Bendazac
Appearance
(Redirected from C16H14N2O3)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.594 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H14N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 282.299 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Bendazac (or bendazolic acid) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for joint and muscular pain.[1]
Synthesis
[edit]Principal action is inhibition of protein denaturation.
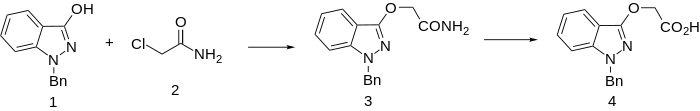
Use of chloroacetamide in the alkylation step, followed by acid hydrolysis produces bendazac (instead of benzydamine).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]
