Western Bloc
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2014) |
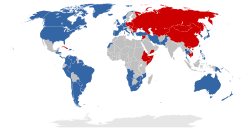
First World: Countries aligned with the Western Bloc (i.e., NATO and allies), led by the United States
Second World: Countries aligned with the Eastern Bloc (i.e., Warsaw Pact, China, and allies), led by the Soviet Union

The Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, was a coalition of countries that were allied with the United States, a member of NATO, and/or opposed the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact during the Cold War. The latter were referred to as the Eastern Bloc. The governments and press of the Western Bloc were more inclined to refer to themselves as the "Free World" or the "Western world", whereas the Eastern Bloc was often called the "Communist world or Second world".
Since the end of the Cold War, until recently, further escalation between China and Russia became tense since the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia in 1999, such as the conflicts in the Middle East (particularly in Iran, Syria and Yemen), Venezuela and Ukraine.[1]
Western Bloc associations
NATO
 Albania (from 2009)
Albania (from 2009) Belgium
Belgium Bulgaria (from 2004)
Bulgaria (from 2004) Canada
Canada Croatia (from 2009)
Croatia (from 2009) Czech Republic (from 1999)
Czech Republic (from 1999) Denmark
Denmark Estonia (from 2004)
Estonia (from 2004) France
France Germany (from 1990)
Germany (from 1990)
 West Germany (1955-1990)
West Germany (1955-1990)
 Greece (from 1952)
Greece (from 1952) Hungary (from 1999)
Hungary (from 1999) Iceland
Iceland Italy
Italy Latvia (from 2004)
Latvia (from 2004) Lithuania (from 2004)
Lithuania (from 2004) Luxembourg
Luxembourg Montenegro (from 2017)
Montenegro (from 2017) Netherlands
Netherlands North Macedonia (from 2020)
North Macedonia (from 2020) Norway
Norway Poland (from 1999)
Poland (from 1999) Portugal
Portugal Romania (from 2004)
Romania (from 2004) Slovakia (from 2004)
Slovakia (from 2004) Slovenia (from 2004)
Slovenia (from 2004) Spain (from 1982)
Spain (from 1982) Turkey (from 1952)
Turkey (from 1952) United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States
Other NATO-affiliated states and partners
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Georgia
Georgia Iraq
Iraq Kosovo
Kosovo Moldova
Moldova Ukraine
Ukraine West Berlin (1949-1990)
West Berlin (1949-1990)
ANZUS
Compact of Free Association
CENTO
 Iran
Iran Iraq (until 1959)
Iraq (until 1959) Pakistan
Pakistan Turkey
Turkey United Kingdom
United Kingdom
Rio Treaty
 Argentina
Argentina Bahamas (from 1982)
Bahamas (from 1982) Bolivia (until 2012)
Bolivia (until 2012) Brazil
Brazil Chile
Chile Colombia
Colombia Costa Rica
Costa Rica Cuba (until 1959, withdrew in 2012)
Cuba (until 1959, withdrew in 2012) Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador (until 2012)
Ecuador (until 2012) El Salvador
El Salvador Guatemala
Guatemala Haiti
Haiti Honduras
Honduras Mexico (until 2004)
Mexico (until 2004) Nicaragua (until 2012)
Nicaragua (until 2012) Panama
Panama Paraguay
Paraguay Peru
Peru Trinidad and Tobago (from 1967)
Trinidad and Tobago (from 1967) United States
United States Uruguay
Uruguay Venezuela
Venezuela
SEATO

 Australia
Australia France (until 1965)
France (until 1965) New Zealand
New Zealand Pakistan (until 1972)
Pakistan (until 1972) Philippines
Philippines Thailand
Thailand South Vietnam (until 1975)
South Vietnam (until 1975) United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States
East Asia
 Republic of China
Republic of China Japan
Japan South Korea
South Korea Hong Kong (until 1997)
Hong Kong (until 1997)
See also
- Allies
- Axis powers
- Eastern Bloc
- Free world
- First World
- Second World
- Third World
- Operation Condor
- Western betrayal
- Western world
References
Sources
- Matloff, Maurice. Makers of Modern Strategy. Ed. Peter Paret. Princeton: Princeton UP, 1971. 702.
- Kissinger, Henry. Diplomacy. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1994. 447,454.
- Lewkowicz, Nicolas. The United States, the Soviet Union and the Geopolitical Implications of the Origins of the Cold War New York and London: Anthem Press, 2018.
