Guanabenz
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a686003 |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Elimination half-life | 6 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.410 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
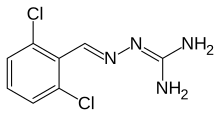
| Formula | C8H8Cl2N4 |
| Molar mass | 231.081 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Guanabenz (pronounced GWAHN-a-benz, sold under the trade name Wytensin) is an alpha agonist of the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor that is used as an antihypertensive drug. It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).[1][2]
The most common side effects during guanabenz therapy are dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, headache and weakness.
Guanabenz can make one drowsy or less alert, therefore driving or operating dangerous machinery is not recommended.
See also
References
- ^ Walker BR, Hare LE, Deitch MW (1982). "Comparative antihypertensive effects of guanabenz and clonidine". The Journal of International Medical Research. 10: 6–14. PMID 7037502.
- ^ Bonham AC, Trapani AJ, Portis LR, Brody MJ (1984). "Studies on the mechanism of the central antihypertensive effect of guanabenz and clonidine". Journal of Hypertension Supplement. 2: S543-6.
