Alexander the Great
Alexander the Great | |
|---|---|
| File:AlexanderAttackingDarius.jpg Alexander the Great fighting Persian king Darius III (not in frame) (Alexander Mosaic from Pompeii, from a 3rd century BC original Greek painting, now lost) |
Alexander the Great (Greek:Μέγας Αλέξανδρος[1], Megas Alexandros; July 356 BC — June 11 323 BC), also known as Alexander III, king of Macedon (336–323 BC), was one of the most successful military commanders in history, conquering most of his known world before his death; he is frequently included in a list along with Napoleon Bonaparte, Julius Caesar, and Ghengis Khan, as the greatest military strategists and tacticians who ever lived. Alexander is also known in the Zoroastrian Middle Persian work Arda Wiraz Nāmag as "the accursed Alexander" due to his conquest of the Persian Empire and the destruction of its capital Persepolis. He is known as Eskandar in Persian and even acclaimed during the construction of the Great Wall Sadd-e Eskandar by the Parthian Dynasty[citation needed]. He is often identified as Dhul-Qarnayn in Middle Eastern traditions and is called al-Iskandar al-Kabeer in Arabic, Sikandar-e-azam in Urdu, Skandar in Pashto, Dul-Qarnayim in Hebrew, and Tre-Qarnayia in Aramaic (the two-horned one), apparently due to an image on coins minted during his rule that seemingly depicted him with the two ram's horns of the Egyptian god Ammon. He is known as Sikandar in Urdu and Hindi, a term also used as a synonym for "expert" or "extremely skilled".
Following the unification of the multiple city-states of ancient Greece under the rule of his father, Philip II of Macedon, (a labour Alexander had to repeat twice because the southern Greeks rebelled after Philip's death), Alexander would conquer the Persian Empire, including Anatolia, Syria, Phoenicia, Gaza, Egypt, Bactria and Mesopotamia and extend the boundaries of his own empire as far as the Punjab. Alexander integrated foreigners (non-Macedonians, non-Greeks known as the Successors[2]) into his army and administration, leading some scholars to credit him with a "policy of fusion." He encouraged marriage between his army and foreigners, and practised it himself. After twelve years of constant military campaigning, Alexander died, possibly of malaria, typhoid, or viral encephalitis. His conquests ushered in centuries of Greek settlement and rule over distant areas, a period known as the Hellenistic Age. Alexander himself lived on in the history and myth of both Greek and non-Greek cultures. Already during his lifetime, and especially after his death, his exploits inspired a literary tradition in which he appears as a legendary hero in the tradition of Achilles.
Early life
Alexander the Great was the son of King Philip II of Macedon and of his fourth wife, Epirote princess Olympias. According to Plutarch (Alexander 3.1,3), Olympias was impregnated not by Philip, who was afraid of her, and her affinity for sleeping in the company of snakes, but by Zeus Ammon. Plutarch relates that both Philip and Olympias dreamt of their son's future birth. Olympias dreamed of a loud burst of thunder and of lightning striking her womb. In Philip's dream, he sealed her womb with the seal of the lion. Alarmed by this, he consulted the seer Aristander of Telmessus, who determined that his wife was pregnant and that the child would have the character of a lion.[3]
Aristotle was Alexander's tutor and he gave Alexander a thorough training in rhetoric and literature and stimulated his interest in science, medicine, and philosophy. After his visit to the Oracle of Ammon at Siwa, according to five historians of antiquity (Arrian, Curtius, Diodorus, Justin, and Plutarch), rumors spread that the Oracle had revealed Alexander's father to be Zeus, rather than Philip. According to Plutarch, his father descended from Heracles through Caranus and his mother descended from Aeacus through Neoptolemus and Achilles.[4] Aristotle gave him a copy of the Iliad which he always kept with him and read frequently.
Ascent of Macedon
When Philip led an attack on Byzantium in 340 BC, Alexander, aged 16, was left as regent of Macedonia. In 339 BC, Philip took a fifth wife, the Macedonian Cleopatra. As Alexander's mother, Olympias, was from Epirus (a land in the western part of the Greek peninsula and not part of Macedon), and Cleopatra was a true Macedonian, this led to a dispute over Alexander's legitimacy as heir to the throne. Attalus, the uncle of the bride, supposedly gave a toast during the wedding feast giving his wish for the wedding to result in a legitimate heir to the throne of Macedon; Alexander hurled his goblet at Attalus shouting "What am I, a bastard then?" Alexander's father apparently had drawn his sword and moved towards Alexander, but then had fallen in a drunken stupor. Alexander remarked "Here is the man planning on conquering from Greece to Asia, and he cannot even move from one table to another." Alexander, his mother, and sister (also named Cleopatra) then left Macedon in anger.
Eventually Philip reconciled with his son, and Alexander returned home; Olympias and Alexander's sister remained in Epirus. In 338 BC Alexander assisted his father at the decisive Battle of Chaeronea against the Greek city-states of Athens and Thebes, in which the cavalry wing led by Alexander annihilated the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite corps regarded as invincible. After the battle, Phillip led a wild celebration, from which Alexander was notably absent (it is believed he was treating the wounded and burying the dead, both of his own troops and of the enemy). Philip was content to deprive Thebes of her dominion over Boeotia and leave a Macedonian garrison in the citadel. A few months later, to strengthen Macedon's control over the Greek city-states, the League of Corinth was formed.
In 336 BC, Philip was assassinated at the wedding of his daughter Cleopatra of Macedonia to King Alexander of Epirus. The assassin was supposedly a former lover of the king, the disgruntled young nobleman Pausanias, who held a grudge against Philip because the king had ignored a complaint he had expressed. Philip's murder was once thought to have been planned with the knowledge and involvement of Alexander or Olympias. Another possible instigator could have been Darius III, the recently crowned King of Persia. Plutarch mentions an irate letter from Alexander to Darius, where Alexander blames Darius and Bagoas, his grand vizier, for his father's murder, stating that it was Darius who had been bragging with the Greek cities of how he managed to assassinate Philip. After Philip's death, the army proclaimed Alexander, then aged 20, as the new king of Macedon. Greek cities like Athens and Thebes, which had been forced to pledge allegiance to Philip, saw in the new king an opportunity to retake their full independence. Alexander moved swiftly and Thebes, which had been most active against him, submitted when he appeared at its gates. The assembled Greeks at the Isthmus of Corinth, with the exception of the Spartans, elected him to the command against Persia, which had previously been bestowed upon his father.
The next year, (335 BC), Alexander felt free to engage the Thracians and the Illyrians in order to secure the Danube as the northern boundary of the Macedonian kingdom. While he was triumphantly campaigning north, the Thebans and Athenians rebelled once again. Alexander reacted immediately and while the other cities once again hesitated, Thebes decided this time to resist with the utmost vigor. The resistance was useless; in the end, the city was conquered with great bloodshed. The Thebans encountered an ever harsher fate when their city was razed to the ground and its territory divided between the other Boeotian cities. Moreover, all of the city's citizens were sold into slavery, sparing only the priests, the leaders of the pro-Macedonian party and the descendants of Pindar, whose house was the only one left untouched. The end of Thebes cowed Athens into submission and it readily accepted Alexander's demand for the exile of all the leaders of the anti-Macedonian party, Demosthenes first of all.
