Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy.
Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass when stationary (called rest mass) also has an equivalent amount of energy whose form is called rest energy, and any additional energy (of any form) acquired by the object above that rest energy will increase the object's total mass just as it increases its total energy.
Human civilization requires energy to function, which it gets from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, or renewable energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven by the energy the planet receives from the Sun (although a small amount is also contributed by geothermal energy). (Full article...)
Selected article
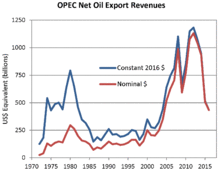
Petrodollar recycling is the international spending or investment of a country's revenues from petroleum exports ("petrodollars"). It generally refers to the phenomenon of major petroleum-exporting states, mainly the OPEC members plus Russia and Norway, earning more money from the export of crude oil than they could efficiently invest in their own economies. The resulting global interdependencies and financial flows, from oil producers back to oil consumers, can reach a scale of hundreds of billions of U.S. dollars per year – including a wide range of transactions in a variety of currencies, some pegged to the U.S. dollar and some not. These flows are heavily influenced by government-level decisions regarding international investment and aid, with important consequences for both global finance and petroleum politics. The phenomenon is most pronounced during periods when the price of oil is historically high.
The term petrodollar was coined in the early 1970s during the oil crisis, and the first major petrodollar surge (1974–1981) resulted in more financial complications than the second (2005–2014). (Full article...)
Selected image

Photo credit: NASA/TRACE
Plasma being channeled by the magnetic field loops of a sunspot.
Did you know?

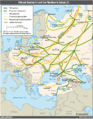
- The 1,222 km long Nordstream pipeline between Russia and the Germany is the world's longest underwater pipeline?
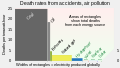
- Due to the vast quantity of coal burnt in fossil fuel power plants, they cause more radioactive contamination than nuclear power plants?
- Chinese energy policy includes using renewable energy for the rural electrification of 3.5 million households by 2010?
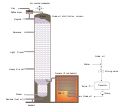
- The 354 MW SEGS solar power plant (pictured) in the Mojave Desert is the world's largest?
- Known reserves of petroleum are typically estimated at around 1.2 trillion barrels, or at 3.74 trillion barrels if oil sands are included?
- The concentration of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide has increased from about 280 parts per million to about 380 ppm since the start of the Industrial Revolution. That's an increase of 35.71%. The estimated population of the world in 1750 was 791 Million people. The estimated population of the world on June 30th, 2007 was 6.6 Billion people. That's an increase of 734.39%.?
- In the 1990s Bougainville conflict, islanders cut off from oil supplies due to a blockade used coconut oil to fuel their vehicles?
- The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is considered a cartel by many observers?
Selected biography
Born in Texas, Hubbert studied geology, mathematics, and physics at the University of Chicago. He pursued his Ph.D. while working for the Amerada Petroleum Company, then worked for the Shell Oil Company from 1943 until 1964. On leaving Shell he became a senior research geophysicist for the United States Geological Survey until retiring in 1976. Hubbert was also a professor at Stanford University and at UC Berkeley.
Hubbert is most well-known for his studies on the capacities of oil fields and natural gas reserves. He predicted that, for any given geographical area, the rate of petroleum production over time would resemble a bell curve. At the 1956 meeting of the American Petroleum Institute, Hubbert predicted that United States petroleum production would peak in the late 1960s or early 1970s. He became famous when his prediction came true in 1970.
In 1974, Hubbert projected that global oil production would peak in 1995 "if current trends continue". Various subsequent predictions have been made by others as trends have fluctuated in the intervening years. Hubbert's theory, and its implications for the world economy, remain controversial.
In the news
- 18 August 2024 – 2024 Lebanese blackout
- Ongoing nationwide blackouts in Lebanon caused by fuel shortages provoke significant governmental conflict, with the Minister of Energy blaming the Central Bank for not paying Iraq for fuel imports and the Central Bank blaming Parliament for not authorizing emergency fund transfers for fuel payments. (Asharq Al-Awsat)
- 17 August 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- The International Atomic Energy Agency declares that the safety of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant is deteriorating, following an investigation into an explosive drone strike that targeted a perimeter access road at the power plant. (Reuters)
- 31 July 2024 – Lukoil oil transit dispute
- Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico threatens to suspend Slovakia's diesel exports to Ukraine if the Ukrainian government continues to suspend pipeline oil transport from Russian oil company Lukoil, which Slovakia claims is causing a national energy crisis. (The Kyiv Independent)
General images
Quotations
- "The world's second-largest emitter of greenhouse gases is China. Yet, China was entirely exempted from the requirements of the Kyoto Protocol. India and Germany are among the top emitters. Yet, India was also exempt from Kyoto." – George W. Bush, 2001
- "The newly industrialized States cannot, for example, be asked to apply restrictive environmental standards to their emerging industries unless the industrialized States first apply them within their own boundaries." – Pope John Paul II, 1990
- "We should work together to make sure the international community upholds the goals and framework established in the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and its Kyoto Protocol and the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities." – Hu Jintao, 2007
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus