Economy of Azerbaijan
| File:Flame Towers.jpg | |
| Currency | 1 Manat = 100 qəpik |
|---|---|
| Calendar year | |
Trade organisations | CIS, ECO, GUAM, WTO (observer) |
| Statistics | |
| GDP | Nom.: PPP: Rank: 67th [1] |
GDP growth | |
GDP per capita | |
GDP by sector | agriculture (5.7%), industry (61.2%), services (33.2%) (2014)[1] |
Population below poverty line | |
| 33.7 (2008) | |
Labour force | 6.12 million (2011[update])[1] |
Labour force by occupation | services (49.6%), industry (12.1%), agriculture and forestry (38.3%) (2008[update])[1] |
| Unemployment | |
Main industries | petroleum and natural gas, petroleum products, oilfield equipment; steel, iron ore, cement; chemicals; petrochemicals; textiles; machinery; cotton; foodstuffs |
| External | |
| Exports | |
Export goods | oil and gas, machinery, cotton, foodstuffs. |
Main export partners | |
| Imports | |
Import goods | machinery and equipment, oil products, foodstuffs, metals, chemicals |
Main import partners | |
FDI stock | |
Gross external debt | $9.833 billion (31 December 2014) [7] |
| Public finances | |
| Revenues | |
| Expenses | |
All values, unless otherwise stated, are in US dollars. | |
Azerbaijan has an economy that has completed its post-Soviet transition into a major oil based economy (with the completion of the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline), from one where the state played the major role. Azerbaijan's GDP grew 41.7% in the first quarter of 2007, possibly the highest of any nation worldwide.[12] Such rates cannot be sustained, but despite reaching 26.4% in 2005 (second highest GDP growth in the world in 2005 only to Equatorial Guinea), and 2006 over 34.6% (world highest), in 2008 dropped to 10.8%, and dropped further to 9.3% in 2009.[13] The real GDP growth rate for 2011 was expected at 3.7% but had dropped to 0.1%.[14] Large oil reserves are a major contributor to the economy. The national currency, the Azerbaijani manat, was stable in 2000, depreciating 3.8% against the dollar. The budget deficit equaled 1.3% of GDP in 2000.
Progress on economic reform has generally lagged behind macroeconomic stabilization. The government has undertaken regulatory reforms in some areas, including substantial opening of trade policy, but inefficient public administration in which commercial and regulatory interests are co-mingled limit the impact of these reforms.[15] The government has largely completed privatization of agricultural lands and small and medium-sized enterprises. In August 2000, the government launched a second-stage privatization program, in which many large state enterprises will be privatized. Since 2001, the economic activity in the country is regulated by the Ministry of Economic Development of Azerbaijan Republic.
Economic history
Modern era
Through the Soviet period, Azerbaijan had always been more developed industrially than Armenia and Georgia, two neighboring Transcaucasia countries - but also less diversified, as a result of slow investment in non-oil sector. With a history of industrial development of more than 100 years, Azerbaijan proved to be a leading nation in Southern Caucasus throughout the turmoil of Soviet Union collapse in early 1990s until nowadays.
Republic era
Oil remains the most prominent product of Azerbaijan's economy with cotton, natural gas and agriculture products contributing to its economic growth over the last five years. More than $60 billion was invested into Azerbaijan's oil by major international oil companies in AIOC consortium operated by BP. Oil production under the first of these PSAs, with the Azerbaijan International Operating Company, began in November 1997 and now is about 500,000 b/d. People visit petroleum spas (or "oil spas") to bathe in the local crude in Naftalan[16] A leading caviar producer and exporter in the past, Azerbaijan's fishing industry today is concentrated on the dwindling stocks of sturgeon and beluga in the Caspian Sea.
Azerbaijan shares all the problems of the former Soviet republics in making the transition from a command to a market economy, but its energy resources brighten its long-term prospects. Azerbaijan has begun making progress on economic reform, and old economic ties and structures are slowly being replaced. An obstacle to economic progress, including stepped up foreign investment, is the continuing conflict with Armenia over the Nagorno-Karabakh region.[17]
In 1992, Azerbaijan became member of the Economic Cooperation Organization.[18] In 2002, the Azerbaijani merchant marine had 54 ships.[19] In March 2001, Azerbaijan concluded a gas agreement with Turkey, providing a future export market for Azerbaijan.

