Babur
| Zahir-ud-din Muhammad Babur ظهیرالدین محمد بابر | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Badshah of the Mughal Empire Babur | |||||
 Illustration of Babur | |||||
| 1st Mughal emperor | |||||
| Reign | 1494 - 1497, 1498 - 1500 (Ferghana) 1504 - 1526 (Kabul) 1497-1498, 1500 - 1501, 1511 - 1512 (Samarkand) 1526 - 1530 (Delhi) 21 April 1526 – 26 December 1530 | ||||
| Predecessor | Ibrahim Lodhi (as Sultan of Delhi) | ||||
| Successor | Humayun | ||||
| Born | 14 February 1483 Andijan, Timurid Empire (present-day Uzbekistan) | ||||
| Died | 26 December 1530 (aged 47) Agra, Mughal Empire (present-day India) | ||||
| Burial | |||||
| Spouse | Aisha Sultan Begum Zainab Sultan Begum Maham Begum Masuma Sultan Begum Bibi Mubarika Gulrukh Begum Dildar Begum Gulnar Aghacha Nazgul Aghacha | ||||
| Issue | Humayun Kamran Mirza Askari Mirza Hindal Mirza Ahmad Mirza Shahrukh Mirza Barbul Mirza Alwar Mirza Faruq Mirza Fakhr-un-Nissa Begum Ishan Daulat Begum Meher Jahan Begum Masuma Sultan Begum Gulzar Begum Gulrukh Begum Gulbadan Begum Gulchehra Begum Altun Bishik (alleged) | ||||
| |||||
| House | Barlas Timurid | ||||
| Dynasty | Mughal | ||||
| Father | Umar Sheikh Mirza, ʿAmīr of Ferghana Valley | ||||
| Mother | Qutlugh Nigar Khanum | ||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam[1] | ||||
Babur (Template:Lang-fa;[2][3] 14 February 1483 – 26 December 1530), born Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the ultimate founder and first Emperor of the Mughal dynasty in the Indian subcontinent. He was a direct descendant of Emperor Timur (Tamerlane) from what is now Uzbekistan.[4][5]
Babur was born in Andijan, in the Fergana Valley, in modern Uzbekistan. Babur ruled nearby Osh in Fergana Valley, located in modern Kyrgyzstan, pondered his future on Sulayman Mountain and even constructed a mosque atop of the mountain. Babur somehow concludes that the confines of the Fergana would cramp his aspirations as a descendant of famous conquering warrior princes. He wrote of the city:
"There are many sayings about the excellence of Osh. On the southeastern side of the Osh fortress is a well-proportioned mountain called Bara-Koh, where, on its summit, Sultan Mahmud Khan built a pavilion. Farther down, on a spur of the same mountain, I had a porticoed pavilion built in 902 (1496-7)"[6]
Babur was the eldest son of Umar Sheikh Mirza, governor of Fergana and great grandson of Timur the Great. He ascended the throne of Fergana in its capital Akhsikent in 1494 at the age of twelve and faced rebellion. He conquered Samarkand two years later, only to lose the vilayat of Fergana soon after. In his attempt to reconquer Fergana, he lost control of Samarkand. In 1501, his attempt to recapture both vilayats went in vain as he was defeated by Muhammad Shaybani Khan. In 1504, he conquered Kabul, which was under the rule of the infant heir of Ulugh Begh. Babur formed a partnership with Safavid ruler Ismail I and reconquered parts of Turkistan, including Samarkand, only to again lose it and the other newly conquered lands to the Sheybanids.
After losing Samarkand for the third time, Babur turned his attention to the South. At that time, the Indo-Gangetic Plain of the northern Indian Subcontinent was ruled by Ibrahim Lodi of the Afghan Lodi dynasty, whereas Rajputana was ruled by a Hindu Rajput Confederacy, led by Rana Sanga of Mewar. According to historical records and Baburnama (autobiography written by Babur himself) Daulat Khan Lodi invited him to attack on Delhi where Ibrahim Lodi was ruling at that time. He sent his ambassador to him to support him in his attack on Delhi. Also in 1524, Daulat Khan Lodi, a rebel of the Lodhi dynasty, invited Babur to overthrow Ibrahim and become ruler. Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodi at the First Battle of Panipat in 1526 CE and founded the Mughal empire. However, he again faced opposition, this time from Rana Sanga of Mewar and Medini Rai,another rajput ruler in the battle of Chanderi who considered Babur a foreigner. The Rana was defeated in the Battle of Khanwa.
Babur married several times. Notable among his sons are Humayun, Kamran Mirza and Hindal Mirza. Babur died in 1530 and was succeeded by Humayun. According to Babur's wishes, he was buried in Bagh-e-Babur in Kabul, Afghanistan. Being a patrilineal descendant of Timur, Babur considered himself a Timurid and Chagatai Turkic.[7] He is considered a national hero in Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan. Many of his poems also have become popular folk songs. He wrote his autobiography, Baburnama, in Chaghatai Turkic and this was translated into Persian during Akbar's reign.
Name
Ẓahīr-ud-Dīn is Arabic for "Defender of the Faith" (of Islam), and Muhammad honours the Islamic prophet.
The difficulty of pronouncing the name for his Central Asian Turco-Mongol army may have been responsible for the greater popularity of his nickname Babur,[8] also variously spelled Baber,[2] Babar,[9] and Bābor.[4] The name is generally taken in reference to the Persian babr, meaning "tiger".[2][3] The word repeatedly appears in Ferdowsi's Shahnameh and was borrowed into the Turkic languages of Central Asia.[9][10] Thackston argues for an alternate derivation from the PIE word "beaver", pointing to similarities between the pronunciation Bābor and the Russian bobr (бобр, "beaver").[11]
Babur bore the royal titles Badshah and al-ṣultānu 'l-ʿazam wa 'l-ḫāqān al-mukkarram pādshāh-e ġāzī. He and later Mughal emperors used the title of mirza and gurkhan as regalia.
Background

Babur's memoirs form the main source for details of his life. They are known as the Baburnama and were written in Chaghatai Turkic, his mother-tongue,[12] though, according to Dale, "his Turkic prose is highly Persianized in its sentence structure, morphology or word formation and vocabulary."[3] Baburnama was translated into Persian during the rule of Babur's grandson Akbar.[12]
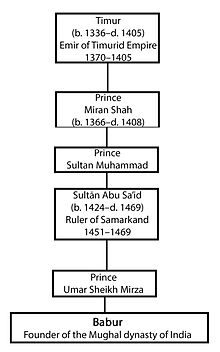
Babur was born on 14 February 1483 in the city of Andijan, Andijan Province, Fergana Valley, contemporary Uzbekistan. He was the eldest son of Umar Sheikh Mirza,[13] ruler of the Fergana Valley, the son of Abū Saʿīd Mirza (and grandson of Miran Shah, who was himself son of Timur) and his wife Qutlugh Nigar Khanum, daughter of Yunus Khan, the ruler of Moghulistan (and great-great grandson of Tughlugh Timur, the son of Esen Buqa I, who was the great-great-great grandson of Chaghatai Khan, the second-born son of Genghis Khan).[14]
Babur hailed from the Barlas tribe, which was of Mongol origin and had embraced Turkic[15] and Persian culture.[16] They had also converted to Islam centuries earlier and resided in Turkestan and Khorasan. Aside from the Chaghatai language, Babur was equally fluent in Persian, the lingua franca of the Timurid elite.[17]
Hence, Babur, though nominally a Mongol (or Moghul in Persian language), drew much of his support from the local Turkic and Iranian people of Central Asia, and his army was diverse in its ethnic makeup. It included Persians (known to Babur as "Sarts" and "Tajiks"), ethnic Afghans, Arabs, as well as Barlas and Chaghatayid Turko-Mongols from Central Asia.[18]
Ruler of Central Asia
As ruler of Fergana
In 1494, eleven years old Babur became the ruler of Fergana, in present-day Uzbekistan, after Umar Sheikh Mirza died "while tending pigeons in an ill-constructed dovecote that toppled into the ravine below the palace".[19] During this time, two of his uncles from the neighbouring kingdoms, who were hostile to his father, and a group of nobles who wanted his younger brother Jahangir to be the ruler, threatened his succession to the throne.[8] His uncles were relentless in their attempts to dislodge him from this position as well as from many of his other territorial possessions to come.[20] Babur was able to secure his throne mainly because of help from his maternal grandmother, Aisan Daulat Begum, although there was also some luck involved.[8]
Most territories around his kingdom were ruled by his relatives, who were descendants of either Timur or Genghis Khan, and were constantly in conflict.[8] At that time, rival princes were fighting over the city of Samarkand to the west, which was ruled by his paternal cousin.[citation needed] Babur had a great ambition to capture the city. In 1497 he besieged Samarkand for seven months before eventually gaining control over it.[21] He was fifteen years old and for him the campaign was a huge achievement.[8] Babur was able to hold the city despite desertions in his army, but he later fell seriously ill.[citation needed] Meanwhile, a rebellion back home, approximately 350 kilometres (220 mi) away, amongst nobles who favoured his brother, robbed him of Fergana.[21] As he was marching to recover it, he lost Samarkand to a rival prince, leaving him with neither.[8] He had held Samarkand for 100 days, and he considered this defeat as his biggest loss, obsessing over it even later in his life after his conquests in India.[8]
In 1501, Babur laid siege to Samarkand once more, but was soon defeated by his most formidable rival, Muhammad Shaybani, Khan of the Uzbeks.[21][22] Samarkand, his lifelong obsession, was lost again. He tried to reclaim Fergana but lost it too and escaping with a small band of followers, he wandered to the mountains of central Asia and took refuge with hill tribes. Thus, during the ten years since becoming the ruler of Fergana, Babur suffered many short-lived victories and was without shelter and in exile, aided by friends and peasants.[23] He finally stayed in Tashkent, which was ruled by his maternal uncle. Babur wrote, "During my stay in Tashkent, I endured much poverty and humiliation. No country, or hope of one!"[23] For three years Babur concentrated on building up a strong army, recruiting widely amongst the Tajiks of Badakhshan in particular. By 1502, he had resigned all hopes of recovering Fergana; he was left with nothing and was forced to try his luck someplace else.[24]
At Kabul
