Fellatio

Fellatio (also known as fellation,[1] and in slang as blowjob, BJ, giving head, or sucking off[2]) is an oral sex act involving the use of the mouth or throat, which is usually performed by a person on the penis of another person. If performed on oneself, the act is called autofellatio.[3][4] Oral stimulation of the scrotum may also be termed fellatio,[5][6] or colloquially as teabagging.[7]
Fellatio can be sexually arousing for both participants, and may lead to orgasm for the receiving partner.[3][4] It may be performed by a sexual partner as foreplay before other sexual activities (such as vaginal or anal intercourse),[3][8] or as an erotic and physically intimate act in its own right.[3][4] Like most forms of sexual activity, oral sex creates a risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs/STDs). However, the transmission risk for oral sex, especially HIV transmission, is significantly lower than for vaginal or anal sex.[9][10][11]
Most countries do not have laws that ban the practice of oral sex, though some cultures may consider it taboo.[3] People may also have negative feelings or sexual inhibitions about giving or receiving oral sex; they may refuse to engage in it of their own volition.[3] Commonly, people do not regard forms of oral sex as affecting the virginity of either partner, though opinions on the matter vary.[12][13][14][15]
Etymology
The English noun fellatio comes from fellātus, which in Latin is the past participle of the verb fellāre, meaning to suck. In fellatio the -us is replaced by the -io; the declension stem ends in -ion-, which gives the suffix the form -ion (cf. French fellation). The -io(n) ending is used in English to create nouns from Latin adjectives and it can indicate a state or action wherein the Latin verb is being, or has been, performed.
Further English words have been created based on the same Latin root. A person who performs fellatio upon another may be termed a fellator; because of Latin's gender based declension, this word may be restricted by some English speakers to describing a male. The equivalent term for a female is fellatrix.
Practice
General


A person who performs fellatio on someone may be referred to as the giving partner, and the other person as the receiving partner. Fellatio can be sexually arousing for participants, and males commonly experience orgasm and ejaculation of semen during the act.[3][4] People may use fellatio as foreplay to sexually arouse their sex partner before vaginal or anal intercourse, or other sexual activity,[3][8] or they may use it as an erotic and physically intimate act in its own right.[3][4] Though a person who receives fellatio is male, his sex partner may be of either sex. When the penis is thrust into someone's mouth, it may be called irrumatio, though the term is rarely used.[16]
The essential aspect of fellatio is for a man's sex partner to take his penis into their mouth, and then move their mouth up and down the penis to a rhythm set by them mimicking the thrusting motion of vaginal or anal intercourse, with saliva acting as a lubricant, and being careful not to bite or scratch with the teeth.[3] The man receiving fellatio can slow the rhythm of the stimulation by holding his partner's head. The man's partner may also orally play with his penis by licking, sucking, kissing or otherwise playing with the tongue and lips.[3] Fellatio may also include the oral stimulation of the scrotum, whether licking, sucking or taking the entire scrotum into the mouth.[5][6]
It is difficult for some people to perform fellatio, due to their sensitivities to the natural gag reflex. Different people have different sensitivities to the reflex, but some people learn to suppress the reflex. Deep-throating is an act in which a man's partner takes the entire erect penis deep into their mouth, in such a way as to enter their throat.
Nancy Friday's book, Men in Love – Men's Sexual Fantasies: The Triumph of Love over Rage, suggests that swallowing semen is high on a man's intimacy scale.[17] The man receiving fellatio receives direct sexual stimulation, while his partner may derive satisfaction from giving him pleasure. Giving and receiving fellatio may happen simultaneously in sex positions like 69 and daisy chain.
Fellatio is sometimes practiced when penile penetration would create a physical difficulty for a sex partner. For example, it may be practiced during pregnancy instead of vaginal intercourse by couples wishing to engage in intimate sexual activity while avoiding the difficulty of vaginal intercourse during later stages of pregnancy.[18] There may be other reasons why a woman may not wish to have vaginal intercourse, such as apprehension of losing her virginity, of becoming pregnant,[12][14] or she may be menstruating.
It is physically possible for men who have sufficient flexibility, penis size or a combination of the two to perform fellatio by oneself as a form of masturbation; this is called autofellatio. Few men possess sufficient flexibility and penis length to safely perform the necessary frontbend.[19] However, increased flexibility achieved via gravity-assisted positions, and physical training such as gymnastics, contortion, or yoga may make it possible for some.
Taste and odor
It may be that "few women praise the taste" of semen.[20] However, as with breast milk, the taste of semen may be altered by diet.[medical citation needed] There are anecdotal reports that higher red meat and dairy intake may increase its generally salty taste.[medical citation needed] Asparagus has been noted to cause bitterness, while parsley, celery, cinnamon, and many kinds of fruit (especially tropical) are noted to sweeten it.[medical citation needed]
Health aspects
Sexually transmitted infections
Chlamydia, human papillomavirus (HPV), gonorrhea, herpes, hepatitis (multiple strains), and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs/STDs), can be transmitted through oral sex.[9][10][21] Any sexual exchange of bodily fluids with a person infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, poses a risk of infection. Risk of STI infection, however, is generally considered significantly lower for oral sex than for vaginal or anal sex, with HIV transmission considered the lowest risk with regard to oral sex.[10][11][22][23]
There is an increased risk of STI transmission if the receiving partner has wounds on his genitals, or if the giving partner has wounds or open sores on or in his or her mouth, or bleeding gums.[10][11][24] Brushing the teeth, flossing, undergoing dental work soon before or after giving fellatio can also increase the risk of transmission, because all of these activities can cause small scratches in the lining of the mouth.[10][11] These wounds, even when they are microscopic, increase the chances of contracting STIs that can be transmitted orally under these conditions.[10][11] Such contact can also lead to more mundane infections from common bacteria and viruses found in, around and secreted from the genital regions. Because of the aforementioned factors, medical sources advise the use of condoms or other effective barrier methods when performing or receiving fellatio with a partner whose STI status is unknown.[9][10][11][21]
HPV and oral cancer link
Links have been reported between oral sex and oral cancer with human papillomavirus (HPV)-infected people.[25] A 2005 research study suggested that performing unprotected oral sex on a person infected with HPV might increase the risk of oral cancer. The study found that 36 percent of the cancer patients had HPV compared to only 1 percent of the healthy control group.[26]
A 2007 study suggested a correlation between oral sex and throat cancer. It is believed that this is due to the transmission of HPV, a virus that has been implicated in the majority of cervical cancers and which has been detected in throat cancer tissue in numerous studies. The study concludes that people who had one to five oral sex partners in their lifetime had approximately a doubled risk of throat cancer compared with those who never engaged in this activity and those with more than five oral sex partners had a 250 percent increased risk.[27][28][29]
Pregnancy and semen exposure
Fellatio cannot result in pregnancy, as there is no way for ingested sperm to reach the uterus and fallopian tubes to fertilize an egg. At any rate, acids in the stomach and digestive enzymes in the digestive tract break down and kill spermatozoa.
Clinical research has tentatively linked fellatio with immune modulation,[30] indicating it may reduce the chance of complications during pregnancy. The potentially fatal complication pre-eclampsia was observed to occur less in women who regularly engaged in fellatio, with those who also ingested their partner's semen being at the least risk.[31] The results were consistent with the fact that semen contains TGF-β1, the exchange of which between partners having a causal reduction in risk of pre-eclampsia caused by an immunological reaction. It is worth noting that fellatio is not the only viable mechanism for the transmission of TGF-β1.[30][32][33]
Cultural views
Semen ingestion
As late as 1976, some doctors were advising women in the eighth and ninth months of pregnancy not to swallow semen lest it induce premature labor,[34] though it is now known to be safe.
Semen ingestion has had central importance in some cultures around the world. In Baruya culture, there is a secret ritual in which boys give fellatio to young males and drink their semen, to "re-engender themselves before marriage".[35] Among the Sambia people of Papua New Guinea, beginning at age seven all males regularly submit to oral penetration by adolescents in a six-stage initiation process, as the Sambia believe that regular ingestion of an older boy's semen is necessary for a prepubescent youth to achieve sexual maturity and masculinity. By the time he enters mid-puberty he in turn participates in passing his semen on to younger males.[36][37]
Virginity
Oral sex is commonly used as a means of preserving virginity, especially among heterosexual pairings; this is sometimes termed technical virginity (which additionally includes anal sex, mutual masturbation and other non-penetrative sex acts, but excludes penile-vaginal sex).[12][13][14][38] The concept of "technical virginity" or sexual abstinence through oral sex is particularly popular among teenagers,[14][24][39] including with regard to teenage girls who not only fellate their boyfriends to preserve their virginities, but also to create and maintain intimacy or to avoid pregnancy.[14] Other reasons given for the practice among teenage girls are peer-group pressure and as their introduction to sexual activity.[14] Additionally, gay males may regard fellatio as a way of maintaining their virginities, with penile-anal penetration defined as resulting in virginity loss, while other gay males may define fellatio as their main form of sexual activity.[12][15]
Legality
Fellatio is legal in most countries. Laws of some jurisdictions regard fellatio as penetrative sex for the purposes of sexual offenses with regard to the act, but most countries do not have laws which ban the practice, in contrast to anal sex or extramarital sex. In Islamic literature, the only forms of sexual activity that are consistently explicitly prohibited within marriage are anal sex and sexual activity during menstrual cycles.[40] However, the exact attitude towards oral sex is a subject of disagreements between modern scholars of Islam. Authorities considering it "objectionable" do so because of the penis's supposedly impure fluids coming in contact with the mouth.[41] Others emphasize that there is no decisive evidence to forbid oral sex.[42]
In Malaysia, fellatio is illegal, but the law is seldom enforced. Under Malaysia's Section 377A of the Penal Code, the introduction of the penis into the anus or mouth of another person is considered a "carnal intercourse against the order of nature" and is punishable with imprisonment of 20 years maximum and whipping.[43]
Tradition

Galienus called fellatio lesbiari since women of the island of Lesbos were supposed to have introduced the practice of using one's lips to give sexual pleasure.[44]
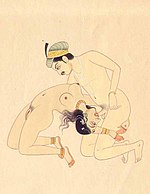
The Ancient Indian Kama Sutra, dating from the first century AD, describes oral sex,[45] discussing fellatio in great detail (the Kama Sutra has a chapter on auparishtaka (or oparishtaka), "mouth congress")[46] and only briefly mentioning cunnilingus. However, according to the Kama Sutra, fellatio is above all a characteristic of eunuchs (or, according to other translations, of effeminate homosexuals or transwomen similar to the modern Hijra of India), who use their mouths as a substitute for female genitalia.
The author of the Kama Sutra states that it is also practiced by "unchaste women", but mentions that there are widespread traditional concerns about this being a degrading or unclean practice, with known practitioners being evaded as love partners in large parts of the country. The author appears to somewhat agree with these attitudes, claiming that "a wise man" should not engage in that form of intercourse while acknowledging that it can be appropriate in some unspecified cases.