Azerbaijan has concluded 21 production-sharing agreements with various oil companies. An export pipeline that transports Caspian oil to the Mediterranean from Baku through Tbilisi, Georgia to Ceyhan, Turkey (the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline) became operational in 2006. The pipeline is expected to generate as much as $160 billion in revenues for the country over the next 30 years. The recent high price of oil is highly beneficial to Azerbaijan's economy as the nation is in the midst of an oil boom. Eastern Caspian producers in Kazakhstan also have expressed interest in accessing this pipeline to transport a portion of their production.
In 2010, Azerbaijan entered into the top eight biggest oil suppliers to EU countries with €9.46 billion.[20] In 2011, the amount of foreign investments in Azerbaijan was $20 billion, a 61% increase from 2010. According to Minister of Economic Development of Azerbaijan, Shahin Mustafayev, in 2011, "$15.7 billion was invested in the non-oil sector, while the rest - in the oil sector."[21]

In 2012, because of its economic performance after the Soviet breakup, Azerbaijan was predicted to become "Tiger of Caucasus".[22][23][24] In 2012, Globalization and World Cities Research Network study ranked Baku as a Gamma-level global city.[25]
In 2015, Turkey and Azerbaijan agreed to boost mutual trade to USD$15 billion by 2023.[26]
Macro-economic trend
The following is a chart of trend of gross domestic product of Azerbaijan at market prices[27] with figures in millions of Manats.
| Year | Gross domestic product | US dollar exchange | Per capita income (as % of USA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 1000,669,000 | 4,414.14 Manats | 1.13 |
| 2000 | 2900,590,500 | 4,473.82 Manats | 1.87 |
| 2005 | 79,378,500 | 4,727.21 Manats | 3.74 |
For purchasing power parity comparisons, the US dollar was exchanged at 1,565.88 Manats only. Currently, the new Manat is in use, with an exchange rate of about 1 manat = $1.10. Mean graduate pay was $5.76 per manhour in 2010.
For more than a century the backbone of the Azerbaijani economy has been petroleum, which represented 50 percent of Azerbaijan’s GDP in 2005, and is projected to double to almost 125 percent of GDP in 2007.[28] Now that Western oil companies are able to tap deepwater oilfields untouched by the Soviets because of poor technology, Azerbaijan is considered one of the most important areas in the world for oil exploration and development. Proven oil reserves in the Caspian Basin, which Azerbaijan shares with Russia, Kazakhstan, Iran, and Turkmenistan, are comparable in size to the North Sea, although exploration is still in the early stages.
Sectors of the economy
Agriculture
Azerbaijan has the largest agricultural basin in the region. About 54,9 percent of Azerbaijan is agricultural lands. At the beginning of 2007 there were 4,755,100 hectares of utilized agricultural area.[29] In the same year the total wood resources counted 136 million m³.[29] Azerbaijan's agricultural scientific research institutes are focused on meadows and pastures, horticulture and subtropical crops, leaf vegetables, viticulture and wine-making, cotton growing and medicinal plants.[30] In some lands it is profitable to grow grain, potatoes, sugar beets, cotton and tobacco. Livestock, dairy products, and wine and spirits are also important farm products. The Caspian fishing industry is concentrated on the dwindling stocks of sturgeon and beluga.
Some portions of most products that were previously imported from abroad have begun to be produced locally (among them are Coca Cola by Coca Cola Bottlers LTD, beer by Baki-Kastel, parquet by Nehir and oil pipes by EUPEC Pipe Coating Azerbaijan).[31]
Manufacturing

In 2007, mining and hydrocarbon industries accounted for well over 95 per cent of the Azerbaijani economy. Diversification of the economy into manufacturing industries remain a long-term issue.[32]
As of late 2000s, the defense industry of Azerbaijan has emerged as an autonomous entity with a growing defense production capability. The ministry is cooperating with the defense sectors of Ukraine, Belarus and Pakistan.[33] Along with other contracts, Azerbaijani defence industries and Turkish companies, Azerbaijan will produce 40mm revolver grenade launchers, 107mm and 122mm MLRS systems, Cobra 4×4 vehicles and joint modernization of BTR vehicles in Baku.[34][35][36][37]
Services
Financial and business services
The GDP growth rates observed in Azerbaijan during last years made the country one of the fastest growing economies in the world. But the banking sector of Azerbaijan has yet to tap the vast growth potential that should be achievable due to the continuation of the high economic growth.[38] For this reason the banking sector remains small in relation to the size of the Azerbaijani economy. Since 2002, important stages of restructuring of the banking system have started to be carried out. Taking into consideration entry of big oil revenues in the country, as a logical result of successful oil strategy, and in this base, as the banks were ready to an effective transfer of their financial resources to the strategic goals, development strategy was made for 2002–2005.
By 1 April 2010, 47 banks, 631 bank branches function in Azerbaijan. One of banks was founded with participation of state capital, 23 of foreign capital. To the same date, 98 non-bank credit organizations operate in the republic along with banks. Growth of real money incomes of population, development of trust in bank system, improving the legal bases of protection of interests of creditors and depositors, in particular launch of ‘Deposits Insurance Fund’ were the criteria characterizing rapid growth of deposits of population. As of 1 April 2010, bank deposits of population were equal to 2,4 billion AZN. 33,3% of them were long-term deposits (higher than a year). As of 1 April 2010, bank credits to customers is 8.5 bn AZN, which makes 70.5% of bank assets. Special weight of private sector in structure of credit investments is higher than 82% (7 bn AZN).[39]
Telecommunications
In the 21st century, a new oil and gas boom helped to improve the situation in the Azerbaijan's science and technology sectors, and the government launched a campaign aimed at modernization and innovation. The government estimates that profits from the information technology and communication industry will grow and become comparable with those from oil production.[40]
Azerbaijan has a large and steadily growing Internet sector, mostly uninfluenced by the global financial crisis; rapid growth is forecast for at least five more years.[41]
The country has also been making progress in developing its telecoms sector. The Ministry of Communications & Information Technologies (MCIT), as well as being an operator through its role in Aztelekom, is both a policy-maker and regulator. Public pay phones are available for local calls and require the purchase of a token from the telephone exchange or some shops and kiosks. Tokens allow a call of indefinite duration. As of 2009, there were 1,397,000 main telephone lines[42] and 1,485,000 internet users.[43] There are five GSM providers: Azercell, Bakcell, Azerfon (Nar Mobile), Aztrank, Catel mobile network operators and one CDMA.
Tourism

Tourism is an important part of the economy of Azerbaijan. The country was a well-known tourist spot in the 1980s. However, the fall of the Soviet Union, and the Nagorno-Karabakh War during the 1990s, damaged the tourist industry and the image of Azerbaijan as a tourist destination.[44]
It was not until the 2000s that the tourism industry began to recover, and the country has since experienced a high rate of growth in the number of tourist visits and overnight stays.[45] In the recent years, Azerbaijan has also becoming a popular destination for religious, spa, and health care tourism.[46] During winter, the Shahdag Winter Complex offers skiing.
The government of Azerbaijan has set the development of Azerbaijan as an elite tourist destination a top priority.[47] It is a national strategy to make tourism a major, if not the single largest, contributor to the Azerbaijani economy.[48] These activities are regulated by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism of Azerbaijan.
Currency system
The Azerbaijani manat is the currency of Azerbaijani, denominated as the manat, subdivided into 100 qapik. The manat is issued by the Central Bank of Azerbaijan, the monetary authority of Azerbaijan. The ISO 4217 abbreviation is AZN. The Latinised symbol is (![]() ).
).
The manat is held in a floating exchange-rate system managed primarily against the US dollar. The rate of exchange (Azerbaijani manat per US$1) for 28 January 2016, was AZN 1.60.
There is a complex relationship between Azerbaijan's balance of trade, inflation, measured by the consumer price index and the value of its currency. Despite allowing the value of the manat to "float", Azerbaijan's central bank has decisive ability to control its value with relationship to other currencies.
Infrastructure
Energy
Two thirds of Azerbaijan is rich in oil and natural gas.[49] The region of the Lesser Caucasus accounts for most of the country's gold, silver, iron, copper, titanium, chromium, manganese, cobalt, molybdenum, complex ore and antimony.[49] In September 1994, a 30-year contract was signed between the State Oil Company of Azerbaijan Republic (SOCAR) and 13 oil companies, among them Amoco, BP, ExxonMobil, Lukoil and Statoil.[50] As Western oil companies are able to tap deepwater oilfields untouched by the Soviet exploitation, Azerbaijan is considered one of the most important spots in the world for oil exploration and development.[51] Meanwhile, the State Oil Fund of Azerbaijan was established as an extra-budgetary fund to ensure the macroeconomic stability, transparency in the management of oil revenue, and the safeguarding of resources for future generations.
Azeriqaz, a sub-company of SOCAR, intends to ensure full gasification of the country by 2021.[52]
Transportation
The convenient location of Azerbaijan on the crossroad of major international traffic arteries, such as the Silk Road and the South-North corridor, highlights the strategic importance of transportation sector for the country’s economy.[53] The transport sector in the country includes roads, railways, aviation, and maritime transport.
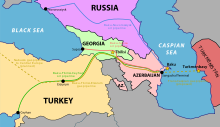
Azerbaijan is also an important economic hub in the transportation of raw materials. The Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline (BTC) became operational in May 2006 and extends more than 1,774 kilometers through the territories of Azerbaijan, Georgia and Turkey. The BTC is designed to transport up to 50 million tons of crude oil annually and carries oil from the Caspian Sea oilfields to global markets.[54] The South Caucasus Pipeline, also stretching through the territory of Azerbaijan, Georgia and Turkey, became operational at the end of 2006 and offers additional gas supplies to the European market from the Shah Deniz gas field. Shah Deniz is expected to produce up to 296 billion cubic meters of natural gas per year.[55] Azerbaijan also plays a major role in the EU-sponsored Silk Road Project.
In 2002, the Azerbaijani government established the Ministry of Transport with a broad range of policy and regulatory functions. In the same year, the country became a member of the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic.[56] The highest priority being; upgrading the transport network and transforming transportation services into one of the key comparative advantages of the country, as this would be highly conducive to the development of other sectors of the economy.
In 2012, the construction of Kars–Tbilisi–Baku railway expected to provide transportation between Asia and Europe through connecting the railways of China and Kazakhstan in the east with Turkey's Marmaray to the European railway system in the west. Broad gauge railways in 2010 stretched for 2,918 km (1,813 mi) and electrified railways numbered 1,278 km (794 mi). By 2010, there were 35 airports and one heliport.[1]
Business environment
As of October 2014, Azerbaijan holds the highest foreign investment per capita among the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries. Germany, for example, has invested approximately $760 million into the Azerbaijani economy, and approximately 177 German companies operate within Azerbaijan. Since gaining its independence, companies have invested $174 billion into Azerbaijan. Foreign investment accounts for around half of that amount.[57]
In 2008, Azerbaijan was cited as the top reformer by the World Bank's Doing Business report:[58]
Azerbaijan led the world as the top reformer in 2007/08, with improvements on seven out of 10 indicators of regulatory reform. Azerbaijan started operating a one-stop shop in January 2008 that halved the time, cost, and number of procedures to start a business. Business registrations increased by 40% in the first 6 months. Azerbaijan also eliminated the minimum loan cutoff of $1,100, more than doubling the number of borrowers covered at the credit registry. Also, taxpayers can now file and pay their taxes online. Azerbaijan’s extensive reforms moved it far up the ranks, from 97 to 33 in the overall ease of doing business.
Other economic indicators
- Data from CIA World Factbook[1] unless noted otherwise
- Investment (gross fixed)
17% of GDP (2011 est.)
- Household income or consumption by percentage share
- lowest 10%: 3.4%
- highest 10%: 27.4% (2008)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices)
1.1% (2012 est.)
- Agriculture
- utilized agricultural land: 47,584 square kilometres (18,372 sq mi) (2011)[29]
- total wood resources: 144,2 million cubic metres
- crops: cotton, grain, rice, grapes, fruit, vegetables, tea, tobacco
- livestock products: beef, mutton, poultry, milk, eggs
- Industrial production growth rate
-3% (2011 est.)
