Lower Township, New Jersey
Lower Township, New Jersey | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Motto: "Home of the Best Sunsets"[1] | |
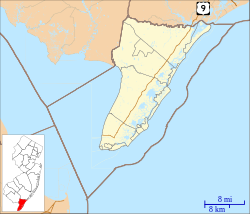
 Location of Lower Township in Cape May County highlighted in red (left). Inset map: Location of Cape May County in New Jersey highlighted in red (right). | |
 Census Bureau map of Lower Township, New Jersey | |
Location in Cape May County Location in New Jersey | |
| Coordinates: 38°59′02″N 74°54′41″W / 38.983768°N 74.911308°W[2][3] | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | |
| Established | April 2, 1723 (as precinct) |
| Incorporated | February 21, 1798 (as township) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Faulkner Act (council–manager) |
| • Body | Township Council |
| • Mayor | Frank Sippel (R, term ends December 31, 2023)[4][5] |
| • Manager | Michael Laffey[6] |
| • Municipal clerk | Julie Picard[7] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 31.06 sq mi (80.45 km2) |
| • Land | 27.38 sq mi (70.91 km2) |
| • Water | 3.69 sq mi (9.54 km2) 11.86% |
| • Rank | 84th of 565 in state 4th of 16 in county[2] |
| Elevation | 20 ft (6 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 22,057 |
| • Estimate | 21,886 |
| • Rank | 127th of 565 in state 1st of 16 in county[13] |
| • Density | 805.6/sq mi (311.0/km2) |
| • Rank | 407th of 565 in state 10th of 16 in county[13] |
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) |
| ZIP Code | |
| Area code(s) | 609 exchanges: 884, 886, 889, 898[15] |
| FIPS code | 3400941610[2][16][17] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0882044[2][18] |
| Website | www |
Lower Township is a township in Cape May County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The township, and all of Cape May County, is part of the Ocean City metropolitan statistical area, and is part of the Philadelphia-Wilmington-Camden, PA-NJ-DE-MD combined statistical area, also known as the Delaware Valley or Philadelphia metropolitan area.[19] As of the 2020 United States census, the township's population was 22,057,[10][11] a decrease of 809 (−3.5%) from the 2010 census count of 22,866,[20][21] which in turn reflected a decrease of 79 (−0.3%) from the 22,945 counted in the 2000 census.[22]
New Jersey Monthly magazine ranked Lower Township as its 34th best place to live in its 2008 rankings of the "Best Places To Live" in New Jersey.[23] The township is part of the state's South Jersey region and the larger Delaware Valley or Philadelphia metropolitan area.
History
[edit]Before the region was settled by Europeans, the Kechemeche tribe of the Lenape Native Americans inhabited South Jersey, and traveled to the barrier islands during the summer to hunt and fish.[24][25][26] On August 28, 1609, English explorer Henry Hudson entered the Delaware Bay and stayed one day on land, north of what is now Cape May Point.[27] In 1630, representatives of the Dutch West India Company purchased a 16 sq mi (41 km2) tract of land along the Delaware from indigenous people, and additional land in the county was purchased 11 years later.[27] Due to the large number of whales in the region of Cape May, Dutch explorers founded Town Bank around 1640 as a whaling village in what is now Lower Township. It was the first European settlement in Cape May County. The village once functioned as the court house for the county, along with Coxehall, built by Dr. Daniel Coxe to be a center for a manorial style of government.[28][29][30] The sole remaining section of the original structure, which was moved several times during its history, is now preserved as Coxe Hall Cottage at Historic Cold Spring Village, a 19th century living history museum in Lower Township.[31]
Lower Township was formed as a precinct on April 2, 1723, and was incorporated by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on February 21, 1798, as one of New Jersey's initial group of 104 townships established by the Township Act of 1798.[24] The township's name came from its location when Cape May was split into three townships in 1723 at the same time that Middle Township and Upper Township were created.[32][33]
Portions of the township were taken to form Cape Island Borough (March 8, 1848; now known as Cape May city), Cape May Point borough (created April 19, 1878; restored to Lower Township on April 8, 1896; re-created April 6, 1908), Holly Beach (April 14, 1885, now part of Wildwood city), South Cape May (August 27, 1894; restored to Lower Township after the borough was dissolved on April 30, 1945), Wildwood Crest (April 6, 1910), and North Cape May (March 19, 1928; restored to Lower Township after it was dissolved on April 30, 1945).[24]
Geography
[edit]
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the township had a total area of 31.06 square miles (80.45 km2), including 27.38 square miles (70.91 km2) of land and 3.69 square miles (9.54 km2) of water (11.86%).[2][3]
Census-designated places (CDPs) located within Lower Township include Diamond Beach (with a 2010 population of 136,[34]), Erma (2,134[35]), North Cape May (3,226[36]) and Villas (9,483[37]).[38] Other unincorporated communities, localities and place names located partially or completely within the township include Bennett, Cold Spring, Cold Spring Inlet, Ephraims Island, Fishing Creek, Higbees Landing, Miami Beach, Schellengers Landing, Sewells Point, South Cape May, Sunset Beach, Town Bank, Weers Landing, and Wildwood Gables.[39][40]
Schellengers Landing is where boats dock and where a bridge between Cape Island and the mainland is located. Schellengers Landing was named after people who moved from New England to New Jersey in the 1600s.[41] There were multiple families with the Schellenger name who had settled the area.[42] Schellengers Landing is connected to Cape May city via a bridge,[41] and is on Route 109.[43] The name of the community is spelled differently in different works.[42]
