Ingushetia
Republic of Ingushetia | |
|---|---|
| Республика Ингушетия | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Ingush | Гӏалгӏай Мохк |
| Anthem: Ġalġayçen gimn (State Anthem of Ingushetia) | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 43°12′N 44°58′E / 43.200°N 44.967°E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal district | North Caucasian[1] |
| Economic region | North Caucasus[2] |
| Capital | Magas[4] |
| Government | |
| • Body | People's Assembly (Parliament)[5] |
| • Head[5] | Mahmud-Ali Kalimatov[6] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3,000 km2 (1,000 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 81st |
| Population | |
| • Total | 412,529 |
| • Estimate (2018)[9] | 488,043 (+18.3%) |
| • Rank | 75th |
| • Density | 140/km2 (360/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 38.3% |
| • Rural | 61.7% |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (MSK |
| ISO 3166 code | RU-IN |
| License plates | 06 |
| OKTMO ID | 26000000 |
| Official languages | Russian;[11] Ingush[12] |
| Website | http://www.ingushetia.ru/ |
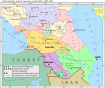
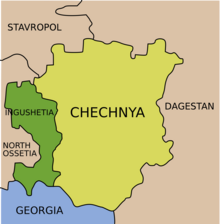
Ingushetia (/ɪŋɡʊˈʃɛtiə/; Russian: Ингуше́тия), officially the Republic of Ingushetia (Russian: Респу́блика Ингуше́тия), is a republic of Russia located in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. The republic is part of the North Caucasian Federal District, and shares land borders with the country of Georgia to its south; and borders the Russian republics of North Ossetia–Alania and Chechnya to its east and west; while having a border with Stavropol Krai to its north.
Its capital is the town of Magas. At 3,000 square km, in terms of area, the republic is the smallest of Russia's federal subjects. It was established on June 4, 1992, after the Chechen-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was split in two.[13][14] The republic is home to the indigenous Ingush, a people of Nakh ancestry. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 412,529.[8]
The republic remains one of the poorest of Russia. Although the violence has died down in recent years,[15][16] the insurgency in neighboring Chechnya has occasionally spilled into Ingushetia. According to Human Rights Watch in 2008, the republic has been destabilized by corruption, a number of high-profile crimes (including kidnapping and murder of civilians by government security forces),[17] anti-government protests, attacks on soldiers and officers, Russian military excesses and a deteriorating human rights situation.[18][19] According to Russian media, Ingushetia has the lowest alcohol consumption in Russia.[20]
Etymology
The name Ingushetia is derived from the ancient village Angusht, which was renamed into Tarskoye and transferred to North Ossetia in 1944 after the deportation of 23 February 1944, a.k.a. operation "Lentil".
The Ingush, a nationality group indigenous to the Caucasus, mostly inhabit Ingushetia. They refer to themselves as Ghalghai (from Ingush: Ghala ("fortress" or "town") and ghai ("inhabitants" or "citizens"). The Ingush speak the Ingush language, which has a very high degree of mutual intelligibility with neighboring Chechen. The Ingush are traditionally a classless society based on a clan system and unwritten law (approximately 350 clans live in Ingushetia today). Every clan, and each clan member, are viewed as equal. Unlike the neighboring nations in the Caucasus (including Chechens), the Ingush never had social superiors or inferiors. The Ingush/Ingushetia were also known by the following names: Gelia (American cartographer J. H. Colton,Strabo[21]), Tschetschna (German geographers Joseph Grassl and Joseph Meyer[22]), Ghalghai/Gelgai (Self), Nakh (self, meaning "people"), Vainakh (self, meaning "our people"), Kist (Georgian), Gergar (Self), Dzurdzuk (Georgian), Ghlighvi (Georgian), Angushtini (Russian), Machaloni (Ossetian), Chechen highlanders called Ingush Makhaloni or Makhloi (according to Chechen historian Khalid Oshayev), Orstkhoi (self), Nart-Orstkhoi (self), Galash (self), Tsori (self), Dzheirakhoi (self), Khamhoi (self), Metshal (self), Fyappi (self), and Nyasareth (self). The self-namings represent different Vainakh tribes which make up the Ingush population today.[23] The history of the Ingush is closely related to Chechens. Byzantine and Georgian missionaries partially Christianised the Ingush, although Christianity was weakened by the Mongol invasions. The remains of several churches, notably the Tkhabya-Yerd and the Albe-Yerd can be found in Ingushetia. The Ingush gradually converted to Islam throughout the 18th-19th century. Vakhushti of Kartli wrote in 1745, that the inhabitants of the village Angushti were Sunni Muslims.
Origin of Ingushetia's population
According to Leonti Mroveli, the XI-century Georgian chronicler, the word Caucasian is derived from the Vainakh ancestor Kavkas.[24] According to Professor George Anchabadze of Ilia State University "The Vainakhs are the ancient natives of the Caucasus. It is noteworthy, that according to the genealogical table drawn up by Leonti Mroveli, the legendary forefather of the Vainakhs was "Kavkas", hence the name Kavkasians, one of the ethnicons met in the ancient Georgian written sources, signifying the ancestors of the Chechens and Ingush. As appears from the above, the Vainakhs, at least by name, are presented as the most "Caucasian" people of all the Caucasians (Caucasus – Kavkas – Kavkasians) in the Georgian historical tradition."[25][26] The Soviet-Russian anthropologists and scientists N.Ya. Marr, V.V. Bounak, R.M. Munchaev, I.M Dyakonov, E.I. Krupnov and G.A. Melikashvilli wrote: "Among Ingush the Caucasian type is preserved better than among any other North Caucasian nation", Professor of anthropology V.V.Bounak "Groznenski Rabochi" 5, VII, 1935. Professor G.F.Debets recognized that Ingush Caucasian anthropologic type is the most Caucasian among Caucasians.[27] In an article in Science Magazine Bernice Wuethrich states that American linguist Dr. Johanna Nichols "has used language to connect modern people of the Caucasus region to the ancient farmers of the Fertile Crescent" and that her research suggests that "farmers of the region were proto-Nakh-Daghestanians". Nichols is quoted as stating that "The Nakh–Dagestanian languages are the closest thing we have to a direct continuation of the cultural and linguistic community that gave rise to Western civilization"[28]
Genetics of Ingushetia's population
The Ingush have 89% of J2 Y-DNA which is the highest known frequency in the world and J2 is closely associated with the Fertile Crescent.[29]
The mitochondrial DNA of the Ingush differs from other Caucasian populations and the rest of the world. "The Caucasus populations exhibit, on average, less variability than other [World] populations for the eight Alu insertion polymorphisms analyzed here. The average heterozygosity is less than that of any other region of the world, with the exception of Sahul. Within the Caucasus, the Ingush have much lower levels of variability than any of the other populations. The Ingush also showed unusual patterns of mtDNA variation when compared with other Caucasus populations (Nasidze and Stoneking, submitted), which indicates that some feature of the Ingush population history, or of this particular sample of the Ingush, must be responsible for their different patterns of genetic variation at both mtDNA and the Alu insertion loci."[30][31]
History
Prehistory







- 10,000–8000 BC
- According to Bernice Wuethrich's article "Peering Into the Past, With Words", Johanna Nichols showed that linguistic evidence indicates the ancestors of Nakh people migrated to the slopes of the Caucasus from the Fertile Crescent where farming and raising sheep and cattle had been discovered. Nichols stated: "The Nakh–Dagestanian languages are the closest thing we have to a direct continuation of the cultural and linguistic community that gave rise to Western civilisation." Anthropologist Henry Harpending of the University of Utah is impressed by her research.[32]
- 6000–4000 BC
- Neolithic era. Pottery is known to the region. Old settlements near Ali-Yurt and Magas, discovered in the modern times, revealed tools made out of stone: stone axes, polished stones, stone knives, stones with holes drilled in them, clay dishes etc. Settlements made out of clay bricks discovered in the plains. In the mountains, there were discovered settlements made out of stone surrounded by walls some of them dated back to 8000 BC.[33]
- 4000–3000 BC
- Invention of the wheel (3000 BC), horseback riding, metal works (copper, gold, silver, iron) dishes, armor, daggers, knives, arrow tips. The artifacts were found near Nasare-Cort, Muzhichi, Ja-E-Bortz (also known as Surkha-khi), Abbey-Gove (also known as Nazran or Nasare).[33]
- 20 BC
- Strabo first mentions Geli, or Galgai in his reference to a nation in the center of the Caucasus. O.W. Wahl in 1875 in his book "The Land of the Czar" page 239 mentioned "These two opinions mentioned by Strabo come after all to the same point ; for the Legi are the modern Lesghi, and the Geli the Ingush tribe Galgai, and the Keraunian Mountains are the northern ranges of the Caucasus as far as the Beshtaú."[34] The same statement about Gelia being Ingush was made by a German professor Karl Koch in 1843 in his book "Reise durch Russland nach dem kaukasischen Isthmus" page 489.[35] Jacobus Van Wijk Roelandszoon, Jacobus van Wijk (Roelandszoon) in 1821 book "Algemeen aardrijkskundig woordenboek volgens de nieuwste staatkundige veranderingen, en de laatste, beste en zekerste berigten" page 1050 also mention that Gelli or Gelad are the Ingush people which is mentioned by Zonaras.[36]
- 900 AD – 1200 AD
- the kingdom in the center of the Caucasus splits into Alania and Noble Alania (known from Russian as Царственные Аланы). German scientist Peter Simon Pallas believed that Ingush people (Kist) were the direct descendants from Alania.[37][38]
- 1239 AD