The Moche culture of ancient Peru worshipped daily life including sexual acts. They depicted fellatio in their ceramics.[47]
In some cultures, such as Cambodia, Chinese in Southeast Asia, northern Manchu tribes along Amur River,[48] Sambians in Papua New Guinea, Thailand, Telugus of India, Hawaii and other Pacific Islanders, briefly taking the penis of a male infant or toddler into one's mouth was considered a nonsexual form of affection or even a form of ritual, greeting, respect, parenting love, or lifesaving.[49][50][51][52][53] According to some sources, it was an ancient Chinese custom for grandmothers, mothers, and elder sisters to calm their baby boys with fellatio.[54][55] It has also been reported that some modern Chinese mothers have performed fellatio to their moribund sons as affection and means for lifesaving, because they culturally believe that when the penis is completely retracted into the abdomen, the boy or man will die.[53][56][57]
Other animals
Flying foxes have been observed engaging in oral sex.[59] Indian flying fox males will lick a female's vulva both before and after copulation, with the length of pre-copulation cunnilingus positively correlated with length of copulation.[60] The fruit bat Cynopterus sphinx, has been observed to engage in fellatio during mating. Pairs spend more time copulating if the female licks the male than if she does not.[58][61] Male Livingstone's fruit bats have been observed engaging in homosexual fellatio, although it is unknown if this is an example of sexual behavior or social grooming.[62] Bonin flying foxes also engage in homosexual fellatio, but the behavior has been observed independently of social grooming.[59]
See also
References
- ^ "fellation". Merriam-Webster. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Archived from the original on 2010-09-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Oral Sex". BBC Advice. BBC. Archived from the original on 2010-09-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Janell L. Carroll (2009). Sexuality Now: Embracing Diversity. Cengage Learning. pp. 265–267. ISBN 978-0-495-60274-3. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e Psychology Applied to Modern Life: Adjustment in the 21st century. Cengage Learning. 2008. p. 422. ISBN 978-0-495-55339-7. Retrieved February 26, 2011.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ a b Comprehensive Textbook of Sexual Medicine. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. 2005. p. 106. ISBN 8180614050. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ a b Our Sexuality. Cengage Learning. 2010. p. 241. ISBN 0495812943. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
Fellatio (fuh-LAY-shee-oh) is oral stimulation of the penis and scrotum.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Sex Slang. Psychology Press. 2007. p. 180. ISBN 0203935772. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ a b "What is oral sex?". NHS Choices. NHS. 2009-01-15. Archived from the original on 2010-09-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c "Global strategy for the prevention and control of sexually transmitted infections: 2006–2015. Breaking the chain of transmission" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2007. Retrieved November 26, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g Dianne Hales (2008). An Invitation to Health Brief 2010-2011. Cengage Learning. pp. 269–271. ISBN 0495391921. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f New Dimensions in Women's Health. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 2011. p. 211. ISBN 1449683754. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d See here and 47-49 for male virginity, how gay and lesbian individuals define virginity loss, and for how the majority of researchers and heterosexuals define virginity loss/"technical virginity" by whether or not a person has engaged in vaginal sex. Laura M. Carpenter (2005). Virginity lost: An Intimate Portrait of First Sexual Experiences. NYU Press. pp. 295 pages. ISBN 0-8147-1652-0. Retrieved October 9, 2011.
- ^ a b The Marriage and Family Experience: Intimate Relationship in a Changing Society. Cengage Learning. 2010. p. 186. ISBN 0-534-62425-1. Retrieved October 8, 2011.
Most people agree that we maintain virginity as long as we refrain from sexual (vaginal) intercourse. But occasionally we hear people speak of 'technical virginity' [...] Data indicate that 'a very significant proportion of teens ha[ve] had experience with oral sex, even if they haven't had sexual intercourse, and may think of themselves as virgins' [...] Other research, especially research looking into virginity loss, reports that 35% of virgins, defined as people who have never engaged in vaginal intercourse, have nonetheless engaged in one or more other forms of heterosexual sexual activity (e.g., oral sex, anal sex, or mutual masturbation).
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f Sonya S. Brady; Bonnie L. Halpern-Felsher (2007). "Adolescents' Reported Consequences of Having Oral Sex Versus Vaginal Sex" (PDF). Pediatrics. 119 (2): 229–236. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1727. PMID 17272611.
- ^ a b Joseph Gross, Michael (2003). Like a Virgin. Here Publishing. pp. 44–45. 0001-8996. Retrieved 2011-03-13.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ "irrumatio in Sex-Lexis". Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ Men in Love - Men's Sexual Fantasies: The Triumph of Love over Rage (1982) by Nancy Friday. ISBN 978-0-440-15903-2
- ^ "Is it safe to swallow semen during pregnancy?". BabyCenter. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ Savage, Dan. Savage Love, page 242 (Plume 1998).
- ^ Bechtel, Stefan; Stains, Laurence Roy; Stains, Larry (1 April 2000). What Women Want: What Every Man Needs to Know About Sex, Romance, Passion and Pleasure. Rodale Press. p. 236. ISBN 1579540937.
- ^ a b "Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2008. Retrieved December 6, 2011. Also see Fact Sheet
- ^ Robert J. Pratt (2003). HIV & AIDS: A Foundation for Nursing and Healthcare Practice. CRC Press. p. 306. ISBN 0340706392. Retrieved August 21, 2013.
- ^ Marshall Cavendish Corporation (2010). Sex and Society, Volume 1. Marshall Cavendish Corporation. p. 61. ISBN 0761479066. Retrieved August 29, 2013.
- ^ a b "Oral Sex and HIV Risk" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). June 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 10, 2013. Retrieved August 30, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The HPV Connection". Archived from the original on 2014-02-27.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Oral Sex Linked To Mouth Cancer Risk". MedIndia. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ D'Souza G; Kreimer AR; Viscidi R; et al. (2007). "Case-control study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer". N. Engl. J. Med. 356 (19): 1944–1956. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa065497. PMID 17494927.
- ^ Khamsi, Roxanne, "Oral sex can cause throat cancer", New Scientist, London, 9 May 2007.
- ^ "New Scientist: "Oral sex can cause throat cancer" - 09 May 2007". Newscientist.com. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ a b "Sex 'primes woman for sperm'". BBC News. 2002-02-06. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ Koelman, CA; et al. (2000). "Correlation between oral sex and a low incidence of preeclampsia: A role for soluble HLA in seminal fluid?". Journal of Reproductive Immunology. 46 (2): 155–166. doi:10.1016/S0165-0378(99)00062-5. PMID 10706945.
- ^ Taylor RN (1997) "Review: Immunobiology of preeclampsia" American Journal of Reproductive Immunology Volume 37 pp. 79-86
- ^ Chaouat et al., (2005) "Fourth International Workshop on Immunology of Pre-eclampsia, December 2004, Reunion, France" Journal of Reproductive Immunology Volume 67 pp. 103-111
- ^ Sandra Margot; Tonianne Robino. The Pregnant Couple's Guide to Sex, Romance, and Intimacy. pp. 122–123. ISBN 978-0-8065-2323-1.
- ^ "New Left Review - Jack Goody: The Labyrinth of Kinship". Retrieved 2007-07-24.
- ^ Herdt, Gilbert (1994). Guardians of the Flutes, Vol. 1. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-32749-3.
- ^ "Intro to Cultural Anthropology: The Sambia". Faculty.mdc.edu. 1999-10-04. Archived from the original on 2011-09-07. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ken Plummer (2002). Modern Homosexualities: Fragments of Lesbian and Gay Experiences. Routledge. pp. 187–191. ISBN 1134922426. Retrieved August 24, 2013.
The social construction of 'sex' as vaginal intercourse affects how other forms of sexual activity are evaluated as sexually satisfying or arousing; in some cases whether an activity is seen as a sexual act at all. For example, unless a woman has been penetrated by a man's penis she is still technically a virgin even if she has had lots of sexual experience.
- ^ Jayson, Sharon (2005-10-19). "'Technical virginity' becomes part of teens' equation". USA Today. Retrieved 2009-08-07.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Regarding 'Oral Sex'". Understanding-islam.com. Retrieved 2013-03-14.
- ^ "Articles and Essays". Zawaj.Com. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ "Islam's Stance on Oral Sex - IslamonLine.net - Ask The Scholar". IslamonLine.net. Archived from the original on 2010-03-24. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Illegal but not abnormal". The Star. March 1, 2009. Archived from the original on June 22, 2011. Retrieved December 9, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Priapeia, translated by Leonard Smithers and Richard Francis Burton: Irrumation". Sacred-texts.com. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ "The actual kama sutra or kamasutra: Part II: On Sexual Union: Chapter IX. On Holding the Lingam in the Mouth by Kamashastra". Kamashastra.com. Archived from the original on 2010-03-13. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The age-old question: Spit or swallow?". The Badger Herald. Retrieved 2010-03-19.
- ^ Berrin, Katherine & Larco Museum. The Spirit of Ancient Peru:Treasures from the Museo Arqueológico Rafael Larco Herrera. New York: Thames & Hudson, 1997.
- ^ Sergeĭ Mikhaĭlovich Shirokogorov (1997). Social Organization of the Manchus: a study of the Manchu clan organization (Chinese Translation). Translated by Gao, Bingzhong. corrected by Liu Xiaomeng. Shanghai: Commercial Press. pp. 1, 12–13. ISBN 9787100019125.
- ^ Gloria Leifer (2014). Introduction to Maternity and Pediatric Nursing. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 575.
- ^ Sergeĭ Mikhaĭlovich Shirokogorov (1924). Social Organization of the Manchus: a study of the Manchu clan organization. Ardent Media. pp. 122, 123.
- ^ Cambodia. PediaPress. p. 575.
- ^ Robin Grille (2014). Parenting for a Peaceful World. New Society Publishers. p. 36.
- ^ a b A. Kleinman; T.Y. Lin (2013). Normal and Abnormal Behavior in Chinese Culture: Volume 2 of Culture, Illness and Healing. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 375. ISBN 9789401749862.
- ^ Avodah K. Offit (1995). Night Thoughts: Reflections of a Sex Therapist. Jason Aronson, Incorporated. p. 63. ISBN 1461629756.
- ^ Irwin M. Marcus; John J. Francis (1975). Masturbation: from infancy to senescence. International Universities Press. p. 371. ISBN 9780823631506.
- ^ C. Michele Thompson (2015). Vietnamese Traditional Medicine: A Social History. NUS Press. p. 375. ISBN 9971698358.
- ^ Martin Roth; Russell Noyes (1988). Handbook of Anxiety: Biological, clinical, and cultural perspectives. Elsevier. p. 314. ISBN 9780444904751.
- ^ a b Tan, Min; Gareth Jones; Guangjian Zhu; Jianping Ye; Tiyu Hong; Shanyi Zhou; Shuyi Zhang; Libiao Zhang (October 28, 2009). Hosken, David (ed.). "Fellatio by Fruit Bats Prolongs Copulation Time". PLoS ONE. 4 (10): e7595. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.7595T. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007595. PMC 2762080. PMID 19862320. Retrieved October 28, 2009.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Sugita, N. (2016). Homosexual Fellatio: Erect Penis Licking between Male Bonin Flying Foxes Pteropus pselaphon. PLoS ONE, 11(11), e0166024.
- ^ Maruthupandian, J., & Marimuthu, G. (2013). Cunnilingus apparently increases duration of copulation in the Indian flying fox, Pteropus giganteus. PLoS ONE, 8(3), e59743.
- ^ "Fellatio keeps male fruit bats keen - life - 29 October 2009 - New Scientist". www.newscientist.com. Retrieved 2009-10-31.
- ^ Courts, S. E. (1996). An ethogram of captive Livingstone's fruit bats Pteropus livingstonii in a new enclosure at Jersey Wildlife Preservation Trust. DODO-JOURNAL OF THE WILDLIFE PRESERVATION TRUSTS, 32, 15-37.