Lower Township borders the Cape May County municipalities of Cape May City, Cape May Point Borough, Middle Township, West Cape May Borough, Wildwood City, Wildwood Crest Borough, and Delaware Bay and the Atlantic Ocean.[44][45][46]
Demographics
[edit]| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1810 | 862 | — | |
| 1820 | 1,001 | 16.1% | |
| 1830 | 999 | −0.2% | |
| 1840 | 1,133 | 13.4% | |
| 1850 | 1,604 | * | 41.6% |
| 1860 | 1,865 | 16.3% | |
| 1870 | 1,783 | −4.4% | |
| 1880 | 1,779 | * | −0.2% |
| 1890 | 1,156 | * | −35.0% |
| 1900 | 1,141 | * | −1.3% |
| 1910 | 1,188 | * | 4.1% |
| 1920 | 1,096 | −7.7% | |
| 1930 | 1,444 | * | 31.8% |
| 1940 | 1,693 | 17.2% | |
| 1950 | 2,737 | 61.7% | |
| 1960 | 6,332 | 131.3% | |
| 1970 | 10,154 | 60.4% | |
| 1980 | 17,105 | 68.5% | |
| 1990 | 20,820 | 21.7% | |
| 2000 | 22,945 | 10.2% | |
| 2010 | 22,866 | −0.3% | |
| 2020 | 22,057 | −3.5% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 21,886 | [10][12] | −0.8% |
| Population sources: 1810–2000[47] 1810–1920[48] 1840[49] 1850–1870[50] 1850[51] 1870[52] 1880–1890[53] 1890–1910[54] 1910–1930[55] 1940–2000[56] 2000[57][58] 2010[20][21] 2020[10][11] * = Lost territory in previous decade[24] | |||
2010 census
[edit]The 2010 United States census counted 22,866 people, 9,579 households, and 6,351 families in the township. The population density was 824.3 per square mile (318.3/km2). There were 14,507 housing units at an average density of 523.0 per square mile (201.9/km2). The racial makeup was 94.24% (21,549) White, 1.99% (456) Black or African American, 0.16% (37) Native American, 0.62% (142) Asian, 0.04% (10) Pacific Islander, 1.20% (275) from other races, and 1.74% (397) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 4.24% (969) of the population.[20]
Of the 9,579 households, 22.6% had children under the age of 18; 49.3% were married couples living together; 12.1% had a female householder with no husband present and 33.7% were non-families. Of all households, 28.7% were made up of individuals and 15.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.38 and the average family size was 2.89.[20]
19.8% of the population were under the age of 18, 7.6% from 18 to 24, 20.4% from 25 to 44, 31.0% from 45 to 64, and 21.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 46.5 years. For every 100 females, the population had 90.1 males. For every 100 females ages 18 and older there were 86.9 males.[20]
The Census Bureau's 2006–2010 American Community Survey showed that (in 2010 inflation-adjusted dollars) median household income was $51,101 (with a margin of error of +/− $2,460) and the median family income was $62,587 (+/− $7,438). Males had a median income of $50,572 (+/− $3,361) versus $35,978 (+/− $2,297) for females. The per capita income for the borough was $28,175 (+/− $1,295). About 6.6% of families and 10.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 20.4% of those under age 18 and 6.5% of those age 65 or over.[59]
2000 census
[edit]As of the 2000 U.S. census,[16] there were 22,945 people, 9,328 households, and 6,380 families residing in the township. The population density was 813.0 inhabitants per square mile (313.9/km2). There were 13,924 housing units at an average density of 493.4 per square mile (190.5/km2). The racial makeup of the township was 96.26% White, 1.39% African American, 0.23% Native American, 0.53% Asian, 0.02% Pacific Islander, 0.65% from other races, and 0.92% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.88% of the population.[57][58]
There were 9,328 households, out of which 28.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.9% were married couples living together, 11.7% had a female householder with no husband present, and 31.6% were non-families. 27.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 15.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.43 and the average family size was 2.95.[57][58]
In the township, the population was spread out, with 23.7% under the age of 18, 6.1% from 18 to 24, 25.1% from 25 to 44, 24.4% from 45 to 64, and 20.7% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 42 years. For every 100 females, there were 90.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 85.2 males.[57][58]
The median income for a household in the township was $38,977, and the median income for a family was $45,058. Males had a median income of $35,201 versus $24,715 for females. The per capita income for the township was $19,786. About 5.3% of families and 7.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.3% of those under age 18 and 5.3% of those age 65 or over.[57][58]
Government
[edit]
Local government
[edit]Lower Township operates within the Faulkner Act, formally known as the Optional Municipal Charter Law, under the Council-Manager form of government, which was adopted in 1984. The township is one of 42 municipalities (of the 564) statewide that use this form of government.[60] The council is comprised of five members—the Mayor, the Council Member-at-Large and three Ward seats—each elected on a partisan basis to four-year terms on a staggered basis, with either two seats (mayor and council at-large) or the three ward seats up for election in even-numbered years on an alternating basis as part of the November general election.[8][61][4] The Mayor presides at all Council meetings and has a voice and vote in the proceedings. Powers are limited to those expressly conferred by the Charter. The Manager serves the Council for an indefinite term of office and may be removed by a majority vote of the Council. The Manager is the chief executive and administrator of the Township.
As of 2023[update], members of the Lower Township Council are Mayor Frank Sippel (R, term ends December 31, 2024; At Large), Deputy Mayor David Perry (R, 2024; At Large), Thomas Conrad (R, 2026; Ward I), Kevin Coombs (R, 2026; Ward II) and Roland A. Roy Jr. (R, 2026; Ward III).[4][62][63][64][65]
Erik Simonsen won a special election in November 2013 to fill the seat of Glenn Douglass, who had resigned two months earlier and whose seat had been filled on an interim basis by Jackie Henderson.[66]
In January 2017, Roland Roy was selected from three candidates nominated by the Republican municipal committee to fill the Third Ward seat vacated by Erik Simonsen when he took office as mayor; Roy served on an interim basis until the November 2017 general election, when he was elected to serve the balance of the term through December 2018.[67][68]
In February 2020, the Township Council selected Keven Coombs to fill the Ward II seat expiring in December 2022 that became vacant when David Perry was chosen to serve as deputy mayor.[69] Earlier that month, Perry had been shifted to deputy mayor after Frank Sippel was selected as mayor to replace Erik K. Simonsen, who resigned to take office in the New Jersey General Assembly.[70]
Federal, state, and county representation
[edit]Lower Township is located in the 2nd Congressional District[71] and is part of New Jersey's 1st state legislative district.[72][73][74]
For the 118th United States Congress, New Jersey's 2nd congressional district is represented by Jeff Van Drew (R, Dennis Township).[75] New Jersey is represented in the United States Senate by Democrats Cory Booker (Newark, term ends 2027)[76] and George Helmy (Mountain Lakes, term ends 2024).[77][78]
For the 2024-2025 session, the 1st legislative district of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Mike Testa (R, Vineland) and in the General Assembly by Antwan McClellan (R, Ocean City) and Erik K. Simonsen (R, Lower Township).[79]
Cape May County is governed by a five-person Board of County Commissioners whose members are elected at-large on a partisan basis to three-year terms of office on a staggered basis, with either one or two seats coming up for election each year; At an annual reorganization held each January, the commissioners select one member to serve as director and another to serve as vice-director.[80] As of 2024[update], Cape May County's Commissioners are Director Leonard C. Desiderio (R, Sea Isle City, 2024),[81] Robert Barr (R, Ocean City; 2025),[82] Will Morey (R, Wildwood Crest; 2026),[83] Melanie Collette (R. Middle Township; 2026),[84] and Vice-Director Andrew Bulakowski (R, Lower Township; 2025).[85][80][86]
The county's constitutional officers are Clerk Rita Marie Rothberg (R, 2025, Ocean City),[87][88] Sheriff Robert Nolan (R, 2026, Lower Township)[89][90] and Surrogate E. Marie Hayes (R, 2028, Ocean City).[91][92][93][86]
Politics
[edit]As of March 2011, there were a total of 14,612 registered voters in Lower Township, of which 3,000 (20.5%) were registered as Democrats, 5,902 (40.4%) were registered as Republicans and 5,702 (39.0%) were registered as Unaffiliated. There were 8 voters registered as Libertarians or Greens.[94]
In the 2012 presidential election, Republican Mitt Romney received 52.6% of the vote (5,493 cast), ahead of Democrat Barack Obama with 46.2% (4,823 votes), and other candidates with 1.1% (120 votes), among the 10,534 ballots cast by the township's 15,217 registered voters (98 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 69.2%.[95][96] In the 2008 presidential election, Republican John McCain received 52.2% of the vote (5,831 cast), ahead of Democrat Barack Obama, who received 45.1% (5,040 votes), with 11,177 ballots cast among the township's 14,435 registered voters, for a turnout of 77.4%.[97] In the 2004 presidential election, Republican George W. Bush received 54.3% of the vote (5,951 ballots cast), outpolling Democrat John Kerry, who received around 44.1% (4,830 votes), with 10,961 ballots cast among the township's 14,709 registered voters, for a turnout percentage of 74.5.[98]
In the 2013 gubernatorial election, Republican Chris Christie received 70.8% of the vote (4,909 cast), ahead of Democrat Barbara Buono with 27.6% (1,913 votes), and other candidates with 1.7% (115 votes), among the 7,142 ballots cast by the township's 14,910 registered voters (205 ballots were spoiled), for a turnout of 47.9%.[99][100] In the 2009 gubernatorial election, Republican Chris Christie received 51.6% of the vote (3,712 ballots cast), ahead of both Democrat Jon Corzine with 40.1% (2,882 votes) and Independent Chris Daggett with 6.0% (433 votes), with 7,190 ballots cast among the township's 14,989 registered voters, yielding a 48.0% turnout.[101]
Education
[edit]


Lower Township School District serves public-school students in pre-kindergarten through sixth grade.[102] As of the 2020–21 school year, the district, comprised of four schools, had an enrollment of 1,519 students and 149.6 classroom teachers (on an FTE basis), for a student–teacher ratio of 10.2:1.[103] Schools in the district (with 2020–21 enrollment data from the National Center for Education Statistics[104]) are David C. Douglass Veterans Memorial School[105] with 312 students in grades PreK-K (in Villas), Carl T. Mitnick School[106] with 440 students in grades 1-2 (in Cold Spring), Maud T. Abrams School[107] with 355 students in grades 3-4 (in Cold Spring), and Charles W. Sandman Consolidated School[108] with 388 students in grades 5-6 (in Cold Spring).[109][110][111] The Lower Township School District participates in the Interdistrict Public School Choice Program, which allows non-resident students to attend the district's schools without cost to their parents, with tuition paid by the state. Seats in the program for non-resident students are specified by the district and are allocated by lottery.[112][113]
For seventh through twelfth grades, public-school students attend the schools of the Lower Cape May Regional School District, in the Erma area of the township, which also serves students from Cape May City and West Cape May, along with students from Cape May Point who attend the district as part of a sending/receiving relationship.[114][115][116][117] Schools in the district (with 2022–23 enrollment data from the National Center for Education Statistics[118]) are Richard M. Teitelman Middle School[119] with 433 students in grades 7-8 and Lower Cape May Regional High School (LCMRHS)[120] with 757 students in grades 9-12.[121][122] In the 2011–12 school year, the city of Cape May paid $6 million in property taxes to cover the district's 120 high-school students, an average of $50,000 per student attending the Lower Cape May district. Cape May officials have argued that the district's funding formula based on assessed property values unfairly penalizes Cape May, which has higher property values and a smaller number of high-school students as a percentage of the population than the other constituent districts, especially Lower Township.[123] The district's board of education is comprisedof nine members, who are elected directly by voters to serve three-year terms of office on a staggered basis, with three seats up for election each year[124][125] Seats on the board are allocated based on population, with Lower Township assigned seven seats.[126]
Students are also eligible to attend Cape May County Technical High School in Cape May Court House, which serves students from the entire county in its comprehensive and vocational programs, which are offered without charge to students who are county residents.[127][128] Special needs students may be referred to Cape May County Special Services School District in Cape May Court House.
Wildwood Catholic Academy (Pre-K–12) in North Wildwood, of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Camden, is the nearest Catholic school. Villas had its own Catholic K–8 school, St. Raymond's School, until 2007, when it merged into Our Lady Star of the Sea School in Cape May.[129] In 2010 Our Lady Star of the Sea merged into Cape Trinity Regional School (Pre-K–8) in North Wildwood.[130] That school in turn merged into Wildwood Catholic Academy in 2020.[131] As of 2020[update] Bishop McHugh Regional School in Dennis Township takes students from Lower Township.[132]
Two of the initial properties of Cape Christian Academy, formed c. 1990 as a merger of South Cape Christian Academy and Cape May County Christian School were in Lower Township.[133] The current consolidated school building is in Middle Township, with a Cape May Courthouse postal address and within the CMCH census-designated place.[134] Richard Degener of the Press of Atlantic City described it as being in Burleigh. Its campus has 6.5 acres (2.6 ha) of area.[133]
Cape May County Library operates the Lower Township Library in Villas.[135]
Transportation
[edit]

Roads and highways
[edit]As of May 2010[update], the township had a total of 179.10 miles (288.23 km) of roadways, of which 131.92 miles (212.30 km) were maintained by the municipality, 33.83 miles (54.44 km) by Cape May County and 6.87 miles (11.06 km) by the New Jersey Department of Transportation and 6.48 miles (10.43 km) by the New Jersey Turnpike Authority.[136]
The most prominent highway serving Lower Township is the Garden State Parkway, which has its southern terminus at the intersection with Route 109, in the township.[137] U.S. Route 9,[138] Route 109,[139] Route 162,[140] and Ocean Drive are other significant roadways within Lower Township.[141]
Public transportation
[edit]NJ Transit offers bus service on the 313 and 315 routes between Cape May / Wildwood / Philadelphia, on the 552 between Cape May and Atlantic City, with seasonal service on the 319 route serving shore points between Cape May and the Port Authority Bus Terminal in New York City's Midtown Manhattan.[142][143]
The Cape May–Lewes Ferry terminal is located in North Cape May.[144] Operated by the Delaware River and Bay Authority, the ferry makes the 17-mile (27 km) trip between Lower Township and Lewes, Delaware in 85 minutes, carrying passengers and vehicles.[145] The Delaware River and Bay Authority operates a shuttle bus service that connects the ferry terminal with the Cape May Transportation Center in Cape May in the summer months and to the Cape May County Park & Zoo in July and August.[146]
Cape May Airport is in Lower Township.[147][148]
Points of interest
[edit]
- Battery 223
- Cape May Lighthouse
- Cape May Winery & Vineyard
- Owen Coachman House
- Cold Spring Grange Hall
- Cold Spring Presbyterian Church
- Fire Control Tower No. 23
- Fishing Creek Schoolhouse
- George Hildreth House
- Hawk Haven Vineyard & Winery
- Historic Cold Spring Village
- Jonathan Pyne House
- Naval Air Station Wildwood Aviation Museum
- Rio Grande Station
- Turdo Vineyards & Winery
Notable people
[edit]People who were born in, residents of, or otherwise closely associated with Lower Township include:
- Bob Andrzejczak (born 1986), politician who represented the 1st Legislative District in the New Jersey General Assembly from 2013 to 2019 and in the New Jersey Senate in 2019[149]
- Maurice Catarcio (1929–2005), professional wrestler for the World Wrestling Federation and record holder in The Guinness Book of World Records[150]
- T. Millet Hand (1902–1956), politician who represented New Jersey's 2nd congressional district in the United States House of Representatives from 1945 to 1956[151]
- Chris Jay, (born 1978), musician, screenwriter, actor and member of the band Army of Freshmen[152]
- Michael Linnington (born 1958), CEO of Wounded Warrior Project[153]
- Charles W. Sandman Jr. (1921–1985), politician who represented New Jersey's 2nd congressional district from 1967 to 1975[154]
- Erik K. Simonsen, politician who represents the 1st Legislative District in the New Jersey General Assembly and had served as mayor of Lower Township from 2016 until 2020[155]
- Matt Szczur (born 1989), Major League Baseball outfielder[156]
References
[edit]- ^ Kuperinsky, Amy. "'The Jewel of the Meadowlands'?: N.J.'s best, worst and weirdest town slogans", NJ Advance Media for NJ.com, January 22, 2015. Accessed July 12, 2016. "Lower Township, also in Cape May County, claims to be 'Home of the Best Sunsets.'"
- ^ a b c d e f 2019 Census Gazetteer Files: New Jersey Places, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 1, 2020.
- ^ a b US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ^ a b c Mayor and Council, Lower Township. Accessed August 23, 2023. "Lower Township adopted the Council-Manager form of government in 1984. The council is comprised of five council members (Mayor, Council Member-at-Large, and 3 Wards), each elected on partisan basis, serving the Township for a four-year term. Because the terms overlap, elections to council are held every two years."
- ^ 2023 New Jersey Mayors Directory, New Jersey Department of Community Affairs, updated February 8, 2023. Accessed February 10, 2023. As of date accessed, Sippel was listed with a term-end year of 2024, which is the end of his three-year committee term, not his one-year mayoral term of office.
- ^ Township Manager, Township of Lower. Accessed August 4, 2022.
- ^ Clerk, Township of Lower. Accessed August 4, 2022.
- ^ a b 2012 New Jersey Legislative District Data Book, Rutgers University Edward J. Bloustein School of Planning and Public Policy, March 2013, p. 8.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Township of Lower, Geographic Names Information System. Accessed March 7, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e QuickFacts Lower township, Cape May County, New Jersey, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 23, 2022.