- Destruction of the Alania capital of Maghas (both names known solely from Muslim Arabs) and Alan confederacy of the Northern Caucasian highlanders, nations, and tribes by Batu Khan (a Mongol leader and a grandson of Genghis Khan) "Magas was destroyed in the beginning of 1239 by the hordes of Batu Khan. Historically Magas was located at approximately the same place on which the new capital of Ingushetia is now built" – D.V.Zayats[39]
- 1300 AD – 1400 AD
- War between the Alans, Tamerlan, Tokhtamysh, and the Battle of the Terek River. The Alan tribes build fortresses, castles, and defense walls locking the mountains from the invaders. Part of the lowland tribes occupied by Mongols. The insurgency against Mongols begins. "One map of the area during the Mongol period gives us a clue why there was not much written about the Vainakh— as the area of Chechnya-Ingushetia on that map is simply marked as ‘‘ungovernable.’’ This is not surprising, as the majority of armies moving north or south would be interested in passing through the mountains and getting to their ultimate destinations as quickly as possible— leaving the peoples between the two passes relatively unmolested.” – Schaefer, Robert W. “Insurgency in Chechnya and the North Caucasus: From Gazavat to Jihad” p. 51. In 1991 the Jordanian historian Abdul-Ghani Khassan presented the photocopy from old Arabic scripts claiming that Alania was in Chechnya and Ingushetia, and the document from Alanian historian Azdin Vazzar (1395–1460) who claimed to be from Nokhcho tribe of Alania.[40][41]
- 1558 AD
- Russian conquest of the Caucasus. 1558 Temryuk of Kabarda sends his emissaries to Moscow requesting help against Ingush tribes from Ivan the Terrible. Ivan the Terrible marries Temryuk's daughter Maria Temryukovna the Circassian (Kabardin) tsaritsa. Alliance formed to gain the ground in the central Caucasus for the expanding Tsardom of Russia against stubborn Vainakh defenders.[42]
- 1562 AD
- Joint Russian, Kabardian, and Nogay forces attack Ingush. According to Russian sources 164 Ingush settlements were completely destroyed in this war. Lowland Ingushetia occupied by Russia and their Kabardian allies.[43]
- 1700s
- After several attempts to gain the access of strategic Darial Gorge, Russian forces lose the battle near village Angusht. Hence the tribe which lived in the village and the nation as a whole is nicknamed Ingush.[citation needed]
Ingushetia in Caucasian War and part of Terek Cossacks Okrug
In XVIII century Ingush were mostly pagan and Christian with some Muslim minority. Beginning 1588 some Chechen societies joined Russia (ru) (ru). In 1785 Chechen leader Sheikh Mansur starts the rebellion against Russia. He gathers his Chechen and Dagestani forces and because of the fear of looting of his own villages from his standing army he orders the attack against Ingush Karabulak settlements. However, the Ingush defeated Mansur and he is forced to retreat.[44] Russian historians claim that the Ingush volunteered to become a part of Russia. This conclusion is based mostly on the document signed on 13 June 1810, by General-Major Delpotso and representatives of 2 Ingush clans. Other clans resisted the Russian conquest. In 1811 Russian envoy of a German origin Moritz von Engelhardt at czar's request visited mountainous Ingushetia and offered Ingush people to join Russia promising many benefits from czar. The representative of the Ingush people rejected the proposal with the reply: "Above my hat I see only sky". This encounter later will be used by Goethe in his "Freisinn"[45] On June 29, 1832, Russian baron Rozen reported in letter No.42 to count Chernishev that "on the 23rd of this month I exterminated eight Ghalghai (Ingush) villages. On the 24th I exterminated nine more villages near Targim." By November 12, 1836 (letter no.560, he was claiming that highlanders of Dzheirkah, Kist, and Ghalghai had been temporarily conquered.[46] In 1829 Imam Shamil starts the rebellion against Russia. He conquers Dagestan, Chechnya and then attacks Ingushetia hoping to convert Ingush people into Islam thus gaining strategic ally. Ingush defeated Imam Shamil forces then and later in 1858 when he tried again two more times to capture Ingushetia. Locked in warfare with two strong opponents and their allies, Ingush forces were decimated. According to Russian officer Fedor Tornau who fought the Ingush with the aid of Ossetian allies, at most Ingush had only six hundred warriors.[47] However, the Russian conquest in Ingushetia was extremely difficult and the Russian forces began to rely on the method of colonization: extermination of the local population and repopulation of the area with Cossack and Ossetian loyalists. Colonization of Ingush land by Russians and Ossetians started in the middle of the 19th century. Russian General Evdokimov and Ossetian colonel Kundukhov in 'Opis no. 436' "gladly reported" that "the result of colonization of Ingush land was successful":
- Ingush village Ghazhien-Yurt was renamed to Stanitsa Assinovskaya in 1847.
- Ingush village Ebarg-Yurt was renamed to Stanitsa Troitskaya in 1847.
- Ingush town Dibir-Ghala was renamed to Stanitsa Sleptsovskaya in 1847.
- Ingush village Magomet-Khite was renamed to Stanitsa Voznesenskaya in 1847.
- Ingush village Akhi-Yurt was renamed to Stanitsa Sunzhenskaya in 1859.
- Ingush village Ongusht was renamed to Stanitsa Tarskaya in 1859.
- Ingush town Ildir-Ghala was renamed to Stanitsa Karabulakskaya in 1859.
- Ingush village Alkhaste was renamed to Stanitsa Feldmarshalskaya in 1860.
- Ingush village Tauzen-Yurt was renamed to Stanitsa Vorontsov-Dashkov in 1861.
- Ingush village Sholkhi was renamed to Khutor Tarski in 1867.[48]
After multiple losses of Imam Shamil at the end of Caucasian War, Russians and Chechens unify their forces. Former Chechen rebels and their men join Russian ranks. 03 November 1858 General Evdokimov ordered (order N1896) a former rebel commander naib Saib-Dulla Gekhinski (Saadulla Ospanov) of Chechnya to attack and destroy Ingush settlements near Assa and Fortanga rivers: Dattikh, Meredzhi, Aseri, Shagot-Koch and others.[49] After the losses, the remaining Ingush clans resorted mostly to underground resistance.[50] The Russians built the fortress Vladikavkaz ("ruler of the Caucasus") on the place of Ingush village of Zaur.[51][52][53][54][55][56][57][58][59] Russian General Aleksey Petrovich Yermolov wrote in a letter to the Tsar of Russia, "It would be a grave mistake for Russia to alienate such a militaristic nation as the Ingush." He suggested the separation of the Ingush and Chechens in order for Russia to win the war in the Caucasus. In another letter from General Ermolov to Lanski (dated 12 January 1827) on the impossibility of forceful Christianization of the Ingush, Yermolov wrote: "This nation, the most courageous and militaristic among all the highlanders, cannot be allowed to be alienated..." The last organized rebellion (the so-called "Nazran insurrection") in Ingushetia occurred in 1858 when 5,000 Ingush started a fight but lost to superior Russian forces. The rebellion signaled the end of the First Russo-Caucasian War. In the same year, the Russian Tsar encouraged the emigration of Ingush and Chechens to Turkey and the Middle East by claiming that "Muslims need to live under Muslim rulers". It seems that he wanted to liberate the land for Ossetians and Cossacks.[50] Some Ingush became exiled to deserted territory in the Middle East where many of them died. The remainder were assimilated. It was estimated that 80% of the Ingush left Ingushetia for the Middle East in 1865.[60][61]
After the Russian Revolution of 1917, the Soviets promised the Ingush that the villages and towns annexed during the colonization would be returned to the Ingush. Ingushetia becomes a major battleground between the old archenemies: general Denikin and Ingush resistance fighters. In his memoirs, general Denikin writes: "Ingush people are the least numerous, most welded, and strongly martial organization. They were, in essence, the supreme arbiter of the North Caucasus. The moral of the appearance was defined long ago in Russian text-books of geography, "the chief occupation – animal husbandry and robbery ..." The last one of the two reached special art in the society. Political aspirations came from the same trend. The Ingush are mercenaries of the Soviet regime, they support it but don’t let the spread of it in their province. At the same time, they tried to strike up relations with Turkey and sought the assistance from the Turks from Elisavetpol, and Germany – from Tiflis. In August, when the Cossacks and Ossetians captured Vladikavkaz, the Ingush intervened and saved the Soviet Board of Commissioners of Terek, but sacked the city and captured the state bank and mint. They robbed all the neighbors: the Cossacks and Ossetians in the name of “correcting historical errors” for a shortage of land, the Bolsheviks – in return for their services, Vladikavkaz citizens – for their helplessness, and the Kabardins – just out of habit. They were hated by everyone, and they did their “craft” in unison, well organized, in a big way, becoming the richest tribe in the Caucasus.”[62]
Ingushetia at part of the Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus
On December 21, 1917 Ingushetia, Chechnya, and Dagestan declared independence from Russia and formed a single state called the "United Mountain Dwellers of the North Caucasus" (also known as Mountainous Republic of the Northern Caucasus), which was recognized by Central Powers (Germany, Austro-Hungary and Turkey), Georgia, and Azerbaijan (which declared their independence from Russia in 1918) as an independent state.[63] For example, Anna Zelkina writes that in May 1918 the first country to recognize independence was Turkey:[64]
The First Congress of the North Caucasus formed a Provisional Government of the North Caucasian Free State (SeveroKavkazskoye Svobodnoye Gosudarstvo) and in May 1918 declared the establishment of the North Caucasian Republic. The only country to recognize it was Turkey.
Later Germany and others followed the recognition. According to P. Kosok:[65]
Azerbaidzhan and Armenia (May 28, 1918). All three states then concluded independent treaties with Turkey, which similarly acknowledged the independence of the Northern Caucasus and concluded a treaty of friendship with it on June 8, 1918. An exchange of diplomatic notes then took place between the head of the German Extraordinary Delegation, General von Lossov, and the North Caucasian Minister of Foreign Affairs, Bammat, resulting in the de facto recognition by Germany of the independence of the Northern Caucasus.
According to British War Office, Germans tried to establish the military base in Ingushetia.[66][67]
...the German Command with the object of securing the presence of German regiments within Ingush territory. The Ingushi declare that all attempts of any foreign armed force to enter into the Terek region will be regarded by the Ingushi as an attack upon themselves, and the Ingushi will oppose all their forces to such attempts.
The capital of the new state was moved to Temir-Khan-Shura (Dagestan).[68][69][70] The first prime minister of the state was elected Tapa Chermoyev, a Chechen prominent statesman; the second prime minister was Ingush statesman Vassan-Girey Dzhabagiev who also was the author of the Constitution of the land in 1917. In 1920 he was reelected for a third term. In 1921 Russians attacked and occupied the country and forcefully merged it with the Soviet state. The Caucasian war for independence continued and the government went into exile.[71]
Ingushetia as Part of Chechen-Ingush ASSR
Cossack General Andrei Shkuro in his book writes:[72]
Ingushetia was the most unanimous and entirely Bolshevik. Ever since the conquest of the Caucasus, the brave and freedom-loving Ingush, who were desperately defending their independence, were partly exterminated and partly driven into barren mountains. The Terek Cossacks were settled on the fertile lands that had belonged to them, and Cossacks founded their villages on the wedge that had cut into Ingushetia. Deprived of the opportunity to earn their bread in an honest way, the Ingush lived by robbery and raids on the Cossack lands. Even in peacetime, the Terek Cossacks bordering Ingush did not go to the field without rifles. Not a day went by without shooting and bloodshed. Considering the Cossacks as oppressors, and the Cossack lands were still theirs, the Ingush mercilessly took revenge on them. The relationship was created completely irreconcilable; further cohabitation was unthinkable. It was necessary either to exterminate the Ingush completely, or to evict the Cossacks from the former Ingush lands, returning those to their former owners. The Bolsheviks, after their occupation of the North Caucasus, convened a congress of representatives of the Ingush and Cossacks of four Terek villages in Vladikavkaz, ordered the latter to move out within a month.
As part of the decossackization campaign a large number of Terek cossacks were deported and their land confiscated in 1920-21.[73] The Sunzha Cossack District (ru), established in 1920 partially on the territory of modern Ingushetia was dissolved in 1929.[74] The Soviets confiscated the remaining Ingush properties by collectivization and dekulakization[75] and unified Chechnya and Ingushetia into Chechen-Ingush ASSR. During World War II Ingush youth were drafted into the Russian army. In August 1942 Nazi German forces captured half of the North Caucasus within thirty-three days moving from Rostov-On-Don to Mozdok 560 km or almost 17 km per day (see Battle of the Caucasus). From Mozdok to Malgobek same thirty three days, 20 km the German forces moved roughly 600 meters per day and were stopped only at Ordzhonikidze (modern-day Vladikavkaz) and Malgobek which were mostly populated by Ingush before the genocide of 23 February 1944. The fighting for the Malgobek was so intense that the small town was captured and recaptured four times until the Germans finally retreated. According to the Soviet military newspaper Red Star, after receiving the news about German brutality toward civilians in Kabardino-Balkaria, Ingush people declare Jihad(Gazavat) against Germans. Stalin planned the expansion of the USSR in the south through Turkey. Muslim Chechens and Ingush could become a threat to the expansion.[76] In February 1944 near the end of World War II, Russian Army and NKVD units flooded the Chechen-Ingush ASSR. The maneuvers were disguised as military exercises of the southern district.
Genocide of 1944

During the World War II, in 1942 German forces entered the North Caucasus. For three weeks Germans captured over half of the North Caucasus. They were only stopped at two Chechen-Ingush cities: Malgobek and Ordzhonikidze (a.k.a. "Vladikavkaz") by heroic resistance of natives of Chechen-Ingush ASSR.[77] Russian propaganda portrayed Chechens and Ingush as "traitors". On 23 February 1944 Ingush and Chechens were falsely accused of collaborating with the Nazis operation code name Lentil starts and the entire Ingush and Chechen populations were deported to Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Siberia on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin while the majority of their men were fighting on the front. The initial phase of the deportation was carried out on United States-supplied Studebaker trucks specifically modified with three submachine gun nest compartments above the deported to prevent escapes. American historian Norman Naimark writes:
Troops assembled villagers and townspeople, loaded them onto trucks – many deportees remembered that they were Studebakers, fresh from Lend-Lease deliveries over the Iranian border – and delivered them at previously designated railheads. …Those who could not be moved were shot. …[A] few fighters aside, the entire Chechen and Ingush nations, 496,460 people, were deported from their homeland.[78]
The deportees were gathered on the railroad stations and during the second phase transferred to the cattle railroad carts. Up to 30% of the population perished during the journey or in the first year of the exile.[79][80][81] The Prague Watchdog claims that "in the early years of their exile about half of the Chechens and Ingush died from hunger, cold and disease".[82] The deportation was classified by the European Parliament in 2004 as genocide.[83] After the deportation Ingush resistance against Russia rises again. Those who escaped the deportation, shepherds who were high in the mountains during the deportation combine forces and form rebel groups which constantly attack Russian forces in Ingushetia. Major rebel groups were led by Akhmed Khuchbarov, Tsitskiev brothers, and Ingush woman-sniper Laisat Baisarova. The last one of the male Ingush rebels was killed in 1977 by the KGB officers, while the female sniper Laisat Baisarova was never captured or killed.[84] American professor Johanna Nichols, who specializes in Chechen and Ingush philology, provided the theory behind the deportation:
In 1944 the nationalities themselves were abolished and their lands resettled when the Chechen and Ingush, together with the Karachay-Balkar, Crimean Tatars, and other nationalities were deported en masse to Kazakhstan and Siberia, losing at least one-quarter and perhaps half of their population in transit. (The reason, never clarified, seems to have been Stalin's wish to clear all Muslims from the main invasion routes in a contemplated attack on Turkey.)[85]
After the return from Central Asia
After 13 years of exile, the Ingush were allowed to return to Chechen-Ingushetia (but not to Ordzhonikidze a.k.a. "Vladikavkaz" or the Prigorodny District). Most of Ingushetia's territory had been settled by Ossetians and part of the region had been transferred to North Ossetia. The returning Ingush faced considerable animosity from the Ossetians. The Ingush were forced to buy their homes back from the Ossetians and Russians. These hardships and injustices led to a peaceful Ingush protest in Grozny on 16 January 1973, which was crushed by the Soviet troops[86] In 1989, the Ingush were officially rehabilitated along with other peoples that had been subjected to repressions.[87]
Ingushetia as Part of the Russian Federation, post-Soviet period
In 1991, when the Chechens declared independence from the Soviet Union to form the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, the Ingush chose to secede from the Chechen-Ingush Republic. Thus, in 1992 the Ingush joined the newly created Russian Federation to try to resolve the conflict with Ossetia peacefully, also in the hope that the Russians would return their land as a token of their loyalty.
Ethnic cleansing of 1992
However, ethnic tensions in North Ossetia which were orchestrated by Ossetian nationalists (per Helsinki Human Right Watch), led to an outbreak of violence in the Ossetian–Ingush conflict in October–November 1992, when another ethnic cleansing of the Ingush population started.[88] According to media reports, Ingush hostages were held in 1992 in Beslan high school gymnasium. The hostages were all kept in the same gymnasium, and deprived of food and water; at least one newborn, and several dozen male Ingush hostages were executed.[89][90][91][92] (In a possible retaliation in 2004, Chechen and Ingush militants took over 500 Osset hostages in Beslan high-school. It was the same building where ossetian militants had held hundreds of Ingush hostages in 1992). Over 60,000 Ingush civilians were forced from their homes in the Prigorodny District of North Ossetia.[50] As a result of the conflict, pro-Russian general Ruslan Aushev, a decorated war hero from the War in Afghanistan, was appointed by the Russian government as the first president of Ingushetia to stop the spread of the conflict. Partial stability returned under his rule.
First and Second Chechen Wars
In 1994, when the First Chechen War started, the number of refugees in Ingushetia from both conflicts doubled. According to the UN, for every citizen of Ingushetia, one refugee arrived from Ossetia or Chechnya. This influx was very problematic for the economy, which collapsed after Aushev's success. The second Russo-Chechen war which started in 1999 brought more refugees (at some point there was one refugee for every Ingush citizen: 240,000 from Chechnya plus 60,000 from North Ossetia at the peak in 2000) and misery to Ingushetia. In 2001, Aushev was forced to leave his presidency and was succeeded by Murat Zyazikov, a former KGB general. The situation worsened under his rule. Many young Ingush men were abducted by Russian and Ossetian death squads.[93][94][95][96] according to Human rights watchdogs Memorial[97] and Mashr.[98] The Ingush mountains are closed for Ingush nationals.[99] The number of rebel attacks in Ingushetia rose, especially after the number of Russian security forces was tripled. For example, according to a Russian news agency a murder of an ethnic-Russian school teacher in Ingushetia was committed by two ethnic-Russian and ethnic-Ossetian soldiers; Issa Merzhoev the Ingush Police detective who solved the crime was shot at and killed by "unknown" assailants shortly after he had identified the murderer.[100] At least four people were injured when a vehicle exploded on 24 March 2008. An upsurge in violence in these months targeted local police officers and security forces. In January 2008, the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation launched a "counter-terrorism" operation in Ingushetia after receiving information that insurgents had been preparing a series of attacks.[101] In the beginning of August 2008, the war between Georgia and South Ossetia broke out, in which the Russian Federation subsequently became involved.[102] After the outbreak of the war, there were virtually no more attacks or abductions of Ingush civilians by "unknown" forces. Most of the Russian forces were transferred to North and South Ossetia[103] 31 August 2008 Magomed Yevloyev, the head of Ingush opposition and the owner of the website ingushetiya.ru, was killed by Russian security forces[104] Shortly before the unrecognised opposition group People's Parliament of Ingushetia Mekhk-Kkhel called for the recognition of the Russian semi-autonomous republic's independence, opposition activist Magomed Khazbiyev proclaimed, "We must ask Europe or America to separate us from Russia."[105][106]
On October 18, 2008, a Russian military convoy came under grenade attack and machine gun fire near Nazran. Official Russian reports of the ambush, which has been blamed on local Muslim separatists, said two soldiers were killed and at least seven injured. Reports from Ingush opposition sources suggested as many as forty to fifty Russian soldiers were killed.[107][108]
On October 30, 2008, Zyazikov was dismissed from his office (he himself claimed he resigned voluntarily). On the next day, Yunus-Bek Yevkurov was nominated by Dmitry Medvedev and approved as President by the People's Assembly of Ingushetia (later the title President was renamed to Head). This move was endorsed by major Russian political parties and by the Ingush opposition.[109][110] Under the current rule of Yevkurov, Ingushetia seems much calmer, showing some semblance of the Russian government. Attacks on policemen have fallen by 40% and abductions by 80%.[111]
Military history
According to professor Johanna Nichols, in all the recorded history and reconstructable prehistory, the Ingush people have never undertaken battle except in defense.[50] In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC Pharnavaz, his son Saurmag the Iberian kings, and the relatives of Ingush people per Leonti Mroveli, received military assistance from Ingush people in defense of Iberia against the Kartli occupation.[112]
During World War I, 500 cavalrymen from an Ingush regiment of the Wild Division attacked the German Iron Division. The Russian Emperor Nicholas II, assessing the performance of the Ingush and Chechen regiments during the Brusilov breakthrough on the Russian-German front in 1915 wrote in a telegram to the Governor-General of the Tersky region Fleisher:
The Ingush regiment pounced upon the German "Iron Division" like an avalanche. It was immediately supported by the Chechen regiment. The Russian history, including the history of our Preobrazhensky regiment, does not know a single instance of a horse cavalry attacking an enemy force armed with heavy artillery: 4.5 thousand killed, 3.5 thousand taken prisoner, 2.5 thousand wounded. Less than in an hour and a half the "Iron Division" ceased to exist, the division that had aroused fear in the best armies of our allies. On behalf of me, the royal court and the whole of the Russian army send our best regards to fathers, mothers, sisters, wives and brides of those brave sons of the Caucasus whose heroism paved the way for the destruction of German hordes. Russia bows low to the heroes and will never forget them. I extend my fraternal greetings, Nicholas II, August 25, 1915.[113]
In 1941, when Germans attacked the USSR, the whole Russian front was retreating 40 km a day. Out of 6,500 defenders of Brest Fortress, 6,000 Soviet troops capitulated. 500 troops were fresh conscripts of Ingush and Chechen origin. Defenders held the fortress for over a month against the Germans and even managed to stage several attacks from the Fortress. The last defender's name has been unknown for a long time; his documents identified him as a man called Barkhanoyev. Decades later, official records revealed it was Umatgirei Barkhanoyev from the Ingush village of Yandare. Recently, the memoirs of Stankus Antanas, a Lithuanian national and former Waffen SS officer, were published in Ingushetia. He recalls that in July 1941, his regiment was ordered to "finish off" the remaining Soviet soldiers in the fortress. When the Nazis decided that no defenders had been left alive, an SS general lined up his soldiers on the parade ground to award them with decorations for capturing the fortress. Then, a Red Army officer came out from the fortress's underground bunker:
He was blind because of his wounds and walked with his left arm extended forward. His right hand rested on a gun holster. He walked along the parade grounds wearing a ragged uniform, but his head was held high. The entire division was shocked at the sight. Approaching a shell-hole, he turned his face toward the west. The German general suddenly saluted this last defender of the Brest Fortress, and the rest of the officers followed suit. The Red Army officer drew a handgun and shot himself in the head. He fell on the ground facing Germany. A deep-drawn sigh aired over the parade grounds. We all stood 'frozen' in awe of this brave man.[114]
In 1994–96 Ingush volunteers fought alongside Chechens in the First Chechen War. Aside from a few incidents (including the killings of Ingush civilians by Russian soldiers), Ingushetia was largely kept out of the war by a determined policy of non-violence pursued by President Ruslan Aushev.[50]
This changed after the beginning of the Second Chechen War, and especially since Murat Zyazikov became the second Russian appointed president of Ingushetia in 2002. The first major rebel attack of the conflict, in which a military convoy was destroyed occurred in May 2000 and caused the deaths of 19 soldiers. In the June 2004 Nazran raid, Chechen and Ingush rebels attacked government buildings and military bases across Ingushetia, resulting in the deaths of at least 90 Ingush people and an unknown number of Russian troops. Among them the Republic's acting interior minister Abukar Kostoyev, his deputy Zyaudin Kotiyev. In response to a sharp escalation in attacks by insurgents since the summer of 2007,[115] Moscow sent in an additional 25,000 MVD and FSB troops, tripling the number of special forces in Ingushetia.
Civil disorder

- 1800s–1860s: Insurgency against Russian conquest.
- 1860s–1890s: Raids of Ingush abreks on the Georgian Military Highway and Mozdok.
- 1890s–1917: Insurgency of Ingush resistance under Chechen abrek Zelimkhan Gushmazukaev and Ingush abrek Sulom-beck Sagopshinski, execution of Russian viceroy to Ingushetia colonel Mitnik by Ingush resistance fighter Buzurtanov.
- 1917–1920s: Insurgency of Ingush resistance fighters against combined Russian White Guards, Cossacks, Ossetians, and general Denikin forces.
- 1920s–1930s: Insurgency of Ingush people against Communists, executions of Communist leader of Ingushetia Chernoglaz by Ingush rebel Uzhakhov. Execution of Communist party leader of Ingushetia Ivanov by Ingush rebels.
- 1944–1977: Ingush rebels avenging the deportation of the Ingush nation. Scores of Russian army units and NKVD, KGB officers killed.
- 1992: Ossetian-Ingush conflict. In combat operations Ingush rebels capture armor which later transferred to Chechens or given back to Russian army after the conflict ended.
- 1994: Nazran. Ingush civilians stop Russian army, flip armor, burn military trucks which were on the march to Chechnya in Russian-Chechen war. First Russian casualties reported from hands of Ingush rebels.
- 1994–1996: Ingush rebels defend Grozny and participate in combat operations on Chechen side.
- 1999–2006: Ingush rebels join Chechen rebels, the independence war turns into Jihad.
- 13 July 2001: Ingush people protest "defiling and desecration" of historical Christian Ingush church Tkhaba-Yerdy after Russian troops made the church into a public toilet. Though Ingush are Muslims they highly respect their Christian past.[116]
- 15 September 2003: Ingush rebels use bomb truck and attack FSB headquarters in Maghas. Several dozens of Russian FSB officers killed including the senior officer overseeing the FSB in Chechen republic. The several story HQ building is severely damaged.[117]
- 6 April 2004: Ingush rebels attack Russian appointed president of Ingushetia Murat Zyazikov. He was wounded when a car bomb was rammed into his motorcade.
- 22 June 2004: Chechen and Ingush rebels raid on Russian troops in Ingushetia. Hundreds of Russian troops killed.
- 31 August 2008: Execution of Magomed Yevloyev Ingush dissident, journalist, lawyer, businessman, and the owner of the news website Ingushetiya.ru, known for being highly critical of Russian regime in Ingushetia. He was shot in the temple.[118] Awarded posthumously, and his name is engraved in stone on the monuments at the Journalists' Memorials in Bayeux, France and Washington D.C., the United States.[119]
- 30 September 2008: A suicide bomber attacked the motorcade of Ruslan Meiriyev, Ingushetia's top police official.
- 10 June 2009: Snipers killed Aza Gazgireyeva, deputy chief justice of the regional Supreme Court, as she dropped her children off at school. Russian news agencies also cited investigators as saying she was likely killed for her role in investigating the 2004 attack on Ingush police forces by Chechen fighters.[120]
- 13 June 2009: Two gunmen sprayed former deputy prime minister Bashir Aushev with automatic-weapon fire as he got out of his car at the gate outside his home in the region's main city, Nazran.[121]
- 22 June 2009: Russian appointed president of Ingushetia Yunus-Bek Yevkurov was badly hurt when a suicide bomber detonated a car packed with explosives as the president's convoy drove past. The attack killed three bodyguards.[122]
- 12 August 2009: Gunmen killed construction minister Ruslan Amerkhanov in his office in the Ingush capital, Magas.[123]
- 17 August 2009: A suicide bomber killed 21 Ingush police officers and unknown numbers of Russian Internal Ministry troops which were stationed in Nazran, after he drove a truck full of explosives into a MVD police base.
- 25 October 2009: Execution of Maksharip Aushev, an Ingush businessman, dissident, and a vocal critic of Russian regime policies in Ingushetia. His body had over 60 bullet holes. Awarded posthumously by the U.S. Department of State in 2009.[124]
- 5 April 2010: A suicide bomber injured three police officers in the town of Karabulak. Two officers died at the hospital as a result of their injuries. While investigators arrived on scene, another car bomb was set off by remote. Nobody was hurt in the second blast.[125]
- 24 January 2011: A suicide bomber, Magomed Yevloyev (same first and last name as the slain Ingush opposition journalist Magomed Yevloyev), killed 37 people at Domodedovo airport, Moscow, Russia.
- 2012: Ingush rebels participate in war against Assad, Iranian, and Russian advisors in Syria which is largely viewed by the Ingush rebels as war against Russia and the Iranian-speaking Ossetians. The rebel Ingush commanders are veterans of Ossetian-Ingush conflict, wars in Chechnya, Daud Khalukhayev from Ingush village of Palanazh (Katsa), and a descendant of Ingush deportees of 1860's Syrian-born Ingush Walid Didigov.[126][127]
- 6 June 2013: Accusation of Ingush rebel leader Ali "Maghas" Taziev in Rostov-On-Don regional Russian court, who was captured after he voluntarily given himself up in on 9 June 2010 to Russian forces in Ingushetia on the agreement that Russians will liberate his relatives held hostage on one of the Russian military bases.
- 27 August 2013: Execution of the head of security of Ingushetia Akhmet Kotiev and his bodyguard by Ingush rebels. Kotiev was actively involved in the assassination of Magomed Yevloyev.
- 10 December 2013: Ingush opposition leader Magomed Khazbiev, who was a close friend of assassinated Magomed Yevloyev, attends Euromaidan in Ukraine and participates in anti-Russian campaign there after which his parents were threatened and harassed in Russia. On his website he writes: "the fact that Putin's slaves harass my parents do not make any sense, if you [Russians] want me to stop you have to kill me like Magomed Yevloyev and Makhsharip Aushev".[128]
- 2 February 2014: Russian FSB officially confirms that in the middle of December 2013 four North Caucasian instructors operate in Ukraine, and prepare Ukrainians for street battles against Russian interests.[129]
- 20 April 2014: Famous Ingush human rights defender Ibrgim Lyanov stated that Ingushetia wants to separate from Russia and become an independent state using the example of the Crimean separation from Ukraine.[130]
- 24 May 2014: Ingush rebel leader Arthur Getagazhev, 4 rebels, and 2 civilians were killed in action in the village of Sagopshi by Russian forces.[131]
- 2 July 2014: After several months of denial, pro-Russian president of Ingushetia finally recognizes that Ingush rebels are fighting in Ukraine against pro-Russia forces.[132]
- 2 July 2014: Ingush rebels attack Russian armored military convoy killing 1 and wounding 7 soldiers.[133]
- 6 July 2014: Russian special forces prepared an ambush near the morgue in Nazran hospital where the body of Arthur Getagazhev was located. The intelligence reported that Ingush rebels will try to recover the body of the slain leader. The intelligence was correct. Radio Free Europe (section specializing in the Caucasus), reports that in the middle of the day 2 Ingush rebels attacked the ambush, according to unofficial source two rebels killed 7 and wounded 4 Russian FSB and spetsnaz officers in less than 40 seconds, after which the rebels left the scene unharmed. The source in Ingush police who wanted to stay anonymous said that exact number of killed are known only by the FSB but nobody would dare to declare if officially.[134] According to pro-Kremlin LifeNews released video the attack lasted less than 19 seconds.[135]
- 17 January 2015: Maghas. Rise of anti-Western sentiments. Over 20,000 Ingush citizens protest against European terrorism toward Muslims.[136][137]
- 28 February 2015: Russian opposition leader Nemtsov's death linked to Ingushetia by Russian police.[138]
- 26 March 2019: Thousands of people in Ingushetia have protested against a controversial border deal with neighboring Chechnya, denouncing land swaps under the agreement and calling for Ingushetia head Yunus-Bek Yevkurov to step down.
- 25 June 2019: Yunus-Bek Yevkurov, has announced his resignation after almost 11 years in the position. De-facto Ingushetia has no active leader. Civil protests continue, Ingush people boycotting the Russian appointed elections.
Administrative divisions
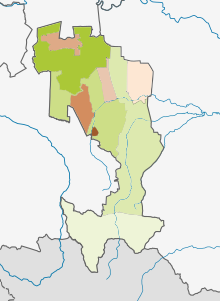
- Cities under republic's jurisdiction (as of 2016):
- Districts:
- Dzheyrakhsky (Джейрахский)
- Sunzhensky (Сунженский)
- Nazranovsky (Назрановский)
- Malgobeksky (Малгобекский)
Demographics
Population: 412,529 (2010 Census);[8] 467,294 (2002 Census).[140]
The Ingush, a nationality group indigenous to the Caucasus, mostly inhabit Ingushetia. They refer to themselves as Ghalghai (from Ingush: Ghala ("fortress" or "town") and ghai ("inhabitants" or "citizens"). The Ingush speak the Ingush language, which has a very high degree of mutual intelligibility with neighboring Chechen.
Vital statistics
| Average population (× 1000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Total fertility rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 273 | 6,889 | 1,867 | 25.3 | 6.8 | 18.4 | ||
| 1996 | 287 | 5,980 | 1,958 | 20.9 | 6.8 | 14.0 | ||
| 1997 | 294 | 6,055 | 1,957 | 20.6 | 6.7 | 14.0 | ||
| 1998 | 299 | 5,929 | 2,064 | 19.8 | 6.9 | 12.9 | ||
| 1999 | 321 | 6,624 | 1,953 | 20.6 | 6.1 | 14.6 | ||
| 2000 | 393 | 8,463 | 2,117 | 21.5 | 5.4 | 16.2 | ||
| 2001 | 450 | 8,753 | 1,875 | 19.4 | 4.2 | 15.3 | ||
| 2002 | 461 | 7,578 | 1,874 | 16.4 | 4.1 | 12.4 | ||
| 2003 | 463 | 7,059 | 1,785 | 15.3 | 3.9 | 11.4 | ||
| 2004 | 454 | 6,794 | 1,751 | 15.0 | 3.9 | 11.1 | ||
| 2005 | 446 | 6,777 | 1,821 | 15.2 | 4.1 | 11.1 | ||
| 2006 | 437 | 7,391 | 1,830 | 16.9 | 4.2 | 12.7 | ||
| 2007 | 430 | 8,284 | 1,625 | 19.3 | 3.8 | 15.5 | ||
| 2008 | 423 | 9,215 | 1,561 | 21.8 | 3.7 | 18.1 | ||
| 2009 | 418 | 9,572 | 1,877 | 22.9 | 4.5 | 18.4 | 2.51 | |
| 2010 | 410 | 11,178 | 1,857 | 27.1 | 4.5 | 22.6 | 2.99 | |
| 2011 | 423 | 11,408 | 1,705 | 27.0 | 4.0 | 23.0 | 2.94 | |
| 2012 | 436 | 9,350 | 1,595 | 21.4 | 3.7 | 17.7 | 2.27 | |
| 2013 | 447 | 9,498 | 1,568 | 21.2 | 3.5 | 17.7 | 2.23 | |
| 2014 | 458 | 9,858 | 1,586 | 21.5 | 3.5 | 18.0 | 2.28 | |
| 2015 | 469 | 8,674 | 1,557 | 18.6 | 3.3 | 15.3 | 1.97 | |
| 2016 | 477 | 8,143 | 1,555 | 17.1 | 3.3 | 13.8 | 1.75 | |
| 2017 | 484 | 8,000 | 1,554 | 16.5 | 3.2 | 13.3 | 1.77 | |
| 2018 | 7,917 | 1,548 | 6,369 | 16.1 | 3.2 | 12.9 | 1.79 | |
| 2019 | 7,977 | 1,465 | 6,512 | 15.9 | 2.9 | 13.0 | 1.83 | |
| 2020 |
Note: Total fertility rate 2009, 2010, 2011 source:[141]
Ethnic groups
According to the 2010 Russian Census (2010),[8] ethnic Ingush make up 94.1% of the republic's population. Other groups include Chechens (4.6%), Russians (0.8%), and a host of smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total population.
| Ethnic group |
1926 Census | 1939 Census | 1959 Census | 1970 Census | 1979 Census | 1989 Census | 2002 Census | 2010 Census1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Ingushes | 47,280 | 61.6% | 79,462 | 58.0% | 44,634 | 40.6% | 99,060 | 66.0% | 113,889 | 74.2% | 138,626 | 74.5% | 361,057 | 77.3% | 385,537 | 94.1% |
| Chechens | 2,553 | 3.3% | 7,746 | 5.7% | 5,643 | 5.1% | 8,724 | 5.8% | 9,182 | 6.0% | 19,195 | 10.3% | 95,403 | 20.4% | 18,765 | 4.6% |
| Russians | 24,185 | 31.5% | 43,389 | 31.7% | 51,549 | 46.9% | 37,258 | 24.8% | 26,965 | 17.6% | 24,641 | 13.2% | 5,559 | 1.2% | 3,321 | 0.8% |
| Ukrainians | 1,501 | 2.0% | 1,921 | 1.4% | 1,763 | 1.6% | 1,068 | 0.7% | 687 | 0.4% | 753 | 0.4% | 189 | 0.0% | 2,009 | 0.5% |
| Others | 1,215 | 1.6% | 4,549 | 3.3% | 6,438 | 5.9% | 3,978 | 2.7% | 2,852 | 1.9% | 2,781 | 1.5% | 5,086 | 1.1% | ||
| 1 2,897people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[142] | ||||||||||||||||
Religion
The Ingush are predominantly Shafi'i Madhhab of Sunni Islam[144] with a Sufi minority, which is often associated with one of two traditional Sufi orders: the Sufi tariqa Naqshbandi, represented in Ingushetia by the brotherhood of Deni Arsanov, and the tariqa Qadiriyyah, associated with Kunta-Haji Kishiev.[145][146]
Geography
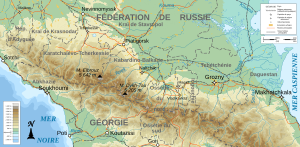
Ingushetia is situated on the northern slopes of the Caucasus. Its area is reported by various sources as either 2,000 square kilometers (770 sq mi)[147] or 3,600 square kilometers (1,400 sq mi);[148] the difference in reporting is mainly due to the inclusion or exclusion of parts of Sunzhensky Districts. The republic borders North Ossetia–Alania (SW/W/NW/N), the Chechnya (NE/E/SE), and the country of Georgia (Mtskheta-Mtianeti) (southwards). The highest point is the Gora Shan[149] (4451 m).
