Prince Richard, Duke of Gloucester: Difference between revisions
→Honours: Platinum Jubilee Medal |
|||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
* [[File:Order of the Crown of Tonga - ribbon bar.gif|45px]] 1 August 2008: Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the [[Order of the Crown of Tonga]]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://matangitonga.to/2008/08/01/royal-orders-presented-palace|title=Royal orders presented at Palace|publisher=Matangi Tonga Online|date=1 August 2008|access-date=26 May 2018}}</ref> |
* [[File:Order of the Crown of Tonga - ribbon bar.gif|45px]] 1 August 2008: Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the [[Order of the Crown of Tonga]]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://matangitonga.to/2008/08/01/royal-orders-presented-palace|title=Royal orders presented at Palace|publisher=Matangi Tonga Online|date=1 August 2008|access-date=26 May 2018}}</ref> |
||
* [[File:Ord.Star.SalomonIsland.png|45px]] 4 August 2008: [[Star of the Solomon Islands]] (SSI)<ref>[http://www.radioaustralia.net.au/programguide/stories/200808/s2323662.htm ] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028174146/http://www.radioaustralia.net.au/programguide/stories/200808/s2323662.htm |date=28 October 2009 }}</ref> |
* [[File:Ord.Star.SalomonIsland.png|45px]] 4 August 2008: [[Star of the Solomon Islands]] (SSI)<ref>[http://www.radioaustralia.net.au/programguide/stories/200808/s2323662.htm ] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028174146/http://www.radioaustralia.net.au/programguide/stories/200808/s2323662.htm |date=28 October 2009 }}</ref> |
||
* [[File:QEII Diamond Jubilee Medal ribbon.png|45px]] 6 February 2012: [[Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal]] |
* [[File:QEII Diamond Jubilee Medal ribbon.png|45px]] 6 February 2012: [[Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal]]{{fact}} |
||
* [[File:Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal.png|45px]] 6 February 2022: [[Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal]] |
* [[File:Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal.png|45px]] 6 February 2022: [[Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal]]{{fact}} |
||
====Foreign==== |
====Foreign==== |
||
Revision as of 15:41, 8 February 2022
| Prince Richard | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duke of Gloucester (more) | |||||
 The Duke in 2008 | |||||
| Born | Prince Richard of Gloucester 26 August 1944 St Matthew's Nursing Home, Northampton, England[1] | ||||
| Spouse | |||||
| Issue |
| ||||
| |||||
| House | Windsor | ||||
| Father | Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester | ||||
| Mother | Lady Alice Montagu Douglas Scott | ||||
| Alma mater | Magdalene College, Cambridge | ||||
| Royal family of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms |
|---|
 |
|
|
Prince Richard, Duke of Gloucester, KG, GCVO, FRIBA (Richard Alexander Walter George; born 26 August 1944) is a member of the British royal family. He is the second son of Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester and Princess Alice, Duchess of Gloucester, as well as the youngest of the nine grandchildren of King George V and Queen Mary. He is currently 31st in line of succession to the British throne, and the highest person on the list who is not a direct descendant of King George VI, who was his uncle. At the time of his birth, he was 5th in line to the throne, behind his first cousins Princess Elizabeth (later Queen Elizabeth II) and Princess Margaret, his father, and his brother.
He practised as an architect until the death of his elder brother placed him in direct line to inherit his father's dukedom of Gloucester, which he assumed in 1974. He married Birgitte van Deurs Henriksen in July 1972. They have three children.
Early life
Prince Richard was born on 26 August 1944 at 12:15 pm at St Matthew's Nursing Home in Northampton, the second son of Duke and Duchess of Gloucester.[1] His father was the third son of King George V and Queen Mary. His mother was the third daughter of the 7th Duke of Buccleuch and Lady Margaret Bridgeman. At the time of his birth, he was second in line to his father's dukedom, behind his elder brother, Prince William of Gloucester, who died in 1972, before inheriting the title and having any children of his own. He was baptised at the Royal Chapel of All Saints in Windsor Great Park on 20 October 1944 by the retired Archbishop of Canterbury, Cosmo Gordon Lang.[6] When Richard was four months old, he accompanied his parents to Australia, where his father served as Governor-General from 1945 to 1947. The family returned to Barnwell Manor in 1947, where Richard spent most of his childhood.
Education and career
Prince Richard's early education took place at home, under the instruction of Rosalind Ramirez, who had also tutored young King Faisal II of Iraq; later, he attended Wellesley House School at Broadstairs and Eton College.[7] In 1963, he matriculated at Magdalene College, Cambridge where he read architecture,[7] graduating with the degree of Bachelor of Arts in June 1966; this was promoted to the rank of MA (Cantab) in 1971.
In 1966, Prince Richard joined the Offices Development Group in the Ministry of Public Building and Works for a year of practical work. He returned to Cambridge in 1967, completing both parts of the Diploma in Architecture degree in June 1969. Upon passing his exams, he became a practising partner in Hunt Thompson Associates in London, an architectural firm.[8]
Marriage and family

On 8 July 1972, Richard married the Danish-born Birgitte van Deurs Henriksen in St Andrew's Church at Barnwell, Northamptonshire; they have three children:
- Alexander Patrick Gregers Richard Windsor, Earl of Ulster (born 24 October 1974 at St Mary's Hospital, London); he married Claire Booth in 2002. The couple have two children.
- Lady Davina Elizabeth Alice Benedikte Windsor (born 19 November 1977 at St Mary's Hospital, London); she married Gary Lewis in 2004, and they divorced in 2018. They have two children.
- Lady Rose Victoria Birgitte Louise Gilman (born 1 March 1980 at St Mary's Hospital, London); she married George Gilman in 2008. The couple have two children.
The Duke and Duchess of Gloucester's official residence is at Kensington Palace in London.[9] They have leased their private home, Barnwell Manor, since 1994.
Activities
Richard ended his architectural career in 1972, after the death of his elder brother Prince William, who crashed his plane in a flying competition. Richard became heir apparent to his father's dukedom and had to take on additional family obligations and royal duties on behalf of the Queen. He became the second Duke of Gloucester (in the fifth creation of that title) upon the death of his father on 10 June 1974.
Richard was elected as a corporate member of the Royal Institute of British Architects (and FRIBA) in 1972. He is President of the Society of Architect Artists.[8] He also serves as a Commissioner of the Historic Building and Monuments Commission for England (English Heritage). He has been Patron of construction charity Construction Youth Trust[10] for many years. With his background in architecture, the Duke of Gloucester takes interest in the work of the Trust and frequently visits their projects, in addition to giving his name to their long standing Duke of Gloucester Young Achiever's Scheme Awards. The Duke is also patron of the Architects Benevolent Society.[11] The Duke is also vice president of Lepra, a UK based charity working towards a world free from prejudice and disability due to leprosy. As part of his active involvement in this role, he attends national and international events in support of the charity's work. He is Royal Patron of the UK branch of the charity Habitat for Humanity,[12] Royal Patron of the St George's Society of New York,[13] and President of The London Society. A keen motorist, Prince Richard passed the Advanced Driving Test of the Institute of Advanced Motorists, of which he was president for more than 32 years. On his appointment in 1971,[14] it was recorded that the new president was "currently [driving] an Austin 1300", reflecting the modest image with which he has always been identified. He stood down as president in January 2005.[15]
The Duke of Gloucester, accompanied by the Duchess, represented his cousin Elizabeth II at the Solomon Islands independence celebrations on 7 July 1978.[16][17] He served as a judge in Prince Edward's charity television special The Grand Knockout Tournament on 15 June 1987.
On 10 April 2008, the Duke of Gloucester was officially installed as inaugural Chancellor of the University of Worcester at a ceremony in Worcester Cathedral. In this role, the Prince officiates at degree ceremonies and major events, as well as promoting the university overseas.[18] The Duke carried out the first of these duties on 5 and 6 November 2008 at the Graduation Award Ceremonies. The Duke is also patron of the Severn Valley Railway and the Pestalozzi International Village Trust. He is patron of the British Homeopathic Association, a charity dedicated to the study, research and promotion of homeopathy.[19] He shares a name with another Duke of Gloucester, Richard III, and has been the patron of the Richard III Society since 1980.[20] He is also a member of the International Advisory Board of the Royal United Services Institute.[21][22] Since 1972, the Duke has been a corporate member of the Royal Institute of British Architects.[23] He is also an honorary fellow of the Institution of Structural Engineers.[24]
During 2009, the Duke became patron of the De Havilland Aircraft Heritage Centre[25] in support of its bid to raise funds through private means and through a bid for Heritage Lottery Funding. Other patronages include: British Society of Soil Science,[26] the International Council on Monuments and Sites,[27] Action on Smoking and Health,[28] British Association of Friends of Museums,[29] British Mexican Society,[30] St Bartholomew's Hospital,[31] as well as numerous other organisations and charities.[7] In July 2011, the Duke visited the Isle of Man to meet with the representative of Manx National Heritage and the Council of Cancer Charities.[23] On 8 November 2011, he opened the new Law School Building at the University of Hertfordshire on the de Havilland campus site of the former de Havilland Aircraft factory.[32] On 19 March 2013, the Duke represented Elizabeth II at the Vatican for the inauguration of Pope Francis.[33]

On 11 March 2015, the Duke visited the Royal School Dungannon in Dungannon, County Tyrone, Northern Ireland to celebrate their 400th anniversary since the founding of the school; presenting a commemorative plaque and raising an anniversary flag on the grounds.[34] On 22 and 26 March 2015, the Duke represented the Queen at the ceremonies marking the reburial and commemorations of Richard III in Leicester Cathedral. Richard III had held the title Duke of Gloucester before his ascension to the English throne.[35] In March 2018, the Duke travelled to Malawi to attend the Commonwealth Day celebrations, and visited projects related to health services, wildlife, and climate change.[36][37]
Titles, styles, honours and arms
Titles and styles
- 26 August 1944 – 10 June 1974: His Royal Highness Prince Richard of Gloucester[38]
- 10 June 1974 – present: His Royal Highness The Duke of Gloucester
Honours

 2 June 1953: Queen Elizabeth II Coronation Medal
2 June 1953: Queen Elizabeth II Coronation Medal 1 January 1974: Knight Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order (GCVO)
1 January 1974: Knight Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order (GCVO) 1975: Grand Prior and Bailiff Grand Cross of the Order of St John (GCStJ)[7]
1975: Grand Prior and Bailiff Grand Cross of the Order of St John (GCStJ)[7]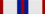 6 February 1977: Queen Elizabeth II Silver Jubilee Medal
6 February 1977: Queen Elizabeth II Silver Jubilee Medal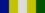 1978: Solomon Islands Independence Medal
1978: Solomon Islands Independence Medal 1980: Vanuatu Independence Medal
1980: Vanuatu Independence Medal 1980: Badge of Honour, New Hebrides[39]
1980: Badge of Honour, New Hebrides[39] 1984: Service Medal of the Order of St John (with 5th bar(2 gold bars))
1984: Service Medal of the Order of St John (with 5th bar(2 gold bars)) 1997: Royal Knight of the Most Noble Order of the Garter (KG)
1997: Royal Knight of the Most Noble Order of the Garter (KG) 6 February 2002: Queen Elizabeth II Golden Jubilee Medal
6 February 2002: Queen Elizabeth II Golden Jubilee Medal 1 August 2008: Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of the Crown of Tonga[40]
1 August 2008: Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of the Crown of Tonga[40] 4 August 2008: Star of the Solomon Islands (SSI)[41]
4 August 2008: Star of the Solomon Islands (SSI)[41] 6 February 2012: Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal[citation needed]
6 February 2012: Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal[citation needed] 6 February 2022: Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal[citation needed]
6 February 2022: Queen Elizabeth II Platinum Jubilee Medal[citation needed]
Foreign
 1973: Knight Grand Cross of the Order of St. Olav
1973: Knight Grand Cross of the Order of St. Olav
- 2015: Sash of Special Category of the Order of the Aztec Eagle[42]
- 1973: Sash of the Order of the Aztec Eagle[43]
 1975: Commander Grand Cross of the Order of the Polar Star
1975: Commander Grand Cross of the Order of the Polar Star 1975: Member, 1st Class of the Order of Tri Shakti Patta
1975: Member, 1st Class of the Order of Tri Shakti Patta 24 February 1975: Nepalese Coronation Medal
24 February 1975: Nepalese Coronation Medal
Honorary military appointments
 Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Australian Army Education Corps[44]
Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Australian Army Education Corps[44]
 Colonel-in-Chief of the Royal New Zealand Army Medical Corps
Colonel-in-Chief of the Royal New Zealand Army Medical Corps
 Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Anglian Regiment[7]
Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Anglian Regiment[7] Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Army Medical Corps[7]
Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Army Medical Corps[7] Deputy Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Logistic Corps[7]
Deputy Colonel-in-Chief, of the Royal Logistic Corps[7] Royal Colonel, of the 6th (V) Battalion, The Rifles[7]
Royal Colonel, of the 6th (V) Battalion, The Rifles[7] The Royal Honorary Colonel, of the Royal Monmouthshire Royal Engineers (Militia)[7]
The Royal Honorary Colonel, of the Royal Monmouthshire Royal Engineers (Militia)[7]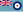 Honorary Air Commodore, of RAF Odiham[7]
Honorary Air Commodore, of RAF Odiham[7] Honorary Air Commodore, of 501 (County of Gloucester) Squadron, Royal Auxiliary Air Force, 16 June 2001.[45]
Honorary Air Commodore, of 501 (County of Gloucester) Squadron, Royal Auxiliary Air Force, 16 June 2001.[45] Honorary Air Marshal, Royal Air Force, 1 September 1996.[46]
Honorary Air Marshal, Royal Air Force, 1 September 1996.[46]
Arms

|
|
Issue
| Name | Birth | Marriage | Issue | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexander Windsor, Earl of Ulster | 24 October 1974 | 22 June 2002 | Claire Booth | Xan Windsor, Lord Culloden Lady Cosima Windsor |
| Lady Davina Windsor | 19 November 1977 | 31 July 2004 Divorced 2018 |
Gary Lewis | Senna Lewis Tāne Lewis |
| Lady Rose Windsor | 1 March 1980 | 19 July 2008 | George Gilman | Lyla Gilman Rufus Gilman |
Ancestry
| Ancestors of Prince Richard, Duke of Gloucester |
|---|
See also
References
- ^ a b "No. 36678". The London Gazette. 29 August 1944. p. 4017.
- ^ As a titled royal, Richard needs no surname, but, when one is used, it is Windsor.
- ^ The Times, 21 October 1944
- ^ The Times, 5 August 1942
- ^ "Yvonne's Royalty Home Page – Royal Christenings". users.uniserve.com. Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2011.
- ^ His godparents were his paternal aunt, Queen Elizabeth, Princess Marie Louise (his cousin), the Countess of Athlone (his cousin, for whom her daughter, Lady May Abel Smith stood proxy), the Duke of Buccleuch (his maternal uncle), the Marquess of Cambridge (his cousin), Lady Sybil Phipps (his maternal aunt), and General the Earl Alexander of Tunis (for whom his wife, then Lady Margaret Alexander, stood proxy). Because of the War, newspapers did not identify the precise location of the christening, saying only that it took place at "a private chapel in the country".[3][4][5]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "HRH The Duke of Gloucester KG GCVO" (PDF). Gov.mt. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ a b "HRH Prince Richard The Duke of Gloucester". University of Worcester. 2008. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^ "Royal residences: Kensington Palace". Official website of the Royal Family. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013.
- ^ "Our Patron". Construction Youth Trust. Retrieved 26 September 2016.
- ^ "Royal Patron for ABS". www.architectsjournal.co.uk. Architects Journal. 6 March 2003. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ "Royal Patron visits HFH Hale County". Habitat for Humanity GB. 30 October 2015. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ^ "Board of Directors". St. George's Society of New York. Archived from the original on 13 April 2013. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ^ "Appointments Register". Motor. 9 October 1971. p. 57.
- ^ Resignation Press Release Archived 17 May 2005 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gloucester, Duke and Duchess of, Solomon Islands Historical Encyclopaedia 1893-1978, Retrieved 2019-02-06.
- ^ "Solomon Islands to Get a Royal Visit'". Solomon Islands Times. 17 June 2008. Retrieved 6 February 2019.
- ^ "HRH Prince Richard The Duke of Gloucester". University of Worcester. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "Royal support for homeopathy". British Homeopathic Association. March 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ Walker, Tim (2 March 2013). "Duke of Gloucester's concern for Richard III's 'dignity'". The Telegraph. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ "Charities and Patronages". The Royal Family. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ "The Duke of Gloucester Lecture Series: Flooding and the British Armed Forces". RUSI. 12 November 2014. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ a b "Duke of Gloucester to visit Isle of Man". BBC. 29 June 2011. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "History of the Institution of Structural Engineers" (PDF). Institution of Structural Engineers. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "Court Circular: May 16". The Times. 15 May 2009. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ "Patron". British Society of Soil Science. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "ICOMOS-UK Launches Cultural Heritage Manifesto in 50th Anniversary Year". ICOMOS-UK. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "ASH Spokespeople". ASH. August 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "About BAFM". British Association of Friends of Museums. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "BMS Organisation". British Mexican Society. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "A Royal visit for St Bartholomew's". Barts Health NHS Trust. 3 October 2017. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ Lennon, Chris (9 November 2011). "Royal opening of University of Hertfordshire law court". Welwyn Hatfield Times. WGC. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ "Cousin stands in for Queen at Pope Francis 'crowning'". Evening Standard. 15 March 2013. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ Murrison, Andrew (11 March 2015). "Duke of Gloucester visits Northern Ireland". gov.uk. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
- ^ "Order of Service for the Reinterment of the Remains of King Richard III" (PDF). 26 March 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 March 2015. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ^ "The Duke of Gloucester visits Malawi". The Royal Family. 15 March 2018. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
- ^ "Royal Visit: The Duke of Gloucester to visit Malawi in the Commonwealth Week". CNBC Africa. 9 March 2018. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
- ^ As a patrilineal grandson of the British monarch, he was styled His Royal Highness Prince Richard of Gloucester from birth.
- ^ Mussell, John W. (2004). Mackay, James (ed.). The Medal Yearbook 2004. Devon, UK: Token Publishing Ltd. p. 236. ISBN 9781870192620.
- ^ "Royal orders presented at Palace". Matangi Tonga Online. 1 August 2008. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ^ [1] Archived 28 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "TRH THE PRINCE OF WALES AND THE DUCHESS OF CORNWALL AWARDED WITH THE MEXICAN ORDER OF THE AZTEC EAGLE". Official website of the Mexican Embassy in the United Kingdom. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ Olvera Ayes, David A (2011). La Orden Mexicana del Águila Azteca: apuntes para su historia. Mexico: Cuadernos del cronista. p. 719. ISBN 978-6070047213.
- ^ a b "Burke's Peerage – The Royal Family – HRH The Duke of Gloucester". Burke's Peerage & Gentry and The Origins Network. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- ^ "No. 56269". The London Gazette (Supplement). 10 July 2001. p. 8120.
- ^ "No. 54519". The London Gazette. 9 September 1996. p. 12011.
- ^ "Duke of Gloucester". britishflags.net. Archived from the original on 1 February 2009.
External links
- Hansard 1803–2005: contributions in Parliament by the Duke of Gloucester
- The Duke of Gloucester at the Royal Family website
- 1944 births
- 20th-century British architects
- 21st-century British people
- Alumni of Magdalene College, Cambridge
- Bailiffs Grand Cross of the Order of St John
- British Anglicans
- British landowners
- Commanders Grand Cross of the Order of the Polar Star
- Dukes of Gloucester
- Earls of Ulster (1928)
- Fellows of the Royal Institute of British Architects
- Fellows of the Society of Antiquaries of London
- Honorary air commodores
- House of Windsor
- Living people
- People educated at Eton College
- People from Northampton
- Princes of the United Kingdom
- Royal Air Force air marshals
- Military personnel from Northamptonshire
- Architects from London
- Barons Culloden
- Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Crown of Tonga


