Transport in Azerbaijan
Railways
There are 2,932 kilometers of rail tracks out of which only 2,117 kilometers are exploitable and 815 kilometers are double tracks. The railways have lost freight market share in recent years taking just 18% of freight in 2003, compared with 21% in 1999. Much of the rail track and rolling stock is in need of repair or replacement. Of the total exploitation length of route 60% or 1272 km are electrified, 40% or 845 km operate on thermal carrier. About 60% of the length of the railway routes or 1126 km are equipped with full automatic blocks and 479 km – with centralized dispatcher. The railways has 176 stations, 2 of which , Bilajari and Shirvan are completely automated, 12 stations have container courts with adapted mechanisms and machines, 3 stations – Keshle, Ganja and Khirdalan are able to supply high cargo containers.
total:
2,122 km in common carrier service; does not include industrial lines
country comparison to the world: 73
broad gauge:
2,122 km of 1520 gauge (1,278 km electrified) (2006)
Railway links with adjacent countries
 Russia - yes - 1520 gauge.
Russia - yes - 1520 gauge.
 Armenia - yes - 1520 gauge - closed for political reasons
Armenia - yes - 1520 gauge - closed for political reasons
 Georgia - yes - 1520 gauge - also new 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in)) (Standard gauge) link to Turkey (under construction)
Georgia - yes - 1520 gauge - also new 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in)) (Standard gauge) link to Turkey (under construction)
 Iran - yes - break-of-gauge 1520/1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in).
Iran - yes - break-of-gauge 1520/1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in).
 Turkey - no - break-of-gauge 1520/1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in). Via enclave.
Turkey - no - break-of-gauge 1520/1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in). Via enclave.
2007
- February 7 - agreement signed for Kars-Tbilisi-Baku railway
- September 12 - Musa Panahov, the Deputy Minister of Transport of Azerbaijan, announces that construction on the Baku-Tiblisi-Kars railway will begin in October. Construction is budgeted at $200 million, of which $50 million has been allocated from the State Oil Fund of Azerbaijan (SOFAZ). The groundbreaking ceremonies are expected to be held in Turkey by October 10, after which the first rails are expected to be laid by March or April 2008.[1]
Template:Stations of the railway with transfer on sea transport
Roadways

There are about 25,000 kilometers of roads in Azerbaijan, serving domestic cargo traffic and giving access to international main highways. Highways are mostly in fair condition and need an upgrade to international standards in a view to accommodate growing transit traffic. Main and rural roads are in poor condition and in urgent need of rehabilitation and maintenance. The total vehicle fleet in Azerbaijan was about 517,000 in 2004, with about 49 private passenger cars per 1,000 inhabitants, which is quite low compared to European benchmarks but rapidly increasing due to the fast economic growth. Road transport accounted for 54% of all freight in 2003, up from about 48% in 1999.
Main highways carrying international traffic are the Baku-Alat-Ganja-Kazakh-Georgian Border corridor (Azerbaijani section of TRACECA corridor) with a length of 503 km and the so-called North-South Corridor that stretches out from the Russian to the Iranian border along 521 km. Road connections are disrupted with Armenia because of the unresolved conflict regarding the possession of the Nagorno-Karabakh. Travel between mainland and the detached enclave of Nakhichevan is made by air or by road through Iran. Nakhichevan has a 9-kilometre strategic border with Turkey.
total: 59,141 km
country comparison to the world: 75
paved: 29,210 km
unpaved: 29,931 km (2004)
Pipelines
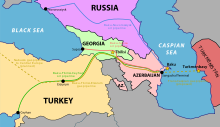
Baku is the centre of a major oil- and gas-producing region, and major long-distance pipelines radiate from the region's oil fields to all neighboring areas. Pipelines are generally highcapacity lines and have diameters of either 1,020 or 1,220 millimeters. The main petroleum pipeline was completed in 2005 under American pressure to limit Russian and Iranian influence in the area. It runs from Baku via Tblissi to Ceyhan in Turkey, therefore the acronym BTC pipeline. It made partly obsolete the old Soviet pipeline pumping crude oil from the onshore and offshore Caspian fields near Baku west across Azerbaijan and Georgia to the port of Batumi, where the oil is either exported in its crude form or processed at Batumi's refinery. Two natural gas lines parallel the old petroleum line as far as Tbilisi, where they turn north across the Caucasus Mountains to join the grid of natural gas pipelines that supply cities throughout Russia and Eastern Europe.
condensate 1 km; gas 3,361 km; oil 1,424 km (2008)
Ports and harbors
Sea and water cargo transportation have vital importance for Azerbaijan, especially in regions where road and rail connections are disputed. Azerbaijan has direct maritime connections only with other Caspian littoral states (Iran, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkmenistan). However, the Volga-Don canal provides a maritime access to the high seas. The main activity is transport of cargo, mainly of oil and oil products. Shipping regions are Caspian, Black, Mediterranean and Marmara Seas. The main shipping company owes 72 ships, 37 of which are tankers (including 1 water-carrier).
Baku International Sea Port is the largest port on the Caspian Sea. Its ferry terminal underwent a major reconstruction supported by a US$16.2 million loan from EBRD. It is now able to handle 30 million tons of freight a year. The Caspian Sea provides vital transport links with other countries and is being used to ship oil until various pipeline projects are completed.
On June 4, 2004 the Ministry of Transport of the Republic of Azerbaijan established the Maritime Administration. As the regulatory authority in maritime transport, its functions include participating in the formulation of state policy, regulating transport demand of goods and passengers and for other types of maritime transport services, as well as implementing state programs, concepts and projects for the development of maritime transport.
Merchant marine
total: 89 ships
country comparison to the world: 52
ships by type: cargo 26, passenger 2, passenger/cargo 9, petroleum tanker 46, roll on/roll off 3, specialized tanker 3
registered in other countries: 3 (Malta 2, Panama 1) (2008)
Airports
There are regular flights between Azerbaijan and former Soviet countries, UK, Germany, France, Austria, Italy, Israel, Iran, Turkey, UAE, China, Georgia and has a cargo flights in UAE, Turkey, Luxembourg, Germany, China, Kyrgystan Afghanistan and Iraq. The national airline is Azerbaijan Airlines (AZAL). There are 5 international airports located in Baku, Ganja, Nakhchivan, Lenkaran, Zaqatala. Heydar Aliyev International Airport in Baku reopened in 1999 after a US$64 million upgrading and extension financed by Turkish company Enka. The airport can now handle 1,600 passengers an hour. The new runways are also able to serve jumbojets. The complete overhaul of International Airport in Nakhchivan has been completed in May 2004. The US$32 million reconstruction project of Ganja Airport has been launched by the Government and was completed by mid 2006. In 2008 were opened two airports in Azerbaijan. The Lenkaran International Airport is in south of Azerbaijan and Zaqatala Airport is in the north-west of Azerbaijan territory.
Airports: 25 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 110
Airports - with paved runways
total: 27
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 6
1,524 to 2,437 m: 13
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 2 (2008)
Airports - with unpaved runways
total: 8
914 to 1,523 m: 1
under 914 m: 7 (2008)
Heliports
total: 1 (2007)
See also
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
- ^ "The cornerstone-laying ceremony of Baku-Tbilisi-Kars Railway to be held in October". Azeri Press Agency. 2007-09-12. Retrieved 2007-09-12.