Period of conquests
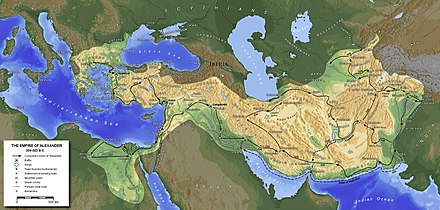
Fall of the Persian Empire
Alexander's army had crossed the Hellespont with about 42,000 soldiers - primarily Macedonians[5] and Greeks, more southern city-states of Greece, but also including some Thracians, Paionians and Illyrians. After an initial victory against Persian forces at the Battle of Granicus, Alexander accepted the surrender of the Persian provincial capital and treasury of Sardis and proceeded down the Ionian coast. At Halicarnassus, Alexander successfully waged the first of many sieges, eventually forcing his opponents, the mercenary captain Memnon of Rhodes and the Persian satrap of Caria, Orontobates, to withdraw by sea. Alexander left Caria in the hands of Ada, who was ruler of Caria before being deposed by her brother Pixodarus. From Halicarnassus, Alexander proceeded into mountainous Lycia and the Pamphylian plain, asserting control over all coastal cities and denying them to his enemy. From Pamphylia onward, the coast held no major ports and so Alexander moved inland. At Termessus, Alexander humbled but did not storm the Pisidian city. At the ancient Phrygian capital of Gordium, Alexander "undid" the tangled Gordian Knot, a feat said to await the future "king of Asia." According to the most vivid story, Alexander proclaimed that it did not matter how the knot was undone, and he hacked it apart with his sword. Another version claims that he did not use the sword, but actually figured out how to undo the knot.

Alexander's army crossed the Cilician Gates, met and defeated the main Persian army under the command of Darius III at the Battle of Issus in 333 BC. Darius fled this battle in such a panic for his life that he left behind his wife, his two daughters, his mother, and much of his personal treasure. Sisygambis, the queen mother, never forgave Darius for abandoning her. She disowned him and adopted Alexander as her son instead. Proceeding down the Mediterranean coast, he took Tyre and Gaza after famous sieges (see Siege of Tyre). Alexander passed near but probably did not visit Jerusalem.
In 332 BC - 331 BC, Alexander was welcomed as a liberator in Egypt and was pronounced the son of Zeus by Egyptian priests of the god Ammon at the Oracle of the god at the Siwa Oasis in the Libyan desert. Henceforth, Alexander referred to the god Zeus-Ammon as his true father, and subsequent currency featuring his head with ram horns was proof of this widespread belief. He founded Alexandria in Egypt, which would become the prosperous capital of the Ptolemaic dynasty after his death. Leaving Egypt, Alexander marched eastward into Assyria (now northern Iraq) and defeated Darius and a third Persian army at the Battle of Gaugamela. Darius was forced to flee the field after his charioteer was killed, and Alexander chased him as far as Arbela. While Darius fled over the mountains to Ecbatana (modern Hamadan), Alexander marched to Babylon.

From Babylon, Alexander went to Susa, one of the Achaemenid capitals, and captured its treasury. Sending the bulk of his army to Persepolis, the Persian capital, by the Royal Road, Alexander stormed and captured the Persian Gates (in the modern Zagros Mountains), then sprinted for Persepolis before its treasury could be looted. Alexander allowed the League forces to loot Persepolis. A fire broke out in the eastern palace of Xerxes and spread to the rest of the city. It was not known if it was a drunken accident or a deliberate act of revenge for the burning of the Athenian Acropolis during the Second Persian War. The Book of Arda Wiraz, a Zoroastrian work composed in the 3rd or 4th century AD, also speaks of archives containing "all the Avesta and Zand, written upon prepared cow-skins, and with gold ink" that were destroyed; but it must be said that this statement is often treated by scholars with a certain measure of skepticism, because it is generally thought that for many centuries the Avesta was transmitted mainly orally by the Magians.
He then set off in pursuit of Darius, who was kidnapped, and then murdered by followers of Bessus, his Bactrian satrap and kinsman. Bessus then declared himself Darius' successor as Artaxerxes V and retreated into Central Asia to launch a guerrilla campaign against Alexander. With the death of Darius, Alexander declared the war of vengeance over, and released his Greek and other allies from service in the League campaign (although he allowed those that wished to re-enlist as mercenaries in his imperial army).
His three-year campaign against first Bessus and then the satrap of Sogdiana, Spitamenes, took him through Media, Parthia, Aria, Drangiana, Arachosia, Bactria, and Scythia. In the process, he captured and refounded Herat and Maracanda. Moreover, he founded a series of new cities, all called Alexandria, including modern Kandahar in Afghanistan, and Alexandria Eschate ("The Furthest") in modern Tajikistan. In the end, both were betrayed by their men, Bessus in 329 BC and Spitamenes the year after.
Hostility toward Alexander
During this time, Alexander adopted some elements of Persian dress and customs at his court, notably the custom of proskynesis, a symbolic kissing of the hand that Persians paid to their social superiors, but a practice of which the Greeks disapproved. The Greeks regarded the gesture as the preserve of deities and believed that Alexander meant to deify himself by requiring it. This cost him much in the sympathies of many of his countrymen. Here, too, a plot against his life was revealed, and one of his officers, Philotas, was executed for treason for failing to bring the plot to his attention. Parmenion, Philotas' father, who was at the head of an army at Ecbatana, was assassinated by command of Alexander, who feared that Parmenion might attempt to avenge his son. Several other trials for treason followed, and many Macedonians were executed. Later on, in a drunken quarrel at Maracanda, he also killed the man who had saved his life at Granicus, Clitus the Black. Later in the Central Asian campaign, a second plot against his life, this one by his own pages, was revealed, and his official historian, Callisthenes of Olynthus (who had fallen out of favor with the king by leading the opposition to his attempt to introduce proskynesis), was implicated on what many historians regard as trumped-up charges. However, the evidence is strong that Callisthenes, the teacher of the pages, must have been the one who persuaded them to assassinate the king.
Invasion of India
Obv: Alexander standing, being crowned by Nike, fully armed and holding Zeus' thunderbolt.
Rev: Greek rider, possibly Alexander, attacking an Indian battle-elephant, possibly during the battle against Porus.
After the death of Spitamenes and his marriage to Roxana (Roshanak in Bactrian) to cement his relations with his new Central Asian satrapies, in 326 BC Alexander was finally free to turn his attention to India. Alexander invited all the chieftains of the former satrapy of Gandhara, in the north of present-day Pakistan, to come to him and submit to his authority. Ambhi, ruler of Taxila, whose kingdom extended from the Indus to the Hydaspes (Jhelum), complied. But the chieftains of some hilly clans including the Aspasios and Assakenois sections of the Kambojas (classical names), known in Indian texts as Ashvayanas and Ashvakayanas (names referring to their equestrian nature), refused to submit.
Alexander personally took command of the shield-bearing guards, foot-companions, archers, Agrianians and horse-javelin-men and led them against the Kamboja clans -- the Aspasios of Kunar/Alishang valleys, the Guraeans of the Guraeus (Panjkora) valley, and the Assakenois of the Swat and Buner valleys. Writes one modern historian: "They were brave people and it was hard work for Alexander to take their strongholds, of which Massaga and Aornus need special mention." [6] A fierce contest ensued with the Aspasios in which Alexander himself was wounded in the shoulder by a dart but eventually the Aspasios lost the fight; 40,000 of them were enslaved. The Assakenois faced Alexander with an army of 30,000 cavalry, 38,000 infantry and 30 elephants.[7] They had fought bravely and offered stubborn resistance to the invader in many of their strongholds like cities of Ora, Bazira and Massaga. The fort of Massaga could only be reduced after several days of bloody fighting in which Alexander himself was wounded seriously in the ankle. When the Chieftain of Massaga fell in the battle, the supreme command of the army went to his old mother Cleophis (q.v.) who also stood determined to defend her motherland to the last extremity. The example of Cleophis assuming the supreme command of the military also brought the entire women of the locality into the fighting. [8] Alexander could only reduce Massaga by resorting to political strategem and actions of betrayal. According to Curtius: "Not only did Alexander slaughter the entire population of Massaga, but also did he reduce its buildings to rubbles." A similar manslaughter then followed at Ora, another stronghold of the Assakenois.
In the aftermath of general slaughter and arson committed by Alexander at Massaga and Ora, numerous Assakenian people fled to a high fortress called Aornos. Alexander followed them close behind their heels and captured the strategic hill-fort but only after the fourth day of a bloody fight. The story of Massaga was repeated at Aornos and a similar carnage on the tribal-people followed here too.
Writing on Alexander's campaign against the Assakenois, Victor Hanson comments: "After promising the surrounded Assacenis their lives upon capitulation, he executed all their soldiers who had surrendered. Their strongholds at Ora and Aornus were also similarly stormed. Garrisons were probably all slaughtered.”[9]
Sisikottos, who had helped Alexander in this compaign, was made the governor of Aornos.
After reducing Aornos, Alexander crossed the Indus and fought and won an epic battle against Porus, a ruler of a region in the Punjab in the Battle of Hydaspes in 326 BC.
After the victory, Alexander was greatly impressed by Porus for his bravery in battle, and therefore made an alliance with him and appointed him as satrap of his own kingdom, even adding some land he did not own before. Alexander then named one of the two new cities that he founded, Bucephala, in honor of the horse who had brought him to India. Alexander continued on to conquer all the headwaters of the Indus River.
East of Porus' kingdom, near the Ganges River, was the powerful empire of Magadha ruled by the Nanda dynasty. Fearing the prospects of facing another powerful Indian army and exhausted by years of campaigning, his army mutinied at the Hyphasis River (modern Beas), refusing to march further east:
- "As for the Macedonians, however, their struggle with Porus blunted their courage and stayed their further advance into India. For having had all they could do to repulse an enemy who mustered only twenty thousand infantry and two thousand horse, they violently opposed Alexander when he insisted on crossing the river Ganges also, the width of which, as they learned, was thirty-two furlongs, its depth a hundred fathoms, while its banks on the further side were covered with multitudes of men-at-arms and horsemen and elephants. For they were told that the kings of the Ganderites and Praesii were awaiting them with eighty thousand horsemen, two hundred thousand footmen, eight thousand chariots, and six thousand fighting elephants." Plutarch, Vita Alexandri, 62 [10]
Alexander, after the meeting with his officer Coenus, was convinced that it was better to return. Alexander was forced to turn south. He sent much of his army to Carmania (modern southern Iran) with his general Craterus, and commissioned a fleet to explore the Persian Gulf shore under his admiral Nearchus, while he led the rest of his forces back to Persia by the southern route through the Gedrosia (present day Makran in southern Pakistan).
In the territory of the Indus, Alexander nominated his officer Peithon as a satrap, a position he would hold for the next ten years until 315 BC, and in the Punjab he left Eudemus in charge of the army, at the side of the satrap Porus and Taxiles. After their death, Eudemus became ruler of the Punjab until 316 BC.
After India

Discovering that many of his satraps and military governors had misbehaved in his absence, Alexander executed a number of them as examples on his way to Susa. As a gesture of thanks, he paid off the debts of his soldiers, and announced that he would send those over-aged and disabled veterans back to Macedonia under Craterus, but his troops misunderstood his intention and mutinied at the town of Opis, refusing to be sent away and bitterly criticizing his adoption of Persian customs and dress and the introduction of Persian officers and soldiers into Macedonian units. Alexander executed the ringleaders of the mutiny, but forgave the rank and file. In an attempt to craft a lasting harmony between his Macedonian and Persian subjects, he held a mass marriage of his senior officers to Persian and other noblewomen at Susa, but few of those marriages seem to have lasted much beyond a year.
His attempts to merge Persian culture with his Greek soldiers also included training a regiment of Persian boys in the ways of Macedonians. It is not certain that Alexander adopted the Persian royal title of shahanshah ("great king" or "king of kings"). However, most historians believe that he did.
It is claimed that Alexander wanted to overrun or integrate Arabian peninsula, but this theory is widely disputed. It was assumed that Alexander would turn westwards and attack Carthage and Italy had he conquered Arabia.
After traveling to Ecbatana to retrieve the bulk of the Persian treasure, his closest friend and lover Hephaestion died of an illness. Alexander was distraught, and on his return to Babylon he fell ill and died.
Personal life
Alexander's greatest emotional attachment is generally considered to have been to his companion, cavalry commander (chiliarchos) and childhood friend, Hephaestion. He studied with Alexander, as did a handful of other children of Macedonian aristocracy, under the tutelage of Aristotle. Hephaestion makes his appearance in history at the point when Alexander reaches Troy. There the two friends made sacrifices at the shrines of the two heroes Achilles and Patroclus; Alexander honoring Achilles, and Hephaestion honoring Patroclus. Aelian in his Varia Historia (12.7) claims that Hephaestion "thus intimated that he was the eromenos ["beloved"] of Alexander, as Patroclus was of Achilles."
This assertion of a sexual relationship between Alexander and Hephaiston is questioned by some historians. Robin Lane Fox writes that while "later gossip claimed that Alexander had a love affair with Hephaiston", no contemporary history states this. However, Fox adds, "the facts show that the two men’s friendship was exceptionally deep and close." [11] Following Hephaestion's death, Alexander mourned him greatly, and did not eat for days.
Plutarch has argued that Alexander's love of males took an ethical approach, inspired by the teachings of his mentor, Aristotle. He gives several examples of Alexander's morality in this domain:
- When Philoxenos, the leader of the seashore, wrote to Alexander that there was a youth in Ionia whose beauty has yet to be seen and asked him in a letter if he (Alexander) would like him (the boy) to be sent over, he (Alexander) responded in a strict and disgusted manner: "You are the most hideous and malign of all men, have you ever seen me involved in such dirty work that you found the urge to flatter me with such hedonistic business?" [12]
Plutarch also wrote:
- When Philoxenus, the commander of his forces on the sea-board, wrote that there was with him a certain Theodorus of Tarentum, who had two youths of surpassing beauty to sell, and enquired whether Alexander would buy them, Alexander was incensed, and cried out many times to his friends, asking them what shameful thing Philoxenus had ever seen in him that he should spend his time in making such disgraceful proposals. [13]
His moral approach towards sexual relations also extended to relations with prisoners of war: "But as for the other captive women, seeing that they were surpassingly stately and beautiful, he merely said jestingly that Persian women were torments to the eyes. And displaying in rivalry with their fair looks the beauty of his own sobriety and self-control, he passed them by as though they were lifeless images for display." [14]
The above quotations would be in line with the thoughts laid about before him by Aristotle, who regarded relationships based purely on carnal relations to be shameful.