- ^ a b c Total Population: Census 2010 - Census 2020 New Jersey Municipalities, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed December 1, 2022.
- ^ a b Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Minor Civil Divisions in New Jersey: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2023, United States Census Bureau, released May 2024. Accessed May 16, 2024.
- ^ a b Population Density by County and Municipality: New Jersey, 2020 and 2021, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed March 1, 2023.
- ^ Look Up a ZIP Code for Villas, NJ, United States Postal Service. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ Area Code Lookup - NPA NXX for Villas, NJ, Area-Codes.com. Accessed September 29, 2014.
- ^ a b U.S. Census website, United States Census Bureau. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ^ Geographic Codes Lookup for New Jersey, Missouri Census Data Center. Accessed April 1, 2022.
- ^ US Board on Geographic Names, United States Geological Survey. Accessed September 4, 2014.
- ^ New Jersey: 2020 Core Based Statistical Areas and Counties, United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 22, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Lower township, Cape May County, New Jersey Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ a b Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2010 for Lower township Archived 2012-04-30 at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ Table 7. Population for the Counties and Municipalities in New Jersey: 1990, 2000 and 2010, New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development, February 2011. Accessed May 1, 2023.
- ^ "Best Places To Live - The Complete Top Towns List 1-100" Archived 2008-02-28 at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Monthly, February 21, 2008. Accessed February 24, 2008.
- ^ a b c d Snyder, John P. The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606-1968, Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. p. 118. Accessed May 29, 2024.
- ^ Holden, Robert F. "History of the Ten Villages of Upper Township: The Island Village of Strathmere, Part 1", The Press of Atlantic City, August 9, 2017. Accessed October 27, 2019.
- ^ A Brief History of Ocean City New Jersey, Ocean City, New Jersey. Accessed December 23, 2017.
- ^ a b "Cape May County", from Historic Roadsides of New Jersey by The Society of Colonial Wars in the State of New Jersey, 1928. Accessed October 27, 2019.
- ^ Cape May County Comprehensive Plan, Cape May County, New Jersey Planning Board. Accessed October 27, 2019.
- ^ "Bizarre History of Cape May --Town Bank was once touted as a whaling town", The Press of Atlantic City, August 1, 2012. Accessed October 27, 2019.
- ^ Lower Township, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed October 27, 2019.
- ^ "Coxe Hall Cottage". Historic Cold Spring Village. August 22, 2016. Retrieved March 10, 2021.
- ^ Stevens, Lewis Townsend. The History of Cape May County, New Jersey: From the Aboriginal Times to the Present Day, p. 92. L.T. Stevens, 1897. Accessed September 3, 2015. "The county of Cape May was divided into three townships, Upper, Middle and Lower, April 2, 1723, of which the official record says:"
- ^ Schaad Jr., Jacob "Bizarre History of Cape May: Lower Township's borders have been constantly changing", ShoreNewsToday, May 15, 2014. Accessed September 3, 2015. "Lower Township has long had an image problem, its name not helping. Middle Township and Upper Township have no problem because it's okay to be at the top or even in the middle, but how much lower can you get than lower?"
- ^ DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data for Diamond Beach CDP, New Jersey Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data for Erma CDP, New Jersey Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data for North Cape May CDP, New Jersey Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data for Villas CDP, New Jersey Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ New Jersey: 2010 - Population and Housing Unit Counts - 2010 Census of Population and Housing (CPH-2-32), United States Census Bureau, August 2012. Accessed October 17, 2012.
- ^ Township of Lower - A Place To Remember, Township of Lower. Accessed July 12, 2008.
- ^ Locality Search, State of New Jersey. Accessed December 18, 2014.
- ^ a b Tischler, Susan (March 1, 2005). "Schellenger's Landing: 100 years of fishing in Cape May". Capemay.com. Cape May, New Jersey: Cape Publishing. Retrieved July 10, 2023. - Tischler was formerly the editor of the magazine.
- ^ a b DeAngelis, Martin (September 18, 2013). "History on the harbor". Press of Atlantic City. Retrieved May 17, 2021.
- ^ Leeburg, Jessica (May 6, 2020). "Ongoing changes to Schellenger's Landing". Capemay.com. Cape May, New Jersey: Cape Publishing. Retrieved July 10, 2023.
- ^ Areas touching Lower Township, MapIt. Accessed February 26, 2020.
- ^ Cape May County, Coalition for a Healthy NJ. Accessed February 26, 2020.
- ^ New Jersey Municipal Boundaries, New Jersey Department of Transportation. Accessed November 15, 2019.
- ^ Barnett, Bob. Population Data for Cape May County Municipalities, 1810 - 2000, WestJersey.org, January 6, 2011. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ Compendium of censuses 1726-1905: together with the tabulated returns of 1905, New Jersey Department of State, 1906. Accessed September 29, 2013.
- ^ Bowen, Francis. American Almanac and Repository of Useful Knowledge for the Year 1843, p. 232, David H. Williams, 1842. Accessed September 29, 2013.
- ^ Raum, John O. The History of New Jersey: From Its Earliest Settlement to the Present Time, Volume 1, p. 260, J. E. Potter and company, 1877. Accessed September 29, 2013. "Lower the most southern township in the state was incorporated in 1798."
- ^ Debow, James Dunwoody Brownson. The Seventh Census of the United States: 1850, p. 137. R. Armstrong, 1853. Accessed September 29, 2013.
- ^ Staff. A compendium of the ninth census, 1870, p. 259. United States Census Bureau, 1872. Accessed July 15, 2012.
- ^ Porter, Robert Percival. Preliminary Results as Contained in the Eleventh Census Bulletins: Volume III - 51 to 75, p. 97. United States Census Bureau, 1890. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ Thirteenth Census of the United States, 1910: Population by Counties and Minor Civil Divisions, 1910, 1900, 1890, United States Census Bureau, p. 336. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ Fifteenth Census of the United States : 1930 - Population Volume I, United States Census Bureau, p. 715. Accessed December 5, 2011.
