas Henry Huxley in 1870 wrote that the "absurd denomination of 'Caucasian'" was in fact a conflation of his Xanthochroi (Nordic) and Melanochroi (Mediterranean) types.[46]
Historically, the racial classification of the Turkic peoples was sometimes given as "Turanid". Turanid racial type or "minor race", subtype of the Europid (Caucasian) race with Mongoloid admixtures, situated at the boundary of the distribution of the Mongoloid and Europid "great races".[47][48]
The Jōmon people of ancient Japan as well as the modern Ainu people are classified as Caucasoid by some anthropologists. Anthropologists like Jantz and Owsley (1997) consider the Ainu as Caucasoid subgroup.[49] Arnold Henry Savage Landor described the Ainu as having deep-set eyes and an eye shape typical of Europeans, with a large and prominent browridge, large ears, hairy and prone to baldness, slightly hook nose with large and broad nostrils, prominent cheek-bones and a medium mouth.[50]
Although Brace (1990) rejected a Caucasoid origin for the Jomon people and said that the Jōmon share many physical characteristics with Caucasians but are a separate genetic stock, a craniometric study by Brace et al. 2001 suggests not only morphological affinities to Caucasoids, but also possible genetic ties at one time (Pleistocene). The study results show a closer morphological relation between Ainu (including other Jōmon remnants) and West Asians rather than between Ainu and East Asians. The study concluded that the Ainu can be described as "Eurasians".[51]
"The fact that Late Pleistocene populations in northwest Europe and northeast Asia show morphological similarities suggests that there may have been actual genetic ties at one time. Those morphological similarities can still be shown between Europe and the descendants of the aboriginal population of the Japanese archipelago, i.e., the Ainu.
— Brace et al. 2001, Old World sources of the first New World human inhabitants: A comparative craniofacial view
Hideo Matsumoto (2009) concluded that populations in India and nearby regions are basically Caucasoid while some have a minor Mongoloid admixture. Similarly Iranian peoples in Central Asia, such as Tajiks in Uzbekistan and Tajiks of Xinjiang are basically Caucasoid with a minor Mongoloid admixture.[52]
A genetic and biogeographical study (Das et al. 2016) resulted in support for a Caucasoid origin of proto-Dravidians (or that most of the first population wave into India was Caucasoid).[53]
Subraces
The postulated subraces vary depending on the author, including but not limited to Mediterranean, Atlantid, Aryan Nordic, East Baltic, Alpine, Dinaric, Turanid, Armenoid, Iranid, Indid, Arabid, and Hamitic.[54]
H. G. Wells argued that across Europe, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, West Asia, Central Asia and South Asia, a Caucasian physical stock existed. He divided this racial element into two main groups: a shorter and darker Mediterranean or Iberian race and a taller and lighter Nordic race. Wells asserted that Semitic and Hamitic populations were mainly of Mediterranean type, and Aryan populations were originally of Nordic type. He regarded the Basques as descendants of early Mediterranean peoples, who inhabited western Europe before the arrival of Aryan Celts from the direction of central Europe.[55]
Origin

Among the earliest anatomically modern human settlements established in Europe were Kostenki-Borshchevo, Voronezh Oblast in southwestern Russia. DNA sequencing of a 37,000-year-old male skeleton from the area, Kostenki XIV or Markina Gora, indicates that these early settlers possessed a similar genetic makeup as modern Europeans, but had dark skin and dark eyes. They also possessed slightly more Neanderthal genes than modern populations in Europe and Asia due to interbreeding with Neanderthals over 45,000 years ago.[56] In a study of Cro-Magnon crania, Jantz and Owsley (2003) have noted that these "Upper Paleolithic crania are, for the most part, larger and more generalized versions of recent Europeans."[57]
William Howells (1997) has argued that Cro-Magnons were Caucasoid based on their cranial traits:
... the Cro-Magnons were already racially European, i.e., Caucasoid. This has always been accepted because of the general appearance of the skulls: straight faces, narrow noses, and so forth. It is also possible to test this arithmetically.... Except for Predmosti 4, which is distant from every present and past population, all of these skulls show themselves to be closer to "Europeans" than to other peoples – Mladec and Abri Pataud comfortably so, the other two much more remotely.[58]
Carleton Coon (1962) argued that Caucasoid traits emerged prior to the Cro-Magnons, and were present in the Skhul and Qafzeh hominids.[59] However, these fossils and the Predmost specimen were held to be Neanderthaloid derivatives because they possessed short cervical vertebrae, lower and narrower pelves, and had some Neanderthal skull traits. Coon further asserted that the Caucasoid race was of dual origin, consisting of early dolichocephalic (e.g. Galley Hill, Combe-Capelle, Téviec) and Neolithic Mediterranean Homo sapiens (e.g. Muge, Long Barrow, Corded), as well as Neanderthal-influenced brachycephalic Homo sapiens dating to the Mesolithic and Neolithic (e.g. Afalou, Hvellinge, Fjelkinge).[60]