Many have discussed Alexander's sexual leanings. Curtius reports, "He scorned sensual pleasures to such an extent that his mother was anxious lest he be unable to beget offspring." To encourage a relationship with a woman, King Philip and Olympias brought in a high-priced Thessalian courtesan named Callixena.
Later in life, Alexander married several princesses of former Persian territories, Roxana of Bactria, Statira, daughter of Darius III, and Parysatis, daughter of Ochus. He fathered two children, (Heracles), born by his concubine Barsine (the daughter of satrap Artabazus of Phrygia) in 327 BC, and Alexander IV of Macedon, born by Roxana shortly after his death in 323 BC.
Many ancient historians report that Alexander also had another favorite, "Bagoas, a eunuch exceptional in beauty and in the very flower of boyhood, with whom Darius was intimate and with whom Alexander would later be intimate." [15] Plutarch recounts an episode (also mentioned by Dicaearchus) during some festivities on the way back from India) in which his men clamor for him to kiss the young man: "Bagoas...sat down close to him, which so pleased the Macedonians, that they made loud acclamations for him to kiss Bagoas, and never stopped clapping their hands and shouting till Alexander put his arms round him and kissed him." Some modern historians point out that the ancient sources cannot be considered definitive. Robin Lane Fox writes: "Later gossip presumed that Bagoas was Alexander’s lover. This is uncertain." [16] And, according to Mary Renault, who wrote a novel about the relationship of Alexander and Bagoas, "No historian states plainly whether they were physical lovers." [17] Whatever Alexander's relationship with Bagoas, it was no impediment to relations with his queen: six months after Alexander's death Roxana gave birth to his son and heir, Alexander IV.
Historical accounts describing Alexander's love for Hephaestion and Bagoas as sexual are strongly contested under the claim that they were written centuries afterwards and thus are necessarily dubious. Others retort that the same can be said about much of our information regarding Alexander. Such debates, however, are generally considered anachronistic by scholars of the period, who point out that the concept of homosexuality as understood today did not exist in Greco-Roman antiquity. Sexual attraction between males was seen as a normal and universal part of human nature, since it was believed that men were attracted to beauty, an attribute of the young, regardless of gender. If Alexander's love life was transgressive, it was not for his love of beautiful youths but for his persistent love of a man his own age. The ancient Greeks saw sex as an activity, not an identifier, a viewpoint shared by contemporary cultures at the time. Although this assumption, that in Ancient Greece homosexuality was commonplace, has come under debate in recent years, and is not accepted in Modern Greece.
His army
The army of Alexander was, for the most part, that of his father Philip. It was composed of light and heavy troops and some engineers, medical and staff units. About one third of the army was composed of his Greek allies from the Hellenic League.
Infantry
The main infantry corps was the phalanx, composed of six regiments (taxies) numbering about 2000 phalangites each. Each soldier had a long pike called a sarissa, which was approximately 18 feet long (it would be increased up to 21 feet under the successors), and a short sword. For protection, the soldier wore a Phrygian-style helmet and a shield. Arrian mentions large shields (the aspis), but this is disputed, as it is difficult to wield both a large pike and a large shield at the same time. Many modern historians claim the phalanx used a smaller shield, called a pelta, the shield used by peltasts. It is unclear whether the phalanx used body armor, but heavy body armor is mentioned in Arrian [18] and other ancient sources. Modern historians believe most of the phalangites did not wear heavy body armor at the time of Alexander.
Another important unit were the hypaspists (shield bearers), arranged into three battalions (lochoi) of 1000 men each. One of the battalions was named the Agema and served as the King's bodyguards. Their armament is unknown and it is difficult to get a clear picture from ancient sources. Sometimes hypaspists are mentioned in the front line of the battle just between the phalanx and the heavy cavalry. Moreover, they seem to have acted as an extension of the phalanx fighting as heavy infantry while keeping a link between the heavily clad phalangites and the companion cavalry. They also accompanied Alexander on flanking marches and were capable of fighting on rough terrain like light troops so it seems they could perform dual functions.
In addition to the units mentioned above, the army included some 6000 Greek allied and mercenary hoplites, also arranged in phalanxes. They carried a shorter spear, a dory, which was six or seven feet long and a large aspis.
Alexander also had light infantry units composed of peltasts, psiloi and others. Peltasts are considered to be light infantry, although they had a helmet and a small shield and were heavier than the psiloi. The best peltasts were the Agrianians from Thrace.
Cavalry
The heavy cavalry included the Companion cavalry raised from the Macedonian nobility, and the Thessalian cavalry. The Companion cavalry (hetairoi, friends) was divided into eight squadrons called ile, 200 strong, except the Royal Squadron of 300. They were equipped with a 12 foot lance, the xyston, and heavy body armor. The horses were partially clad in armor as well. The riders did not carry shields, as the xyston required both hands to wield. The organization of the Thessalian cavalry was similar to the Companion Cavalry, but they had a shorter spear and fought in a looser formation.
Of light cavalry, the prodromoi (forerunners) secured the wings of the army during battle and went on reconnaissance missions. Several hundred allied horses rounded out the cavalry.
Death
On the afternoon of June 10 - 11, 323 BC, Alexander died of a mysterious illness in the palace of Nebuchadrezzar II of Babylon. He was just one month shy of attaining 33 years of age. Various theories have been proposed for the cause of his death which include poisoning by the sons of Antipater or others, sickness that followed a drinking party, or a relapse of the malaria he had contracted in 336 BC.
It is known that on May 29, Alexander participated in a banquet organized by his friend Medius of Larissa. After some heavy drinking, immediately before or after a bath, he was forced into bed due to severe illness. The rumors of his illness circulated with the troops causing them to be more and more anxious. On June 9, the generals decided to let the soldiers see their king alive one last time. They were admitted to his presence one at a time. While the king was too ill to speak, confined himself to move his hand. The day after, Alexander was dead.
The poisoning theory derives from the story held in antiquity by Justin and Curtius. The original story stated that Cassander, son of Antipater, viceroy of Greece, brought the poison to Alexander in Babylon in a mule's hoof, and that Alexander's royal cupbearer, Iollas, brother of Cassander, administered it. Many had powerful motivations for seeing Alexander gone, and were none the worse for it after his death. Deadly agents that could have killed Alexander in one or more doses include hellebore and strychnine. In R. Lane Fox's opinion, the strongest argument against the poison theory is the fact that twelve days had passed between the start of his illness and his death and in the ancient world, such long-acting poisons were probably not available.