- ^ Table 6: New Jersey Resident Population by Municipality: 1940 - 2000, Workforce New Jersey Public Information Network, August 2001. Accessed May 1, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e Census 2000 Profiles of Demographic / Social / Economic / Housing Characteristics for Lower township, Cape May County, New Jersey Archived 2004-01-15 at the Wayback Machine, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e DP-1: Profile of General Demographic Characteristics: 2000 - Census 2000 Summary File 1 (SF 1) 100-Percent Data for Lower township, Cape May County, New Jersey Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ DP03: Selected Economic Characteristics from the 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates for Lower township, Cape May County, New Jersey Archived 2020-02-12 at archive.today, United States Census Bureau. Accessed July 16, 2012.
- ^ Inventory of Municipal Forms of Government in New Jersey, Rutgers University Center for Government Studies, July 1, 2011. Accessed June 1, 2023.
- ^ "Forms of Municipal Government in New Jersey", p. 12. Rutgers University Center for Government Studies. Accessed June 1, 2023.
- ^ 2023 Municipal User Friendly Budget, Lower Township. Accessed August 23, 2023.
- ^ 2023 County & Municipal Elected Officials Cape May County, NJ -- July 2023, Cape May County, New Jersey, August 3, 2023. Accessed August 23, 2023.
- ^ Summary Results Report 2022 November Cape May General Election November 8, 2022 Official Results, Cape May County, New Jersey, updated November 17, 2022. Accessed January 1, 2023.
- ^ 2020 General Election Successful Candidates, Cape May County, New Jersey, updated December 4, 2020. Accessed January 1, 2021.
- ^ Campbell, Braden. "Middle Township Democrat Michael Clark wins seat, unofficially", The Press of Atlantic City, November 5, 2013. Accessed December 18, 2014. "In Lower Township, Republican Erik Simonsen won the open Ward 3 Council seat with 1,290 votes.... Simonsen will serve out the remainder of Douglass' one-year unexpired term. Douglass resigned from his seat in September after he found out he must in order to collect his state pension after retiring from the New Jersey Department of Corrections. His seat has been held by North Cape May resident Jackie Henderson since his resignation.... He joins Mayor Michael Beck, Norris Clark, Thomas Conrad and James Neville. All are Republicans save Beck, who is an independent."
- ^ South, Christopher. "Lower Township Council votes in Roland Roy Jr. as Ward 3 councilman", The Gazette of Cape May, January 25, 2017. Accessed January 11, 2018. "Lower Township Council appointed Roland Roy, Jr. to fill the vacant Ward 3 council seat at its Jan. 18 meeting. Roy will replace Mayor Erik Simonsen, who was elected mayor in November and took office at the reorganization meeting earlier this month. Roy was appointed by a unanimous vote of Township Council."
- ^ 2017 General Election Official Results, Cape May County, New Jersey, updated November 9, 2017. Accessed January 1, 2018.
- ^ Price, Carl. "Coombs Sworn to Lower Township Council", Cape May County Herald, February 25, 2020. Accessed February 26, 2020. "Kevin Coombs, second from right, was sworn to Lower Township Council at the Feb. 19 meeting. The Lower Township Regular Republican Organization submitted three candidates to fill the seat of Second Ward Councilman David Perry until the election in November. Perry became deputy mayor after Mayor Frank Sippel became mayor when former Mayor Erik Simonsen was elected to state Assembly."
- ^ Price, Carl. "Perry Takes Oath as Lower's Deputy Mayor", Cape May County Herald, February 8, 2020. Accessed February 26, 2020. "Since Mayor Erik Simonsen vacated his position, after winning a seat on the State Assembly, there has been a shift on Lower Township Council. Deputy Mayor Frank Sippel became mayor, and Councilman David Perry became deputy mayor."
- ^ Plan Components Report, New Jersey Redistricting Commission, December 23, 2011. Accessed February 1, 2020.
- ^ Municipalities Sorted by 2011-2020 Legislative District, New Jersey Department of State. Accessed February 1, 2020.
- ^ 2019 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government, New Jersey League of Women Voters. Accessed October 30, 2019.
- ^ Districts by Number for 2011-2020, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 6, 2013.
- ^ Directory of Representatives: New Jersey, United States House of Representatives. Accessed January 3, 2019.
- ^ U.S. Sen. Cory Booker cruises past Republican challenger Rik Mehta in New Jersey, PhillyVoice. Accessed April 30, 2021. "He now owns a home and lives in Newark's Central Ward community."
- ^ https://www.nytimes.com/2024/08/23/nyregion/george-helmy-bob-menendez-murphy.html
- ^ Tully, Tracey (August 23, 2024). "Menendez's Senate Replacement Has Been a Democrat for Just 5 Months". The New York Times. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- ^ Legislative Roster for District 1, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 12, 2024.
- ^ a b Board of County Commissioners, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022. "Cape May County Government is governed by a Board of County Commissioners. These individuals are elected at large by the citizens of Cape May County and hold spaced 3-year terms." Note that as of date accessed, Desiderio is listed with an incorrect term-end year of 2020.
- ^ Leonard C. Desiderio, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ E. Marie Hayes, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Will Morey, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Jeffrey L. Pierson, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Andrew Bulakowski, Cape May County New Jersey. Accessed January 30, 2023.
- ^ a b 2021 County & Municipal Elected Officials Cape May County, NJ -- July 2021, Cape May County, New Jersey, September 13, 2021. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ County Clerk, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Members List: Clerks, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Sheriff's Page Page, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Members List: Sheriffs, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Surrogate, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Members List: Surrogates, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Constitutional Officers, Cape May County, New Jersey. Accessed April 28, 2022.
- ^ Voter Registration Summary - Cape May, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, March 23, 2011. Accessed October 17, 2012.
- ^ "Presidential General Election Results - November 6, 2012 - Cape May County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast - November 6, 2012 - General Election Results - Cape May County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. March 15, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ 2008 Presidential General Election Results: Cape May County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 23, 2008. Accessed October 17, 2012.
- ^ 2004 Presidential Election: Cape May County, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 13, 2004. Accessed October 17, 2012.
- ^ "Governor - Cape May County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ "Number of Registered Voters and Ballots Cast - November 5, 2013 - General Election Results - Cape May County" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Elections. January 29, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ 2009 Governor: Cape May County Archived 2012-10-17 at the Wayback Machine, New Jersey Department of State Division of Elections, December 31, 2009. Accessed October 17, 2012.
- ^ Lower Township Board of Education District Policy 0110 - Identification, Lower Township School District. Accessed August 4, 2022. "Purpose: The Board of Education exists for the purpose of providing a thorough and efficient system of free public education in grades Pre-Kindergarten through six in the Lower Township School District. Composition: The Lower Township School District is comprised of all the area within the municipal boundaries of Lower Township."
- ^ District information for Lower Township Elementary School District, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed February 15, 2022.
- ^ School Data for the Lower Township School District, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed February 15, 2022.
- ^ David C. Douglass Veterans Memorial School, Lower Township School District. Accessed February 11, 2020.
- ^ Carl T. Mitnick School, Lower Township School District. Accessed February 11, 2020.
- ^ Maud T. Abrams School, Lower Township School District. Accessed February 11, 2020.
- ^ Charles W. Sandman Consolidated School, Lower Township School District. Accessed February 11, 2020.
- ^ Student-Parent Handbook 2019-2020, Lower Township School District. Accessed August 4, 2022.
- ^ School Performance Reports for the Lower Township Elementary School District, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed April 1, 2024.
- ^ New Jersey School Directory for the Lower Township School District, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed February 1, 2024.
- ^ Interdistrict Public School Choice Program List of Operating Choice Districts: 2018-2019 School Year, New Jersey Department of Education, September 18, 2017. Accessed January 11, 2018.
- ^ Lower Township Elementary District Choice Program Profile, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed January 11, 2018.
- ^ Lower Cape May Board of Education District Policy 0110 - Identification, Lower Cape May Regional School District. Accessed August 29, 2024. "Purpose: The Board of Education exists for the purpose of providing a thorough and efficient system of free public education in grades seven through twelve. Composition: The Lower Cape May Regional School District is comprised of all the area within the municipal boundaries of Cape May, Lower Township, and West Cape May."
- ^ Johnson, Virgil; and Kirtland, James L. "A Feasibility Study to Reconfigure the Lower Cape May Regional School District", Statistical Forecasting LLC, June 2013. Accessed August 29, 2024. "Cape May City is one of three constituent communities served by the Lower Cape May Regional School District ('Lower Cape May Regional'), a limited purpose school district providing education for the middle and high school students from Cape May City, Lower Township, and West Cape May.... Students from Cape May Point attend on a sending-receiving basis."
- ^ Interdistrict Public School Choice, Lower Cape May Regional School District. Accessed August 29, 2024. "Lower Cape May Regional High School is a four year comprehensive public High School that serves students from Cape May, West Cape May, Lower Township, Cape May Point and now Choice School students."
- ^ Linehan, Mary. "Cape May makes new push to dissolve Lower Cape May Regional school district", The Gazette of Cape May, June 20, 2013. Accessed January 11, 2018. "The regional school district was formed in 1956 and now serves as a limited purpose regional school district educating students from Cape May, Cape May Point, West Cape May and Lower Township. Cape May Point students attend on a 'sending-receiving' basis."
- ^ School Data for the Lower Cape May Regional High School District, National Center for Education Statistics. Accessed February 1, 2024.
- ^ General Information, Richard M. Teitelman Middle School. Accessed August 29, 2024.
- ^ General Information, Lower Cape May Regional High School. Accessed August 29, 2024.
- ^ School Performance Reports for the Lower Cape May Regional School District, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed April 3, 2024.
- ^ New Jersey School Directory for the Lower Cape May Regional School District, New Jersey Department of Education. Accessed February 1, 2024.
- ^ Fichter, Jack. "Cape May Paying $50K Per Student to Regional School District", Cape May County Herald, January 4, 2012. Accessed March 21, 2018. "Cape May — Taxpayers here pay $50,000 per year for each student sent to the Lower Cape May Regional High School District, a total of $6 million per year.... Deputy Mayor Jack Wichterman said Cape May was paying $6 million to send 120 kids to the regional school district.... 'We have no say in the formula that's utilized to determine how much money we pay to that school district,' he said. 'There are several formulas that can be used and the one that the Lower Township members of that school board chose to use is the one that penalizes the City of Cape May because our real estate values are so much higher than they are in Lower Township.'"
- ^ Annual Comprehensive Financial Report of the Lower Cape May Regional School District, New Jersey Department of Education, for year ending June 30, 2018. Accessed February 3, 2020. "The Lower Cape May Regional School District (District) is a Type II school district located in Cape May County, New Jersey and covers an area of approximately 34 square miles. As a Type II school district, it functions independently through a Board of Education. The Board is comprisedof nine members elected to three-year terms. These terms are staggered so that three members' terms expire each year. The purpose of the School District is to provide educational services for all of Lower Cape May Regional's students in grades 7 through 12."
- ^ Board of Education, Lower Cape May Regional School District. Accessed February 11, 2020.
- ^ Crowley, Terence J. A Response to the Cape May Study to Reconfigure the Lower Cape May Regional School District, Lower Cape May Regional School District, January 6, 2014. Accessed February 11, 2020. "The Lower Cape May Regional District (Regional) is classified as a Limited Purpose District.... It is a Type II district and apportions the Board of Education seats based upon the most recent United States Census. It has nine seats on the Board and that are apportioned as follows: Cape May City 1; West Cape May 1; Lower Township 7."
