Mecamylamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 40% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.433 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
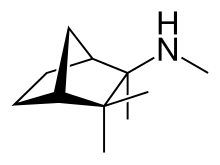
| Formula | C11H21N |
| Molar mass | 167.291 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Mecamylamine (INN, BAN; or mecamylamine hydrochloride (USAN); brand names Inversine, Vecamyl[1]) is a non-selective, non-competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) that was introduced in the 1950s as an antihypertensive drug.[2] In the United States, it was withdrawn from the market for the treatment of hypertension in 2009.[3]
Chemically, mecamylamine is a secondary aliphatic amine, with a pKaH of 11.2[4]
Pharmacology and clinical applications
Mecamylamine has been used as an orally-active ganglionic blocker in treating autonomic dysreflexia and hypertension,[5] but, like most ganglionic blockers, it is more often used now as a research tool.
Mecamylamine is also sometimes used as an antiaddictive drug to help people stop smoking tobacco,[6] and is now more widely used for this application than it is for lowering blood pressure. This effect is thought to be due to its blocking α3β4 nicotinic receptors in the brain. It has also been reported to bring about sustained relief from tics in Tourette syndrome when a series of more usually used agents had failed.[medical citation needed]
In a recent double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase II trial in Indian patients with major depression, (S)-mecamylamine (TC-5214) appeared to have efficacy as an augmentation therapy. This is the first substantive evidence that shows that compounds where the primary pharmacology is antagonism to neuronal nicotinic receptors will have antidepressant properties.[7][8] TC-5214 is currently in Phase III of clinical development as an add-on treatment and on stage II as a monotherapy treatment for major depression. The first results reported from the Phase III trials showed that TC-5214 failed to meet the primary goal and the trial did not replicate the effects that had been encouraging in the Phase II trial.[9][10] Development is funded by Targacept and AstraZeneca.[11] It did not produce meaningful, beneficial results on patients as measured by changes on the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale after eight weeks of treatment as compared with placebo.
(S)-(+)-Mecamylamine dissociates more slowly from α4β2 and α3β4 receptors than does the (R)-(−)-enantiomer.[12]
A large SAR study of mecamylamine and its analogs was reported by a group from Merck in 1962.[13] Another, more recent SAR study was undertaken by Suchocki et al.[14]
A comprehensive review of the pharmacology of mecamylamine was published in 2001.[15]
Toxicology
The LD50 for the HCl salt[16] in mice: 21 mg/kg (i.v.); 37 mg/kg (i.p.); 96 mg/kg (p.o.).[17]
See also
References
- ^ "Mecamylamine". drugs.com. Retrieved May 15, 2015.
- ^ Bacher I, Wu B, Shytle DR, George TP (November 2009). "Mecamylamine - a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist with potential for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 10 (16): 2709–21. doi:10.1517/14656560903329102. PMID 19874251.
- ^ "Drug Profile: Mecamylamine - Targacept".
- ^ Schanker, L. S.; et al. (1957). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 120: 528.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ T. O. Soine (1966). C. O. Wilson, O. Gisvold and R. F. Doerge (ed.). Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry (5th Edition ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott. pp. 468–546.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ Shytle RD, Penny E, Silver AA, Goldman J, Sanberg PR (July 2002). "Mecamylamine (Inversine): an old antihypertensive with new research directions". J Hum Hypertens. 16 (7): 453–7. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001416. PMID 12080428.
- ^ Lippiello PM, Beaver JS, Gatto GJ, et al. (2008). "TC-5214 (S-(+)-mecamylamine): a neuronal nicotinic receptor modulator with antidepressant activity". CNS Neurosci Ther. 14 (4): 266–77. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00054.x. PMID 19040552.
- ^ Rabenstein RL, Caldarone BJ, Picciotto MR (December 2006). "The nicotinic antagonist mecamylamine has antidepressant-like effects in wild-type but not beta2- or alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit knockout mice". Psychopharmacology (Berl.). 189 (3): 395–401. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0568-z. PMID 17016705.
- ^ John Carroll. "Key AZ/Targacept depression drug flunks first Phase III test". Fiercebiotech.com. Retrieved 2011-11-09.
- ^ "Targacept Shares Fall After Depression Medicine Misses Goal". News.businessweek.com. 2007-01-15. Retrieved 2011-11-09.
- ^ "AstraZeneca Pipeline as of the 27th of January 2011". Retrieved 2011-11-09.
- ^ Papke RL, Sanberg PR, Shytle RD (May 2001). "Analysis of mecamylamine stereoisomers on human nicotinic receptor subtypes". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297 (2): 646–56. PMID 11303054.
- ^ Stone, C. A.; et al. (1962). J. Med. Pharm. Chem. 5: 665–690.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Suchocki, J. A.; May, E. L.; Martin ,T. J.; George, C.; Martin, B. R. (1991). "Synthesis of 2-exo- and 2-endo-mecamylamine analogs. Structure-activity relationships for nicotinic antagonism in the central nervous system". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 34 (3): 1003–1010. doi:10.1021/jm00107a019. PMID 2002445.
- ^ Young, J. M.; et al. (2001). "Mecamylamine: New therapeutic uses and toxicity/risk profile". Clin. Ther. 23 (4): 532–565. doi:10.1016/s0149-2918(01)80059-x. PMID 11354389.
- ^ In view of the time period when these data were generated, they presumably refer to the HCl salt of the racemic drug
- ^ Spinks, A.; et al. (1958). "The pharmacological actions of pempidine and its ethyl homologue". Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 13 (4): 501–520. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00246.x. PMC 1481871. PMID 13618559.
