Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass.
All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primarily by radiant energy from the sun. The energy industry provides the energy required for human civilization to function, which it obtains from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, renewable energy, and geothermal energy. (Full article...)
Selected article
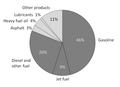
Deposits of oil shale occur around the world, including major deposits in the United States of America. Estimates of global deposits range from 2.8 trillion to 3.3 trillion barrels (450×109 to 520×109 m3) of recoverable oil.
The chemical process of pyrolysis can convert the kerogen in oil shale into synthetic crude oil. Heating oil shale to a sufficiently high temperature will drive off a vapor which processing can distill (retort) to yield a petroleum-like shale oil—a form of unconventional oil—and combustible oil-shale gas (the term shale gas can also refer to gas occurring naturally in shales). Industry can also burn oil shale directly as a low-grade fuel for power generation and heating purposes and can use it as a raw material in chemical and construction-materials processing.
Oil shale has gained attention as an energy resource as the price of conventional sources of petroleum has risen and as a way for some areas to secure independence from external suppliers of energy. At the same time, oil-shale mining and processing involve a number of environmental issues, such as land use, waste disposal, water use, waste-water management, greenhouse-gas emissions and air pollution. Estonia and China have well-established oil shale industries, and Brazil, Germany, Israel and Russia also utilize oil shale.
Selected image

Photo credit: From an image by Wolfgang Beyer
Strombolian volcanic eruptions can eject incandescent cinder, lapilli and lava bombs to altitudes of tens to hundreds of meters.
Did you know?

- Buildings constructed to the German Passivhaus standard use 75% to 95% less energy for space heating and cooling than current new buildings in the United States?
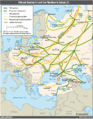
- Crossing 4,000 km (2,500 miles), the Druzhba pipeline is the world's longest oil pipeline?
- Coal is ground to a powder before being burnt in fossil fuel power plants?
- Compact fluorescent lamps (pictured) use about 1/4 of the energy of normal incandescent light bulbs, and pay for themselves after about 500 hours of use?
- Nuclear power in France produces 78% of all the country's electricity - more than in any other nation?
- Positive lightning bolts are typically six to ten times more powerful than normal lightning — and aircraft are not designed to withstand them?
- Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy which permeates all of space?
Selected biography
Maxwell studied natural philosophy, moral philosophy, and mental philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, before graduating in mathematics at the University of Cambridge, where he would conduct much of his career. He built on Michael Faraday's work on magnetic induction, using elements of geometry and algebra to demonstrate that electric and magnetic fields travel through space, in the form of waves, and at the constant speed of light. Finally, in 1861, Maxwell proposed that light consisted of undulations in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. In the same year he was elected to the Royal Society.
In 1864, Maxwell presented what are now known as Maxwell's equations to the Royal Society. These collectively describe the behaviour of both the electric and magnetic fields, as well as their interactions with matter.
In the news
- 22 August 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- The International Atomic Energy Agency announces an investigation of the Kursk Nuclear Power Plant following accusations from Russia that a Ukrainian drone targeted the power plant. (Reuters)
- 22 August 2024 – Belarus–China relations
- Belarus and China agree to greatly strengthen mutual trade, financial, energy, and security cooperation, which includes enhancing industrial supply chains and collaboration with the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area. (Reuters)
- 18 August 2024 – 2024 Lebanese blackout
- Ongoing nationwide blackouts in Lebanon caused by fuel shortages provoke significant governmental conflict, with the Minister of Energy blaming the Central Bank for not paying Iraq for fuel imports and the Central Bank blaming Parliament for not authorizing emergency fund transfers for fuel payments. (Asharq Al-Awsat)
- 17 August 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- The International Atomic Energy Agency declares that the safety of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant is deteriorating, following an investigation into an explosive drone strike that targeted a perimeter access road at the power plant. (Reuters)
General images
Quotations
- "If we already have the Kyoto protocol, why invent another proposal and not just implement one that already exists? If a country is incapable of implementing the result of an international treaty that has established rules and regulations, it won't end up implementing those rules voluntarily."" – Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, 2007
- "Climate change is a challenge China must cope with to realize sustainable development... Implementing a climate change containment policy may cost a fortune, but the cost will be even higher if we delay. Early action is imperative." – Ma Kai, 2007
- "The consequences of restricting the development of developing nations will be much more serious than the consequences of global warming." – Ma Kai, 2007
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus