LabPlot: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: Reverted |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
It has a [[graphical user interface]], a [[command-line interface]] and an interactive and animated [[notebook interface]] to mathematical and statistical packages and programming languages. |
It has a [[graphical user interface]], a [[command-line interface]] and an interactive and animated [[notebook interface]] to mathematical and statistical packages and programming languages. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The LabPlot team promotes a collaborative community through various communication channels.<ref>{{Cite web|title=LabPlot Support|date=28 July 2024|url=https://labplot.kde.org/support/|publisher=LabPlot Team}}</ref> The developers strongly support the idea of [[mentorship]] of students and actively participate in such programs as the Season of KDE (SoK)<ref>{{Cite web|title=The Season of KDE (SoK)|date=28 July 2024|url=https://mentorship.kde.org/blog/2024-01-15-sok-24-welcome/|publisher=KDE}}</ref> or [[Google Summer of Code]] <ref>{{Cite web|title=Google Summer of Code Program 2024|date=28 July 2024|url=https://summerofcode.withgoogle.com/programs/2024/organizations/kde-community|publisher=Google}}</ref>. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The LabPlot team aims at protecting users privacy and data confidentiality. LabPlot is designed to be compliant with [[KDE]] Telemetry Policy, which forbids the usage of unique identification.<ref>{{Cite web|title=KDE Telemetry Policy|date=28 July 2024|url=https://community.kde.org/Policies/Telemetry_Policy|publisher=KDE}}</ref> |
||
== '''Features'''<ref>{{Cite web|title=LabPlot features|date=28 July 2024|url=https://labplot.kde.org/features/|publisher=LabPlot Team}}</ref> == |
== '''Features'''<ref>{{Cite web|title=LabPlot features|date=28 July 2024|url=https://labplot.kde.org/features/|publisher=LabPlot Team}}</ref> == |
||
== General features == |
== General features == |
||
LabPlot is a project-based data management, visualization and analysis tool with a tree-like structure for organizing objects. It features data containers like Spreadsheets and Matrices, and a Worksheet for flexible visualization. The program offers Notes for annotations, [[undo]] history, [[Autosave | autosave]], and locale-sensitive features. It supports [[command-line interface | command-line]] parameters, multiple color schemes, and customizable layouts through a window docking system. |
LabPlot is a project-based data management, visualization and analysis tool with a tree-like structure for organizing objects. It features data containers like Spreadsheets and Matrices, and a Worksheet for flexible visualization. The program offers Notes for annotations, [[undo]] history, [[Autosave | autosave]], and locale-sensitive features. It supports [[command-line interface | command-line]] parameters, multiple color schemes, and customizable layouts through a window docking system, providing a comprehensive and tailored user experience for data analysis and visualization. |
||
== Data visualization == |
== Data visualization == |
||
LabPlot is a data visualization and analysis tool designed for large datasets. It offers a wide range of 2D plotting options, including [[scatter plot | scatter plots]], [[line chart | line plots]], [[bar chart | bar plots]], [[histogram | histograms]], [[box plot | box plots]], [[rug plot | rug plots]], [[Kernel density estimation | KDE plots]], [[Q-Q plot | Q-Q plots]], [[Pareto chart | Pareto plots]], [[sparkline | sparklines]] and Lollipop plots. The software supports multiple axes, flexible positioning of elements, and smooth navigation. It provides various color map options, user-defined themes, and advanced features like [[LaTeX]] support. |
LabPlot is a powerful data visualization and analysis tool designed for large datasets. It offers a wide range of 2D plotting options, including [[scatter plot | scatter plots]], [[line chart | line plots]], [[bar chart | bar plots]], [[histogram | histograms]], [[box plot | box plots]], [[rug plot | rug plots]], [[Kernel density estimation | KDE plots]], [[Q-Q plot | Q-Q plots]], [[Pareto chart | Pareto plots]], [[sparkline | sparklines]] and Lollipop plots, with extensive customization capabilities. The software supports multiple axes, flexible positioning of elements, and smooth navigation. It provides various color map options, user-defined themes, and advanced features like [[LaTeX]] support. Balancing analytical power with user-friendliness, this versatile tool is suitable for both casual users and professionals in scientific and technical fields. |
||
== Data analysis and statistics == |
== Data analysis and statistics == |
||
| Line 35: | Line 41: | ||
== Notebook interface == |
== Notebook interface == |
||
Labplot features an interactive and animated [[notebook interface | computational notebook]] that integrates with mathematics and statistics packages and programming languages like [[Python (programming language) | Python]], [[R (programming language) | R]], [[Julia (programming language) | Julia]], [[Maxima (software) | Maxima]], [[GNU Octave]], [[Scilab]], [[SageMath]], [[KAlgebra]], [[Qalculate!]], [[Lua (programming language) | Lua]]. It supports multiple notebooks and languages simultaneously. Users can create interactive plots from notebook variables and display statistics and plots directly from the context menu. The program offers [[Markdown]] and [[LaTeX]] support. It can read [[Project_Jupyter#Jupyter_Notebook | Jupyter]] and [[Cantor (software) | Cantor projects,]] provides syntax highlighting, integrated help, and supports exporting notebooks to [[PDF]]. |
Labplot features an interactive and animated [[notebook interface | computational notebook]] that integrates with mathematics and statistics packages and programming languages like [[Python (programming language) | Python]], [[R (programming language) | R]], [[Julia (programming language) | Julia]], [[Maxima (software) | Maxima]], [[GNU Octave]], [[Scilab]], [[SageMath]], [[KAlgebra]], [[Qalculate!]], [[Lua (programming language) | Lua]]. It supports multiple notebooks and languages simultaneously, enhancing productivity. Users can create interactive plots from notebook variables and display statistics and plots directly from the context menu. The program offers extensive editing capabilities, robust plotting, [[Markdown]], and [[LaTeX]] support. It can read [[Project_Jupyter#Jupyter_Notebook | Jupyter]] and [[Cantor (software) | Cantor projects,]] provides syntax highlighting, integrated help, and supports exporting notebooks to [[PDF]] for easy sharing and presentation. |
||
== Data import and export == |
== Data import and export == |
||
LabPlot offers |
LabPlot offers extensive features for data handling and analysis. It has no practical limits on data size other than the physical constraints of your computer. LabPlot supports importing various file formats like [[Comma-separated values | CSV]], [[Microsoft Excel]], [[OpenDocument | ODF]], [[SAS (software) | SAS]], [[SPSS]], [[MATLAB]], [[SQL]], [[JSON]], [[binary file | binary files]], [[hierarchical data format | HDF5]], [[MQTT]], [[FITS]], [[NetCDF]], [[ROOT | ROOT (CERN)]], [[LTspice]], [[Ngspice]] and more, ensuring compatibility with diverse data sources. [[Real-time data]] can be read through Unix/[[User datagram protocol | UDP]]/[[Transmission Control Protocol | TCP]] sockets and [[serial port | serial ports]]. Users can export data to formats such as [[PDF]], [[PNG]], [[JPG]], [[SVG]], and [[BMP file format | BMP]], or directly to the clipboard, and print notes, worksheets, and plots. Data can be exported to [[Comma-separated values | CSV]], [[Microsoft Excel]], [[SQL]] databases, and [[LaTeX]] tables. The [[drag and drop]] functionality and templates for import filters simplify the process. Sharing the project via [[email]], [[Nextcloud]], etc. directly from the main menu is also supported. Additionally, the program includes nearly 2000 real-world data sets, making it a valuable resource for educators and students. |
||
== Plot digitization == |
== Plot digitization == |
||
LabPlot |
LabPlot efficiently extracts and analyzes data from image files across various coordinate systems. It supports [[error bar]] analysis and offers both manual and automated [[data extraction]] methods. The software can process multiple curves from a single image, includes basic image editing tools, and integrates extracted data into spreadsheets for immediate use. These features significantly streamline the data processing workflow, saving time and effort for users. |
||
== Data generation and processing == |
== Data generation and processing == |
||
LabPot offers a suite of features for data management and analysis in spreadsheets. It adheres to Tidy Data principles, supports various data types, and provides sorting and search capabilities. The software includes tools for [[Data transformation (statistics) | data transformation]], [[normalization (statistics) | normalization]], and [[feature scaling | standardization]], as well as [[random number generation]] and [[sampling (statistics) | sampling methods]]. It offers functionality to restructure pivoted data, selectively drop or mask data, and create [[heat map]] visualizations with [[color blindness | color-vision deficiency]] friendly options. |
LabPot offers a robust suite of features for enhanced data management and analysis in spreadsheets. It adheres to Tidy Data principles, supports various data types, and provides efficient sorting and search capabilities. The software includes tools for [[Data transformation (statistics) | data transformation]], [[normalization (statistics) | normalization]], and [[feature scaling | standardization]], as well as [[random number generation]] and [[sampling (statistics) | sampling methods]]. It offers functionality to restructure pivoted data, selectively drop or mask data, and create [[heat map]] visualizations with [[color blindness | color-vision deficiency]] friendly options. This versatile tool caters to data scientists, analysts, and researchers across various fields. |
||
== Documentation == |
== Documentation == |
||
LabPlot features a user guide, tutorials, and instructional videos to facilitate learning. Users can access project examples and educational data sets. The software includes a gallery of plots with downloadable project files. It is available in multiple languages. |
LabPlot features a user guide, tutorials, and instructional videos to facilitate learning. Users can access project examples and educational data sets for hands-on experience. The software includes a gallery of plots with downloadable project files, allowing for customization and exploration of visualization options. It is available in multiple languages. |
||
== History == |
== History == |
||
LabPlot was initiated by Stefan Gerlach, a scientist and IT administrator at the [[University of Konstanz]].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Homepage of Dr. Stefan Gerlach|date=30 June 2016|url=http://theorie.physik.uni-konstanz.de/gerlach/|publisher=Theoretische Physik Uni Konstanz}}</ref> |
LabPlot was initiated by Stefan Gerlach, a scientist and IT administrator at the [[University of Konstanz]].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Homepage of Dr. Stefan Gerlach|date=30 June 2016|url=http://theorie.physik.uni-konstanz.de/gerlach/|publisher=Theoretische Physik Uni Konstanz}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The LabPlot team promotes a collaborative community through various communication channels.<ref>{{Cite web|title=LabPlot Support|date=28 July 2024|url=https://labplot.kde.org/support/|publisher=LabPlot Team}}</ref> The developers support the idea of [[mentorship]] of students and actively participate in such programs as the Season of KDE (SoK)<ref>{{Cite web|title=The Season of KDE (SoK)|date=28 July 2024|url=https://mentorship.kde.org/blog/2024-01-15-sok-24-welcome/|publisher=KDE}}</ref> or [[Google Summer of Code]] <ref>{{Cite web|title=Google Summer of Code Program 2024|date=28 July 2024|url=https://summerofcode.withgoogle.com/programs/2024/organizations/kde-community|publisher=Google}}</ref>. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
* [https://labplot.kde.org LabPlot Homepage] |
* [https://labplot.kde.org LabPlot Homepage] |
||
* [https://invent.kde.org/education/labplot/ LabPlot source code at KDE invent] |
|||
* [https://sourceforge.net/projects/labplot/ LabPlot project page at Source Forge] |
|||
* [https://floss.social/@LabPlot LabPlot account at Mastodon] |
|||
* [https://twitter.com/labplot LabPlot account at X] |
|||
* [https://www.youtube.com/@LabPlot LabPlot tutorials on YouTube] |
|||
* [https://tube.kockatoo.org/c/labplot/videos LabPlot tutorials on PeerTube] |
|||
* [https://lemmy.kde.social/c/labplot LabPlot account at Lemmy] |
|||
* [https://matrix.to/#/!jDLqWTaTGNKnenBSNA:kde.org?via=kde.org&via=matrix.org LabPlot room on Matrix] |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 20:12, 28 July 2024
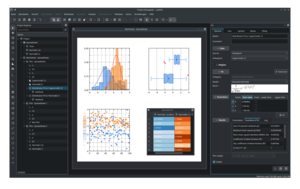 Screenshot of LabPlot of 2022 | |
| Original author(s) | Stefan Gerlach |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | KDE |
| Initial release | 2001 (version 0.1, under the name QPlot) 2003 (version 1.0, renamed to LabPlot) |
| Stable release | 2.11.1
/ 16 July 2024[1] |
| Repository | invent |
| Written in | C, C++ |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows OS X Linux FreeBSD Haiku |
| Type | Scientific plotting Data analysis Curve fitting Regression analysis Statistical analysis Data processing Plot digitization Notebook interface Real-time data |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
| Website | labplot |
LabPlot is a free and open-source, cross-platform computer program for interactive scientific plotting, curve fitting, nonlinear regression, data processing and data analysis. LabPlot is available, under the GPL-2.0-or-later license, for Windows, macOS, Linux, FreeBSD and Haiku operating systems.
It has a graphical user interface, a command-line interface and an interactive and animated notebook interface to mathematical and statistical packages and programming languages.
Community
The LabPlot team promotes a collaborative community through various communication channels.[2] The developers strongly support the idea of mentorship of students and actively participate in such programs as the Season of KDE (SoK)[3] or Google Summer of Code [4].
User privacy and data confidentiality
The LabPlot team aims at protecting users privacy and data confidentiality. LabPlot is designed to be compliant with KDE Telemetry Policy, which forbids the usage of unique identification.[5]
Features[6]
General features
LabPlot is a project-based data management, visualization and analysis tool with a tree-like structure for organizing objects. It features data containers like Spreadsheets and Matrices, and a Worksheet for flexible visualization. The program offers Notes for annotations, undo history, autosave, and locale-sensitive features. It supports command-line parameters, multiple color schemes, and customizable layouts through a window docking system, providing a comprehensive and tailored user experience for data analysis and visualization.
Data visualization
LabPlot is a powerful data visualization and analysis tool designed for large datasets. It offers a wide range of 2D plotting options, including scatter plots, line plots, bar plots, histograms, box plots, rug plots, KDE plots, Q-Q plots, Pareto plots, sparklines and Lollipop plots, with extensive customization capabilities. The software supports multiple axes, flexible positioning of elements, and smooth navigation. It provides various color map options, user-defined themes, and advanced features like LaTeX support. Balancing analytical power with user-friendliness, this versatile tool is suitable for both casual users and professionals in scientific and technical fields.
Data analysis and statistics
The program features a column statistics spreadsheet that details statistical properties and excels in regression analysis with both linear and non-linear curve fitting using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm, supporting numerous predefined and user-defined models. It includes Maximum likelihood estimation for fitting various statistical distributions and offers advanced data processing like baseline subtraction, data reduction (line simplification) with e.g. the Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm, numerical differentiation and integration, and data smoothing. Sophisticated signal processing functions such as Fourier transforms and filtering, Hilbert transforms, convolution, and correlation analyses are supported. Quick statistical previews and visualizations are available for quantitative and categorical data. Enhanced functionality includes a mathematical expression parser and a function values dialog with syntax highlighting for complex data generation and manipulation.
Notebook interface
Labplot features an interactive and animated computational notebook that integrates with mathematics and statistics packages and programming languages like Python, R, Julia, Maxima, GNU Octave, Scilab, SageMath, KAlgebra, Qalculate!, Lua. It supports multiple notebooks and languages simultaneously, enhancing productivity. Users can create interactive plots from notebook variables and display statistics and plots directly from the context menu. The program offers extensive editing capabilities, robust plotting, Markdown, and LaTeX support. It can read Jupyter and Cantor projects, provides syntax highlighting, integrated help, and supports exporting notebooks to PDF for easy sharing and presentation.
Data import and export
LabPlot offers extensive features for data handling and analysis. It has no practical limits on data size other than the physical constraints of your computer. LabPlot supports importing various file formats like CSV, Microsoft Excel, ODF, SAS, SPSS, MATLAB, SQL, JSON, binary files, HDF5, MQTT, FITS, NetCDF, ROOT (CERN), LTspice, Ngspice and more, ensuring compatibility with diverse data sources. Real-time data can be read through Unix/ UDP/ TCP sockets and serial ports. Users can export data to formats such as PDF, PNG, JPG, SVG, and BMP, or directly to the clipboard, and print notes, worksheets, and plots. Data can be exported to CSV, Microsoft Excel, SQL databases, and LaTeX tables. The drag and drop functionality and templates for import filters simplify the process. Sharing the project via email, Nextcloud, etc. directly from the main menu is also supported. Additionally, the program includes nearly 2000 real-world data sets, making it a valuable resource for educators and students.
Plot digitization
LabPlot efficiently extracts and analyzes data from image files across various coordinate systems. It supports error bar analysis and offers both manual and automated data extraction methods. The software can process multiple curves from a single image, includes basic image editing tools, and integrates extracted data into spreadsheets for immediate use. These features significantly streamline the data processing workflow, saving time and effort for users.
Data generation and processing
LabPot offers a robust suite of features for enhanced data management and analysis in spreadsheets. It adheres to Tidy Data principles, supports various data types, and provides efficient sorting and search capabilities. The software includes tools for data transformation, normalization, and standardization, as well as random number generation and sampling methods. It offers functionality to restructure pivoted data, selectively drop or mask data, and create heat map visualizations with color-vision deficiency friendly options. This versatile tool caters to data scientists, analysts, and researchers across various fields.
Documentation
LabPlot features a user guide, tutorials, and instructional videos to facilitate learning. Users can access project examples and educational data sets for hands-on experience. The software includes a gallery of plots with downloadable project files, allowing for customization and exploration of visualization options. It is available in multiple languages.
History
LabPlot was initiated by Stefan Gerlach, a scientist and IT administrator at the University of Konstanz.[7]
External links
- LabPlot Homepage
- LabPlot source code at KDE invent
- LabPlot project page at Source Forge
- LabPlot account at Mastodon
- LabPlot account at X
- LabPlot tutorials on YouTube
- LabPlot tutorials on PeerTube
- LabPlot account at Lemmy
- LabPlot room on Matrix
See also
- List of statistical software
- List of information graphics software
- Comparison of numerical-analysis software
References
- ^ "LabPlot 2.11.1 – LabPlot". 16 July 2024.
- ^ "LabPlot Support". LabPlot Team. 28 July 2024.
- ^ "The Season of KDE (SoK)". KDE. 28 July 2024.
- ^ "Google Summer of Code Program 2024". Google. 28 July 2024.
- ^ "KDE Telemetry Policy". KDE. 28 July 2024.
- ^ "LabPlot features". LabPlot Team. 28 July 2024.
- ^ "Homepage of Dr. Stefan Gerlach". Theoretische Physik Uni Konstanz. 30 June 2016.