Kabul was ruled by Ulugh Begh Mirza of the Arghun Dynasty, who died leaving only an infant as heir.[23] The city was then claimed by Mukin Begh, who was considered to be a usurper and was opposed by the local populace. In 1504, Babur was able to cross the snowy Hindu Kush mountains and capture Kabul from the remaining Arghunids, who were forced to retreat to Kandahar.[21] With this move, he gained a new kingdom, re-established his fortunes and would remain its ruler until 1526.[24] In 1505, because of the low revenue generated by his new mountain kingdom, Babur began his first expedition to India; in his memoirs, he wrote, "My desire for Hindustan had been constant. It was in the month of Shaban, the Sun being in Aquarius, that we rode out of Kabul for Hindustan". It was a brief raid across the Khyber Pass.[23]
In the same year, Babur united with Sultan Husayn Mirza Bayqarah of Herat, a fellow Timurid and distant relative, against their common enemy, the Uzbek Shaybani.[25] However, this venture did not take place because Husayn Mirza died in 1506 and his two sons were reluctant to go to war.[23] Babur instead stayed at Herat after being invited by the two Mirza brothers. It was then the cultural capital of the eastern Muslim world. Though he was disgusted by the vices and luxuries of the city,[26] he marvelled at the intellectual abundance there, which he stated was "filled with learned and matched men".[27] He became acquainted with the work of the Chagatai poet Mir Ali Shir Nava'i, who encouraged the use of Chagatai as a literary language. Nava'i's proficiency with the language, which he is credited with founding,[28] may have influenced Babur in his decision to use it for his memoirs. He spent two months there before being forced to leave because of diminishing resources;[25] it later was overrun by Shaybani and the Mirzas fled.[26]
Babur became the only reigning ruler of the Timurid dynasty after the loss of Herat, and many princes sought refuge from him at Kabul because of Shaybani's invasion in the west.[26] He thus assumed the title of Padshah (emperor) among the Timurids—though this title was insignificant since most of his ancestral lands were taken, Kabul itself was in danger and Shaybani continued to be a threat.[26] Babur prevailed during a potential rebellion in Kabul, but two years later a revolt among some of his leading generals drove him out of Kabul. Escaping with very few companions, Babur soon returned to the city, capturing Kabul again and regaining the allegiance of the rebels. Meanwhile, Shaybani was defeated and killed by Ismail I, Shah of Shia Safavid Persia, in 1510.[29]
Babur and the remaining Timurids used this opportunity to reconquer their ancestral territories. Over the following few years, Babur and Shah Ismail formed a partnership in an attempt to take over parts of Central Asia. In return for Ismail's assistance, Babur permitted the Safavids to act as a suzerain over him and his followers.[30] Thus, in 1513, after leaving his brother Nasir Mirza to rule Kabul, he managed to take Samarkand for the third time; he also took Bokhara but lost both again to the Uzbeks.[24][26] Shah Ismail reunited Babur with his sister Khānzāda, who had been imprisoned by and forced to marry the recently deceased Shaybani.[31] Babur returned to Kabul after three years in 1514. The following 11 years of his rule mainly involved dealing with relatively insignificant rebellions from Afghan tribes, his nobles and relatives, in addition to conducting raids across the eastern mountains.[26] Babur began to modernise and train his army despite it being, for him, relatively peaceful times.[32]
Foreign relations
| Mughal emperors | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Babur began relations with the Safavids when he met Ali Mirza Safavi at Samarkand; their good relations lasted even after Babur was approached by the Ottomans. The Safavids army led by Najm-e Sani massacred civilians in Central Asia and then sought the assistance of Babur, who advised the Safavids to withdraw. The Safavids, however, refused and were defeated during the Battle of Ghazdewan by the warlord Ubaydullah Khan.[33]
Babur's early relations with the Ottomans were poor because the Ottoman Sultan Selim I provided his rival Ubaydullah Khan with powerful matchlocks and cannons.[34] In 1507, when ordered to accept Selim I as his rightful suzerain, Babur refused and gathered Qizilbash servicemen in order to counter the forces of Ubaydullah Khan during the Battle of Ghazdewan. In 1513, Selim I reconciled with Babur (fearing that he would join the Safavids), dispatched Ustad Ali Quli the artilleryman and Mustafa Rumi the matchlock marksman, and many other Ottoman Turks, in order to assist Babur in his conquests; this particular assistance proved to be the basis of future Mughal-Ottoman relations.[35] From them, he also adopted the tactic of using matchlocks and cannons in field (rather than only in sieges), which would give him an important advantage in India.[32]
Formation of the Mughal Empire

Babur still wanted to escape from the Uzbeks, and he chose India as a refuge instead of Badakhshan, which was to the north of Kabul. He wrote, "In the presence of such power and potency, we had to think of some place for ourselves and, at this crisis and in the crack of time there was, put a wider space between us and the strong foeman."[32] After his third loss of Samarkand, Babur gave full attention to the conquest of North India, launching a campaign; he reached the Chenab River, now in Pakistan, in 1519.[24] Until 1524, his aim was to only expand his rule to Punjab, mainly to fulfill the legacy of his ancestor Timur, since it used to be part of his empire.[32] At the time parts of north India were under the rule of Ibrahim Lodi of the Lodi dynasty, but the empire was crumbling and there were many defectors. He received invitations from Daulat Khan Lodi, Governor of Punjab and Ala-ud-Din, uncle of Ibrahim.[36] He sent an ambassador to Ibrahim, claiming himself the rightful heir to the throne, but the ambassador was detained at Lahore and released months later.[24]
Babur started for Lahore, Punjab, in 1524 but found that Daulat Khan Lodi had been driven out by forces sent by Ibrahim Lodi.[37] When Babur arrived at Lahore, the Lodi army marched out and his army was routed.[38] In response, Babur burned Lahore for two days, then marched to Dipalpur, placing Alam Khan, another rebel uncle of Lodi, as governor.[39] Alam Khan was quickly overthrown and fled to Kabul. In response, Babur supplied Alam Khan with troops who later joined up with Daulat Khan Lodi, and together with about 30,000 troops, they besieged Ibrahim Lodi at Delhi.[40] He easily defeated and drove off Alam's army and Babur realised Lodi would not allow him to occupy the Punjab.[40]
First battle of Panipat

In November 1525 Babur got news at Peshawar that Daulat Khan Lodi had switched sides, and he drove out Ala-ud-Din.[clarification needed] Babur then marched onto Lahore to confront Daulat Khan Lodi, only to see Daulat's army melt away at their approach.[24] Daulat surrendered and was pardoned. Thus within three weeks of crossing the Indus River Babur had become the master of Punjab.[41]
Babur marched on to Delhi via Sirhind. He reached Panipat on 20 April 1526 and there met Ibrahim Lodi's numerically superior army of about 100,000 soldiers and 100 elephants.[24][36] In the battle that began on the following day, Babur used the tactic of Tulugma, encircling Ibrahim Lodi's army and forcing it to face artillery fire directly, as well as frightening its war elephants.[36] Ibrahim Lodi died during the battle, thus ending the Lodi dynasty.[24]
Babur wrote in his memoirs about his victory:
By the grace of the Almighty God, this difficult task was made easy to me and that mighty army, in the space of a half a day was laid in dust.[24]
After the battle, Babur occupied Delhi and Agra, took the throne of Lodi, and laid the foundation for the eventual rise of Mughal rule in India. However, before he became North India's ruler, he had to fend off challengers, such as Rana Sanga.[42]
Battle of Khanwa

The Battle of Khanwa was fought between Babur and the Rajput ruler Rana Sanga on 17 March 1527. Rana Sanga wanted to overthrow Babur, whom he considered to be a foreigner ruling in India, and also to extend the Rajput territories by annexing Delhi and Agra. He was supported by Afghan chiefs who felt Babur had been deceptive by refusing to fulfill promises made to them. Upon receiving news of Rana Sangha's advance towards Agra, Babur took a defensive position at Khanwa (currently in the Indian state of Rajasthan), from where he hoped to launch a counterattack later. According to K.V. Krishna Rao, Babur won the battle because of his "superior generalship" and modern tactics: the battle was one of the first in India that featured cannons. Rao also notes that Rana Sanga faced "treachery" when the Hindu chief Silhadi joined Babur's army with a garrison of 6,000 soldiers.[43]
Battle of Chanderi
This battle took place in the aftermath of the Battle of Khanwa. On receiving news that Rana Sanga had made preparations to renew the conflict with him, Babur decided to isolate the Rana by inflicting a military defeat on one of his staunchest allies, Medini Rai Khangar, who was the ruler of Malwa.[44][45]
Upon reaching Chanderi, on January 20, 1528, Babur offered Shamsabad to Medini Rao in exchange for Chanderi as a peace overture, but the offer was rejected.[45] The outer fortress of Chanderi was taken by Babur's army at night, and the next morning the upper fort was captured. Babur himself expressed surprise that the upper fort had fallen within an hour of the final assault.[44] Medini Rai organized a Jauhar ceremony during which women and children within the fortress immolated themselves.[44][45] A small number of soldiers also collected in Medini Rao's house and proceeded to kill each other in collective suicide. This sacrifice does not seem to have impressed Babur who does not express a word of admiration for the enemy in his autobiography.[44]
Personal life and relationships
There are no descriptions about Babur's physical appearance, except from the paintings in the translation of the Baburnama prepared during the reign of Akbar.[23] In his autobiography, Babur claimed to be strong and physically fit, and claimed to have swum across every major river he encountered, including twice across the Ganges River in North India.[46] Unlike his father, he had ascetic tendencies and did not have any great interest in women. In his first marriage, he was "bashful" towards Aisha Sultan Begum, later losing his affection for her.[47] However, he acquired several more wives and concubines over the years, and as required for a prince, he was able to ensure the continuity of his line.

Babur's first wife, Aisha Sultan Begum, was his paternal cousin, the daughter of Sultan Ahmad Mirza, his father's brother. She was an infant when betrothed to Babur, who was himself five years old. They married eleven years later, c. 1498–99. The couple had one daughter, Fakhr-un-Nissa, who died within a year in 1500. Three years later, after Babur's first defeat at Fergana, Aisha left him and returned to her father's household.[48][32] In 1504, Babur married Zaynab Sultan Begum, who died childless within two years. In the period 1506–08, Babur married four women, Maham Begum (in 1506), Masuma Sultan Begum, Gulrukh Begum and Dildar Begum.[48] Babur had four children by Maham Begum, of whom only one survived infancy. This was his eldest son and heir, Humayun. Masuma Sultan Begum died during childbirth; the year of her death is disputed (either 1508 or 1519). Gulrukh bore Babur two sons, Kamran and Askari, and Dildar Begum was the mother of Babur's youngest son, Hindal.[48] Babur later married Mubaraka Yusufzai, a Pashtun woman of the Yusufzai tribe. Gulnar Aghacha and Nargul Aghacha were two Circassian slaves given to Babur as gifts by Tahmasp Shah Safavi, the Shah of Persia. They became "recognized ladies of the royal household."[48]
During his rule in Kabul, when there was a time of relative peace, Babur pursued his interests in literature, art, music and gardening.[32] Previously, he never drank alcohol and avoided it when he was in Herat. In Kabul, he first tasted it at the age of thirty. He then began to drink regularly, host wine parties and consume preparations made from opium.[26] Though religion had a central place in his life, Babur also approvingly quoted a line of poetry by one of his contemporaries: "I am drunk, officer. Punish me when I am sober". He quit drinking for health reasons before the Battle of Khanwa, just two years before his death, and demanded that his court do the same. But he did not stop chewing narcotic preparations, and did not lose his sense of irony. He wrote, "Everyone regrets drinking and swears an oath (of abstinence); I swore the oath and regret that."[49]
Death and legacy
Babur died at the age of 47 on 5 January [O.S. 26 December 1530] 1531 and was succeeded by his eldest son, Humayun.

After death, his body was moved to Kabul, Afghanistan, where it lies in Bagh-e Babur (Babur Gardens).[50]
It is generally agreed that, as a Timurid, Babur was not only significantly influenced by the Persian culture, but that his empire also gave rise to the expansion of the Persianate ethos in the Indian subcontinent.[4][5]
For example, F. Lehmann states in the Encyclopædia Iranica:
His origin, milieu, training, and culture were steeped in Persian culture and so Babur was largely responsible for the fostering of this culture by his descendants, the Mughals of India, and for the expansion of Persian cultural influence in the Indian subcontinent, with brilliant literary, artistic, and historiographical results.[16]
Although all applications of modern Central Asian ethnicities to people of Babur's time are anachronistic, Soviet and Uzbek sources regard Babur as an ethnic Uzbek.[51][52][53] At the same time, during the Soviet Union Uzbek scholars were censored for idealising and praising Babur and other historical figures such as Ali-Shir Nava'i.[54]

Babur is considered a national hero in Uzbekistan.[55] On 14 February 2008, stamps in his name were issued in the country to commemorate his 525th birth anniversary.[56] Many of Babur's poems have become popular Uzbek folk songs, especially by Sherali Jo'rayev.[57] Some sources claim that Babur is a national hero in Kyrgyzstan too.[58] In October 2005, Pakistan developed the Babur Cruise Missile, named in his honour.
