Core cities of Japan
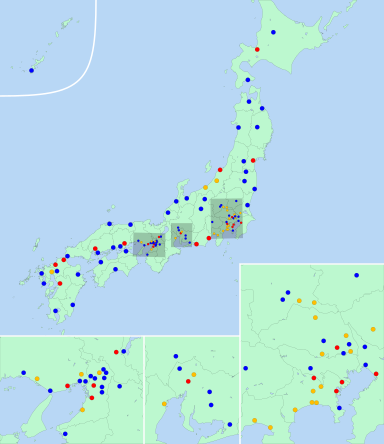
■ ― Designated cities
■ ― Core cities
■ ― Special cities
| Administrative divisions of Japan |
|---|
| Prefectural |
| Prefectures |
| Sub-prefectural |
| Municipal |
| Sub-municipal |
A core city (中核市, Chūkakushi) is a class or category of Japanese cities. It is a local administrative division created by the national government.[1] Core cities are delegated many functions normally carried out by prefectural governments, but not as many as designated cities. To become a candidate for core city status, a city must have a population greater than 300,000 and an area greater than 100 square kilometers, although special exceptions may be made by order of the cabinet for cities with populations under 300,000 but over 200,000.[2] After the abolition of special city status on April 1, 2015, any city with a population above 200,000 may apply for core city status.[3]
Application for designation is made by a city with the approval of both the city and prefectural assemblies.
History
The term "core city" was created by the first clause of Article 252, Section 22 of the Local Autonomy Law of Japan.[4]
List of core cities
As of 1 April 2020, 60 cities have been designated core cities[3]:
| Name | Japanese | Population (2012) | Date of designation | Region | Prefecture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akashi | 明石市 | 290,927 | 2018-04-01 | Kansai | Hyōgo |
| Akita | 秋田市 | 322,224 | 1997-04-01 | Tōhoku | Akita |
| Amagasaki | 尼崎市 | 451,353 | 2009-04-01 | Kansai | Hyōgo |
| Aomori | 青森市 | 297,348 | 2006-10-01 | Tōhoku | Aomori |
| Asahikawa | 旭川市 | 351,765 | 2000-04-01 | Hokkaidō | |
| Fukui | 福井市 | 266,612 | 2019-04-01 | Chūbu | Fukui |
| Fukushima | 福島市 | 289,355 | 2018-04-01 | Tōhoku | Fukushima |
| Fukuyama | 福山市 | 462,144 | 1998-04-01 | Chūgoku | Hiroshima |
| Funabashi | 船橋市 | 610,492 | 2003-04-01 | Kantō | Chiba |
| Gifu | 岐阜市 | 412,718 | 1996-04-01 | Chūbu | Gifu |
| Hachinohe | 八戸市 | 241,613 | 2017-01-01 | Tōhoku | Aomori |
| Hachiōji | 八王子市 | 579,799 | 2015-04-01 | Kantō | Tokyo |
| Hakodate | 函館市 | 279,056 | 2005-10-01 | Hokkaidō | |
| Higashiōsaka | 東大阪市 | 508,267 | 2005-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Himeji | 姫路市 | 536,218 | 1996-04-01 | Kansai | Hyōgo |
| Hirakata | 枚方市 | 407,997 | 2014-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Iwaki | いわき市 | 332,994 | 1999-04-01 | Tōhoku | Fukushima |
| Kagoshima | 鹿児島市 | 607,257 | 1996-04-01 | Kyushu | Kagoshima |
| Kashiwa | 柏市 | 404,863 | 2008-04-01 | Kantō | Chiba |
| Kanazawa | 金沢市 | 462,796 | 1996-04-01 | Chūbu | Ishikawa |
| Kawagoe | 川越市 | 345,361 | 2003-04-01 | Kantō | Saitama |
| Kawaguchi | 川口市 | 561,788 | 2018-04-01 | Kantō | Saitama |
| Kōchi | 高知市 | 342,568 | 1998-04-01 | Shikoku | Kōchi |
| Kōfu | 甲府市 | 197,318 | 2019-04-01 | Chūbu | Yamanashi |
| Kōriyama | 郡山市 | 331,140 | 1997-04-01 | Tōhoku | Fukushima |
| Koshigaya | 越谷市 | 328,079 | 2015-04-01 | Kantō | Saitama |
| Kurashiki | 倉敷市 | 477,086 | 2002-04-01 | Chūgoku | Okayama |
| Kure | 呉市 | 236,595 | 2016-04-01 | Chūgoku | Hiroshima |
| Kurume | 久留米市 | 301,821 | 2008-04-01 | Kyushu | Fukuoka |
| Maebashi | 前橋市 | 338,481 | 2009-04-01 | Kantō | Gunma |
| Matsue | 松江市 | 208,160 | 2018-04-01 | Chūgoku | Shimane |
| Matsuyama | 松山市 | 516,823 | 2000-04-01 | Shikoku | Ehime |
| Mito | 水戸市 | 269,162 | 2020-04-01 | Kantō | Ibaraki |
| Miyazaki | 宮崎市 | 402,289 | 1998-04-01 | Kyushu | Miyazaki |
| Morioka | 盛岡市 | 299,734 | 2008-04-01 | Tōhoku | Iwate |
| Naha | 那覇市 | 321,695 | 2013-04-01 | Kyushu | Okinawa |
| Nagano | 長野市 | 380,581 | 1999-04-01 | Chūbu | Nagano |
| Nagasaki | 長崎市 | 440,911 | 1997-04-01 | Kyushu | Nagasaki |
| Nara | 奈良市 | 365,421 | 2002-04-01 | Kansai | Nara |
| Neyagawa | 寝屋川市 | 238,819 | 2019-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Nishinomiya | 西宮市 | 483,878 | 2008-04-01 | Kansai | Hyōgo |
| Ōita | 大分市 | 476,008 | 1997-04-01 | Kyushu | Ōita |
| Okazaki | 岡崎市 | 374,085 | 2003-04-01 | Chūbu | Aichi |
| Ōtsu | 大津市 | 339,469 | 2009-04-01 | Kansai | Shiga |
| Sasebo | 佐世保市 | 259,676 | 2016-04-01 | Kyushu | Nagasaki |
| Shimonoseki | 下関市 | 277,937 | 2005-10-01 | Chūgoku | Yamaguchi |
| Suita | 吹田市 | 357,917 | 2020-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Takamatsu | 高松市 | 420,356 | 1999-04-01 | Shikoku | Kagawa |
| Takasaki | 高崎市 | 371,820 | 2011-04-01 | Kantō | Gunma |
| Takatsuki | 高槻市 | 355,840 | 2003-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Tottori | 鳥取市 | 196,538 | 2018-04-01 | Chūgoku | Tottori |
| Toyama | 富山市 | 421,393 | 2005-04-01 | Chūbu | Toyama |
| Toyohashi | 豊橋市 | 375,804 | 1999-04-01 | Chūbu | Aichi |
| Toyonaka | 豊中市 | 390,457 | 2012-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Toyota | 豊田市 | 420,680 | 1998-04-01 | Chūbu | Aichi |
| Utsunomiya | 宇都宮市 | 513,722 | 1996-04-01 | Kantō | Tochigi |
| Wakayama | 和歌山市 | 368,684 | 1997-04-01 | Kansai | Wakayama |
| Yamagata | 山形市 | 254,519 | 2019-04-01 | Tōhoku | Yamagata |
| Yao | 八尾市 | 270,735 | 2018-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Yokosuka | 横須賀市 | 415,259 | 2001-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa |
Former core cities
| Name | Japanese | Date of designation | Date of reclassification | Region | Prefecture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hamamatsu | 浜松市 | 1996-04-01 | 2007-04-01 (Designated city) | Chūbu | Shizuoka |
| Kumamoto | 熊本市 | 1996-04-01 | 2012-04-01 (Designated city) | Kyushu | Kumamoto |
| Niigata | 新潟市 | 1996-04-01 | 2007-04-01 (Designated city) | Chūbu | Niigata |
| Okayama | 岡山市 | 1996-04-01 | 2009-04-01 (Designated city) | Chūgoku | Okayama |
| Sagamihara | 相模原市 | 2003-04-01 | 2010-04-01 (Designated city) | Kantō | Kanagawa |
| Sakai | 堺市 | 1996-04-01 | 2006-04-01 (Designated city) | Kansai | Osaka |
| Shizuoka | 静岡市 | 1996-04-01 | 2005-04-01 (Designated city) | Chūbu | Shizuoka |
Scheduled to become a core city
| Name | Japanese | Population (2012) | Scheduled date | Region | Prefecture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chigasaki | 茅ヶ崎市 | 236,222 | 2020-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa |
| Fuji | 富士市 | 253,455 | TBD | Chūbu | Shizuoka |
| Kishiwada | 岸和田市 | 198,615 | 2020-04-01 | Kansai | Osaka |
| Matsumoto | 松本市 | 243,431 | 2020-04-01 | Chūbu | Nagano |
| Odawara | 小田原市 | 197,413 | 2020-04-01 | Kantō | Kanagawa |
| Ichinomiya | 一宮市 | 378,996 | 2021 (aiming) | Chūbu | Aichi |
| Tsukuba | つくば市 | 216,221 | TBD | Kantō | Ibaraki |
| Tokorozawa | 所沢市 | 342,321 | TBD | Kantō | Saitama |
| Yokkaichi | 四日市市 | 307,599 | 2020 (aiming) | Kansai | Mie |
Cities that meet the requirements but have not yet been nominated
The following cities have populations greater than 200,000 but have not yet been nominated. (Cities planning to apply for core city status are not shown.)
 Matsudo, Chiba
Matsudo, Chiba Ichikawa, Chiba
Ichikawa, Chiba Machida, Tokyo
Machida, Tokyo Fujisawa, Kanagawa
Fujisawa, Kanagawa Ageo, Saitama
Ageo, Saitama Ichihara, Chiba
Ichihara, Chiba Chōfu, Tokyo
Chōfu, Tokyo Fuchū, Tokyo
Fuchū, Tokyo Tsu, Mie
Tsu, Mie Tokushima, Tokushima
Tokushima, Tokushima
See also
References
- ^ Web-Japan.org, "Local self-government," p. 3; retrieved 2012-11-28.
- ^ 日本財団図書館(電子図書館) Revised Local Autonomy Law. nippon.zaidan.info.
- ^ a b 日本總務省 - 中核市・施行時特例市. soumo.go.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ 日本財団図書館(電子図書館) Revised Local Autonomy Law. nippon.zaidan.info.
External links
- "Japan's Evolving Nested Municipal Hierarchy: The Race for Local Power in the 2000s," by A.J. Jacobs at Urban Studies Research, Vol. 2011 (2011); doi:10.1155/2011/692764
- "Large City System of Japan"; graphic shows core cities compared with other Japanese city types at p. 1 [PDF 7 of 40]
- "Growth in Second Tier Cities - Urban Policy Lessons from Japan" briefing by CLAIR London on classes of Japanese cities (PDF)
