Asia Cooperation Dialogue
Asia Cooperation Dialogue | |
|---|---|
 Member states in yellow | |
| Type | Regional cooperation organizations |
| Members | 34 Countries
|
| Leaders | |
• Secretary-General | |
| Establishment | 2002 |
| Area | |
• Total | 46,872,864[2] km2 (18,097,714 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 4,317,290,284 |
• Density | 92/km2 (238.3/sq mi) |
Website www | |
The Asia Cooperation Dialogue (ACD) is an inter-governmental organization created on 18 June 2002 to promote Asian cooperation at a continental level and to help integrate separate regional organizations such as ASEAN, SAARC, the Gulf Cooperation Council, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation and the Eurasian Economic Union.
History
The idea of an Asia Cooperation Dialogue was raised at the First International Conference of Asian Political Parties (held in Manila between 17–20 September 2000) by Surakiart Sathirathai, then deputy leader of the now defunct Thai Rak Thai Party, on behalf of his party leader, Thaksin Shinawatra, then Prime Minister of Thailand. It was suggested that Asia as a continent should have its own forum to discuss Asia-wide cooperation. Afterwards, the idea of the ACD was formally put forward during the 34th ASEAN Foreign Ministers Meeting in Hanoi, 23–24 July 2001 and at the ASEAN Foreign Ministers Retreat in Phuket, 20–21 February 2002.
Ministerial meetings
| Meeting | Country | Year |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 18–19 June 2002 | |
| 2nd | 21–22 June 2003 | |
| 3rd | 21–22 June 2004 | |
| 4th | 4–6 April 2005 | |
| 5th | 23–24 May 2006 | |
| 6th | 5–6 June 2007 | |
| 7th | 16–17 October 2008 | |
| 8th[3] | 15–16 October 2009 | |
| 9th | 8–9 November 2010 | |
| 10th | 10–11 October 2012 | |
| 11th[4] | 29 March 2013 | |
| 12th[5] | 26 November 2013 | |
| 13th[6] | 25 November 2014 | |
| 14th[7] | 9–10 March 2016 | |
| 15th[8] | 16–17 January 2017 | |
| 16th[9] | 30 April 2019 |
Summits
| Meeting | Country | Year |
|---|---|---|
| I | 15–17 October 2012 | |
| II | 8–10 October 2016 | |
| III | 2018[10] |
Objectives
The main objectives of the ACD are to:
- Promote interdependence among Asian countries in all areas of cooperation by identifying Asia's common strengths and opportunities which will help reduce poverty and improve the quality of life for Asian people whilst developing a knowledge-based society within Asia and enhancing community and people empowerment;
- Expand the trade and financial market within Asia and increase the bargaining power of Asian countries in lieu of competition and, in turn, enhance Asia's economic competitiveness in the global market;
- Serve as the missing link in Asian cooperation by building upon Asia's potentials and strengths through supplementing and complementing existing cooperative frameworks so as to become a viable partner for other regions;
- Ultimately transform the Asian continent into an Asian Community, capable of interacting with the rest of the world on a more equal footing and contributing more positively towards mutual peace and prosperity.
Member states

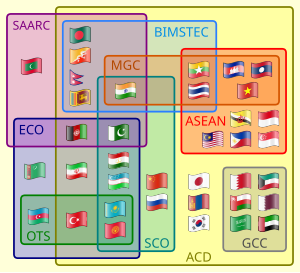
The ACD was founded by 18 members. Since March 2016, the organization consists of 34 states[11] as listed below (including all current members of ASEAN and the GCC). Overlapping regional organization membership in italics.
| Name | Accession date | Regional organization |
|---|---|---|
| 17 October 2012 | SAARC, ECO | |
| 18 June 2002 | GCC, AL | |
| 18 June 2002 | SAARC, BIMSTEC | |
| 27 September 2004 | SAARC, BIMSTEC | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN, MGC | |
| 18 June 2002 | SCO | |
| 18 June 2002 | SAARC, BIMSTEC, MGC, SCO | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN | |
| 21 June 2004 | ECO | |
| 18 June 2002 | — | |
| 21 June 2003 | CIS, ECO, SCO | |
| 18 June 2002 | — | |
| 21 June 2003 | GCC, AL | |
| 16 October 2008 | CIS, ECO, SCO | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN, MGC | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN | |
| 21 June 2004 | — | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN, BIMSTEC, MGC | |
| 10 March 2016 | SAARC, BIMSTEC | |
| 21 June 2003 | GCC, AL | |
| 18 June 2002 | SAARC, SCO, ECO | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN, | |
| 18 June 2002 | GCC, AL | |
| 4 April 2005 | CIS, CoE, SCO | |
| 4 April 2005 | GCC, AL | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN | |
| 21 June 2003 | SAARC, BIMSTEC | |
| 5 June 2006 | CIS, ECO, SCO | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN, BIMSTEC, MGC | |
| 26 September 2013 | CoE,[t 3] ECO | |
| 21 June 2004 | GCC, AL | |
| 5 June 2006 | CIS, ECO, SCO | |
| 18 June 2002 | ASEAN, MGC |
See also
- Asia Council
- Pan-Asianism
- One Belt One Road
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Asian Currency Unit
- Asian Clearing Union
- Asian Development Bank
- Asian Parliamentary Assembly
- Continental regional organizations
- International organization
- Continental union
- East Asia Community
- Eurasian Economic Union
- Asia–Europe Meeting
- Conference on Interaction and Confidence-Building Measures in Asia
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
References
- ^ "Top Stories : Thailand nominates ACD Secretary General and highlights priority areas in Asia-wide cooperation – Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Kingdom of Thailand". www.mfa.go.th. Retrieved 10 April 2018.
- ^ Corresponds to the terrestrial surface. Including the Exclusive Economic Zones of each member state, the total area is 73 936 667 km².
- ^ "Arrangements for media coverage of the 8th Asia Cooperation Dialogue Ministerial Meeting October 2009" (PDF). Retrieved 15 September 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Thaksin's Statement at the 11th Asia Cooperation Dialogue Ministerial Meeting". wordpress.com. 3 April 2013. Retrieved 10 April 2018.
- ^ "12th Asia Cooperation Dialogue Ministerial Meeting held in Bahrain". xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 10 April 2018.
- ^ "32 ministers to attend Riyadh conference". Arab News.com. 2 November 2009. Retrieved 30 May 2015.
- ^ "Chairman's Statement 14th Asia Cooperation Dialogue (ACD) Ministerial Meeting" (PDF).
- ^ "15th ACD Ministerial Meeting, 16–17 January 2017, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates". 17 January 2017.
- ^ "16th ACD Ministerial Meeting, 30 April 2019, Doha, Qatar". 17 January 2017.
- ^ "Asia Cooperation Dialogue". www.acd-dialogue.org. Retrieved 10 April 2018.
- ^ a b "No: 253, 26 September 2013, Press Release on Turkey's Membership to the Asia Cooperation Dialogue". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Turkey. 26 September 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
- ^ "Assistant Foreign Minister Zhai Jun Attends the 7th Asia Cooperation Dialogue Foreign Ministers'Meeting in Kazakhstan". Retrieved 28 June 2010.
Further reading
- Why We Need an Asian Union
- European Policy Centre (2005-01): EU and Asian Integration Processes Compared
- The Guardian (2005-04-12): Hopes and Fears of an Asian Union
- International Herald Tribune (2005-06-18): Toward an 'Asian Union'?
- Asia Times (2005-10-01): Hedging China with FTAs
- International Herald Tribune (2005-12-16): An Asian Union? Not Yet
- Bangkok Post (2006-05-19): Towards a Truly Pan-Asian Community
- China Daily (2007-04-21): Asian Integration Still a Long Way Off
- Tehran Times (2010-03-14): Ahmadinejad Proposes Establishment of Asian Union
