Christmas in Ukraine
| Christmas in Ukraine | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Also called | Ukrainian: Різдво, Rizdvo |
| Observed by | Christians, many non-Christians |
| Type | Christian, cultural |
| Significance | Commemoration of the nativity of Jesus |
| Celebrations | Gift-giving, family and other social gatherings, symbolic decoration, feasting, etc. |
| Observances | Church services |
| Date |
|
| Frequency | Annual |
| Related to | Nativity Fast |
In Ukraine, Christmas celebrations traditionally start on Christmas Eve, which is celebrated from December 24 to January 6, the date of the celebration of the baptism of Jesus, known in Ukraine as Vodokhreshche or Yordan, according to the Gregorian calendar and Revised Julian calendar by the Orthodox Church of Ukraine (OCU), the Catholic Church in Ukraine (including the Latin and Greek Catholics) and Ukrainian Protestants.
The Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Moscow Patriarchate (except for the Romanian parishes)[1] and some parishes of the OCU celebrate Christmas according to the Julian calendar, so the Gregorian holidays last from January 6 to January 19.
Christmas was largely erased from the Ukrainian calendar for much of the 20th century due to the Soviet Union's anti-religious policies, but many of its traditions survived and are being revived again. In 2023, for the first time since 1917, Christmas Day in Ukraine was officially on December 25.
History
[edit]In Ukraine, the Christmas holiday became the official celebration with the baptism of Rus' ordered by Prince Vladimir in the year 988.[2] However, given the early Christian community of Kievan Rus', the celebration may have a longer history.

In the 19th century, a lavishly decorated Christmas tree became central to the holiday, a tradition originally imported by Nicholas I's wife, Alexandra Feodorovna, from her native Prussia. The tradition of giving gifts to children on Christmas took root around the same time.[3] Christmas gifts were traditionally brought by Ded Moroz or Grandfather Frost, the Ukrainian counterpart of Saint Nicholas or Father Christmas, albeit a little taller and less stout. Rooted in Slavic folklore, Ded Moroz is accompanied by his beautiful granddaughter, Snegurka, the snowmaiden), who rides with him on a sleigh pulled by a trio of horses.[3]
During the early Soviet period, all religious celebrations were discouraged under the official state policy of atheism. The Bolsheviks argued that Christmas was a pagan sun-worshipping ritual with no basis in scientific fact and denounced the Christmas tree as a bourgeois German import.[3] In 1929, all religious holidays, including Christmas, were abolished by a decree of the Stalinist regime.[4] However, in a surprising turn of state politics in 1935, many Ukrainian Christmas traditions were revived as part of a secular New Year's celebration after Joseph Stalin's advisers convinced the Vozhd of the proletarians' need for a break from their hard work in the middle of a long, cold winter.[4] The Christmas tree was repurposed as a "New Year's fir tree" to be admired by all children throughout the Soviet Union, including those in republics that had not historically celebrated Christmas due to their different religious traditions, such as the Central Asian ones. Other Ukrainian Christmas attributes and traditions, such as gift-giving, Did Moroz's visits and Christmas decorations, lost their religious significance and became associated with New Year's celebrations, which were secular in nature.[3]
In 1991, after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Christmas was reinstated alongside other religious holidays.[3] Especially in recent years, there has been a shift from Did Moroz, who came to be associated with the Soviet-era heritage, to the more traditional Saint Nicholas, who used to be more popular in Western Ukraine.[5]
Ukraine declared the 25 December as a state holiday in 2017 for the Christmas commerations and festivities in the Ukrainian Orthodox Church. It was declared an official holiday in 2023 for the first time in 106 years as part of an ongoing effort to remove Russian influence in the country.
Date of celebration
[edit]

Traditional Ukrainian Christmas festivities last from December 24 to January 6, the date of the celebration of the baptism of Jesus, which known in Ukraine as Vodokhreshche or Yordan,[6] according to the Orthodox Church of Ukraine (OCU),[7] the Catholic Church (including Latin and Ukrainian Greek Catholics[8]), and most Protestants.
As of 2017, 25 December, Christmas Day by the Gregorian calendar, became an official government holiday in Ukraine. The Eastern Orthodox Churches predominantly follow the Julian calendar, and 7 January is also a public holiday in Ukraine.[9] In December 2020, the head of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine (OCU), Metropolitan Epiphanius, said that changing the date of Christmas to 25 December in Ukraine is possible after both the church and the faithful are ready for such a decision, after conducting educational work. It was stated that the postponement of the celebration of the nativity of The Lord would entail a change in the dates of all fixed holidays to 13 days ago.[10] In December 2020, the head of the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church (UGCC), Patriarch Sviatoslav, stated that the Greek Catholic Church would resolve this issue "together with our Orthodox brothers". He also noted that this issue is not dogmatic, it should overcome church divisions, not cause new ones, and in his opinion, the transition to celebrating Christmas in a new style — 25 December, should be initiated by the laity.
About a hundred parishes of the Romanian national minority in Ukraine, which are part of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Moscow Patriarchate, have always celebrated Christmas on December 25 according to the Revised Julian calendar, just like the Romanian Orthodox Church.[1]
On 18 October 2022, the OCU allowed dioceses to hold Christmas services according to the Revised Julian calendar, i.e., 25 December. In the case of a divine service, its participants are released from the restrictions of fasting on this day.[11]
On 24 December 2022, during an audience, Major Archbishop Sviatoslav handed over to Metropolitan Epiphanius for review a letter outlining the considerations of the UGCC hierarchs regarding the calendar reform. The primates decided to create a joint working group on specific proposals for calendar reform. The joint group is initiated on the occasion of the celebration of the 1700th anniversary of the First Ecumenical Council, held in Nicaea in 325. In this Council, in particular, the calendar principles of church life were determined.[12][13][14]
On February 2, 2023, the Holy Synod of the OCU allowed and approved the procedure for blessing parishes and monasteries for the full use of the Revised Julian calendar,[15] and on May 24, 2023, to hold a meeting of the Council of Bishops, where the issue of calendar reform will be raised.[16]
In February 2023 the UGCC decided to switch to the Revised Julian calendar for fixed holidays (і.e., except for Easter) from September 2023.[17] Parishes of the UGCC that are not ready to switch to the new style in 2023 have a transition period until September 1, 2025, to make the change.[8]
Effective 24 May 2023, the OCU officially declared that 25 December will be the permanent date for Christmas commemorations and festivities for the Ukrainian Orthodox faithful, as the Church officially formalized the adoption of the Revised Julian calendar for fixed feasts and solemnities in line with the other Orthodox churches of the world, with Easter kept in the old Julian Calendar.[7][18][19] On July 27, the Local Council approved the transition.[20]
On 28 June 2023 President of Ukraine, Volodymyr Zelenskyy, submitted to the Verkhovna Rada (Ukraine's national parliament) a draft law removing the Julian Calendar Christmas holiday on January 7 and confirming the December 25 date as the sole day of celebrations, reflecting changes in the OCU and UGCC calendars.[21][22] Parliament passed this law on 14 July 2023 with 241 deputies voting in the affirmative.[23] Zelensky signed the law on 28 July 2023.[24][25]
According to a study conducted by the international company Deloitte in November 2023, after the transition of Ukrainian Christian churches to the new style, the majority of Ukrainians (about 45%) will celebrate Christmas on December 25 and only 17% on January 7, and 32% plan to celebrate twice.[26][27] In 2023, for the first time since 1917, Christmas Day in Ukraine was marked on just one day - December 25, the same date across almost all Christian faiths around the globe.[28]
The Armenian Diocese of Ukraine of the Armenian Apostolic Church and the Armenian Catholic Church in Ukraine celebrates Christmas from January 5 to January 6 along with Epiphany according to the Gregorian calendar.[29][30]
Sviatyi Vechir (Holy Evening)
[edit]
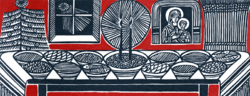
Christmas Eve on December 24 is called Sviatyi Vechir (Святий вечір) or Sviatvechir (Святвечір) in Ukraine ("Holy Evening"), and has many customs and rituals, most of which predate the introduction of Christianity to Ukraine. Traditions include decorating house and dinner table with special attributes (a symbolic sheaf of wheat called the didukh, garlic, hay, and others), performing koliadky ('carols') and so on. Each ritual has its own meaning and purpose, as such a few wisps of hay on the embroidered tablecloth as a reminder of the manger in Bethlehem. One prominent custom of the night is a special supper, called Sviata Vecheria ("Holy Supper").[31]
On the afternoon of the day, a St. Basil Divine Liturgy is held in parishes to mark the formal close of the Christmas Fast within the OCU and UGCC that began in November, which includes commemorations of the Holodomor of the 1930s, the liturgy follows a Christmas version of the Royal Hours.
Ukrainians of the OCU and UGCC fast and abstain on Sviatyi Vechir (Latin Church Catholics and Protestants may choose also to follow tradition on said day) - it is one of a few paramony days in the Eastern Rite calendar wherein mandatory fasting and abstinence is observed; only when the first star is seen in the evening sky, or just after the faithful have received Communion in the afternoon service, may the supper begin. The family comes together to have a dinner which usually includes 12 dishes (the number can vary from 7–17). These twelve dishes are traditionally vegan plus fish, and do not contain meat, milk, or eggs.[32] While the dishes served can vary regionally, as well as from family to family, the two mandatory dishes are uzvar and kutia, both reckoned by ethnographer Khvedir Vovk to be remnants of ancient rituals which date back to the neolithic era.[33] Kutia (a dish of grain, honey and poppy seeds) is traditionally served first at the meal, after being offered by the head of the household to the frost. A spoonful is tossed at the ceiling, and in rural townships the number of poppy seeds which stick portends the bountyfulness of the fields, orchards and farm animals in the coming year. It is rarely served at other times of the year.[34] Uzvar is a beverage, made with cooked dried fruits and berries. It can be mixed in with the kutia, or served separately at the end of the meal. Servings of both dishes are also set aside overnight in the pokuttia, the corner of the house with the Orthodox/Eastern Catholic icons or Latin Catholic images of saints, for deceased ancestors within the family or, in recent cases, for family members killed during the Russo-Ukrainian War (especially those who were KIA in the Armed Forces of Ukraine and other uniformed organizations).
The All-Night Christmas Vigil then follows, families then troop to their local parish churches or Protestant churches to attend as thanksgiving for the Savior's birth in a stable. OCU and UGCC Divine Liturgy, Catholic Midnight Mass or a Protestant service would then traditionally follow. On Christmas Eve night a shopka (vertep), a traditional portable nativity scene, carried by children or adults alike, and used to represent the Nativity and other figures in a puppet form, is brought out in public, the portable tall box is either accompanied by singing carollers or crowds either before or after the vigil service.[35]
The principal national television and online services on the night are beamed live from:
- for the OCU, Saint Sophia Cathedral, Kyiv
- for the UGCC, Cathedral of the Resurrection of Christ, Kyiv
- for Latin Rite Catholics: Cathedral Basilica of the Assumption, Lviv and/or Co-Cathedral of St. Alexander, Kyiv
Christmas Day
[edit]Following the Vigil, on December 25 families return to the aforementioned places of worship for Mass, Divine Liturgy or a holiday service. Unlike the previous day, meat and other foods are eaten during the day. This day and the days following up to January 4 are fast-free days.
Koliadky (Caroling)
[edit]At the end of the Sviata Vechera, and the vigil that follows, Ukrainian families often sing carols (koliadky). In some communities the ancient Ukrainian tradition of caroling is carried on by groups of young people and members of organizations and churches calling at homes and collecting donations. Well-known carols include Nova radist stala, Boh predvichnyi narodyvsia,[36] Dobryi vechir tobi, pane hospodariu, Vo Vyfleiemi nyni novyna, Nebo i zemlia nyni torzhestvuiut, and Boh sia rozhdaie.