One of the enduring features of Babur's life was that he left behind the lively and well-written autobiography known as Baburnama.[11] Quoting Henry Beveridge, Stanley Lane-Poole writes:
His autobiography is one of those priceless records which are for all time, and is fit to rank with the confessions of St. Augustine and Rousseau, and the memoirs of Gibbon and Newton. In Asia it stands almost alone.[59]
In his own words, "The cream of my testimony is this, do nothing against your brothers even though they may deserve it." Also, "The new year, the spring, the wine and the beloved are joyful. Babur make merry, for the world will not be there for you a second time."[60]

Babri Masjid
Babri Masjid ("Babur's Mosque") in Ayodhya, is said to have been constructed on the orders of one of Mir Baqi, one of the commanders of his army. In 2003, by the order of an Indian Court, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) was asked to conduct a more indepth study and an excavation to ascertain the type of structure that was beneath the mosque.[61] The excavation was conducted from 12 March 2003 to 7 August 2003, resulting in 1360 discoveries. The ASI submitted its report to the Allahabad high court.[62]
The summary of the ASI report indicated the presence of a 10th-century temple under the mosque.[63][64] The ASI team said that, human activity at the site dates back to the 13th century BCE. The next few layers date back to the Shunga period (second-first century BCE) and the Kushan period. During the early medieval period (11–12th century CE), a huge but short-lived structure of nearly 50 metres north-south orientation was constructed. On the remains of this structure, another massive structure was constructed: this structure had at least three structural phases and three successive floors attached with it. The report concluded that it was over the top of this construction that the disputed structure was constructed during the early 16th century.[65]
Ancestry
| Ancestors of Babur | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes
- ^ Christine Isom-Verhaaren, Allies with the Infidel, (I.B. Tauris, 2013), 58.
- ^ a b c EB (1878).
- ^ a b c Dale, Stephen Frederic (2004). The garden of the eight paradises: Bābur and the culture of Empire in Central Asia, Afghanistan and India (1483–1530). Brill. pp. 15, 150. ISBN 90-04-13707-6.
- ^ a b c F. Lehmann: Ẓahīr-al-Dīn Moḥammad Bābor. In Encyclopædia Iranica. Online Ed. December 1988 (updated August 2011). "Bābor, Ẓahīr-al-Dīn Moḥammad (6 Moḥarram 886-6 Jomādā I 937/14 February 1483 – 26 December 1530), Timurid prince, military genius, and literary craftsman who escaped the bloody political arena of his Central Asian birthplace to found the Mughal Empire in India. His origin, milieu, training, and education were steeped in Muslim culture and so Bābor played significant role for the fostering of this culture by his descendants, the Mughals of India, and for the expansion of Islam in the Indian subcontinent, with brilliant literary, artistic, and historiographical results."
- ^ a b Robert L. Canfield, Robert L. (1991). Turko-Persia in historical perspective, Cambridge University Press, p. 20. "The Mughals-Persianized Turks who invaded from Central Asia and claimed descent from both Timur and Genghis – strengthened the Persianate culture of Muslim India".
- ^ The Babur-nama Ed. & trans. Wheeler M. Thackston (New York) 2002 pp4-5
- ^ Richards, John F. (1995), The Mughal Empire, Cambridge University Press, p. 6, ISBN 978-0-521-56603-2
- ^ a b c d e f g Eraly 2007, pp. 18–20.
- ^ a b EB (1911).
- ^ Thumb, Albert, Handbuch des Sanskrit, mit Texten und Glossar, German original, ed. C. Winter, 1953, Snippet, p. 318
- ^ a b Babur, Emperor of Hindustan (2002). The Baburnama: Memoirs of Babur, Prince and Emperor. translated, edited and annotated by W. M. Thackston. Modern Library. ISBN 0-375-76137-3.
- ^ a b Dilip Hiro (2006). Babur Nama: Journal of Emperor Babur. Mumbai: Penguin Books India. p. xviii. ISBN 978-0-14-400149-1.
- ^ "Mirza Muhammad Haidar". Silk Road Seattle. University of Washington. Retrieved 7 November 2006.
On the occasion of the birth of Babar Padishah (the son of Omar Shaikh)
- ^ Babur. Babur Nama. Penguin Books. p. vii. ISBN 978-0-14-400149-1.
- ^ "Bābur (Mughal emperor)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 29 August 2016.
- ^ a b Lehmann, F. "Memoirs of Zehīr-ed-Dīn Muhammed Bābur". Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- ^ "Iran: The Timurids and Turkmen". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 29 August 2016.
- ^ Manz, Beatrice Forbes (1994). "The Symbiosis of Turk and Tajik". Central Asia in Historical Perspective. Boulder, Colorado & Oxford. p. 58. ISBN 0-8133-3638-4.
- ^ "Babu, the first Moghul emperor: Wine and tulips in Kabul". The Economist. 16 December 2010. pp. 80–82. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ Lal, Ruby (25 September 2005). Domesticity and Power in the Early Mughal World. p. 69. ISBN 0-521-85022-3.
It was over these possessions, provinces controlled by uncles, or cousins of varying degrees, that Babur fought with close and distant relatives for much of his life.
- ^ a b c d Ewans, Martin (September 2002). Afghanistan: A Short History of Its People and Politics. HarperCollins. pp. 26–27. ISBN 0-06-050508-7.
Babur, while still in his teens, conceived the ambition of conquering Samarkand. In 1497, after a seven months' siege, he took the city, but his supporters gradually deserted him and Ferghana was taken from him in his absence. Within a few months he was compelled to retire from Samarkand ... Eventually he retook Samarkand, but was again forced out, this time by an Usbek leader, Shaibani Khan ... Babur decided in 1504 to trek over the Hindu Kush to Kabul, where the current ruler promptly retreated to Kandahar and left him in undisputed control of the city.
- ^ "The Memoirs of Babur". Silk Road Seattle. University of Washington. Retrieved 8 November 2006.
After being driven out of Samarkand in 1501 by the Uzbek Shaibanids ...
- ^ a b c d e f Eraly 2007, pp. 21–23.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Mahajan, V.D. (2007). History of medieval India (10th ed.). New Delhi: S Chand. pp. 428–29. ISBN 81-219-0364-5.
- ^ a b Brend, Barbara (20 December 2002). Perspectives on Persian Painting: Illustrations to Amir Khusrau's Khamsah. Routledge (UK). p. 188. ISBN 0-7007-1467-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g Eraly 2007, pp. 24–26.
- ^ Lamb, Christina (February 2004). The Sewing Circles of Herat: A Personal Voyage Through Afghanistan. HarperCollins. p. 153. ISBN 0-06-050527-3.
- ^ Hickmann, William C. (19 October 1992). Mehmed the Conqueror and His Time. p. 473. ISBN 0-691-01078-1.
Eastern Turk Mir Ali Shir Neva'i (1441–1501), founder of the Chagatai literary language
- ^ Doniger, Wendy (September 1999). Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions. Merriam-Webster. p. 539. ISBN 0-87779-044-2.
- ^ Sicker, Martin (August 2000). The Islamic World in Ascendancy: From the Arab Conquests to the Siege in Vienna. p. 189. ISBN 0-275-96892-8.
Ismail was quite prepared to lend his support to the displaced Timurid prince, Zahir ad-Din Babur, who offered to accept Safavid suzerainty in return for help in regaining control of Transoxiana.
- ^ Erdogan, Eralp, "Babür İmparatorluğu'nun Kuruluş Safhasında Şah İsmail ile Babür İttifakı", History Studies, Volume 6 Issue 4, pp. 31–39, July 2014
- ^ a b c d e f Eraly 2007, pp. 27–29.
- ^ Stuart Cary Welch. The Emperors' Album: Images of Mughal India. Metroplitian Museum of Art. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-87099-499-9.
- ^ Farooqi, Naimur Rahman (2008). Mughal-Ottoman relations: a study of political & diplomatic relations ... Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ Farooqi, Naimur Rahman (2008). Mughal-Ottoman relations: a study of political & diplomatic relations ... Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ a b c Chaurasia, Radhey Shyam (2002). History of medieval India : from 1000 A.D. to 1707 A.D. New Delhi: Atlantic Publ. pp. 89–90. ISBN 81-269-0123-3.
- ^ Satish Chandra, Medieval India:From Sultanat to the Mughals, Vol. 2, (Har-Anand, 2009), 27.
- ^ Satish Chandra, Medieval India:From Sultanat to the Mughals, Vol. 2, 27.
- ^ Satish Chandra, Medieval India:From Sultanat to the Mughals, Vol. 2, 27–28.
- ^ a b Satish Chandra, Medieval India:From Sultanat to the Mughals, Vol. 2, 28.
- ^ Keay, John (12 April 2011). India: A History. Revised and Updated. Grove/Atlantic, Inc. ISBN 978-0-8021-9550-0.
- ^ Mahajan, V. D. (2007). History of medieval India (10th ed.). New Delhi: S Chand. pp. 432–36. ISBN 81-219-0364-5.
- ^ Rao, K. V. Krishna. Prepare Or Perish: A Study of National Security. Lancer Publishers. p. 453. ISBN 978-81-7212-001-6.
- ^ a b c d Lane-pool, Stanley. "Babar". Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Chandra, Satish (2006). Medieval India: From Sultanat to the Mughals (1206–1526). Vol. 2. Har-Anand Publications.
- ^ Elliot, Henry Miers (1867–1877). "The Muhammadan Period". The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. John Dowson (ed.). London: Trubner.
... and on the same journey, he swam twice across the Ganges, as he said he had done with every other river he had met with.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Memoirs of Babur, Volume 1, chpt. 71". Memoirs of Zehīr-ed-Dīn Muhammed Bābur Emperor of Hindustan, Written by himself, in the Chaghatāi Tūrki. Translated by John Leyden and William Erskine, Annotated and Revised by Lucas King. Oxford University Press. 1921.
Āisha Sultan Begum, the daughter of Sultan Ahmed Mirza, to whom I had been betrothed in the lifetime of my father and uncle, having arrived in Khujand, I now married her, in the month of Shābān. In the first period of my being a married man, though I had no small affection for her, yet, from modesty and bashfulness, I went to her only once in ten, fifteen, or twenty days. My affection afterwards declined, and my shyness increased; in so much, that my mother the Khanum, used to fall upon me and scold me with great fury, sending me off like a criminal to visit her once in a month or forty days.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b c d Babur; Dilip Hiro. "Babur's wives and children". In Dilip Hiro (ed.). Babur Nama:Journal of Emperor Babur (2006 ed.). Penguin. p. 362. ISBN 978-0-14-400149-1.
- ^ Pope, Hugh (2005). Sons of the Conquerors, Overlook Duckworth, pp. 234–35.
- ^ Mahajan, V.D. (2007). History of medieval India (10th ed.). New Delhi: S Chand. p. 438 ed. ISBN 81-219-0364-5.
- ^ Prokhorov, A. M., ed. (1969–1978). "Babur". Great Soviet Encyclopedia (in Russian). Moscow: Soviet Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 16 September 2013. Retrieved 16 September 2013.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Muminov, Ibrohim, ed. (1972). "Bobur". Uzbek Soviet Encyclopedia (in Uzbek). Vol. 2. Tashkent: Uzbek Soviet Encyclopedia. pp. 287–95.
- ^ Bobur, Zahiriddin Muhammad (1989). "About This Edition". In Aʼzam Oʻktam (ed.). Boburnoma (in Uzbek). Tashkent: Yulduzcha. p. 3.
- ^ William Fierman, ed. (1991). Soviet Central Asia. Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press. p. 147. ISBN 0-8133-7907-5.
- ^ "Grandeur and Eternity: Zahiriddin Muhammad Bobur in Minds of People Forever". Embassy of Uzbekistan in Korea. 22 February 2011. Retrieved 14 February 2012.
- ^ "The country's history on postage miniatures". Uzbekistan Today. Archived from the original on 14 June 2015. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Sherali Joʻrayev: We Haven't Stopped. We Still Exist". BBC's Uzbek Service (in Uzbek). 13 April 2007. Retrieved 8 October 2013.
- ^ Dust in the Wind: Retracing Dharma Master Xuanzang's Western Pilgrimage by 經典雜誌編著, Zhihong Wang, p. 121
- ^ Lane-Poole, Stanley. "Babar". pp. 12–13. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ^ Sen, Sailendra (2013). A Textbook of Medieval Indian History. Primus Books. p. 151. ISBN 978-93-80607-34-4.
- ^ Ratnagar, Shereen (2004). "Archaeology at the Heart of a Political Confrontation: The Case of Ayodhya" (PDF). Current Anthropology. 45 (2): 239–59. doi:10.1086/381044.
- ^ "ASI submits report on Ayodhya excavation". Rediff.com. 22 August 2003. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ^ Suryamurthy, R (26 August 2003). "ASI findings may not resolve title dispute". The Tribune.
- ^ Prasannan, R. (7 September 2003) "Ayodhya: Layers of truth" The Week (India), from Web Archive
- ^ "Proof of temple found at Ayodhya: ASI report". Rediff.com. 25 August 2003. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
References
- Baynes, T. S., ed. (1878), , Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (9th ed.), New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, p. 179
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911), , Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. 92
- "'Turks and Afghan' and 'The Mughal Period'", Cambridge History of India, vol. Vol. III & IV, Cambridge, 1928
{{citation}}:|volume=has extra text (help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Eraly, Abraham (2007), Emperors Of The Peacock Throne: The Saga of the Great Moghuls, Penguin Books Limited, ISBN 978-93-5118-093-7
Further reading
- Alam, Muzaffar & Subrahmanyan, Sanjay (Eds.) The Mughal State 1526–1750 (Delhi) 1998
- Balabanlilar, Lisa (2012). Imperial Identity in the Mughal Empire: Memory and Dynastic Politics in Early Modern South and Central Asia. London: I.B. Tauris.
- Gascoigne, Bamber The Great Moghuls (London) 1971. (Last revised 1987)
- Gommans, Jos Mughal Warfare (London) 2002
- Gordon, Stewart. When Asia was the World: Traveling Merchants, Scholars, Warriors, and Monks who created the "Riches of the East" Da Capo Press, Perseus Books, 2008. ISBN 0-306-81556-7.
- Hasan, Mohibbul (1985). Babur: Founder of the Mughal Empire in India. New Delhi: Manohar Publications.
- Irvine, William The Army of the Indian Moghuls. (London) 1902. (Last revised 1985)
- Jackson, Peter The Delhi Sultanate. A Political and Military History (Cambridge) 1999
- Richards, John F. The Mughal Empire (Cambridge) 1993
