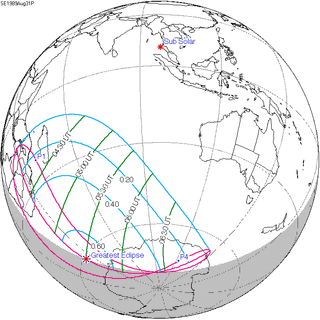
Solar eclipse of August 31, 1989
| Solar eclipse of August 31, 1989 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | −1.1928 |
| Magnitude | 0.6344 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 61°18′S 23°36′E / 61.3°S 23.6°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 5:31:47 |
| References | |
| Saros | 154 (5 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9485 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on August 31, 1989. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 1989
- A total lunar eclipse on February 20.
- A partial solar eclipse on March 7.
- A total lunar eclipse on August 17.
- A partial solar eclipse on August 31.
Solar eclipses of 1986–1989
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1986 to 1989 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 119 | April 9, 1986 Partial |
−1.0822 | 124 | October 3, 1986 Hybrid |
0.9931 | |
| 129 | March 29, 1987 Hybrid |
−0.3053 | 134 | September 23, 1987 Annular |
0.2787 | |
| 139 | March 18, 1988 Total |
0.4188 | 144 | September 11, 1988 Annular |
−0.4681 | |
| 149 | March 7, 1989 Partial |
1.0981 | 154 | August 31, 1989 Partial |
−1.1928 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 22 eclipse events, progressing from north to south between April 8, 1902 and August 31, 1989: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| April 7–8 | January 24–25 | November 12 | August 31-September 1 | June 19–20 |
| 108 | 114 | 116 | ||
 April 8, 1902 |
 August 31, 1913 |
 June 19, 1917 | ||
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 April 8, 1921 |
 January 24, 1925 |
 November 12, 1928 |
 August 31, 1932 |
 June 19, 1936 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 April 7, 1940 |
 January 25, 1944 |
 November 12, 1947 |
 September 1, 1951 |
 June 20, 1955 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 April 8, 1959 |
 January 25, 1963 |
 November 12, 1966 |
 August 31, 1970 |
 June 20, 1974 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | |
 April 7, 1978 |
 January 25, 1982 |
 November 12, 1985 |
 August 31, 1989 | |
References
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC