Yukaghir languages
This article is missing information about the sounds of Yukaghir languages. (January 2015) |
| Yukaghir | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Russian Far East |
| Ethnicity | Yukaghirs, Chuvans, Anauls |
| Linguistic classification | Uralic–Yukaghir? |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | yuka1259 |
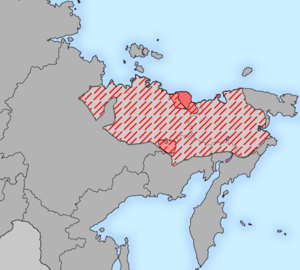 Extent of Yukaghir languages in the 17th (hatched) and 20th (solid) centuries | |
The Yukaghir languages (/ˈjuːkəɡɪər, juːkəˈɡɪər/; also Yukagir, Jukagir) are a small family of two closely related languages—Tundra and Kolyma Yukaghir—spoken by the Yukaghir in the Russian Far East living in the basin of the Kolyma River. At the 2002 Russian census, both Yukaghir languages taken together had 604 speakers.[1] Recent reports from the field reveal that this number is far too high: the Yukaghir languages have at most seventy to eighty speakers.[2][3] The entire family is thus to be regarded as moribund.[4]
Classification and grammatical features
The relationship of the Yukaghir languages with other language families is uncertain, though it has been suggested that they are distantly related to the Uralic languages, thus forming the putative Uralic–Yukaghir language family.[5]
Tundra and Kolyma Yukaghir are the only two remnants of what used to be one of the dominant languages/language families of northeastern Siberia, spreading from the River Anadyr in the east to the River Lena in the west.[6] On the basis of the evidence of early sources, it can be assumed that there existed a Yukaghir dialect continuum, with what is today Tundra Yukaghir and Kolyma Yukaghir at the extremes.[7]
These two languages share only a relatively small part of the vocabulary and are not mutually intelligible. The basic grammatical structures, however, are very similar. Both languages have residual vowel harmony and a complex phonotactics of consonants. Both have rich agglutinative morphology and are strictly head-final. There is practically no finite subordination and very few coordinate structures. The most spectacular feature of TY and KY grammar is the split intransitive alignment system based on discourse-pragmatic features. In absence of narrow focus, the system is organised on the nominative–accusative basis; when focused, direct objects and subjects of intransitive verbs are co-aligned (special focus case, special focus agreement).
Members
The two extant varieties of Yukaghir are:
- Tundra Yukaghir (Northern Yukaghir, also known as Wadul): 30 to 150 speakers in 1989. Last spoken in the tundra belt extending between the lower Indigirka to the lower Kolyma basin (69°N 154°E / 69°N 154°E). Formerly spoken in a much wider area extending to the Lena basin in the west.
- Kolyma Yukaghir (Forest Yukaghir, Southern Yukaghir, also known as Odul): 5 to 10 speakers in 2009 [4]. Last spoken in the forest zone near the sources of the Kolyma, divided between the Sakha Republic and the Magadan Oblast (around 65°N 153°E / 65°N 153°E), previously in the wider area of the upper Kolyma region.
Extinct varieties include Omok and Chuvan, which survived until perhaps the 18th century.
See also
References
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on October 6, 2014. Retrieved December 1, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ [3]
- ^ Collinder, Björn (1940) Jukagirisch und Uralisch. Uppsala: Almqvist & Wiksell.
- ^ Dolgikh, Boris O. (1960) Rodovoj i plemennoj sostav narodov Sibiri v XVII v. Moskva: Izdatel'stvo Akademii Nauk SSSR
- ^ Nikoleava, Irina (2008) Chuvan and Omok languages? In: A. Lubotsky et al. (Eds.) Evidence and Counter-Evidence. Festschrift Frederik Kortland. Amsterdam: Rodopi, pp. 313-336.
Further reading
- Luobbal Sámmol Sámmol Ánte (Ante Aikio): The Uralic-Yukaghir lexical correspondences: genetic inheritance, language contact or chance resemblance? (pdf) (To appear in: Finnisch-Ugrische Forschungen 62) Academia.edu.
- Häkkinen, Jaakko: Early contacts between Uralic and Yukaghir. Suomalais-Ugrilaisen Seuran Toimituksia − Mémoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne 264, pp. 91–101. Helsinki: Suomalais-ugrilainen seura, 2012. Online article (pdf)
- Jochel'son Vladimir I. 1900. Materialy po izucheniju jukagirskogo jazyka i fol’klora. ('Materials for the Study of Yukaghir Language and Folklore'). Sankt-Peterburg: Akademija nauk.
- Jochelson, Waldemar. 1926. The Yukaghir and the Yukaghirized Tungus. Memoirs of the American Museum of Natural History, 9, 13. Publications of the Jesup North Pacific Expedition. Leiden: Brill.
- Krejnovich, Erukhim A. 1958. Jukagirskij jazyk. ('The Yukaghir Language') Moscow and Leningrad: Nauka.
- Krejnovich, Erukhim A. 1982. Issledovanija i materialy po jukagirskomu jazyku. ('Investigations and Materials on the Yukaghir Language') Leningrad: Nauka.
- Kurilov, Gavril N. 2001. Jukagirsko-russkij slovar'. ('Yukaghir-Russian Dictionary') Novosibirsk: Nauka.
- Maslova, Elena. 2001. Yukaghir Texts. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
- Maslova, Elena. 2003. A Grammar of Kolyma Yukaghir. Berlin/New York: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Maslova, Elena. 2003. Tundra Yukaghir. LINCOM Europa. Languages of the World/Materials 372.
- Nikolaeva, Irina. 2006. A Historical Dictionary of Yukaghir. Berlin/New York: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Vakhtin, Nikolaj B. 1991. The Yukagir language in sociolinguistic perspective. Steszew, Poland: International Institute of Ethnolinguistic and Oriental Studies.
- Willerslev, Rane 2007. Soul Hunters: Hunting, Animism, and Personhood among the Siberian Yukaghirs. Berkeley: University tot California Press.
- Willerslev, Rane 2012. On the Run in Siberia. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.