- Electricity
- production: 22,55 billion kWh (2008)
- consumption: 18,8 billion kWh (2008)
- exports: 812 million kWh (2008)
- imports: 596 million kWh (2008)
- Current account balance
- $11,12 billion (2011 est.)
- Exports - commodities
- petroleum and natural gas, petroleum products, oilfield equipment; steel, iron ore, cement; chemicals, petrochemicals, textiles, machinery, cotton, foodstuffs.
- Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
- $7,146 billion (2011 est.)
- Debt - external
- $3.89 billion (2011 est.)
- Currency
- 1 Manat = 100 gepik
- Exchange rates
- Azerbaijani manat per US dollar - 1.60 (for 28 January 2016)[59]
- Azerbaijani manat per Euro - 1.74 (for 28 January 2016)[59]
- Fiscal year
- Calendar year
See also
- List of companies of Azerbaijan
- Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline
- State Oil Company of Azerbaijan
- Petroleum industry in Azerbaijan
- Agriculture in Azerbaijan
- Tourism in Azerbaijan
- Baku
- Military of Azerbaijan
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q [www.tradingeconomics.com/azerbaijan/t "tradinge conomics= cia.gov"].
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ "Export Figures of Azerbaijan". CIA World Factbook. 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ "Export Partners of Azerbaijan". CIA World Factbook. 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2016.
- ^ . 2014 http://atlas.media.mit.edu/en/profile/country/aze/. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "Import Partners of Azerbaijan". CIA World Factbook. 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2016.
- ^ "Foreign Direct Investment of Azerbaijan". CIA World Factbook. 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ "External Debt of Azerbaijan". CIA World Factbook. 2014. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ "Azerbaijan at BBB- according to Fitch Ratings" (in Turkish). London. 27 January 2012. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Moody's changes outlook on Azerbaijan's sovereign ratings to positive from stable".
- ^ "Sovereigns Ratings List".
- ^ "Azerbaijan Rating Stable". London. 13 January 2012.
- ^ "RosBusinessConsulting - News Online". Rbcnews.com. Retrieved 26 March 2010.
- ^ "Today.Az - GDP growth makes 3.4% in Azerbaijan in 2009". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "Background Note: Azerbaijan". United States Department of State. 23 March 2012.
- ^ "Azerbaijan on CIA's Worldfactbook". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 19 August 2014.
- ^ Azerbaijani answer to oil glut: Bathe in it - Asia - Pacific - International Herald Tribune Archived 28 November 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Zhalko-Tytarenko, Andrew. "Iran's other side: the South Caucasus". diplomatonline.com. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- ^ "Brief Introduction of ECO's history". www.ecosecretariat.org. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- ^ "Azerbaijan Transportation". NationsEncyclopedia.com. Retrieved 24 May 2007.
- ^ "Today.Az - Azerbaijan among top 8 biggest oil suppliers to EU countries". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ Lada Yevgrashina (17 January 2012). "Azerbaijan investment up 61 pct to $20 bln in 2011". Reuters. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ "Is Azerbaijan the new "Caucasus tiger"?". www.agccommunication.eu. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- ^ Safarov, Fuad. "Muhammad Asif Noor: "Tiger of Caucasus" pose as an opportunity for Pakistan to get involved in mutually beneficial cooperative engagements"". vestnikkavkaza.net. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- ^ Afag, Aliyeva. Известное СМИ Германии: Азербайджан - "тигр Кавказа". aze.az (in Russian). Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- ^ "The World According to GAWC 2012". GAWC. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- ^ "Turkey, Azerbaijan intend to boost mutual trade to $15 billion by 2023". 15 January 2015. Retrieved 16 January 2015.[dead link]
- ^ estimated Archived 11 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine by the International Monetary Fund
- ^ Azerbaijan: Energy profile Archived 4 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine (Enerpub, 13 December 2007)
- ^ a b c "Natural resources". The State Statistical Committee of the Republic of Azerbaijan. Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-26.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Azerbaijan: Status of Database". Central Asia and Caucasus Institute. Archived from the original on 20 March 2007. Retrieved 28 May 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Industry" (PDF). Statistical Yearbook of Azerbaijan 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 February 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-26.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Snow, Nick. "Azerbaijan looks beyond energy successes for economic growth". www.ogj.com. Oil & Gas Journal. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
- ^ "Azerbaijan: Baku Signals New Determination For Defense Reform". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "News.Az - Azerbaijan, Turkey to produce revolver grenade launchers". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ Azerbaijan’s Ministry of Defense Industry plans to assume several projects on technical modernization of Armed Forces Archived 2 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "News.Az - Azerbaijan, Turkey sign contract on joint rocket production". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ Azerbaijani Defense Industry Ministry conducts negotiations with Turkish "Otokar" Company on production of armored vehicles Archived 25 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Azerbaijan Banking System: An Overview July 2007" (PDF). Retrieved July 2007.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)[dead link] - ^ "Azerbaijan – General Information". Heydar Aliyev Foundation. Retrieved 22 May 2007.
- ^ "Azerbaijan aims for hi-tech state". Euronews. Retrieved 19 December 2010.
- ^ "Azerbaijan is in TOP 10 of countries showing dynamic growth in Internet and mobile communications penetration". bakutel.az. Retrieved 15 April 2013.
- ^ CIA.gov, CIA World Factbook Telephones – main lines in use, Azerbaijan 1,397,000 main lines
- ^ CIA.gov, CIA World Factbook Internet users, Azerbaijan Internet users: 1,485,000.
- ^ "Rapid Tourism Assessment for the Azerbaijan Tourism Sector Development Program - Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)". Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- ^ Azərbaycan Qarabağın turizm imkanlarını təbliğ edir Template:Az icon
- ^ Ismayilov, Rovshan. "Azerbaijan: Baku Boom Has Yet to Hit Regions". EurasiaNet. Archived from the original on 19 August 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Cree, Richard. "Azerbaijan on Director magazine". www.director.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2 July 2014. Retrieved 14 August 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Ministry of Culture and Tourism of Azerbaijan: Goals". Tourism.az. 6 February 2004. Archived from the original on 28 November 2010. Retrieved 4 January 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Azerbaijan – General Information". Heydar Aliyev Foundation. Archived from the original on 28 May 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Azerbaijan – General Information". Heydar Aliyev Foundation. Archived from the original on 5 May 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Azerbaijan: Economy". globalEDGE. Retrieved 29 May 2007. [dead link]
- ^ "SOCAR plans to completed full gasification of Azerbaijan only by 2021". Azerbaijan Business Center. Retrieved 6 June 2010.
- ^ Ziyadov, Taleh. "The New Silk Roads" (PDF). Central Asia-Caucasus Institute Silk Road Studies Program.
- ^ Zeyno Baran (2005). "The Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline: Implications for Turkey" (PDF). The Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline: Oil Window to the West. The Central Asia-Caucasus Institute, Silk Road Studies Program: 103–118. Retrieved 30 December 2007.
- ^ "SCP Commissioning Commences" (Press release). BP. 1 June 2006. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 4 June 2008.
{{cite press release}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "List of Contracting Parties to the Convention on Road Traffic" (PDF). UN Economic Commission for Europe. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 May 2011. Retrieved 2010-01-23.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Jafarova, Aynur (1 October 2014). "Azerbaijan leading country in CIS for foreign investment per capita". AzerNews. Retrieved 1 October 2014.
- ^ World Bank Group. "Top 10 reformers from Doing Business 2009". Retrieved 28 September 2008.
- ^ a b http://www.cbar.az/ Central Bank of the Azerbaijan Republic, accessed 24 July 2015
Further reading
- Habibov, Nazim: "Poverty in Azerbaijan" in the Caucsus Analytical Digest No. 34
- Küpeli, Ismail (2013). Aserbaidschan - ein autoritärer Rentierstaat? Politik und Ökonomie unter dem Aliyev-Regime. Göttingen: Optimus Verlag. ISBN 978-3-86376-042-7.
External links
- Azerbaijan Economy
- Template:Dmoz
- Hübner, Gerald: "As If Nothing Happened? How Azerbaijan’s Economy Manages to Sail Through Stormy Weather" in the Caucasus Analytical Digest No. 18