In villages (farming communities), the head of the household brings in a sheaf of grain called the didukh which represents the importance of the ancient and rich wheat crops of Ukraine, the staff of life through the centuries. Didukh means literally "grandfather spirit" so it symbolizes the family's ancestors. In Ukrainian city homes the didukh may be purchased, and is often made of woven grain and dried grasses and flowers.[37]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Kralyuk, Petro (2 January 2023). "«Є сподівання, що ПЦУ і УГКЦ перейдуть на святкування Різдва 25 грудня» – професор Петро Кралюк" ["There is hope that OCU and UGCC will celebrate Christmas on December 25" - Professor Petro Kralyuk]. Radio Svoboda (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 27 March 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2023.
- ^ Moreau, A. Scott; Corwin, Gary R.; Corwin, Gary; McGee, Gary B. (2004), Introducing World Missions: A Biblical, Historical, and Practical Survey, Baker Academic, p. 102, ISBN 978-0-8010-2648-5
- ^ a b c d e Weber, Hannah (25 December 2020). "Yolka: the story of Russia's 'New Year tree', from pagan origins to Soviet celebrations". The Calvert Journal. Archived from the original on 13 January 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2021.
- ^ a b "How New Year was celebrated in the USSR (Photos)". Beyond Russia. 29 December 2019. Archived from the original on 29 December 2019. Retrieved 12 June 2021.
- ^ "Kiev Brings Back Orthodox Santa Claus Instead of Soviet-Era Father Frost". The Moscow Times. 20 November 2014. Archived from the original on 20 November 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ^ "Christmas Traditions of Ukraine". Ukrainian Fraternal Association. Archived from the original on 28 September 2023. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ^ a b "Orthodox Church of Ukraine to switch to Revised Julian calendar, celebrate Christmas on Dec. 25". The Kyiv Independent. 24 May 2023. Archived from the original on 24 May 2023. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- ^ a b "Ukraine Catholic Church moves from Russian-affiliated Julian calendar". The Pillar. 6 February 2023. Archived from the original on 6 February 2023. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- ^ "Рада зробила 25 грудня вихідним днем" [The council made December 25 a day off]. BBC News Україна (in Ukrainian). 16 November 2017. Archived from the original on 30 December 2017. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ Rokitna, Anastasia (19 December 2020). "Епіфаній назвав умову перенесення святкування Різдва на 25 грудня" [Epiphany named the move of the Holy Day of Resurrection to the 25th birthday]. RBC - Ukraine (in Ukrainian). UBT. Archived from the original on 20 December 2020. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ^ "OCU allowed Christmas services on December 25". Ukrainian Pravda (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 25 December 2022. Retrieved 18 October 2022.
- ^ "Heads of OCU, UGCC agree to set up working group to reform church calendar". www.ukrinform.net. 24 December 2022. Archived from the original on 25 December 2022. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "During the meeting of His Beatitude Sviatoslav with His Beatitude Epiphanius, they talked about the reform of the church calendar". Українська Греко-Католицька Церква (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 24 December 2022. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "There was a meeting of the Primate of the OCU with the Father and the Primate of the UGCC". OCU (in Ukrainian). 24 December 2022. Archived from the original on 24 December 2022. Retrieved 24 December 2022.
- ^ "Decree of the Holy Synod on the procedure for blessing parishes and monasteries for the use of the Revised Julian calendar". OCU (in Ukrainian). 2 February 2023. Archived from the original on 3 February 2023. Retrieved 3 February 2023.
- ^ "Official notice of the meeting of the Holy Synod on February 2, 2023". OCU (in Ukrainian). 2 February 2023. Archived from the original on 31 May 2023. Retrieved 3 February 2023.
- ^ "Historical decision: the UGCC in Ukraine switches to a new calendar". Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church. Archived from the original on 11 November 2023. Retrieved 19 July 2023.
- ^ RFE/RL. "Orthodox Church Of Ukraine Approves Calendar Switch In Widening Diversion From Russia". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Archived from the original on 25 May 2023. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- ^ "Orthodox Church of Ukraine Decides to Celebrate Christmas on Dec. 25". Get the Latest Ukraine News Today – KyivPost. 24 May 2023. Archived from the original on 18 June 2023. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- ^ "Orthodox Church of Ukraine finally adopts new calendar". NV. Archived from the original on 28 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ "Zelensky Introduces Proposed Draft Law to Change Holiday Dates". Get the Latest Ukraine News Today – KyivPost. 29 June 2023. Archived from the original on 29 June 2023. Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- ^ "Zelensky submitted to the Verkhovna Rada a law on changing holiday dates". babel.ua. 28 June 2023. Archived from the original on 29 June 2023. Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- ^ "Parliament changes dates of Christmas, Statehood Day, Day of Defenders". Ukrinform. 14 July 2023. Archived from the original on 14 July 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ Toropin, Konstantin; Stambaugh, Alex (29 July 2023). "Ukraine moves Christmas to December 25, distancing itself from Russian tradition". Cable News Network. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine moves official Christmas Day holiday to Dec. 25, denouncing Russian-imposed traditions". AP News. 29 July 2023. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ "More donations to the Armed Forces, new traditions and the continuation of the boycott of sellers still working in the Russian Federation – Deloitte research on New Year's shopping of Ukrainians". "Deloitte" in Ukraine (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 13 December 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ "The vast majority of Ukrainians will celebrate Christmas on December 25 – survey". Religious Pravda (in Ukrainian). 8 December 2023. Archived from the original on 25 December 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ Waterhouse, James (23 December 2023). "Ukraine war: New Christmas date marks shift away from Russia". BBC News. Archived from the original on 23 December 2023. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ^ "Do Lvivians know that Armenians celebrate Christmas on January 6?". tvoemisto.tv. Archived from the original on 18 June 2023. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- ^ Терещук, Галина (6 January 2020). "Christmas in Lviv: three dates of the family holiday". Радіо Свобода (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 18 June 2023. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- ^ Hughes 1997, pp. 32–47.
- ^ "Christmas in Ukraine". Why Christmas. Archived from the original on 7 December 2020. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ^ "Traditional Recipe of Ukrainian Kutia". Ethnocook. 18 January 2018. Archived from the original on 28 November 2022. Retrieved 27 November 2022.
- ^ "Sviat Vechir". Archived from the original on 9 January 2008. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- ^ Soviet Studies in Literature. International Arts and Science Press. 1990. Archived from the original on 25 December 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ^ "Boh predvičnyj". Metropolitan Cantor Institute. Byzantine Catholic. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 12 August 2015.
- ^ Ukrainian Christmas traditions, archived from the original on 26 September 2023, retrieved 25 December 2023
Sources
[edit]- Hughes, Ellen (1997). Christmas in Ukraine. Chicago: World Book Inc. ISBN 978-0-7166-0897-4.
Further reading
[edit]- Kutia, Star of the Ukrainian Christmas Eve Supper
- Kylymnyk, Stepan, 1955–1969; Ukrainskyi Rik u Narodnykh Zvychayakh v Narodnomu Osvitlenni [Ukrainian Year in Folk Customs from Historical Perspective], Winnipeg, Toronto
- Tracz, Orysia 2015, First Star I See Tonight, Mazepa Publications Zhuravli, Winnipeg
- Voropai, Oleksa 1958, Zvychai Nashoho Narodu [Customs of Our People], Ukrainske Vydavnytstvo, Munich
- "Святвечір, колядки та вертеп. Традиції святкування Різдва в Україні" [Christmas Eve, carols and a nativity scene. Traditions of celebrating Christmas in Ukraine]. Life (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 24 December 2023.