However, the warrior culture of Macedon favoured the sword over strychnine, and many ancient historians, like Plutarch and Arrian, maintained that Alexander was not poisoned, but died of natural causes. Instead, it is likely that Alexander died of malaria or typhoid fever, which were rampant in ancient Babylon. Other illnesses could have also been the culprit, including acute pancreatitis or the West Nile virus. Recently, theories have been advanced stating that Alexander may have died from the treatment not the disease. Hellebore, believed to have been widely used as a medicine at the time but deadly in large doses, may have been overused by the impatient king to speed his recovery, with deadly results. Disease-related theories often cite the fact that Alexander's health had fallen to dangerously low levels after years of heavy drinking and suffering several appalling wounds (including one in India that nearly claimed his life), and that it was only a matter of time before one sickness or another finally killed him.
No story is conclusive. Alexander's death has been reinterpreted many times over the centuries, and each generation offers a new take on it. What is certain is that Alexander died of a high fever on June 10 or 11 of 323 BC.
On his death bed, his marshals asked him to whom he bequeathed his kingdom. Since Alexander had no heir (his son Alexander IV would be born after his death), it was a question of vital importance. There is some debate to what Alexander replied. Some believe that Alexander said, "To the strongest!". It should be taken into note however that he might have said, "To Craterus". This is possible because the Greek pronunciation of "the strongest" and "Craterus" is different only by accent. The phrase and name are in fact, separated by only one letter in the ancient Greek language. Most scholar's believe that if Alexander did intend to choose one of his generals, his obvious choice would've been Craterus because he was the commander of the largest part of the army (infantry), because he had proven himself to be an excellent strategist, and because he displayed traits of the "ideal" Macedonian. Regardless of his reply, Craterus was eventually assassinated before he could organize a coup with the infantry and Alexander's empire was split into 4 kingdoms.

Alexander's death has been surrounded by as much controversy as many of the events of his life. Before long, accusations of foul play were being thrown about by his generals at one another, making it incredibly hard for a modern historian to sort out the propaganda and the half-truths from the actual events. No contemporary source can be fully trusted because of the incredible level of self-serving recording, and as a result what truly happened to Alexander the Great may never be known.
Alexander's body was placed in a gold anthropid sarcophagus, which was in turn placed in a second gold casket and covered with a purple robe. Alexander's coffin was placed, together with his armour, in a gold carriage which had a vaulted roof supported by an Ionic peristyle. The decoration of the carriage was very rich and is described in great detail by Diodoros.
According to legend, Alexander was preserved in a clay vessel full of honey (which acts as a preservative) and interred in a glass coffin. According to Aelian (Varia Historia 12.64), Ptolemy stole the body and brought it to Alexandria, where it was on display until Late Antiquity. It was here that Ptolemy IX, one of the last successors of Ptolemy I, replaced Alexander's sarcophagus with a glass one, and melted the original down in order to strike emergency gold issues of his coinage. The citizens of Alexandria were outraged at this and soon after Ptolemy IX was killed. Its current whereabouts are unknown.
The so-called "Alexander Sarcophagus," discovered near Sidon and now in the Istanbul Archaeological Museum, is now generally thought to be that of Abdylonymus, whom Hephaestion appointed as the king of Sidon by Alexander's order. The sarcophagus depicts Alexander and his companions hunting and in battle with the Persians.
Legacy and division of the empire

After Alexander's death, in 323 BCE, the rule of his Empire was given to Alexander's half-brother Philip Arridaeus and Alexander's son Alexander IV. However, since Philip was mentally ill and the son of Alexander still a baby, a regent was named in Perdiccas. In the meantime, the former generals of Alexander were named satraps of the various regions of his Empire. After a conflict between Seleucus and Perdiccas, the Treaty of Triparadisus was established in 320 BCE, in which Antipater was named as the new regent, and the satrapies again shared between the various generals. From that time, Alexander's officers were focused on the explicit formation of rival monarchies and territorial states.
Ultimately, the conflict was settled after the Battle of Ipsus in Phrygia in 301 BC. Alexander's empire was divided at first into four major portions: Cassander ruled in Macedon, Lysimachus in Thrace, Seleucus in Mesopotamia and Iran, and Ptolemy in the Levant and Egypt. Antigonus ruled for a while in Asia Minor and Syria but was eventually defeated by the other generals at Ipsus (301 BC). Control over Indian territory passed to Chandragupta Maurya, the first Maurya emperor, who further expanded his dominions after a settlement with Seleucus.
By 270 BC, Hellenistic states consolidated, with:
- The Antigonid Empire centered on Macedon.
- The Seleucid Empire in Asia
- The Ptolemaic kingdom in Egypt, Palestine and Cyrenaica
By the 1st century BC though, most of the Hellenistic territories in the West had been absorbed by the Roman Republic. In the East, they had been dramatically reduced by the expansion of the Parthian Empire and the secession of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom.
Alexander's conquests also had long term cultural effects, with the flourishing of Hellenistic civilization throughout the Middle East and Central Asia, and the development of Greco-Buddhist art in the Indian subcontinent.
Influence on Ancient Rome

Alexander and his exploits were admired by many Romans who wanted to associate themselves with his achievements, although very little is known about Roman-Macedonian diplomatic relations of that time. Julius Caesar wept in Spain at the mere sight of Alexander's statue and Pompey the Great rummaged through the closets of conquered nations for Alexander's 260-year-old cloak, which the Roman general then wore as the costume of greatness. However in his zeal to honor Alexander, Augustus accidentally broke the nose off the Macedonian's mummified corpse while laying a wreath at the hero's shrine in Alexandria, Egypt. The unbalanced emperor Caligula later took the dead king's armor from that tomb and donned it for luck. The Macriani, a Roman family that rose to the imperial throne in the 3rd century A.D., always kept images of Alexander on their persons, either stamped into their bracelets and rings or stitched into their garments. Even their dinnerware bore Alexander's face, with the story of the king's life displayed around the rims of special bowls.[19]
In the summer of 1995, during the archaeological work of the season centered on excavating the remains of domestic architecture of early-Roman date, a statue of Alexander was recovered from the structure, which was richly decorated with mosaic and marble pavements and probably was constructed in the 1st century AD and occupied until the 3rd century.[20]
General timeline
Alexander's character
Modern opinion on Alexander has run the gamut from the idea that he believed he was on a divinely-inspired mission to unite the human race, to the view that he was a megalomaniac bent on world domination. Such views tend to be anachronistic, however, and the sources allow for a variety of interpretations. Much about Alexander's personality and aims remains enigmatic.
Alexander is remembered as a legendary hero in Europe and much of both Southwest Asia and Central Asia, where he is known as Iskander or Iskandar Zulkarnain. To Zoroastrians, on the other hand, he is remembered as the destroyer of their first great empire and as the destroyer of Persepolis. Ancient sources are generally written with an agenda of either glorifying or denigrating the man, making it difficult to evaluate his actual character. Most refer to a growing instability and megalomania in the years following Gaugamela, but it has been suggested that this simply reflects the Greek stereotype of an orientalizing king. The murder of his friend Clitus, which Alexander deeply and immediately regretted, is often cited as a sign of his paranoia, as is his execution of Philotas and his general Parmenion for failure to pass along details of a plot against him. However, this may have been more prudence than paranoia.
Modern Alexandrists continue to debate these same issues, among others, in modern times. One unresolved topic involves whether Alexander was actually attempting to better the world by his conquests, or whether his purpose was primarily to rule the world.
Partially in response to the ubiquity of positive portrayals of Alexander, an alternate character is sometimes presented which emphasizes some of Alexander's negative aspects. Some proponents of this view cite the destructions of Thebes, Tyre, Persepolis, and Gaza as examples of atrocities, and argue that Alexander preferred to fight rather than negotiate. It is further claimed, in response to the view that Alexander was generally tolerant of the cultures of those whom he conquered, that his attempts at cultural fusion were severely practical and that he never actually admired Persian art or culture. To this way of thinking, Alexander was, first and foremost, a general rather than a statesman.
Alexander's character also suffers from the interpretation of historians who themselves are subject to the bias and idealisms of their own time. Good examples are W. W. Tarn, who wrote during the late 19th century and early 20th century, and who saw Alexander in an extremely good light, and Peter Green, who wrote after World War II and for whom Alexander did little that was not inherently selfish or ambition-driven. Tarn wrote in an age where world conquest and warrior-heroes were acceptable, even encouraged, whereas Green wrote with the backdrop of the Holocaust and nuclear weapons.
Stories and legends
According to one story, the philosopher Anaxarchus checked the vainglory of Alexander, when he aspired to the honors of divinity, by pointing to Alexander's wound, saying, "See the blood of a mortal, not the ichor of a god." In another version, Alexander himself pointed out the difference in response to a sycophantic soldier. A strong oral tradition, although not attested in any extant primary source, lists Alexander as having epilepsy, known to the Greeks as the Sacred Disease and thought to be a mark of divine favor.
Alexander had a sister named Thessalonice married to Cassander who later founded the city of Thessaloniki after his wife. There exists a popular Greek legend[21] about a mermaid or Gorgon that lived in the Aegean for hundreds of years and was thought to be Thessalonica. The legend states that when sailors in the Aegean encountered her she asked them a question: "Is Alexander the king alive?" to which the right answer would be "He lives and still rules." Any other answer would spur her rage and mean doom for the ship.
Alexander had a legendary horse named Bucephalos (meaning "ox-headed"), latinized Bucephalus, supposedly descended from the Mares of Diomedes. Alexander himself, while still a young boy, tamed this horse after experienced horse-trainers failed to do so.
There is an apocryphal tale, appearing in a redaction of the pseudo-historical Alexander Romance, which details another end for the last true Pharaoh of Egypt. Soon after Alexander's divinity was confirmed by the Oracle of Zeus Ammon, a rumor was begun that Nectanebo II did not travel to Nubia but instead to the court of Philip II of Macedon in the guise of an Egyptian magician. He coupled with Philip's wife Olympias and from his issue came Alexander. This myth would hold strong appeal for Egyptians who desired continuity in rule and harbored a strong dislike for foreign rule.
Another legend tells of Alexander's campaign down into the Syrian world toward Egypt. On the way, he planned to lay siege to the city of Jerusalem. As the victorious armies of the Greeks approached the city, word was brought to the Jews in Jerusalem that the armies were on their way. The high priest at that time, who was a godly old man by the name of Jaddua (mentioned also in the Bible book of Nehemiah) took the sacred writings of Daniel the prophet and, accompanied by a host of other priests dressed in white garments, went forth and met Alexander some distance outside the city — surrendering the city to Alexander's army.
All this is from the report of Josephus, the Jewish historian, who tells us that Alexander left his army and hurried to meet this body of priests. When he met them, he told the high priest that he had had a vision the night before in which God had shown him an old man, robed in a white garment, who would show him something of great significance to himself, according to the account, the high priest then opened the prophecies of Daniel and read them to Alexander.
These prophecies were probably Daniel 11:2-5, where it was predicted that a Greek (Hebrew: Yavan)[1] King will arise to conquer Persia and "who will rule with great power" and later "And when he shall stand up, his kingdom shall be broken, and shall be divided toward the four winds of heaven" (KJV translation).
In the prophecies Alexander was able to see the predictions that he would become that notable goat with the horn in his forehead, who would come from the West and smash the power of Persia and conquer the world. He was so overwhelmed by the accuracy of this prophecy and, of course, by the fact that it spoke about him, that he promised that he would save Jerusalem from siege, and sent the high priest back with honors.
Greek and Latin sources
Apart from the cuneiform evidence from Babylonia that is now being disclosed, the Greek and Latin sources for Alexander's life are, from the perspective of ancient history, relatively numerous. Alexander himself left only a few inscriptions and some letter-fragments of dubious authenticity, but a large number of his contemporaries wrote full accounts. The key contemporary historians are considered Callisthenes, his general Ptolemy, Aristobulus, Nearchus and Onesicritus. Another influential account was penned by Cleitarchus, who, while not a direct witness of Alexander's expedition, used the sources which had just been published. His work was to be the backbone of that of Timagenes, who heavily influenced many surviving historians. Unfortunately, all these works were lost. Instead, the modern historian must rely on authors who used these and other early sources.
The five main accounts are by Arrian, Curtius, Plutarch, Diodorus, and Justin.
- Anabasis Alexandri (The Campaigns of Alexander in Greek) by the Greek historian Arrian of Nicomedia, writing in the 2nd century AD, and based largely on Ptolemy and, to a lesser extent, Aristobulus and Nearchus. It is considered generally the most trustworthy source.
- Historiae Alexandri Magni, a biography of Alexander in ten books, of which the last eight survive, by the Roman historian Quintus Curtius Rufus, written in the 1st century AD, and based largely on Cleitarchus through the mediation of Timagenes, with some material probably from Ptolemy;
- Life of Alexander (see Parallel Lives) and two orations On the Fortune or the Virtue of Alexander the Great (see Moralia), by the Greek historian and biographer Plutarch of Chaeronea in the second century, based largely on Aristobulus and especially Cleitarchus.
- Bibliotheca historia (Library of world history), written in Greek by the Sicilian historian Diodorus Siculus, from which Book 17 relates the conquests of Alexander, based almost entirely on Timagenes's work. The books immediately before and after, on Philip and Alexander's "Successors," throw light on Alexander's reign.
- The Epitome of the Philippic History of Pompeius Trogus by Justin, which contains factual errors and is highly compressed. It is difficult in this case to understand the source, since we only have an epitome, but it is thought that also Pompeius Trogus may have limited himself to use Timagenes for his Latin history. To these five main sources some like to add the Metz Epitome, an anonymous late Latin work that narrates Alexander's campaigns from Hyrcania to India. Much is also recounted incidentally in other authors, including Strabo, Athenaeus, Polyaenus, Aelian, and others.
The "problem of the sources" is the main concern (and chief delight) of Alexander-historians. In effect, each presents a different "Alexander", with details to suit. Arrian is mostly interested in the military aspects, while Curtius veers to a more private and darker Alexander. Plutarch can't resist a good story, light or dark. All, with the possible exception of Arrian, include a considerable level of fantasy, prompting Strabo to remark, "All who wrote about Alexander preferred the marvellous to the true." Nevertheless, the sources tell us much, and leave much to our interpretation and imagination. Perhaps Arrian's words are most appropriate:
- One account says that Hephaestion laid a wreath on the tomb of Patroclus; another that Alexander laid one on the tomb of Achilles, calling him a lucky man, in that he had Homer to proclaim his deeds and preserve his memory. And well might Alexander envy Achilles this piece of good fortune; for in his own case there was no equivalent:his one failure, the single break, as it were, in the long chain of his successes, was that he had no worthy chronicler to tell the world of his exploits.