More recent osteological analysis of Cro-Magnon fossils indicates that they had larger skulls than modern populations, and possessed a dolichocephalic (long-head) and low cranium, with a wide face. It also suggests that some Cro-Magnons may have had brown skin.[61] The very light skin tone found in modern Northern Europeans is a relatively recent phenomenon.[62] It may have appeared in the European line as recently as 6 to 12 thousand years ago, indicating that Cro-Magnons had brown skin.[63]
According to geneticist David Reich, based on ancient human genomes that his laboratory sequenced in 2016, ancient West Eurasians descend from a mixture of as few as four ancestral components related to the Eastern Hunter Gatherers (EHG), the Neolithic Iran, the Neolithic Levant and Natufians, and the Western Hunter Gatherers (WHG):[64] As one editorial opinion expressed it:
[W]hatever we currently believe about the genetic nature of differences among populations is most likely wrong... "[W]hites" are not derived from a population that existed from time immemorial, as some people believe. Instead "whites" represent a mixture of four ancient populations that lived 10,000 years ago and were each as different from one another as Europeans and East Asians are today.[65]
A recent genetic study published in the "European Journal of Human Genetics"in Nature (2019) showed that populations such as West Asians (Arabs), Europeans, Northern Africans, South Asians (Indians) and some Central Asians are closely related to each other and can be distinguished from Sub-Saharan Africans or East Asian populations.[66]
Usage in the United States
In the United States, the term "Caucasoid" is used in disciplines such as craniometry, epidemiology, forensic medicine, forensic anthropology, and forensic archaeology. It is also associated with notions of racial typology.
Besides its use in anthropology and related fields, the term "Caucasian" has often been used in the United States in a different, social context to describe a group commonly called "white people".[67] "White" also appears as a self-reporting entry in the U.S. Census.[68] Naturalization as a United States citizen was restricted to "free white persons" by the Naturalization Act of 1790, and later extended to other resident populations by the Naturalization Act of 1870, Indian Citizenship Act of 1924 and Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952. The Supreme Court in United States v. Bhagat Singh Thind (1923) decided that Asian Indians were ineligible for citizenship because, though deemed "Caucasian" anthropologically, they were not white like European descendants since most laypeople did not consider them to be "white" people. This represented a change from the Supreme Court's earlier opinion in Ozawa v. United States, in which it had expressly approved of two lower court cases holding "high caste Hindus" to be "free white persons" within the meaning of the naturalization act. Government lawyers later recognized that the Supreme Court had "withdrawn" this approval in Thind.[69] In 1946, the U.S. Congress passed a new law establishing a small immigration quota for Indians, which also permitted them to become citizens. Major changes to immigration law, however, only later came in 1965, when many earlier racial restrictions on immigration were lifted.[70] This resulted in confusion about whether American Hispanics are included as "white", as the term Hispanic originally applied to Spanish heritage but has since expanded to include all people with origins in Spanish speaking countries. In other countries, the term Hispanic is not nearly as associated with race, but with the Spanish language and cultural affiliation.
The United States National Library of Medicine often used the term "Caucasian" as a race in the past. However, it later discontinued such usage in favor of the more narrow geographical term European, which traditionally only applied to a subset of Caucasoids.[71]
See also
- Anthropometry
- Historical race concepts
- Leucism
- Peoples of the Caucasus
- Race and ethnicity in the United States Census
- Race and genetics
References
Notes
- ^ The traditional anthropological term Caucasoid is a conflation of the demonym Caucasian and the Greek suffix eidos (meaning "form", "shape", "resemblance"), implying a resemblance to the native inhabitants of the Caucasus. It etymologically contrasts with the terms Negroid, Mongoloid and Australoid (Freedman, B. J. (1984). "For debate... Caucasian". British Medical Journal. 288 (6418). Routledge: 696–98. doi:10.1136/bmj.288.6418.696. PMC 1444385. PMID 6421437.) For a contrast with the "Mongolic" or Mongoloid race, see footnote #4 pp. 58–59 in Beckwith, Christopher. (2009). Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-13589-2. OCLC 800915872.
- ^ Pearson, Roger (1985). Anthropological glossary. R.E. Krieger Pub. Co. p. 79. Retrieved July 21, 2015.
- ^ Coon, Carleton Stevens (1939). The Races of Europe. New York: The Macmillan Company. pp. 400–01.
This third racial zone stretches from Spain across the Straits of Gibraltar to Morocco, and thence along the southern Mediterranean shores into Arabia, East Africa, Mesopotamia, and the Persian highlands; and across Afghanistan into India [...] The Mediterranean racial zone stretches unbroken from Spain across the Straits of Gibraltar to Morocco, and thence eastward to India[...] A branch of it extends far southward on both sides of the Red Sea into southern Arabia, the Ethiopian highlands, and the Horn of Africa.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Ainu". Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 441–442.
- ^ a b
- Baum 2006, pp. 84–85: "Finally, Christoph Meiners (1747–1810), the University of Göttingen “popular philosopher” and historian, first gave the term Caucasian racial meaning in his Grundriss der Geschichte der Menschheit (Outline of the History of Humanity, 1785)… Meiners pursued this “Göttingen program” of inquiry in extensive historical-anthropological writings, which included two editions of his Outline of the History of Humanity and numerous articles in Göttingisches Historisches Magazin"
- William R. Woodward (June 9, 2015). Hermann Lotze: An Intellectual Biography. Cambridge University Press. p. 260. ISBN 978-1-316-29785-8.
...the five human races identified by Johann Friedrich Blumenbach – Negroes, American Indians, Malaysians, Mongolians, and Caucasians. He chose to rely on Blumenbach, leader of the Göttingen school of comparative anatomy
; also at [1] - Nicolaas A. Rupke (2002). Göttingen and the Development of the Natural Sciences. Wallstein-Verlag. ISBN 978-3-89244-611-8.
For it was at Gottingen in this period that the outlines of a system of classification were laid down in a manner that still shapes the way in which we attempt to comprehend the different varieties of humankind — including usage of such terms as "Caucasian".
- Charles Simon-Aaron (2008). The Atlantic Slave Trade: Empire, Enlightenment, and the Cult of the Unthinking Negro. Edwin Mellen Press. ISBN 978-0-7734-5197-1.
Here, Blumenbach placed the white European at the apex of the human family; he even gave the European a new name — i.e., Caucasian. This relationship also inspired the academic labors of Karl Otfried Muller, C. Meiners and K.A. Heumann, the more important thinkers at Gottingen for our project. (This list is not intended to be exhaustive).
- RACAR, Revue D'art Canadienne: Canadian Art Review. Society for the Promotion of Art History Publications in Canada. 2004.
It is in the context of the shift to the human as both subject and object that Foucault has placed the "invention" of the human sciences, and it is also in this context that the various human histories as conceived and taught at Gottingen — from the theories of race proposed by Christoph Meiners and Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (who would coin the word "Caucasian" in the 1790s) to new theories of history as interpreted by Johann Christoph Gatterer and August Ludwig von Schlozer to a new art history as conceived by Fiorillo — can be considered.
- ^ Pickering, Robert (2009). The Use of Forensic Anthropology. CRC Press. p. 82. ISBN 978-1-4200-6877-1.
- ^ Pickering, Robert (2009). The Use of Forensic Anthropology. CRC Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-1-4200-6877-1.
- ^ Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1865). Thomas Bendyshe (ed.). The Anthropological Treatises of Johann Friedrich Blumenbach. Anthropological Society. pp. 265, 303, 367.
- ^ a b Caspari, Rachel (2003). "From types to populations: A century of race, physical anthropology, and the American Anthropological Association" (PDF). American Anthropologist. 105 (1): 65–76. doi:10.1525/aa.2003.105.1.65.
- ^ See these sources:
- Ousley, S.; Jantz, R.; Freid, D. (2009). "Understanding race and human variation: why forensic anthropologists are good at identifying race". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 139 (1): 68–76. doi:10.1002/ajpa.21006. PMID 19226647.
Although a shift in terminology has been underway in forensic anthropology, with ancestry used more often in place of race, in many case reports the classic physical anthropology terms such as Caucasoid, Mongoloid, or Negroid are still seen
- Sue Black; Eilidh Ferguson (April 19, 2016). Forensic Anthropology: 2000 to 2010. CRC Press. pp. 126–127. ISBN 978-1-4398-4589-9.
Semantically speaking, the term race appears to pertain to the individual and has largely been succeeded in physical anthropology by the more impersonal term ancestry. The distinction between these terms is considered to be important. Race may be regarded as a "socially constructed mechanism for self identification and group membership" and so biologically meaningless, whereas ancestry is a "scientifically derived descriptor of the biological component of population variation" (Konigsberg et al. 2009: 77–78). So, why do the rather politically sensitive terms Caucasoid, Mongoloid, or Negroid still appear in published literature (Ousley et al. 2009)? There are considered to be four basic ancestry groups into which an individual can be placed by physical appearance, not accounting for admixture: the sub-Saharan African group ("Negroid"), the European group ("Caucasoid"), the Central Asian group ("Mongoloid"), and the Australasian group ("Australoid"). The rather outdated names of all but one of these groups were originally derived from geography: The Caucasoid group traversed the Caucasus Mountains as they spread into Europe and eastern Asia. Since the majority of native peoples from the Indian subcontinent, northern and northeastern Africa and the Near East fall into this group, to say that the group is of "European" ancestry does not really suffice. Plus, the terms Caucasoid or Caucasian do not have the same oppressive, persecutory connotations as the other terms and so are less likely to cause offense.
- Robert B. Pickering; David Bachman (January 22, 2009). The Use of Forensic Anthropology. CRC Press. pp. 82–83. ISBN 978-1-4200-6878-8.
Race is both a cultural and a biological term. For more than a century, scientists and philosophers have tried to define race and describe races. Some scientists define only three races: caucasoid, mongoloid, and negroid, while other scientists have defined more than 10. In our current climate of multicultural sensitivity, some scholars, not forensic anthropologists, suggest that race does not exist, or at least it should not be talked about....From the forensic perspective, using the "three-race" model still has some value in describing broad genetic and morphological characteristics. This model is used by many people to describe themselves and others. Therefore, it falls to the forensic investigator to use the term defined by the model in trying to identify the dead. The model is not perfect, but it does help us understand some of the variation in shape and form on some parts of the skeleton, particularly the skull.
- Pekka Saukko; Bernard Knight (November 4, 2015). Knight's Forensic Pathology Fourth Edition. CRC Press. p. 120. ISBN 978-1-4441-6508-1.
There is no consensus as to whether forensic anthropologists or osteologists should include assessments of 'race' or ancestry in skeletal reports as according to Iscan and Steyn it seems to remain tentative at best.111 As of the osteological range present little difficulty, as Brothwell usual, those at the extreme ends remarks ... usual warnings about dogmatic opinions are even more important in this field.... There are three main racial groups: Caucasian, Mongoloid and Negroid.
- Ousley, S.; Jantz, R.; Freid, D. (2009). "Understanding race and human variation: why forensic anthropologists are good at identifying race". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 139 (1): 68–76. doi:10.1002/ajpa.21006. PMID 19226647.
- ^ See for example:
- Herbst, Philip (June 15, 1997). The color of words: an encyclopaedic dictionary of ethnic bias in the United States. Intercultural Press. ISBN 978-1-877864-97-1.
Though discredited as an anthropological term and not recommended in most editorial guidelines, it is still heard and used, for example, as a category on forms asking for ethnic identification. It is also still used for police blotters (the abbreviated Cauc may be heard among police) and appears elsewhere as a euphemism. Its synonym, Caucasoid, also once used in anthropology but now dated and considered pejorative, is disappearing.
- Mukhopadhyay, Carol C. (June 30, 2008). "Getting Rid of the Word "Caucasian"". In Mica Pollock (ed.). Everyday Antiracism: Getting Real About Race in School. New Press. pp. 14–. ISBN 978-1-59558-567-7.
Yet there is one striking exception in our modem racial vocabulary: the term "Caucasian." Despite being a remnant of a discredited theory of racial classification, the term has persisted into the twenty-first century, within as well as outside of the educational community. It is high time we got rid of the word Caucasian. Some might protest that it is "only a label." But language is one of the most systematic, subtle, and significant vehicles for transmitting racial ideology. Terms that describe imagined groups, such as Caucasian, encapsulate those beliefs. Every time we use them and uncritically expose students to them, we are reinforcing rather than dismantling the old racialized worldview. Using the word Caucasian invokes scientific racism, the false idea that races are naturally occurring, biologically ranked subdivisions of the human species and that Caucasians are the superior race. Beyond this, the label Caucasian can even convey messages about which groups have culture and are entitled to recognition as Americans.
- Dewanjuly, Shaila (July 6, 2013). "Has 'Caucasian' Lost Its Meaning?". New York Times. Retrieved March 16, 2018.
AS a racial classification, the term Caucasian has many flaws, dating as it does from a time when the study of race was based on skull measurements and travel diaries… Its equivalents from that era are obsolete — nobody refers to Asians as "Mongolian" or blacks as "Negroid."… There is no legal reason to use it. It rarely appears in federal statutes, and the Census Bureau has never put a checkbox by the word Caucasian. (White is an option.)… The Supreme Court, which can be more colloquial, has used the term in only 64 cases, including a pair from the 1920s that reveal its limitations… In 1889, the editors of the original Oxford English Dictionary noted that the term Caucasian had been "practically discarded." But they spoke too soon. Blumenbach's authority had given the word a pseudoscientific sheen that preserved its appeal. Even now, the word gives discussions of race a weird technocratic gravitas, as when the police insist that you step out of your "vehicle" instead of your car…. Susan Glisson, who as the executive director of the William Winter Institute for Racial Reconciliation in Oxford, Miss., regularly witnesses Southerners sorting through their racial vocabulary, said she rarely hears "Caucasian." "Most of the folks who work in this field know that it's a completely ridiculous term to assign to whites," she said. "I think it's a term of last resort for people who are really uncomfortable talking about race. They use the term that's going to make them be as distant from it as possible."
- Herbst, Philip (June 15, 1997). The color of words: an encyclopaedic dictionary of ethnic bias in the United States. Intercultural Press. ISBN 978-1-877864-97-1.
- ^ Freedman, B. J. (1984). "For debate... Caucasian". British Medical Journal. 288 (6418). Routledge: 696–98. doi:10.1136/bmj.288.6418.696. PMC 1444385. PMID 6421437.
- ^ For example, such as in the Allgemeine Erdbeschreibung published by Meyer in 1777: Allgemeine Erdbeschreibung: Asien - Volume 3. Meyer. 1777. p. 1435.
- ^ Meiners, Christoph (1785). Grundriss der Geschichte der Menschheit. Im Verlage der Meyerschen Buchhandlung. pp. 25–. Meiners' term was given wider circulation in the 1790s by
- ^ See for example:
- Luigi Marino, I Maestri della Germania (1975) OCLC 797567391; translated into German as Praeceptores Germaniae: Göttingen 1770–1820 OCLC 34194206;
- B. Isaac, The invention of racism in classical antiquity, Princeton University Press, 2004, p. 105 OCLC 51942570;
- Londa Schiebinger, The Anatomy of Difference: Race and Sex in Eighteenth-Century Science, Eighteenth-Century Studies, Vol. 23, No. 4, Special Issue: The Politics of Difference, Summer, 1990, pp. 387–405;
- B. Rupp-Eisenreich, "Des Choses Occultes en Histoire des Sciences Humaines: le Destin de la ‘Science Nouvelle’ de Christoph Meiners", L'Ethnographie v.2 (1983), p. 151;
- F. Dougherty, "Christoph Meiners und Johann Friedrich Blumenbach im Streit um den Begriff der Menschenrasse," in G. Mann and F. Dumont, eds., Die Natur des Menschen , pp. 103–04.
- Hochman, Leah (October 10, 2014). The Ugliness of Moses Mendelssohn: Aesthetics, Religion & Morality in the Eighteenth Century. Routledge. pp. 74–. ISBN 978-1-317-66997-5.
- Mikkelsen, Jon M. (August 1, 2013). Kant and the Concept of Race: Late Eighteenth-Century Writings. SUNY Press. pp. 196–. ISBN 978-1-4384-4363-8.
- An article published online gives a synopsis of Meiners' life and theories: N. Painter, "Why White People are Called Caucasian?", Yale University, September 27, 2007."Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 20, 2013. Retrieved October 9, 2006.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Another online document reviews the early history of race theory.18th and 19th Century Views of Human Variation The treatises of Blumenbach can be found online here.
- ^ The New American Cyclopaedia: A Popular Dictionary of General Knowledge, Volume 4. Appleton. 1870. p. 588.
- ^ a b Bhopal R (December 2007). "The beautiful skull and Blumenbach's errors: the birth of the scientific concept of race". BMJ. 335 (7633): 1308–09. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.969.2221. doi:10.1136/bmj.39413.463958.80. PMC 2151154. PMID 18156242.
- ^ Baum 2006, p. 88: "The connection between Meiners's ideas about a Caucasian branch of humanity and Blumenbach's later conception of a Caucasian variety (eventually, a Caucasian race) is not completely clear. What is clear is that the two editions of Meiners's Outline were published between the second edition of Blumenbach's On the Natural Variety of Mankind and the third edition, where Blumenbach first used the term Caucasian. Blumenbach cited Meiners once in 1795, but only to include Meiners's 1793 division of humanity into "handsome and white" and "ugly and dark" peoples among several alternative "divisions of the varieties of mankind." Yet Blumenbach must have been aware of Meiners's earlier designation of Caucasian and Mongolian branches of humanity, as the two men knew each other as colleagues at the University of Göttingen. The way that Blumenbach embraced the term Caucasian suggests that he worked to distance his own anthropological thinking from that of Meiners while recovering the term Caucasian for his own more refined racial classification: he made no mention of Meiners's 1785 usage and gave the term a new meaning.
- ^ On the Natural Variety of Mankind, 3rd ed. (1795) in Bendyshe: 264–65; "racial face," 229.
- ^ a b The Races of Europe by Carleton Coon 1939 Archived February 25, 2005, at archive.today (Hosted by the Society for Nordish Physical Anthropology)
- ^ The Races of Europe, Chapter XIII, Section 2 Archived May 11, 2006, at archive.today
- ^ Jackson Jr, J. P. (2001). ""In Ways Unacademical": The Reception of Carleton S. Coon's The Origin of Races". Journal of the History of Biology. 34 (2): 247–85. doi:10.1023/a:1010366015968.
- ^ "Miriam Claude Meijer, Race and Aesthetics in the Anthropology of Petrus Camper", 1722–1789, Amsterdam: Rodopi, 1999, pp. 169–74.
- ^ Bertoletti, Stefano Fabbri. 1994. The anthropological theory of Johann Friedrich Blumenbach. In Romanticism in science, science in Europe, 1790–1840.
- ^ See individual literature for such Caucasoid identifications, while the following article gives a brief overview: How "Caucasoids" Got Such Big Crania and Why They Shrank: From Morton to Rushton, Leonard Lieberman, Current Anthropology, Vol. 42, No. 1, February 2001, pp. 69–95.
- ^ "People and races", Alice Mossie Brues, Waveland Press, 1990, notes how the term Caucasoid replaced Caucasian.
- ^ Blumenfeld, Jodi (2000). "Racial Identification in the Skull and Teeth". U. Western Ontario Journal of Anthropology. 8 (4): 20–30.
- ^ Bass, William M. 1995. Human Osteology: A Laboratory and Field Manual. Columbia: Missouri Archaeological Society, Inc.
- ^ Eckert, William G. 1997. Introduction to Forensic Science. United States of America: CRC Press, Inc.
- ^ Gill, George W. 1998. "Craniofacial Criteria in the Skeletal Attribution of Race. " In Forensic Osteology: Advances in the Identification of Human Remains. (2nd edition) Reichs, Kathleen l(ed.), pp. 293–315.
- ^ Krogman, Wilton Marion and Mehmet Yascar Iscan 1986. The Human Skeleton in Forensic Medicine. Springfield: Charles C.Thomas.
- ^ Racial Identification in the Skull and Teeth, Totem: The University of Western, Ontario Journal of Anthropology, Volume 8, Issue 1 2000 Article 4.
- ^ Diana Smay, George Armelagos (2000). "Galileo wept: A critical assessment of the use of race of forensic anthropolopy" (PDF). Transforming Anthropology. 9 (2): 22–24. doi:10.1525/tran.2000.9.2.19. Retrieved July 13, 2016.
- ^ Adhikari, K.; Fuentes-Guajardo, M.; Quinto-Sánchez, M.; Mendoza-Revilla, J.; Chacón-Duque, J. C.; Acuña-Alonzo, V.; Gómez-Valdés, J. (2016). "A genome-wide association scan implicates DCHS2, RUNX2, GLI3, PAX1 and EDAR in human facial variation". Nature Communications. 7: 11616. Bibcode:2016NatCo...711616A. doi:10.1038/ncomms11616. PMC 4874031. PMID 27193062.
- ^ Adhikari, K.; Fuentes-Guajardo, M.; Quinto-Sánchez, M.; Mendoza-Revilla, J.; Chacón-Duque, J. C.; Acuña-Alonzo, V.; Gómez-Valdés, J. (2016). "A genome-wide association scan in admixed Latin Americans identifies loci influencing facial and scalp hair features". Nature Communications. 7: 10815. Bibcode:2016NatCo...710815A. doi:10.1038/ncomms10815.
- ^ Meyers Konversations-Lexikon, 4th edition, 1885–90, T11, p. 476.
- ^ The Veddoid periphery, Hadhramaut to Baluchistan
- ^ Coon, Carleton (1966). The Living Races of Man. Knopf. pp. 207–208. Retrieved December 28, 2017.
- ^ a b Reich et al. 2009.
- ^ Metspalu et al. 2011.
- ^ a b Moorjani et al. 2013.
- ^ Moorjani 2013.
- ^ Basu 2016.
- ^ Basu et al. 2016, p. 1598.
- ^ Rathee, Suresh Kanta; Pathmanathan, Gayathiri; Bulbeck, David; Raghavan, Pathmanathan (2013). "Indian Craniometric Variability and Affinities". International Journal of Evolutionary Biology. 2013: 836738. doi:10.1155/2013/836738. PMC 3886603. PMID 24455409.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ T. H. Huxley, On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind, Journal of the Ethnological Society of London (1870).
- ^ Simpson, George Eaton; Yinger, John Milton (1985). Racial and cultural minorities: an analysis of prejudice and discrimination, Environment, development, and public policy. Springer. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-306-41777-1.
- ^ American anthropologist, American Anthropological Association, Anthropological Society of Washington (Washington, D.C,), 1984 v. 86, nos. 3–4, p. 741.