A 150-kilometer (93 mi) stretch of the Caucasus Mountains runs through the territory of the republic.
Rivers
Major rivers include:
Natural resources
Ingushetia is rich in marble, timber, dolomite, plaster, limestone, gravel, granite, clay, thermal medical water, rare metals, mineral water, oil (over 60 billion tons), and natural gas reserves.
Climate
Ingushetia's climate is mostly continental.
- Average January temperature: −10 °C (14 °F)
- Average July temperature: 21 °C (70 °F)
- Average annual precipitation: 450–650 mm (18–26 in)
- Average annual temperature: +10 °C (50 °F)
Politics
Up until the dissolution of the Soviet state, Ingushetia was part of the Chechen-Ingush ASSR of the Russian Soviet Socialist Republic. In the late 1920s – early 1930s the Soviet officials were eager to enforce the Chechen-Ingush merger as an “objective” and “natural” process. The Soviet linguist Nikolay Yakovlev, who was a supporter of the merger, suggested that an inclusive name of "Veinakh" (“our people”) had to be used for both the Chechens and Ingush. According to his views, the rapid urbanization and rapprochement of the Chechens and Ingush within one and the same republic might encourage the formation of a common culture and language and the establishment of a unified “Veinakh” people.
During the late 80s, together with the separatist tendencies across the Soviet Union, the Second Congress of the Ingush People was held in Grozny on September 9–10, 1989. The gathering was directed at the top leadership of the Soviet Union, and included a request to "restore the Ingush people’s autonomy within their historical borders, the Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic with a capital in the right-bank part of the city of Ordzhonikidze".The Ingush Republic was to be organized out of six traditional Ingush districts (including the contested Prigorodny District). The rise of the Russian Federation gave the Ingushetians the independence they vowed for. During the 1990s, Ingushetia was ruled by its elected president Ruslan Aushev, a former Soviet general and hero of the war in Afghanistan.
The head of government and the highest executive post in Ingushetia is the Head.
Recent heads:
- Ruslan Aushev: November 10, 1992 (Head of the Republic until March 7, 1993) – December 28, 2001
- Akhmed Malsagov (interim): December 28, 2001 – May 23, 2002
- Murat Zyazikov: May 23, 2002 – October 30, 2008[150]
- Yunus-Bek Yevkurov: October 30, 2008–present (acting)
Recent Chairmen of the Government:
- Ruslan Tatiyev: March 1993 – July 1993
- Tamerlan Didigov: July 1993 – March 1994
- Mukharbek Didigov: March 1994 – December 1996
- Belan Khamchiyev: December 1996 – August 1998
- Magomet-Bashir Darsigov: August 1998 – November 25, 1999
- Akhmed Malsagov: November 25, 1999 – June 15, 2002
- Sultan Gireyev (acting): June 15, 2002 – August 26, 2002
- Viktor Aleksentsev: August 26, 2002 (acting to September 30, 2002) – June 19, 2003
- Timur Mogushkov: June 19, 2003 – June 30, 2005
- Ibragim Malsagov: June 30, 2005 – March 2008
- Kharum Dzeytov: March 2008 – November 2008
- Rashid Gaysanov: November 2008–present
The parliament of the Republic is the People's Assembly, composed of 34 deputies elected for a four-year term. The People's Assembly is headed by the Chairman. As of 2006, the Chairman of the People's Assembly is Makhmud Sultanovich Sakalov.
The Constitution of Ingushetia was adopted on February 27, 1994.
Ingushetia is a member of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization.
The capital was moved from Nazran to Magas in December 2002.
The most recent election was held in 2013.
Economy
There are some natural resources in Ingushetia: mineral water in Achaluki, oil and natural gas in Malgobek, forests in Dzheirakh, metals in Galashki. The local government is considering the development of tourism; however, this is problematic due to the uneasy situation in the republic itself and the proximity of some conflict zones. However, Ingushetia continues to remain as one of Russia's poorest republics, largely due to the ongoing conflict, corruption and civil disorders. Unemployment is estimated to be around 53%, and growing poverty is a major issue.
Education
Ingush State University, the first institute of higher education in the history of Ingushetia, was founded in 1994 in Ordzhonikidzevskaya.[151]
Notable people
- Tamerlan Akhriev, inventor of a ceramic rotor engine.[152][153]
- Idris Bazorkin, writer.[154]
- Ruslan Aushev, infantry general, hero of USSR, first president of Ingushetia.
- Rakhim Chakkhiev, boxer.[155]
- Ismail Esmurziev, engineer.[156]
- Issa Kodzoev, writer.[157]
- Issa Kostoyev, policeman who captured serial killer Andrei Chikatilo.[158]
- Nazyr Mankiev, wrestler.[159]
- Murad Ozdoev, WWII ace.
- Sulom-Beck Oskanov, Air Force general.
- Magomet Sagov, Ph.D., academician (Academy of Sciences of the USSR).[160]
- Islam Timurziev, boxer.
- Amurhan Yandiev, detective who captured serial killer Andrei Chikatilo.[161][162]
- Djemaldin Yandiev, poet.[163]
- Tamara Yandieva, actress, singer.[164][165][166][167]
- Movsar Evloev, mixed martial artist, currently in UFC
See also
References
Notes
- ^ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", No. 20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ^ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ^ Constitutional Law #57-RZ
- ^ Constitution of the Republic of Ingushetia, Article 108
- ^ a b Constitution of the Republic of Ingushetia, Article 64
- ^ Official website of the Republic of Ingushetia. Head of the Republic of Ingushetia (in Russian)
- ^ "Сведения о наличии и распределении земель в Российской Федерации на 01.01.2019 (в разрезе субъектов Российской Федерации)". Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography. Archived from the original on February 9, 2022. Retrieved August 29, 2023.
- ^ a b c d Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1 [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- ^ "26. Численность постоянного населения Российской Федерации по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2018 года". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- ^ "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- ^ Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ^ Constitution of the Republic of Ingushetia, Article 14
- ^ a b Law of June 4, 1992
- ^ a b Official website of the Republic of Ingushetia. Social-Economic Characteristics (in Russian)
- ^ "Russia's North Caucasus Insurgency Widens as ISIS' Foothold Grows". www.worldpoliticsreview.com. Retrieved October 3, 2017.
Russia's North Caucasus insurgency has gone relatively quiet, but reduced casualty numbers belie a still-worrying situation where long-standing grievances remain.
- ^ Walker, Shaun (April 4, 2017). "Why suspicion over St Petersburg metro attack is likely to fall on Islamist groups". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved October 3, 2017.
A renewed crackdown on any suspected militant activity in the run-up to the Sochi winter Olympics in 2014 and the departure of many militants to fight in Syria led to a weakening of the North Caucasus insurgency.
- ^ "Ingushetia's cycle of violence". BBC. October 3, 2009. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ Urgent Need for Vigorous Monitoring in the North Caucasus. Human Rights Watch/Reuters, April 15, 2008. (archive link)
- ^ People & Power – Ingushetia: A second Chechnya – October 28, 2009, Al Jazeera English on YouTubeAl Jazeera English on YouTube (dead link)
- ^ "В докладе Роспотребнадзора названы самые пьющие регионы России".
- ^ http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4b/Colton%2C_G.W._Turkey_In_Asia_And_The_Caucasian_Provinces_Of_Russia._1856_%28A%29.jpg
- ^ http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/5d/Karte_des_Kaukasischen_Isthmus_-_Entworfen_und_gezeichnet_von_J-Grassl_-_1856.jpg
- ^ Khasan Sampiev. "The Land of Towers". Archived from the original on February 26, 2009.
- ^ The work of Leonti Mroveli: "The history of the Georgian Kings"dealing with the history of Georgia and the Caucasus since ancient times to the 5th century AD, is included in medieval code of Georgian annals "Kartlis Tskhovreba".
- ^ "Caucasian Knot | An Essay On the History of the Vainakh People. On the origin of the Vainakhs". Eng.kavkaz-uzel.ru. Retrieved November 3, 2012.
- ^ "Microsoft Word - 4C04B861-0826-0853BD.doc" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2012. Retrieved November 3, 2012.
- ^ "G.F.Debets". Archived from the original on September 27, 2006.
- ^ "Peering Into the Past, With Words".;Bernice Wuethrich, "Science" 2000: Vol. 288 no. 5469 p. 1158
- ^ Oleg Balanovsky, Khadizhat Dibirova, Anna Dybo, Oleg Mudrak, Svetlana Frolova, Elvira Pocheshkhova, Marc Haber, Daniel Platt, Theodore Schurr, Wolfgang Haak, Marina Kuznetsova, Magomed Radzhabov, Olga Balaganskaya, Alexey Romanov, Tatiana Zakharova, David F. Soria Hernanz, Pierre Zalloua, Sergey Koshel, Merritt Ruhlen, Colin Renfrew, R. Spencer Wells, Chris Tyler-Smith, Elena Balanovska, and The Genographic Consortium Parallel Evolution of Genes and Languages in the Caucasus Region Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011 : msr126v1-msr126
- ^ Ivane Nasidze; et al. (2001). "Alu insertion polymorphisms and the genetic structure of human populations from the Caucasus". European Journal of Human Genetics. 9 (4): 267–272. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200615. PMID 11313770. S2CID 7021736.