Alexander's legend
Alexander was a legend in his own time. His court historian Callisthenes portrayed the sea in Cilicia as drawing back from him in proskynesis. Writing after Alexander's death, another participant, Onesicritus, went so far as to invent a tryst between Alexander and Thalestris, queen of the mythical Amazons. When Onesicritus read this passage to his patron, Alexander's general and later King Lysimachus reportedly quipped, "I wonder where I was at the time."
In the first centuries after Alexander's death, probably in Alexandria, a quantity of the more legendary material coalesced into a text known as the Alexander Romance, later falsely ascribed to the historian Callisthenes and therefore known as Pseudo-Callisthenes. This text underwent numerous expansions and revisions throughout Antiquity and the Middle Ages, exhibiting a plasticity unseen in "higher" literary forms. Latin and Syriac translations were made in Late Antiquity. From these, versions were developed in all the major languages of Europe and the Middle East, including Armenian, Georgian, Persian, Arabic, Turkish, Hebrew, Serbian, Slavonic, Romanian, Hungarian, German, English, Italian, and French. The "Romance" is regarded by most Western scholars as the source of the account of Alexander given in the Qur'an (Sura The Cave). It is the source of many incidents in Ferdowsi's "Shahnama". A Mongolian version is also extant.
Some believe that, excepting certain religious texts, it is the most widely-read work of pre-modern times.
Alexander in the Qur'an
Alexander was often identified in Persian and Arabic-language sources as Dhul-Qarnayn, Arabic for the "Two-Horned One", possibly a reference to the appearance of a horn-headed figure that appears on coins minted during his rule and later imitated in ancient Middle Eastern coinage. If this theory is followed, Islamic accounts of the Alexander legend, particularly in the Qur'an and in Persian legends, combined the Pseudo-Callisthenes legendary, pseudo-religious material about Alexander. The same legends from the Pseudo-Callisthenes were combined in Persia with Sasanid Persian ideas about Alexander in the Iskandarnamah. Alexander built a wall of iron and melted copper in which Gog and Magog are confined. However, some Muslim scholars disagree that Alexander was Dhul Qarnayn.
Mount Rushmore Type Mountain of Alexander
In honor of the hero, carving of Alexander the Great on the mountain of St. George in Northern Greece has begun. The mountain is comparable to Mount Rushmore in the United States.[2]
Main towns founded by Alexander
Around seventy towns or outposts are claimed to have been founded by Alexander.[22] Some of the main ones are:
- Alexandria, Egypt
- Alexandria Asiana, Iran
- Alexandria in Ariana, Afghanistan
- Alexandria of the Caucasus, Afghanistan
- Alexandria on the Oxus, Afghanistan
- Alexandria of the Arachosians, Afghanistan
- Alexandria on the Indus (Alexandria Bucephalous), Pakistan
- Alexandria Eschate, "The furthest", Tajikistan
- Iskenderun (Alexandretta), Turkey
- Kandahar (Alexandropolis), Afghanistan
- Iskandiriyah(Alexandria),Iraq
Alexander as City-Planner
- By selecting the right angle of the streets, Alexander made the city breathe with the etesian winds [the northwestern winds that blow during the summer months], so that as these blow across a great expanse of sea, they cool the air of the town, and so he provided its inhabitants with a moderate climate and good health. Alexander also laid out the walls so that they were at once exceedingly large and marvelously strong.
- --Diodorus Siculus, Library of History, volume 8.
In popular culture
Novels
- From 1969 to 1981, Mary Renault wrote a historical fiction trilogy on the life of Alexander: Fire From Heaven (about his early life), The Persian Boy (about his conquest of Persia, his expedition to India, and his death, seen from the viewpoint of Bagoas, a Persian eunuch and Alexander's eromenos), and Funeral Games (about the events following his death). Alexander also appears briefly in Renault's novel The Mask of Apollo, and is alluded to directly in The Last of the Wine and indirectly in The Praise Singer. In addition to the fiction, Renault also wrote a non-fiction biography, The Nature of Alexander.
- French writer Roger Peyrefitte wrote Les Conquetes d'Alexandre and other novels about Alexander the Great.
- A further trilogy of novels about Alexander was written in Italian by Valerio Massimo Manfredi and subsequently published in an English translation, entitled The Son of the Dream, The Sands of Ammon and The Ends of the Earth.
- David Gemmel's Dark Prince features Alexander as the chosen vessel for a world-destroying demon king. ISBN 0-345-37910-1.
- Steven Pressfield's 2004 book The Virtues of War is told from the first-person perspective of Alexander. Pressfield's novel The Afghan Campaign is told from the point of view of a soldier in Alexander's army. Alexander makes several brief appearances in the novel.
- Rudyard Kipling's story "The Man Who Would Be King" (1888) provides some glimpses of Alexander's legacy. Made into a movie of the same title in 1975, starring Sean Connery and Michael Caine.
TV series
- Alexander the Great (1968), TV series, starring William Shatner as Alexander, directed by Phil Karlson.
- Alexander Senki (1997), Anime / TV series, starring Toshihiko Seki as Alexander, directed by Yoshinori Kanemori, and with character designs by Peter Chung (of Aeon Flux fame). It was based on the novel Alexander Senki by Hiroshi Aramata. Also known as Alexander (International: English title); Reign: The Conqueror (USA). The series (US version, Reign: The Conqueror) debuted on Cartoon Network's Adult Swim block variety show in 2003.
- The 1996 miniseries Gulliver's Travels, starring Ted Danson, featured a visit from Alexander the Great.
- In the Smallville season 1 episode "Rogue", Lex Luthor shows Clark Kent the armor that Alexander the Great wore in battle. The breastplate is gold, with red and blue diamonds (the colors that represent Superman), and a snake shaped like the letter S.
- In the Footsteps of Alexander the Great (1998), mini-series, hosted by Michael Wood, directed by David Wallace.
- Iskandar is briefly mentioned in the visual novel game and anime series Fate/stay night as an example of the Rider-class Servant. It was hinted that he was the most powerful of the characters, but died in a two-versus-one battle.
- In the miniseries Yu-Gi-Oh! Capsule Monsters, Alexander the Great was a character in the Capsule Monster World.
Movies
- Sikander (1941), a Hindi movie directed by Sohrab Modi which depicts Alexander the Great's Indian conquest.
- Alexander the Great (1956) starring Richard Burton as Alexander, directed by Robert Rossen and produced by MGM.
- Sikandar-e-Azam (1965) a Hindi movie directed by Kedar Kapoor starring Dara Singh as Alexandar depicts Alexandar's Indian conquest with Porus.
- Alexander (2004), starring Colin Farrell as Alexander, directed by Oliver Stone. Based on the biography Alexander the Great (ISBN 0-14-008878-4) by Robin Lane Fox. It was released on November 24, 2004.
- Baz Luhrmann had been planning to make a very different film about Alexander, starring Leonardo DiCaprio, but the release of Stone's film eventually persuaded him to abandon the project.[23]
- Alexander the Great (2006)...
Other works

- The 2000 album Born from the string quartet bond, includes a song titled "Alexander the Great".
- The British heavy metal band Iron Maiden had a song entitled "Alexander the Great" on their album Somewhere in Time (1986). The song describes Alexander's life, but contains one inaccuracy: In the song it is stated that Alexander's army would not follow him into India.
- Brazilian musician Caetano Veloso's 1998 album Livro includes an epic song about Alexander called "Alexandre".
- Alexander is a character in the computer games Empire Earth andRise of Nations: Thrones and Patriots. He is a civilization leader in the 2005 computer gameSid Meier's Civilization IV , where Alexander is the lone leader of the Greek civilization and has the leader traits "Aggressive" and "Philosophical". In the Rome Total War expansion pack, Alexander, Alexander the Great's conquests are chronicled in a campaign and six battles are modeled on Alexander's early battles. Alexander the Great is also featured in the game called Rise and Fall: Civilizations at War released by Midway games.
- In Alan Moore's Watchmen, one of the main characters, Ozymandias, goes into detail about how he followed in Alexander the Great's footsteps in order to achieve enlightenment.
Footnotes
- ^ The name Αλέξανδρος derives from the Greek words άλεξ (to repel, shield, protect) and άνδρας (man), literally meaning "protector of men." For further details on the origins of the name, see related section in disambiguation article.
- ^ Whether the Macedonians of Alexander's time and before were Hellenes (Greeks) is disputed by scholars. The question largely depends on the classification of the Ancient Macedonian language. By separating Macedonians and Greeks in this sentence and others, no position in this debate is implied.
- ^ Plutarch, Alexander 2.2-3.
- ^ Plutarch, Alexander 2.1.
- ^ See note 1
- ^ Alexander the Great, 2003, p 123, I. Worthington.
- ^ Curtius.
- ^ (Ancient India, 1971, p 99, Dr R. C. Majumdar; History and Culture of Indian People, The Age of Imperial Unity, Foreign Invasion, p 46, Dr R. K Mukerjee.
- ^ Carnage and Culture: Landmark Battles in the Rise to Western Power, 2002, p 86, Victor Hanson.
- ^ Plutarch, Vita Alexandri, 62
- ^ The Search for Alexander, Little, Brown and Co. Boston, 1980, p. 261.
- ^ Plutarch, On the Luck and Virtue of Alexander A, 12.
- ^ Plutarch, Parallel Lives: Alexander, 22, 1.
- ^ Plutarch, Parallel Lives: Alexander, 21.
- ^ Curtius, VI.5.23.
- ^ The Search for Alexander ~ Little, Brown and Co. Boston, 1980, p. 67.
- ^ The Nature of Alexander, Pantheon Books: New York, 1975, p. 47.
- ^ Arrian, 1.28.7.
- ^ Frank L. Holt, Alexander the Great and the Mystery of the Elephant Medallions, University of California Press.
- ^ Salima Ikram. Nile Currents
- ^ Teacher's Guide - "In The Footsteps Of Alexander The Great" (pdf)
- ^ Alexander the Great: his towns
- ^ "Kidman: 'Luhrmann Not Doing Alexander Film'", IMDb.com, November 1, 2004
Literature
- Arrian, The Campaigns of Alexander, English translation by Aubrey de Sélincourt (1971, first published 1958) Penguin Classics published by the Penguin Group, London ISBN 0-14-044253-7
- De Santis, Marc G. “At The Crossroads of Conquest.” Military Heritage. December 2001. Volume 3, No. 3: 46-55, 97 (Alexander the Great, his military, his strategy at the Battle of Gaugamela and his defeat of Darius making Alexander the King of Kings).
- Fuller, J.F. C; A Military History of the Western World: From the earliest times to the Battle of Lepanto; New York: Da Capo Press, Inc., 1987 and 1988. ISBN 0-306-80304-6
- Gergel, Tania Editor Alexander the Great (2004) published by the Penguin Group, London ISBN 0-14-200140-6 Brief collection of ancient accounts translated into English
- Green, Peter. Alexander of Macedon: 356-323 B.C. A Historical Biography. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1991.
- Kurke, Lance B. The Wisdom of Alexander the Great: enduring leadership lessons from the man who created an empire. (2004) published by AMACOM, New York ISBN 0-8144-0820-6
- Lane Fox, Robin, Alexander the Great, London (Allen Lane) 1973, ISBN 0-86007-707-1
- Renault, Mary. The Nature of Alexander (1975) Pantheon Books ISBN 0-394-73825-X Renault's non-fiction analysis of Alexander's personality and motivations
- Cartledge, Paul. Alexander the Great (2005)
Non-Greek/Latin perspectives
- A. Shapur Shahbazi, "Iranians and Alexander", American Journal of Ancient History n.s. 2 (2003), 5-38: the Persian side of the story.
- R.J. van der Spek, "Darius III, Alexander the Great and Babylonian scholarship" in: Achaemenid History 13 (2003), 289-346: an overview of several Babylonian sources
- Two chapters of Jona Lendering's Dutch book Alexander de Grote, which uses the cuneiform sources, are available in translation. In this chapter, he argues that at Gaugamela, Alexander attacked a Persian army that was looking for an excuse to run away; and in this chapter, he offers a Babylonian perspective on Alexander's final days.
External links
Primary Sources
- Alexander the Great: An annotated list of primary sources from Livius.org
- Alexander the Great Alexander the Great forum, articles, and referenced information.
- Wiki Classical Dictionary, extant sources and fragmentary and lost sources
- Plutarch, Life of Alexander (in English)
- Justin, Epitome of the Philippic History of Pompeius Trogus (in English)
- Plutarch, Of the Fortune or Virtue of Alexander the Great (in English)
- Quintus Curtius Rufus, Histories of Alexander (in Latin)
- Alexander's Death from Alexander the Great on the Web: 1,000 resources about Alexander the Great
- Alexander The Great in the French museum Le Louvre
Projects
- Alexander the Great on the Web, a comprehensive directory of some 1,000 sites
- In the footsteps of Alexander the Great: an archaeological adventure across Turkey, with travel article and archaeological links
- Livius Project articles on Alexander by Jona Lendering
- Pothos.org: Alexander's Home on the Web
- Wiki Classical Dictionary: Category Alexander the Great, a Mediawiki based project, with stricter guidelines and editors
- Alexander the Great Coins, a site depicting Alexander's coins and later coins featuring Alexander's image
- Alexander the Great Site, a site dedicated to Alexander. Features Articles about Alexander, his life, armies, mysteries surrounding his death, and the Hellenistic Period that came after this great Hellenic Leader.
- Alexander Tells History from his perspective; broken down into 33 segments, covering his childhood, education, upbringing, influences, strategy, leadership, friendship as well as the numerous clashes he had against Darius of the Persian Empire.
Narratives
- Alexander the Great of Macedon, a project by John J. Popovic
Discussion
- Pothos Forum
- Alexander the Great Forum, a forum for Alexander the Great and the history surrounding him.
Bibliography
- PDF: A Bibliography of Alexander the Great by Waldemar Heckel (please note that Heckel ignores the Babylonian sources and publications on these sources; cf. this review)
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