- ^ Powell, Joseph F.; Rose, Jerome C. "Report on the Osteological Assessment of the Kennewick Man Skeleton (CENWW.97.Kennewick)". National Park Service. Retrieved September 10, 2011.
- ^ Landor, Arnold Henry Savage (1893). Alone with the Hairy Ainu: or, 3,800 Miles on a Pack Saddle in Yezo and a Cruise to the Kurile Islands. London: John Murray. pp. 229–230.
- ^ Old World sources of the first New World human inhabitants: A comparative craniofacial view - C. Loring Brace*†, A. Russell Nelson*‡, Noriko Seguchi*, Hiroaki Oe§, Leslie Sering*, Pan Qifeng¶, Li Yongyii , and Dashtseveg Tumen** *Museum of Anthropology, University of Michigan, 1109 Geddes Avenue, Ann Arbor, MI 48109; ‡Department of Anthropology, University of Wyoming, Laramie, WY 82071; §Department of Statistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109; ¶Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, 27 Wangfujing Dajie, Beijing 100710, China; i Department of Anatomy, Chengdu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 13 Xing Lo Road, Chengdu, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China; and **Department of Anthropology, Mongolian Academy of Sciences, Ulaanbaatar-51, Mongolia Communicated by Kent V. Flannery, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, June 18, 2001 (received for review January 2, 2001) (https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/98/17/10017.full.pdf)
- ^ Matsumoto, H. (2009). The origin of the Japanese race based on genetic markers of immunoglobulin G. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, (85)2. Pages 69, 72, 74 & 75. Wayback Machine link.
- ^ Das R, Upadhyai P. "Tracing the biogeographical origin of South Asian populations using DNA SatNav" (PDF).
Our hypothesis is supported by archaeological, linguistic and genetic evidences that suggest that there were two prominent waves of immigrations to India. A majority of the Early Caucasoids were proto-Dravidian language speakers that migrated to India putatively ~ 6000 YBP.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Grolier Incorporated (2001). Encyclopedia Americana, Volume 6. Grolier Incorporated. p. 85. ISBN 978-0-7172-0134-1.
- ^ Wells, H. G. (1921). The outline of history, being a plain history of life and mankind. The Macmillan Company. pp. 119–23, 236–38. Retrieved August 8, 2017.
- ^ "The Earliest Europeans". Archaeology. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- ^ Reply to Jantz, R. L.; Owsley, D. W. (2003). "Reply to Van Vark et al.: Is European Upper Paleolithic cranial morphology a useful analogy for early Americans?". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 121 (2): 185. doi:10.1002/ajpa.10188.
- ^ "Getting Here: The Story of Human Evolution", 1997, Compass Press, p. 188.
- ^ The Origin of Races. Random House Inc., 1962, p. 570.
- ^ Coon, Carleton Stevens (1939). The Races of Europe. The Macmillan Company. pp. 26–28, 50–55.
- ^ Simpson, Pat. "Beauty and the Beast: Imaging Human Evolution at the Darwin Museum, Moscow in the Early Revolutionary Period". AAH Conference 2012. Retrieved February 4, 2015.
- ^ Norton HL; Kittles RA; Parra E; et al. (March 2007). "Genetic evidence for the convergent evolution of the very light skin found in Northern Europeans and some East Asians". Mol. Biol. Evol. 24 (3): 710–22. doi:10.1093/molbev/msl203. PMID 17182896.
- ^ Gibbons A (April 2007). "American Association of Physical Anthropologists meeting. European skin turned pale only recently, gene suggests". Science. 316 (5823): 364. doi:10.1126/science.316.5823.364a. PMID 17446367.
- ^ Iosif Lazaridis; et al. (2016). "Genomic insights into the origin of farming in the ancient Near East" (PDF). Nature. 536 (7617): 419–424. Bibcode:2016Natur.536..419L. doi:10.1038/nature19310. PMC 5003663. PMID 27459054. Retrieved April 18, 2018.
bottom-left: Western Hunter Gatherers (WHG), top-left: Eastern Hunter Gatherers (EHG), bottom-right: Neolithic Levant and Natufians, top-right: Neolithic Iran. This suggests the hypothesis that diverse ancient West Eurasians can be modelled as mixtures of as few as four streams of ancestry related to these population
- ^ Editors (March 23, 2018) "How Genetics Is Changing Our Understanding of 'Race'" (editorial), The New York Times
- ^ Pakstis, Andrew J.; Gurkan, Cemal; Dogan, Mustafa; Balkaya, Hasan Emin; Dogan, Serkan; Neophytou, Pavlos I.; Cherni, Lotfi; Boussetta, Sami; Khodjet-El-Khil, Houssein; Ben Ammar ElGaaied, Amel; Salvo, Nina Mjølsnes (2019-12). "Genetic relationships of European, Mediterranean, and SW Asian populations using a panel of 55 AISNPs". European Journal of Human Genetics. 27 (12): 1885–1893. doi:10.1038/s41431-019-0466-6. ISSN 1476-5438.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Painter, Nell Irvin (2003). "Collective Degradation: Slavery and the Construction of Race. Why White People are Called Caucasian" (PDF). Yale University. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 20, 2013. Retrieved October 9, 2006.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Karen R. Humes; Nicholas A. Jones; Roberto R. Ramirez, eds. (March 2011). "Definition of Race Categories Used in the 2010 Census" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. p. 3. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- ^ Coulson, Doug (2015). "British Imperialism, the Indian Independence Movement, and the Racial Eligibility Provisions of the Naturalization Act: United States v. Thind Revisited". Georgetown Journal of Law & Modern Critical Race Perspectives. 7: 1–42. SSRN 2610266.
- ^ "Not All Caucasians Are White: The Supreme Court Rejects Citizenship for Asian Indians", History Matters
- ^ "Other Notable MeSH Changes and Related Impact on Searching: Ethnic Groups and Geographic Origins". NLM Technical Bulletin. 335 (Nov–Dec). 2003.
The MeSH term Racial Stocks and its four children (Australoid Race, Caucasoid Race, Mongoloid Race, and Negroid Race) have been deleted from MeSH in 2004. A new heading, Continental Population Groups, has been created with new identification that emphasize geography.
Bibliography
- Camberg, Kim (December 13, 2005). "Long-term tensions behind Sydney riots". BBC News. Retrieved March 3, 2007.
- Leroi, Armand Marie (March 14, 2005). "A Family Tree in Every Gene". The New York Times. p. A23.
- Lewontin, Richard (2005). "Confusions About Human Races". Race and Genomics, Social Sciences Research Council. Retrieved December 28, 2006.
- Painter, Nell Irvin (2003). "Collective Degradation: Slavery and the Construction of Race. Why White People are Called Caucasian" (PDF). Yale University. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 20, 2013. Retrieved October 9, 2006.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Risch N, Burchard E, Ziv E, & Tang H (July 2002). "Categorization of humans in biomedical research: genes, race and disease". Genome Biol. 3 (7): comment2007.2001–12. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-comment2007. PMC 139378. PMID 12184798.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Rosenberg NA; Pritchard JK; Weber JL; et al. (December 2002). "Genetic structure of human populations". Science. 298 (5602): 2381–85. Bibcode:2002Sci...298.2381R. doi:10.1126/science.1078311. PMID 12493913.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - Rosenberg NA, Mahajan S, Ramachandran S, Zhao C, Pritchard JK, & Feldman MW (December 2005). "Clines, Clusters, and the Effect of Study Design on the Inference of Human Population Structure". PLoS Genet. 1 (6): e70. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0010070. PMC 1310579. PMID 16355252.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Templeton, Alan R. (September 1998). "Human races: A genetic and evolutionary perspective". American Anthropologist. 100 (3): 632–50. doi:10.1525/aa.1998.100.3.632. JSTOR 682042.
- Literature
- Augstein, HF (1999). "From the Land of the Bible to the Caucasus and Beyond". In Harris, Bernard; Ernst, Waltraud (eds.). Race, Science and Medicine, 1700–1960. New York: Routledge. pp. 58–79. ISBN 978-0-415-18152-5.
- Baum, Bruce (2006). The rise and fall of the Caucasian race: a political history of racial identity. New York: New York University Press. ISBN 978-0-8147-9892-8.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Blumenbach, Johann Friedrich (1775) On the Natural Varieties of Mankind – the book that introduced the concept
- Cavalli-Sforza, Luigi Luca (2000). Genes, Peoples and Languages. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-7139-9486-5.
- Gould, Stephen Jay (1981). The Mismeasure of Man. New York: Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-01489-1. – a history of the pseudoscience of race, skull measurements, and IQ inheritabilit
- Guthrie, Paul (1999). The Making of the Whiteman: From the Original Man to the Whiteman. Chicago: Research Associates School Times. ISBN 978-0-948390-49-4.
- Piazza, Alberto; Cavalli-Sforza, Luigi Luca; Menozzi, Paolo (1996). The History and Geography of Human Genes. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-02905-4.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) – a major reference of modern population genetics - Stoddard, Theodore Lothrop (1924). Racial Realities in Europe. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons.
- Wolf, Eric R.; Cole, John N. (1999). The Hidden Frontier: Ecology and Ethnicity in an Alpine Valley. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-21681-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help)