- ^ Nasidze I, Risch GM, Robichaux M, Sherry ST, Batzer MA, Stoneking M (April 2001). "Alu insertion polymorphisms and the genetic structure of human populations from the Caucasus" (PDF). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 9 (4): 267–72. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200615. PMID 11313770. S2CID 7021736.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bernice Wuethrich (May 19, 2000). "Peering Into the Past, With Words". Science. 288 (5469): 1158. doi:10.1126/science.288.5469.1158. S2CID 82205296.
- ^ a b N.D. Kodzoev. History of Ingush nation.
- ^ "The Land of the Czar". Wahl. 1875. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Reise durch Russland nach dem kaukasischen Isthmus". Karl Koch. 1843. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Algemeen aardrijkskundig woordenboek volgens de nieuwste staatkundige veranderingen, en de laatste, beste en zekerste berigten". Jacobus van Wijk. 1821. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Броневский, Семен (July 20, 2017). "Новѣйшия географическия и историческия извѣстия о Кавказѣ". В Тип. С. Скливановскаго – via Google Books.
- ^ "Авторские Материалы". Archived from the original on February 17, 2008. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ D.V.Zayats (2001). "Maghas – "The Sun City" – New Capital of Ingushetia". Archived from the original on May 2, 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Аланский историк из чеченцев". Chechenews.com. August 29, 2010. Archived from the original on December 30, 2013. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Категория: Мировая история. "Аланский историк". 95live.ru. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ История ингушского народа. Глава 4. "История ингушского народа. Глава 4. ГЛАВА 4 ИНГУШЕТИЯ В XV-XVIII ВВ. § 1. Жизнь ингушей на равнинах и в горах На равнинах Ингушетииaccessdate=2014-02-28".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ История ингушского народа. Глава 4. "История ингушского народа. Глава 4. ГЛАВА 4 ИНГУШЕТИЯ В XV-XVIII ВВ. § 1. Жизнь ингушей на равнинах и в горах На равнинах Ингушетииaccessdate=2014-02-28".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Istoriya Voini i Vladichestva russkikh na Kavkaze".
- ^ "Freisinn". Goethe. 1815. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Албогачиева М. "Многоликая Ингушетия". Groznycity.ru. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Vospominaniya Kavkazskogo Ofitsera" (PDF).
- ^ "Немного о истории Владикавказа - часть 2 - 6 Января 2011 - История геноцида Ингушского|Чеченского народа". Vainax.ru. January 6, 2011. Archived from the original on March 5, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Akty sobrannye kavkazskoj arxeograficheskoj komissiej (PDF).
- ^ a b c d e Johanna Nichols (February 1997). "The Ingush (with notes on the Chechen): Background information". University of California, Berkeley. Archived from the original on December 8, 2006. Retrieved February 10, 2007.
- ^ P.G.Butkov. Materials of the new history of the Caucasus years 1722–1803 St. Petersburg 1869 (page 165).
- ^ E.Bronevski. New geographical and historical perspectives of the Caucasus. Moscow, 1823 (vol.2 page 159).
- ^ U. Klaprot. Travel in the Caucasus and Georgia 1807–1808. Berlin 1812 (page 651).
- ^ N.Grabovski. Ingush nation (their life and traditions) Tiflis 1876 (page 2).
- ^ K.Raisov. New illustrated guide in the Crimea and the Caucasus. Odessa 1897 (page 295).
- ^ G.G. Moskvitch. Illustrated practical guide in the Caucasus. Odessa 1903 (pages 161–162).
- ^ N.M. Suetin. Geodesy of the Vladikavkaz. Vladikavkaz 1928 (page 12).
- ^ V.P. Khristianovich. Mountainous Ingushetia Rostov-on-Don 1928 (page 65).
- ^ E.I.Krupnov. Middle age Ingushetia Moscow, 1971 (page 166).
- ^ "Caucasus and central Asia newsletter. Issue 4" (PDF). University of California, Berkeley. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 27, 2008.
- ^ "Chechnya: Chaos of Human Geography in the North Caucasus, 484 BC – 1957 AD". www.semp.us. November 2007. Archived from the original on December 20, 2010.
- ^ Denikin, Anton Ivanovich (1925). Ocherki Russkoi Smuti.
- ^ MINORITY RIGHTS GROUP INTERNATIONAL, THE NORTH CAUCASUS:Minorities at a Crossroads
- ^ Anna Zelkina, Religion, State and Society, Vol. 21, No. I, 1993
- ^ "Revolution and Sovietization in the North Caucasus" “Caucasian Review”, 1955, No. 1, pp.47-54. No. 3, pp.45-53
- ^ Great Britain. War Office. General Staff, 20 September 1918 p.393
- ^ War Office. "Volume 27". War Office. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ http://1900.ethnia.org/polity.php?ASK_CODE=KC__&ASK_YY=1919&ASK_MM=05&ASK_DD=07&SL=en
- ^ Ben Cahoon. "Russian Civil War Polities". Worldstatesmen.org. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Общественное движение ЧЕЧЕНСКИЙ КОМИТЕТ НАЦИОНАЛЬНОГО СПАСЕНИЯ". Savechechnya.com. June 24, 2008. Archived from the original on February 23, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Вассан-Гирей Джабагиев". Vainah.info. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Шкуро, А. Г. (2016). Гражданская война в России. Записки белого партизана (in Russian). Directmedia. p. 336. ISBN 978-5-4475-8722-2.
- ^ Martin, Terry (2001). The Affirmative Action Empire: Nations and Nationalism in the Soviet Union, 1923-1939. Cornell University Press. p. 61. ISBN 9780801486777.
- ^ Perovic, Jeronim (2018). "State and society". From Conquest to Deportation: The North Caucasus under Russian Rule. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0190889890.
- ^ "Spetspereselentsi: history of mass repressions and deportations of Ingushes in 20th century". Ingushetiya news agency. March 2005. Archived from the original on October 19, 2007.
- ^ "The Ingush People". Linguistics.berkeley.edu. November 28, 1992. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ "Через 63 года в отношении защитников Малгобека восстановлена историческая справедливость". Российская газета.
- ^ Fires of Hatred: Ethnic Cleansing in Twentieth-Century Europe, Cambridge, Mass. and London: Harvard University Press, 2001, p. 96-97.
- ^ "Explore Chechnya's Turbulent Past ~ 1944: Deportation | Wide Angle". Pbs.org. July 25, 2002. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ Arbatov, Alekseĭ; Antonia Handler Chayes (1997). Managing Conflict in the Former Soviet Union. MIT Press. p. 40. ISBN 0-262-51093-6.
The conditions were so horrendous that around 25 percent of the [Ingush] deportees perished on the journey
- ^ Dunlop, John B. (1998). Russia Confronts Chechnya. Cambridge University Press. p. 70. ISBN 0-521-63619-1.
A total of 144,704 (23.7 percent) of all deported Chechens, Ingush, Balkars (1944) and Karachai (1943) died in the period from 1944 through 1948
- ^ "Prague Watchdog - Crisis in Chechnya - The deportation of 1944 – how it really was". Watchdog.cz. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ "The 60th Anniversary of the 1944 Chechen and Ingush Deportation: History, Legacies, Current Crisis". Archived from the original on January 20, 2009.
- ^ "Chechen Journal Dosh".
- ^ "The Ingush (with notes on the Chechen): Background information".
- ^ Ingushetia.ru news agency (January 2008). "35 years later. Ingush protest of 1973". www.ingushetiya.ru. Archived from the original on January 19, 2008. Retrieved January 16, 2008.
- ^ О реабилитации репрессированных народов Archived June 30, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Economist 1992. Ethnic cleansing comes to Russia. The Economist, November 28, 1992, p. 60.
- ^ "Bashir Izmailov Witness Testimony". Archived from the original on December 15, 2005. Retrieved 2005-12-15.
- ^ "Ruslan Belkharoyev Witness Testimony". Old.ingushetiyaru.org. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Terror lingers in Russia's Caucasus region, Chicago Tribune, 12 October 2004
- ^ "ИНГУШЕТИЯ.РУ – Новости". Old.ingushetiyaru.org. October 26, 2005. Archived from the original on May 18, 2013. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ N.Evloev (January 2008). "A message of Nazir Evloev Press Secretary of Ingushetia MVD (Police)". www.ingushetiya.ru. Archived from the original on February 26, 2009. Retrieved January 20, 2008.
- ^ В Москве осетины похищают ингушей! (in Russian). Archived from the original on June 30, 2009.
- ^ "Ingush FSB Officer Shot Dead".
- ^ За похищениями ингушей в Москве стоят высокопоставленные чиновники Северной Осетии (in Russian). Archived from the original on April 4, 2009.
- ^ "Abduction Failed: Fifteen North Ossetia Law Enforcers Detained in Ingushetia". Memo.ru. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ "АНО "МАШР" – Главная". Mashr.org. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ M.Malsagov (September 2007). "Annexation of Ingush Mountains". www.ingushetiya.ru. Archived from the original on September 11, 2007. Retrieved September 7, 2007.
- ^ B.Polonkoev (August 2007). "The Murderers are not Insurgents". www.gazeta.ru. Retrieved September 29, 2007.
- ^ CNN (March 2008). "The Russian republic rocked by car bomb". Archived from the original on March 28, 2008. Retrieved March 24, 2008.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ "BBC NEWS - Europe - Q&: Conflict in Georgia". bbc.co.uk.
- ^ R.Khautiev (August 2008). "Silence in Ingushetia". www.ingushetiya.ru. Retrieved August 17, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ BBC (August 31, 2008). "Kremlin critic shot in Ingushetia". BBC. Retrieved August 31, 2008.
- ^ Blomfield, Adrian (September 1, 2008). "Russia faces new Caucasus uprising in Ingushetia". London: Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ "Tension in Ingushetia after journalist's death". Ft.com. September 3, 2008. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ "Russians ambushed in Ingushetia". BBC News. October 18, 2008. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ "Two Russian soldiers killed in attack in Ingushetia". Monsters and Critics. October 18, 2008. Archived from the original on September 8, 2012. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ Отправлен в отставку президент Ингушетии Мурат Зязиков, 31.10.2008 (in Russian)
- ^ Echo of Moscow, Указом президента России Дмитрия Медведева новым главой Ингушетии стал Юнус-Бек Евкуров, 31.10.2008 (in Russian)
- ^ "The peaceful exception". The Economist. April 9–15, 2011.
- ^ Khasan Sampiev. "The Land of Towers". Archived from the original on February 17, 2008.
- ^ "Чечня FREE.RU - Новости Чечни, России и мира". Чечня FREE.RU.
- ^ Russian News and Information Agency RIA Novosti. "Russian News and Information Agency RIA Novosti: DEFENSE OF THE MOTHERLAND IS EVERY MUSLIM'S DUTY".
- ^ TIMELINE OF VIOLENCE IN INGUSHETIA: SUMMER-FALL 2007 Archived October 31, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Ingushetia accuses Russian military desecrating monuments". Russian newsru.com. July 15, 2001.
- ^ "FSB building in Magas bombed". English pravda.ru. September 15, 2003. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Gheddo, Piero. "Magomed Yevloyev, critic of the Kremlin, killed by police". Asianews.it. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "77 Names Added to Slain Journalists Memorial in Washington D.C". Fox News. March 30, 2009.
- ^ "Senior judge killed in Ingushetia". Al Jazeera. Retrieved September 24, 2012.
- ^ "Another Killing in Region Bordering Chechnya". nytimes.com.
- ^ Ingushetia president survives assassination attempt. – The Guardian, 22 June 2009
- ^ "Ingush minister shot dead at work". BBC. August 12, 2009. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Secretary Clinton Honors Two Champions of Human Rights Day » US Mission Geneva". Geneva.usmission.gov. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Ingushetia hit by suicide attack". BBC News. April 5, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ "Syria crisis: Border town shows conflict's patchwork forces". BBC News.
- ^ "В Сирии воюют ингуши, и возглавляют одни из самых дерзких боевых групп повстанцев - HABAR.ORG". habar.org. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014.
- ^ "Магомед Хазбиев: Если хотите меня остановить - убейте". Ingushetiyaru.org. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "На Украину выехали 4 инструктора боевиков с Северного Кавказа". Lifenews.ru. February 2, 2014. Archived from the original on January 8, 2016. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "В Ингушетии заговорили о выходе из РФ по крымскому сценарию". censor.net.ua. Retrieved April 20, 2014.
- ^ "Российские официальные структуры сообщают об убийстве руководителя ингушских партизан – Артура Гетагажева" [Russian officials declare Getagazhev dead]. habar.org. Archived from the original on February 12, 2015.
- ^ "Ingush are fighting in Ukraine on both sides".
- ^ "Побочные эффекты". Эхо Кавказа.
- ^ "Война в Ингушетии продолжается" [War in Ingushetia continues]. Эхо Кавказа.
- ^ "Нападение боевиков на морг в Ингушетии сняла камера".
- ^ "В Ингушетии митинг против карикатур на пророка Мухаммеда собрал до 20 тысяч человек". newsru.com.
- ^ ЗАО ИД «Комсомольская правда». "Обращение главы Ингушетии к 20-тысячному антикарикатурному митингу: "Западная истерия вокруг ислама - это госэкстремизм"". ЗАО ИД «Комсомольская правда».
- ^ Andrew Roth [@ARothWP] (February 28, 2015). "Image of car purported to have carried Nemtsov's murderers has Ingush plates" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "О ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИИ ПОСЕЛКА ГОРОДСКОГО ТИПА СУНЖА СУНЖЕНСКОГО РАЙОНА РЕСПУБЛИКИ ИНГУШЕТИЯ, Закон Республики Ингушетия от 25 ноября 2016 года №43-РЗ". docs.cntd.ru. Retrieved March 20, 2018.
- ^ Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ^ "Каталог публикаций::Федеральная служба государственной статистики". Gks.ru. May 8, 2010. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "ВПН-2010". perepis-2010.ru.
- ^ "Caucasus Times poll". Caucasus Times. May 20, 2010. Archived from the original on October 7, 2016. Retrieved August 28, 2016.
- ^ Stefano Allievi and Jørgen S. Nielsen (2003). Muslim networks and transnational communities in and across Europe. Vol. 1.
- ^ Johanna Nichols (February 1997). "The Ingush (with notes on the Chechen): Background information". University of California, Berkeley. Archived from the original on December 8, 2006. Retrieved February 10, 2007.
- ^ Stephen Bowers; et al. (2004). "Islam in Ingushetia and Chechnya". Faculty Publications and Presentations of the Helms School of Government of Liberty University. 29.
- ^ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (May 21, 2004). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Archived from the original on September 28, 2011. Retrieved November 1, 2011.
- ^ Социально-экономические характеристики (in Russian). Official website of Ingushetia. Retrieved April 19, 2013.
- ^ "Die Hoechsten". Gipfel-und-grenzen.de. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ "Медведев отправил в отставку президента Ингушетии". Old.lenta.ru. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ "Хмцсьяйхи Цнясдюпярбеммши Смхбепяхрер". Humanities.edu.ru. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ Шах. "Вайнахские новости - Керамический роторный двигатель Тамерлана Ахриева ждет испытаний". E-kavkaz.com. Archived from the original on June 27, 2014. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ "Rotary Internal Combustion Engine". Ntpo.com. December 24, 2006. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ Идрис Базоркин. "Идрис Базоркин". Livelib.ru. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "2008 Beijing Olympics Results: Rakhim Chakhkiev Wins Gold". Transworldnews.com. August 23, 2008. Archived from the original on June 30, 2009. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "ИССА КОДЗОЕВ – Учитель, Писатель, Патриот". .rfi.fr. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ Гарант-Интернет (Garant-Internet), www.garweb.ru. "Обзор публикаций СМИ | Интернет-конференция Председателя Верховного Суда Российской Федерации Лебедева Вячеслава Михайловича | Гарант-Интернет". Garweb.ru. Retrieved January 7, 2011.
- ^ Kaku, Michio (June 10, 2012). "International Herald Tribune". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on September 25, 2008. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ [2] Archived July 13, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Амурхан ЯНДИЕВ: "Серийные убийства станут нормой жизни" - Известия". Izvestia.ru. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Я бледнел, но обнимался с Чикатило Амурхан Яндиев". Peoples.ru. January 28, 2007. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Яндиев Джамалдин Хамурзиевич (1916-1979)". Krkrub.kubannet.ru. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- ^ "Тамара Яндиева". Kinopoisk.ru. July 23, 1955. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ "Яндиева Тамара - Биография - Актеры советского и российского кино - Биография Анны Яновской". Rusactors.ru. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ Заголовок. "Биография Тамара Яндиева". Peoples.ru. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ "Тамара Яндиева официальный сайт концертного агентства - организация заказ выступлений гастролей - актер ведущий - заказ артиста актера пригласить заказать – организация концертов - контакты - менеджмент". Concert-star.ru. December 12, 2010. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
Sources
- Конституционный закон №57-РЗ от 7 декабря 2010 г. «О государственном гимне Республики Ингушетия», в ред. Конституционного закона №2-РЗП от 4 июля 2011 г «О внесении изменений в некоторые законодательные акты Республики Ингушетия в связи с принятием Закона Республики Ингушетия от 11 октября 2010 года №3-РЗП "О поправке к Конституции"». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Ингушетия", №211–212, 18 декабря 2010 г. (Constitutional Law #57-RZ of December 7, 2010 On the State Anthem of the Republic of Ingushetia, as amended by the Constitutional Law #2-RZP of July 4, 2011 On Amending Various Legislative Acts of the Republic of Ingushetia Due to the Adoption of the Law of the Republic Ingushetia #3-RZP of October 11, 2010 "On the Amendment to the Constitution". Effective as of the day of the official publication.). (in Russian)
- 27 февраля 1994 г. «Конституция Республики Ингушетия», в ред. Закона №1-РЗП от 8 мая 2013 г. «О поправке к Конституции Республики Ингушетия». Опубликован: Сборник Конституций субъектов Федерации "Конституции Республик в составе Российской Федерации", выпуск 1, 1995. (February 27, 1994 Constitution of the Republic of Ingushetia, as amended by the Law #1-RZP of May 8, 2013 On the Amendment to the Constitution of the Republic of Ingushetia. ). (in Russian)
- Верховный Совет РСФСР. Закон от 4 июня 1992 г. «Об образовании Республики Ингушетия в составе РСФСР». (Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR. Law of June 4, 1992 On Establishing the Republic of Ingushetia Within the RSFSR. ). (in Russian)
External links
- News from Ingushetia
- News and History of Ingushetia
- Official website of Ingushetia (in Russian)
- Unofficial website of Ingushetia (in Russian)
- Ingush Music/Video/Literature website (in Russian)
- Magas, Ingush youth website (in Russian)
- Head of Ingushetia's website (in Russian)
- Ingushetia's Republic News Portal (in Russian)
- Ingushetia Videos (in Russian)
- National Project: People of Ingushetia (in Russian)