R (programming language)
 | |
| Paradigms | Multi-paradigm: Array, object-oriented, imperative, functional, procedural, reflective |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman |
| Developer | R Core Team[1] |
| First appeared | August 1993[2] |
| Stable release | 3.5.1 ("Feather Spray")[3]
/ July 2, 2018 |
| Typing discipline | Dynamic |
| License | GNU GPL v2[4] |
| Filename extensions | .r, .R, .RData, .rds, .rda |
| Website | www |
| Influenced by | |
| Influenced | |
| Julia[5] | |
| |
R is a programming language and free software environment for statistical computing and graphics that is supported by the R Foundation for Statistical Computing.[6] The R language is widely used among statisticians and data miners for developing statistical software[7] and data analysis.[8] Polls, surveys of data miners, and studies of scholarly literature databases show that R's popularity has increased substantially in recent years.[9] As of August 2018,[update] R ranks 18th in the TIOBE index, a measure of popularity of programming languages.[10]
R is a GNU package.[11] The source code for the R software environment is written primarily in C, Fortran, and R.[12] R is freely available under the GNU General Public License, and pre-compiled binary versions are provided for various operating systems. While R has a command line interface, there are several graphical front-ends, most notably RStudio.[13] Integrated development environments are available.[14]
History
R is an implementation of the S programming language combined with lexical scoping semantics inspired by Scheme.[15] S was created by John Chambers in 1976, while at Bell Labs. There are some important differences, but much of the code written for S runs unaltered.[16]
R was created by Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman[17] at the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and is currently developed by the R Development Core Team, of which Chambers is a member[18]. R is named partly after the first names of the first two R authors and partly as a play on the name of S.[19] The project was conceived in 1992, with an initial version released in 1995 and a stable beta version in 2000.[20][21][22]
Statistical features
R and its libraries implement a wide variety of statistical and graphical techniques, including linear and nonlinear modeling, classical statistical tests, time-series analysis, classification, clustering, and others. R is easily extensible through functions and extensions, and the R community is noted for its active contributions in terms of packages. Many of R's standard functions are written in R itself, which makes it easy for users to follow the algorithmic choices made. For computationally intensive tasks, C, C++, and Fortran code can be linked and called at run time. Advanced users can write C, C++,[23] Java,[24] .NET[25] or Python code to manipulate R objects directly.[26] R is highly extensible through the use of user-submitted packages for specific functions or specific areas of study. Due to its S heritage, R has stronger object-oriented programming facilities than most statistical computing languages. Extending R is also eased by its lexical scoping rules.[27]
Another strength of R is static graphics, which can produce publication-quality graphs, including mathematical symbols. Dynamic and interactive graphics are available through additional packages.[28]
R has Rd, its own LaTeX-like documentation format, which is used to supply comprehensive documentation, both on-line in a number of formats and in hard copy.[29]
Programming features
R is an interpreted language; users typically access it through a command-line interpreter. If a user types 2+2 at the R command prompt and presses enter, the computer replies with 4, as shown below:
> 2 + 2
[1] 4
This calculation is interpreted as the sum of two single-element vectors, resulting in a single-element vector. The prefix [1] indicates that the list of elements following it on the same line starts with the first element of the vector (a feature that is useful when the output extends over multiple lines).
Like other similar languages such as APL and MATLAB, R supports matrix arithmetic. R's data structures include vectors, matrices, arrays, data frames (similar to tables in a relational database) and lists.[30] R's extensible object system includes objects for (among others): regression models, time-series and geo-spatial coordinates. The scalar data type was never a data structure of R.[31] Instead, a scalar is represented as a vector with length one.[32]
R supports procedural programming with functions and, for some functions, object-oriented programming with generic functions. A generic function acts differently depending on the classes of arguments passed to it. In other words, the generic function dispatches the function (method) specific to that class of object. For example, R has a generic print function that can print almost every class of object in R with a simple print(objectname) syntax.[33]
Although used mainly by statisticians and other practitioners requiring an environment for statistical computation and software development, R can also operate as a general matrix calculation toolbox – with performance benchmarks comparable to GNU Octave or MATLAB.[34] Arrays are stored in column-major order.[35]
Packages
The capabilities of R are extended through user-created packages, which allow specialized statistical techniques, graphical devices, import/export capabilities, reporting tools (knitr, Sweave), etc. These packages are developed primarily in R, and sometimes in Java, C, C++, and Fortran.[citation needed] The R packaging system is also used by researchers to create compendia to organise research data, code and report files in a systematic way for sharing and public archiving.[36]
A core set of packages is included with the installation of R, with more than 12,500 additional packages (as of May 2018[update]) available at the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN),[37] Bioconductor, Omegahat,[38] GitHub, and other repositories.[39]
The "Task Views" page (subject list) on the CRAN website[40] lists a wide range of tasks (in fields such as Finance, Genetics, High Performance Computing, Machine Learning, Medical Imaging, Social Sciences and Spatial Statistics) to which R has been applied and for which packages are available. R has also been identified by the FDA as suitable for interpreting data from clinical research.[41]
Other R package resources include Crantastic,[42] a community site for rating and reviewing all CRAN packages, and R-Forge,[43] a central platform for the collaborative development of R packages, R-related software, and projects. R-Forge also hosts many unpublished beta packages, and development versions of CRAN packages.
The Bioconductor project provides R packages for the analysis of genomic data, such as Affymetrix and cDNA microarray object-oriented data-handling and analysis tools, and has started to provide tools for analysis of data from next-generation high-throughput sequencing methods.[44]
Milestones
A list of changes in R releases is maintained in various "news" files at CRAN.[45] Some highlights are listed below for several major releases.
| Release | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0.16 | This is the last alpha version developed primarily by Ihaka and Gentleman. Much of the basic functionality from the "White Book" (see S history) was implemented. The mailing lists commenced on April 1, 1997. | |
| 0.49 | 1997-04-23 | This is the oldest source release which is currently available on CRAN.[46] CRAN is started on this date, with 3 mirrors that initially hosted 12 packages.[47] Alpha versions of R for Microsoft Windows and the classic Mac OS are made available shortly after this version.[citation needed] |
| 0.60 | 1997-12-05 | R becomes an official part of the GNU Project. The code is hosted and maintained on CVS. |
| 0.65.1 | 1999-10-07 | First versions of update.packages and install.packages functions for downloading and installing packages from CRAN.[48] |
| 1.0 | 2000-02-29 | Considered by its developers stable enough for production use.[49] |
| 1.4 | 2001-12-19 | S4 methods are introduced and the first version for Mac OS X is made available soon after. |
| 2.0 | 2004-10-04 | Introduced lazy loading, which enables fast loading of data with minimal expense of system memory. |
| 2.1 | 2005-04-18 | Support for UTF-8 encoding, and the beginnings of internationalization and localization for different languages. |
| 2.11 | 2010-04-22 | Support for Windows 64 bit systems. |
| 2.13 | 2011-04-14 | Adding a new compiler function that allows speeding up functions by converting them to byte-code. |
| 2.14 | 2011-10-31 | Added mandatory namespaces for packages. Added a new parallel package. |
| 2.15 | 2012-03-30 | New load balancing functions. Improved serialization speed for long vectors. |
| 3.0 | 2013-04-03 | Support for numeric index values 231 and larger on 64 bit systems. |
| 3.4 | 2017-04-21 | Just-in-time compilation (JIT) of functions and loops to byte-code enabled by default. |
| 3.5 | 2018-04-23 | Packages byte-compiled on installation by default. Compact internal representation of integer sequences. Added a new serialization format to support compact internal representations. |
Interfaces
The most commonly used graphical integrated development environment for R is RStudio.[50] A similar development interface is R Tools for Visual Studio.
Interfaces with more of a point-and-click approach include Rattle GUI, R Commander, and RKWard.
Some of the more common editors with varying levels of support for R include Eclipse,[51] Emacs (Emacs Speaks Statistics), Kate,[52] LyX,[53] Notepad++,[54] Visual Studio Code, WinEdt,[55] and Tinn-R.[56]
R functionality is accessible from several scripting languages such as Python,[57] Perl,[58] Ruby,[59] F#,[60] and Julia.[61]. Interfaces to other, high-level programming languages, like Java[62] and .NET C#[63][64] are available as well.
Implementations
The main R implementation is written in R, C, and Fortran, and there are several other implementations aimed at improving speed or increasing extensibility. A closely related implementation is pqR (pretty quick R) by Radford M. Neal with improved memory management and support for automatic multithreading. Renjin and FastR are Java implementations of R for use in a Java Virtual Machine. CXXR, rho, and Riposte[65] are implementations of R in C++. Renjin, Riposte, and pqR attempt to improve performance by using multiple processor cores and some form of deferred evaluation.[66] Most of these alternative implementations are experimental and incomplete, with relatively few users, compared to the main implementation maintained by the R Development Core Team.
TIBCO built a runtime engine called TERR, which is part of Spotfire.[67]
Microsoft R Open is a fully compatible R distribution with modifications for multi-threaded computations.[68]
R Communities
R has vibrant and active local communities worldwide for users to network, share ideas and learn[69][70].
There are regular R-user meetups[71] and a more focussed R-Ladies[72] groups which promotes gender diversity.
useR! conferences
The official annual gathering of R users is called "useR!".[73] The first such event was useR! 2004 in May 2004, Vienna, Austria.[74] After skipping 2005, the useR! conference has been held annually, usually alternating between locations in Europe and North America.[75] Subsequent conferences have included:[73]
- useR! 2006, Vienna, Austria
- useR! 2007, Ames, Iowa, USA
- useR! 2008, Dortmund, Germany
- useR! 2009, Rennes, France
- useR! 2010, Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA
- useR! 2011, Coventry, United Kingdom
- useR! 2012, Nashville, Tennessee, USA
- useR! 2013, Albacete, Spain
- useR! 2014, Los Angeles, California, USA
- useR! 2015, Aalborg, Denmark
- useR! 2016, Stanford, California, USA
- useR! 2017, Brussels, Belgium
Future conferences planned are as follows:[73]
- useR! 2018, Brisbane, Australia
- useR! 2019, Toulouse, France
- useR! 2020, Boston, Massachusetts, USA
R Journal
The R Journal is the open access, refereed journal of the R project for statistical computing. It features short to medium length articles on the use, and development of R, including packages, programming tips, CRAN news, and foundation news.
Comparison with SAS, SPSS, and Stata
This section has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
R is comparable to popular commercial statistical packages, such as SAS, SPSS, and Stata, but R is available to users at no charge under a free software license.[76]
In January 2009, the New York Times ran an article charting the growth of R, the reasons for its popularity among data scientists and the threat it poses to commercial statistical packages such as SAS.[77]
Commercial support for R
While R is an open-source project supported by the community developing it, some companies strive to provide commercial support and/or extensions for their customers. This section gives some examples of such companies.
In 2007 Richard Schultz, Martin Schultz, Steve Weston and Kirk Mettler founded Revolution Analytics to provide commercial support for Revolution R, their distribution of R, which also includes components developed by the company. Major additional components include: ParallelR, the R Productivity Environment IDE, RevoScaleR (for big data analysis), RevoDeployR, web services framework, and the ability for reading and writing data in the SAS file format.[78] Revolution Analytics also offer a distribution of R designed to comply with established IQ/OQ/PQ criteria which enables clients in the pharmaceutical sector to validate their installation of REvolution R.[79] In 2015, Microsoft Corporation completed the acquisition of Revolution Analytics.[80] and has since integrated the R programming language into SQL Server 2016, SQL Server 2017, Power BI, Azure SQL Database, Azure Cortana Intelligence, Microsoft R Server and Visual Studio 2017.[81]
In October 2011 Oracle announced the Big Data Appliance, which integrates R, Apache Hadoop, Oracle Linux, and a NoSQL database with Exadata hardware.[82] As of 2012[update], Oracle R Enterprise[83] became one of two components of the "Oracle Advanced Analytics Option"[84] (alongside Oracle Data Mining).[citation needed]
IBM offers support for in-Hadoop execution of R,[85] and provides a programming model for massively parallel in-database analytics in R.[86]
Other major commercial software systems supporting connections to or integration with R include: JMP,[87] Mathematica,[88] MATLAB,[89] Microsoft Power BI,[90] Pentaho,[91] Spotfire,[92] SPSS,[93] Statistica,[94] Platform Symphony,[95] SAS,[96] Tableau Software,[97] Esri ArcGis,[98] Dundas[99] and Statgraphics.[100]
Tibco offers a runtime-version R as a part of Spotfire.[101]
Mango offers a validation package for R, ValidR[102][103], to make it compliant with drug approval agencies, like FDA. These agencies allow for the use of any statistical software in submissions, if only the software is validated, either by the vendor or sponsor itself[104].
Examples
Basic syntax
The following examples illustrate the basic syntax of the language and use of the command-line interface.
In R, the generally preferred[105] assignment operator is an arrow made from two characters <-, although = can usually be used instead.[106]
> x <- c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) # Create ordered collection (vector)
> y <- x^2 # Square the elements of x
> print(y) # print (vector) y
[1] 1 4 9 16 25 36
> mean(y) # Calculate average (arithmetic mean) of (vector) y; result is scalar
[1] 15.16667
> var(y) # Calculate sample variance
[1] 178.9667
> lm_1 <- lm(y ~ x) # Fit a linear regression model "y = B0 + (B1 * x)"
# store the results as lm_1
> print(lm_1) # Print the model from the (linear model object) lm_1
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) x
-9.333 7.000
> summary(lm_1) # Compute and print statistics for the fit
# of the (linear model object) lm_1
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Residuals:
1 2 3 4 5 6
3.3333 -0.6667 -2.6667 -2.6667 -0.6667 3.3333
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -9.3333 2.8441 -3.282 0.030453 *
x 7.0000 0.7303 9.585 0.000662 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 3.055 on 4 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.9583, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9478
F-statistic: 91.88 on 1 and 4 DF, p-value: 0.000662
> par(mfrow = c(2, 2)) # Request 2x2 plot layout
> plot(lm_1) # Diagnostic plot of regression model
Structure of a function
The ease of function creation by the user is one of the strengths of using R. Objects remain local to the function, which can be returned as any data type.[107] Below is an example of the structure of a function:
functionname <- function(arg1, arg2, ... ){ # declare name of function and function arguments
statements # declare statements
return(object) # declare object data type
}
sumofsquares <- function(x){ # a user-created function
return(sum(x^2)) # return the sum of squares of the elements of vector x
}
> sumofsquares(1:3)
[1] 14
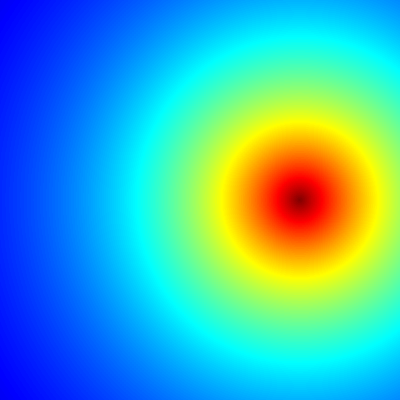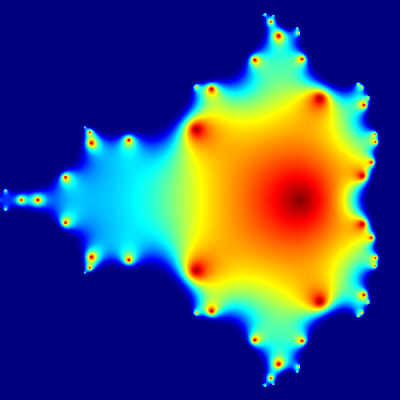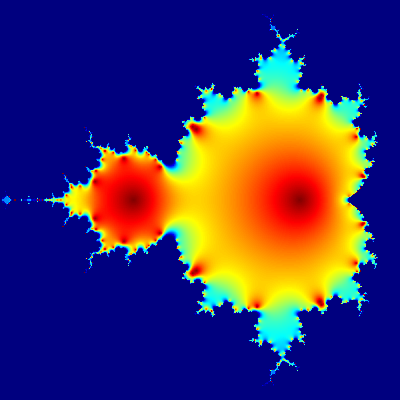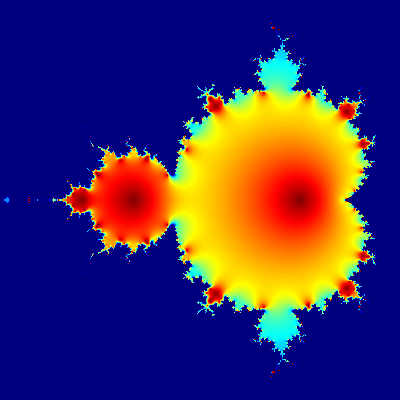
Mandelbrot set
Short R code calculating Mandelbrot set through the first 20 iterations of equation z = z2 + c plotted for different complex constants c. This example demonstrates:
- use of community-developed external libraries (called packages), in this case caTools package
- handling of complex numbers
- multidimensional arrays of numbers used as basic data type, see variables
C,ZandX.
install.packages("caTools") # install external package
library(caTools) # external package providing write.gif function
jet.colors <- colorRampPalette(c("red", "blue", "#007FFF", "cyan", "#7FFF7F",
"yellow", "#FF7F00", "red", "#7F0000"))
dx <- 400 # define width
dy <- 400 # define height
C <- complex(real = rep(seq(-2.2, 1.0, length.out = dx), each = dy),
imag = rep(seq(-1.2, 1.2, length.out = dy), dx))
C <- matrix(C, dy, dx) # reshape as square matrix of complex numbers
Z <- 0 # initialize Z to zero
X <- array(0, c(dy, dx, 20)) # initialize output 3D array
for (k in 1:20) { # loop with 20 iterations
Z <- Z^2 + C # the central difference equation
X[, , k] <- exp(-abs(Z)) # capture results
}
write.gif(X, "Mandelbrot.gif", col = jet.colors, delay = 100)
See also
- Comparison of numerical analysis software
- Comparison of statistical packages
- List of numerical analysis software
- List of statistical packages
- Rmetrics
- RStudio
References
- ^ Hornik, Kurt (26 November 2015). "R FAQ". The Comprehensive R Archive Network. 2.1 What is R?. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ a b Ihaka, Ross (1998). R : Past and Future History (PDF) (Technical report). Statistics Department, The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand.
{{cite tech report}}: Unknown parameter|conference=ignored (help) - ^ "The Comprehensive R Archive Network". Retrieved 6 August 2018.
- ^ "R license". r-project. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ "Introduction". The Julia Manual. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ R language and environment
- Hornik, Kurt (4 October 2017). "R FAQ". The Comprehensive R Archive Network. 2.1 What is R?. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
- Hornik, Kurt (4 October 2017). "R FAQ". The Comprehensive R Archive Network. 2.13 What is the R Foundation?. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
- R Core Team (2016). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL http://www.R-project.org/.
- ^ widely used
- Fox, John; Andersen, Robert (January 2005). "Using the R Statistical Computing Environment to Teach Social Statistics Courses" (PDF). Department of Sociology, McMaster University. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - Vance, Ashlee (6 January 2009). "Data Analysts Captivated by R's Power". New York Times. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
R is also the name of a popular programming language used by a growing number of data analysts inside corporations and academia. It is becoming their lingua franca...
- Fox, John; Andersen, Robert (January 2005). "Using the R Statistical Computing Environment to Teach Social Statistics Courses" (PDF). Department of Sociology, McMaster University. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
- ^ Vance, Ashlee (6 January 2009). "Data Analysts Captivated by R's Power". New York Times. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
R is also the name of a popular programming language used by a growing number of data analysts inside corporations and academia. It is becoming their lingua franca...
- ^ R's popularity
- David Smith (2012); R Tops Data Mining Software Poll, Java Developers Journal, May 31, 2012.
- Karl Rexer, Heather Allen, & Paul Gearan (2011); 2011 Data Miner Survey Summary, presented at Predictive Analytics World, Oct. 2011.
- Robert A. Muenchen (2012). "The Popularity of Data Analysis Software".
- Tippmann, Sylvia (29 December 2014). "Programming tools: Adventures with R". Nature. 517: 109–110. doi:10.1038/517109a.
- ^ "TIOBE Index - The Software Quality Company". TIOBE. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ GNU project
- "GNU R". Free Software Foundation (FSF) Free Software Directory. 23 April 2018. Retrieved 7 August 2018.
- R Project (n.d.). "What is R?". Retrieved 7 August 2018.
- ^ "Wrathematics" (27 August 2011). "How Much of R Is Written in R". librestats. Retrieved 7 August 2018.
- ^ "7 of the Best Free Graphical User Interfaces for R". linuxlinks.com. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ^ "List of R Editors". r-dir. Retrieved 7 August 2018.
- ^ Morandat, Frances; Hill, Brandon; Osvald, Leo; Vitek, Jan (2012). "Evaluating the design of the R language: objects and functions for data analysis" (PDF). ECOOP'12 Proceedings of the 26th European conference on Object-Oriented Programming. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
- ^ "R: What is R?". R-Project. Retrieved 7 August 2018.
- ^ Gentleman, Robert (9 December 2006). "Individual Expertise profile of Robert Gentleman". Archived from the original on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 20 July 2009.
- ^ Thieme, Nick (August 2018). "R generation". Significance. 15 (4): 14–19. doi:10.1111/j.1740-9713.2018.01169.x.
- ^ Kurt Hornik. The R FAQ: Why is R named R?. ISBN 3-900051-08-9. Retrieved 29 January 2008.
- ^ "R : Past and Future History -- A Free Software Project". cran.r-project.org. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ "Over 16 years of R Project history". Revolutions. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Ihaka, Ross. "The R Project: A Brief History and Thoughts About the Future" (PDF). stat.auckland.ac.nz.
- ^ Eddelbuettel, Dirk; Francois, Romain (2011). "Rcpp: Seamless R and C++ Integration". Journal of Statistical Software. 40 (8). doi:10.18637/jss.v040.i08.
- ^ Temple Lang, Duncan (6 November 2010). "Calling R from Java" (PDF). Nuiton. Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ .NET Framework
- "Making GUIs using C# and R with the help of R.NET".
- "R.NET homepage".
- Haynold, Oliver M. (April 2011). An Rserve Client Implementation for CLI/.NET (PDF). R/Finance 2011. Chicago, IL, USA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 November 2015.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
- ^ R manuals. "Writing R Extensions". r-project.org. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
- ^ Jackman, Simon (Spring 2003). "R For the Political Methodologist" (PDF). The Political Methodologist. 11 (1). Political Methodology Section, American Political Science Association: 20–22. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 July 2006. Retrieved 3 August 2006.
- ^ "CRAN Task View: Graphic Displays & Dynamic Graphics & Graphic Devices & Visualization". The Comprehensive R Archive Network. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ "Rd format". hep.by. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ^ Dalgaard, Peter (2002). Introductory Statistics with R. New York, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. pp. 10–18, 34. ISBN 0387954759.
- ^ Ihaka, Ross; Gentlman, Robert (September 1996). "R: A Language for Data Analysis and Graphics" (PDF). Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics. 5 (3). American Statistical Association: 299–314. doi:10.2307/1390807. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ "Data structures · Advanced R." adv-r.had.co.nz. Retrieved 26 September 2016.
- ^ R Core Team. "Print Values". R Documentation. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ "Speed comparison of various number crunching packages (version 2)". SciView. 2003. Archived from the original on 16 October 2007. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ An Introduction to R, Section 5.1: Arrays. Retrieved in 2010-03 from https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/R-intro.html#Arrays.
- ^ Marwick, Ben; Boettiger, Carl; Mullen, Lincoln (26 August 2017). "Packaging data analytical work reproducibly using R (and friends)". PeerJ Preprints. doi:10.7287/peerj.preprints.3192v1. ISSN 2167-9843.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "The Comprehensive R Archive Network". Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ "Omegahat.net". Omegahat.net. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- ^ packages available from repositories
- Robert A. Muenchen (2012). "The Popularity of Data Analysis Software".
- Tippmann, Sylvia (29 December 2014). "Programming tools: Adventures with R". Nature. 517: 109–110. doi:10.1038/517109a.
- "Search all R packages and function manuals | Rdocumentation". Rdocumentation. 16 June 2014. Retrieved 16 June 2014.
- ^ "CRAN Task Views". cran.r-project.org. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ^ "FDA: R OK for drug trials".
- ^ "It's crantastic!".
- ^ "R-Forge: Welcome".
- ^ Huber, W; Carey, VJ; Gentleman, R; Anders, S; Carlson, M; Carvalho, BS; Bravo, HC; Davis, S; Gatto, L; Girke, T; Gottardo, R; Hahne, F; Hansen, KD; Irizarry, RA; Lawrence, M; Love, MI; MacDonald, J; Obenchain, V; Oleś, AK; Pagès, H; Reyes, A; Shannon, P; Smyth, GK; Tenenbaum, D; Waldron, L; Morgan, M (2015). "Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor". Nature Methods. 12 (2). Nature Publishing Group: 115–121. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3252. PMC 4509590. PMID 25633503.
- ^ Changes in versions 3.0.0 onward:
- "R News". cran.r-project.org. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ^ "Index of /src/base/R-0".
- ^ "ANNOUNCE: CRAN".
- ^ https://cran.r-project.org/src/base/NEWS.0
- ^ Peter Dalgaard. "R-1.0.0 is released". Retrieved 6 June 2009.
- ^ "Poll: R GUIs you use frequently". kdnuggets.com. Retrieved 16 August 2017.
- ^ Unknown. "StatET for R".
- ^ "Syntax Highlighting". Kate Development Team. Archived from the original on 7 July 2008. Retrieved 9 July 2008.
- ^ Paul E. Johnson; Gregor Gorjanc. "LyX with R through Sweave". Retrieved 4 April 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "NppToR: R in Notepad++". sourceforge.net. 8 May 2013. Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ Uwe Ligges. "RWinEdt: R Interface to 'WinEdt'". Retrieved 4 April 2017.
- ^ "Tinn-R". Retrieved 4 April 2017.
- ^ Gautier, Laurent (21 October 2012). "A simple and efficient access to R from Python". Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ Florent Angly. "Statistics::R - Perl interface with the R statistical program - metacpan.org".
- ^ alexgutteridge. "GitHub - alexgutteridge/rsruby: Ruby - R bridge". GitHub.
- ^ BlueMountain Capital. "F# R Type Provider".
- ^ "Embedded R within Julia".
- ^ "Rserve TCP/IP server".
- ^ "RserveCLI2 - a .NET/CLR client for Rserve".
- ^ "R.NET".
- ^ Talbot, Justin; DeVito, Zachary; Hanrahan, Pat (1 January 2012). "Riposte: A Trace-driven Compiler and Parallel VM for Vector Code in R". Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques. ACM: 43–52. doi:10.1145/2370816.2370825.
- ^ Neal, Radford (25 July 2013). "Deferred evaluation in Renjin, Riposte, and pqR". Radford Neal's blog. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- ^ Jackson, Joab (May 16, 2013). TIBCO offers free R to the enterprise. PC World. Retrieved July 20, 2015.
- ^ "Microsoft R Open: The Enhanced R Distribution". Retrieved 30 June 2018.
- ^ "Local R User Group Directory". Revolutions Blog. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ "A list of R conferences and meetings". Jumping Rivers. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ "R Project for Statistical Computing". Meetup. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ "R Ladies". R Ladies. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ a b c "useR!". Retrieved from https://www.r-project.org/conferences.html
- ^ "useR! 2004 - The R User Conference". 27 May 2004. Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ R Project (9 August 2013). "R-related Conferences". Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ Burns, Patrick (27 February 2007). "Comparison of R to SAS, Stata and SPSS" (PDF). Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ R as competition for commercial statistical packages
- Vance, Ashlee (7 January 2009). "Data Analysts Are Mesmerized by the Power of Program R: [Business/Financial Desk]". The New York Times.
- Vance, Ashlee (8 January 2009). "R You Ready for R?". The New York Times.
- ^ Morgan, Timothy Prickett (2011-02-07). "'Red Hat for stats' goes toe-to-toe with SAS". The Register, 7 February 2011. Retrieved from https://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/02/07/revolution_r_sas_challenge/.
- ^ "Analyzing clinical trial data for FDA submissions with R". Revolution Analytics. 14 January 2009. Retrieved 15 April 2016.
- ^ Sirosh, Joseph. "Microsoft Closes Acquisition of Revolution Analytics". blogs.technet.com. Microsoft. Retrieved 22 November 2015.
- ^ "Introducing R Tools for Visual Studio". Retrieved 12 July 2017.
- ^ Oracle Corporation's Big Data Appliance
- Doug Henschen (2012); Oracle Makes Big Data Appliance Move With Cloudera, InformationWeek, January 10, 2012.
- Jaikumar Vijayan (2012); Oracle's Big Data Appliance brings focus to bundled approach, ComputerWorld, January 11, 2012.
- Timothy Prickett Morgan (2011); Oracle rolls its own NoSQL and Hadoop Oracle rolls its own NoSQL and Hadoop, The Register, October 3, 2011.
- ^ Chris Kanaracus (2012); Oracle Stakes Claim in R With Advanced Analytics Launch, PC World, February 8, 2012.
- ^ Doug Henschen (2012); Oracle Stakes Claim in R With Advanced Analytics Launch, InformationWeek, April 4, 2012.
- ^ "What's New in IBM InfoSphere BigInsights v2.1.2". IBM. Archived from the original on 6 September 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "IBM PureData System for Analytics" (PDF). IBM. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 8 May 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ JMP (2013). "Analytical Application Development with JMP". SAS Institute Inc. Retrieved 19 September 2013.
- ^ "New in Mathematica 9: Built-in Integration with R". Wolfram. 2013. Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ Henson, Robert (23 July 2013). "MATLAB R Link". The MathWorks, Inc. Retrieved 18 September 2013.
- ^ davidiseminger. "Create Power BI visuals using R - Power BI". docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 16 March 2018.
- ^ "Data Science Pack". Pentaho Corporation. Retrieved 20 April 2017.
- ^ Gibson, Brendan (8 March 2010). "Spotfire Integration with S+ and R". Spotfire. Archived from the original on 19 March 2012. Retrieved 19 September 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Clark, Mike (October 2007). "Introduction to SPSS 16". University of North Texas Research and Statistical Support. Retrieved 19 September 2013.
- ^ StatSoft (n.d.). "Using the R Language Platform". StatSoft Inc. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- ^ Parmar, Onkar (31 March 2011). ""R" integrated with Symphony". Platform Computing Corporation. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- ^ SAS (11 November 2010). "Calling Functions in the R Language (SAS/IML)". Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- ^ Tableau (17 December 2013). "R is Here!". Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ "Building a Bridge to the R Community". Esri. 20 July 2015. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ Dundas. "R Integrated with Dundas BI". Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- ^ "Statgraphics R Interface".
- ^ Tibco. "Unleash the agility of R for the Enterprise". Retrieved 15 May 2014.
- ^ "ValidR on Mango website". Retrieved 21 January 2018.
- ^ Andy Nicholls at Mango Solutions. "ValidR Enterprise: Developing an R Validation Framework" (PDF). Retrieved 21 January 2018.
- ^ FDA. "Statistical Software Clarifying Statement" (PDF). Retrieved 21 January 2018.
- ^ most used assignment operator in R is
<-- R Development Core Team. "Writing R Extensions". Retrieved 14 June 2012.
[...] we recommend the consistent use of the preferred assignment operator '<-' (rather than '=') for assignment.
- "Google's R Style Guide". Retrieved 2 June 2016.
- Wickham, Hadley. "Style Guide". Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- Bengtsson, Henrik (January 2009). "R Coding Conventions (RCC) – a draft". Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- R Development Core Team. "Writing R Extensions". Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ R Development Core Team. "Assignments with the = Operator". Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ^ Kabacoff, Robert (2012). "Quick-R: User-Defined Functions". statmethods.net. Retrieved 28 October 2013.
External links
- Official website
 of the R project
of the R project - Tidyverse.org site
- RStudio site
- Bioconductor site
- Array programming languages
- Cross-platform free software
- Data mining and machine learning software
- Data-centric programming languages
- Dynamically typed programming languages
- Free data visualization software
- Free plotting software
- Free statistical software
- Functional languages
- GNU Project software
- Literate programming
- Numerical analysis software for Linux
- Numerical analysis software for MacOS
- Numerical analysis software for Windows
- Programming languages created in 1993
- R (programming language)
- Science software