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions, Cape May County Technical High School. Accessed October 27, 2019. "All residents of Cape May County are eligible to attend Cape May County Technical High School.... The Cape May County Technical High School is a public school so there is no cost to residents of Cape May County."
- ^ Technical High School Admissions, Cape May County Technical High School. Accessed October 27, 2019. "All students who are residents of Cape May County may apply to the Technical High School."
- ^ Ianeri, Brian (May 12, 2009). "Our Lady Star of the Sea school in Cape May to close in 2010". Press of Atlantic City. Retrieved September 11, 2020.
- ^ DiPasquale, Donna (June 22, 2010). "After 92 years, Star of the Sea School closes its doors". Cape Publishing, Inc. Retrieved September 11, 2020. - The author was the principal of Our Lady Star of the Sea Regional School.
- ^ Franklin, Chris (June 4, 2020). "2 Jersey Shore Catholic schools slated to close have been saved". Nj.com. NJ Advance Media. Retrieved September 11, 2020.
- ^ "Areas We Serve". Bishop McHugh Regional Catholic School of Dennis Township. Retrieved September 14, 2020.
- ^ a b Degener, Richard (September 23, 1993). "PROPERTIED CLASS / CAPE CHRISTIAN ACADEMY BUYS LAND FOR CENTRAL CAMPUS". The Press of Atlantic City. p. C1. - Available from Newsbank, ID# news/0EAEAA6D18083359.
- ^ "Home". Cape Christian Academy. Retrieved July 15, 2021.
10 Oyster Road Cape May Court House, NJ 08210
- See map of CDP from the 2010 U.S. Census - page 1 and page 2. In contrast it is across from but not in the Burleigh CDP: Seen here. - ^ "Lower Township". Cape May County Library. Retrieved September 18, 2020.
- ^ Cape May County Mileage by Municipality and Jurisdiction, New Jersey Department of Transportation, May 2010. Accessed July 18, 2014.
- ^ Garden State Parkway Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated August 2014. Accessed February 12, 2023.
- ^ U.S. Route 9 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated July 2013. Accessed February 12, 2023.
- ^ Route 109 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated June 2017. Accessed February 10, 2023.
- ^ Route 162 Straight Line Diagram, New Jersey Department of Transportation, updated June 2017. Accessed February 10, 2023.
- ^ Cape May County Highway Map, New Jersey Department of Transportation. Accessed February 12, 2023.
- ^ Cape May County Bus / Rail Connections, NJ Transit, backed up by the Internet Archive as of January 28, 2010. Accessed September 29, 2014.
- ^ South Jersey Transit Guide Archived 2018-09-29 at the Wayback Machine, Cross County Connection, as of April 1, 2010. Accessed September 29, 2014.
- ^ Directions, Cape May–Lewes Ferry. Accessed September 29, 2014.
- ^ Welcome Aboard, Cape May–Lewes Ferry. Accessed September 29, 2014.
- ^ Ground Transportation Services, Cape May–Lewes Ferry. Accessed May 26, 2016.
- ^ "Zoning Map" (PDF). Lower Township. Retrieved September 23, 2020. - The zoning map shows the airport in the township boundaries. See also: 2010 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP (INDEX): Lower township, NJ, United States Census Bureau. Accessed August 15, 2018. Pages: 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- ^ Airport Operations, Cape May Airport. Accessed August 15, 2018. "Cape May Airport (WWD) 507 Terminal Drive, Bldg. 102 Rio Grande, NJ 08242"
- ^ Avedissian, Eric. "A soldier's story: Bob Andrzejczak lost a leg, not his resolve; The hardest part about the aftermath of attack in Iraq was not the pain ... it was calling home", Ocean City Sentinel, May 20, 2015. Accessed January 11, 2018. "Andrzejczak grew up in Lower Township in North Cape May, a bedroom community straddling the Delaware Bay."
- ^ "Catarcio, Maurice A.", Northeast Obits, May 13, 2005, backed up by the Internet Archive as of August 29, 2014. Accessed November 22, 2016. "He was Republican Leader in Lower Township for ten years."
- ^ Staff. "T. Millet Hand, 54, Legislator, Dead; U.S. Representative From Second Jersey District -- Once Cape May Mayor", The New York Times, December 27, 1956. Accessed August 10, 2016. "Thomas Millet Hand Representative in Congress from the Second New Jersey District, died this evening at his home in nearby Cold Spring apparently of a heart attack."
- ^ Weinberg, David "Cape musician Chris Jay forms unlikely friendship with Russian boxer Magomed Abdusalamov", The Press of Atlantic City, March 8, 2013. Accessed April 21, 2017. "The 34-year-old Lower Township native grew up in a musical household. Both of his parents, Ed and Lisa Jurewicz, are retired music teachers and own Mr. J's Music Shop in North Cape May, which is connected to their home."
- ^ "Michael Linnington Named to Head Wounded Warrior Project", Cape May County Herald, June 22, 2016. Accessed January 25, 2021. "Wounded Warrior Project (WWP) Board of Directors June 16 announced the appointment of Michael S. Linnington, formerly of Villas, to the position of chief executive officer, effective July 18."
- ^ Kerr, Peter. "Ex-Rep. Charles Sandman. Nixon Supporter, Dies", The New York Times, August 27, 1985. Accessed September 29, 2013. "He was 64 and lived in Erma Park, N.J"
- ^ Assemblyman Erik K. Simonsen (R), New Jersey Legislature. Accessed February 26, 2020. "Public / Party Service: Township of Lower Council 2011-19, Mayor 2017-19"
- ^ Caldwell, Dave. "Two Sports, One Big Choice", The New York Times, December 16, 2010. Accessed September 11, 2016. "Szczur, a senior from Erma, N.J., gained attention late in the 2009 season after the National Marrow Donor Program determined that his bone marrow was a match for a 13-month-old girl with juvenile leukemia."